Data-driven Adaptive Adjustment Strategy for Strong Wind Alarm in High-speed Railway
-
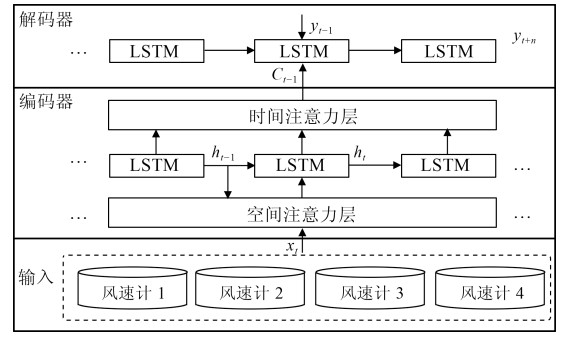
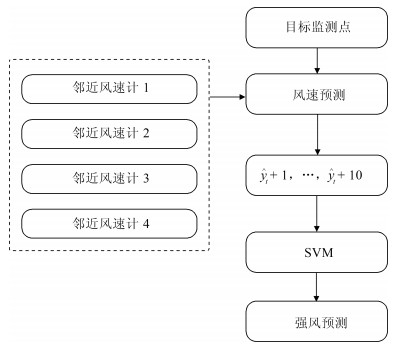
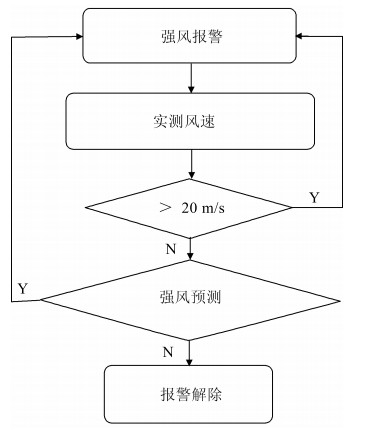
摘要: 高速铁路在中国发展迅速,带来了全新的交通变革.较快的运行速度在带来效率提升的同时也增加了沿线强风对其运行安全的威胁.为了安全运行,铁路沿线部署了大量风速监测传感器,一旦监测到强风,将通过调度中心发出信号,调度沿线列车减速慢行甚至停车.在报警过程中,如何确定报警保持时间极具挑战.如果保持过短,则可能发生重复报警,增加处置次数,加重工作人员负担;若取消过晚,则影响轨道通过能力,带来不必要的效率损失.为此,本文提出一种高速铁路强风报警解除时间调整策略,用于改善这一问题.该策略通过轨道沿线部署的风速计装置,结合时空信息对短时未来强风情况进行预测,基于预测情况,自适应调整报警解除时间.该策略能够有效减少报警冗余时长,提高列车运行效率.Abstract: The rapid development of high-speed railways in China has changed the way people travel. The faster speed induces a growing threat of strong wind on safety. A large number of anemometers have been deployed alongside the railway for monitoring the strong wind. Dispatchers in the dispatch centers issue the scheduling instructions to the train drivers according to the measured wind speed. It is not trivial for the dispatchers to decide when to stop an alarm. If the alarm lasts too short, repeated alarms may occur, increasing the number of treatments and the burden on the staff. If it is stopped too late, track passing capacity will be affected and unnecessary efficiency loss may be caused. In this paper, an adjustment strategy for the stop time of high-speed railway alarm based on wind speed prediction is proposed to solve this emerged challenge. The strategy can effectively reduce the alarm redundancy time and improve operational efficiency.
-
Key words:
- High-speed railway /
- wind speed prediction /
- strong wind prediction /
- alarm duration adjustment
1) 本文责任编委 董海荣 -
表 1 高速铁路不同风速下行驶速度规定
Table 1 Speed constraints for the high-speed train at different wind speeds
风速(m/s) 列车运行规定(km/h) 15~20 限速300 20~25 限速200 25~30 限速120 > 30 禁止通行 表 2 实验数据集
Table 2 Dataset for experiments
测量点 数量 均值(m/s) 最大值(m/s) 最小值(m/s) 测量点1 $1\, 209\, 600$ $3.64$ $20.0$ $-0.7$ 测量点2 $1\, 209\, 600$ $3.63$ $24.9$ $-0.4$ 测量点3 $1\, 209\, 600$ $3.63$ $29.9$ $-1.0$ 测量点4 $1\, 209\, 600$ $3.63$ $29.5$ $-1.2$ 测量点5 $1\, 209\, 600$ $3.62$ $22.7$ $-0.3$ 表 3 风速预测准确度
Table 3 Performances of the wind prediction
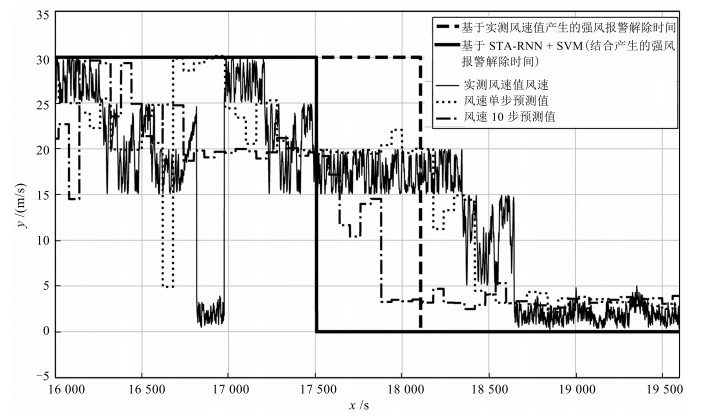
模型 MAE (m/s) RMSE (m/s) MAPE (%) ARIMA 1-step 2.02 3.46 1.35 5-step 2.14 3.50 1.36 10-step 2.24 3.57 1.37 LSTM(128) 1-step 1.21 1.60 0.65 5-step 1.39 1.87 0.69 10-step 1.51 2.25 0.75 STA-RNN 1-step 0.98 1.25 0.20 5-step 1.11 1.40 0.22 10-step 1.21 1.80 0.25 表 4 强风预测效果
Table 4 Performances of the strong wind prediction
模型 精确度 召回率 $\rm F_{\rm score}$ STA-RNN 1.0 0.65 0.79 STA-RNN+SVM 1.0 0.73 0.84 -
[1] 王瑞, 陈苒, 包云. JR东日本铁路大风监测技术研究, 中国铁路, 2018, 07:96-102 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhongguotl201807020Wang Rui, Chen Ran, Bao Yun. The study on JR-East monitoring technology of strong wind. China Railway, 2018, 07:96-102 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhongguotl201807020 [2] 窦垭锡, 蔺伟, 刘畅.高速铁路大风报警信息实时传输系统方案研究.铁道运输与经济, 2018, 40(09):57-61, 85 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdysyjj201809012Dou Ya-Xi, Lin Wei, Liu Chang. A research on the scheme of the real-time wind alarm transmission system of high-speed railway. Railway Transport and Economy, 2018, 40(09):57-61, 85 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdysyjj201809012 [3] 王瑞.高速铁路大风监测系统运用规则优化研究.铁道运输与经济, 2018, 40(4):48-51, 57 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdysyjj201804009Wang Rui. A study on the application rules of high-speed railway wind monitoring system. Railway Transport and Economy, 2018, 40(4):48-51, 57 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/tdysyjj201804009 [4] Landberg L. Short-term prediction of the power production from wind farms. Journal of Wind Engineering and Industrial Aerodynamics, 1999, 80(1-2):207-220 doi: 10.1016/S0167-6105(98)00192-5 [5] Negnevitsky M, Johnson P, Santoso S. Short term wind power forecasting using hybrid intelligent systems. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Power Engineering Society General Meeting. Tampa, FL, USA: IEEE, 2007. 1-4 [6] Negnevitsky M, Potter C W. Innovative short-term wind generation prediction techniques. In: Proceedings of the 2006 Power Systems Conference and Exposition. Atlanta, GA, USA: IEEE, 2006. 60-65 [7] Ma L, Luan S Y, Jiang C W, Liu H L, Zhang Y. A review on the forecasting of wind speed and generated power. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2009, 13(4):915-920 doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2008.02.002 [8] Kiplangat D C, Asokan K, Kumar K S. Improved week-ahead predictions of wind speed using simple linear models with wavelet decomposition. Renewable Energy, 2016, 93:38-44 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2016.02.054 [9] Box G E P, Jenkins G M, Reinsel G C, Ljung, G M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control. John Wiley & Sons, 2015 [10] Cadenas E, Rivera W, Campos-Amezcua R, Heard C. Wind speed prediction using a univariate ARIMA model and a multivariate NARX model. Energies, 2016, 9(2):109 doi: 10.3390/en9020109 [11] Yunus K, Thiringer T, Chen P. ARIMA-based frequency-decomposed modeling of wind speed time series. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2016, 31(4):2546-2556 doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2015.2468586 [12] Singh S N, Mohapatra A. Repeated wavelet transform based ARIMA model for very short-term wind speed forecasting. Renewable Energy, 2019, 136:758-768. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2019.01.031 [13] Li L, Ota K, Dong M. Deep learning for smart industry:efficient manufacture inspection system with fog computing. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(10):4665-4673 doi: 10.1109/TII.2018.2842821 [14] Li H, Ota K, Dong M. Learning IoT in edge:deep learning for the internet of things with edge computing. IEEE Network, 2018, 32(1):96-101 doi: 10.1109/MNET.2018.1700202 [15] Ota K, Dao M S, Mezaris V, Mezaris V, De Natale F G. Deep learning for mobile multimedia: a survey. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications (TOMM), 2017, 13(3s): 34: 1-34: 22 [16] Kaur T, Kumar S, Segal R. Application of artificial neural network for short term wind speed forecasting, In: Proceedings of the 2016 Biennial International Conference On Power and Energy Systems: Towards Sustainable Energy. Bengaluru, India: IEEE, 2016. 1-5 [17] Chang G W, Lu H J, Chang Y R, Lee Y D. An improved neural network-based approach for short-term wind speed and power forecast. Renewable Energy, 2017, 105:301-311 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2016.12.071 [18] Hu Q, Zhang R, Zhou Y. Transfer learning for short-term wind speed prediction with deep neural networks. Renewable Energy, 2016, 85:83-95 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2015.06.034 [19] 汤鹏杰, 王瀚漓, 许恺晟. LSTM逐层多目标优化及多层概率融合的图像描述.自动化学报, 2018, 44(7):1237-1249 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160733Tang Peng-Jie, Wang Han-Li1, Xu Kai-Sheng. Multi-objective layer-wise optimization and multi-level probability fusion for image description generation using LSTM. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(7):1237-1249 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160733 [20] Dong D, Sheng Z, Yang T. Wind power prediction based on recurrent neural network with long short-term memory units. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Renewable Energy and Power Engineering. Toronto, Canada: IEEE, 2018. 34-38 [21] Qu X Y, Kang X N, Zhang C, Jiang S, Ma X D. Short-term prediction of wind power based on deep long short-term memory. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE PES Asia-Pacific Power and Energy Engineering Conference. Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2016. 1148-1152 [22] Zhu Q M, Chen J F, Shi D Y, Zhu L, Bai X, Duan X Z, Liu Y L. Learning temporal and spatial correlations jointly: a unified framework for wind speed prediction. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2019, DOI: 10.1109/TSTE.2019.2897136 [23] Kalchbrenner N, Blunsom P. Recurrent continuous translation models. In: Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Seattle, WA, USA: ACL, 2013. 1700-1709 [24] Venugopalan S, Rohrbach M, Donahue J, Mooney R, Darrell T, Saenko K. Sequence to sequence-video to text. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 4534-4542 [25] Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le Q V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2014. 3104-3112 [26] Cho K, Van Merrienboer B, Bahdanau D, Bengio Y. On the properties of neural machine translation: encoder-decoder approaches[Online], available: https: //arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1259.pdf.October 7, 2014 [27] Qin Y, Song D, Chen H, Cheng W, Jiang G, Cottrell G. A dual-stage attention-based recurrent neural network for time series prediction. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, CA, USA: AAAI Press, 2017. 2627-2633 [28] Vapnik V N. An overview of statistical learning theory. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1999, 10(5):988-999 doi: 10.1109/72.788640 [29] Du P, Wang J, Yang W, Niu T. Multi-step ahead forecasting in electrical power system using a hybrid forecasting system. Renewable Energy, 2018, 122:533-550 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.01.113 [30] Xing Z, Pei J, Keogh E. A brief survey on sequence classification. ACM SIGKDD Explorations Newsletter, 2010, 12(1):40-48 doi: 10.1145/1882471.1882478 [31] He Y, Pei J, Chu X, Wang Y, Jin Z, Peng G. Characteristic subspace learning for time series classification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Data Mining. Singapore, Singapore: IEEE, 2018: 1019-1024 [32] Liang Y, Ke S, Zhang J, Yi X, Zheng Y. GeoMAN: multi-level attention networks for geo-sensory time series prediction. In: Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Stockholm, Sweden: Morgan Kaufmann, 2018. 3428-3434 [33] Chen J, Hu K, Wang Q, Sun Y, Shi Z, He S. Narrowband internet of things:implementations and applications. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2017, 4(6):2309-2314 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2017.2764475 [34] Zhou C, Gu Y, He S, Shi Z. A robust and efficient algorithm for coprime array adaptive beamforming. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2017, 67(2):1099-1112 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=dfd568a5657d9cf3ae1fe8872afdad51&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [35] Li C, He S, Shi Z, Chen J. Efficient antenna allocation algorithms in millimetre wave wireless communications. IET Communications, 2017, 12(5):543-551 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=73ac8d295985331f17bf3ae8336dfc63 -




 下载:
下载: