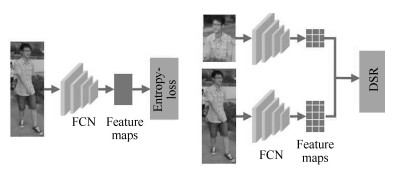
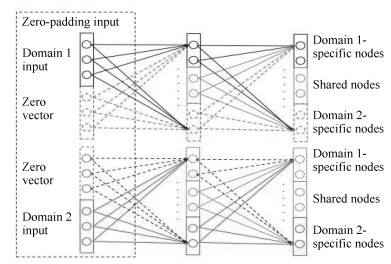
-
摘要: 行人重识别是计算机视觉领域近年来非常热的一个研究课题,可以被视为图像检索的一个子问题,其目标是给定一个监控行人图像检索跨设备下的该行人图像.传统的方法依赖手工特征,不能适应数据量很大的复杂环境.近年来随着深度学习的发展,大量基于深度学习的行人重识别方法被提出.本文先简单介绍了该问题的定义及传统方法的局限,并列举了一些适用于深度学习方法的行人重识别数据集.此外我们详细地总结了一些比较典型的基于深度学习的行人重识别方法,并比较了部分算法在Market1501数据集上的性能表现.最后我们对该问题未来的研究方向做了一个展望.Abstract: Person re-identification (ReID) is a popular research topic in computer vision. It aims to retrieve the given pedestrian image across the device, which can be regarded as a sub-problem of image retrieval. The traditional methods rely on hand-crafted features and can not adapt to the complicated environment with a large number of data. In recent years, with the development of deep learning, a large number of ReID methods based on deep learning have been proposed. This paper briefly introduces the definition of the problem and the limitations of the traditional methods, and then lists some popular databases suitable for deep learning. Moreover, we summarize some typical deep learning based methods in detail, and compare the performance of some algorithms on Market1501. Finally, we make a prospect for the future research direction of person ReID.
-
Key words:
- Person re-identification /
- deep learning /
- computer vision /
- convolutional neural networks
1) 本文责任编委 赖剑煌 -
表 1 典型行人重识别数据集
Table 1 Typical ReID datasets
数据集 发布时间 ID数 图片数 序列数 室内相机 室外相机 检测器 评估 ViPeR 2007 632 1 264 × 0 2 手动 CMC PRID2011 2011 934 24 541 400 0 2 手动 CMC CUHK03 2014 1 467 13 164 × 10 0 手动+ DPM CMC + mAP Market1501 2015 1 501 32 217 × 0 6 手动+ DPM CMC + mAP CUHK-SYSU 2016 8 432 99 809 × 0 0 DPM CMC + mAP MARS 2016 1 261 1 119 003 20 715 0 6 DPM + GMMCP CMC + mAP DukeMTMC-reID 2017 1 812 36 441 × 0 8 手动 CMC + mAP SYSU-MM01 2017 491 287 628 × 3 3 未知 CMC + mAP LPW 2018 2 731 590 000+ 7 694 0 11 手动+ DPM CMC + mAP MSMT17 2018 4 101 126 441 × 3 12 Faster RCNN CMC + mAP LVreID 即将发布 3 772 2 989 436 14 943 3 12 Faster RCNN CMC + mAP 表 2 基于GAN网络的方法比较
Table 2 The comparison of GAN based methods
算法 GAN CycleGAN PTGAN SPGAN PNGAN 基础 GAN CycleGAN CycleGAN CycleGAN InfoGAN 额外 标签平滑 标签平滑 前景分割 孪生网络 姿态估计 目标 数据增广 相机偏差 数据域偏差 数据域偏差 姿态偏差 表 3 基于深度学习的行人重识别方法总结比较
Table 3 Comparison of deep learning based ReID methods
表 4 典型行人重识别方法在Market1501上性能比较
Table 4 Comparison of the performance of typical ReID methods on Market1501
方法 rank-1 mAP 损失函数 基础网络 简单描述 发表 LOMO + XQDA[7] 43.8 22.2 传统方法基准 CVPR2015 LSTM Siamese[34] 61.6 35.3 对比损失 LSTM 图像分块+孪生网络 ECCV2016 Gate Reid[33] 65.9 39.6 对比损失 CNN 孪生网络+多尺度全局特征个 ECCV2016 Spindle Net[45] 76.9 - 分类损失 CNN 姿态对齐+ IDE CVPR2017 GAN[39] 78.1 56.2 分类损失 Resnet50 GAN + IDE +数据增广 ICCV2017 Part-Aligned[67] 81.0 63.4 三元组损失 GoogleNet 姿态对齐+度量学习 ICCV2017 Deep Transfer[25] 83.7 65.5 分类损失 GoogleNet ID损失+验证损失+迁移学习 Arxiv2016 TriHard[37] 84.9 69.1 三元组损失 Resnet50 难样本挖掘+三元组损失 Arxiv2017 DML[28] 87.7 68.8 分类损失 MobileNets[68] IDE +互学习 CVPR2018 CamStyle[65] 88.1 68.7 分类损失 Resnet50 CycleGAN + IDE +相机偏差 CVPR2018 GLAD [44] 89.9 73.9 分类损失 GoogleNet 姿态对齐+特征融合+重检索 ACMMM2017 AlignedReID[43] 91.8 79.8 三元组损失 Resnet50 难样本挖掘+图片切块+自动对齐+互学习 Arxiv2017 PNGAN[64] 95.5 89.9 分类损失 Resnet50 InfoGAN +姿态估计+ IDE +属性损失 Arxiv2017 SPGAN[62] 51.5 22.8 分类损失 Resnet50 CycleGAN + IDE +数据域偏差+无监督 CVPR2018 -
[1] Goodfellow I, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial nets. In:Proceedings of the 2014 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Montréal, Canada:MIT Press, 2014. 2672-2680 [2] Zajdel W, Zivkovic Z, Krose B J A. Keeping track of humans:have I seen this person before? In:Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Barcelona, Spain:IEEE, 2005. 2081-2086 [3] Zheng L, Yang Y, Hauptmann A G. Person re-identification:past, present and future, arXiv preprint arXiv:1610.02984, 2016. [4] Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In:Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, CA, USA:IEEE, 2005. 886-893 [5] Lowe D G. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In:Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Kerkyra, Greece:IEEE, 1999. 1150-1157 [6] Köstinger M, Hirzer M, Wohlhart P, Both P M, Bischof H. Large scale metric learning from equivalence constraints. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, RI, USA:IEEE, 2012. 2288-2295 [7] Liao S C, Hu Y, Zhu X Y, Li S Z. Person re-identification by local maximal occurrence representation and metric learning. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, MA, USA:IEEE, 2015. 2197-2206 [8] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Delving deep into rectifiers:surpassing human-level performance on ImageNet classification. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile:IEEE, 2015. 1026-1034 [9] Lu C C, Tang X O. Surpassing human-level face verification performance on LFW with Gaussian face. In:Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Austin, Texas, USA:AAAI, 2015. 3811-3819 [10] Gray D, Brennan S, Tao H. Evaluating appearance models for recognition, reacquisition, and tracking. In:Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Workshop on Performance Evaluation of Tracking and Surveillance (PETS). Rio de Janeiro:IEEE, 2007. 1-7 [11] Hirzer M, Beleznai C, Roth P M, Bischof H. Person re-identification by descriptive and discriminative classification. In:Proceedings of the 2011 Scandinavian Conference on Image Analysis. Berlin, Heidelberg:Springer, 2011. 91-102 [12] Li W, Zhao R, Xiao T, Wang X G. DeepReID:deep filter pairing neural network for person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, OH, USA:IEEE, 2014. 152-159 [13] Zheng L, Shen L Y, Tian L, Wang S J, Wang J D, Tian Q. Scalable person re-identification:a benchmark. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile:IEEE, 2015. 1116-1124 [14] Xiao T, Li S, Wang B C, Lin L, Wang X G. End-to-end deep learning for person search. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1604.01850, 2016. [15] Zheng L, Bie Z, Sun Y F, Wang J D, Su C, Wang S J, et al. Mars:a video benchmark for large-scale person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham:Springer, 2016. 868-884 [16] Ristani E, Solera F, Zou R, Cucchiara R, Tomasi C. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In:Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham:Springer, 2016. 17-35 [17] Wu A C, Zheng W S, Yu H X, Gong S G, Lai J H. RGB-infrared cross-modality person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy:IEEE, 2017. 5390-5399 [18] Song G, Leng B, Liu Y, Hetang C, Cai S F. Region-based quality estimation network for large-scale person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2018 Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence. New Orleans:AAAI, 2018. [19] Wei L H, Zhang S L, Gao W, Tian Q. Person transfer GAN to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. arXiv:1711.08565, 2018. [20] Li J N, Zhang S L, Wang J D, Gao W, Tian Q. LVreID:person re-identification with long sequence videos. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1712.07286, 2017. [21] Felzenszwalb P F, Girshick R B, McAllester D, Ramanan D. Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(9):1627-1645 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.167 [22] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN:towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In:Proceedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Montreal, Quebec, Canada:MIT Press, 2015. 91-99 [23] Dehghan A, Modiri Assari S, Shah M. GMMCP tracker:globally optimal generalized maximum multi clique problem for multiple object tracking. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, MA, USA:IEEE, 2015. 4091-4099 [24] Karanam S, Gou M R, Wu Z Y, Rates-Borras A, Camps O, Radke R J. A Systematic evaluation and benchmark for person re-identification:features, metrics, and datasets, arXiv preprint arXiv:1605.09653, 2016. [25] Geng M Y, Wang Y W, Xiang T, Tian Y H. Deep transfer learning for person re-identification. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1611.05244, 2016. [26] Lin Y T, Zheng L, Zheng Z D, Wu Y, Yang Y. Improving person re-identification by attribute and identity learning. arXiv preprint arXiv:1703.07220, 2017. [27] Matsukawa T, Suzuki E. Person re-identification using CNN features learned from combination of attributes. In:Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Cancun, Mexico:IEEE, 2016. 2428-2433 [28] Zhang Y, Xiang T, Hospedales T M, Lu H C. Deep mutual learning. arXiv:1706.00384, 2017. [29] Zheng L, Zhang H H, Sun S Y, Chandraker M, Yang Y, Tian Q. Person re-identification in the wild. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA:IEEE, 2017. 3346-3355 [30] Zheng Z D, Zheng L, Yang Y. Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy:IEEE, 2017. 3774-3782 [31] Zheng Z D, Zheng L, Yang Y. A discriminatively learned CNN embedding for person reidentification. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2018, 14(1):Article No. 13 [32] Shi H L, Yang Y, Zhu X Y, Liao S C, Lei Z, Zheng W S, et al. Embedding deep metric for person re-identification:a study against large variations. In:Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham:Springer, 2016. 732-748 [33] Varior R R, Haloi M, Wang G. Gated Siamese convolutional neural network architecture for human re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham:Springer, 2016. 791-808 [34] Varior R R, Shuai B, Lu J W, Xu D, Wang G. A Siamese long short-term memory architecture for human re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham:Springer, 2016. 135-153 [35] Wang Y C, Chen Z Z, Wu F, Wang G. Person re-identification with cascaded pairwise convolutions. In:Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Salt Lake City, Utah, USA:IEEE, 2018. 1470-1478 [36] Cheng D, Gong Y H, Zhou S P, Wang J J, Zheng N N. Person re-identification by multi-channel parts-based CNN with improved triplet loss function. In:Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, NV, USA:IEEE, 2016. 1335-1344 [37] Hermans A, Beyer L, Leibe B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1703.07737, 2017. [38] Liu H, Feng J S, Qi M B, Jiang J G, Yan S C. End-to-end comparative attention networks for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7):3492-3506 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2700762 [39] Ristani E, Tomasi C. Features for multi-target multi-camera tracking and re-identification. arXiv:1803.10859, 2018. [40] Chen W H, Chen X T, Zhang J G, Huang K Q. Beyond triplet loss:a deep quadruplet network for person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA:IEEE, 2017. 1320-1329 [41] Xiao Q Q, Luo H, Zhang C. Margin sample mining loss:a deep learning based method for person re-identification. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1710.00478, 2017. [42] Xiao Q Q, Cao K L, Chen H N, Peng F Y, Zhang C. Cross domain knowledge transfer for person re-identification. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1611.06026, 2016. [43] Zhang X, Luo H, Fan X, Xiang W L, Sun Y X, Xiao Q Q, et al. AlignedReID:surpassing human-level performance in person re-identification. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1711.08184, 2017. [44] Wei L, Zhang S, Yao H, Gao W, Tian Q. GLAD:global-local-alignment descriptor for scalable person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2018, 21(4):986-999 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dbnydxxb200703019 [45] Zhao H Y, Tian M Q, Sun S Y, Shao J, Yan J J, Yi S, et al. Spindle net:person re-identification with human body region guided feature decomposition and fusion. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA:IEEE, 2017. 907-915 [46] Zheng L, Huang Y J, Lu H C, Yang Y. Pose invariant embedding for deep person re-identification. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1701.07732, 2017. [47] Dai J, Zhang P P, Lu H C, Wang H Y. Video person re-identification by temporal residual learning. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1802.07918, 2018. [48] Li Y J, Zhuo L, Li J F, Zhang J, Liang X, Tian Q. Video-based person re-identification by deep feature guided pooling. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Honolulu, HI, USA:IEEE, 2017. 1454-1461 [49] Liu H, Jie Z, Jayashree K, et al. Video-based person re-identification with accumulative motion context. IEEE transactions on circuits and systems for video technology, 2017, 28(10):2788-2802 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fcf0184b7ea04fee35ca78c9e93626fe [50] Ma X L, Zhu X T, Gong S G, Xie X D, Hu J M, Lam K M, et al. Person re-identification by unsupervised video matching. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 65:197-210 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.11.018 [51] McLaughlin N, Martinez del Rincon J, Miller P. Recurrent convolutional network for video-based person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA:IEEE, 2016. 1325-1334 [52] Wang T Q, Gong S G, Zhu X T, Wang S J. Person re-identification by video ranking. In:Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham:Springer, 2014. 688-703 [53] Wang T Q, Gong S G, Zhu X T, Wang S J. Person re-identification by discriminative selection in video ranking. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(12):2501-2514 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2522418 [54] You J J, Wu A C, Li X, Zheng W S. Top-push video-based person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA:IEEE, 2016. 1345-1353 [55] Zhang D, Wu W, Cheng H, et al. Image-to-video person re-identification with temporally memorized similarity learning. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2017, 28(10):2622-2632 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e87c80639a2e57dd4da4d5479c6049ff [56] Zhang W, Ma B P, Liu K, Huang R. Video-based pedestrian re-identification by adaptive spatio-temporal appearance model. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(4):2042-2054 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2672440 [57] Zhao R, Ouyang W L, Wang X G. Person re-identification by saliency learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(2):356-370 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2544310 [58] Wu Y, Lin Y T, Dong X Y, Yan Y, Ouyang W L, Yang Y. Exploit the unknown gradually:one-shot video-based person re-identification by stepwise learning. In:Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, Utah, USA:IEEE, 2018. 5177-5186 [59] Zhu J Y, Park T, Isola P, Efros A A. Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy:IEEE, 2017. 2242-2251 [60] Yi Z L, Zhang H, Tan P, Gong M L. DualGAN:unsupervised dual learning for image-to-image translation. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy:IEEE, 2017. 2868-2876 [61] Kim T, Cha M, Kim H, Lee J K, Kim J. Learning to discover cross-domain relations with generative adversarial networks. arXiv:1703.05192, 2017. [62] Deng W J, Zheng L, Ye Q X, Kang G L, Yang Y, Jiao J B. Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re-identification. arXiv:1711.07027, 2018. [63] Huang Y, Xu J S, Wu Q, Zheng Z D, Zhang Z X, Zhang J. Multi-pseudo regularized label for generated data in person re-identification. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1801.06742, 2018. [64] Qian X L, Fu Y W, Xiang T, Wang W X, Qiu J, Wu Y, et al. Pose-normalized image generation for person re-identification. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1712.02225, 2018. [65] Zhong Z, Zheng L, Zheng Z D, Li S Z, Yang Y. Camera style adaptation for person re-identification. arXiv:1711.10295, 2018. [66] Chen X, Duan Y, Houthooft R, Schulman J, Sutskever I, Abbeel P. InfoGAN:interpretable representation learning by information maximizing generative adversarial nets. arXiv:1606.03657, 2016. [67] Zhao L M, Li X, Zhuang Y T, Wang J D. Deeply-learned part-aligned representations for person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy:IEEE, 2017. 3239-3248 [68] Howard A G, Zhu M L, Chen B, Kalenichenko D, Wang W J, Weyand T, et al. MobileNets:efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1704.04861, 2017. [69] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In:Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, Nevada, USA:IEEE, 2016. 770-778 [70] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, et al. Going deeper with convolutions. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, Massachusetts, USA:IEEE, 2015. 1-9 [71] Sarfraz M S, Schumann A, Eberle A, Stiefelhagen R. A pose-sensitive embedding for person re-identification with expanded cross neighborhood re-ranking. arXiv:1711.10378, 2018. [72] Jiao J N, Zheng W S, Wu A C, Zhu X T, Gong S G. Deep low-resolution person re-identification. In:Proceedings of the 2018 Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence. New Orleans:AAAI, 2018. [73] He L X, Liang J, Li H Q, Sun Z. Deep spatial feature reconstruction for partial person re-identification:alignment-free approach. arXiv:1801.00881, 2018. [74] Fan H H, Zheng L, Yang Y. Unsupervised person re-identification:clustering and fine-tuning. arXiv preprint, arXiv:1705.10444, 2017. [75] Zhong Z, Zheng L, Cao D L, Li S Z. Re-ranking person re-identification with k-reciprocal encoding. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, Hawaii, USA:IEEE, 2017. 3652-3661 [76] Liu H, Feng J S, Jie Z Q, Jayashree K, Zhao B, Qi M B, et al. Neural person search machines. In:Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy:IEEE, 2017. 493-501 -




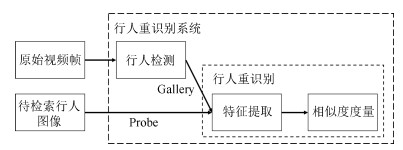
 下载:
下载: