|
[1]
|
Coleman A. Railroads of North Carolina. Arcadia Publishing, 2008.
|
|
[2]
|
翟婉明, 赵春发. 现代轨道交通工程科技前沿与挑战. 西南交通大学学报, 2016, 51(2): 209−226 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.0012 Zhai Wan-Ming, Zhao Cun-Fa. Frontiers and challenges of sciences and technologies in modern railway engineering. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016, 51(2): 209−226 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.02.001
|
|
[3]
|
3 Lu Q W, He B B, Wu M Z, Zhang Z C, Luo J T, Zhang Y K. Establishment and analysis of energy consumption model of heavy-haul train on large long slope. Energies, 2018, 11(4): 965 doi: 10.3390/en11040965
|
|
[4]
|
4 Wei W, Zhang J, Zhao X B, Zhang Y. Heavy haul train impulse and reduction in train force method. Australian Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 16(2): 118−125 doi: 10.1080/14484846.2018.1457259
|
|
[5]
|
5 Cherkashin U M, Zakharov S M, Semechkin A E. An overview of rolling stock and track monitoring systems and guidelines to provide safety of heavy and long train operation in the Russian railways. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part F Journal of Rail and Rapid Transit, 2009, 223(2): 199−208
|
|
[6]
|
6 Dong H R, Ning B, Cai B G, Hou Z S. Automatic train control system development and simulation for high-speed railways. IEEE Circuits and System, 2010, 10(2): 6−18
|
|
[7]
|
7 Erofeyev E. Calculation of optimum train control using dynamic programming method. Moscow Railway Engineering Institute: Moscow, Russia, 1967, 811: 16−30
|
|
[8]
|
8 Howlett P. A new look at the rate of change of energy consumption with respect to journey time on an optimal train journey. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological, 2016, 94(12): 387−408
|
|
[9]
|
9 Howlett P G, Pudney P J, Xuan V. Local energy minimization in optimal train control. Automatica, 2009, 45(11): 2692−2698 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.07.028
|
|
[10]
|
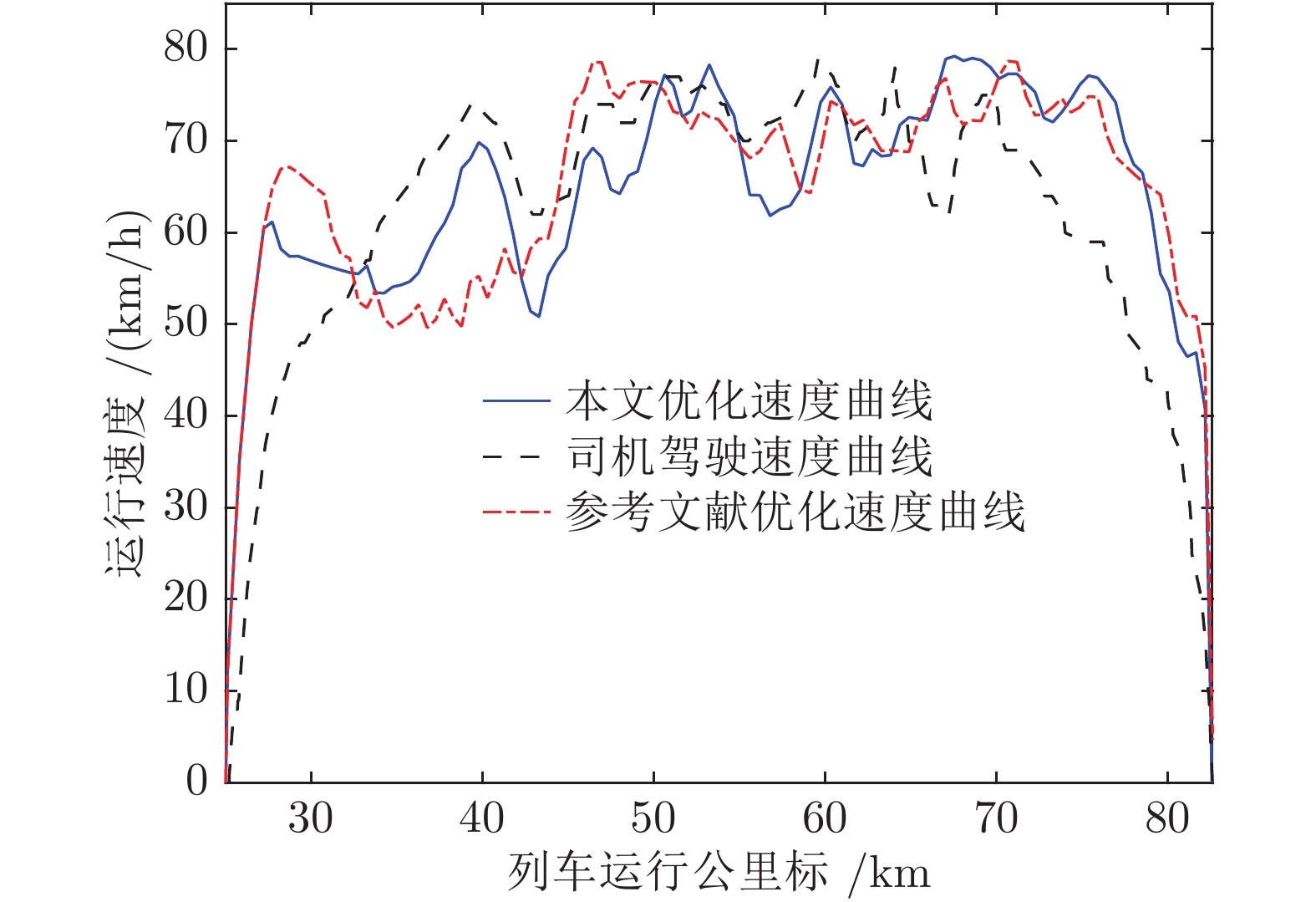
10 Wang P L, Goverde R M P. Multiple-phase train trajectory optimization with signalling and operational constraints. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2016, 69(8): 255−275
|
|
[11]
|
11 Wang P L, Goverde R M P. Multi-train trajectory optimization for energy-efficient timetabling. European Journal of Operational Research, 2018, 272(2): 621−635
|
|
[12]
|
12 Scown B, Roach D, Wilson P. Freight train driving strategies developed for undulating track through train dynamics research. CORE 2000: Railway Technology for 21st Century, 2000: 236−247
|
|
[13]
|
13 Zhang L, Zhuan X. Optimal operation of heavy-haul trains equipped with electronically controlled pneumatic brake systems using model predictive control methodology. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2013, 22(1): 13−22
|
|
[14]
|
陈荣武, 刘莉, 郭进. 基于遗传算法的列车运行能耗优化算法. 交通运输工程学报, 2012, 12(1): 112−11814 Chen Rong-Wu, Liu Li, Guo Jin. Optimization algorithm of train operation energy consumption based on genetic algorithm. Journal of Transportation Engineering, 2012, 12(1): 112−118
|
|
[15]
|
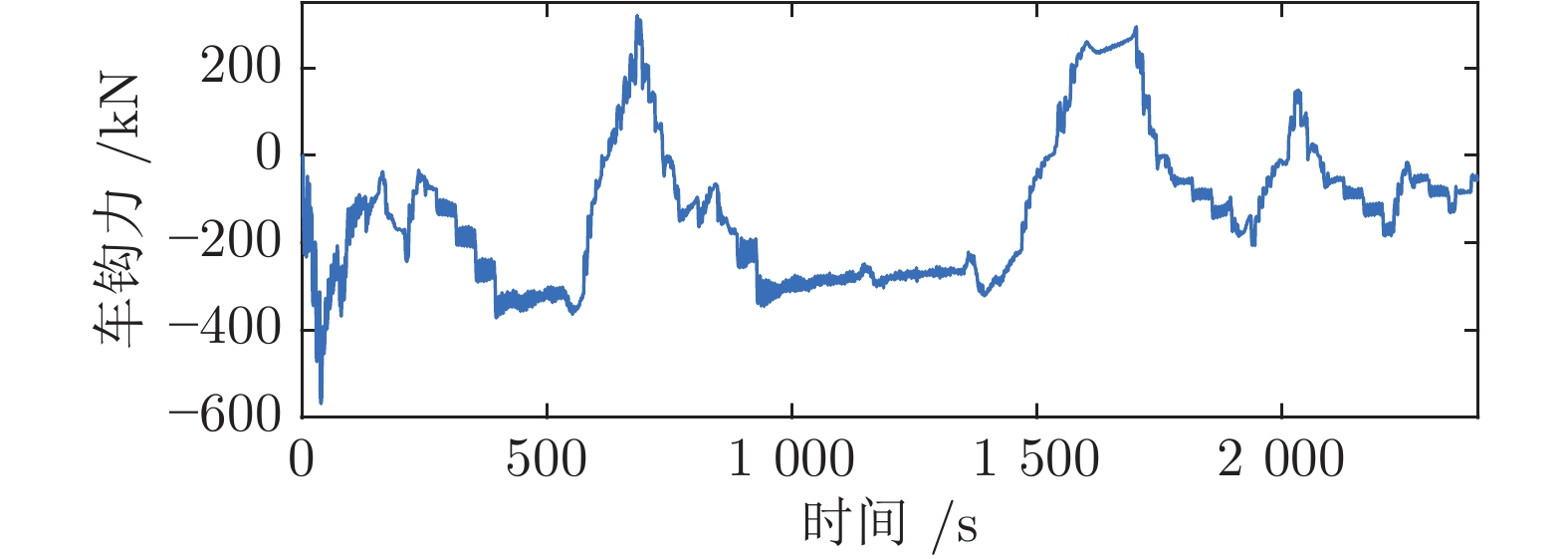
15 Zou R, Luo S, Ma W. Simulation analysis on the coupler behaviour and its influence on the braking safety of locomotive. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2018, 56(11): 1−21
|
|
[16]
|
16 Wu G, Huang W, Yuan Y. Improvements for the stability of heavy-haul couplers with arc surface contact. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2018, 56(3): 1−15
|
|
[17]
|
翟婉明. 列车 − 轨道耦合动力学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007.Zhai Wan-Ming. Vehicle-Orbit Coupling Dynamics, Beijing: Science Press, 2007.
|
|
[18]
|
金弟, 刘杰, 杨博, 何东晓, 刘大有. 局部搜索与遗传算法结合的大规模复杂网络社区探测. 自动化学报, 2011, 37(7): 873−88218 Jin Di, Liu Jie, Yang Bo, He Dong-Xiao, Liu Da-You. Genetic algorithm with local search for community detection in large-scale complex networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(7): 873−882
|
|
[19]
|
苏锑, 杨明, 王春香, 唐卫, 王冰. 一种基于分类回归树的无人车汇流决策方法. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(1): 35−4319 Su Ti, Yang Ming, Wang Chun-Xiang, Tang Wei, Wang Bing. Classification and regression tree based traffic merging for method self-driving vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(1): 35−43
|
|
[20]
|
张日东, 王树青, 李平. 基于支持向量机的非线性系统预测控制. 自动化学报, 2007, 33(10): 1066−107320 Zhang Ri-Dong, Wang Shu-Qing, Li Ping. Support vector machine based predictive control for nonlinear systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2007, 33(10): 1066−1073
|
|
[21]
|
徐杨, 陆丽萍, 褚端峰, 黄子超. 无人车辆轨迹规划与跟踪控制的统一建模方法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(4): 799−80621 Xu Yang, Lu Li-Ping, Chu Duan-Feng, Huang Zi-Chao. Unified modeling of trajectory planning and tracking for unmanned vehicle. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(4): 799−806
|
|
[22]
|
唐晓铭, 邓梨, 虞继敏, 屈洪春. 基于区间二型 T-S 模糊模型的网络控制系统的输出反馈预测控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(3): 604−61622 Tang Xiao-Ming, Deng Li, Yu Ji-Min, Qu Hong-Chun. Output feedback model predictive control for interval type-2 T-S fuzzy networked control systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 604−616
|
|
[23]
|
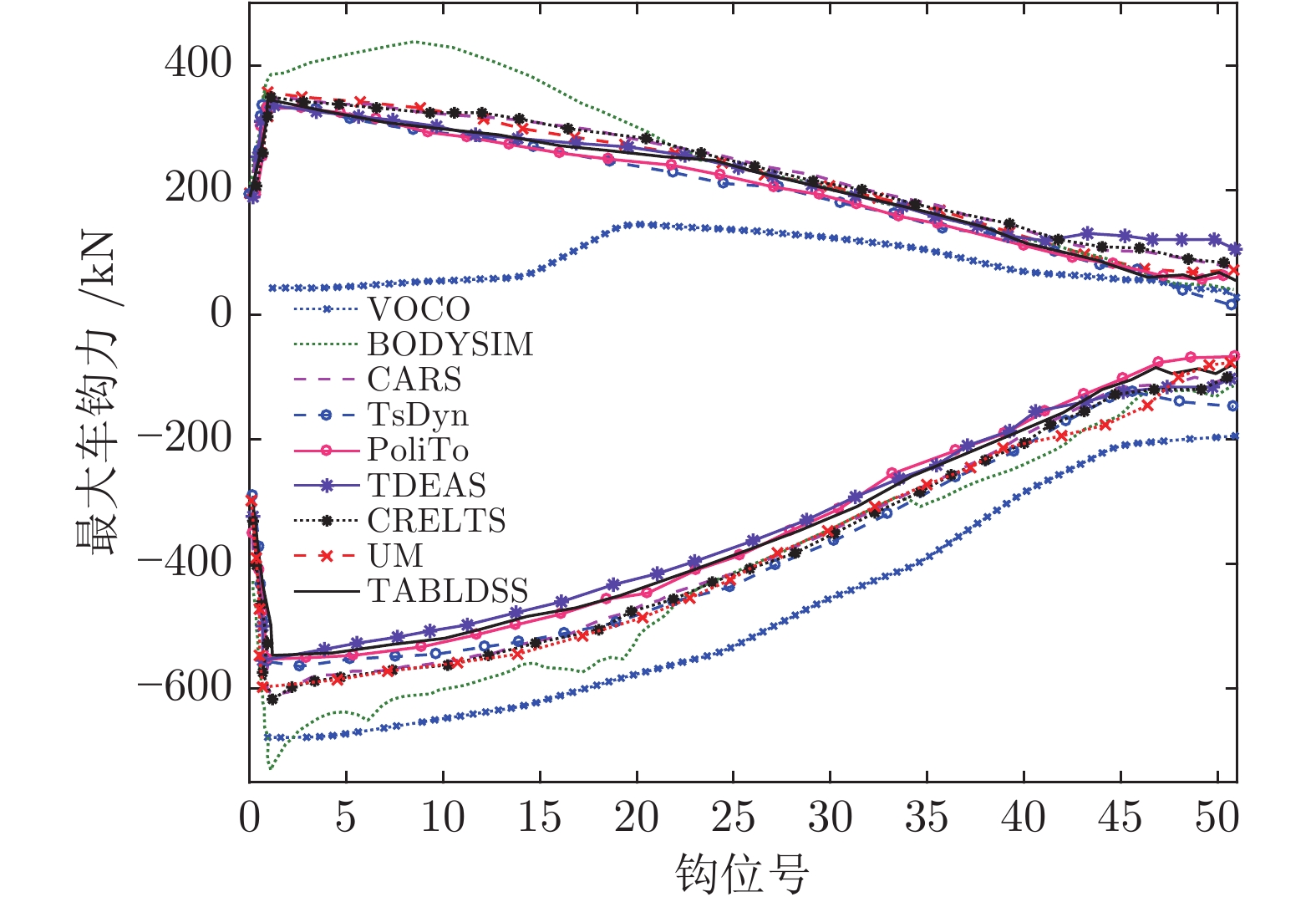
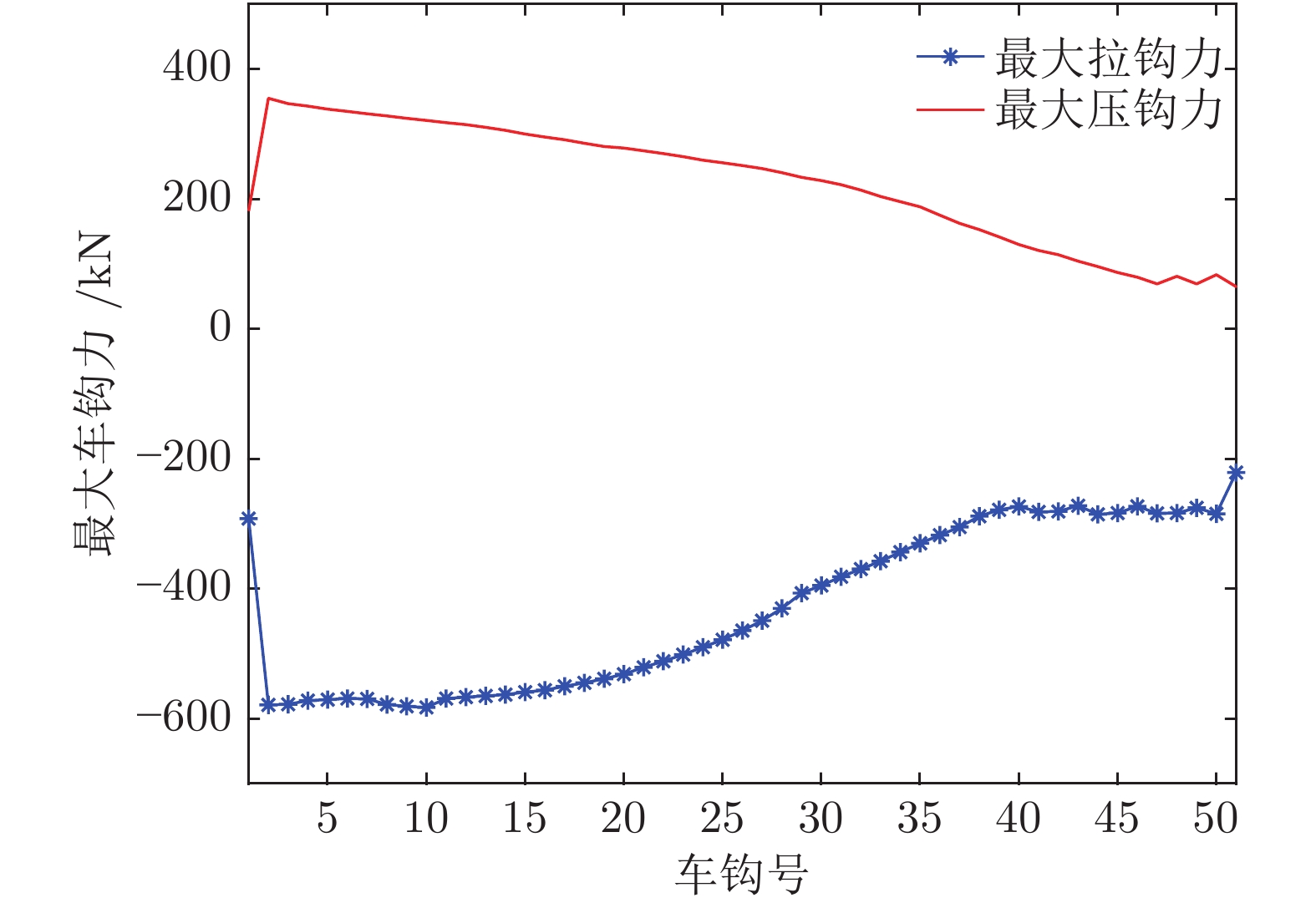
23 Spiryagin M, Wu Q, Cole C. International benchmarking of longitudinal train dynamics simulators: benchmarking questions. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2017, 55(4): 450−463 doi: 10.1080/00423114.2016.1270457
|
|
[24]
|
24 Wu Q, Spiryagin M, Cole C, Chang C Y, Guo G, Sakalo A, et al. International benchmarking of longitudinal train dynamics simulators: results. Vehicle System Dynamics, 2018, 56(3): 343−365 doi: 10.1080/00423114.2017.1377840
|




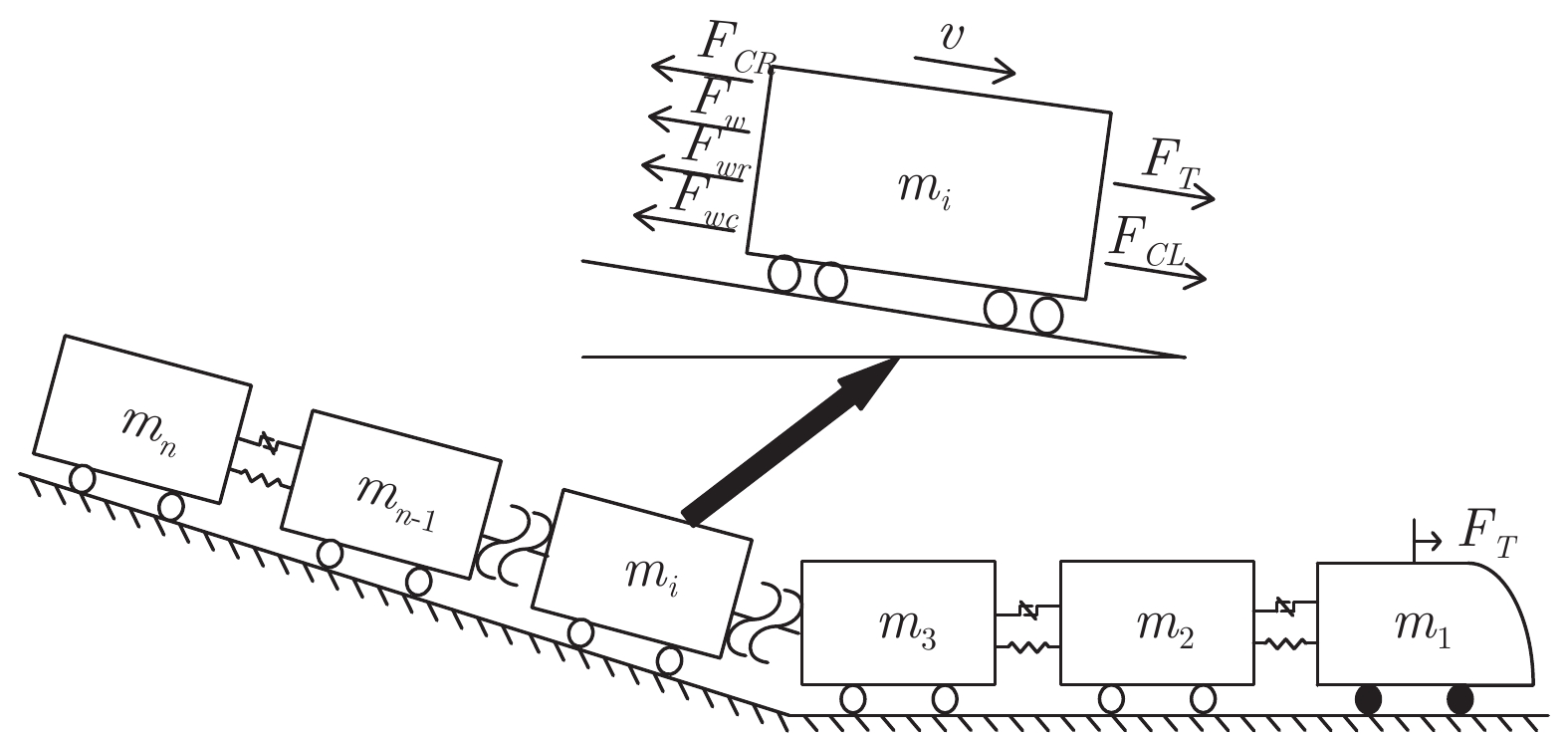
 下载:
下载: