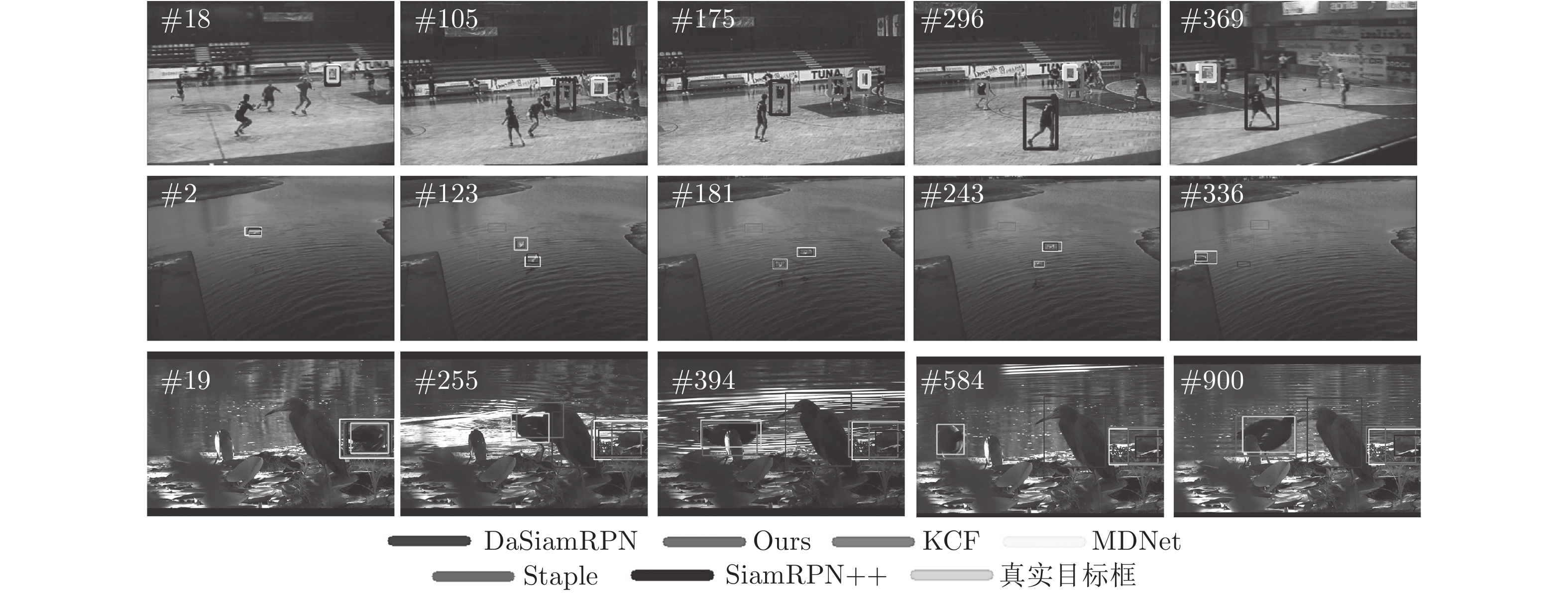
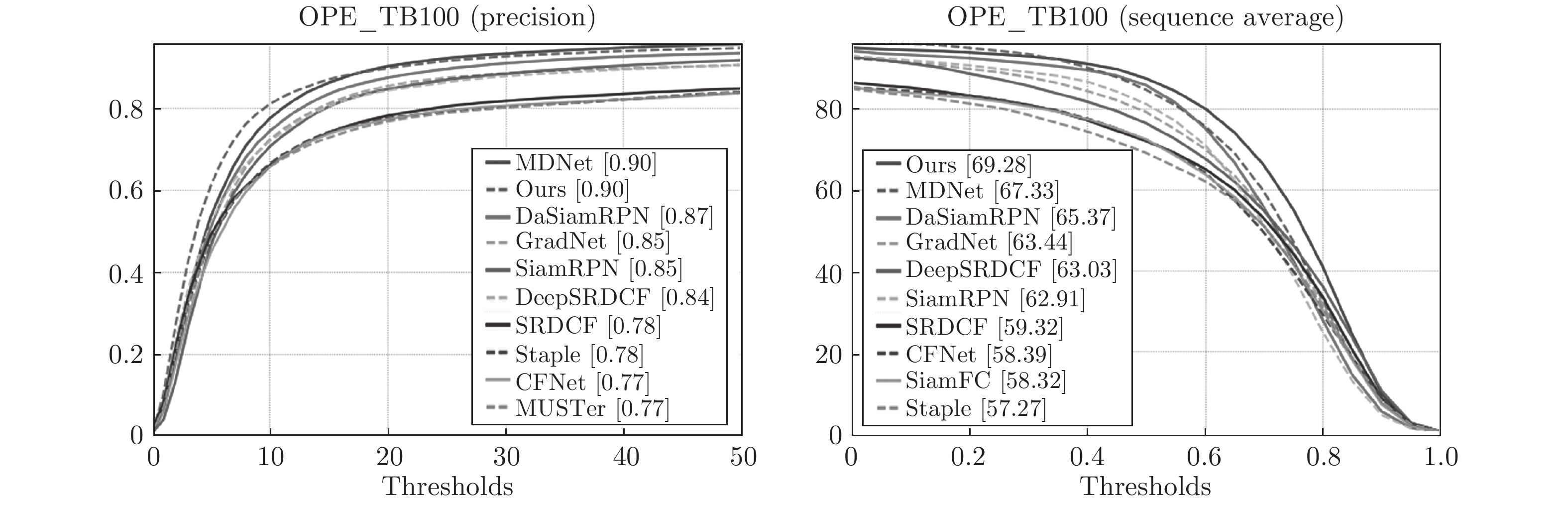
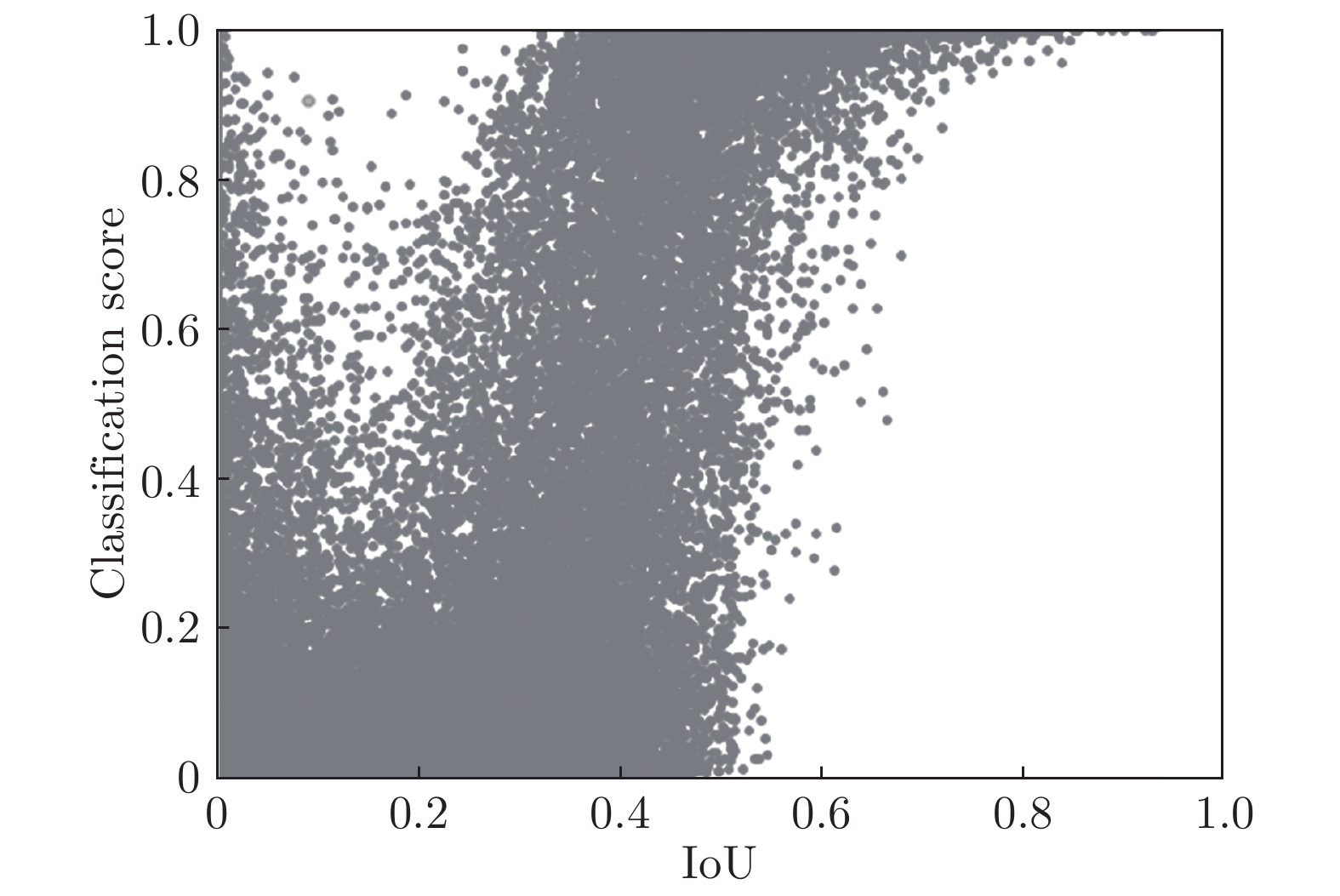
-
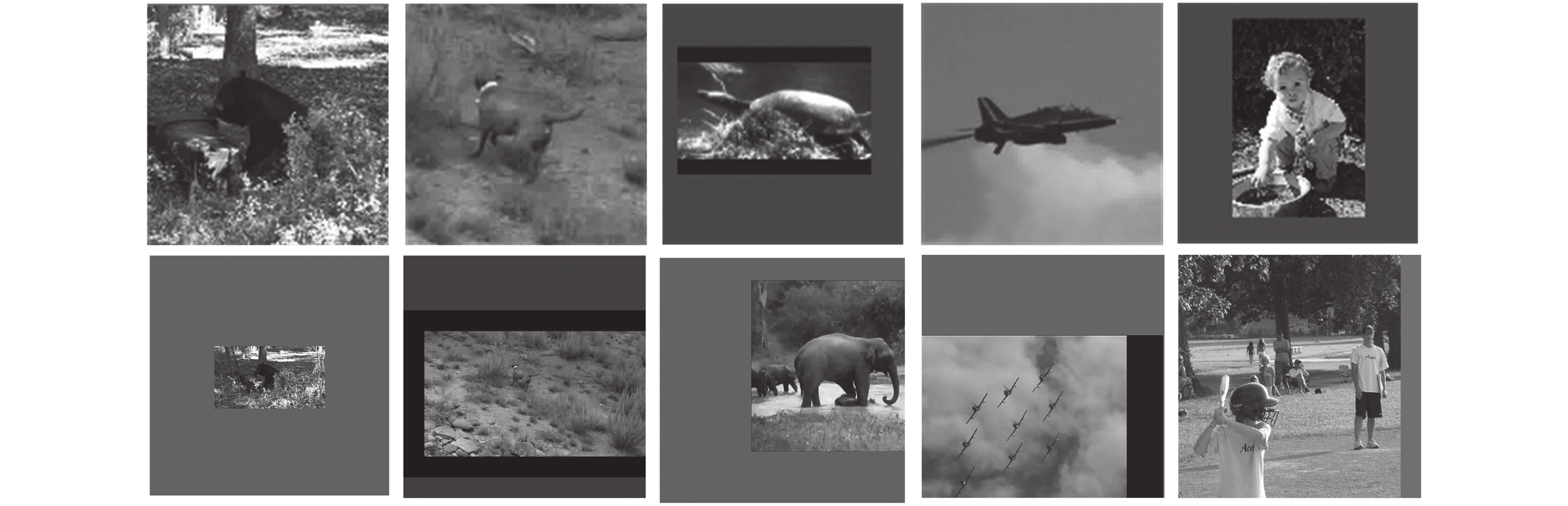
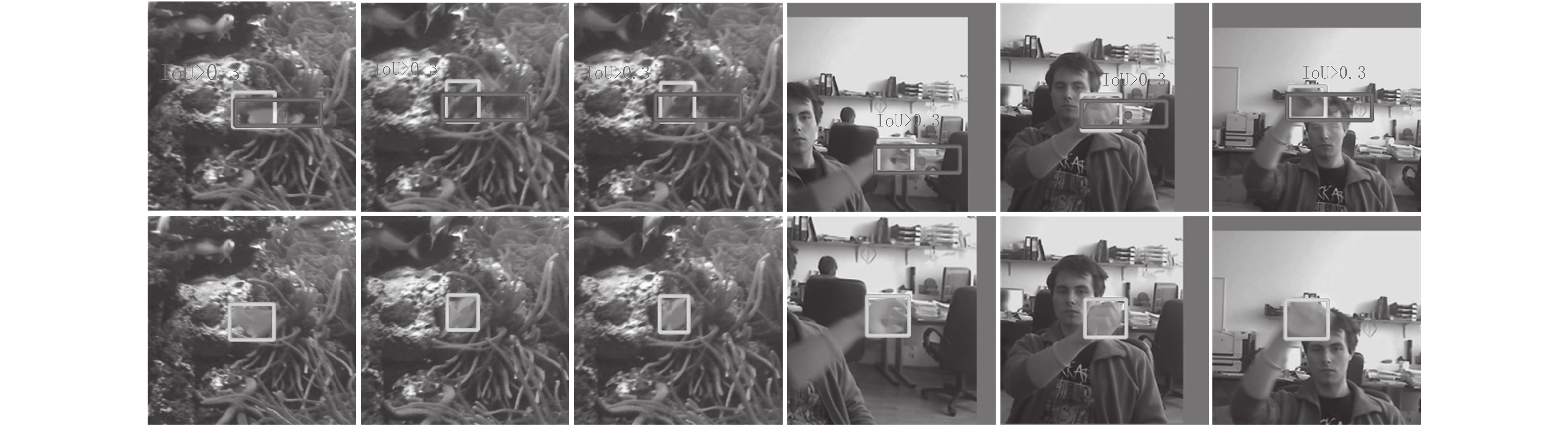
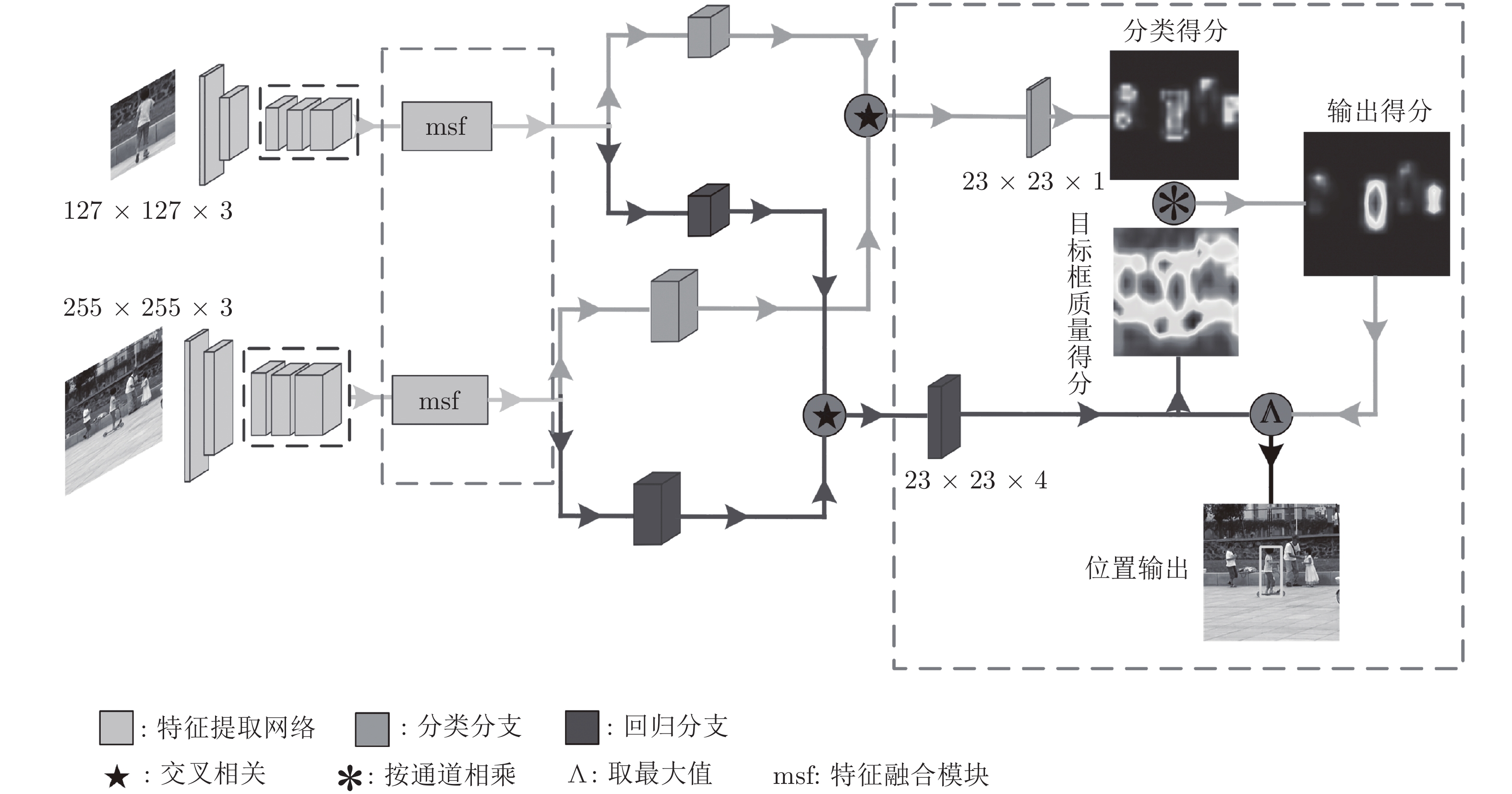
摘要: 为解决孪生网络跟踪器鲁棒性差的问题, 重新设计了孪生网络跟踪器的分类与回归分支, 提出一种基于像素上直接预测方式的高鲁棒性跟踪算法—无锚框全卷积孪生跟踪器(Anchor-free fully convolutional siamese tracker, AFST). 目前高性能的跟踪算法, 如SiamRPN、SiamRPN++、CRPN都是基于预定义的锚框进行分类和目标框回归. 与之相反, 提出的AFST则是直接在每个像素上进行分类和预测目标框. 通过去掉锚框, 大大简化了分类任务和回归任务的复杂程度, 并消除了锚框和目标误匹配问题. 在训练中, 还进一步添加了同类不同实例的图像对, 从而引入了相似语义干扰物, 使得网络的训练更加充分. 在VOT2016、GOT-10k、OTB2015三个公开的基准数据集上的实验表明, 与现有的跟踪算法对比, AFST达到了先进的性能.Abstract: In order to solve the problem of poor robustness of siamese trackers, this paper redesigns the classification and regression branches, and proposes a high robustness siamese tracker AFST (Anchor-free fully convolutional siamese tracker) based on direct prediction on pixels. Current high-performance object tracker, such as SiamRPN, SiamRPN++, CRPN, are based on predefined anchor boxes for classification and regression. On the contrary, the proposed AFST is to directly classify and predict the target box on each pixel. By removing the anchor, this paper greatly simplifies the complexity of classification task and regression task, and eliminates the problem of mismatching between anchor and target. In the training, we have further added image pairs of different instances of the same kind, thereby introducing similar semantic interferers, making the network training more adequate. Experiments on three open benchmarks datasets, VOT2016, GOT-10k and OTB2015, show that AFST achieves advanced performance compared with existing tracking algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Siamese tracker /
- prediction on pixels /
- similar semantic interferers /
- anchor-free /
- center score
-
表 1 消融实验
Table 1 Ablation experiments
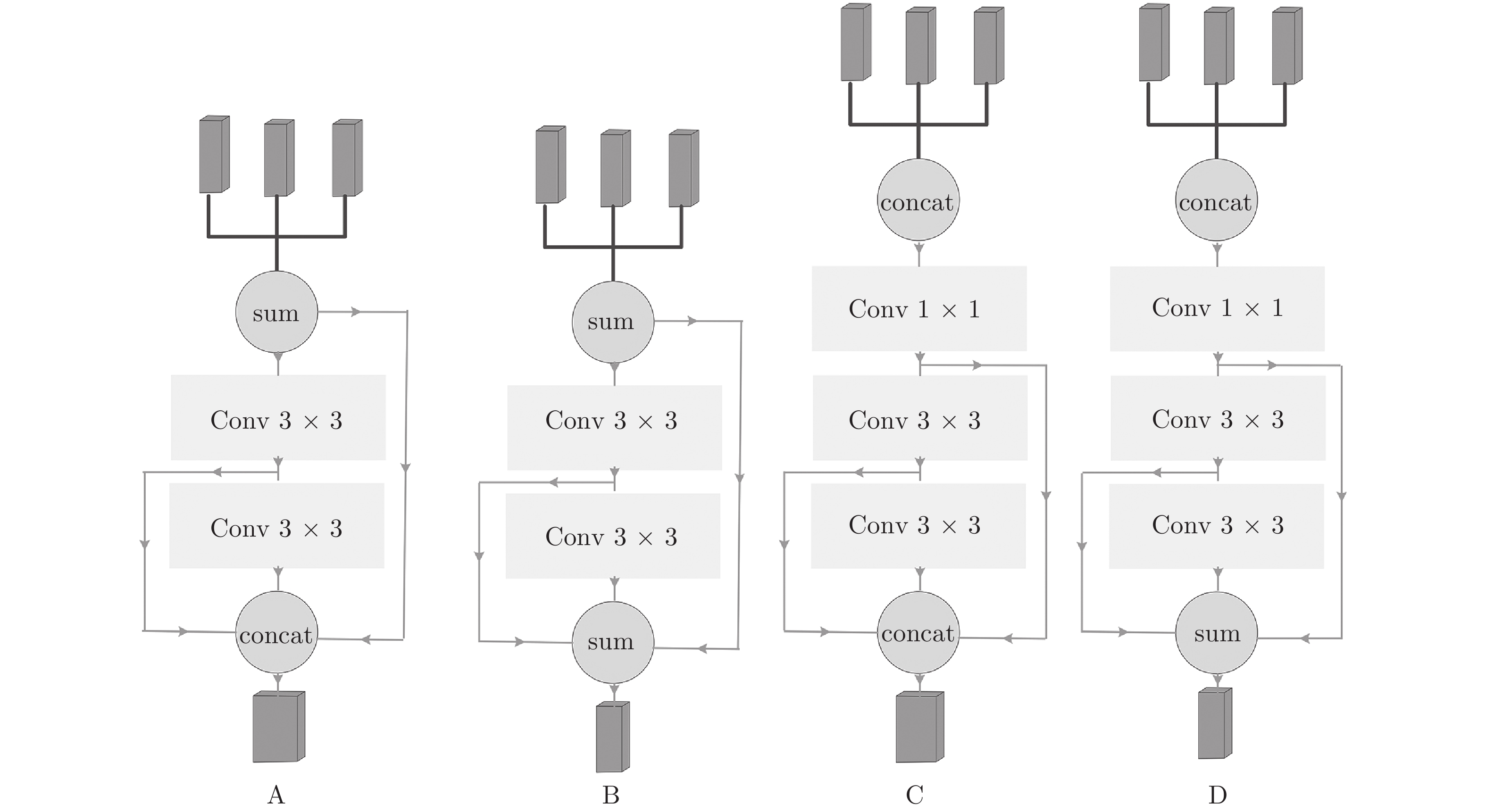
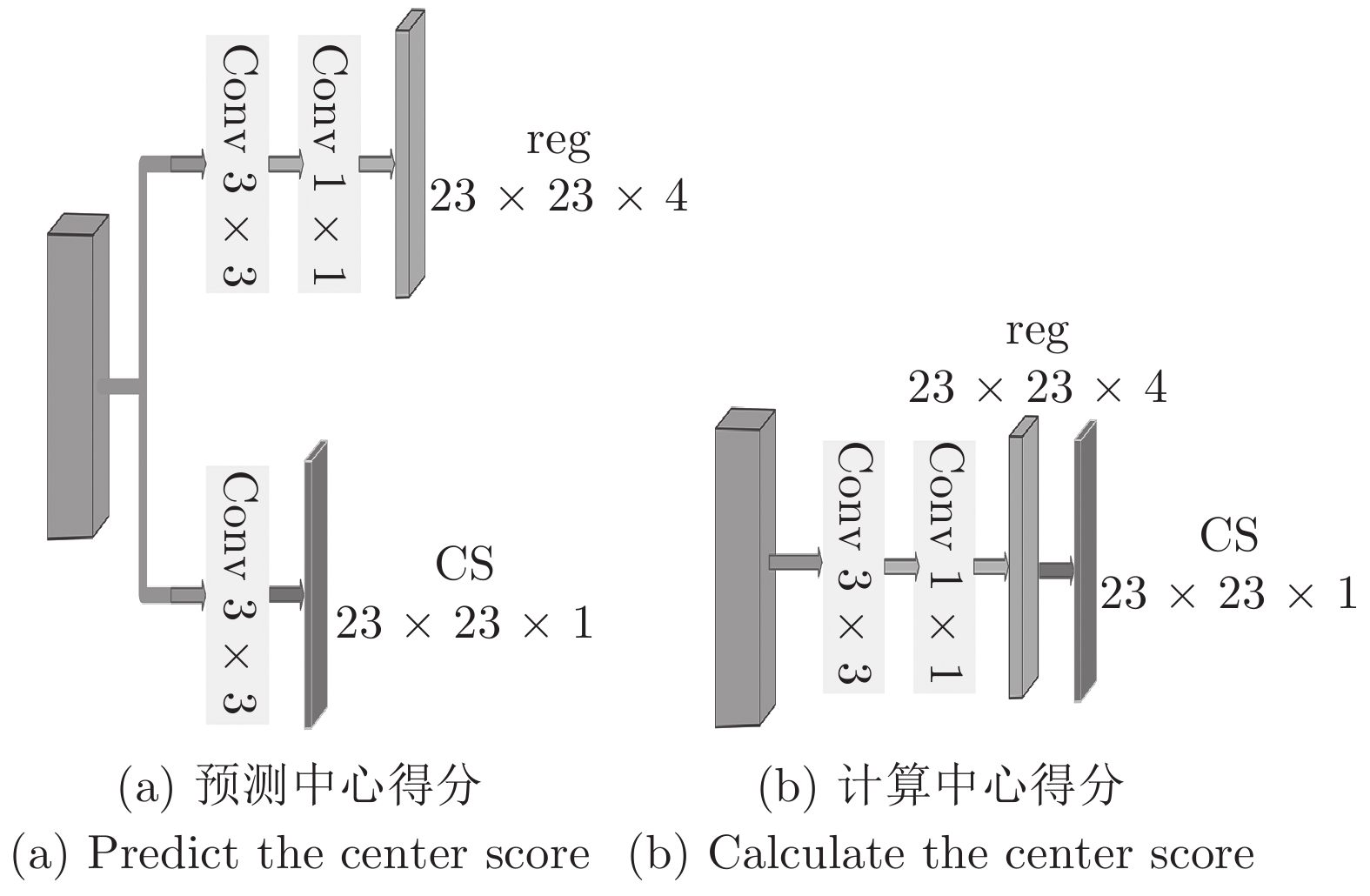
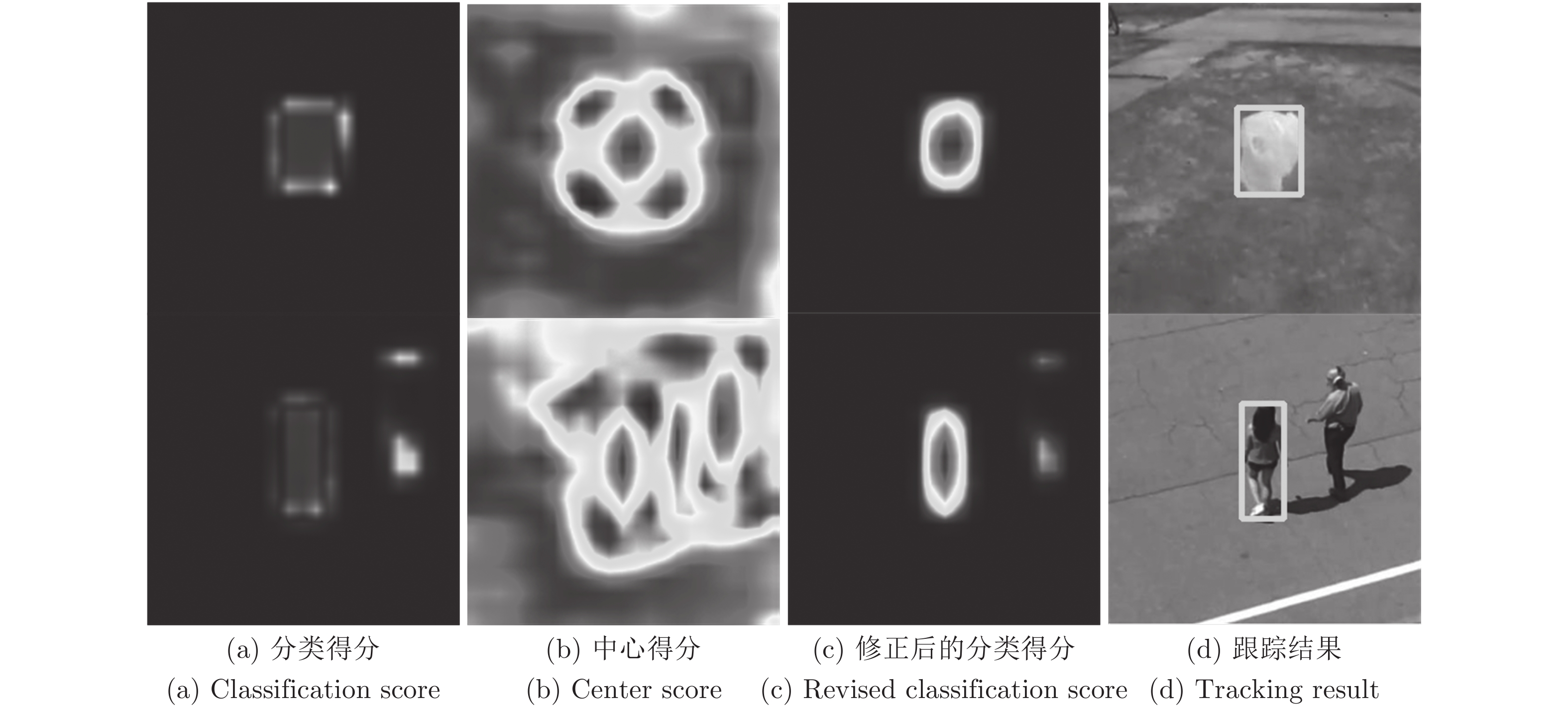
序号 主干网络 子网络 质量得分 A R EAO 融合方式 新采样策略 1 Alex cls none 0.530 0.466 0.235 none none 2 ResNet50 cls none 0.579 0.386 0.280 none none 3 ResNet50 cls + reg none 0.592 0.333 0.345 none none 4 ResNet50 cls + reg none 0.602 0.302 0.355 sum none 5 ResNet50 cls + reg none 0.607 0.242 0.382 sum yes 6 ResNet50 cls + reg CS 0.610 0.224 0.415 concat yes 7 ResNet50 cls + reg CS 0.614 0.238 0.397 sum yes 8 ResNet50 cls + reg CS 0.624 0.205 0.412 msf yes 表 2 VOT2016上与多个跟踪器对比
Table 2 Compare with multiple trackers on VOT2016
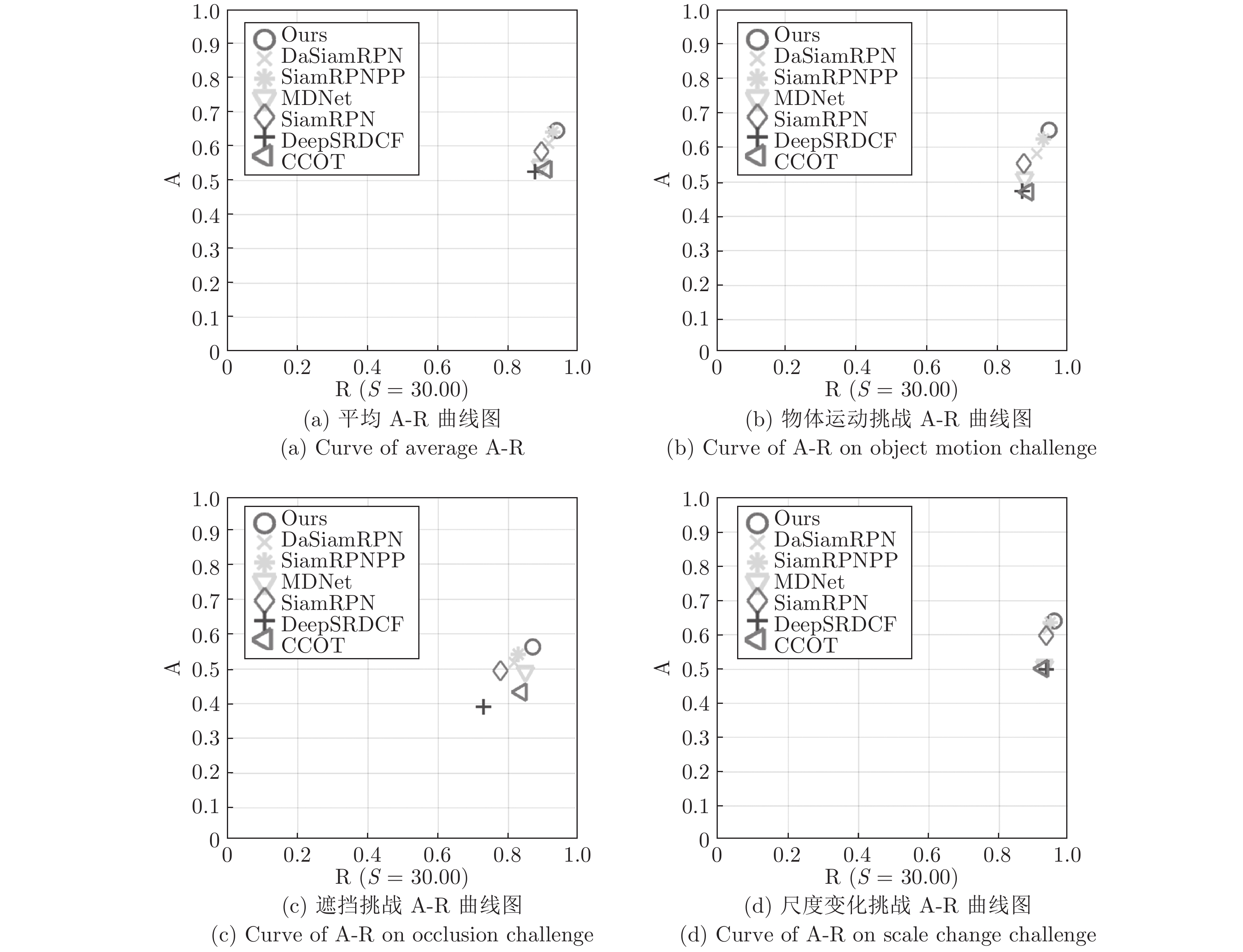
CCOT ECO MDNet DeepSRDCF SiamRPN DaSiamRPN Ours SiamRPN++ A 0.541 0.550 0.542 0.529 0.560 0.609 0.651 0.642 R 0.238 0.200 0.337 0.326 0.260 0.224 0.149 0.196 EAO 0.331 0.375 0.257 0.276 0.344 0.411 0.485 0.464 表 3 不同挑战因素下的失败率
Table 3 Failure rates under different challenge factors
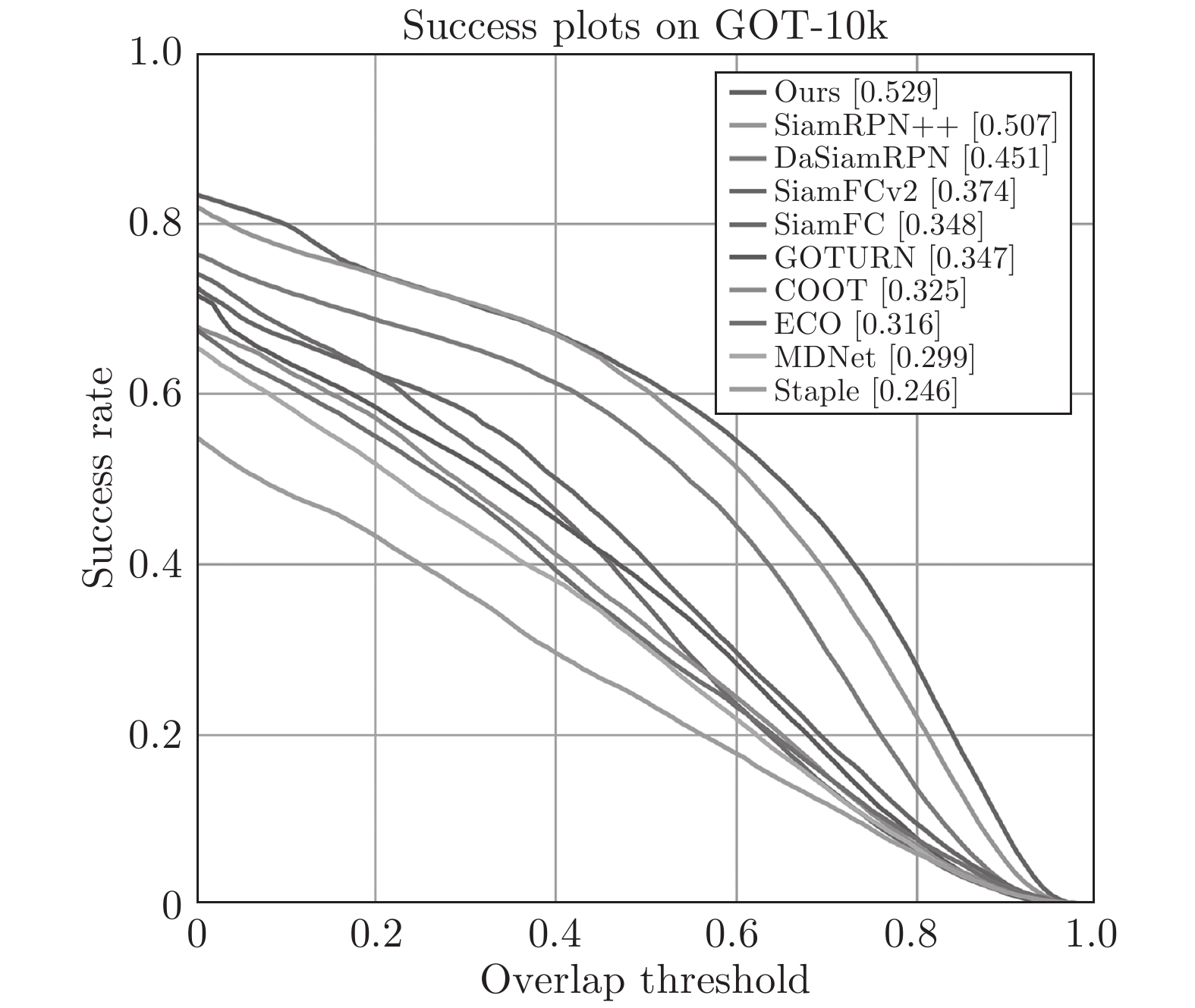
相机运动 目标丢失 光照变化 物体运动 遮挡 尺度变化 平均 加权 CCOT 24 11 2 20 14 13 14.0 16.6 Ours 20 3 2 9 11 7 8.7 10.2 DaSiamRPN 26 4 2 15 16 10 12.2 14.2 SiamRPN 33 13 1 22 20 11 16.7 20.1 SiamRPN++ 20 7 1 12 15 9 10.7 12.4 MDNet 33 18 4 21 13 12 17.0 21.1 DeepSRDCF 28 17 3 23 25 11 17.9 20.3 表 4 GOT-10k上与多个跟踪器对比
Table 4 Compare with multiple trackers on GOT-10k
SiamFC ECO MDNet DeepSRDCF SiamRPN++ Ours AO 0.348 0.316 0.299 0.451 0.507 0.529 SR75 0.098 0.111 0.099 0.216 0.311 0.370 SR5 0.353 0.303 0.303 0.543 0.605 0.617 -
[1] Li B, Yan J J, Wu W, Zhu Z, Hu X L. High performance visual tracking with siamese region proposal network. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8971−8980 [2] Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques J F, Vedaldi A, Torr P H. Fully-convolutional siamese networks for object tracking. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 850−865 [3] Zhu Z, Wang Q, Li B, Wu W, Yan J J, Hu W M. Distractor-aware siamese networks for visual object tracking. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 101−117 [4] Li B, Wu W, Wang Q, Zhang F Y, Xing J L, Yan J J. SiamRPN++: Evolution of siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 4282−4291 [5] Fan H, Ling H B. Siamese cascaded region proposal networks for real-time visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7952−7961 [6] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Procoeedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Pro cessing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. 91−99 [7] Tao R, Gavves E, Smeulders A W M. Siamese instance search for tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1420−1429 [8] Held D, Thrun S, Savarese S. Learning to track at 100 fps with deep regression networks. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 749−765 [9] Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S, et al. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211−252 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [10] Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 740−755 [11] Lin T Y, Dollar P, Girshick R, He K M, Hariharan B, Belongie S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2117−2125 [12] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C Y, et al. Ssd: Single shot multibox detector. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 21−37 [13] Lin T Y, Goyal P, Girshick R, He K M, Dollar P. Focal loss for dense object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2980−2988 [14] Cai Z W, Vasconcelos N. Cascade R-CNN: Delving into high quality object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 6154−6162 [15] Zhang S F, Wen L Y, Bian X, Lei Z, Li S Z. Single-shot refinement neural network for object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4203−4212 [16] Jiang B R, Luo R X, Mao J Y, Xiao T T, Jiang Y N. Acquisition of localization confidence for accurate object detection. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 784−799 [17] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788 [18] Law H, Deng J. Cornernet: Detecting objects as paired keypoints. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 734−750 [19] Yang Z, Liu S H, Hu H, Wang L W, Lin S. Reppoints: Point set representation for object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 9657−9666 [20] Tian Z, Shen C H, Chen H, He T. Fcos: Fully convolutional one-stage object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 9627−9636 [21] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [22] Kristan M, Leonardis A, Matas J, Felsberg M, Chi Z Z. The visual object tracking VOT2016 challenge results. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision Workshop. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 191−217 [23] Huang L, Zhao X, Huang K. GOT-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2019: 1−1 [24] Nam H, Han B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 4293−4302 [25] Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M. Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834−1848 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226 [26] Li P X, Chen B Y, Ouyang W L, Wang D, Yang X Y, Lu H C. Gradnet: Gradient-guided network for visual object tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 6162−6171 [27] Danelljan M, Hager G, Shahbaz Khan F, Felsberg M. Convolutional features for correlation filter based visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 58−66 [28] Valmadre J, Bertinetto L, Henriques J, Vedaldi A, Torr P H. End-to-end representation learning for correlation filter based tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2805−2813 -




 下载:
下载: