-
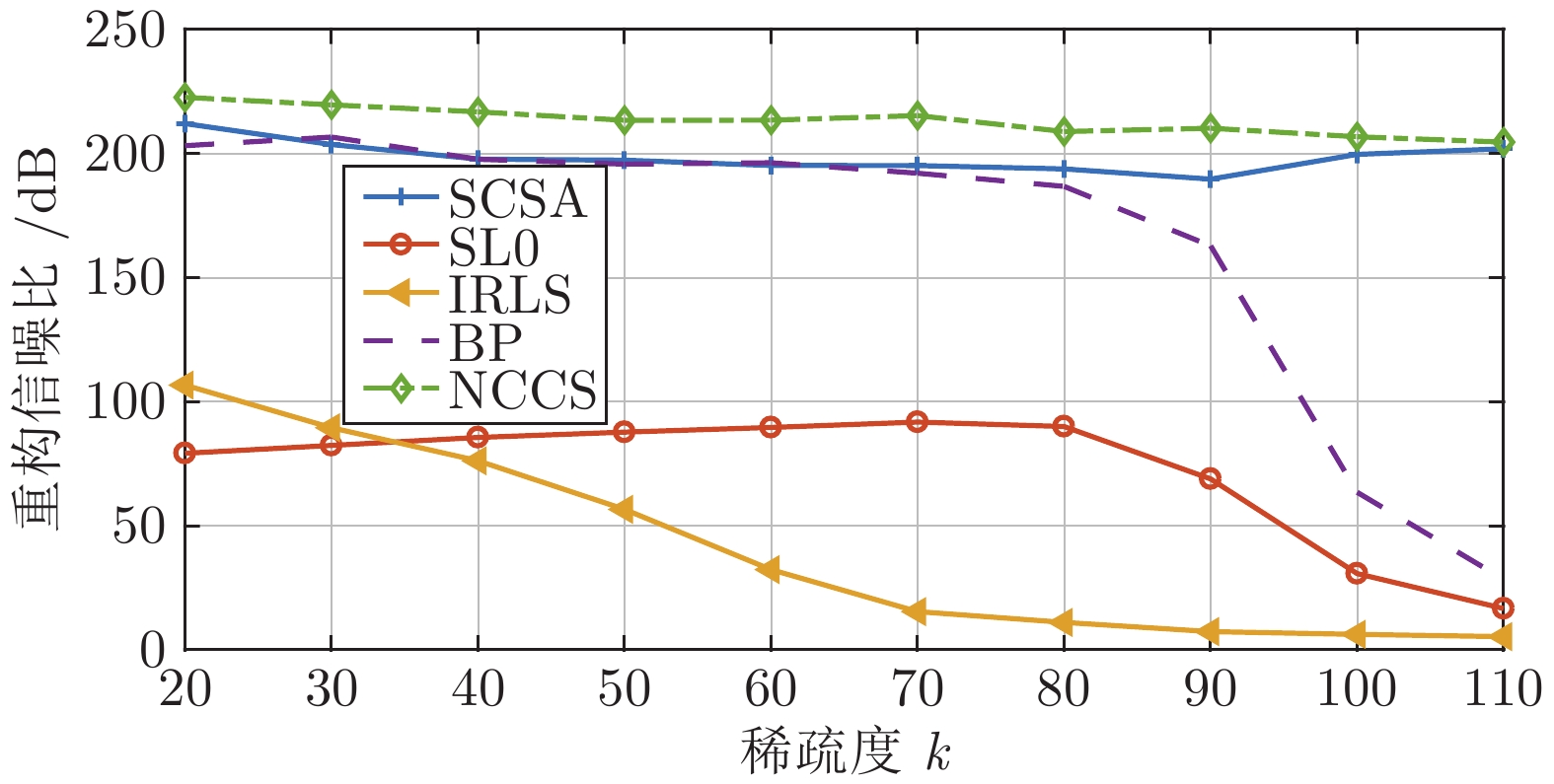
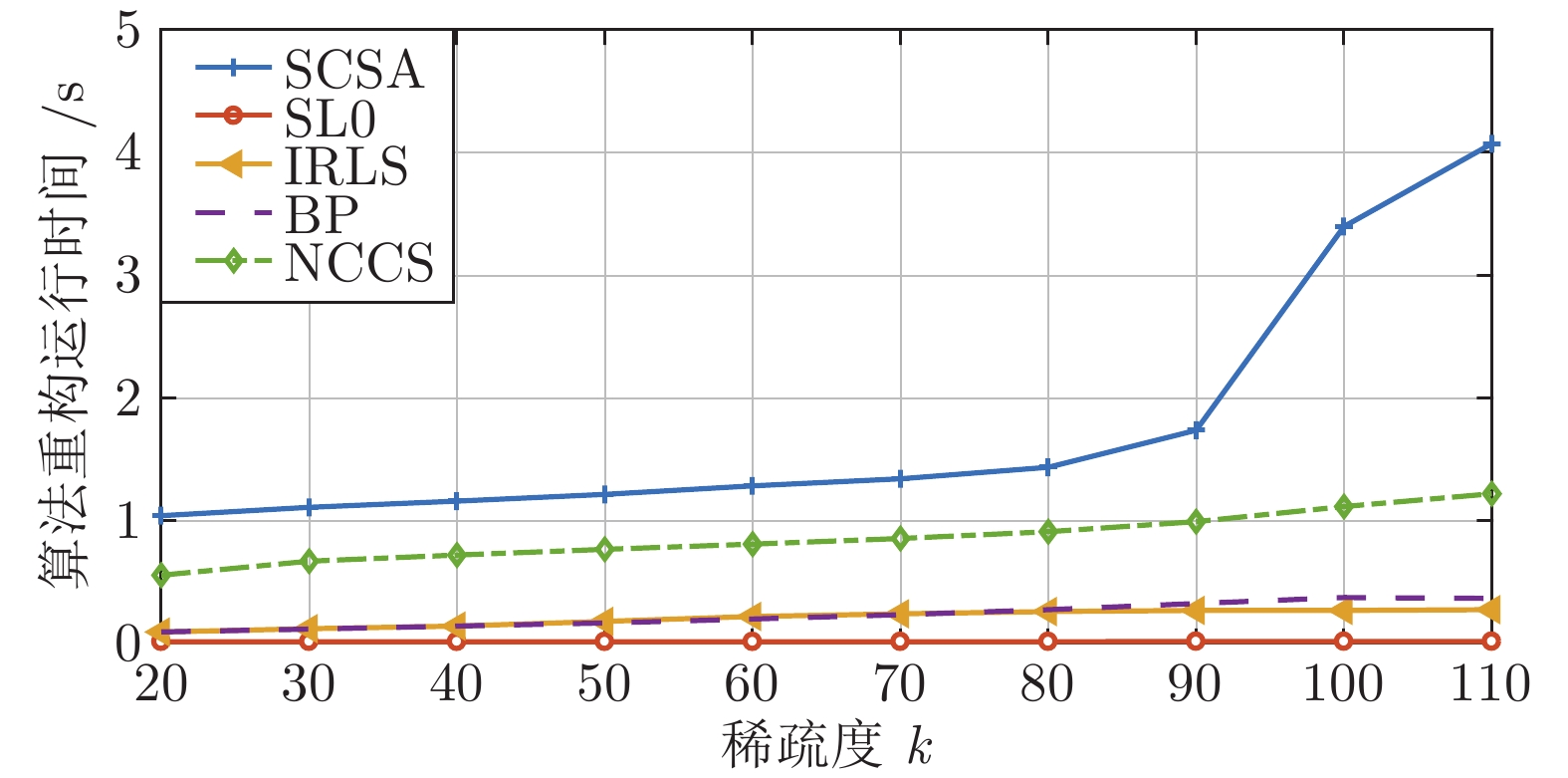
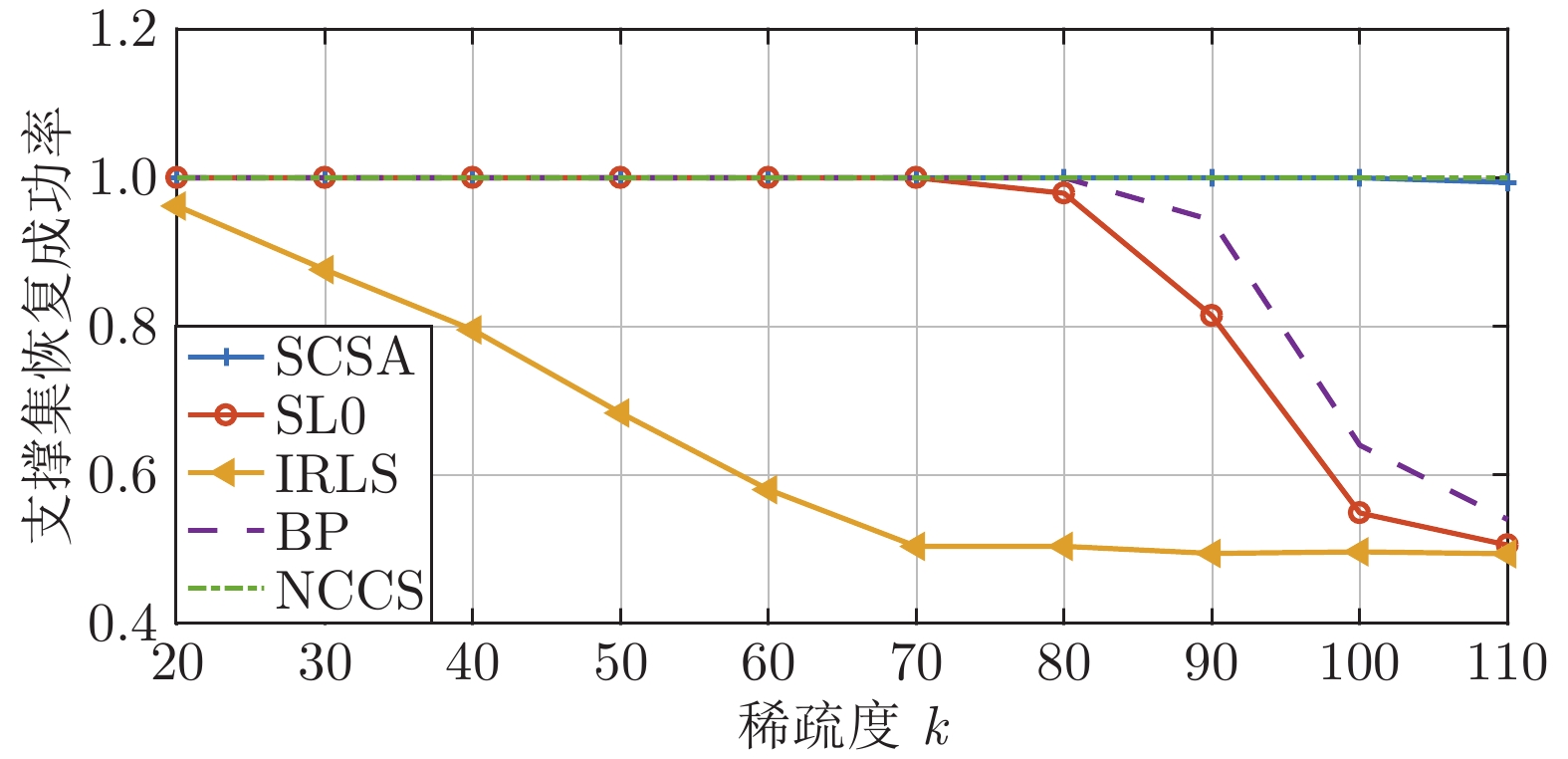
摘要: 基于泛函深度作用的思想, 通过将两种非凸稀疏泛函进行复合, 构造了一种新的稀疏信号重构模型, 实现了对0范数的深度逼近. 综合运用MM (Majorize minimization)技术、外点罚函数法和共轭梯度法, 提出一种求解该模型的算法, 称为NCCS (Non-convex composite sparse)算法. 为降低重构信号陷入局部极值的可能性, 提出在算法的每步迭代中以BP (Basis pursuit)模型的解作为初始迭代值. 为验证所建模型和所提算法的有效性, 进行了多项数值实验. 实验结果表明, 相较于SL0 (Smoothed
$L_0$ )算法、IRLS (Iterative reweighed least squares)算法、SCSA (Successive concave sparsity approximation)算法以及BP 算法等经典算法, 提出的算法在重构误差、信噪比、归一化均方差、支撑集恢复成功率等方面都有更优的表现.Abstract: Based on the idea of deep composition of functionals, this paper constructs a new sparse signal reconstruction model by combining two non-convex sparse functionals to achieve the depth of 0 norm approaching. Using the MM (Majorize minimization) technology, the exterior penalty function method and the conjugate gradient method, an algorithm for solving the model is proposed, which is called the NCCS (Non-convex composite sparse) algorithm. In order to reduce the possibility of the reconstructed signal falling into a local extreme value, it is proposed to use the solution of the BP (Basis pursuit) model as the initial iterative value in each iteration of the algorithm. To verify the effectiveness of the model and the proposed algorithm, a number of numerical experiments have been carried out in this paper. The experimental results show that compared with classic algorithms such as the SL0 (Smoothed$L_0 $ ) algorithm, IRLS (Iterative reweighed least squares) algorithm, SCSA (Successive concave sparsity approximation) algorithm and BP algorithm, the algorithm proposed in this paper has better performance in reconstruction error, signal-to-noise ratio, normalized mean square error, and support set recovery success rate. -
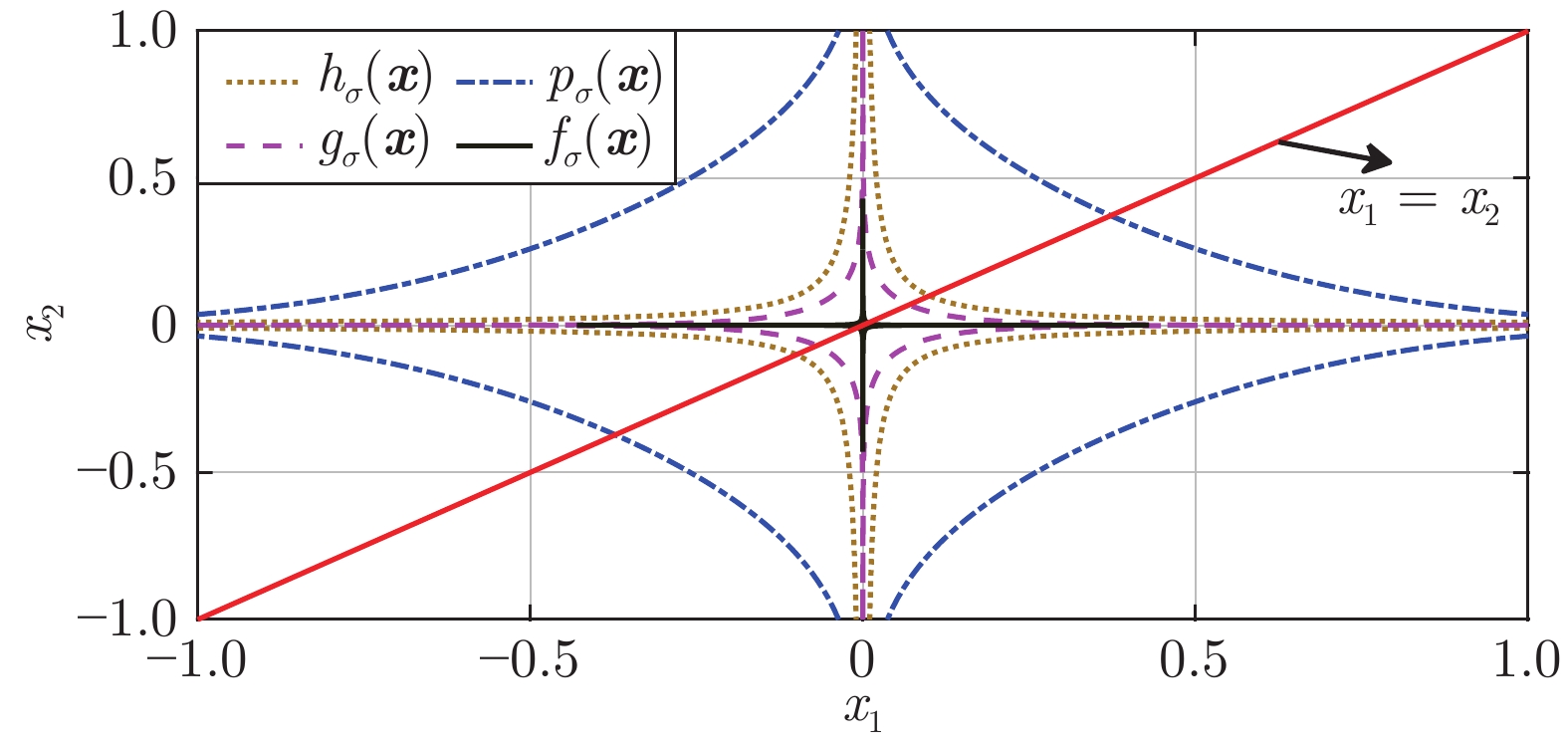
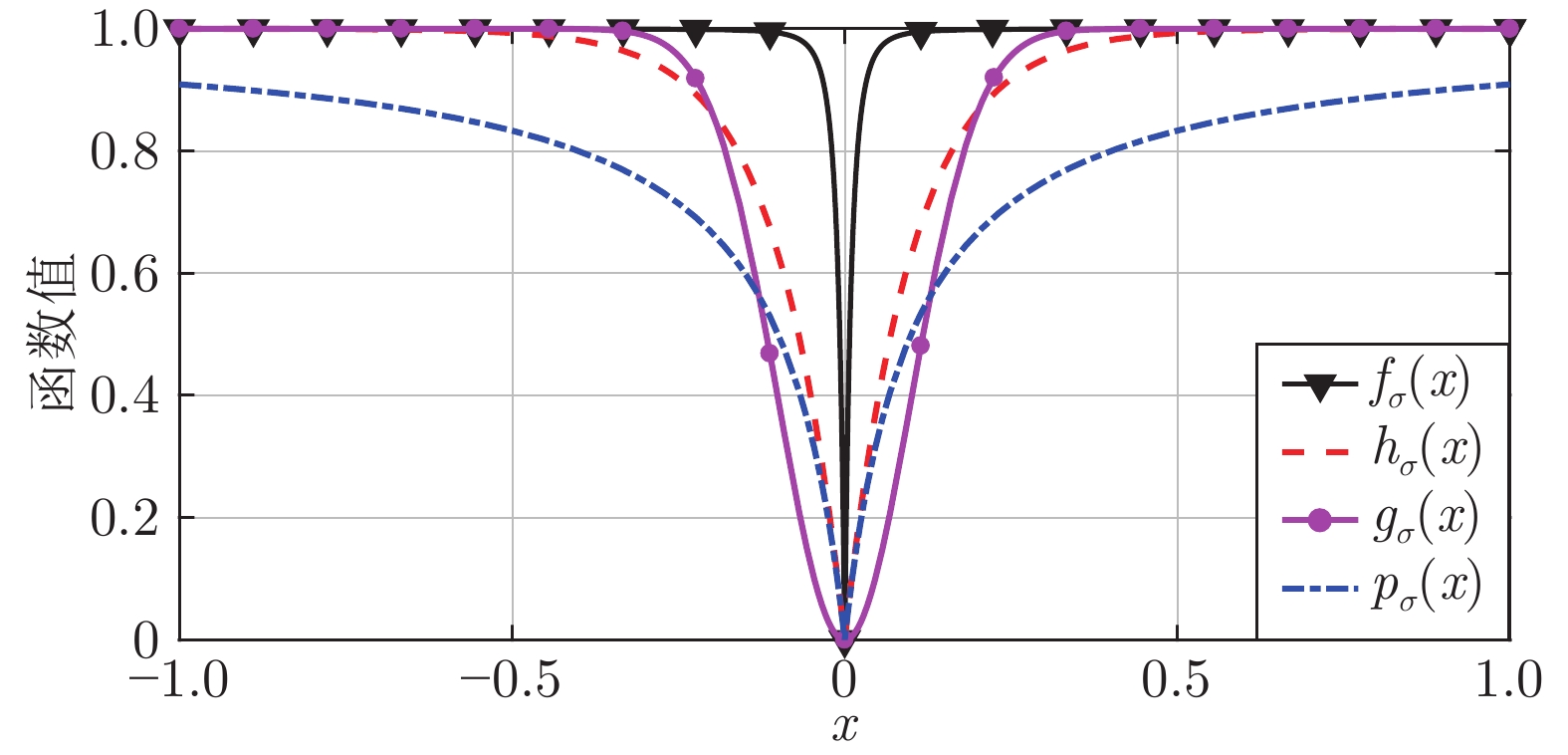
图 2
${p_\sigma }({\boldsymbol{x}})$ 、${h_\sigma }({\boldsymbol{x}})$ 、${g_\sigma }({\boldsymbol{x}})$ 和函数${f_\sigma }({\boldsymbol{x}})$ 在$\sigma = 0.1$ 时的二元函数分布Fig. 2 The bivariate distribution of
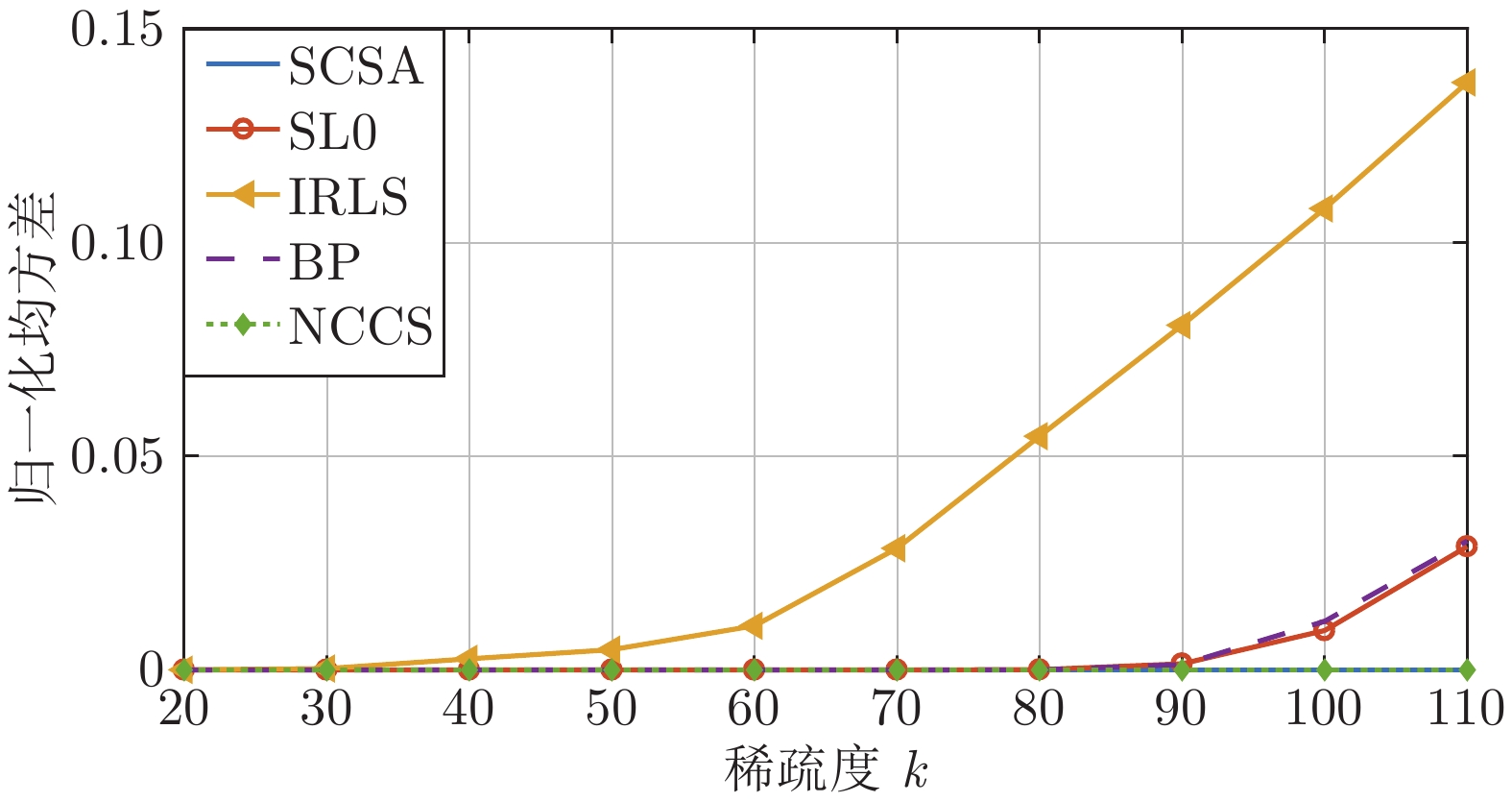
${p_\sigma }({\boldsymbol{x}}),$ ${h_\sigma }({\boldsymbol{x}}),$ ${g_\sigma }({\boldsymbol{x}})$ and the function${f_\sigma }({\boldsymbol{x}})$ at$\sigma = 0.1$ 表 1 5种算法的归一化均方差的数值记录
Table 1 Numerical records of the normalized mean square error of five algorithms
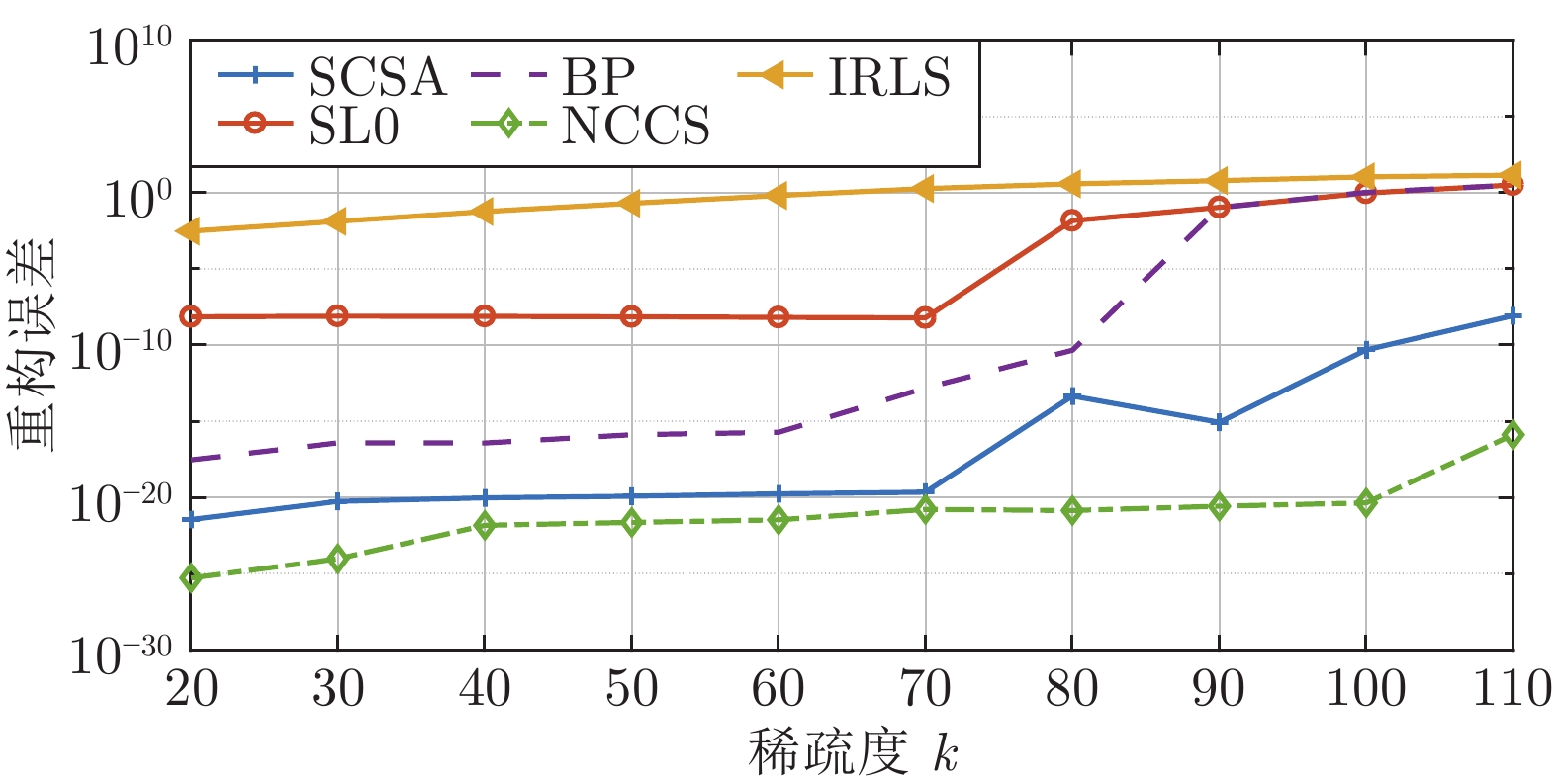
算法 归一化均方差$(NMSE)$ k = 20 k = 30 k = 40 k = 50 k = 60 k = 70 k = 80 k = 90 k = 100 k = 110 SL0 4.11×10−10 2.86×10−10 2.06×10−10 1.55×10−10 1.16×10−10 9.38×10−11 1.46×10−4 1.28×10−3 9.22×10−3 3.13×10−2 IRLS 2.02×10−4 4.08×10−4 1.15×10−3 4.23×10−3 1.07×10−2 2.79×10−2 5.04×10−2 7.20×10−2 1.14×10−1 1.38×10−1 BP 1.65×10−22 4.49×10−22 5.68×10−22 4.95×10−22 4.19×10−22 4.38×10−15 1.18×10−5 9.52×10−4 1.03×10−2 3.57×10−2 SCSA 2.05×10−23 1.94×10−22 1.94×10−22 2.45×10−22 2.50×10−22 2.96×10−22 3.18×10−22 1.27×10−16 1.27×10−13 3.57×10−12 NCCS 5.36×10−27 2.10×10−26 4.81×10−24 4.98×10−24 5.87×10−15 1.85×10−17 3.35×10−16 2.62×10−17 3.58×10−16 1.00×10−16 -
[1] Donoho D L. Compressed sensing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4): 1289~1306. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2006.871582 [2] Gross D, Liu R K, Flammia R T, Becker R, Eisert R. Quantum state tomography via compressed sensing. Physical Review Letters, 2010, 105(15): 150401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.150401 [3] Wiaux Y, Jacques L, Puy G, Scaife A M M, Vandergheynst P. Compressed sensing imaging techniques for radio interf- erometryMonthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Soci- ety, 2010, 395(3): 1733~1742. [4] Lustig M, Donoho D, Pauly J M. Sparse MRI: The applica- tion of compressed sensing for rapid MR imaging. Magnet- ic Resonance in Medicine, 2010, 58(6): 1182~1195. [5] Shi Bao-Shun, Lian Qiu-Sheng, Chen Shu-Zhen. Compres- sed sensing magnetic resonance imaging based on dictionary updating and block matching and three dimensional filtering regularization. Image Processing Iet, 2016, 10(1): 68~79. doi: 10.1049/iet-ipr.2014.0870 [6] Herman M, Strohmer T. High-Resolution Radar via Compr- essed Sensing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(6): 2275~2284. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2014277 [7] Chartrand R. Exact reconstruction of sparse signals via nonconvex minimization. IEEE Signal Processing letters, 2007, 14(10): 707~710. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2007.898300 [8] Peng Ji-Gen, Yue, Shi-Gang, Li Hai-Yang. NP/CMP equivalence: A phenomenon hidden among sparsity models ℓ0 minimization and ℓP minimization for information processing. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2015, 61(7): 4028~4033. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2015.2429611 [9] Tropp J A, Gilbert A C. Signal Recovery From Random Measurements Via Orthogonal Matching Pursuit. IEEE Tr- ansactions on Information Theory, 2007, 53(12): 4655~4666. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2007.909108 [10] Beck A, Teboulle M. A Fast Iterative Shrinkage Thresholdi- ng Algorithm for Linear Inverse Problems. Siam J Imaging sciences, 2009, 2(1): 183~202. doi: 10.1137/080716542 [11] Dai W, Milenkovic O. Subspace Pursuit for Compressive Sensing Signal Reconstruction. IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2009, 55(5): 2230~2249. doi: 10.1109/TIT.2009.2016006 [12] Saadat S A, Safari A, Needell D. Sparse Reconstruction of Regional Gravity Signal Based on Stabilized Orthogonal Matching Pursuit (SOMP). Pure and Applied Geophysics, 2016, 173(6): 2087~2099. doi: 10.1007/s00024-015-1228-1 [13] Figueiredo M A T, Nowak R D, Wright S J. Gradient Projection for Sparse Reconstruction: Application to Comp- ressed Sensing and Other Inverse Problems. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2008, 1(4): 586~ 597. [14] Foucart S, Rauhut H, Rauhut H. A mathematical introducti- on to compressive sensing. Springer New York, 2013, 5: 65~75. [15] Emmanuel J C, Michael B W, Stephen P B. Enhancing spa- rsity by reweighted L1 minimization. Journal of Fourier Analysis and Applications, 2008, 14(5): 877~905. [16] Chartrand R, Yin W. Iteratively reweighted algorithms for compressive sensing. In: Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2008. 3869−3872 [17] Zhang Z, Xu Y, Yang J, Li X, Zhang D. A Survey of Sparse Representation: Algorithms and Applications. IEEE Access, 2017, 3: 490~530. [18] Chen S S, Donoho D L, Saunders M A. Atomic decomposetion by basis pursuit. SIAM Review, 2001, 43(1): 129~159. doi: 10.1137/S003614450037906X [19] Chartrand R, Staneva V. Restricted isometry properties and nonconvex compressive sensing. Inverse Problems, 2010, 24(3): 657~682. [20] 赵瑞珍, 林婉娟, 李浩, 胡绍海. 基于光滑ℓ0范数和修正牛顿法的压缩感知重建算法. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2012, 24(4): 478~484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2012.04.008Zhao Rui-Zhen, Lin Wan-Juan, Li Hao, Hu Shao-Hai. Reco- nstruction Algorithm for Compressive Sensing Based on Smoothed ℓ0 Norm and Revised Newton Method. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2012, 24(4): 478~484 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2012.04.008 [21] Mohimani H, Babaie Z M, Jutten C. A Fast Approach for Overcomplete Sparse Decomposition Based on Smoothed L0 Norm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(1): 289~301. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2007606 [22] Zhang C J, Hao D B, Hou C B, Yin X J. A New Approach for Sparse Signal Recovery in Compressed Sensing Based on Minimizing Composite Trigonometric Function. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 44894~44904. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2855958 [23] Malek M M, Babaie M, Koochakzadeh A, Jansson M, Rojas C R. Successive Concave Sparsity Approximation for Compressed Sensing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Proces- sing, 2016, 64(21): 5657~5671. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2585096 [24] Li Hai-Yang, Zhang Qian, Cui An-Gang, Peng Ji-Gen. Mi- nimization of Fraction Function Penalty in Compressed Se- nsing. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2020, 31(5): 1626~1637. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2921404 [25] Hunter D R, Lange K. A Tutorial on MM Algorithms. The American Statistician, 2004, 58(1): 30~37. doi: 10.1198/0003130042836 [26] 袁亚湘, 孙文瑜. 最优化理论与方法. 北京: 科学出版社, 1997. 455−482Yuan Ya-Xiang, Sun Wen-Yu. Optimization Theory and Method. Beijing: Science Press, 1997. 455−482 [27] Emmanuel J, Michael B W, Stephen P B. Enhancing Sparsity by Reweighted ℓ1 Minimization. Journal of Fourier Anal- ysis & Applications, 2007, 14(5): 877-905. [28] Clarke F H . Optimization and Non-smooth Analysis. New York: Classics in Applied Mathematics, SIAM, 1983. 37−187 [29] Al-Naffouri T Y, Masood M. Distribution agnostic structured sparsity recovery algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Systems, Signal Processing and Their Applications (WoSSPA). Algiers, Algeria: IEEE, 2013. 283−290 [30] 陈金立, 李伟, 朱筱嵘, 陈宣, 李家强. 基于修正近似双曲正切函数的平滑 L0 范数算. 计算机工程与设计, 2018, 39(12): 3717−3721,3754Chen Jin-Li, Li Wei, Zhu Xiao-Rong, Chen Xuan, Li Jia-Qiang. Smooth L0 norm calculation based on modified approximate hyperbolic tangent function. Computer Engineering and Design, 2018, 39(12): 3717−3721, 3754 -








 下载:
下载: