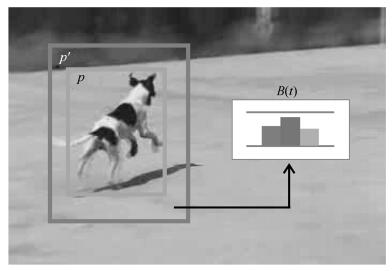
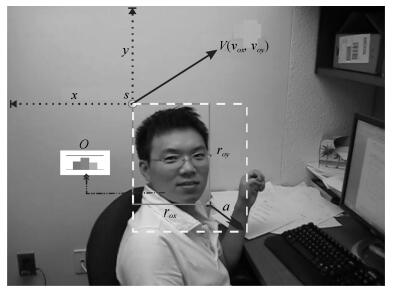
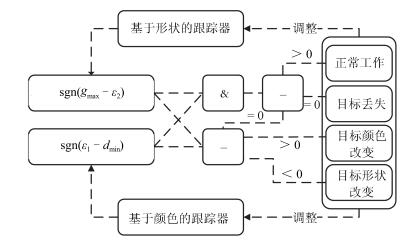
A Synthetic Target Tracking Algorithm Based on a New Color Distribution Model With Background Suppression
-
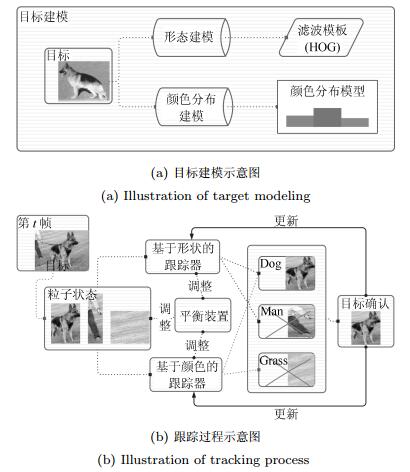
摘要: 传统的基于直方图分布的目标颜色模型, 由于跟踪过程的实时性要求其区间划分不宜过细, 因此易导致同一区间有差异的颜色难以区分; 此外, 还存在易受背景干扰的问题. 本文提出一种新的背景抑制目标颜色分布模型, 并在此基础上设计了一个合成式的目标跟踪算法. 新的颜色分布模型将一阶及二阶统计信息纳入模型, 并设计了基于人类视觉特性的权重计算方式, 能有效区分同一区间内的差异色且抑制背景颜色在模型中的比重; 算法基于该颜色模型构建目标的产生式模型, 并引入结合方向梯度直方图(Histogram of oriented gradient, HOG) 特征的相关滤波器对目标形状进行判别式建模, 同时将两个模型相互融合; 针对融合参数不易设计的难点, 分析并建立了一套定性原则, 用于判定模型各自的可信度并指导模型更新; 最终利用粒子群算法的搜索机制对候选目标的位置、尺度进行搜索, 其中适应值函数设计为两个跟踪器的融合结果. 实验结果表明, 本文算法在绝大多数情况下准确率较对比算法更优且能满足实时性要求.Abstract: The traditional histogram distribution based target color model easily fails to discern colors within a color interval that cannot be too small due to the real-time tracking requirement. Moreover, the model is prone to background interference. In this paper, a new target color distribution model with background suppression is proposed and synthetic target tracking algorithm based on the new model is presented. The new model takes the flrst- and second-order statistical information into account and makes use of human visual characteristics for weight computation. This approach allows to distinguish difierent colors within the same color interval and to suppress the proportion of background colors in the target model. The proposed algorithm builds up a target generative model on the basis of the new color model and flgures out a target shape discriminative model using the correlation fllter in terms of histogram of oriented gradient (HOG) features. These two models are then fused for target tracking. A set of qualitative principles for setting fusion parameters is given for evaluating the individual confldence of both models and for model updating. Finally, a particle swarm optimization algorithm is applied to identify the locations and scales of candidate targets using a fltness function determined by the tracking result of the fusion model. The experimental results show that the proposed algorithm in most cases outperforms the other algorithms in terms of accuracy while meeting the requirement of real time tracking.
-
Key words:
- Color model /
- background suppression /
- correlation fllter /
- model fusion /
- particle swarm optimization
1) 本文责任编委 杨健 -
表 1 3个算法的总体性能平均值
Table 1 Average global performance of three algorithms
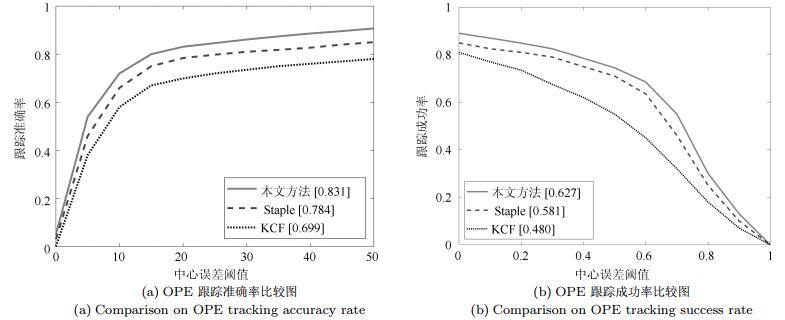
算法 CLE平均值 OS平均值 平均帧率(帧/s) 本文 14.82 0.6616 33.82 Staple 30 0.5108 26.42 KCF 59.67 0.4626 121.82 表 2 3个算法在18个视频的CLE值比较
Table 2 CLE values of three algorithms on 18 videos
序列名 序列特点 本文 Staple KCF BlurFace 1, 2 3 4 6 BlurOwl 1, 2, 3 9 62 70 Butterfly 4 35 39 130 Couple 2, 3 9 23 43 Diving 3, 4 35 83 136 DragonBaby 1 13 22 24 Football 6 6 10 9 Girl2 3, 4, 6 8 77 11 Human2 3, 5, 6 15 18 68 Human4 4, 5, 6 7 9 71 Human5 1, 3 8 30 132 Human6 1, 4, 6 7 7 20 Iceskater1 3, 4 38 93 40 Jogging 6 5 45 7 Jumping 1, 2 6 12 10 Singer1 3, 5 7 10 10 Skating1 3, 4, 5 18 47 13 Skating2 3, 4 30 33 37 表 3 3个算法在18个视频的OS指标比较
Table 3 OS values of three algorithms on 18 videos
序列名 本文 Staple KCF BlurFace 0.9029 0.8491 0.8567 BlurOwl 0.8082 0.4263 0.1458 Butterfly 0.4284 0.4040 0.1251 Couple 0.6693 0.5306 0.0674 Diving 0.3006 0.2445 0 DragonBaby 0.5863 0.5019 0.4336 Football 0.7317 0.5825 0.6068 Girl2 0.7515 0.1100 0.7002 Human2 0.7896 0.7322 0.6035 Human4 0.6606 0.6661 0.3389 Human5 0.7243 0.4862 0.1808 Human6 0.7835 0.8054 0.5969 Iceskater1 0.4493 0.1979 0.4054 Jogging 0.7373 0.1747 0.6131 Jumping 0.6841 0.2468 0.4596 Singer1 0.8253 0.6952 0.8169 Skating1 0.6910 0.4105 0.7030 Skating2 0.5231 0.4797 0.3890 -
[1] Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M H. Online object tracking: A benchmark. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 2411-2418 [2] Zhang K, Zhang L, Yang M H. Real-time compressive cracking. In: Proceedings of the 2012 European Conference on Computer Vision. Florence, Italy: Springer-Verlag, 2012. 864-877 [3] Hare S, Golodetz S, Saffari A, Vineet V, Cheng M M, Hicks S L, Torr P H S. Struck: Structured output tracking with kernels. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 23(5): 263-270 http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7360205/citations [4] Bolme D S, Beveridge J R, Draper B A, Lui Y M. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters. In: Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 2544-2550 [5] Henriques J F, Caseiro R, Martins P, Batista J. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583-596 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390 [6] Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Golodetz S, Miksik O, Torr P H S. Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 1401-1409 [7] 刘大千, 刘万军, 费博雯, 曲海成. 前景约束下的抗干扰匹配目标跟踪方法. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(6): 1139-1152 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160475Liu Da-Qian, Liu Wan-Jun, Fei Bo-Wen, Qu Hai-Cheng. A new method of anti-interference matching under foreground constraint for target tracking. Acta Automatic Sinica, 2018, 44(6): 1139-1152 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160475 [8] 张焕龙, 胡士强, 杨国胜. 基于外观模型学习的视频目标跟踪方法综述. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 52(1): 177-190 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JFYZ201501019.htm [9] Nummiaro K, Koller-Meier E, Gool L V. An adaptive color-based particle filter. Image and Vision Computing, 2003, 21(1): 99-110 doi: 10.1016/S0262-8856(02)00129-4 [10] Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P. Kernel-based object tracking. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(5): 564-575 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1195991 [11] Dalal N, Triggs B. Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2005. 886-893 [12] 胡扬, 张东波, 段琪. 目标鲁棒识别的抗旋转HDO局部特征描述. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(4): 665-673 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150837Hu Yang, Zhang Dong-Bo, Duan Qi. An improved rotation-invariant HDO local description for object recognition. Acta Automatic Sinica, 2017, 43(4): 665-673 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150837 [13] Jin J, Dundar A, Bates J, Farabet C, Culurciello E. Tracking with deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 47th Annual Conference on Information Sciences and Systems. Baltimore, USA: IEEE, 2013. 1-5 [14] Wang L, Liu T, Wang G, Chan K L, Yang Q X. Video tracking using learned hierarchical features. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(4): 1424-1435 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2403231 [15] 张慧, 王坤峰, 王飞跃. 深度学习在目标视觉检测中的应用进展与展望. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160822Zhang Hui, Wang Kun-Feng, Wang Fei-Yue. Advances and perspectives on applications of deep learning in visual object detection. Acta Automatic Sinica, 2017, 43(8): 1289-1305 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160822 [16] 管皓, 薛向阳, 安志勇, 深度学习在视频目标跟踪中的应用进展与展望, 自动化学报, 2016, 42(6): 834-847 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150705Guan Hao, Xue Xiang-Yang, An Zhi-Yong. Advances on application of deep learning for video object tracking. Acta Automatic Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 834-847 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150705 [17] Sun C, Wang D, Lu H C, Yang M H. Learning spatial-aware regressions for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8962-8970 [18] Possegger H, Mauthner T, Bischof H. In defense of color-based model-free tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 2113-2120 [19] Danelljan M, Khan F S, Felsberg M, Van de Weijer J. Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 1090-1097 [20] Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M H. Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834-1848 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226 [21] Comaniciu D, Ramesh V, Meer P. Real-time tracking of non-rigid objects using mean shift. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hilton Head Island, USA: IEEE, 2000. 2142-2149 [22] Mueller M, Smith N, Ghanem B. Context-aware correlation filter tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1387-1395 [23] Choi J, Chang H J, Yun S, Fischet J, Demiris Y, Choi J Y. Attentional correlation filter network for adaptive visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4828-4837 [24] Wang N, Zhou W G, Tian Q, Hong R C, Wang M, Li H Q. Multi-cue correlation filters for robust visual tracking. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4844-4853 [25] 陈志敏, 吴盘龙, 薄煜明, 田梦楚, 岳聪, 顾福飞. 基于自控蝙蝠算法智能优化粒子滤波的机动目标跟踪方法, 电子学报, 2018, 46(4): 886-894 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.04.017Chen Zhi-Min, Wu Pan-Long, Bo Yu-Ming, Tian Meng-Chu, Yue Cong, Gu Fu-Fei. Adaptive control bat algorithm intelligent optimization particle filter for maneuvering target tracking. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2018, 46(4): 886-894 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2018.04.017 [26] 刘畅, 赵巍, 刘鹏, 唐降龙, 目标跟踪中辅助目标的选择、跟踪与更新, 自动化学报, 2018, 44(7): 1195-1211 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160532Liu Chang, Zhao Wei, Liu Peng, Tang Xiang-Long. Auxiliary objects selecting, tracking and updating in target tracking. Acta Automatic Sinica, 2018, 44(7): 1195-1211 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c160532 -





 下载:
下载: