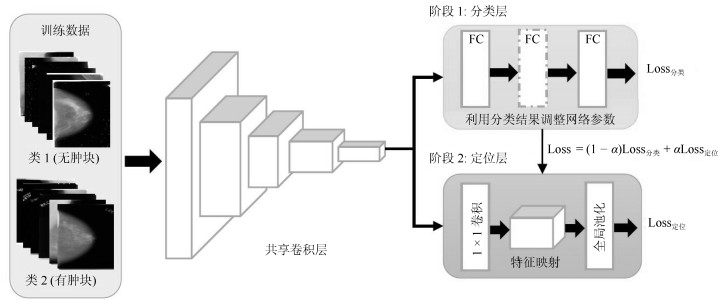
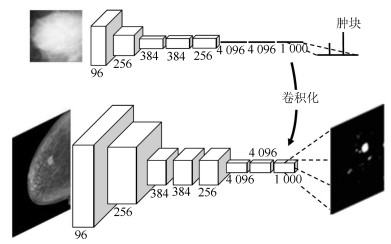
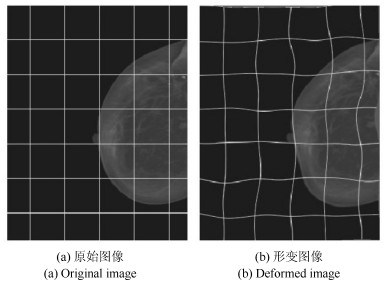
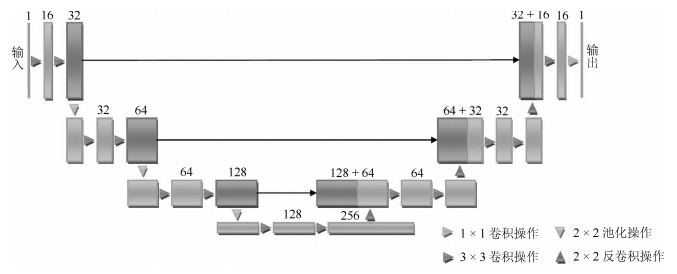
-
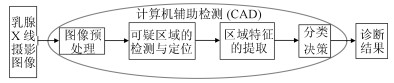
摘要: 早期筛查和及时治疗是控制乳腺癌死亡率最为有效的方法.乳腺X线摄影检查作为医学界公认的最有效的早期乳腺癌筛检工具, 可以很好地反映出乳腺存在的异常情况.在临床应用中, 乳腺癌的X线摄影直接征象为钙化和肿块, 对乳腺X线摄影中钙化点的检测技术已经相当的成熟, 但对肿块区域的检测和分类依旧是一项具有挑战性的任务. 因此, 本文对近几年提出的基于全乳腺X线摄影的肿块检测方法进行简要综述, 分别从基于传统的乳腺肿块检测与分割方法和基于深度学习的乳腺肿块检测方法进行介绍, 并讨论了乳腺X线摄影中肿块检测未来研究的发展趋势.
-
关键词:
- 乳腺X线摄影 /
- 乳腺肿块检测 /
- 计算机辅助检测和诊断 /
- 深度学习
Abstract: Early screening and timely treatment are the most effective ways to control the mortality of breast cancer. Mammography is recognized as the most effective early breast cancer screening tool in the medical field nowadays, and it can well reflect abnormalities in the breast. In clinical application, the direct signs of breast cancer in mammography are calcification and mass. The detection technique of calcification in mammography is quite mature, but the detection and classification of the breast mass is still a challenging task. Therefore, this paper briefly reviews the methods of mass detection based on full mammography in recent years. We introduce the mass detection methods based on traditional mass detection and segmentation methods and deep learning mass detection methods, respectively. Finally, we summarize the proposed mass detection methods, and we also discuss the development trend of future research on mass detection in mammography.-
Key words:
- Mammography /
- breast mass detection /
- computer aided diagnosis and detection /
- deep learning
1) 本文责任编委 黄庆明 -
表 1 基于乳腺X线摄影相关研究的综述论文简介
Table 1 The introduction of review papers based on mammography
综述文献 综述的主要内容 发表时间 Vyborny等[6] 回顾了早期基于乳腺X线摄影的CAD技术发展, 包括图像预处理、乳腺钙化检测、乳腺肿块检测以及乳腺异常状态的良恶性分类.文中从形态学、滤波、模板匹配等方面对乳腺肿块检测方法进行了介绍. 1994年 Cheng等[26] 对乳腺钙化CAD系统中图像增强、钙化检测与分割以及良恶性分类分别进行了介绍. 2003年 Cheng等[27] 对乳腺肿块CAD系统中图像增强、乳腺肿块检测与分割以及良恶性分类分别进行了介绍.文中从阈值分割、统计学方法、区域增长、聚类、边缘检测等具体算法对乳腺肿块的检测与分割进行详细介绍. 2006年 Rangayyan等[28] 从乳腺图像的对比度增强、乳腺钙化检测和分析、乳腺肿块检测和分析、双侧乳腺的不对称分析和乳腺结构扭曲检测5个方面对乳腺X线摄影CAD技术进行较为全面的综述. 文中着重对解决针状和星状病变的肿块检测问题的方法进行总结. 2007年 Elter等[8] 回顾了基于乳腺X线摄影的乳腺钙化和肿块的分割与分类技术.其中, 作者将乳腺肿块的检测与分割方法分为区域增长、轮廓、水平集和动态规划等算法. 2009年 Oliver等[29] 针对乳腺肿块检测与分割的研究进行综述, 分别从单视图和多视图两个角度进行概述.其中, 对基于单视图的乳腺肿块检测方法介绍分为无监督的检测方法(基于区域、轮廓和聚类的目标分割方法)和有监督的检测方法(基于模型的目标分割方法)两种, 对文献进行科学有效的归类. 2010年 He等[30] 总结了基于乳腺X线摄影的乳腺密度和乳腺实质组织自动分割方法, 并利用分割结果对乳腺密度进行分类, 从而进一步对患乳腺癌的风险进行评估.文中并未对于乳腺异常(如: 肿块或钙化等)分析方法进行介绍. 2015年 Hamidinekoo等[12] 对近几年提出的基于深度学习方法实现乳腺X线摄影中乳腺肿块和钙化分析以及乳腺组织病理学图像分析的研究进展进行综述.文中只简要介绍基于深度学习实现的乳腺肿块检测方法, 未进行详细介绍与方法归类. 2018年 表 2 基于传统的乳腺肿块检测与分割方法总结
Table 2 Summary of traditional methods for mass detection and segmentation in mammography
方法名称 解决问题 优点 缺点 基于图像增强 乳腺肿块呈现的形态各异, 直接提取图像的低层特征难以区分肿块与正常组织 可以提高肿块与乳腺正常组织对比度, 是提升乳腺肿块区域的检测与分割效果的关键 适用于具有一定显著性特征的乳腺肿块检测任务, 需与传统经典检测与分割算法相结合 基于阈值分割 经典的图像分割方法, 广泛应用于医学图像分析 适用于肿块、肿瘤性疾病特点; 计算简单; 运算效率高 只考虑像素本身的灰度值, 缺乏对空间特征的考虑 基于模板匹配 人工设计的检测模型泛化能力很有限, 对特征形态各异的肿块没有很好的鲁棒性特征表示 思路和实现方法相对简单, 不需要设计复杂的特征提取方案, 也不需要对乳腺组织进行细致分割 需要特征丰富的组织模板; 计算成本高、时间开销大 基于特定医学理论知识的形态学特征模型 有效利用乳腺肿块的相关临床观察特点和诊断经验, 提出对乳腺肿块形态特征假设 将医学知识和计算机技术有效结合, 更科学、更准确地提出目标病灶处理方案 模型设计通常具有高复杂性的多参数特点; 选择和优化模型中参数存在困难 组合分割 利用不同分割技术, 弥补各种分割方法自身局限性 结合多种特征可以更好地拟合乳腺肿块的特点 算法的复杂度往往很高, 还易出现过度检测的情况 表 3 基于深度学习的乳腺肿块检测方法总结
Table 3 Summary of deep learning methods for mass detection in mammography
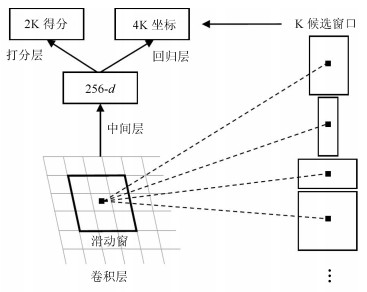
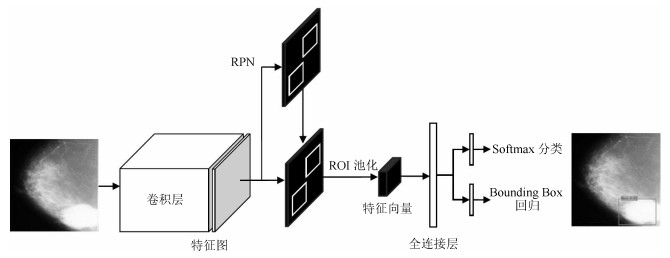
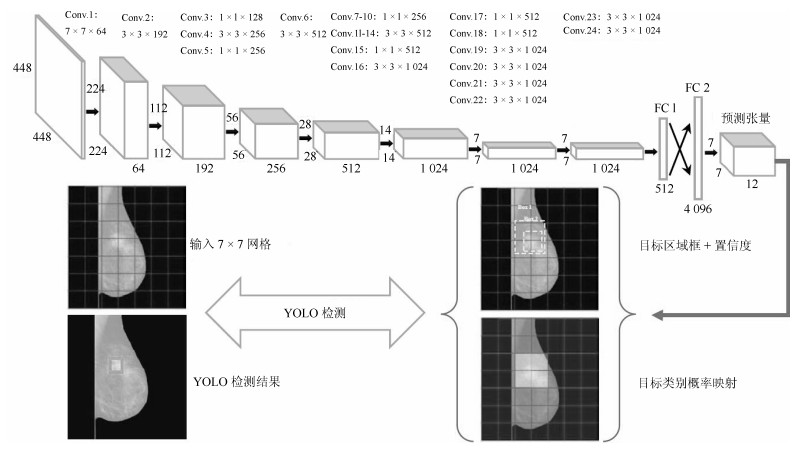
方法名称 解决问题 优点 缺点 基于候选框的乳腺肿块检测 传统的乳腺肿块检测与分割方法局限于浅层特征, 缺少鲁棒性表达 利用候选框方法提取ROI, 结合深度学习特征提取, 在目标检测精度上具有优势 忽视引入全局信息, 使易混淆的目标区分性较差; 检测速度慢 基于回归的乳腺肿块检测 基于候选框的乳腺肿块检测效率慢, 缺少图像全局信息, 不利于医学图像病灶的检测 将检测任务转化为回归问题, 加快了检测速度; 引入图像的全局信息, 降低假阳性检测比例 对乳腺X线摄影中小肿块目标不敏感, 易漏检 基于弱监督学习的乳腺肿块定位 医学图像需要专业医生标注肿块真实的ROI, 获取大量标注的医学数据存在困难 训练数据仅为图像中目标类别的注释信息, 不需要具有精准的ROI标注, 减少医学图像数据标注成本 网络结构设计、模型训练以及目标函数优化的难度增加 基于全卷积网络的乳腺肿块检测 对乳腺X线摄影数据进行下采样调整图像大小, 将不利于捕获小肿块特征, 易出现漏检 与输入数据尺寸大小无关, 适合处理全尺寸乳腺X线摄影数据, 更易检测出细小的肿块目标 存储开销大; 计算效率低下 表 4 常用乳腺X线摄影数据集及相关参数
Table 4 Popular mammography datasets and their relevant parameters
数据集名称 病例数量 图片数量 视角 异常种类 BI-RADS 标注方式 发布时间 DDSM[83] 2 605 10 420 MLO, CC 所有种类 有 ROI轮廓点 1999年 MIAS[84] 161 322 MLO 所有种类 无 ROI中心和半径 2003年 BancoWeb 320 1 473 MLO, CC 所有种类 有 只有部分数据 2010年 LAPIMO [85] 标注ROI INBreast[86] 115 410 MLO, CC 肿块、钙化、扭曲、不对称 有 ROI轮廓点 2011年 BCDR-FM[87] 1 010 3 703 MLO, CC 所有种类 有 医生观察到的病灶轮廓、异常和预计算图像描述符 2012年 BCDR-DM 724 3 612 表 5 乳腺X线摄影数据集上乳腺肿块检测方法的性能对比
Table 5 Comparison of state-of-the-art mass detection methods on mammography datasets
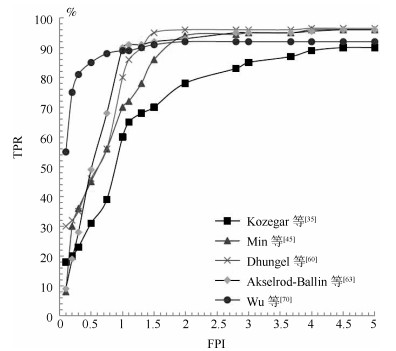
数据集 方法 传统/深度 TPR FPI 发表时间 DDSM Dhungel等[60] 深度 75 % 4.8 2015年 70 % 4 Al-masni等[72] 深度 99 % 0.22 2018年 Wu等[70] 深度 81 % 1.1 2018年 Castro等[79] 深度 60 % 1.864 2018年 Min等[45] 传统 77 % 3.97 2017年 Wang等[43] 传统 94 % 2.11 2018年 INBreast Dhungel等[60] 深度 96${\pm}$3 % 1.2 2015年 87${\pm}$14 % 0.8 Akselrod-Ballin等[63] 深度 93 % 0.56 2017年 Wu等[70] 深度 88 % 0.75 2018年 Castro等[79] 深度 80 % 0.912 2018年 Kozegar等[35] 传统 87 % 3.67 2013年 Min等[45] 传统 94 % 1.99 2017年 -
[1] Ferlay J, Shin H R, Bray F, Forman D, Mathers C, Parkin D M. Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. International Journal of Cancer, 2010, 127(12): 2893-2917 doi: 10.1002/ijc.25516 [2] Siegel R L, Miller K D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, 2017, 67(1): 7-30 doi: 10.3322/caac.21387 [3] Biswas S K, Mukherjee D P. Recognizing architectural distortion in mammogram: A multiscale texture modeling approach with GMM. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2011, 58(7): 2023-2030 doi: 10.1109/TBME.2011.2128870 [4] 邵昊阳, 张英涛, 鲜敏, 李致勋, 唐降龙. 基于多域先验的乳腺超声图像协同分割. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(4): 580-592 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150199Shao Hao-Yang, Zhang Ying-Tao, Xian Min, Li Zhi-Xun, Tang Xiang-Long. Breast ultrasound image co-segmentation by means of multiple-domain knowledge. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4): 580-592 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150199 [5] Elmore J G, Jackson S L, Abraham L, Miglioretti D L, Carney P A, Geller B M, Yankaskas B C, Kerlikowske K, Onega T, Rosenberg R D, Sickles E A, Buist D S M. Variability in interpretive performance at screening mammography and radiologists' characteristics associated with accuracy. Radiology, 2009, 253(3): 641-651 doi: 10.1148/radiol.2533082308 [6] Vyborny C J, Giger M L. Computer vision and artificial intelligence in mammography. American Journal of Roentgenology, 1994, 162(3): 699-708 doi: 10.2214/ajr.162.3.8109525 [7] 张胜君, 陈后金, 李艳凤, 姚畅, 程琳. 乳腺X线图像结构扭曲检测的研究. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(8): 1764-1772 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.01764Zhang Sheng-Jun, Chen Hou-Jin, Li Yan-Feng, Yao Chang, Cheng Lin. Detection of architectural distortion in mammograms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(8): 1764-1772 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.01764 [8] Elter M. Horsch A. CADx of mammographic masses and clustered microcalcifications: A review. Medical physics, 2009, 36(6Part1): 2052-2068 doi: 10.1118/1.3121511 [9] Bassett L W, Bunnell D H, Jahanshahi R, Gold R H, Arndt R D, Linsman J. Breast cancer detection: One versus two views. Radiology, 1987, 165(1): 95-97 doi: 10.1148/radiology.165.1.3628795 [10] Karssemeijer N, Te Brake G M. Detection of stellate distortions in mammograms. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1996, 15(5): 611-619 doi: 10.1109/42.538938 [11] 张海. 乳腺融合影像学. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2017. 2Zhang Hai. Multi-modality Fusion Imageology on Breast. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House, 2017. 2 [12] Hamidinekoo A, Denton E, Rampun A, Honnor K, Zwiggelaar R. Deep learning in mammography and breast histology, an overview and future trends. Medical Image Analysis, 2018, 47: 45-67 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2018.03.006 [13] Chu J, Min H, Liu L, Lu W. A novel computer aided breast mass detection scheme based on morphological enhancement and SLIC superpixel segmentation. Medical Physics, 2015, 42(7): 3859-3869 doi: 10.1118/1.4921612 [14] Dhungel N, Carneiro G, Bradley A P. Fully automated classification of mammograms using deep residual neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. Melbourne, VIC, Australia: IEEE, 2017. 310-314 [15] Moayedi F, Azimifar Z, Boostani R, Katebi S. Contourlet-based mammography mass classification using the SVM family. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2010, 40(4): 373-383 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2009.12.006 [16] Vikhe P S, Thool V R. Mass detection in mammographic images using wavelet processing and adaptive threshold technique. Journal of Medical Systems, 2016, 40(4): 82 doi: 10.1007/s10916-016-0435-3 [17] Akselrod-Ballin A, Karlinsky L, Alpert S, Hasoul S, Ben-Ari R, Barkan E. A Region based convolutional network for tumor detection and classification in breast mammography. In: Proceedings of the Deep Learning and Data Labeling for Medical Applications. Athens, Greece: Springer, Cham, 2016. 197-205 [18] Hamissi S, Merouani H F. Novel fully automated computer aided-detection of suspicious regions within mammograms. In: Proceedings of the Second International Conference on the Innovative Computing Technology. Casablanca, Morocco: IEEE, 2012. 153-157 [19] 李艳凤, 陈后金, 杨娜, 张胜君. 基于解剖学特征的乳腺X线图像胸肌分割. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(8): 1265-1272 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01265Li Yan-Feng, Chen Hou-Jin, Yang Na, Zhang Sheng-Jun. Pectoral muscle segmentation in mammograms based on anatomic features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(8): 1265-1272 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2013.01265 [20] Kom G, Tiedeu A, Kom M. Automated detection of masses in mammograms by local adaptive thresholding. Computers in Biology and Medicine, 2007, 37(1): 37-48 doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2005.12.004 [21] Casti P, Mencattini A, Salmeri M, Ancona A, Mangeri F, Pepe M L, Rangayyan R M. Contour-independent detection and classification of mammographic lesions. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2016, 25: 165-177 doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2015.11.010 [22] 史晓燕, 王伏生, 侯志超, 姜鸿南. 乳腺癌肿物大小的相关检查及早期乳腺癌的诊治. 中国药物与临床, 2016, 16(10): 1446-1450 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC201610021.htmShi Xiao-Yan, Wang Fu-Sheng, Hou Zhi-Chao, Jiang Hong-Nan. Related examination diagnosis of breast mass size and breast cancer early treatment. Chinese Remedies and Clinics, 2016, 16(10): 1446-1450 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YWLC201610021.htm [23] Gallego-Ortiz C, Martel A L. Improving the accuracy of computer-aided diagnosis for breast MR imaging by differentiating between mass and non-mass lesions. Radiology, 2016, 278(3): 679-688 doi: 10.1148/radiol.2015150241 [24] Lecun Y, Bengio Y, Hinton G. Deep learning. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444 doi: 10.1038/nature14539 [25] Kooi T, Litjens G, Van Ginneken B, Gubern-Mérida A, Sánchez C I, Mann R, Heeten A, Karssemeijera N. Large scale deep learning for computer aided detection of mammographic lesions. Medical Image Analysis, 2017, 35: 303-312 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2016.07.007 [26] Cheng H D, Cai X, Chen X, Hu L, Lou X. Computer-aided detection and classification of microcalcifications in mammograms: A survey. Pattern Recognition, 2003, 36(12): 2967-2991 doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(03)00192-4 [27] Cheng H D, Shi X J, Min R, Hu L M, Cai X P, Du H N. Approaches for automated detection and classification of masses in mammograms. Pattern Recognition, 2006, 39(4): 646-668 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2005.07.006 [28] Rangayyan R M, Ayres F J, Desautels J E L. A review of computer-aided diagnosis of breast cancer: Toward the detection of subtle signs. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2007, 344(3-4): 312-348 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2006.09.003 [29] Oliver A, Freixenet J, Martí J, Pérez E, Pont J, Denton E R E, Zwiggelaar R. A review of automatic mass detection and segmentation in mammographic images. Medical Image Analysis, 2010, 14(2): 87-110 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2009.12.005 [30] He W, Juette A, Denton E R E, Oliver A, Martí R, Zwiggelaar R. A review on automatic mammographic density and parenchymal segmentation. International Journal of Breast Cancer, 2015, 2015: 276217 http://pubmedcentralcanada.ca/pmcc/articles/PMC4481086/ [31] Campanini R, Dongiovanni D, Iampieri E, Lanconelli N, Masotti M, Palermo G, Riccardi A, Roffilli M. A novel featureless approach to mass detection in digital mammograms based on support vector machines. Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2004, 49(6): 961-975 doi: 10.1088/0031-9155/49/6/007 [32] Qian W, Li L, Clarke L P, Mao F, Clark R A. Adaptive CAD modules for mass detection in digital mammography. In: Proceedings of the 20th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 1998. 1013-1016 [33] Zheng Y. Breast cancer detection with gabor features from digital mammograms. Algorithms, 2010, 3(1): 44-62 doi: 10.3390/a3010044 [34] Lahmiri S, Boukadoum M. Hybrid discrete wavelet transform and gabor filter banks processing for features extraction from biomedical images. Journal of Medical Engineering, 2013, 2013: 104684 http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4782617/ [35] Kozegar E, Soryani M, Minaei B, Domingues I. Assessment of a novel mass detection algorithm in mammograms. Journal of Cancer Research and Therapeutics, 2013, 9(4): 592-600 doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.126453 [36] Hu K, Gao X, Li F. Detection of suspicious lesions by adaptive thresholding based on multiresolution analysis in mammograms. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2011, 60(2): 462-472 doi: 10.1109/TIM.2010.2051060 [37] Anitha J, Peter J D, Pandian S I A. A dual stage adaptive thresholding (DuSAT) for automatic mass detection in mammograms. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2017, 138: 93-104 doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2016.10.026 [38] Tourassi G D, Vargas-Voracek R, Catarious Jr. D M, Floyd Jr. C E. Computer-assisted detection of mammographic masses: A template matching scheme based on mutual information. Medical Physics, 2003, 30(8): 2123-2130 doi: 10.1118/1.1589494 [39] Mazurowski M A, Lo J Y, Harrawood B P, Tourassi G D. Mutual information-based template matching scheme for detection of breast masses: From mammography to digital breast tomosynthesis. Journal of Biomedical Informatics, 2011, 44(5): 815-823 doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2011.04.008 [40] Kobatake H, Murakami M, Takeo H, Nawano S. Computerized detection of malignant tumors on digital mammograms. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1999, 18(5): 369-378 doi: 10.1109/42.774164 [41] Eltonsy N H, Tourassi G D, Elmaghraby A S. A concentric morphology model for the detection of masses in mammography. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2007, 26(6): 880-889 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2007.895460 [42] Gao X, Wang Y, Li X, Tao D. On combining morphological component analysis and concentric morphology model for mammographic mass detection. IEEE Transactions on Information Technology in Biomedicine, 2010, 14(2): 266-273 doi: 10.1109/TITB.2009.2036167 [43] Wang H, Feng J, Bu Q, Liu F, Zhang M, Ren Y, Lv Y. Breast mass detection in digital mammogram based on gestalt psychology. Journal of Healthcare Engineering, 2018, 2018: 4015613 http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC5954872/ [44] Saidin N, Sakim H A M, Ngah U K, Shuaib I L. Computer aided detection of breast density and mass, and visualization of other breast anatomical regions on mammograms using graph cuts. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2013, 2013: 205384 http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/24106523 [45] Min H, Chandra S S, Dhungel N, Crozier S, Bradley A P. Multi-scale mass segmentation for mammograms via cascaded random forests. In: Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. Melbourne, VIC, Australia: IEEE, 2017. 113-117 [46] Makandar A, Halalli B. Combined segmentation technique for suspicious mass detection in mammography. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Trends in Automation, Communications and Computing Technology Bangalore, India: IEEE, 2015. 1-5 [47] He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, United states: IEEE, 2016. 770-778 [48] 吴帅, 徐勇, 赵东宁. 基于深度卷积网络的目标检测综述. 模式识别与人工智能, 2018, 31(4): 335-346 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MSSB201804006.htmWu Shuai, Xu Yong, Zhao Dong-Ning. Survey of object detection based on deep convolutional network. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 31(4): 335-346 https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MSSB201804006.htm [49] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, MA, United states: IEEE, 2015. 3431-3440 [50] Tian C, Xu Y, Fei L, Wang J, Wen J, Luo N. Enhanced CNN for image denoising. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2019, 4(1): 17-23 doi: 10.1049/trit.2018.1054 [51] Esteva A, Kuprel B, Novoa R A, Ko J, Swetter S M, Blau H M, Thrun S. Dermatologist-level classification of skin cancer with deep neural networks. Nature, 2017, 542(7639): 115-118 doi: 10.1038/nature21056 [52] 田娟秀, 刘国才, 谷珊珊, 鞠忠建, 刘劲光, 顾冬冬. 医学图像分析深度学习方法研究与挑战. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 401-424 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170153Tian Juan-Xiu, Liu Guo-Cai, Gu Shan-Shan, Ju Zhong-Jian, Liu Jin-Guang, Gu Dong-Dong. Deep learning in medical image analysis and its challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 401-424 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170153 [53] Lo B S-C, Freedman M T, Lin J-S, Mun S K. Automatic lung nodule detection using profile matching and back-propagation neural network techniques. Journal of Digital Imaging, 1993, 6(1): 48-54 doi: 10.1007/BF03168418 [54] Chan H P, Lo B S-C, Sahiner B, Lam K L, Helvire M A. Computer-aided detection of mammographic microcalcifications: Pattern recognition with an artificial neural network. Medical Physics, 1995, 22(10): 1555-1567 doi: 10.1118/1.597428 [55] Sahiner B, Chan H P, Petrick N, Wei D, Helvie M A, Adler D D, Goodsitt M M. Classification of mass and normal breast tissue: A convolution neural network classifier with spatial domain and texture images. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1996, 15(5): 598-610 doi: 10.1109/42.538937 [56] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, OH, United states: IEEE, 2014. 580-587 [57] Uijlings J R, Van De Sande K E, Gevers T, Smeulders A W. Selective search for object recognition. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2013, 104(2): 154-171 doi: 10.1007/s11263-013-0620-5 [58] Ren S, He K, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Proceedings of the 29th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, QC, Canada: NIPS, 2015. 91-99 [59] Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1440-1448 [60] Dhungel N, Carneiro G, Bradley A P. Automated mass detection in mammograms using cascaded deep learning and random forests. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Image Computing: Techniques and Applications. Adelaide, SA, Australia: IEEE, 2015. 1-8 [61] Dhungel N, Carneiro G, Bradley A P. A deep learning approach for the analysis of masses in mammograms with minimal user intervention. Medical Image Analysis, 2017, 37: 114-128 doi: 10.1016/j.media.2017.01.009 [62] Zhang Y, Sohn K, Villegas R, Pan G, Lee H. Improving object detection with deep convolutional networks via bayesian optimization and structured prediction. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, MA, United states: IEEE, 2015. 249-258 [63] Akselrod-Ballin A, Karlinsky L, Hazan A, Bakalo R, Horesh A-B, Shoshan Y, Barkan E. Deep learning for automatic detection of abnormal findings in breast mammography. In: Proceedings of the Deep Learning in Medical Image Analysis and Multimodal Learning for Clinical Decision Support. Quebec City, Canada: Springer, Cham, 2017. 321-329 [64] Ben-Ari R, Zlotnick A, Hashoul S. A weakly labeled approach for breast tissue segmentation and breast density estimation in digital mammography. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging. Prague, Czech Republic: IEEE, 2016. 722-725 [65] Ribli D, Horváth A, Unger Z, Pollner P, Csabai I. Detecting and classifying lesions in mammograms with deep learning. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): 4165 doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22437-z [66] Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L J, Li K, Li F-F. Imagenet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, FL, USA: IEEE, 2009. 248-255 [67] Simonyan K, Zisserman A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv preprint, 2014. arXiv: 1409.1556 [68] DREAM challenge. The DREAM challenge[Online], available: http://dreamchallenges.org, May 15, 2019 [69] Kisilev P, Sason E, Barkan E, Hashoul S. Medical image description using multi-task-loss CNN. In: Proceedings of the Deep Learning and Data Labeling for Medical Applications. Athens, Greece: Springer, 2016. 121-129 [70] Wu Y, Shi W, Cui L, Wang H, Bu Q, Feng J. Automatic mass detection from mammograms with region-based convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the Chinese Conference on Image and Graphics Technologies. Beijing, China: Springer, 2018. 442-450 [71] Szegedy C, Ioffe S, Vanhoucke V, Alemi A A. Inception-v4, inception-ResNet and the impact of residual connections on learning. In: Proceedings of the 31st AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, CA, United states: AAAI. 2017. 4278-4284 [72] Al-masni M A, Al-antari M A, Park J M, Gi G, Kim T Y, Rivera P, Valarezo E, Choi M T, Han S M, Kim T S. Simultaneous detection and classification of breast masses in digital mammograms via a deep learning YOLO-based CAD system. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2018, 157: 85-94 doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2018.01.017 [73] Al-masni M A, Al-antari M A, Park J M, Gi G, Kim T Y, Rivera P, Valarezo E, Han S M, Kim T S. Detection and classification of the breast abnormalities in digital mammograms via regional convolutional neural network. In: Proceedings of the 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. Jeju, South Korea: IEEE. 2017. 1230-1233 [74] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, United states: IEEE, 2016. 779-788 [75] Oquab M, Bottou L, Laptev I, Sivic J. Is object localization for free?-Weakly-supervised learning with convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, MA, United States: IEEE, 2015. 685-694 [76] Jie Z, Wei Y, Jin X, Feng J, Liu W. Deep self-taught learning for weakly supervised object localization. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, HI, United States: IEEE, 2017. 4294-4302 [77] Lin M, Chen Q, Yan S. Network in network. arXiv preprint, 2013. arXiv: 1312.4400 [78] Hwang S, Kim H E. Self-transfer learning for fully weakly supervised object localization. arXiv preprint, 2016. arXiv: 1602.01625 [79] Castro E, Cardoso J S, Pereira J C. Elastic deformations for data augmentation in breast cancer mass detection. In: Proceedings of the Biomedical and Health Informatics. Las Vegas, NV, United States: IEEE, 2018. 230-234 [80] Song X, Gao X, Ding Y, Wang Z. A handwritten Chinese characters recognition method based on sample set expansion and CNN. In: Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Systems and Informatics. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2016. 843-849 [81] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. U-net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015. 234-241 [82] De Moor T, Rodriguez-Ruiz A, Gubern Mérida A G, Mann R, Teuwen J. Automated soft tissue lesion detection and segmentation in digital mammography using a u-net deep learning network. In: Proceedings of the 14th International Workshop on Breast Imaging. Atlanta, GA, United States: SPIE, 2018. 10718 [83] Heath M, Bowyer K, Kopans D, Moore R, Kegelmeyer W P. The digital database for screening mammography. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Digital Mammography. Toronto, Canada, Medical Physics Publishing: 2001. 212-218 [84] Suckling J, Parker J, Dance D, Astley S, Hutt I, Boggis C, Ricketts I, Stamatakis E, Cerneaz N, Kok S, Taylor P, Betal D, Savage J. MIAS datasese. Mammographic Image Analysis Society (MIAS) database v1.21 [Online], available: https://www.repository.cam.ac.uk/handle/1810/250394, May 15, 2019 [85] Matheus B R N, Schiabel H. Online mammographic images database for development and comparison of CAD schemes. Journal of Digital Imaging, 2011, 24(3): 500-506 doi: 10.1007/s10278-010-9297-2 [86] Moreira I C, Amaral I, Domingues I, Cardoso A, Cardoso M J, Cardoso J S. INbreast: Toward a full-field digital mammographic database. Academic Radiology, 2012, 19(2): 236-248 doi: 10.1016/j.acra.2011.09.014 [87] Guevara Lopez M A, González Posada N, Moura D, Pollán R, Franco-Valiente J, Ortega C, Del Solar M, Díaz-Herrero G, Pereira M A Ramos I, Pinheiro Loureiro J, Cardoso Fernandes T, Ferreira M Araújo B. BCDR: A breast cancer digital repository. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Experimental Mechanics. Porto, Portugal: INEGI, 2012. The BCDR-Breast Cancer Digital Repository dataset[Online], available: https://bcdr.ceta-ciemat.es, May 15, 2019 [88] Orel S G, Kay N, Reynolds C, Sullivan D C. BI-RADS categorization as a predictor of malignancy. Radiology, 1999, 211(3): 845-850 doi: 10.1148/radiology.211.3.r99jn31845 [89] Carneiro G, Nascimento J, Bradley A P. Unregistered multiview mammogram analysis with pre-trained deep learning models. In: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2015. 652-660 -




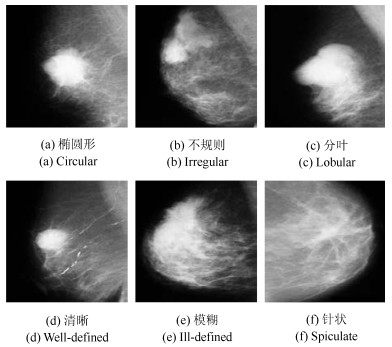
 下载:
下载: