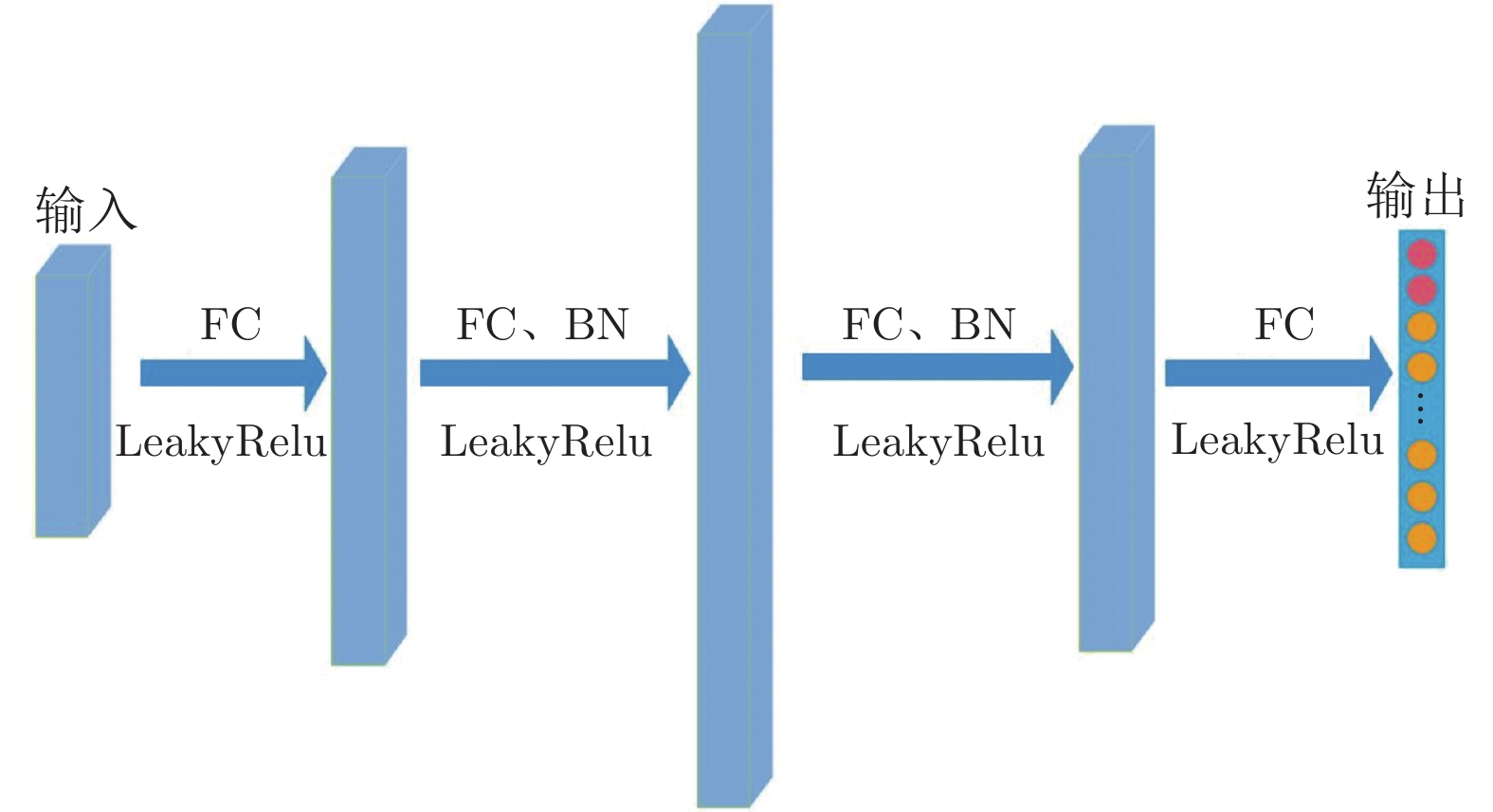
-
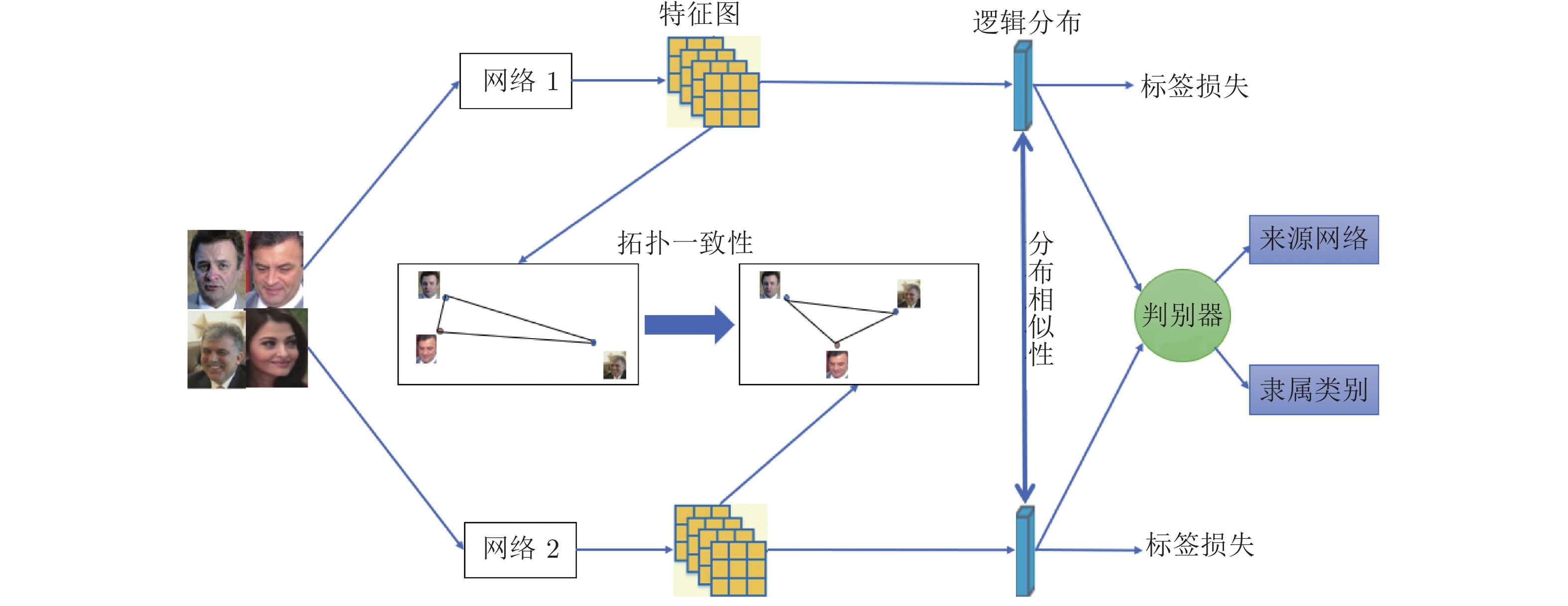
摘要: 针对基于互学习的知识蒸馏方法中存在模型只关注教师网络和学生网络的分布差异, 而没有考虑其他的约束条件, 只关注了结果导向的监督, 而缺少过程导向监督的不足, 提出了一种拓扑一致性指导的对抗互学习知识蒸馏方法(Topology-guided adversarial deep mutual learning, TADML). 该方法将教师网络和学生网络同时训练, 网络之间相互指导学习, 不仅采用网络输出的类分布之间的差异, 还设计了网络中间特征的拓扑性差异度量. 训练过程采用对抗训练, 进一步提高教师网络和学生网络的判别性. 在分类数据集CIFAR10、CIFAR100和Tiny-ImageNet及行人重识别数据集Market1501上的实验结果表明了TADML的有效性, TADML取得了同类模型压缩方法中最好的效果.Abstract: The existing mutual-deep-learning based knowledge distillation methods have the limitations: the discrepancy between the teacher network and the student network is only used to supervise the knowledge transfer neglecting other constraints, and the result-driven supervision is only used neglecting process-driven supervision. This paper proposes a topology-guided adversarial deep mutual learning network (TADML). This method trains multiple classification sub-networks of the same task simultaneously and each sub-network learns from others. Moreover, our method uses an adversarial network to adaptively measure the differences between pairwise sub-networks and optimizes the features without changing the model structure. The experimental results on three classification datasets: CIFAR10, CIFAR100 and Tiny-ImageNet and a person re-identification dataset Market1501 show that our method has achieved the best results among similar model compression methods.
-
表 1 损失函数对分类精度的影响比较(%)
Table 1 Comparison of classification performance with different loss function (%)
损失构成 CIFAR10 CIFAR100 LS 92.90 70.47 LS + LJS 93.18 71.70 LS + LJS + Ladv 93.52 72.75 LS + L1 + Ladv 93.04 71.97 LS + L2 + Ladv 93.26 72.02 LS + L1 + LJS + Ladv 92.87 71.63 LS + L2 + LJS + Ladv 92.38 70.90 LS + LJS + Ladv + LT 93.05 71.81 表 2 判别器结构对分类精度的影响比较(%)
Table 2 Comparison of classification performance with different discriminator structures (%)
结构 CIFAR100 256fc-256fc 71.57 500fc-500fc 72.09 100fc-100fc-100fc 72.33 128fc-256fc-128fc 72.51 64fc-128fc-256fc-128fc 72.28 128fc-256fc-256fc-128fc 72.23 表 3 判别器输入对分类精度的影响比较(%)
Table 3 Comparison of classification performance with different discriminator inputs (%)
输入约束 CIFAR100 Conv4 72.33 FC 72.51 Conv4 + FC 72.07 FC + DAE 71.97 FC + Label 72.35 FC + Avgfc 71.20 表 4 采样数量对分类精度的影响比较(%)
Table 4 Comparison of classification performance with different sampling strategies (%)
网络结构 Vanila Random K = 2 K = 4 K = 8 K = 16 K = 32 K = 64 Resnet32 71.14 72.12 31.07 60.69 72.43 72.84 72.50 71.99 Resnet110 74.31 74.59 22.64 52.33 74.59 75.18 75.01 74.59 表 5 网络结构对分类精度的影响比较(%)
Table 5 Comparison of classification performance with different network structures (%)
网络结构 原始网络 DML[13] ADML TADML 网络 1 网络 2 网络 1 网络 2 网络 1 网络 2 网络 1 网络 2 网络 1 网络 2 ResNet32 ResNet32 70.47 70.47 71.86 71.89 72.85 72.89 73.07 73.13 ResNet32 ResNet110 70.47 73.12 71.62 74.08 72.66 74.18 73.14 74.86 ResNet110 ResNet110 73.12 73.12 74.59 74.55 75.08 75.10 75.52 75.71 WRN-10-4 WRN-10-4 72.65 72.65 73.06 73.01 73.77 73.75 73.97 74.08 WRN-10-4 WRN-28-10 72.65 80.77 73.58 81.11 74.61 81.43 75.11 82.13 表 6 网络结构对行人重识别平均识别精度的影响比较(%)
Table 6 Comparison of person re-identification mAP with different network structures (%)
网络结构 原始网络 DML[13] ADML TADML 网络 1 网络 2 网络 1 网络 2 网络 1 网络 2 网络 1 网络 2 网络 1 网络 2 InceptionV1 MobileNetV1 65.26 46.07 65.34 52.87 65.60 53.22 66.03 53.91 MobileNetV1 MobileNetV1 46.07 46.07 52.95 51.26 53.42 53.27 53.84 53.65 表 7 本文算法与其他压缩算法的实验结果
Table 7 Experimental results of the proposed algorithm and other compression algorithms
对比算法 参数量
(MB)CIFAR10
(%)CIFAR100
(%)Tiny-ImageNet
(%)ResNet20 0.27 91.42 66.63 54.45 ResNet164 2.6 93.43 72.24 61.55 Yim 等[10] 0.27 88.70 63.33 - SNN-MIMIC[22] 0.27 90.93 67.21 - KD[8] 0.27 91.12 66.66 57.65 FitNet[9] 0.27 91.41 64.96 55.59 Quantization[20] 0.27 91.13 - - Binary Connect[21] 15.20 91.73 - - ANC[23] 0.27 91.92 67.55 58.17 TSANC[24] 0.27 92.17 67.43 58.20 KSANC[24] 0.27 92.68 68.58 59.77 DML[13] 0.27 91.82 69.47 57.91 ADML 0.27 92.23 69.60 59.00 TADML 0.27 93.05 70.81 60.11 -
[1] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [2] Zhang X Y, Zhou X Y, Lin M X, Sun J. ShuffleNet: An extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake, USA: IEEE, 2018. 6848−6856 [3] Guo Y W, Yao A B, Zhao H, Chen Y R. Network sketching: Exploiting binary structure in deep CNNs. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4040−4048 [4] Tai C, Xiao T, Wang X G,E W N. Convolutional neural networks with low-rank regularization. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations, San Ju-an, Puerto Rico, 2016 [5] Chen W, Wilson J T, Tyree S, Weinberger K Q, Chen Y X. Compressing neural networks with the hashing trick. In: Proce-edings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learni-ng, Lille, France: 2015. 37: 2285−2294 [6] Denton E L, Zaremba W, Bruna J, LeCun Y, Fergus R. Exploiting linear structure within convolutional networks for efficient evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada: 2014. 1269−1277 [7] Li Z, Hoiem D. Learning without forgetting. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision, Amsterdam, Netherlands: 2016. 614−629 [8] Hinton G E, Vinyals O, Dean J. Distilling the knowledge in a neural network. arXiv preprint, 2015, arXiv: 1503.02531 [9] Romero A, Ballas N, Kahou S E, Chassang A, Gatta C, Bengio Y. Fitnets: Hints for thin deep nets. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations. San Di-ego, USA, 2015 [10] Yim J, Joo D, Bae J H, Kim J. A Gift from knowledge distillation: Fast optimization, network minimization and transfer learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 7130−7138 [11] Peng B Y, Jin X, Li D S, Zhou S F, Wu Y C, Liu J H, et al. Correlation congruence for knowledge distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2017. 5006−5015 [12] Park W, Kim D, Lu Y, Cho M. Relational knowledge distillation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3967−3976 [13] Zhang Y, Xiang T, Hospedales T M, Lu H C. Deep mutual learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4320−4328 [14] Batra T, Parikh D. Cooperative Learning with Visual Attributes. arXiv preprint, 2017, arXiv: 1705.05512 [15] Zhang H, Goodfellow I J, Metaxas D N, Odena A. Self-attention generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning, Long Beach, USA: 2019. 7354−7363 [16] Zagoruyko S, Komodakis N. Wide residual networks. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference, York, UK: 2016. 1−12 [17] Krizhevsky A, Hinton G. Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images. Handbook of Systemic Autoimmune Diseases, 2009.1(4). [18] Mirza M, Osindero S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv preprint, 2014, arXiv: 1411.1784 [19] Shu C Y, Li P, Xie Y, Qu Y Y, Kong H. Knowledge Squeezed Adversarial Network Compression. In: Proceedings of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA: 2020. 11370−11377 [20] Zhu C Z, Han S, Mao H Z, Dally W J. Trained ternary quantization. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, France, 2017. [21] Courbariaux M, Bengio Y, David J P. Binaryconnect: Training deep neural networks with binary weights during propagations. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: 2015. 3123− 3131 [22] Ba J, Caruana R. Do deep nets really need to be deep? In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, Montreal, Canada: 2014. 2654−2662 [23] Belagiannis V, Farshad A, Galasso F. Adversarial network compression. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision, Munich, Germany: 2018. 11132: 431−449 [24] Xu Z, Hsu Y C, H J W. Training student networks for acceleration with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of British Machine Vision Conference, Newcastle, UK: 2018. 61 -




 下载:
下载: