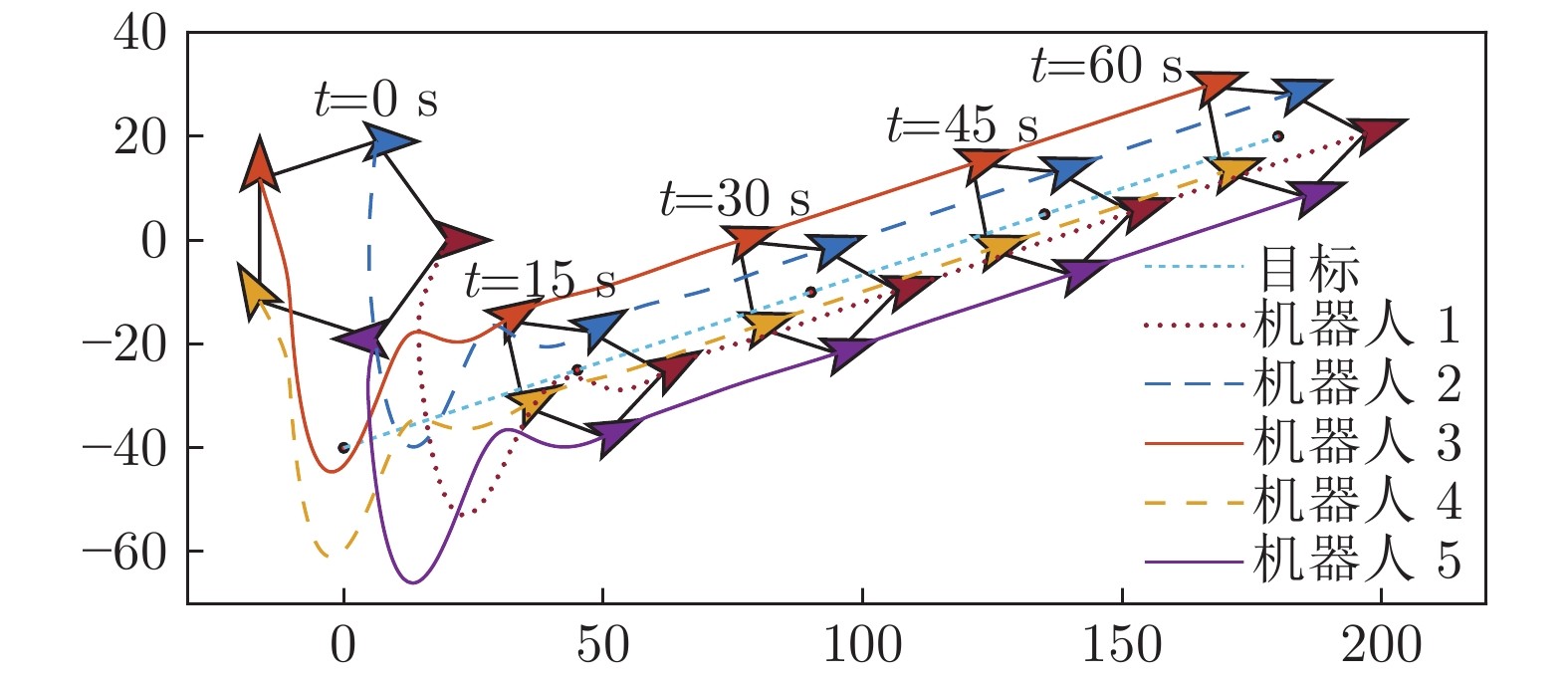
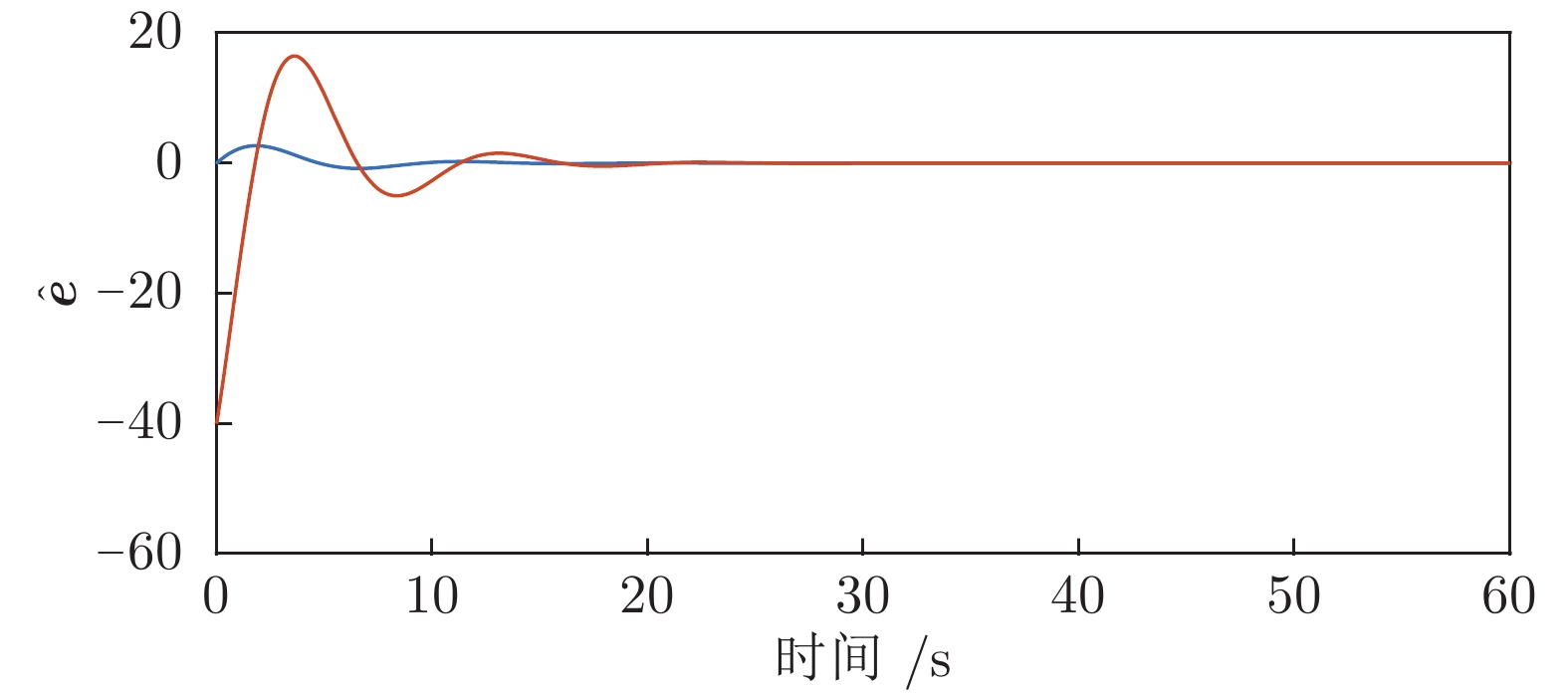
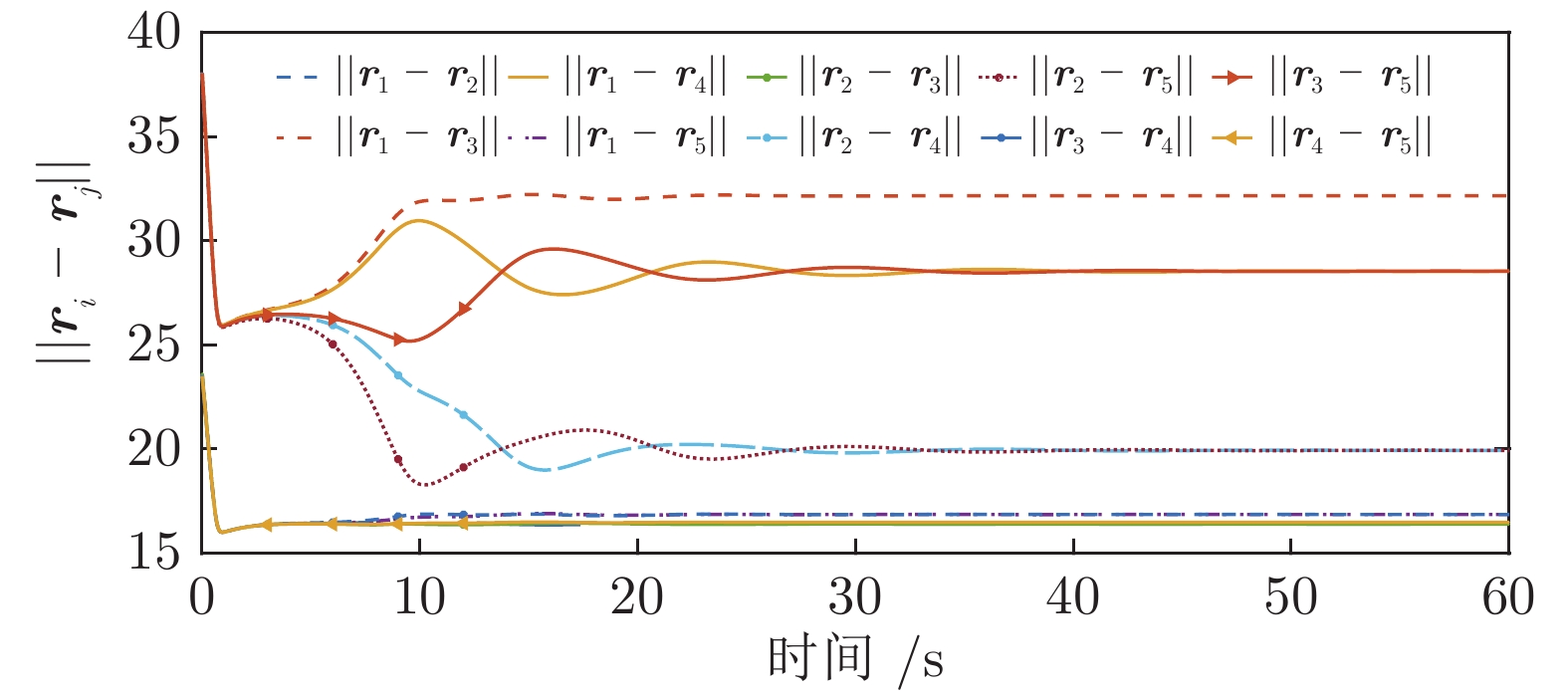
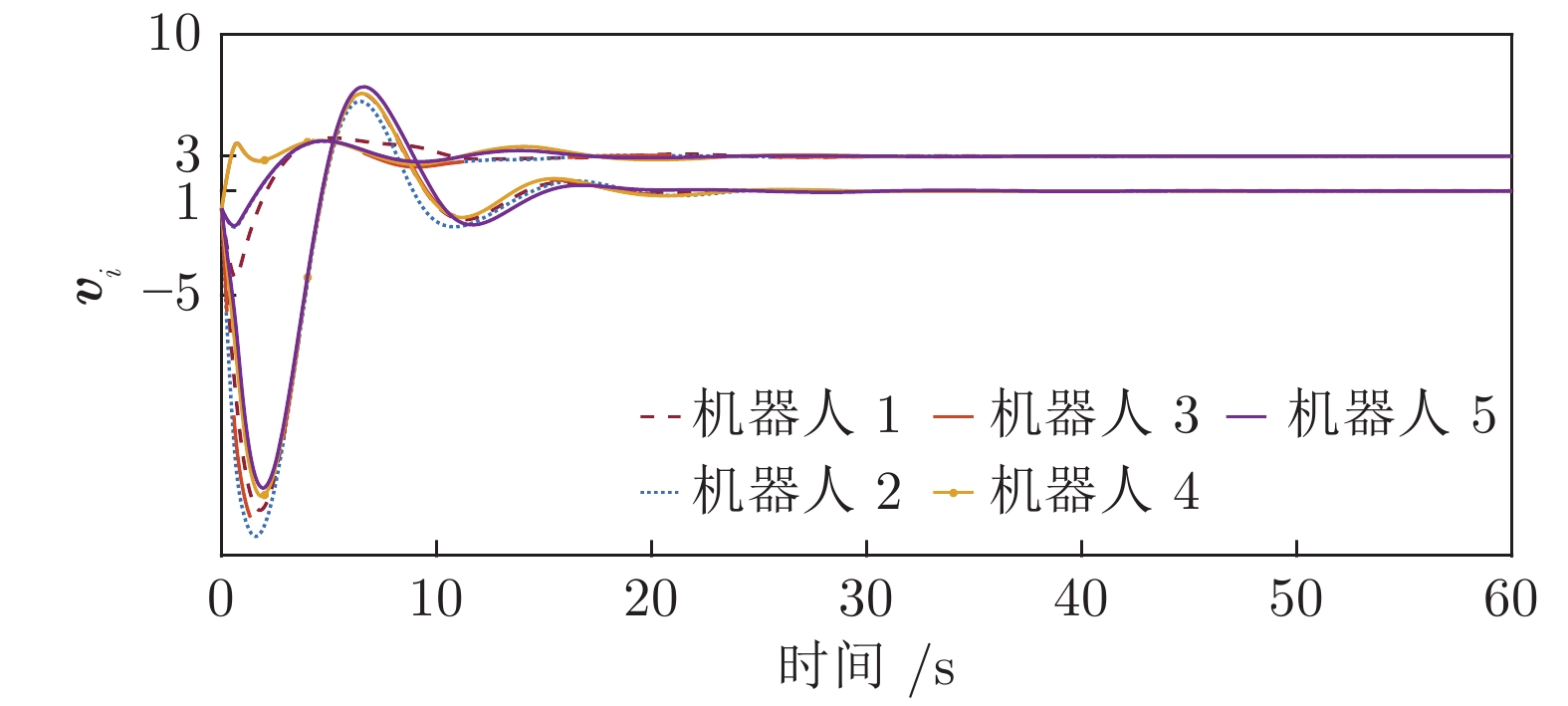
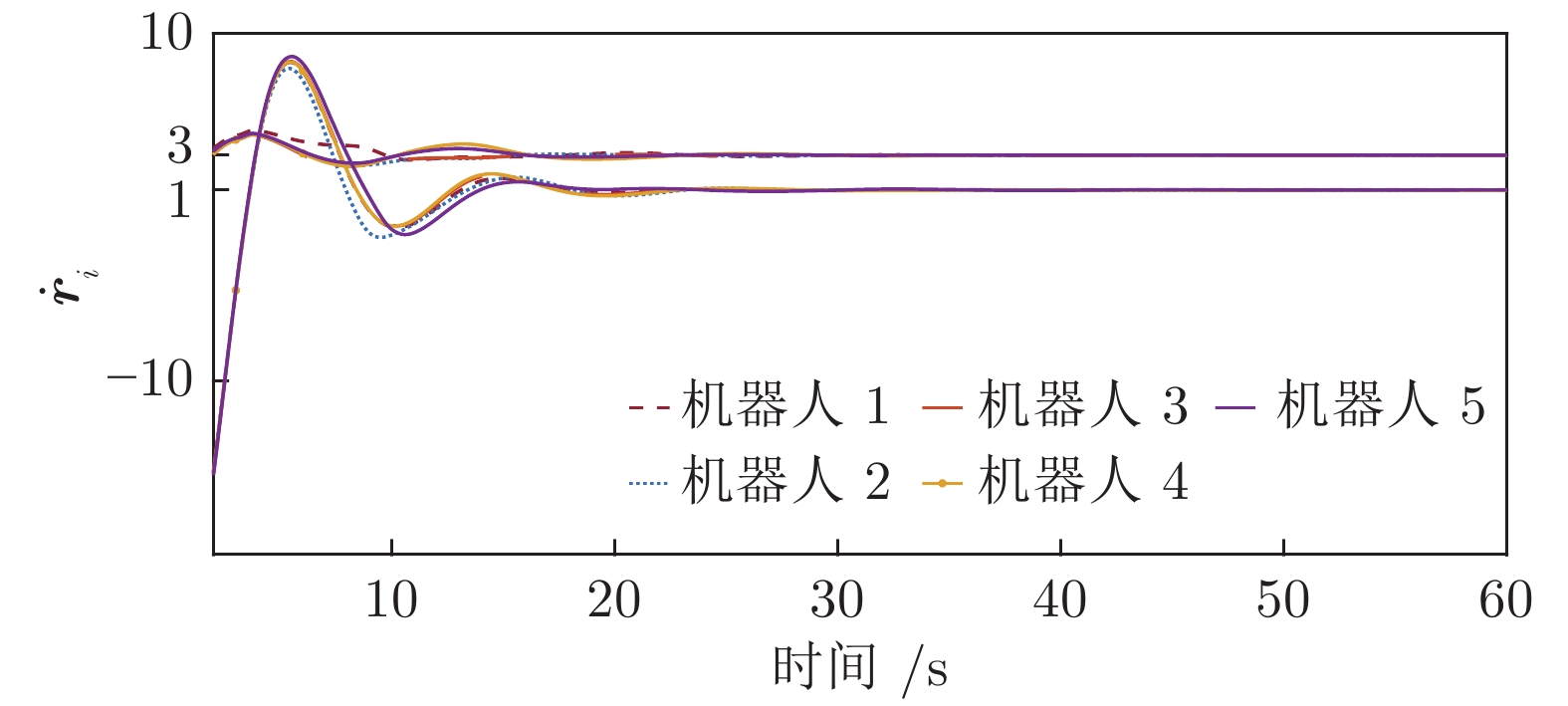
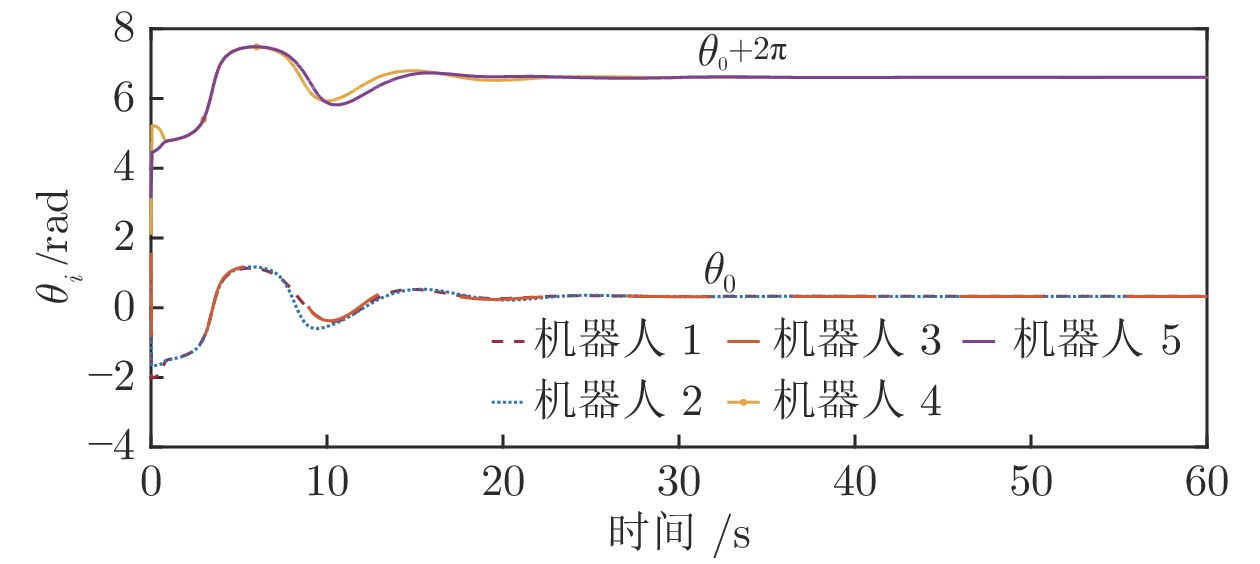
|
[1]
|
洪奕光, 翟超. 多智能体系统动态协调与分布式控制设计. 控制理论与应用, 2011, 28(10): 1506-1512.Hong Yi-Guang, Zhai Chao. Dynamic coordination and distributed control design of multi-agent systems. Control Theory & Application, 2011, 28(10): 1506-1512.
|
|
[2]
|
Knorn S, Chen Z Y, Middleton R H. Overview: Collective control of multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2016, 3(4): 334-347. doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2015.2468991
|
|
[3]
|
李玉玲, 杨洪勇, 刘凡, 杨怡泽. 带有不匹配干扰的二阶多自主体系统有限时间包容控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(9): 1783-1790.Li Yu-Ling, Yang Hong-Yong, Liu Fan, Yang Yi-Ze. Finite-time containment control of second-order multi-agent systems with mismatched disturbances. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(9): 1783-1790.
|
|
[4]
|
刘娟, 张皓, 王祝萍. 基于自触发的异构多智能体协同输出调节. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(10): 1893-1902.Liu Juan, Zhang Hao, Wang Zhu-Ping. Cooperative output regulation of heterogeneous multi-agent systems by self-triggered. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(10): 1893-1902.
|
|
[5]
|
刘凡, 杨洪勇, 杨怡泽, 李玉玲, 刘远山. 带有不匹配干扰的多智能体系统有限时间积分滑模控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(4): 749-758.Liu Fan, Yang Hong-Yong, Yang Yi-Ze, Li Yu-Ling, Liu Yuan-Shan. Finite-time integral sliding mode control for multi-agent systems with mismatched disturbances. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(4): 749-758.
|
|
[6]
|
Huang Y, Duan M M, Mo L P. Multiagent containment control with nonconvex states constraints, nonuniform time delays, and switching directed networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2019, 31(11): 5021-5028.
|
|
[7]
|
金尚泰, 李澈, 任叶, 侯忠生. 未知异构非线性多智能体系统的无模型自适应编队控制述. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(6): 1519-1524.Jin Shang-Tai, Li Che, Ren Ye, Hou Zhong-Sheng. Model-free adaptive formation control for unknown heterogeneous nonlinear multi-agent systems. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(6): 1519-1524.
|
|
[8]
|
Chen F, Ren W, Cao Y C. Surrounding control in cooperative agent networks. Systems & Control Letters, 2010, 59(11): 704-712.
|
|
[9]
|
Lou Y C, Hong Y G. Distributed surrounding design of target region with complex adjacency matrices. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control. 2015, 60(1): 283-288. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2014.2322917
|
|
[10]
|
Brockett R W. Differential Geometric Control Theory. Massachusetts: Birkhauser, 1983. 181−191
|
|
[11]
|
Yamamoto Y, Yun X. Coordinating locomotion and manipulation of a mobile manipulator. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control. 1994, 39(6): 1326-1332. doi: 10.1109/9.293207
|
|
[12]
|
Arranz L, Seuret A, Pascoal A. Circular formation control for cooperative target tracking with limited information. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2019, 356(4): 1771-1788. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.12.011
|
|
[13]
|
Paliotta C, Lefeber E, Pettersen K Y, Pinto J, Costa M, de Figueiredo Borges de Sousa J T. Trajectory tracking and path following for underactuated marine vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2019, 27(4): 1423-1437. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2018.2834518
|
|
[14]
|
Chen Z Y, Zhang H T. A remark on collective circular motion of jointly connected multi-agents. Automatica, 2011, 47(9): 1929-1937. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.03.012
|
|
[15]
|
Yu X, Liu L, Feng G. Distributed circular formation control of nonholonomic vehicles without direct distance measurements. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(8): 2730-2737. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2790259
|
|
[16]
|
Lan Y, Yan G F, Lin Z Y. Distributed control of cooperative target enclosing based on reachability and invariance analysis. Systems & Control Letters, 2010, 59(7): 381-389.
|
|
[17]
|
Frew E W, Lawrence D A, Morris S. Coordinated standoff tracking of moving targets using Lyapunov guidance vector fields. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2008, 31(2): 290-306.
|
|
[18]
|
Yu X, Liu L. Cooperative control for moving-target circular formation of nonholonomic vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2017, 62(7): 3448-3454. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2016.2614348
|
|
[19]
|
Chen Z Y. A cooperative target-fencing protocol of multiple vehicles. Automatica, 2019, 107: 591-594. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.05.034
|
|
[20]
|
Isidori A. Nonlinear Control Systems. New York: Springer-Verlag, 1989. 147−161
|
|
[21]
|
Slotine J J E, Li W P. Applied Nonlinear Control. New Jersey: Prentice-Hall, 1991. 100−156
|




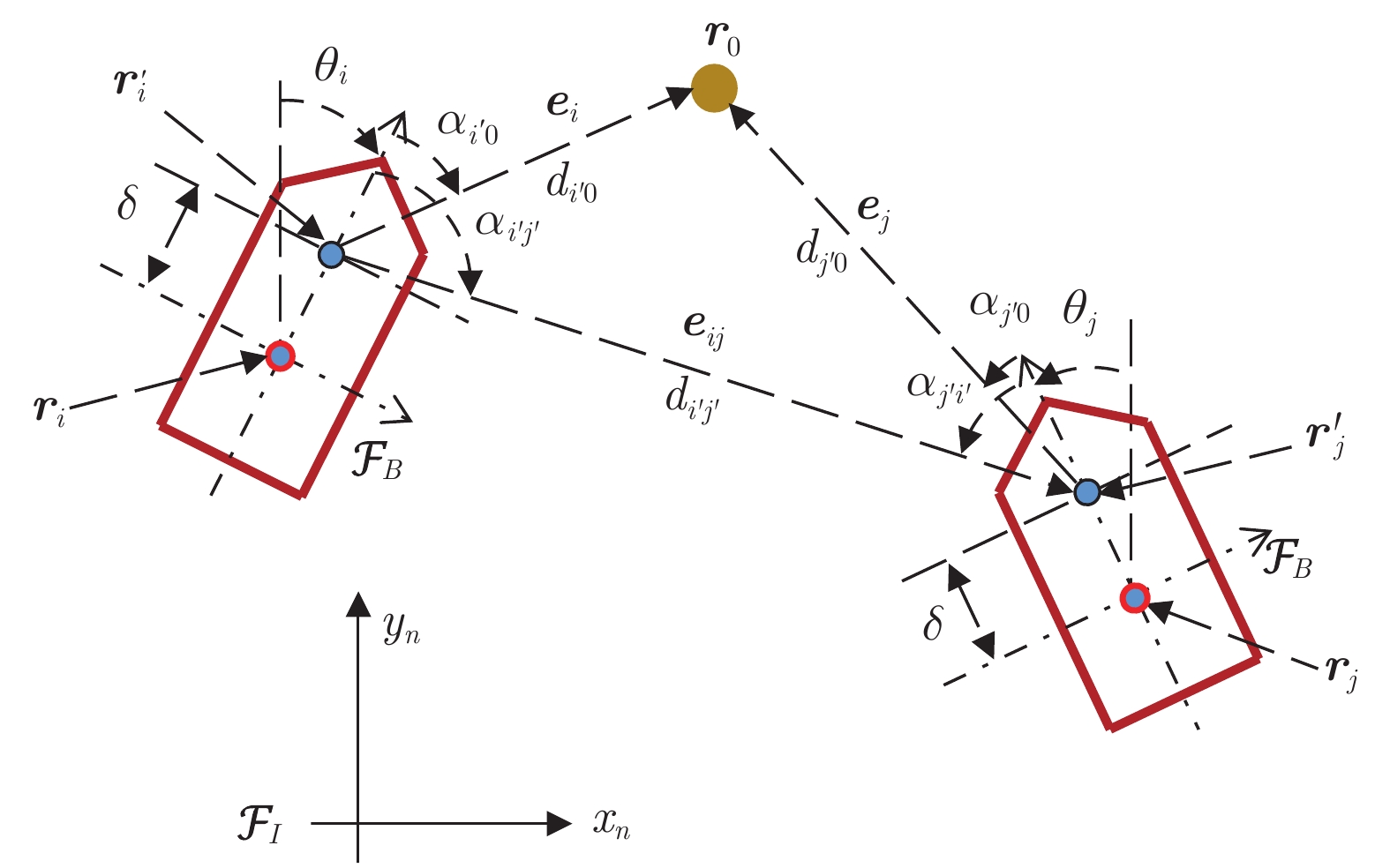
 下载:
下载: