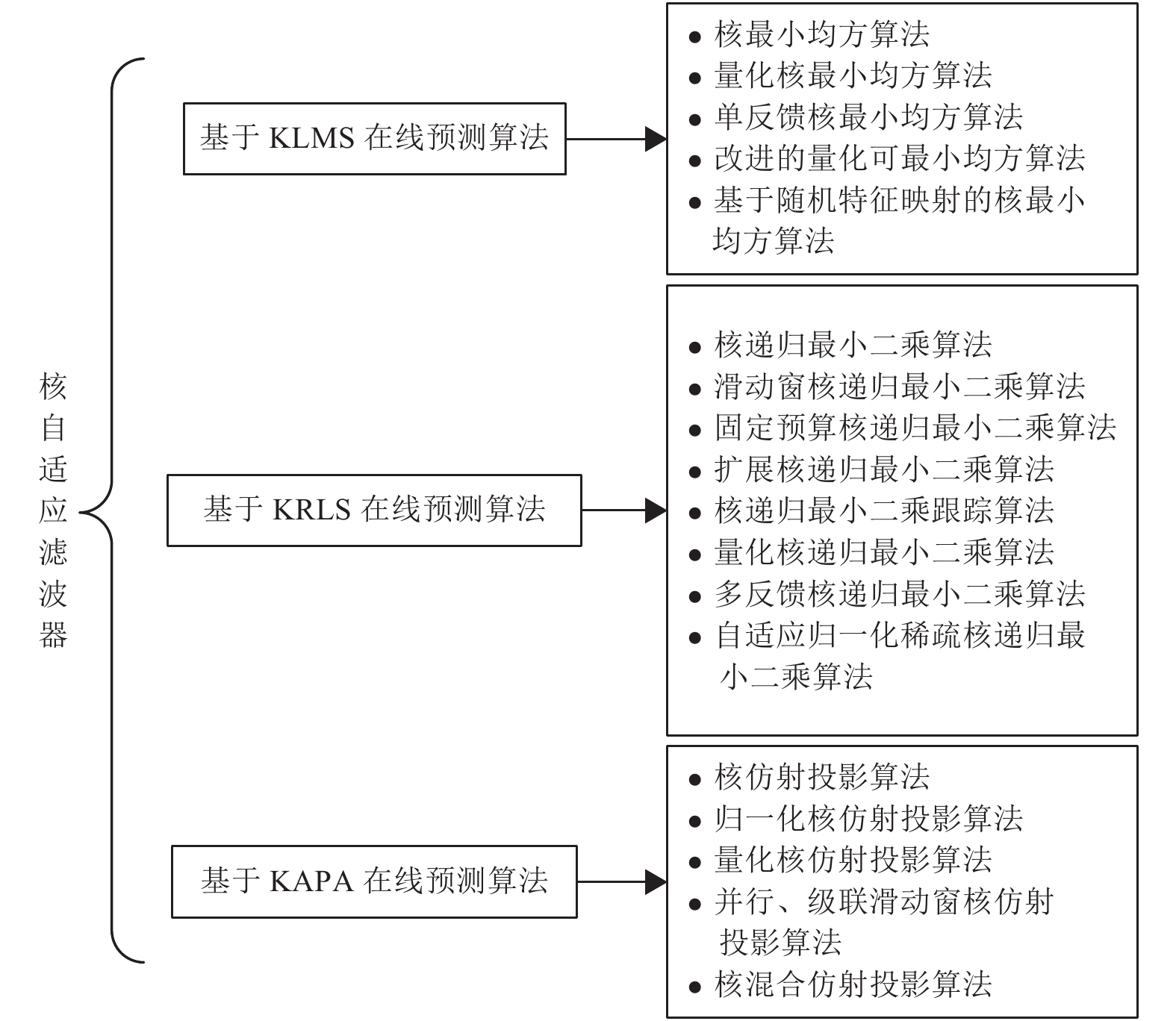
-
摘要: 核自适应滤波器(Kernel adaptive filter, KAF)是时间序列在线预测的重点研究领域之一, 本文对核自适应滤波器的最新进展及未来研究方向进行了分析和总结. 基于核自适应滤波器的时间序列在线预测方法, 能较好地解决预测、跟踪问题. 本文首先概述了三类核自适应滤波器的基本模型, 包括核最小均方算法、核递归最小二乘算法和核仿射投影算法(Kernel affine projection algorithm, KAPA). 在此基础上, 从核自适应滤波器在线预测的内容和机理入手, 综述基于核自适应滤波器的时间序列在线预测方法. 最后, 本文将介绍这一领域潜在的研究方向和发展趋势, 并展望未来的挑战.Abstract: Kernel adaptive filter (KAF) is one of the significant research fields of time series online prediction. In this paper, the latest development and future research directions of kernel adaptive filter are analyzed and summarized. The time series online prediction algorithms based on kernel adaptive filter can better solve the problem of prediction and tracking. This paper first generalizes the basic models of three types of kernel adaptive filters, including kernel least mean square, kernel recursive least squares and kernel affine projection algorithm (KAPA). On this basis, starting from the content and mechanism of online prediction of kernel adaptive filter, the time online prediction methods for kernel adaptive filter are reviewed. Finally, this paper will introduce the potential research direction and development tendency in this field, and look forward to the challenges ahead.
-
表 1 不同KAF方法的时间序列在线预测特性对比结果
Table 1 Comparison of online prediction characteristics of time series of different KAF methods
表 2 每次迭代过程涉及的计算复杂度比较
Table 2 Comparison of computational complexity involved in each iteration
核自适应滤
波器类型在线稀
疏类型计算复杂度 KLMS[19] VQ 更新$ {\alpha} \left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L^2} } )$ 在线VQ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ SF 更新$ {\omega} \left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ 更新$ {e}\left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ KRLS[20] VQ 更新$ {\alpha} \left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ 在线VQ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ 更新$ {P}\left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L^2} } )$ ALD 更新$ {\alpha} \left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L^2} } )$(${\rm O}( { {L^2} } )$
假如字典改变)更新ALD ${\rm O}( { {L^2} } )$ 更新${P}\left( i \right)$ ${\rm O}( { {L^2} } )$ SW 更新$ {\alpha} \left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {K^2} } )$(${\rm O}( { {K} } )$
假如字典改变)更新${P}\left( i \right)$ ${\rm O}( { {K^2} } )$ 更新${D}\left( i \right)$ ${\rm O}( { {K^2} } )$ FB 更新$ {\alpha} \left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {K^2} } )$(${\rm O}( { {K} } )$
假如字典改变)更新${P}\left( i \right)$ ${\rm O}( { {K^2} } )$ 更新$ {{\hat K}_n}\left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {K^2} } )$ MF 更新$ {\alpha} \left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ 更新$ {e}\left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ 更新${D}\left( i \right)$ ${\rm O}( { {L^2} } )$ CC 更新$ {\alpha} \left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {K^2} } )$(${\rm O}( { {K} } )$
假如字典改变)更新$ {e}\left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {K^2} } )$ 更新${D}\left( i \right)$ ${\rm O}( { {K^2} } )$ KAPA[21] VQ 更新$ {\alpha} \left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ 在线VQ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ 更新${P}\left( i \right)$ ${\rm O}( { {L^2} } )$ HC 更新$ {e}\left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ 更新$ {\bf{\zeta }}\left( i \right) $ ${\rm O}( { {L} } )$ -
[1] Gan M, Chen C L P, Li H X, Chen L. Gradient radial basis function based varying-coefficient autoregressive model for nonlinear and nonstationary time series. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(7): 809−812 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2369415 [2] Schamberg G, Ba D, Coleman T P. A modularized efficient framework for non-Markov time series estimation. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(12): 3140−3154 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2793870 [3] Gonzalez J P, San Roque A M S M, Perez E A. Forecasting functional time series with a new Hilbertian ARMAX model: Application to electricity price forecasting. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems, 2018, 33(1): 545−556 doi: 10.1109/TPWRS.2017.2700287 [4] Rahman M M, Islam M, Murase K, Yao X. Layered ensemble architecture for time series forecasting. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(1): 270−283 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2401038 [5] Zhu J, Chen N, Peng W W. Estimation of bearing remaining useful life based on multiscale convolutional neural network. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(4): 3208−3216 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2844856 [6] Chang F J, Chen P A, Lu Y R, Huang E, Chang K Y. Real-time multi-step-ahead water level forecasting by recurrent neural networks for urban flood control. Journal of Hydrology, 2014, 517: 836−846 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2014.06.013 [7] Vapnik V N. The Nature of Statistical Learning Theory. New York: Springer, 2000. [8] Girosi F, Jones M, Poggio T. Regularization theory and neural networks architectures. Neural Computation, 1995, 7(2): 219−269 doi: 10.1162/neco.1995.7.2.219 [9] Platt J. A resource-allocating network for function interpolation. Neural Computation, 1991, 3(2): 213−225 doi: 10.1162/neco.1991.3.2.213 [10] Huang G B, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N. A generalized growing and pruning RBF (GGAP-RBF) neural network for function approximation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2005, 16(1): 57−67 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2004.836241 [11] Suykens J A K, Vandewalle J. Least squares support vector machine classifiers. Neural Processing Letters, 1999, 9(3): 293−300 doi: 10.1023/A:1018628609742 [12] Scholkopf B, Smola A J. Learning with Kernels: Support Vector Machines, Regularization, Optimization, and Beyond. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2001. [13] Liu W F, Principe J C, Haykin S. Kernel Adaptive Filtering: A Comprehensive Introduction. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2010. [14] Scholkopf B, Smola A, Muller K R. Nonlinear component analysis as a kernel eigenvalue problem. Neural Computation, 1998, 10(5): 1299−1319 doi: 10.1162/089976698300017467 [15] Feng D Z, Bao Z, Jiao L C. Total least mean squares algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1998, 46(8): 2122−2130 doi: 10.1109/78.705421 [16] Henon M. A two-dimensional mapping with a strange attractor. The Theory of Chaotic Attractors. New York, NY: Springer, 1976. 94-102 [17] Kivinen J, Smola A J, Williamson R C. Online learning with kernels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(8): 2165−2176 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.830991 [18] Richard C, Bermudez J C M, Honeine P. Online prediction of time series data with kernels. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(3): 1058−1067 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.2009895 [19] Liu W F, Pokharel P P, Principe J C. The kernel least-mean-square algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(2): 543−554 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2007.907881 [20] Engel Y, Mannor S, Meir R. The kernel recursive least-squares algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(8): 2275−2285 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.830985 [21] Liu W F, Principe J C. Kernel affine projection algorithms. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2008, 2008(1): 784292 doi: 10.1155/2008/784292 [22] Chen B D, Zhao S L, Zhu P P, Príncipe J C. Quantized kernel least mean square algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(1): 22−32 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2011.2178446 [23] Zhao J, Liao X F, Wang S Y, Tse C K. Kernel least mean square with single feedback. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(7): 953−957 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2014.2377726 [24] Zheng Y F, Wang S Y, Feng J C, Tse C K. A modified quantized kernel least mean square algorithm for prediction of chaotic time series. Digital Signal Processing, 2016, 48: 130−136 doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2015.09.015 [25] Liu Y Q, Sun C, Jiang S D. A kernel least mean square algorithm based on randomized feature networks. Applied Sciences, 2018, 8(3): 458 doi: 10.3390/app8030458 [26] Van Vaerenbergh S, Via J, Santamaria I. A sliding-window kernel RLS algorithm and its application to nonlinear channel identification. In: Proceedings of 2006 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics Speech and Signal Processing. Toulouse, France: IEEE, 2006. 789—792 [27] Liu W F, Park I, Wang Y W, Principe J C. Extended kernel recursive least squares algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2009, 57(10): 3801−3814 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2022007 [28] Van Vaerenbergh S, Santamaria I, Liu W F, Principe J C. Fixed-budget kernel recursive least-squares. In: Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Dallas, TX, USA: IEEE, 2010. 1882−1885 [29] Van Vaerenbergh S, Lazaro-Gredilla M, Santamaria I. Kernel recursive least-squares tracker for time-varying regression. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(8): 1313−1326 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2200500 [30] Chen B D, Zhao S L, Zhu P P, Principe J C. Quantized kernel recursive least squares algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2013, 24(9): 1484−1491 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2258936 [31] Wang S Y, Wang W, Duan S K, Wang L D. Kernel recursive least squares with multiple feedback and its convergence analysis. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2017, 66(10): 1237−1241 [32] Zhang S H, Han M, Wang J, Wang D. Multivariate time series online prediction based on adaptive normalized sparse kernel recursive least squares algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Information Science and Technology. Da Nang, Vietnam: IEEE, 2017. 38−44 [33] Ogunfunmi T, Paul T. On the complex kernel-based adaptive filter. In: Proceedings of 2011 IEEE International Symposium of Circuits and Systems. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2011. 1263−1266 [34] Gil-Cacho J M, Van Waterschoot T, Moonen M, Jensen S H. Nonlinear acoustic echo cancellation based on a parallel-cascade kernel affine projection algorithm. In: Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Kyoto, Japan: IEEE, 2012. 33−36 [35] Yang X H, Qu H, Zhao J, Chen B D. Hybrid affine projection algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision. Singapore, Singapore: IEEE, 2014. 964−968 [36] Ren X W, Yu Q H, Chen B D, Zheng N N, Ren P J. A reconfigurable parallel FPGA accelerator for the kernel affine projection algorithm. In: Proceedings of 2015 IEEE International Conference on Digital Signal Processing. Singapore, Singapore: IEEE, 2015. 906−910 [37] Singh A, Ahuja N, Moulin P. Online learning with kernels: Overcoming the growing sum problem. In: Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing. Santander, Spain: IEEE, 2012. 1−6 [38] Haykin S. Adaptive Filter Theory. Dorling Kindersley, India: Pearson Education, 2008. [39] Zhao S L, Chen B D, Zhu P P, Principe J C. Fixed budget quantized kernel least-mean-square algorithm. Signal Processing, 2013, 93(9): 2759−2770 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2013.02.012 [40] Rzepka D. Fixed-budget kernel least mean squares. In: Proceedings of the 17th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation. Krakow, Poland: IEEE, 2012. 1-4 [41] Fan H J, Song Q. A linear recurrent kernel online learning algorithm with sparse updates. Neural Networks, 2014, 50: 142−153 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2013.11.011 [42] Liu W f, Park I, Principe J C. An information theoretic approach of designing sparse kernel adaptive filters. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2009, 20(12): 1950−1961 doi: 10.1109/TNN.2009.2033676 [43] Ma W T, Duan J D, Man W S, Zhao H Q, Chen B D. Robust kernel adaptive filters based on mean p-power error for noisy chaotic time series prediction. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2017, 58: 101−110 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2016.11.010 [44] Chen B D, Xing L, Zhao H Q, Zheng N N, Principe J C. Generalized correntropy for robust adaptive filtering. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(13): 3376−3387 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2016.2539127 [45] Chen B D, Wang J J, Zhao H Q, Zheng N N, Principe J C. Convergence of a fixed-point algorithm under maximum correntropy criterion. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2015, 22(10): 1723−1727 doi: 10.1109/LSP.2015.2428713 [46] Chen B D, Zhao S L, Zhu P P, Principe J C. Mean square convergence analysis for kernel least mean square algorithm. Signal Processing, 2012, 92(11): 2624−2632 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2012.04.007 [47] Gao W, Chen J, Richard C, Huang J G. Online dictionary learning for kernel LMS. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2014, 62(11): 2765−2777 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2014.2318132 [48] Han M, Wang Y N. Nonlinear time series online prediction using reservoir Kalman filter. In: Proceedings of 2009 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Atlanta, USA: IEEE, 2009. 1090−1094 [49] Zhou H W, Huang J Q, Lu F, Thiyagalingam J, Kirubarajan T. Echo state kernel recursive least squares algorithm for machine condition prediction. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2018, 111: 68−86 doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2018.03.047 [50] Wang X Y, Han M. Multivariate time series prediction based on multiple kernel extreme learning machine. In: Proceedings of 2014 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2014. 198−201 [51] Xu M L, Zhang S H, Han M. Multivariate time series modeling and prediction based on reservoir independent components. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing (ICICIP). Wuhan, China: IEEE, 2015. 325−330 [52] Han M, Zhang S H, Xu M L, Qiu T, Wang N. Multivariate chaotic time series online prediction based on improved kernel recursive least squares algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(4): 1160−1172 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2789686 [53] Han M, Ren W J, Xu M L, Qiu T. Nonuniform state space reconstruction for multivariate chaotic time series. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(5): 1885−1895 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2816657 [54] 韩敏, 任伟杰, 许美玲. 一种基于L1范数正则化的回声状态网络. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(11): 2428−2435Han Min, Ren Wei-Jie, Xu Mei-Ling. An improved echo state network via L1-norm regularization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(11): 2428−2435 [55] 唐舟进, 任峰, 彭涛, 王文博. 基于迭代误差补偿的混沌时间序列最小二乘支持向量机预测算法. 物理学报, 2014, 63(5): 050505 doi: 10.7498/aps.63.050505Tang Zhou-Jin, Ren Feng, Peng Tao, Wang Wen-Bo. A least square support vector machine prediction algorithm for chaotic time series based on the iterative error correction. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(5): 050505 doi: 10.7498/aps.63.050505 [56] 刘畅, 郎劲. 基于混核LSSVM的批特征风功率预测方法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(6): 1264−1273Liu Chang, Lang Jin. Wind power prediction method using hybrid kernel LSSVM with batch feature. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(6): 1264−1273 [57] 梅英, 谭冠政, 刘振焘, 武鹤. 基于大脑情感学习模型和自适应遗传算法的混沌时间序列预测. 物理学报, 2018, 67(8): 080502 doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20172104Mei Ying, Tan Guan-Zheng, Liu Zhen-Tao, Wu He. Chaotic time series prediction based on brain emotional learning model and self-adaptive genetic algorithm. Acta Physica Sinica, 2018, 67(8): 080502 doi: 10.7498/aps.67.20172104 [58] 杨臻明, 岳继光, 王晓保, 萧蕴诗. 基于独立成分分析的含噪声时间序列预测. 控制与决策, 2013, 28(4): 501−505Yang Zhen-Ming, Yue Ji-Guang, Wang Xiao-Bao, Xiao Yun-Shi. Noisy time series prediction using independent component analysis. Control and Decision, 2013, 28(4): 501−505 [59] 宋晓祥, 郭艳, 李宁, 余东平. 基于稀疏贝叶斯学习的协同进化时间序列缺失数据预测算法. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(7): 217−223 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.07.033Song Xiao-Xiang, Guo Yan, Li Ning, Yu Dong-Ping. Missing data prediction algorithm based on sparse Bayesian learning in coevolving time series. Computer Science, 2019, 46(7): 217−223 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.07.033 [60] 宋晓祥, 郭艳, 李宁, 王萌. 基于压缩感知的时间序列缺失数据预测算法. 计算机科学, 2019, 46(6): 35−40 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.06.004Song Xiao-Xiang, Guo Yan, Li Ning, Wang Meng. Missing data prediction based on compressive sensing in time series. Computer Science, 2019, 46(6): 35−40 doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1002-137X.2019.06.004 [61] Paul T K, Ogunfunmi T. On the convergence behavior of the affine projection algorithm for adaptive filters. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2011, 58(8): 1813−1826 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2011.2106091 [62] Slavakis K, Theodoridis S, Yamada I. Online kernel-based classification using adaptive projection algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2008, 56(7): 2781−2796 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2008.917376 [63] Yukawa M. Multikernel adaptive filtering. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2012, 60(9): 4672−4682 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2012.2200889 [64] 张帆. Adaline神经网络随机逼近LMS算法的仿真研究. 电子设计工程, 2009, 17(9): 88−90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2009.09.034Zhang Fan. Simulation study of stochastic approximation LMS algorithm of adaline neural network. Electronic Design Engineering, 2009, 17(9): 88−90 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6236.2009.09.034 [65] Han M, Zhong K, Qiu T, Han B. Interval type-2 fuzzy neural networks for chaotic time series prediction: A concise overview. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(7): 2720−2731 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2834356 [66] 李海林, 梁叶. 基于动态时间弯曲的股票时间序列联动性研究. 数据采集与处理, 2016, 31(1): 117−129Li Hai-Lin, Liang Ye. Co-movement research of stock time series based on dynamic time warping. Journal of Data Acquisition & Processing, 2016, 31(1): 117−129 [67] Li H L. Piecewise aggregate representations and lower-bound distance functions for multivariate time series. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and its Applications, 2015, 427: 10−25 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2015.01.063 [68] 韩敏, 王亚楠. 基于Kalman滤波的储备池多元时间序列在线预报器. 自动化学报, 2010, 36(1): 169−173 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00169Han Min, Wang Ya-Nan. Multivariate time series online predictor with Kalman filter trained reservoir. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(1): 169−173 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2010.00169 [69] Aghabozorgi S, Teh Y W. Stock market co-movement assessment using a three-phase clustering method. Expert Systems with Applications, 2014, 41(4): 1301−1314 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2013.08.028 [70] Jeon S, Hong B, Chang V. Pattern graph tracking-based stock price prediction using big data. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2018, 80: 171−187 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2017.02.010 [71] 万校基, 李海林. 基于特征表示的金融多元时间序列数据分析. 统计与决策, 2015, (23): 151−155Wan Xiao-Ji, Li Hai-Lin. Financial multivariate time series data analysis based on feature representation. Statistics and Decision, 2015, (23): 151−155 [72] Lu L, Zhao H Q, Chen B D. Time series prediction using kernel adaptive filter with least mean absolute third loss function. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2017, 90(2): 999−1013 doi: 10.1007/s11071-017-3707-7 [73] Takizawa M A, Yukawa M. Efficient dictionary-refining kernel adaptive filter with fundamental insights. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2016, 64(16): 4337—4350 [74] Anava O, Hazan E, Mannor S, Shamir O. Online learning for time series prediction. In: Proceedings of the 26th Annual Conference on Learning Theory. Princeton University, USA: JMLR.org, 2013. 172−184 [75] Santos J D A, Barreto G A. An outlier-robust kernel RLS algorithm for nonlinear system identification. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2017, 90(3): 1707−1726 doi: 10.1007/s11071-017-3760-2 [76] Hong Y S T. Dynamic nonlinear state-space model with a neural network via improved sequential learning algorithm for an online real-time hydrological modeling. Journal of Hydrology, 2012, 468-469: 11−21 doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2012.08.001 [77] Chen B D, Liang J L, Zheng N N, Principe J C. Kernel least mean square with adaptive kernel size. Neurocomputing, 2016, 191: 95−106 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2016.01.004 [78] Song Q. Time series prediction based on online learning. In: Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Machine Learning and Applications. Miami, USA: IEEE, 2015. 857−864 [79] Tuia D, Munoz-Mari J, Rojo-Alvarez J L, Martinez-Ramon M, Camps-Valls G. Explicit recursive and adaptive filtering in reproducing kernel Hilbert spaces. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2014, 25(7): 1413−1419 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2013.2293871 [80] Wang S Y, Zheng Y F, Duan S K, Wang L D, Tan H T. Quantized kernel maximum correntropy and its mean square convergence analysis. Digital Signal Processing, 2017, 63: 164−176 doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2017.01.010 [81] Constantin I, Lengelle R. Performance analysis of kernel adaptive filters based on RLS algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Microelectronics. Beirut, Lebanon: IEEE, 2013. 1−4 [82] Van Vaerenbergh S, Santamaria I, Lazaro-Gredilla M. Estimation of the forgetting factor in kernel recursive least squares. In: Proceedings of 2012 IEEE International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing. Santander, Spain: IEEE, 2012. 1−6 [83] Crammer K, Dekel O, Keshet J, Shalev-Shwartz S, Singer Y. Online passive-aggressive algorithms. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2006, 7: 551−585 [84] Mairal J, Bach F, Ponce J, Sapiro G. Online learning for matrix factorization and sparse coding. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11: 19−60 [85] Guan N Y, Tao D C, Luo Z G, Yuan B. Online nonnegative matrix factorization with robust stochastic approximation. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2012, 23(7): 1087−1099 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2012.2197827 [86] Duchi J, Hazan E, Singer Y. Adaptive subgradient methods for online learning and stochastic optimization. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 2121−2159 [87] Zhao P L, Hoi S C H, Jin R. Double updating online learning. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12: 1587−1615 [88] Wang Z, Crammer K, Vucetic S. Breaking the curse of kernelization: Budgeted stochastic gradient descent for large-scale SVM training. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2012, 13(1): 3103−3131 [89] Le T, Nguyen T D, Nguyen V, Phung D. Approximation vector machines for large-scale online learning. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2017, 18(1): 3962−4016 [90] Hoi S C H, Wang J L, Zhao P L. LIBOL: A library for online learning algorithms. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1): 495−499 [91] Bottou L, Le Cun Y. Large-scale online learning. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2003. 217—224 [92] Dieuleveut A, Flammarion N, Bach F. Harder, better, faster, stronger convergence rates for least-squares regression. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2017, 18(101): 1−51 [93] Lin J H, Zhou D X. Online learning algorithms can converge comparably fast as batch learning. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(6): 2367−2378 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2677970 [94] Flores A, de Lamare R C. Set-membership adaptive kernel NLMS algorithms: Design and analysis. Signal Processing, 2019, 154: 1−14 doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2018.07.007 [95] Liu Y Q, Sun C, Jiang S D. Kernel filtered-x LMS algorithm for active noise control system with nonlinear primary path. Circuits, Systems, and Signal Processing, 2018, 37(12): 5576−5594 doi: 10.1007/s00034-018-0832-6 [96] Lei Y W, Shi L, Guo Z C. Convergence of unregularized online learning algorithms. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2017, 18(171): 1−3 [97] Ma Y T, Zheng T. Stabilized sparse online learning for sparse data. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2017, 18(131): 1−36 [98] Wada T, Fukumori K, Tanaka T. Dictionary learning for gaussian kernel adaptive filtering with variablekernel center and width. In: Proceedings of 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Calgary, Canada: IEEE, 2018. 2766−2770 [99] Wang S Y, Dang L J, Chen B D, Ling C X, Wang L D, Duan S K. Kernel online learning algorithm with scale adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2018, 65(11): 1788−1792 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2017.2765523 [100] Ohnishi M, Yukawa M. Online nonlinear estimation via iterative L2-space projections: Reproducing kernel of subspace. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(15): 4050−4064 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2846271 [101] Shin B S, Yukawa M, Cavalcante R L G, Dekorsy A. Distributed adaptive learning with multiple kernels in diffusion networks. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2018, 66(21): 5505−5519 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2868040 -




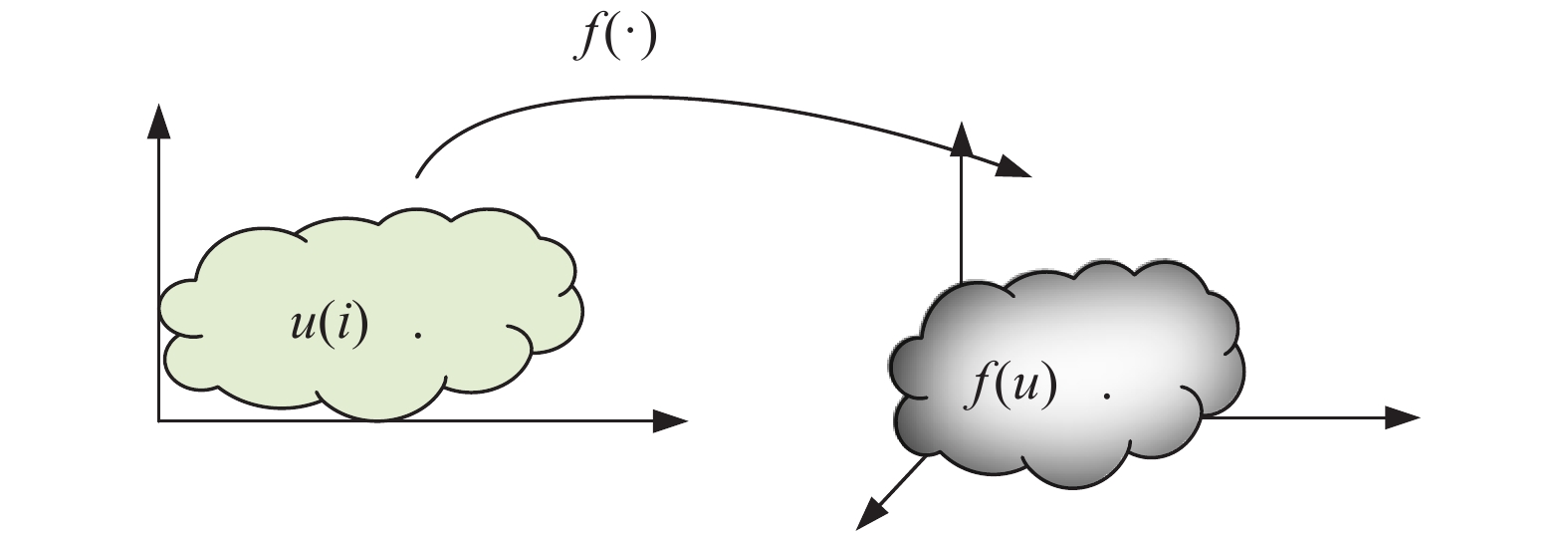
 下载:
下载: