Research Progress on Application of Generative Adversarial Networks in Various Fields
-
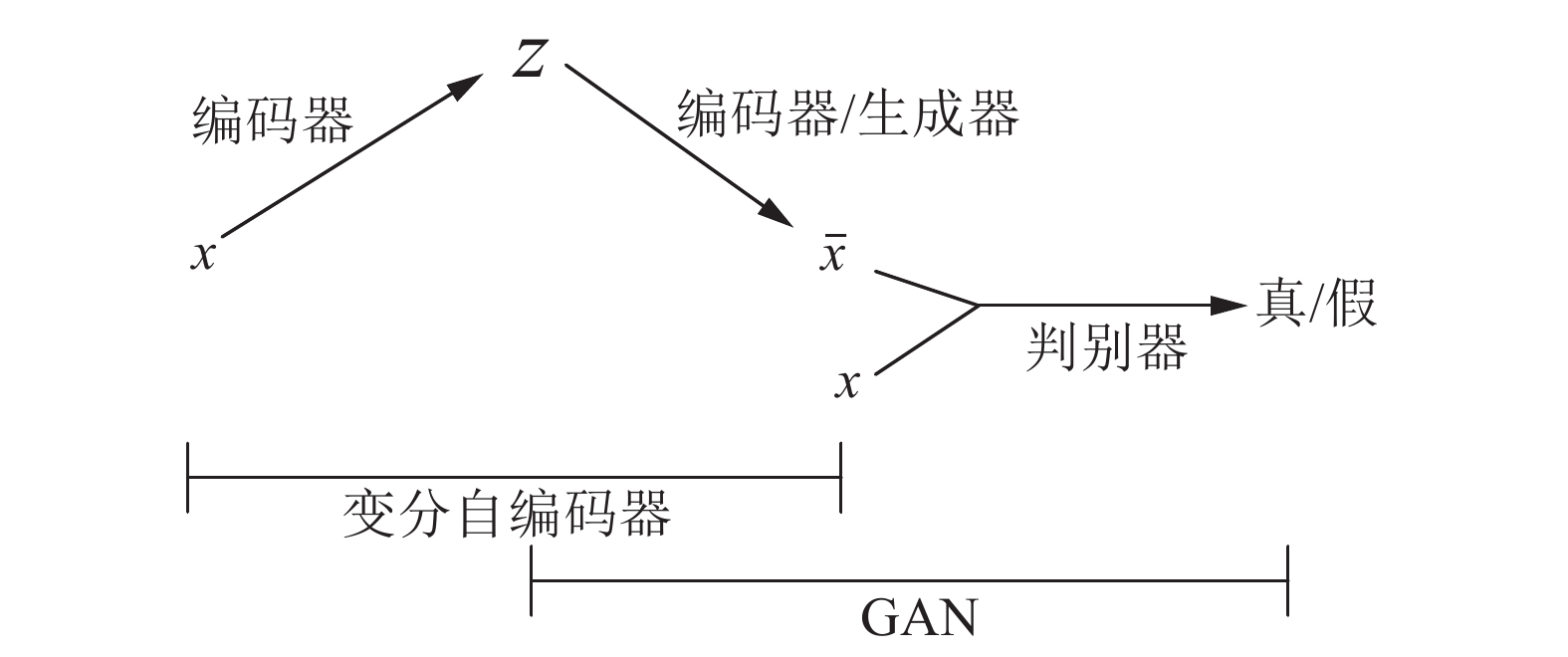
摘要: 随着深度学习的快速发展, 生成式模型领域也取得了显著进展. 生成对抗网络(Generative adversarial network, GAN)是一种无监督的学习方法, 它是根据博弈论中的二人零和博弈理论提出的. GAN具有一个生成器网络和一个判别器网络, 并通过对抗学习进行训练. 近年来, GAN成为一个炙手可热的研究方向. GAN不仅在图像领域取得了不错的成绩, 还在自然语言处理(Natural language processing, NLP)以及其他领域崭露头角. 本文对GAN的基本原理、训练过程和传统GAN存在的问题进行了阐述, 进一步详细介绍了通过损失函数的修改、网络结构的变化以及两者结合的手段提出的GAN变种模型的原理结构, 其中包括: 条件生成对抗网络(Conditional GAN, CGAN)、基于Wasserstein 距离的生成对抗网络(Wasserstein-GAN, WGAN)及其基于梯度策略的WGAN (WGAN-gradient penalty, WGAN-GP)、基于互信息理论的生成对抗网络(Informational-GAN, InfoGAN)、序列生成对抗网络(Sequence GAN, SeqGAN)、Pix2Pix、循环一致生成对抗网络(Cycle-consistent GAN, Cycle GAN)及其增强Cycle-GAN (Augmented CycleGAN). 概述了在计算机视觉、语音与NLP领域中基于GAN和相应GAN变种模型的基本原理结构, 其中包括: 基于CGAN的脸部老化应用(Face aging CGAN, Age-cGAN)、双路径生成对抗网络(Two-pathway GAN, TP-GAN)、表示解析学习生成对抗网络(Disentangled representation learning GAN, DR-GAN)、对偶学习生成对抗网络(DualGAN)、GeneGAN、语音增强生成对抗网络(Speech enhancement GAN, SEGAN)等. 介绍了GAN在医学、数据增强等领域的应用情况, 其中包括: 数据增强生成对抗网络(Data augmentation GAN, DAGAN)、医学生成对抗网络(Medical GAN, MedGAN)、无监督像素级域自适应方法(Unsupervised pixel-level domain adaptation method, PixelDA). 最后对GAN未来发展趋势及方向进行了展望.Abstract: With the rapid development of deep learning, the field of generative models has also made significant progress. Generative adversarial network (GAN) is an unsupervised learning method based on the zero-sum game theory in game theory. GAN has a generator network and a discriminator network and trains through adversarial learning. In the past two years, GAN has become a hot research direction. GAN has not only achieved good results in the field of computer vision, but also emerged in natural language processing (NLP) and other fields. This paper expounds the basic principles of GAN, the training process and the problems existing in traditional GAN, and further introduces the principal structure of the GAN variant model proposed by the modification of the loss function, the change of the network structure and the combination of the two, e.g., conditional GAN (CGAN), Wasserstein-GAN (WGAN), WGAN-gradient penalty (WGAN-GP), informational GAN (InfoGAN), sequence GAN (SeqGAN), Pix2Pix, cycle-consistent GAN (CycleGAN) and augmented CycleGAN, and so on. Then in the areas of computer vision, speech synthetics and analysis and NLP, we review the structure of the principle networks and models, including Age-cGAN for face aging, two-pathway GAN (TP-GAN), disentangled representation learning GAN (DR-GAN), DualGAN, GeneGAN, speech enhancement GAN (SEGAN), gumbel-softmax GAN, and so forth. Then we also introduce the applications of GAN in the field of medicine, data enhancement,etc, including data augmentation GAN (DAGAN), medical GAN (MedGAN), unsupervised pixel-level domain adaptation method (PixelDA), and so on. Finally, the future trends and directions of GAN are prospected.
-
表 1 GAN模型变种
Table 1 Variant of GAN model
表 2 GAN在图像领域的应用
Table 2 GAN's application in the field of computer vision
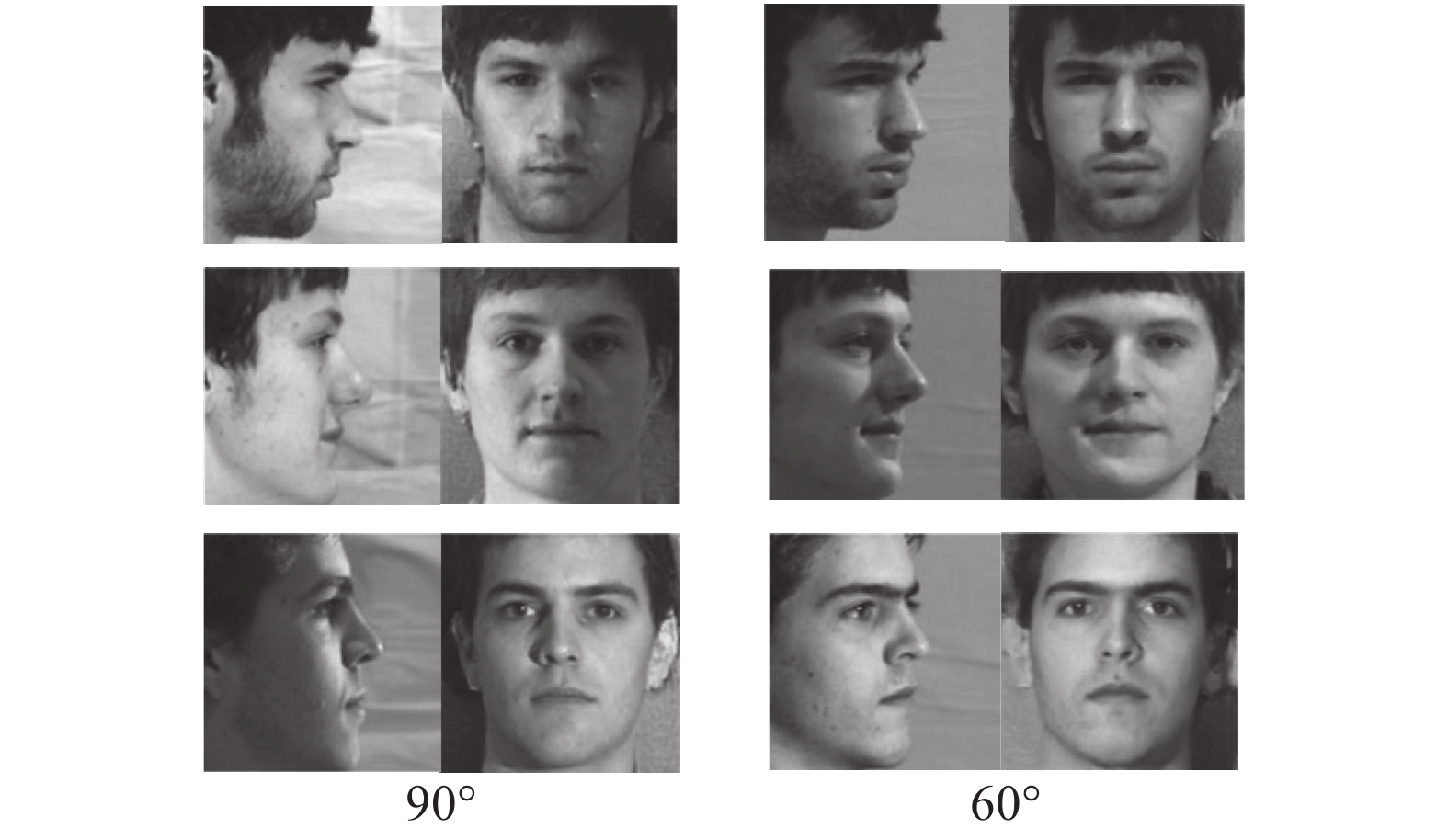
内容 模型 人脸图像识别与图像生成 基于 CGAN 的人脸识别模型[28], Age-cGAN[29], GLCA-GAN[30], TP-GAN[31], DR-GAN[33], SGAN[34],
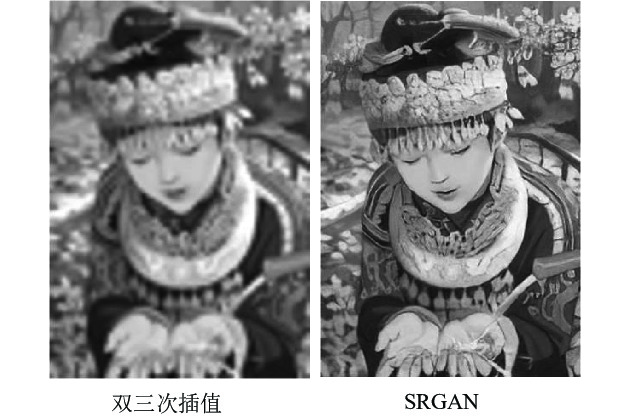
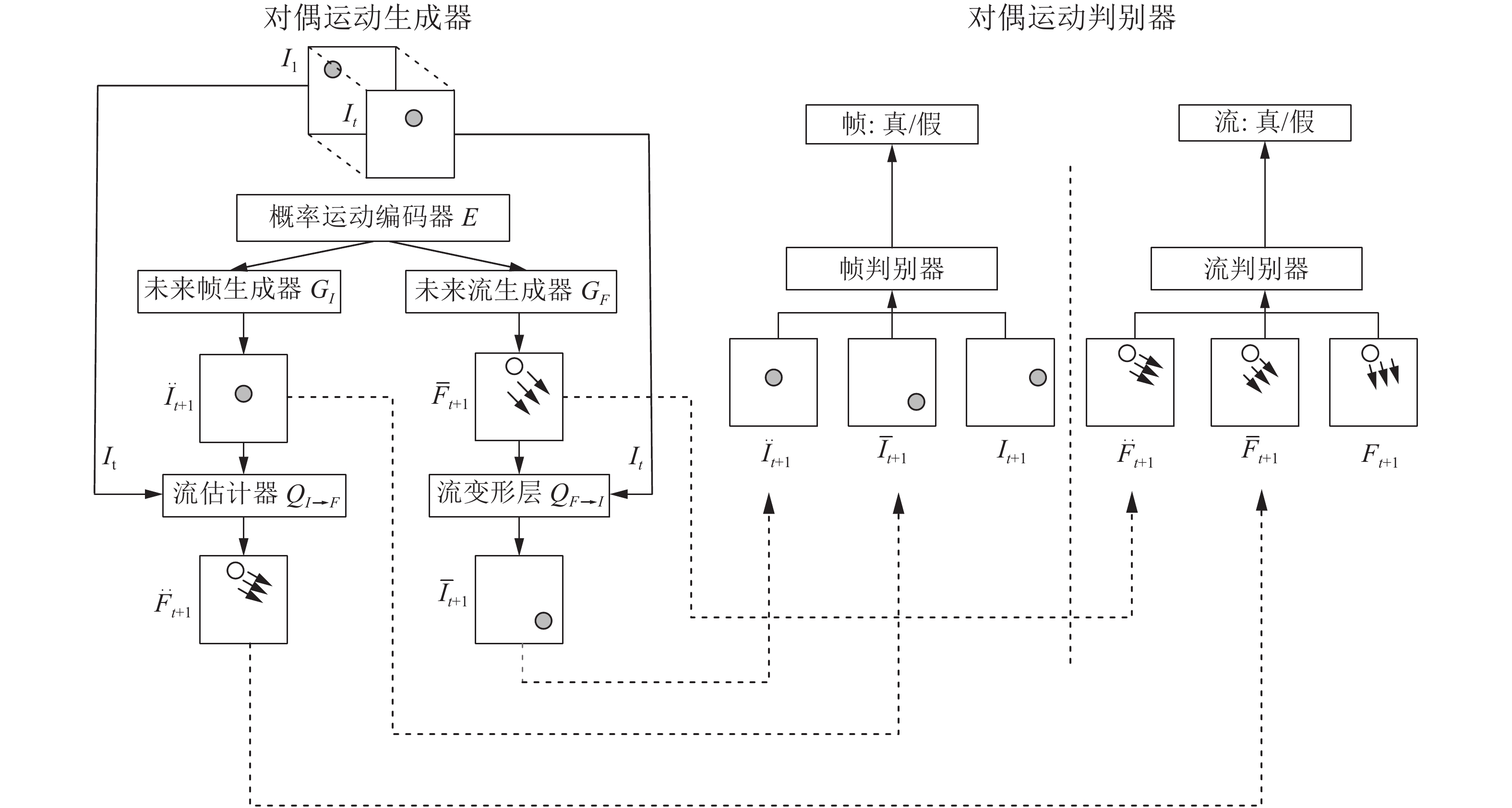
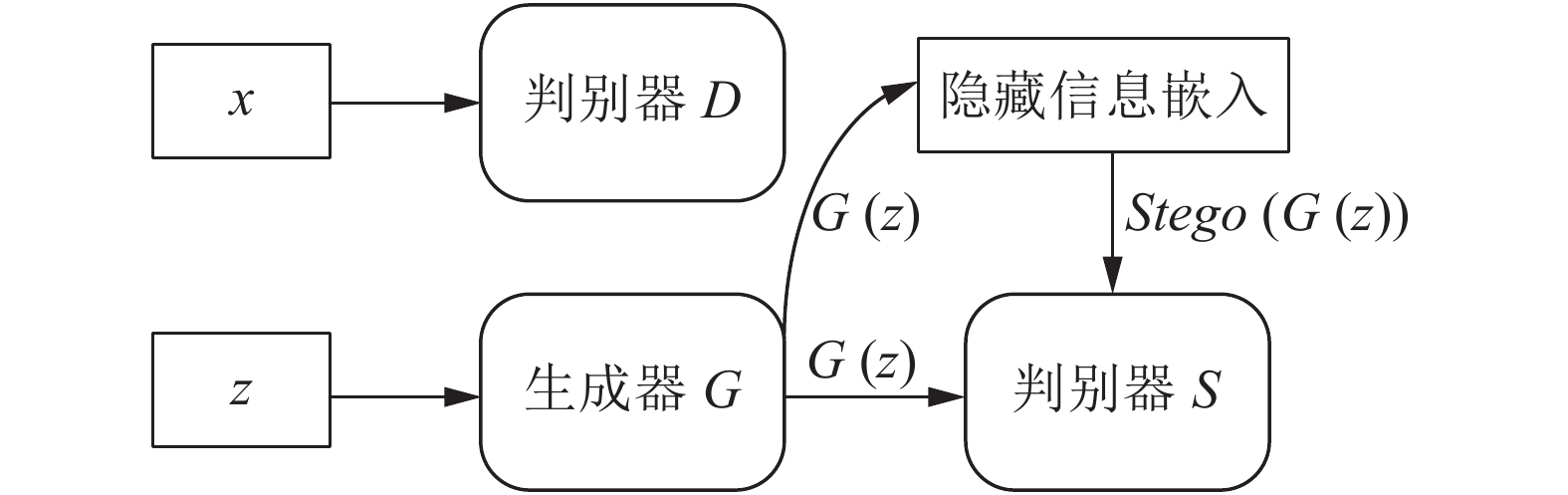
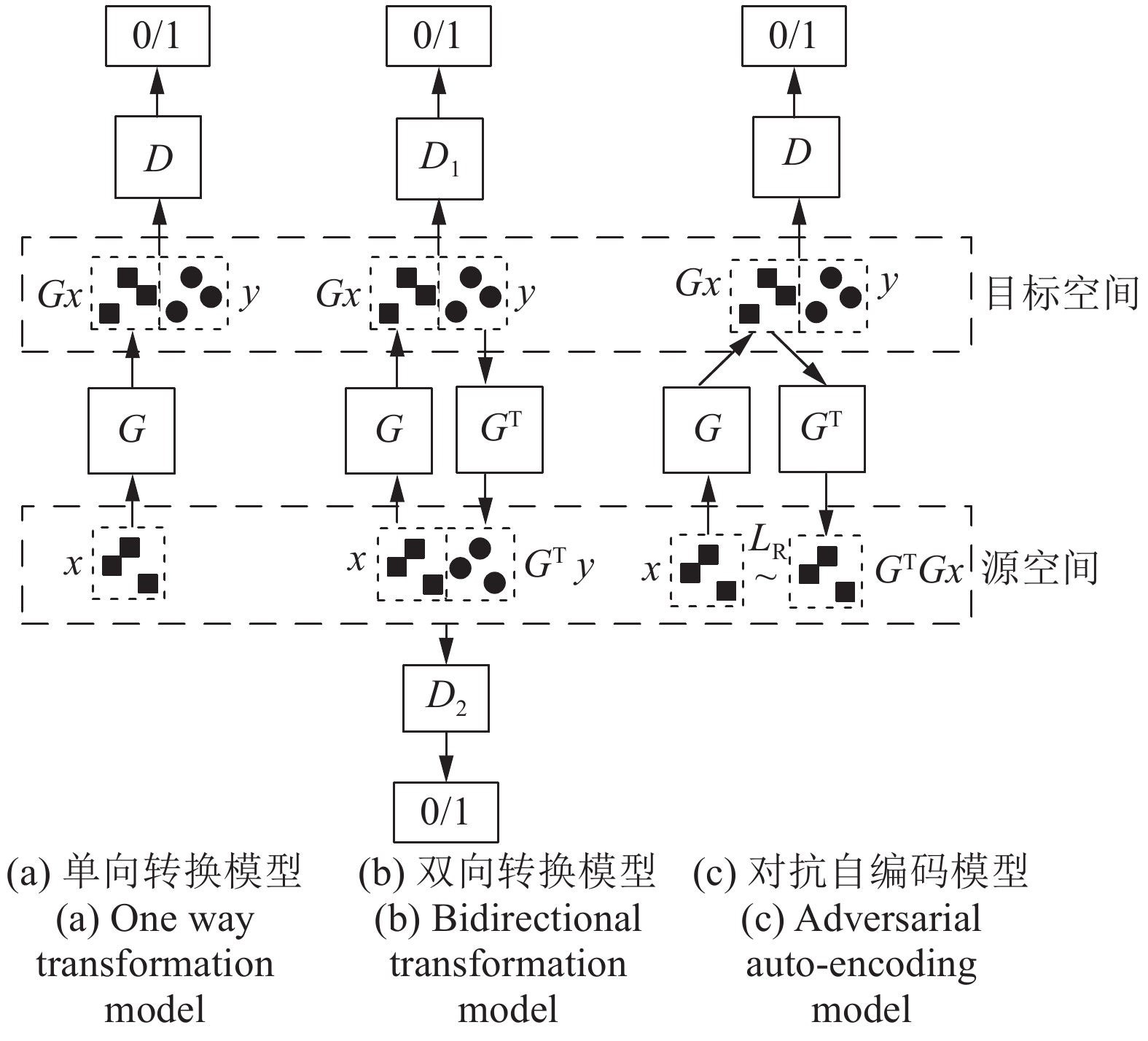
MGAN[35], BigGAN[37]图像超分辨率 SRGAN[38], c-CycleGAN[39] 图像复原与多视角图像生成 基于 GAN 的语义图像修复模型[41], PGGAN[42], VariGAN[45] 图像转换 DualGAN[47], GeneGAN[48], S2-GAN[49], DA-GAN[50] 文本描述到图像生成 Text to image GAN[52], GAWWN[53], RTT-GAN[54] 图像语义分割 基于GAN的语义分割模型[55-56], Contrast-GAN[57] 图像着色 Auto-painter[58], DCGAN 用于图像着色[59] 视频预测 基于GAN的下帧图像生成模型[61], 利用 3D-CNN 作为生成器的 GAN[62], Dual motion GAN[63] 视觉显著性预测 SalGAN[64], MC-GAN[65] 图像密写 S-GAN[66] 3D 图像生成 3D-GAN[67], VON[68] 表 3 GAN在语音与NLP领域的应用
Table 3 GAN's application in the field of speech and NLP
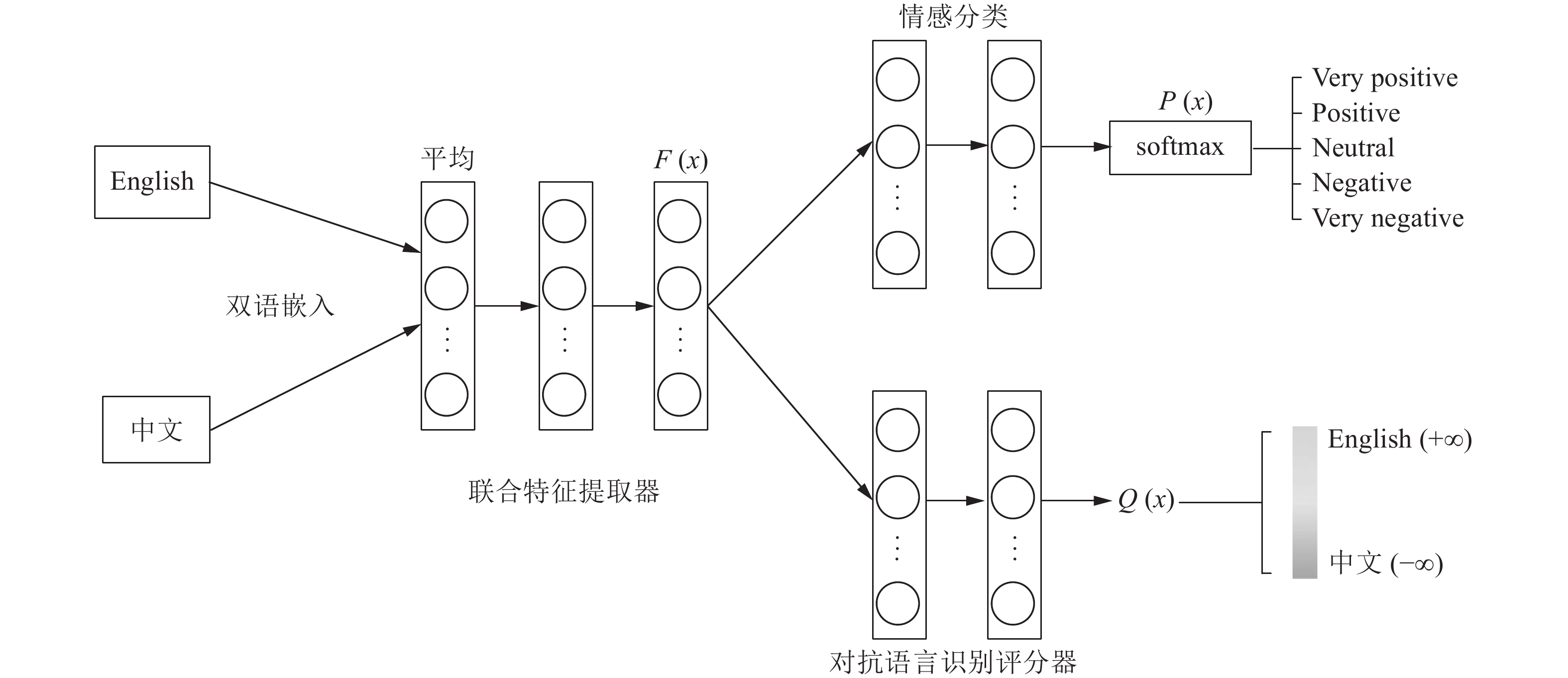
内容 模型 语音增强 SEGAN[69], 基于 Pix2Pix 的语音增强模型[71] 音乐生成 MuseGAN[72] 语音识别 基于 GAN 的语音识别模型[73], 基于多任务对抗学习模式的语音识别模型[74], WGAN 用于语音识别[75], VoiceGAN[76], MTGAN[77], Residual GAN[78] 对话模型的评估与生成 基于 SeqGAN 的对话评估模型[79], 基于 SeqGAN 的对话生成模型[80] 生成离散序列 Gumbel-softmax GAN[82] 双语字典 基于 GAN 的双语字典模型[83] 文本分类与生成 对抗多任务学习模型[86], 基于 WGAN 的文本生成模型[87], DP-GAN[88] 语篇分析 ADAN[89] 机器翻译 BR-CSGAN[92], Multi-CSGAN-NMT[93], Adversarial-NMT[94], BGAN-NMT[95] 表 4 GAN在其他领域的应用
Table 4 GAN's application in other fields
内容 模型 人体姿态估计 基于 RL 与 GAN 的姿态估计模型[96], 基于 GAN 的姿态估计模型[97], 基于双向 LSTM 的 CGAN 模型[98] 恶意软件检测 MalGAN[99] 数据集标记与数据增强 基于 GAN 的仿真无监督学习框架[100], RenderGAN[101], DAGAN[102] 物理应用 基于 GAN 的高能粒子物理图像生成模型[104] 医学领域 RefineGAN[105], 基于 CGAN 的多对比度 MRI 图像生成模型[106], MedGAN[107], 基于 GAN 的视网膜血管图像生成模型[108], 基于 WGAN 的 CCTA 模型[109] 隐私保护 基于 GAN 的用户信息攻击模型[110] 域适应学习领域 PixelDA[112], 基于 GAN 的域自适应分类任务[113], 基于 GAN 的域间联合嵌入特征空间模型[114] 自动驾驶 基于 GAN 的驾驶场景预测模型[115], 基于 VAE 与 GAN 的路况预测模型[116] -
[1] Silver D, Huang A J, Maddison C J, Guez A, Sifre L, van den Driessche G, et al. Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search. Nature, 2016, 529(7587): 484−489 doi: 10.1038/nature16961 [2] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial networks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014, 3: 2672−2680 [3] 王坤峰, 苟超, 段艳杰, 林懿伦, 郑心湖, 王飞跃. 生成式对抗网络GAN的研究进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(3): 321−332Wang Kun-Feng, Gou Chao, Duan Yan-Jie, Lin Yi-Lun, Zheng Xin-Hu, Wang Fei-Yue. Generative adversarial networks: The state of the art and beyond. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(3): 321−332 [4] Kingma D P, Welling M. Auto-encoding variational Bayes. arXiv: 1312.6114v10, 2013. [5] Ratliff L J, Burden S A, Sastry S S. Characterization and computation of local Nash equilibria in continuous games. In: Proceedings of the 51st Annual Allerton Conference on Communication, Control, and Computing. Monticello, IL, USA: IEEE, 2013. 917−924 [6] Larsen A B L, S\onderby S K, Larochelle H, Winther O. Autoencoding beyond pixels using a learned similarity metric. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. New York City, USA: ACM, 2016. 1558−1566 [7] Radford A, Metz L, Chintala S. Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations. San Juan, Puerto Rico, 2015. [8] Salimans T, Goodfellow I J, Zaremba W, Cheung V, Radford A, Chen X. Improved techniques for training GANs. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain, 2016. 2226−2234 [9] Arjovsky M, Bottou L. Towards principled methods for training generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1701.04862v1, 2017. [10] Mirza M, Osindero S. Conditional generative adversarial nets. arXiv: 1411.1784, 2014. [11] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImagEnet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2012 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, Nevada, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2012. 1106−1114 [12] Arjovsky M, Chintala S, Bottou L. Wasserstein GAN. arXiv: 1701.07875v3, 2017. [13] Tieleman T, Hinton G. Lecture 6.5-rmsprop: Divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude. COURSERA: Neural Networks for Machine Learning, 2012, 4: 26−31 [14] Gulrajani I, Ahmed F, Arjovsky M, Dumoulin V, Courville A C. Improved training of Wasserstein GANs. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, CA, USA: Curran Associates, Inc., 2017. 5767−5777 [15] Chen X, Duan Y, Houthooft R, Schulman J, Sutskever I, Abbeel P. InfoGAN: Interpretable representation learning by information maximizing generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 29: Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems 2016. Barcelona, Spain: Curran Associates Inc., 2016. 2172−2180 [16] Yu L T, Zhang W N, Wang J, Yu Y. SeqGAN: Sequence generative adversarial nets with policy gradient. In: Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, California, USA: AAAI, 2017. 2852−2858 [17] 刘全, 翟建伟, 章宗长, 钟珊, 周倩, 章鹏, 等. 深度强化学习综述. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(1): 1−27 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.00001Liu Quan, Zhai Jian-Wei, Zhang Zong-Zhang, Zhong Shan, Zhou Qian, Zhang Peng, et al. A survey on deep reinforcement learning. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(1): 1−27 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2019.00001 [18] Isola P, Zhu J Y, Zhou T H, Efros A A. Image-to-image translation with conditional adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5967−5976 [19] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015. 234−241 [20] Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, Efros A A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2242−2251 [21] He D, Xia Y C, Qin T, Wang L W, Yu N H, Liu T Y, et al. Dual learning for machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2016. 820−828 [22] Almahairi A, Rajeswar S, Sordoni A, Bachman P, Courville A C. Augmented CycleGAN: Learning many-to-many mappings from unpaired data. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. 195−204 [23] Che T, Li Y R, Jacob A P, Bengio Y, Li W J. Mode regularized generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1612.02136, 2016. [24] Gretton A, Borgwardt K M, Rasch M J, Schölkopf B, Smola A J. A kernel method for the two-sample-problem. In: Proceedings of the 2007 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: MIT Press, 2007. 513−520 [25] Heusel M, Ramsauer H, Unterthiner T, Nessler B, Hochreiter S. GANs trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local Nash equilibrium. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, CA, USA, 2017. 6626−6637 [26] Lopez-Paz D, Oquab M. Revisiting classifier two-sample tests. arXiv: 1610.06545, 2016. [27] Xu Q T, Huang G, Yuan Y, Guo C, Sun Y, Wu F, et al. An empirical study on evaluation metrics of generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1806.07755, 2018. [28] Gauthier J. Conditional generative adversarial nets for convolutional face generation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Class Project for Stanford CS231N: Convolutional Neural Networks for Visual Recognition. 2014. 2 [29] Antipov G, Baccouche M, Dugelay J L. Face aging with conditional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP). Beijing, China: IEEE, 2017. 2089−2093 [30] Li P P, Hu Y B, Li Q, He R, Sun Z N. Global and local consistent age generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2018. 1073−1078 [31] Huang R, Zhang S, Li T Y, He R. Beyond face rotation: Global and local perception GAN for photorealistic and identity preserving frontal view synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2458−2467 [32] Johnson J, Alahi A, Li F F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 694−711 [33] Tran L, Yin X, Liu X M. Disentangled representation learning GAN for pose-invariant face recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1283−1292 [34] Jetchev N, Bergmann U, Vollgraf R. Texture synthesis with spatial generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1611.08207, 2016. [35] Li C, Wand M. Precomputed real-time texture synthesis with markovian generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 702−716 [36] Ulyanov D, Lebedev V, Vedaldi A, Lempitsky V. Texture networks: Feed-forward synthesis of textures and stylized images. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York City, USA: ACM, 2016. 1349−1357 [37] Brock A, Donahue J, Simonyan K. Large scale GAN training for high fidelity natural image synthesis. arXiv: 1809.11096, 2018. [38] Ledig C, Theis L, Huszár F, Caballero J, Cunningham A, Acosta A, et al. Photo-realistic single image super-resolution using a generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 105−114 [39] Lu Y Y, Tai Y W, Tang C K. Attribute-guided face generation using conditional CycleGAN. arXiv: 1705.09966, 2017. [40] Chen Z M, Tong Y G. Face super-resolution through wasserstein GANs. arXiv: 1705.02438v1, 2017. [41] Yeh R A, Chen C, Lim T Y, Schwing A G, Hasegawa-Johnson M, Do M N. Semantic image inpainting with deep generative models. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6882−6890 [42] Demir U, Unal G. Patch-based image Inpainting with generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1803.07422, 2018. [43] Iizuka S, Simo-Serra E, Ishikawa H. Globally and locally consistent image completion. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2017, 36(4): Article No. 107 [44] Pathak D, Krähenbühl P, Donahue J, Darrell T, Efros A A. Context encoders: Feature learning by inpainting. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 2536−2544 [45] Zhao B, Wu X, Cheng Z Q, Liu H, Jie Z Q, Feng J S. Multi-view image generation from a single-view. arXiv: 1704.04886, 2017. [46] Sohn K, Lee H, Yan X C. Learning structured output representation using deep conditional generative models. In: Proceedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. 3483−3491 [47] Yi Z L, Zhang H, Tan P, Gong M L. DualGAN: Unsupervised dual learning for image-to-image translation. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2868−2876 [48] Zhou S C, Xiao T H, Yang Y, Feng D Q, He Q Y, He W R. GeneGAN: Learning object transfiguration and attribute subspace from unpaired data. arXiv: 1705.04932, 2017. [49] Wang X L, Gupta A. Generative image modeling using style and structure adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, the Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 318−335 [50] Ma S, Fu J L, Chen C W, Mei T. DA-GAN: Instance-level image translation by deep attention generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018. 5657−5666 [51] Liu M Y, Breuel T, Kautz J. Unsupervised image-to-image translation networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, CA, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 700−708 [52] Reed S, Akata Z, Yan X C, Logeswaran L, Schiele B, Lee H. Generative adversarial text to image synthesis. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York City, USA: ACM, 2016. 1060−1069 [53] Reed S E, Akata Z, Mohan S, Tenka S, Schiele B, Lee H. Learning what and where to draw. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain, 2016. 217−225 [54] Liang X D, Hu Z T, Zhang H, Gan C, Xing E P. Recurrent topic-transition GAN for visual paragraph generation. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 3382−3391 [55] Luc P, Couprie C, Chintala S, Verbeek J. Semantic segmentation using adversarial networks. arXiv: 1611.08408, 2016. [56] Souly N, Spampinato C, Shah M. Semi and weakly supervised semantic segmentation using generative adversarial network. arXiv: 1703.09695v1, 2017. [57] Liang X D, Zhang H, Xing E P. Generative semantic manipulation with contrasting GAN. arXiv: 1708.00315, 2017. [58] Liu Y F, Qin Z C, Wan T, Luo Z B. Auto-painter: Cartoon image generation from sketch by using conditional Wasserstein generative adversarial networks. Neurocomputing, 2018, 311: 78−87 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.05.045 [59] Koo S. Automatic colorization with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 212−217 [60] Suárez P L, Sappa A D, Vintimilla B X. Infrared image colorization based on a triplet DCGAN architecture. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 212−217 [61] Vondrick C, Torralba A. Generating the future with adversarial transformers. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2992−3000 [62] Vondrick C, Pirsiavash H, Torralba A. Generating videos with scene dynamics. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain, 2016. 613−621 [63] Liang X D, Lee L S, Dai W, Xing E P. Dual motion GAN for future-flow embedded video prediction. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 1762−1770 [64] Pan J T, Ferrer C C, McGuinness K, O'Connor N E, Torres J, Sayrol E, et al. Salgan: Visual saliency prediction with generativse adversarial networks. arXiv: 1701.01081, 2017. [65] Fernando T, Denman S, Sridharan S, Fookes C. Task specific visual saliency prediction with memory augmented conditional generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Lake Tahoe, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1539−1548 [66] Volkhonskiy D, Borisenko B, Burnaev E. Generative Adversarial Networks for Image Steganography. 2016. [67] Wu J J, Zhang C K, Xue T F, Freeman W T, Tenenbaum J B. Learning a probabilistic latent space of object shapes via 3D generative-adversarial modeling. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2016. 82−90 [68] Zhu J Y, Zhang Z T, Zhang C K, Wu J J, Torralba A, Tenenbaum J B. Visual object networks: Image generation with disentangled 3D representation. In: Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montréal, Canada: ACM, 2018. 118−129 [69] Pascual S, Bonafonte A, Serrà J. SEGAN: Speech enhancement generative adversarial network. In: Proceedings of the 18th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Stockholm, Sweden: ISCA, 2017. 3642−3646 [70] Mao X D, Li Q, Xie H R, Lau R Y K, Wang Z, Smolley A P. Least squares generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2813−2821 [71] Michelsanti D, Tan Z H. Conditional generative adversarial networks for speech enhancement and noise-robust speaker verification. In: Proceedings of the 18th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Stockholm, Sweden: ISCA, 2017. 2008−2012 [72] Dong H W, Hsiao W Y, Yang L C, Yang Y H. MuseGAN: Symbolic-domain music generation and accompaniment with multi-track sequential generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1709.06298v1, 2017. [73] Sriram A, Jun H, Gaur Y, Satheesh S. Robust speech recognition using generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Calgary, AB, Canada: IEEE, 2018. 5639−5643 [74] Shinohara Y. Adversarial multi-task learning of deep neural networks for robust speech recognition. In: Proceedings of the 17th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. San Francisco, CA, USA: ISCA, 2016. 2369−2372 [75] Cai W, Doshi A, Valle R. Attacking speaker recognition with deep generative models. arXiv: 1801.02384, 2018. [76] Gao Y, Singh R, Raj B. Voice impersonation using generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Calgary, Canada: IEEE, 2018. 2506−2510 [77] Ding W H, He L. MTGAN: Speaker verification through multitasking triplet generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 19th Annual Conference of the International Speech Communication Association. Hyderabad, India: ISCA, 2018. 3633−3637 [78] Juvela L, Bollepalli B, Wang X, Kameoka H, Airaksinen M, Yamagishi J, et al. Speech waveform synthesis from MFCC sequences with generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Calgary, AB, Canada: IEEE, 2018. 5679−5683 [79] Kannan A, Vinyals O. Adversarial evaluation of dialogue models. arXiv: 1701.08198, 2017. [80] Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le Q V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2014 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Quebec, Canada, 2014. 3104−3112 [81] Li J W, Monroe W, Shi T L, Jean S, Ritter A, Jurafsky D. Adversarial learning for neural dialogue generation. In: Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Copenhagen, Denmark: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017. 2157−2169 [82] Kusner M J, Hernández-Lobato J M. GANS for sequences of discrete elements with the gumbel-softmax distribution. arXiv: 1611.04051, 2016. [83] Zhang M, Liu Y, Luan H B, Sun M S. Adversarial training for unsupervised bilingual lexicon induction. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Vancouver, Canada: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017. 1959−1970 [84] Mikolov T, Le Q V, Sutskever I. Exploiting similarities among languages for machine translation. arXiv: 1309.4168, 2013. [85] Zhang Y, Gaddy D, Barzilay R, Jaakkola T. Ten pairs to tag-multilingual POS tagging via coarse mapping between embeddings. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Association for Computational Linguistics. San Diego California, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016. 1307−1317 [86] Liu P F, Qiu X P, Huang X J. Adversarial multi-task learning for text classification. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Vancouver, Canada: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017. 1−10 [87] Press O, Bar A, Bogin B, Berant J, Wolf L. Language generation with recurrent generative adversarial networks without pre-training. arXiv: 1706.01399, 2017. [88] Xu J J, Ren X C, Lin J Y, Sun X. DP-GAN: Diversity-promoting generative adversarial network for generating informative and diversified text. arXiv: 1802.01345, 2018. [89] Chen X L, Sun Y, Athiwaratkun B, Cardie C, Weinberger K. Adversarial deep averaging networks for cross-lingual sentiment classification. arXiv: 1606.01614, 2016. [90] Iyyer M, Manjunatha V, Boyd-Graber J, Daumé Ⅲ H. Deep unordered composition rivals syntactic methods for text classification. In: Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing of the Asian Federation of Natural Language Processing. Beijing, China: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2015. 1681−1691 [91] Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. arXiv: 1409.0473, 2014. [92] Yang Z, Chen W, Wang F, Xu B. Improving neural machine translation with conditional sequence generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of the 2018 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. New Orleans, Louisiana, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018. 1346−1355 [93] Yang Z, Chen W, Wang F, Xu B. Generative adversarial training for neural machine translation. Neurocomputing, 2018, 321: 146−155 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.09.006 [94] Wu L J, Xia Y C, Zhao L, Qin T, Lai J H, Liu T Y. Adversarial neural machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 10th Asian Conference on Machine Learning. Beijing, China: PMLR, 2018. 534−549 [95] Zhang Z R, Liu S J, Li M, Chen E H. Bidirectional generative adversarial networks for neural machine translation. In: Proceedings of the 22nd Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning. Brussels, Belgium: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018. 190−199 [96] Merel J, Tassa Y, TB D, Srinivasan S, Lemmon J, Wang Z Y, et al. Learning human behaviors from motion capture by adversarial imitation. arXiv: 1707.02201, 2017. [97] Chou C J, Chien J T, Chen H T. Self adversarial training for human pose estimation. arXiv: 1707.02439, 2017. [98] Sadoughi N, Busso C. Novel realizations of speech-driven head movements with generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Calgary, AB, Canada: IEEE, 2018. 6169−6173 [99] Hu W W, Tan Y. Generating adversarial malware examples for black-box attacks based on GAN. arXiv: 1702.05983, 2017. [100] Shrivastava A, Pfister T, Tuzel O, Susskind J, Wang W D, Webb R. Learning from simulated and unsupervised images through adversarial training. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2242−2251 [101] Sixt L, Wild B, Landgraf T. RenderGAN: Generating realistic labeled data. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 2018, 5: 66 doi: 10.3389/frobt.2018.00066 [102] Antoniou A, Storkey A, Edwards H. Data augmentation generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1711.04340, 2017. [103] Huang G, Liu Z, Van Der Maaten L, Weinberger K Q. Densely connected convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 2261−2269 [104] de Oliveira L, Paganini M, Nachman B. Learning particle physics by example: Location-aware generative adversarial networks for physics synthesis. Computing and Software for Big Science, 2017, 1(1): 4 doi: 10.1007/s41781-017-0004-6 [105] Quan T M, Nguyen-Duc T, Jeong W K. Compressed sensing MRI reconstruction using a generative adversarial network with a cyclic loss. arXiv: 1709.00753, 2017. [106] Dar S U H, Yurt M, Karacan L, Erdem A, Erdem E, Çukur T. Image synthesis in multi-contrast MRI with conditional generative adversarial networks. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2019, 38(10): 2375−2388 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2019.2901750 [107] Choi E, Biswal S, Malin B, Duke J, Stewart W F, Sun J M. Generating multi-label discrete patient records using generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1703.06490, 2017. [108] Son J, Park S J, Jung K H. Retinal vessel segmentation in fundoscopic images with generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1706.09318, 2017. [109] Wolterink J M, Leiner T, Isgum I. Blood vessel geometry synthesis using generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1804.04381, 2018. [110] Hitaj B, Ateniese G, Perez-Cruz F. Deep models under the GAN: Information leakage from collaborative deep learning. In: Proceedings of the 2017 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security. Dallas, TX, USA: ACM, 2017. 603−618 [111] 刘建伟, 孙正康, 罗雄麟. 域自适应学习研究进展. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(8): 1576−1600Liu Jian-Wei, Sun Zheng-Kang, Luo Xiong-Lin. Review and research development on domain adaptation learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(8): 1576−1600 [112] Bousmalis K, Silberman N, Dohan D, Erhan D, Krishnan D. Unsupervised pixel-level domain adaptation with generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, HI, USA: IEEE, 2017. 95−104 [113] Zhang Y, Barzilay R, Jaakkola T S. Aspect-augmented adversarial networks for domain adaptation. Transactions of the Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017, 5: 515−528 doi: 10.1162/tacl_a_00077 [114] Sankaranarayanan S, Balaji Y, Castillo C D, Chellappa R. Generate to adapt: Aligning domains using generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1704.01705, 2017. [115] Ghosh A, Bhattacharya B, Chowdhury S B R. Sad-GAN: Synthetic autonomous driving using generative adversarial networks. arXiv: 1611.08788, 2016. [116] Santana E, Hotz G. Learning a driving simulator. arXiv: 1608.01230, 2016. [117] Furlanello T, Zhao J P, Saxe A M, Itti L, Tjan B S. Active long term memory networks. arXiv: 1606.02355, 2016. [118] Kumar A, Irsoy O, Ondruska P, Iyyer M, Bradbury J, Gulrajani I, et al. Ask me anything: Dynamic memory networks for natural language processing. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on International Conference on Machine Learning. New York City, NY, USA: ACM, 2016. 1378−1387 [119] Kurach K, Lucic M, Zhai X H, Michalski M, Gelly S. A large-scale study on regularization and normalization in GANs. arXiv: 1807.04720, 2018. -




 下载:
下载: