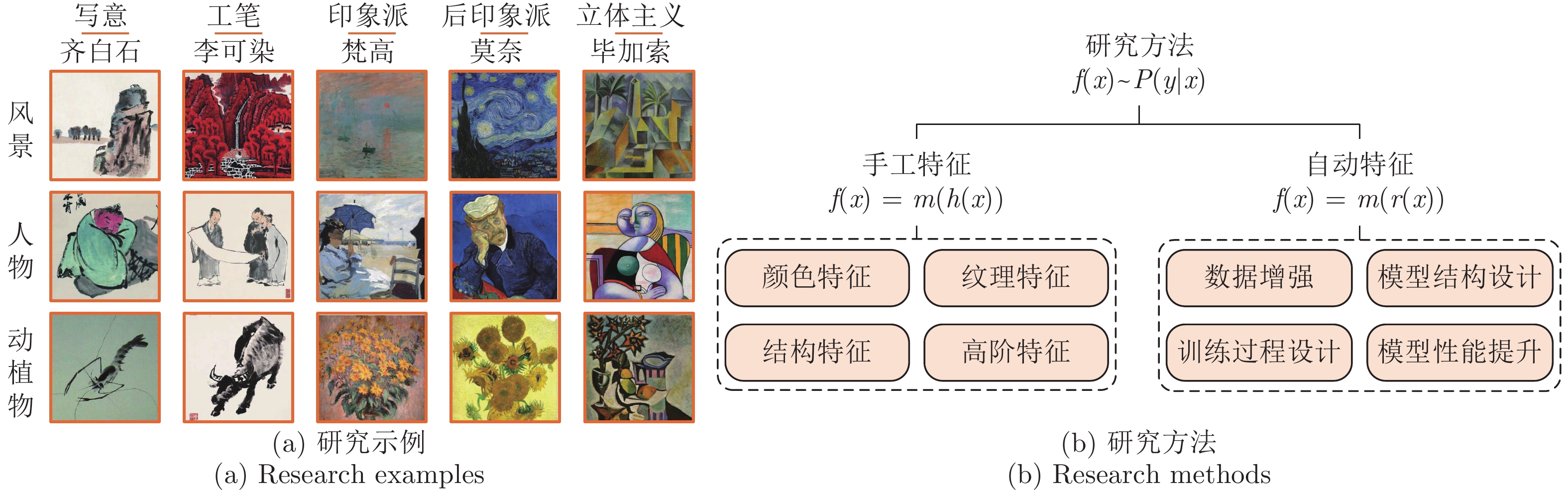
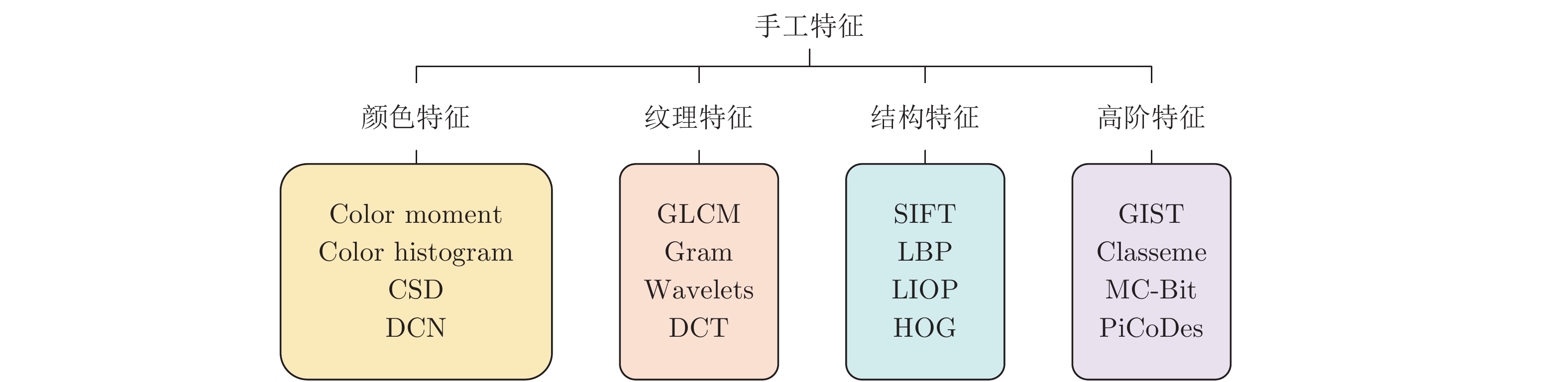
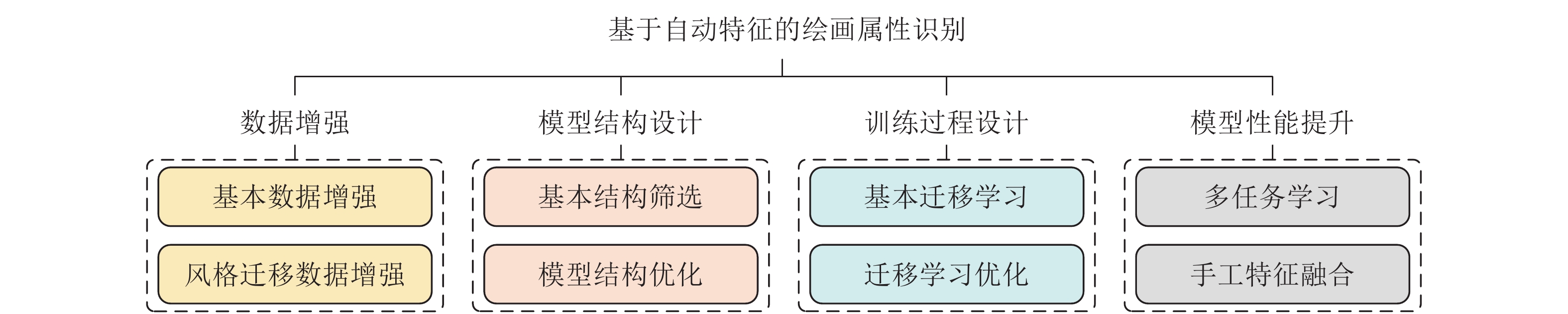
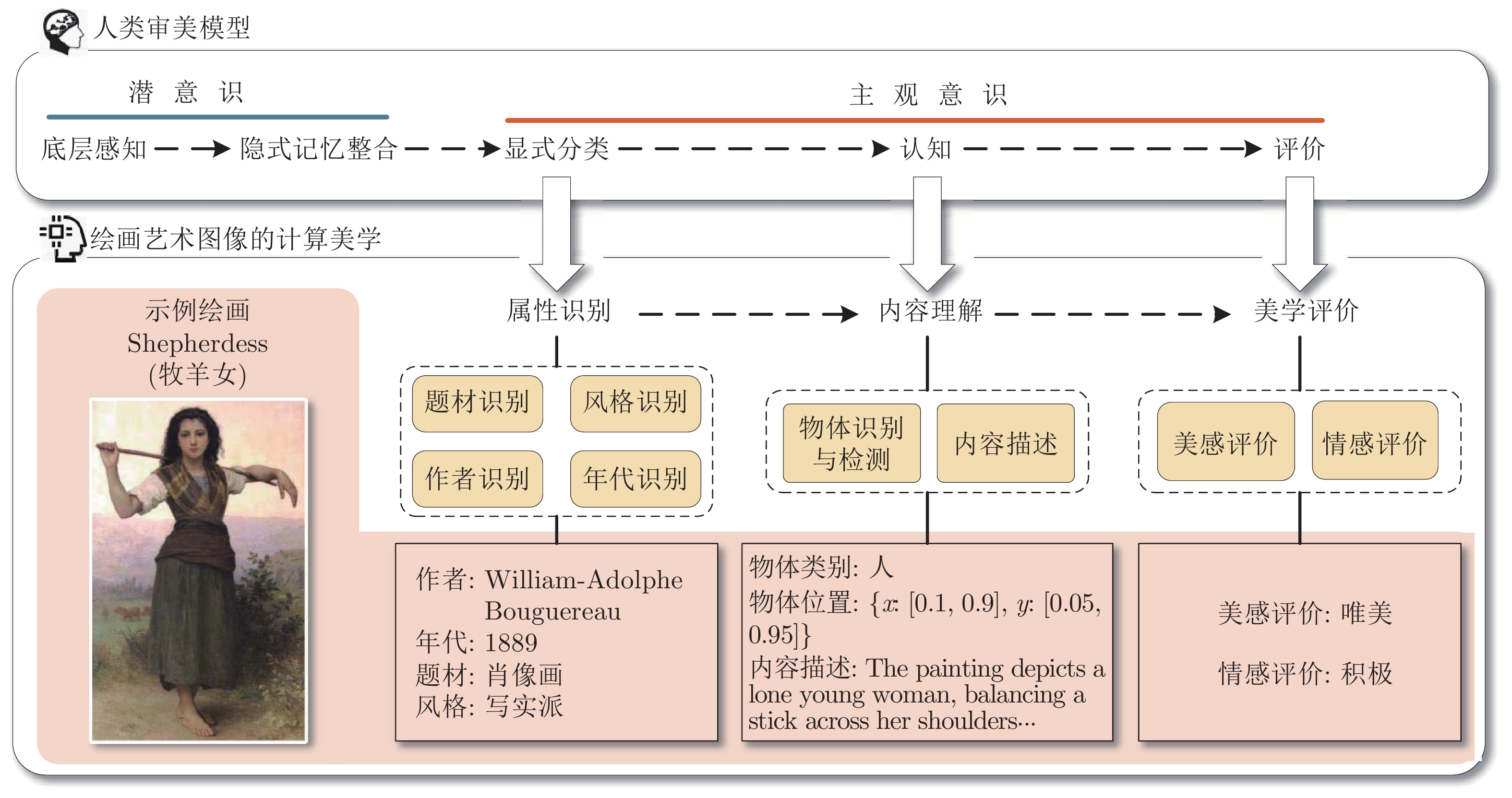
Computational Aesthetics of Fine Art Paintings: The State of the Art and Outlook
-
摘要: 绘画艺术是人类艺术创作的重要组成部分, 绘画艺术图像的计算美学是利用机器实现可计算的人类审美过程, 其在大规模绘画的自动化分析和机器对感性的计算建模上具有重要的应用价值和科学意义. 针对其交叉学科的特点, 本文首次从人类审美的感知、认知和评价三个关键过程出发, 将绘画艺术图像的计算美学研究完整地归纳为属性识别、内容理解和美学评价三方面研究内容, 对其中的问题建模、数据获取和前沿方法等关键科学问题进行了归纳总结, 并对绘画计算美学的三方面研究内容进行了对比、思考和展望.Abstract: Fine art painting is an essential component of art. The computational aesthetics of fine art painting is a computable human aesthetic process realized by machines, which has significant application value and scientific significance in the automatic analysis of large-scale paintings and computational modeling for aesthetic. Given its interdisciplinary characteristics, for the first time, the computational aesthetics of fine art paintings is completely summarized into three aspects: Attribute recognition, content understanding, and aesthetic judgments according to the key processes of human aesthetics that include perception, cognition, and evaluation. The key scientific issues involved in each aspect are summarized, such as problem modeling, data acquisition, and frontier methods. Also, the three research contents of computational aesthetics of fine art painting are compared, and the future development of this field is discussed.
-
表 1 不同手工特征下的绘画属性识别正确率 (%)
Table 1 Painting attribute recognition accuracy for different manual features (%)
表 2 不同分类器下的绘画属性识别正确率 (%)
Table 2 Painting attribute recognition accuracy for different classifiers (%)
表 3 不同网络结构下的绘画艺术图像属性识别正确率 (%)
Table 3 Painting attribute recognition accuracy for different sturcture of neural networks (%)
表 4 不同初始化方式下的绘画属性识别错误率[20] (%)
Table 4 Painting attribute recognition error rate for different initialization methods[20] (%)
风格识别 题材识别 作者识别 平均的错误率下降率 随机初始化 迁移学习 随机初始化 迁移学习 随机初始化 迁移学习 AlexNet 69.2 56.7 51.2 35.0 53.7 27.3 33.0 ResNet-14 62.3 51.5 48.7 32.9 44.3 19.6 35.1 ResNet-50 67.2 49.9 51.6 31.0 57.8 18.1 44.7 ResNet-98 69.7 52.1 53.5 31.4 60.9 18.7 45.3 ResNet-131 71.9 53.5 55.2 31.8 65.3 19.9 45.8 DPN-14 54.2 47.8 41.5 27.7 32.8 16.4 31.7 DPN-50 55.4 46.4 43.2 26.3 35.2 16.0 36.6 DPN-98 56.9 44.8 45.0 26.0 36.6 15.6 40.3 DPN-131 60.5 45.0 47.3 25.3 40.4 14.1 45.7 平均的错误率下降率 20.7 38.7 59.9 39.8 表 5 不同预训练数据集下的绘画属性识别的性能
Table 5 Painting attribute recognition performance for different pre-trained dataset
CaffeNet HybridNet LaMemNet SentimentNet FlickrNet 预训练场景 物体分类 物体分类 记忆度检测 乐观度检测 风格分类 预训练数据集 ImageNet Places + ImageNet LaMem DeepSent FlickrStyle 预训练图片数 (张) 120 万 350 万 6 万 1269 8 万 预训练类别 1000 类 1183 类 [0, 1]* [0, 1]* 20 类 风格识别正确率 (%) 54.2 56.3 52.6 55.8 50.7 题材识别正确率 (%) 77.2 77.6 75.9 77.4 75.5 作者识别正确率 (%) 76.3 79.1 72.5 78.7 71.4 [0, 1]*: 0到1的连续等级范围 表 6 单任务与多任务学习的绘画属性识别的性能[73] (%)
Table 6 Painting attribute recognition performance for sigle-task and multi-task learning[73] (%)
作者识别 类型识别 材质识别 平均的错误率下降率 单任务模学习错误率 23.3 8.3 2.8 − 多任务学习错误率 21.5 6.3 2.0 − 错误率下降率 7.73 24.10 28.57 20.13 表 7 绘画属性识别任务的公开数据集
Table 7 Datasets for painting attribute recognition
类型 数据集 文献 年份 来源 总数量 类型 小规模 Painting-91 [77] 2014 - 4.3万 绘画艺术 小规模 Pandora7k [42] 2016 - 7.7万 绘画艺术 大规模 Pandora18k [78] 2017 WikiArt 1.8 万 绘画艺术 大规模 TICC Printmaking [79] 2017 荷兰国立博物馆 5.8 万 绘画艺术 大规模 WikiArt [41] 2015 WikiArt 8.1 万 绘画艺术 大规模 Rijks2014 [80] 2014 荷兰国内博物馆 11.2 万 绘画艺术 大规模 OmniArt [73] 2017 三个博物馆* 43.2 万 绘画艺术及摄影 大规模 Art500k [81] 2017 三个博物馆* 55.4 万 绘画艺术 丰富标注 SemArt [82] 2018 网络艺术博物馆 2.1 万 绘画艺术 丰富标注 iMet2019 [83] 2019 大都会艺术博物馆 15.6 万 艺术品 丰富标注 iMet2020 - 2020 大都会艺术博物馆 16.8 万 艺术品 丰富标注 BAM [84] 2017 Behance 2500 万 绘画及平面设计等 三个博物馆*: 包括荷兰国立博物馆、网络艺术博物馆、大都会艺术博物馆 表 8 绘画属性识别数据集的标注信息
Table 8 Labeling information for painting attribute recognition dataset
类型 数据集 标题 作者 年份 题材 派系 风格 材质 类型 情绪 关键词标签 小规模 Painting91 √ √ 小规模 Pandora7k √ √ √ √ 大规模 Pandora18k √ √ √ √ 大规模 TICC Printmaking √ √ √ √ 大规模 WikiArt √ √ √ √ 大规模 Rijks2014 √ √ √ √ √ 大规模 OmniArt √ √ √ √ 大规模 Art500k √ √ √ √ √ √ √ 丰富标注 SemArt √ √ 丰富标注 iMet2019 √ 丰富标注 iMet2020 √ 丰富标注 BAM √ √ √ √ √ 表 9 典型的绘画属性识别方法在WikiArt数据集上的性能比较
Table 9 Performance comparison for typical painting attribute recognition methods in WikiArt dataset
序号 任务 年份 文献 方法简介 分类器 数据量 类别数 正确率 (%) 1 风格 2015 [43] 颜色、SIFT、GIST、GLCM SVM 3000 10 62.37 2 风格 2016 [86] 利用 AlexNet 迁移学习 − 80000 27 54.50 3 风格 2016 [87] 利用 CaffeNet 迁移学习 − 80000 22 55.90 4 风格 2018 [68] 在扩增自然数据集上预训练 ResNet − 86087 27 56.43 5 风格 2016 [75] Deep feature、Gram、余弦相似度距离 SVM 82442 25 58.19 6 风格 2019 [46] 由绘画图像块的深度特征经过投票分类 MLP 26400 22 66.71 7 风格 2020 [20] 图片通道和笔触通道形成双通道特征 SVM 30825 25 58.99 8 题材 2016 [86] 利用 AlexNet 迁移学习 − 65000 10 74.14 9 题材 2017 [53] 利用 ResNet 迁移学习 − 79434 26 61.15 10 题材 2018 [68] 在扩增自然数据集上预训练 ResNet − 96014 10 77.16 11 题材 2015 [43] 颜色、SIFT, GIST、GLCM SVM 1800 6 84.56 12 题材 2015 [41] GIST、Classeme、PiCoDes、Deep feature SVM 63691 10 60.28 13 题材 2020 [20] 图片通道和笔触通道形成双通道特征 SVM 28760 10 76.27 14 作者 2016 [86] 利用 AlexNet 迁移学习 − 20000 23 76.11 15 作者 2017 [88] 利用 ResNet 迁移学习 − 17100 57 77.70 16 作者 2018 [68] 在扩增自然数据集上预训练 ResNet − 20320 23 81.94 17 作者 2015 [41] GIST、Classeme、PiCoDes、Deep feature SVM 18599 23 63.06 18 作者 2020 [20] 图片通道和笔触通道形成双通道特征 SVM 9766 19 88.38 表 10 绘画物体识别与检测任务的公开数据集
Table 10 Datasets for object recognition and detection in paintings
表 11 绘画内容描述任务的公开数据集
Table 11 Datasets for content description of paintings
表 12 典型的绘画内容理解方法及其性能
Table 12 Typical painting content understanding methods and performances
表 13 公开的绘画美感和情感数据集
Table 13 Database for emotion and aesthetic of paintings
类型 数据库 文献 图片数 类别数 等级数 标注/张* 说明 美感 国画美感数据库 [109] 511 5 9 20 气势美、清幽美和生机美上的 9 个等级 美感 JenAestheticsβ [112] 281 − 4 − 从丑到美 4 个等级 美感 JenaAesthetics [137] 1629 − 100 20 美感的 100 个等级 情感 国画情感数据库 [109] 511 3 9 20 愉悦度、唤醒度、优势度上的 9 个等级 情感 ArtPhoto 绘画 [113] 807 8 − − 气愤、激动、害怕等 8 种情感 情感 Affective 抽象绘画# [113] 228 8 − 14 气愤、激动、害怕等 8 种情感 情感 MART 抽象绘画 [121] 500 − 7 20 消极到积极的 7 个等级 情感 WikiArt Emotions [136] 4105 20 − − 害怕、快乐、爱、悲伤等情感 标注/张*: 每张图片的标注次数; Affective 抽象绘画#: 我们对文献 [113] 的抽象绘画数据集的命名 -
[1] Zangwill N. The concept of the aesthetic. European Journal of Philosophy, 1998, 6(1): 78−93 doi: 10.1111/1468-0378.00051 [2] Fechner G T. Vorschule der Aesthetik. Leipzing: Breitkopf, 1876. 1−7 [3] Hoenig F. Defining computational aesthetics. In: Proceedings of the 1st Eurographics Conference on Computational Aesthetics in Graphics, Visualization and Imaging. Girona, Spain: Eurographics Association, 2005. 13−18 [4] Leder H, Belke B, Oeberst A, Augustin D. A model of aesthetic appreciation and aesthetic judgments. British Journal of Psychology, 2004, 95(4): 489−508 doi: 10.1348/0007126042369811 [5] Newman M E J. Scientific collaboration networks. I. Network construction and fundamental results. Physical Review E, 2001, 64(1): 016131 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.64.016131 [6] Bastian M, Heymann S, Jacomy M. Gephi: An open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Weblogs and Social Media. San Jose, USA: AAAI, 2009. [7] 王伟凝, 蚁静缄, 贺前华. 可计算图像美学研究进展. 中国图象图形学报, 2012, 17(8): 893−901 doi: 10.11834/jig.20120801Wang Wei-Ning, Yi Jing-Jian, He Qian-Hua. Review for computational image aesthetics. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2012, 17(8): 893−901 doi: 10.11834/jig.20120801 [8] 白茹意, 郭小英, 贾春花, 耿海军. 绘画图像美学研究方法综述. 中国图象图形学报, 2019, 24(11): 1860−1881 doi: 10.11834/jig.190118Bai Ru-Yi, Guo Xiao-Ying, Jia Chun-Hua, Geng Hai-Jun. Overview of research methods of painting aesthetics. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2019, 24(11): 1860−1881 doi: 10.11834/jig.190118 [9] Fiorucci M, Khoroshiltseva M, Pontil M, Traviglia A, Del Bue A, James S. Machine learning for cultural heritage: A survey. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 133: 102−108 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2020.02.017 [10] Perc M. Beauty in artistic expressions through the eyes of networks and physics. Journal of The Royal Society Interface, 2020, 17(164): 20190686 doi: 10.1098/rsif.2019.0686 [11] Liu C, Jiang H. Classification of traditional Chinese paintings based on supervised learning methods. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing. Guilin, China: IEEE, 2014. 641−644 [12] Yu H, Li M J, Zhang H J, Feng J F. Color texture moments for content-based image retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 2002 International Conference on Image Processing. Rochester, USA: IEEE, 2002. 929−932 [13] Jiang S Q, Huang Q M, Ye Q X, Gao W. An effective method to detect and categorize digitized traditional Chinese paintings. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2006, 27(7): 734−746 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2005.10.017 [14] Manjunath B S, Ohm J R, Vasudevan V V, Yamada A. Color and texture descriptors. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2001, 11(6): 703−715 doi: 10.1109/76.927424 [15] Khan R, van de Weijer J, Khan F S, Muselet D, Ducottet C, Barat C. Discriminative color descriptors. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 2866−2873 [16] Falomir Z, Museros L, Sanz I, Gonzalez-Abril L. Categorizing paintings in art styles based on qualitative color descriptors, quantitative global features and machine learning (QArt-Learn). Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 97: 83−94 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2017.11.056 [17] Lu G M, Gao Z, Qin D N, Zhao X, Liu M J. Content-based identifying and classifying traditional chinese painting images. In: Proceedings of the 2008 Congress on Image and Signal Processing. Sanya, Hainan, China: IEEE, 2008. 570−2574 [18] Haralick R M. Statistical and structural approaches to texture. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1979, 67(5): 786−804 doi: 10.1109/PROC.1979.11328 [19] Gatys L A, Ecker A S, Bethge M. Image style transfer using convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2414−2423 [20] Zhong S H, Huang X S, Xiao Z J. Fine-art painting classification via two-channel dual path networks. International Journal of Machine Learning and Cybernetics, 2020, 11(1): 137−152 doi: 10.1007/s13042-019-00963-0 [21] 盛家川. 基于小波变换的国画特征提取及分类. 计算机科学, 2014, 41(2): 317−319 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2014.02.069Sheng Jia-Chuan. Automatic categorization of traditional chinese paintings based on wavelet transform. Computer Science, 2014, 41(2): 317−319 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-137X.2014.02.069 [22] 黎宇帆, 邢鸿雁, 陈静旋, 杨敏之. 基于Gabor理论的山水画皴法分类. 计算机科学与应用, 2014, 4(3): 59−65 doi: 10.12677/CSA.2014.43011Li Yu-Fan, Xing Hong-Yan, Chen Jing-Xuan, Yang Min-Zhi. Classification of landscape painting texturing based on gabor. Computer Science and Application, 2014, 4(3): 59−65 doi: 10.12677/CSA.2014.43011 [23] Zujovic J, Gandy L, Friedman S, Pardo B, Pappas T N. Classifying paintings by artistic genre: An analysis of features & classifiers. In: Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Workshop on Multimedia Signal Processing. Rio De Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2009. 1−5 [24] Jiang W, Wang Z, Jin J S, Han Y H, Sun M J. DCT-CNN-based classification method for the gongbi and xieyi techniques of Chinese ink-wash paintings. Neurocomputing, 2019, 330: 280−286 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.11.003 [25] Misumi M, Orii H, Sharmin T, Mishma K, Tsuruoka T. Image classification for the painting style with SVM. In: Proceedings of the 4th ⅡAE International Conference on Industrial Application Engineering. Beppu, Japan: The Institute of Industrial Applications Engineers, 2016. 245−249 [26] Lowe D G. Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2): 91−110 doi: 10.1023/B:VISI.0000029664.99615.94 [27] Van De Sande K, Gevers T, Snoek C. Evaluating color descriptors for object and scene recognition. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(9): 1582−1596 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.154 [28] Abdel-Hakim A E, Farag A A. Csift: A SIFT descriptor with color invariant characteristics. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York, USA: IEEE, 2006. 1978−1983 [29] Saleh B, Abe K, Arora R S, Elgammal A. Toward automated discovery of artistic influence. arXiv: 1408.3218, 2014 [30] Bay H, Tuytelaars T, Van Gool L. SURF: Speeded up robust features. In: Proceedings of the 9th European Conference on Computer Vision. Graz, Austria: Springer, 2006. 404−417 [31] Rublee E, Rabaud V, Konolige K, Bradski G. ORB: An efficient alternative to SIFT or SURF. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 2564−2571 [32] Haladova Z, Sikudova E. Combination of global and local features for efficient classification of paintings. In: Proceedings of the 29th Spring Conference on Computer Graphics. Smolenice, Slovakia: ACM, 2013. 13−20 [33] Ojala T, Pietikainen M, Harwood D. A comparative study of texture measures with classification based on featured distributions. Pattern Recognition, 1996, 29(1): 51−59 doi: 10.1016/0031-3203(95)00067-4 [34] Wang Z H, Fan B, Wu F C. Local intensity order pattern for feature description. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 603−610 [35] Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2005. 886−893 [36] Oliva A, Torralba A. Modeling the shape of the scene: A holistic representation of the spatial envelope. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2001, 42(3): 145−175 doi: 10.1023/A:1011139631724 [37] Torresani L, Szummer M, Fitzgibbon A. Efficient object category recognition using classemes. In: Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision. Heraklion, Greece: Springer, 2010. 776−789 [38] Bergamo A, Torresani L. Meta-class features for large-scale object categorization on a budget. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 3085−3092 [39] Bergamo A, Torresani L, Fitzgibbon A W. PiCoDes: Learning a compact code for novel-category recognition. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Granada, Spain: NIPS, 2011. 2088−2096 [40] Shechtman E, Irani M. Matching local self-similarities across images and videos. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Minneapolis, USA: IEEE, 2007. 1−8 [41] Saleh B, Elgammal A. A unified framework for painting classification. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining Workshop. Atlantic City, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1254−1261 [42] Florea C, Condorovici R, Vertan C, Butnaru R, Florea L, Vranceanu R. Pandora: Description of a painting database for art movement recognition with baselines and perspectives. In: Proceedings of the 24th European Signal Processing Conference. Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2016. 918−922 [43] Agarwal S, Karnick H, Pant N, Patel U. Genre and style based painting classification. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2015. 588−594 [44] Condorovici R G, Florea C, Vertan C. Automatically classifying paintings with perceptual inspired descriptors. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2015, 26: 222−230 doi: 10.1016/j.jvcir.2014.11.016 [45] Cornelis B, Dooms A, Cornelis J, Leen F, Schelkens P. Digital painting analysis, at the cross section of engineering, mathematics and culture. In: Proceedings of the 19th European Signal Processing Conference. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 1254−1258 [46] Sandoval C, Pirogova E, Lech M. Two-stage deep learning approach to the classification of fine-art paintings. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 41770−41781 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2907986 [47] Csurka G, Dance C R, Fan L X, Willamowski J, Bray C. Visual categorization with bags of keypoints. In: Proceedings of the 8th European Conference on Computer Vision. Prague, Czech Republic: Springer, 2004. 1−22 [48] Lazebnik S, Schmid C, Ponce J. Beyond bags of features: Spatial pyramid matching for recognizing natural scene categories. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. New York, USA: IEEE, 2006. 2169−2178 [49] Bosch A, Zisserman A, Munoz X. Representing shape with a spatial pyramid kernel. In: Proceedings of the 6th ACM International Conference on Image and Video Retrieval. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: ACM, 2007. 401−408 [50] 张浩, 徐丹. 基于深度学习的少数民族绘画情感分析方法. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2019, 49(2): 204−215 doi: 10.1360/N112018-00249Zhang Hao, Xu Dan. Ethnic painting analysis based on deep learning. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2019, 49(2): 204−215 doi: 10.1360/N112018-00249 [51] Hong Y Y, Kim J. Art painting identification using convolutional neural network. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research, 2017, 12(4): 532−539 [52] Smirnov S, Eguizabal A. Deep learning for object detection in fine-art paintings. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Metrology for Archaeology and Cultural Heritage. Cassino, Italy: IEEE, 2018. 45−49 [53] Badea M, Florea C, Florea L, Vertan C. Efficient domain adaptation for painting theme recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Symposium on Signals, Circuits and Systems. Iasi, Romania: IEEE, 2017. 1−4 [54] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84−90 doi: 10.1145/3065386 [55] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv: 1409.1556, 2014 [56] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A. Going deeper with convolutions. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 1−9 [57] Szegedy C, Vanhoucke V, Ioffe S, Shlens J, Wojna Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2818−2826 [58] Huang G, Liu Z, van der Maaten L, Weinberger K Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2261−2269 [59] Meng Q Y, Zhang H H, Zhou M Q, Zhao S F, Zhou P B. The classification of traditional Chinese painting based on CNN. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Cloud Computing and Security. Haikou, China: Springer, 2018. 232−241 [60] David O E, Netanyahu N S. DeepPainter: Painter classification using deep convolutional autoencoders. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Artificial Neural Networks. Barcelona, Spain: Springer, 2016. 20−28 [61] Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S A, Huang Z H, Karpathy A, Khosla A, Bernstein M, Berg A C, Li F F. Imagenet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211−252 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [62] Kelek M O, Calik N, Yildirim T. Painter classification over the novel art painting data set via the latest deep neural networks. Procedia Computer Science, 2019, 154: 369−376 doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2019.06.053 [63] Lecoutre A, Negrevergne B, Yger F. Recognizing art style automatically in painting with deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 9th Asian Conference on Machine Learning. Seoul, Korea: PMLR, 2017. 327−342 [64] Elgammal A, Mazzone M, Liu B C, Kim D, Elhoseiny M. The shape of art history in the eyes of the machine. arXiv: 1801.07729, 2018 [65] Sabatelli M, Kestemont M, Daelemans W, Geurts P. Deep transfer learning for art classification problems. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 631−646 [66] Bojarski M, Choromanska A, Choro-manski K, Firner B, Jackel L, Muller U, Zieba K. Visualbackprop: Efficient visualization of CNNs. arXiv: 1611.05418, 2017 [67] Pan S J, Yang Q. A survey on transfer learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2010, 22(10): 1345−1359 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2009.191 [68] Cetinic E, Lipic T, Grgic S. Fine-tuning convolutional neural networks for fine art classification. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 114: 107−118 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.07.026 [69] Zhou B L, Lapedriza A, Xiao J X, Torralba A, Oliva A. Learning deep features for scene recognition using places database. In: Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Quebec, Canada: NIPS, 2014. 487−495 [70] Khosla A, Raju A S, Torralba A, Oliva A. Understanding and predicting image memorability at a large scale. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 2390−2398 [71] You Q Z, Luo J B, Jin H L, Yang J C. Robust image sentiment analysis using progressively trained and domain transferred deep networks. In: Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Austin, USA: AAAI, 2015. 381−388 [72] Karayev S, Trentacoste M, Han H, Agarwala A, Darrell T, Hertzmann A, Winne-moeller H. Recognizing image style. In: Proceedings of the 2014 British Machine Vision Conference. Nottingham, UK: BMVA, 2014 [73] Strezoski G, Worring M. OmniArt: Multi-task deep learning for artistic data analysis. arXiv: 1708.00684, 2017 [74] Garcia N, Renoust B, Nakashima Y. ContextNet: Representation and exploration for painting classification and retrieval in context. International Journal of Multimedia Information Retrieval, 2020, 9(1): 17−30 doi: 10.1007/s13735-019-00189-4 [75] Chu W T, Wu Y L. Deep correlation features for image style classification. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: ACM, 2016. 402−406 [76] Huang X S, Zhong S H, Xiao Z J. Fine-art painting classification via two-channel deep residual network. In: Proceedings of the 18th Pacific Rim Conference on Multimedia. Harbin, China: Springer, 2017. 79−88 [77] Khan F S, Beigpour S, van de Weijer J, Felsberg M. Painting-91: A large scale database for computational painting categorization. Machine Vision and Applications, 2014, 25(6): 1385−1397 doi: 10.1007/s00138-014-0621-6 [78] Florea C, Toca C, Gieseke F. Artistic movement recognition by boosted fusion of color structure and topographic description. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Santa Rosa, USA: IEEE, 2017. 569−577 [79] van Noord N, Postma E. Learning scale-variant and scale-invariant features for deep image classification. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 61: 583−592 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.06.005 [80] Mensink T, van Gemert J. The rijksmuseum challenge: Museum-centered visual recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval. Glasgow, United Kingdom: ACM, 2014. [81] Mao H, Cheung M, She J. DeepArt: Learning joint representations of visual arts. In: Proceedings of the 25th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Mountain View, USA: ACM, 2017. 1183−1191 [82] Garcia N, Vogiatzis G. How to read paintings: Semantic art understanding with multi-modal retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 676−691 [83] Zhang C Y, Kaeser-Chen C, Vesom G, Choi J, Kessler M, Belongie S. The iMet collection 2019 challenge dataset. arXiv: 1906.00901, 2019 [84] Wilber M J, Fang C, Jin H L, Hertzmann A, Collomosse J, Belongie S. BAM! The behance artistic media dataset for recognition beyond photography. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1211−1220 [85] Saleh B, Elgammal A. Large-scale classification of fine-art paintings: Learning the right metric on the right feature. arXiv: 1505.00855, 2015 [86] Tan W R, Chan C S, Aguirre H E, Tanaka K. Ceci n'est pas une pipe: A deep convolutional network for fine-art paintings classification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Phoenix, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3703−3707 [87] Hentschel C, Wiradarma T P, Sack H. Fine tuning CNNs with scarce training data - adapting imagenet to art epoch classification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. Phoenix, USA: IEEE, 2016. 3693−3697 [88] Viswanathan N. Artist Identification with Convolutional Neural Networks, Technical Report, SVL Lab, Stanford University, USA, 2017. [89] Inoue N, Furuta R, Yamasaki T, Aizawa K. Cross-Domain weakly-supervised object detection through progressive domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 5001−5009 [90] Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, Efros A A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2242−2251 [91] Crowley E J, Zisserman A. In search of art. In: Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. [92] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137−1149 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [93] Gu Q Q, King R. Deep learning does not generalize well to recognizing cats and dogs in Chinese paintings. In: Proceedings of the 22nd International Conference on Discovery Science. Split, Croatia: Springer, 2019. 166−175 [94] Ginosar S, Haas D, Brown T, Malik J. Detecting people in cubist art. In: Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 101−116 [95] Baraldi L, Cornia M, Grana C, Cucchiara R. Aligning text and document illustrations: Towards visually explainable digital humanities. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2018. 1097−1102 [96] Carraggi A, Cornia M, Baraldi L, Cucchiara R. Visual-Semantic alignment across domains using a semi-supervised approach. In: Proceedings of the 2018 European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 625−640 [97] Stefanini M, Cornia M, Baraldi L, Corsini M, Cucchiara R. Artpedia: A new visual-semantic dataset with visual and contextual sentences in the Artistic Domain. In: Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing. Trento, Italy: Springer, 2019. 729−740 [98] Cornia M, Stefanini M, Baraldi L, Corsini M, Cucchiara R. Explaining digital humanities by aligning images and textual descriptions. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2020, 129: 166−172 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.11.018 [99] Garcia N, Renoust B, Nakashima Y. Understanding art through multi-modal retrieval in paintings. arXiv: 1904.10615, 2019 [100] Garcia N, Renoust B, Nakashima Y. Context-aware embeddings for automatic art analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2019 on International Conference on Multimedia Retrieval. Ottawa, Canada: ACM, 2019. 25−33 [101] Sheng S R, Moens M F. Generating captions for images of ancient artworks. In: Proceedings of the 27th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Nice, France: ACM, 2019. 2478−2486 [102] Bongini P, Becattini F, Bagdanov A D, Del Bimbo A. Visual question answering for cultural heritage. arXiv: 2003.09853, 2020 [103] Crowley E, Zisserman A. The state of the art: Object retrieval in paintings using discriminative regions. In: Proceedings of the 2014 British Machine Vision Conference. Nottingham, UK: BMVA Press, 2014. [104] Westlake N, Cai H P, Hall P. Detecting people in artwork with CNNs. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 825−841 [105] Madhu P, Kosti R, Muhrenberg L, Bell P, Maier A, Christlein V. Recognizing characters in art history using deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 1st Workshop on Structuring and Understanding of Multimedia HeritAge Contents. Nice, France: ACM, 2019. 15−22 [106] Papineni K, Roukos S, Ward T, Zhu W J. BLEU: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics. Philadelphia, USA: ACL, 2002. 311−318 [107] Vedantam R, Lawrence Zitnick C, Parikh D. Cider: Consensus-based image description evaluation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 4566−4575 [108] 李霞, 卢官明, 闫静杰, 张正言. 多模态维度情感预测综述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(12): 2142−2159Li Xia, Lu Guan-Ming, Yan Jing-Jie, Zhang Zheng-Yan. A survey of dimensional emotion prediction by multimodal cues. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(12): 2142−2159 [109] 湛颖, 高妍, 谢凌云. 中国国画艺术美感特征分析与分类. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(12): 2514−2522Zhan Ying, Gao Yan, Xie Ling-Yun. Feature analysis and classification for aesthetic of Chinese traditional painting. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(12): 2514−2522 [110] Li C C, Chen T. Aesthetic visual quality assessment of paintings. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2009, 3(2): 236−252 doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2009.2015077 [111] Matsuda Y. Color Design. Tokyo: Asakura Shoten, 1995. 13−18 [112] Amirshahi S A, Hayn-Leichsenring G U, Denzler J, Redies C. Color: A crucial factor for aesthetic quality assessment in a subjective dataset of paintings. arXiv: 1609.05583, 2016 [113] Machajdik J, Hanbury A. Affective image classification using features inspired by psychology and art theory. In: Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Firenze, Italy: ACM, 2010. 83−92 [114] Valdez P, Mehrabian A. Effects of color on emotions. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 1994, 123(4): 394−409 doi: 10.1037/0096-3445.123.4.394 [115] Itten J. The Art of Color: The Subjective Experience and Objective Rationale of Color. New York: Wiley, 1997. 15−26 [116] Amirshahi S A, Denzler J. Judging aesthetic quality in paintings based on artistic inspired color features. In: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2017. 1−8 [117] Sartori A. Affective analysis of abstract paintings using statistical analysis and art theory. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Multimodal Interaction. Istanbul, Turkey: ACM, 2014. 384−388 [118] Sartori A, Culibrk D, Yan Y, Sebe N. Who's afraid of itten: Using the art theory of color combination to analyze emotions in abstract paintings. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Brisbane, Australia: ACM, 2015. 311−320 [119] Sartori A, Yan Y, Ozbal G, Salah A A A, Salah A A, Sebe N. Looking at Mondrian's victory Boogie-Woogie: What do I feel? In: Proceedings of the 24th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Buenos Aires, Argentina: AAAI, 2015. 2503−2509 [120] Sartori A, Culibrk D, Yan Y, Job R, Sebe N. Computational modeling of affective qualities of abstract paintings. IEEE MultiMedia, 2016, 23(3): 44−54 doi: 10.1109/MMUL.2016.20 [121] Yanulevskaya V, Uijlings J, Bruni E, Sartori A, Zamboni E, Bacci F, Melcher D, Sebe N. In the eye of the beholder: Employing statistical analysis and eye tracking for analyzing abstract paintings. In: Proceedings of the 20th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Nara, Japan: ACM, 2012. 349−358 [122] Leong J, Chung A. Affective Classification of Abstract Paintings Using Artificial Neural Networks, Technical Report, University of Waterloo, Canada, 2014. [123] Sartori A, Snyazar B, Salah A A A, Salah A A, Sebe N. Emotions in abstract art: Does texture matter? In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Image Analysis and Processing. Genoa, Italy: Springer, 2015. 671−682 [124] 王征, 李皓月, 许洪山, 孙美君. 基于卷积神经网络和SVM的中国画情感分类. 南京师大学报(自然科学版), 2017, 40(3): 74−79Wang Zheng, Li Hao-Yue, Xu Hong-Shan, Sun Mei-Jun. Chinese painting emotion classification based on convolution neural network and SVM. Journal of Nanjing Normal University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 40(3): 74−79 [125] Tan W, Wang J, Wang Y, Lewis M, Jarrold W, Davis U. CNN Models for Classifying Emotions Evoked by Paintings, Technical Report, SVL Lab, Stanford University, USA, 2018. [126] Yanulevskaya V, van Gemert J C, Roth K, Herbold A K, Sebe N, Geusebroek J M. Emotional valence categorization using holistic image features. In: Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Image Processing. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2008. 101−104 [127] Lang P J. International Affective Picture System (IAPS): Technical Manual and Affective Ratings, Technical Report, NIMH Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention, University of Florida, USA, 1997. [128] Cetinic E, Lipic T, Grgic S. A deep learning perspective on beauty, sentiment, and remembrance of art. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 73694−73710 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2921101 [129] Katsurai M, Satoh S. Image sentiment analysis using latent correlations among visual, textual, and sentiment views. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2016. 2837−2841 [130] Kong S, Shen X H, Lin Z, Mech R, Fowlkes C. Photo aesthetics ranking network with attributes and content adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 662−679 [131] Murray N, Marchesotti L, Perronnin F. AVA: A large-scale database for aesthetic visual analysis. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 2408−2415 [132] Ren J, Shen X H, Lin Z, Mech R, Foran D J. Personalized image aesthetics. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 638−647 [133] 李博, 郭琛, 任慧. 基于加权K近邻算法的抽象画图像情感分布预测. 中国传媒大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 25(1): 36−40Li Bo, Guo Chen, Ren Hui. Emotion distribution prediction of abstract painting image based on weighted KNN algorithm. Journal of Communication University of China (Science and Technology), 2018, 25(1): 36−40 [134] Alameda-Pineda X, Ricci E, Yan Y, Sebe N. Recognizing emotions from abstract paintings using non-linear matrix completion. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 5240−5248 [135] Hevner K. Experimental studies of the elements of expression in music. The American Journal of Psychology, 1936, 48(2): 246−268 doi: 10.2307/1415746 [136] Mohammad S, Kiritchenko S. WikiArt emotions: An annotated dataset of emotions evoked by art. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Language Resources and Evaluation. Miyazaki, Japan: ELRA, 2018. [137] Amirshahi S A, Redies C, Denzler J. How self-similar are artworks at different levels of spatial resolution? In: Proceedings of the 2013 Symposium on Computational Aesthetics. Anaheim, USA: ACM, 2013. 93−100 [138] Herbrich R, Minka T, Graepel T. TrueSkillTM: A bayesian skill rating system. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT, 2006. 569−576 [139] Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel Art: From Intelligent Art to Artistic Intelligence, Technical Report, The Alfred North Whitehead College, Beijing, China, 2017. [140] 郭超, 鲁越, 林懿伦, 卓凡, 王飞跃. 平行艺术: 人机协作的艺术创作. 智能科学与技术学报, 2019, 1(4): 335−341Guo Chao, Lu Yue, Lin Yi-Lun, Zhuo Fan, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel art: Artistic creation under human-machine collaboration. Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technology, 2019, 1(4): 335−341 [141] Guo C, Bai T X, Lu Y, Lin Y L, Xiong G, Wang X, et al. Skywork-daVinci: A novel CPSS-based painting support system. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2020. 673−678 [142] 李力, 林懿伦, 曹东璞, 郑南宁, 王飞跃. 平行学习—机器学习的一个新型理论框架. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(1): 1−8Li Li, Lin Yi-Lun, Cao Dong-Pu, Zheng Nan-Ning, Wang Fei-Yue. Parallel learning — a new framework for machine learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1): 1−8 -




 下载:
下载: