Tamura Coarseness for OTH Radar Image Evaluation and Its Application in Adaptive Optimization of Interference Suppression
-
摘要: 针对OTH (Over-the-horizon) 雷达距离−多普勒(Range-Doppler, RD)图, 本文首次提出采用纹理粗糙度作为RD图质量的评价指标, 即计算RD图所转化灰度图的Tamura纹理粗糙度. 分析表明, 粗糙度指标能准确反映RD图受干扰情况, 对于不同灰度转换函数具有稳健性. 作为应用举例, 本文将图像粗糙度用于改进射频干扰抑制算法, 使干扰抑制达到自适应优化. 实验结果表明, Tamura粗糙度能够正确反映RD图干扰抑制情况, 优化粗糙度指标能够使干扰抑制自适应达到最优.Abstract: Tamura coarseness is introduced as a reasonable index for evaluating the quality of range-Doppler (RD) map in OTH (Over-the-horizon) radar. Tamura coarseness is calculated as the texture coarseness of a gray image which is transformed from the RD map. The analysis shows that Tamura coarseness can correctly reflect the radio frequency interference in the RD image and is also robust when the gray transforming function changes. As an example of its application, Tamura coarseness is adopted to improve the interference suppression algorithm, so that the suppression can be optimized adaptively. Simulation results show that Tamura coarseness can be used as a quality index of the RD image, which helps to suppress the interference perfectly.
-
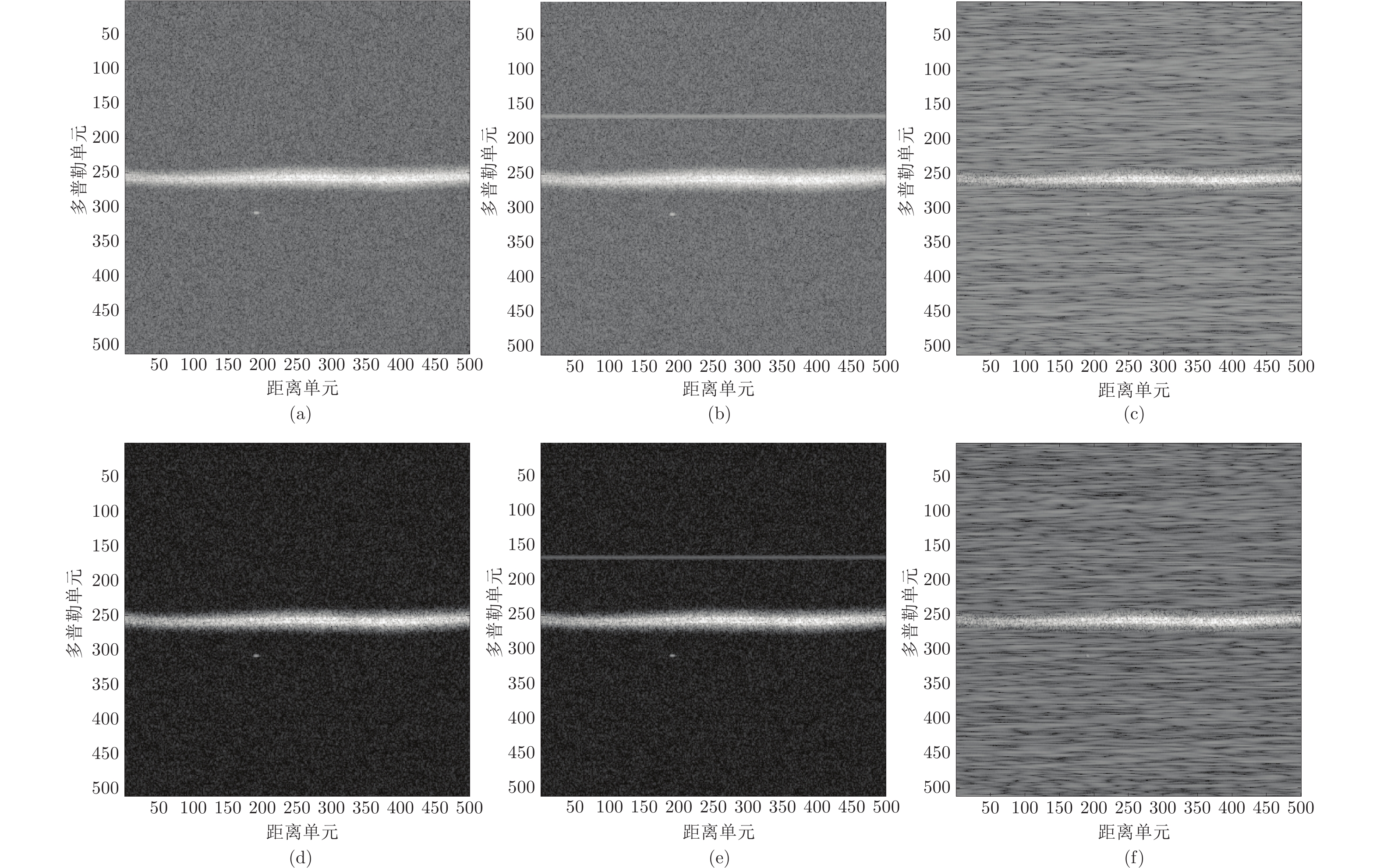
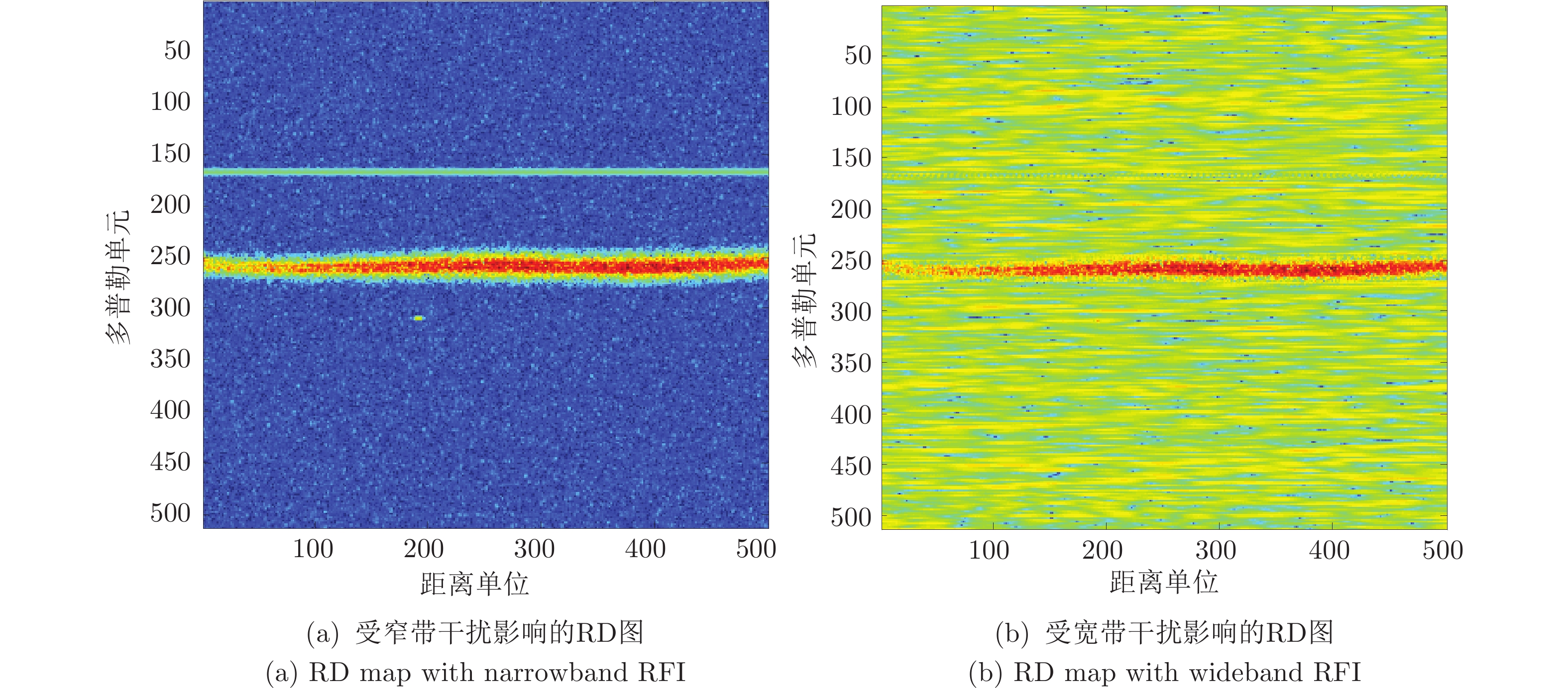
图 2 不同干扰情形下的RD灰度图: (a) ~ (c)分别表示无动态范围转换的无干扰、有窄带射频干扰、有宽带射频干扰的RD灰度图; (d) ~ (f)分别表示对应的动态范围为80 dB转换的RD灰度图
Fig. 2 RD gray-scale images: (a) ~ (c) are images without dynamic range conversion, for no RFI, narrowband RFI, and wideband RFI, respectively; (d) ~ (f) are corresponding images with dynamic range conversion for 80 dB
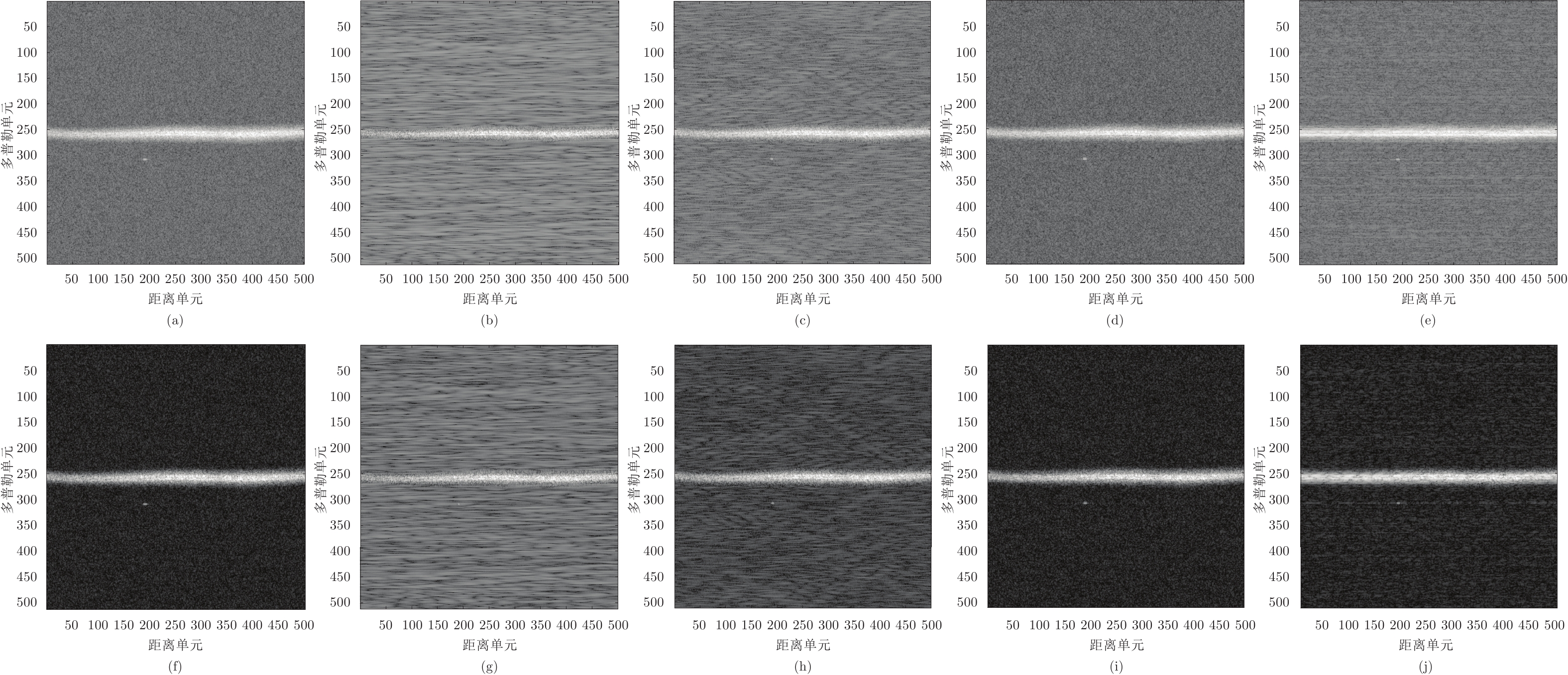
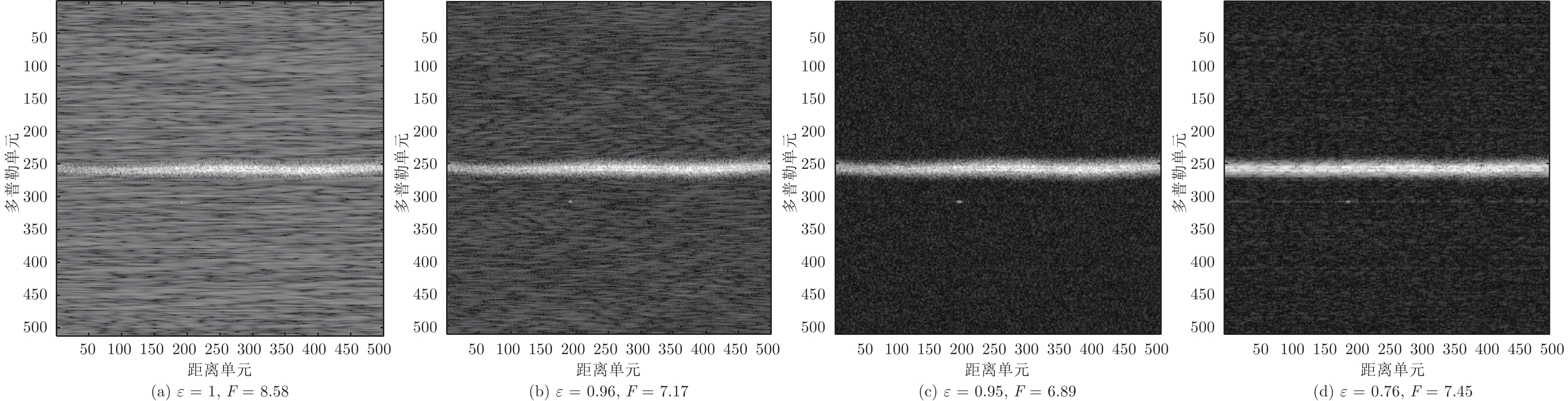
图 3 不同干扰抑制结果的RD灰度图: (a) ~ (e)分别表示无动态范围转换的无干扰、有宽带干扰、干扰未完全抑制、干扰完全抑制、干扰过度抑制的RD灰度图; (f) ~ (j)分别表示对应的动态范围为80 dB转换的RD灰度图
Fig. 3 RD gray-scale image for various interference suppression results: (a) ~ (e) are images without interference, broadband RFI, incomplete suppression, complete suppression, and excessive suppression, without dynamic range conversion; (f) ~ (j) are the corresponding images with dynamic range conversion for 80 dB
表 1 不同干扰类型的RD图粗糙度
Table 1 Coarseness of RD images for various kinds of interference
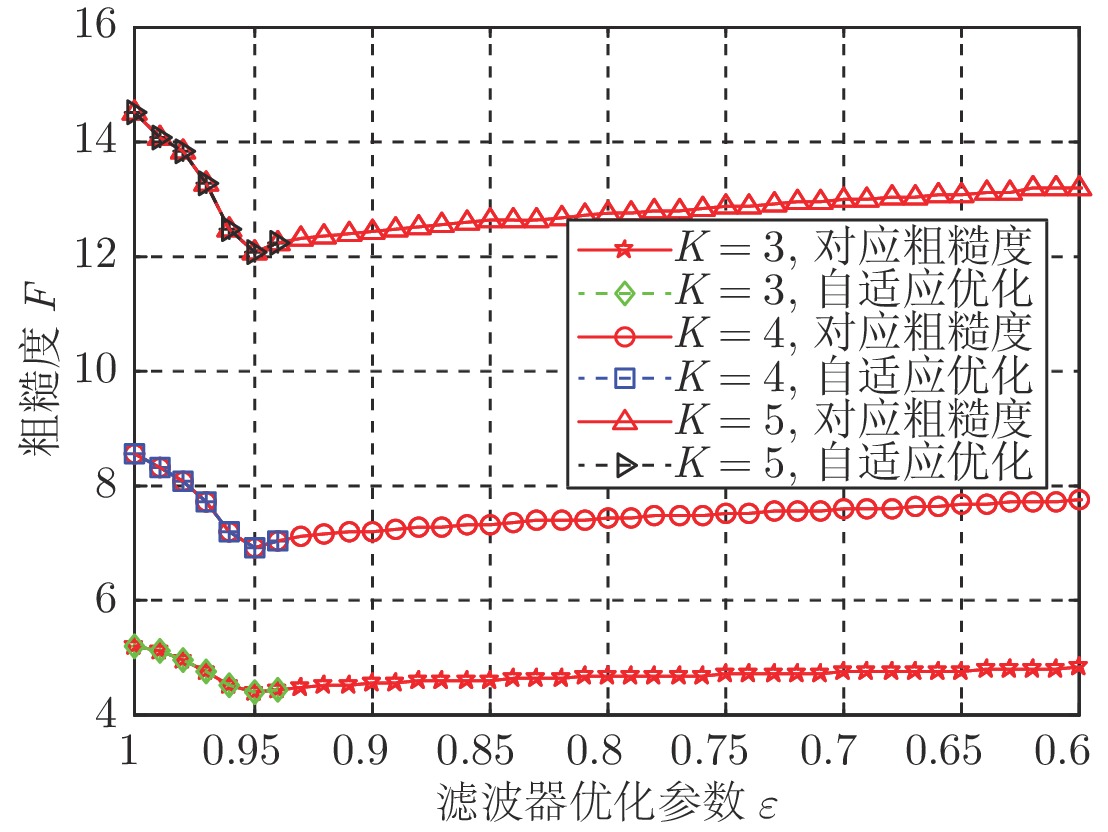
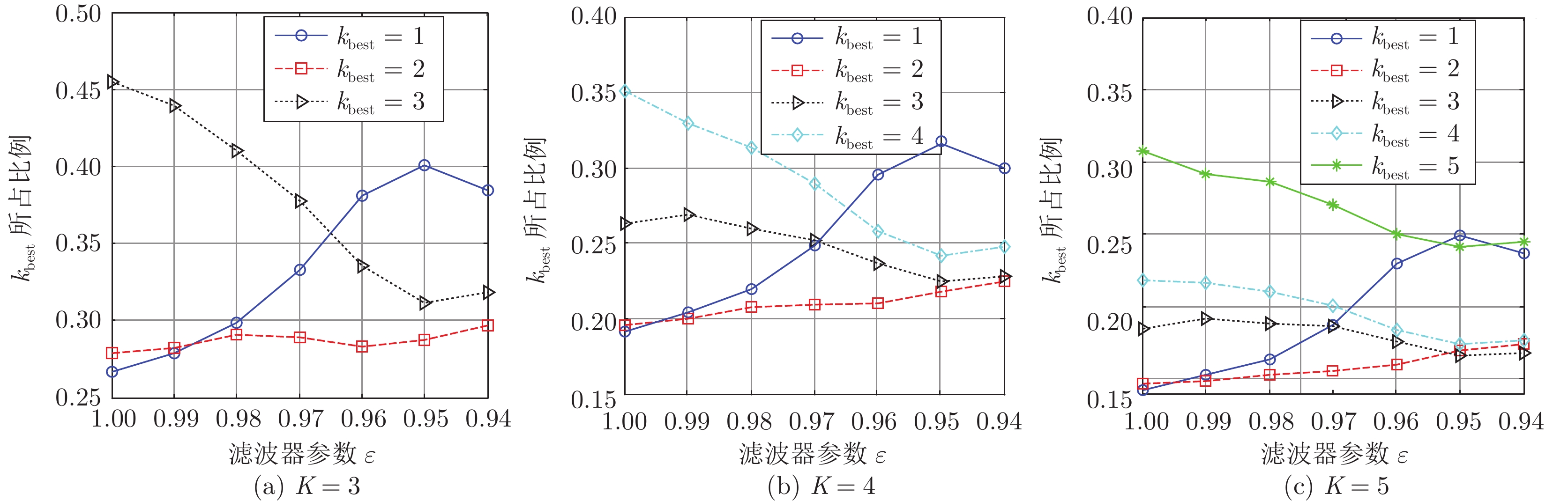
无动态转换时灰度级 有动态转换时灰度级 256 64 32 256 64 32 无干扰 6.92 6.92 6.91 6.84 6.84 6.83 窄带RFI 7.37 7.37 7.36 7.31 7.31 7.30 宽带RFI 8.58 8.58 8.55 8.58 8.58 8.56 表 2 不同干扰抑制程度的RD图粗糙度
Table 2 Coarseness of RD images for various levels of RFI suppression
无动态转换时灰度级 有动态转换时灰度级 256 64 32 256 64 32 无干扰 6.92 6.92 6.91 6.84 6.84 6.83 有干扰 8.58 8.58 8.55 8.58 8.58 8.56 未完全抑制 7.68 7.68 7.66 7.68 7.68 7.67 完全抑制 7.12 7.12 7.10 6.89 6.89 6.89 过度抑制 7.68 7.68 7.67 7.67 7.67 7.66 表 3 不同目标情况下RD图的粗糙度
Table 3 Coarseness of RD images of various targets
目标个数 0 1 5 10 15 20 无干扰 6.84 6.84 6.85 6.86 6.87 6.89 有干扰 8.58 8.58 8.58 8.58 8.58 8.58 未完全抑制 7.68 7.68 7.69 7.69 7.69 7.70 完全抑制 6.89 6.89 6.90 6.91 6.92 6.94 过度抑制 7.67 7.67 7.69 7.69 7.70 7.71 -
[1] 周文瑜, 焦培南. 超视距雷达技术. 北京:电子工业出版社, 2008. 132−134Zhou Wen-Yu, Jiao Pei-Nan. Over-the-horizon Radar Technology. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2008. 132−134 [2] Wang W, Wyatt L R. Radio frequency interference cancellation for sea-state remote sensing by high-frequency radar. IET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2011, 5(4): 405-415 doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2010.0041 [3] 孔舒亚, 王亮. 压缩感知合成孔径雷达自适应射频干扰抑制方法. 电子测量技术, 2019, 42(13): 107-111Kong Shu-Ya, Wang Liang. Adaptive suppression method for SAR narrowband interference based on compressed sensing. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2019, 42(13): 107-111 [4] 文必洋, 韩金柱, 周企豪, 李艳. 高频地波雷达空域射频干扰抑制算法. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2017, 44(4): 132-137Wen Bi-Yang, Han Jin-Zhu, Zhou Qi-Hao, Li Yan. Radio frequency interference suppression algorithm in the spatial domain for high-frequency radars. Journal of Xidian University, 2017, 44(4): 132-137 [5] 罗忠涛. 新体制天波超视距雷达信号处理研究 [博士学位论文], 电子科技大学, 中国, 2015.Luo Zhong-Tao. Study on Signal Processing for Future Sky-wave Over-the-horizon Radar System [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, China, 2015. [6] 朱永恒, 黎明, 牛炯, 张玲, 纪永刚. 基于方向分析的高频地波雷达射频干扰抑制[J]. 中国海洋大学学报, 2018, 48(7): 142-148Zhu Yong-Heng, Li Ming, Niu Jiong, Zhang Ling, Ji Yong-Gang. Reasearch on radio frequency interference suppression for HFSWR[J]. Periodical Of Ocean University Of China, 2018, 48(7): 142-148 [7] 刘建成, 全厚德, 李召瑞, 刘东林, 赵宏志. 多路延迟正交合成的多径信道射频干扰对消. 电子与信息学报, 2017, 39(3): 654-661Liu Jian-Cheng, Quan Hou-De, Li Zhao-Rui, Liu Dong-Lin, Zhao Hong-Zhi. RF interference cancellation based on multi-tap delay and orthogonal combination in multipath channel. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2017, 39(3): 654-661 [8] Luo Z T, He Z S, Li J. An effective scheme for radio frequency interference suppression in high-frequency radar. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Radar Conference. Arlington, VA, USA: IEEE, 2015. 539−544 [9] Luo Z T, Song T C, He Z S, Hu J F. Approach for transient interference detection based on straight line extraction for high-frequency sky-wave radar. Electronics Letters, 2017, 53(9): 618-620 doi: 10.1049/el.2016.4125 [10] 罗忠涛, 吴太锋, 何子述, 陈绪元. 基于图像分割的高频雷达射频干扰提取算法. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(4): 776-781 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.04.10Luo Zhong-Tao, Wu Tai-Feng, He Zi-Shu, Chen Xu-Yuan. Extration of radio frequency interference based on image segmentation for high-frequency radar. Systems Engineering And Electronics, 2018, 40(4): 776-781 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.04.10 [11] Tamura H, Mori S, Yamawaki T, Textural features corresponding to visual perception, IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics [12] Liu Y Q, Huang T Q. Exposing video inter-frame forgery by Zernike opponent chromaticity moments and coarseness analysis. Multimedia Systems, 2017, 23(2): 223-238 doi: 10.1007/s00530-015-0478-1 [13] 陈苏婷, 胡海锋, 张闯. 基于激光散斑成像的零件表面粗糙度建模. 物理学报, 2015, 64(23): 105-113Chen Su-Ting, Hu Hai-Feng, Zhang Chuang. Surface roughness modeling based on laser speckle imaging. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64(23): 105-113 [14] 王顺杰, 齐春, 程玉胜. Tamura纹理特征在水下目标分类中的应用[J]. 应用声学, 2012, 31(2): 135-139 doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2012.02.013Wang Shun-Jie, Qi Chun, Cheng Yu-Sheng. Application of Tamura texture feature to classify underwater targets[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2012, 31(2): 135-139 doi: 10.11684/j.issn.1000-310X.2012.02.013 [15] Zhang X D, Shen P Y, Gao J R, X X, Qi D, Zhang L, et al. A license plate recognition system based on Tamura texture in complex conditions. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Information and Automation. Harbin, China: IEEE, 2010. 1947−1952 [16] Gupta A, Garg M, Mittal A. A comparative performance evaluation of the 2010 segmented image with obstacle for textural coarseness. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research. Coimbatore, India: IEEE, 2010. 1−6 [17] Majtner T, Svoboda D. Extension of tamura texture features for 3D fluorescence microscopy. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on 3D Imaging, Modeling, Processing, Visualization and Transmission. Zurich, Switzerland: IEEE, 2012. 301−307 [18] Luo Z T, He Z S, Lu K, Chen X Y. Optimal receive filter design under similarity constraint in coloured noise. ET Radar, Sonar and Navigation, 2015, 9(7): 888-899 doi: 10.1049/iet-rsn.2014.0421 -




 下载:
下载: