Registration Algorithm Based on Fuzzy Shape Context and Local Vector Similarity Constraint
-
摘要: 非刚性点集配准研究是模式识别领域的一项重要基础研究.本文在当前流行的非刚性点集配准算法的基础上提出了两个主要贡献: 1)模糊形状上下文(Fuzzy shape context, FSC)特征; 2)基于局部向量特征的局部空间向量相似性约束项.本文首先进行基于特征互补的对应关系评估, 在这一步骤中定义了模糊形状上下文特征, 然后基于模糊形状上下文特征差异和全局特征差异设计了特征互补的高斯混合模型.其次, 进行基于约束互补的空间变化更新.在这一步骤中, 定义了局部向量特征, 建立了局部空间向量相似性约束项.本文算法通过使用特征互补的高斯混合模型进行对应关系评估, 并将配准问题转化为可以用期望最大化(Expectation maximization, EM)算法解决的参数优化问题, 通过创建包含局部空间向量相似性约束项的能量方程优化了空间变换更新.本文首先测试了模糊形状上下文特征的检索率, 然后采用公开数据集测试了算法在点集配准与图像配准的性能.在与当前流行的十种算法的对比实验中, 本文算法均给出了精确的配准结果, 并在大部分实验中精度超过了当前流行算法.
-
关键词:
- 非刚性点集配准 /
- 高斯混合模型 /
- 模糊形状上下文特征 /
- 局部向量特征 /
- 局部空间向量相似性约束
Abstract: Non-rigid point set registration is an essential research in pattern recognition. Two main contributions are presented based on the current popular non-rigid point set registration algorithm in this paper: 1) Fuzzy shape context feature 2) Local spatial vector similarity constraints based on local vector feature. The correspondence of complementary of features is evaluated, firstly. At the same time, a fuzzy shape context (FSC) feature is defined and the Gaussian mixture model based on the fuzzy shape context distance and the global feature distance is designed. The spatial transformation of complementary of constraint is updated, secondly. Meanwhile, a local vector feature is defined and the local spatial vector similarity constraint based on local vector feature is built. The proposed algorithm estimates correspondence by using the Gaussian mixture model of complementary of feature. The proposed algorithm updates parameters of transformation by using the expectation maximization algorithm, and completes transformation updating by building energy function that has local spatial vector similarity constraints. Firstly, the retrieval rate of FSC is tested. The performance of point set registration and image registration of the proposed algorithm was tested by using public data sets, secondly. In the comparison experiments of currently popular 10 algorithms, accurate registration results of the proposed algorithm where acquired, and surpassed the popular algorithms in most of the registration precision.-
Key words:
- Non-rigid point set registration /
- Gaussian mixture model /
- fuzzy shape context feature /
- local vector feature /
- local spatial vector similarity constraint
1) 本文责任编委 白翔 -
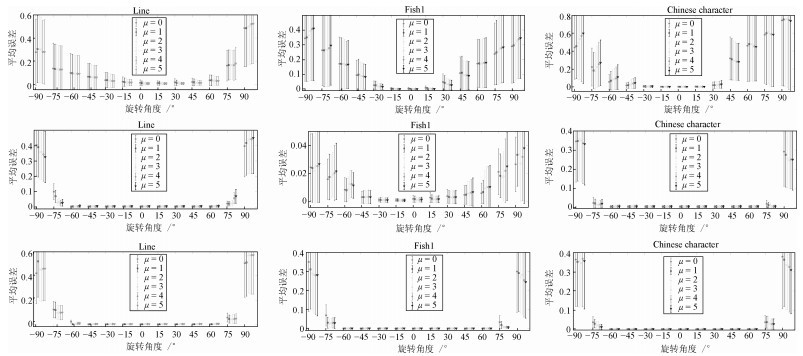
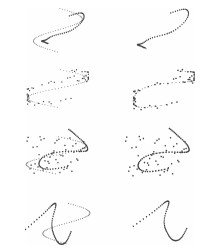
图 8 人造轮廓点集的三种不同配准模式下, 本文算法的六种参数取值的配准结果(其中第一列至第三列分别是点集Line[18]、Fish1[18]、Chinese character[18]的配准结果; 第一行至第三行分别是: 1)旋转变化加固定级别形变处理、2)旋转变化加固定级别噪音与形变处理、3)旋转变化加固定级别冗余点与形变处理)
Fig. 8 The results of point set registration using the six parameter settings under the three different registration patterns (The first to third columns are the registration results of the point set Line[18], Fish1[18], and Chinese character[18], respectively. The first to third columns are 1) rotations + fixed deformation, 2) rotations + fixed noise and deformation, and 3) rotations + fixed outliers and deformation, respectively)
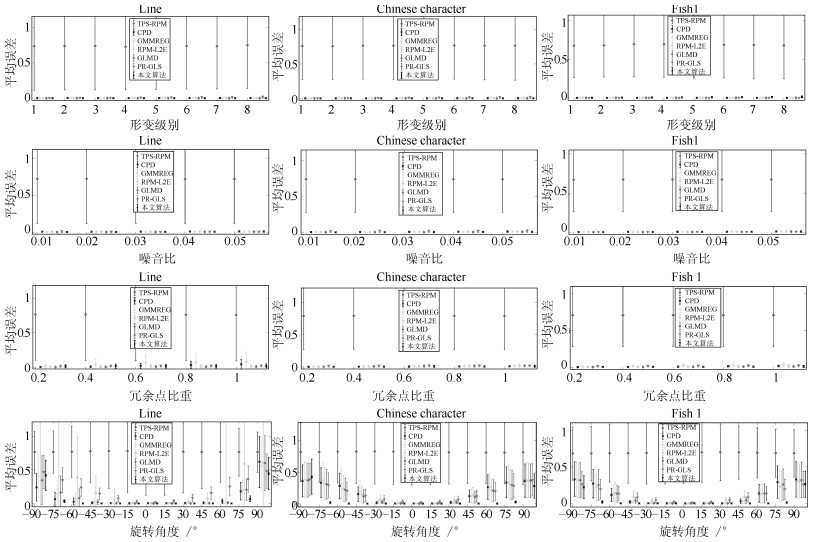
图 9 人造轮廓点集的四种不同配准模式下, 本文算法与TPS-RPM[18]、CPD[20−21]、GMMREG[22]、RPM-L2E[23], GLMD[24]、PR-GLS[26]的比较实验结果.第一行至第四行分别是1)形变变化、2)噪音变化+ 4级固定形变、3)冗余点变化+ 4级固定形变、4)旋转变化+ 4级固定形变
Fig. 9 Comparison results of the proposed method, TPS-RPM[18], CPD[20, 21], GMMREG[22], RPM-L2E[23], GLMD[24] and PR-GLS[26] under four different registration patterns. The first to fourth rows are 1) deformation, 2) noises + fixed 4 level deformation, 3) outliers + fixed 4 level deformation and 4) rotations + 4 level deformation, respectively
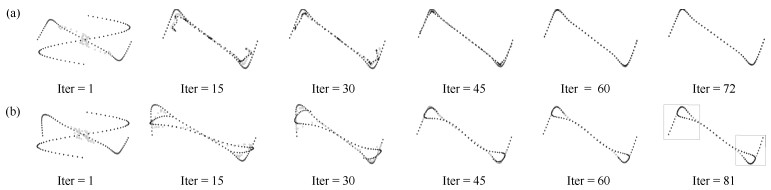
图 10 点集Line[18]的配准实例(第一列是配准前, 第二列是配准后.第一行至第四行分别是四种非刚性配准模式: 8级形变处理、4级噪音处理+ 4级形变处理、4级冗余点处理+ 4级形变处理、13级旋转处理+ 4级形变处理.)
Fig. 10 Registration example of Line[18] point set (The first to fourth rows are four different types of non-rigid registration patterns: 8 level deformation, 4 level noise + 4 level deformation, 4 level outliers + 4 level deformation, 13 level rotation + 4 level deformation.)
图 11 点集Fish1[18]的配准实例(第一列是配准前, 第二列是配准后.第一行至第四行分别是四种非刚性配准模式: 8级形变处理、4级噪音处理+ 4级形变处理、4级冗余点处理+ 4级形变处理、13级旋转处理+ 4级形变处理.)
Fig. 11 Registration example of Fish1[18] point set (The first to fourth rows are four different types of non-rigid registration patterns: 8 level deformation, 4 level noise + 4 level deformation, 4 level outliers + 4 level deformation, 13 level rotation + 4 level deformation.)
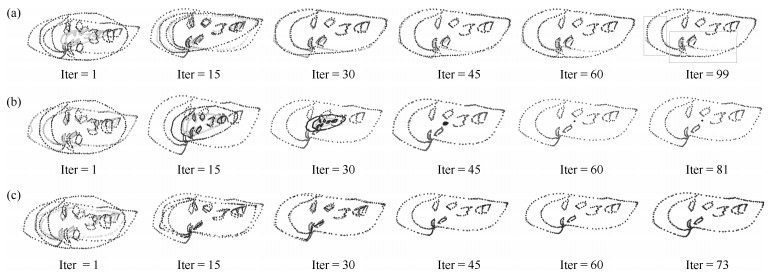
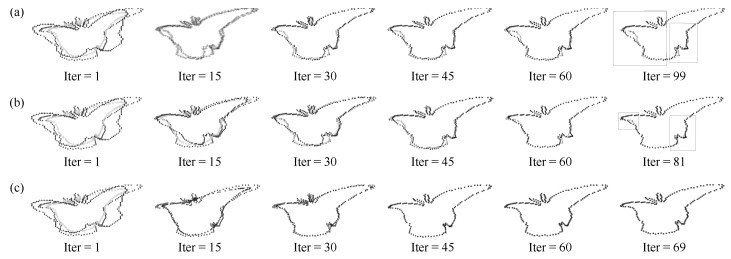
图 12 点集Chinese character[18]的配准实例(第一列是配准前, 第二列是配准后.第一行至第四行分别是四种非刚性配准模式: 8级形变处理、4级噪音处理+ 4级形变处理、4级冗余点处理+ 4级形变处理、13级旋转处理+ 4级形变处理.)
Fig. 12 Registration example of Chinese character[18] point set (The first to fourth rows are four different types of non-rigid registration patterns: 8 level deformation, 4 level noise + 4 level deformation, 4 level outliers + 4 level deformation, 13 level rotation + 4 level deformation.)
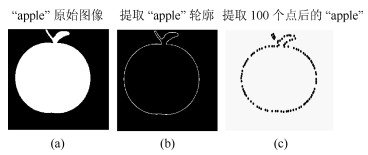
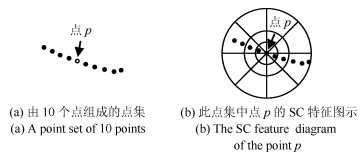
表 1 SC、Latecki等、Mokhtarian等和FSC的检索率
Table 1 Retrieval rate of shape context, Latecki et al., Mokhtarianet et al. and fuzzy shape
表 2 FGM[49]、Leordeanu等[45]、GLMD[24]、本文算法在汽车与摩托车真实图像中的平均配准
Table 2 Matching rates on cars and motorbikes for our method, FGM[49], Leordeanu et al.[45] and GLMD[24]
FGM Leordeanu等 GLMD 本文算法 80 % 80 % 93 % 97 % 表 3 CMU hotel和CMU house序列图像的平均配准率
Table 3 The average registration rate of CMU hotel and CMU house sequence images
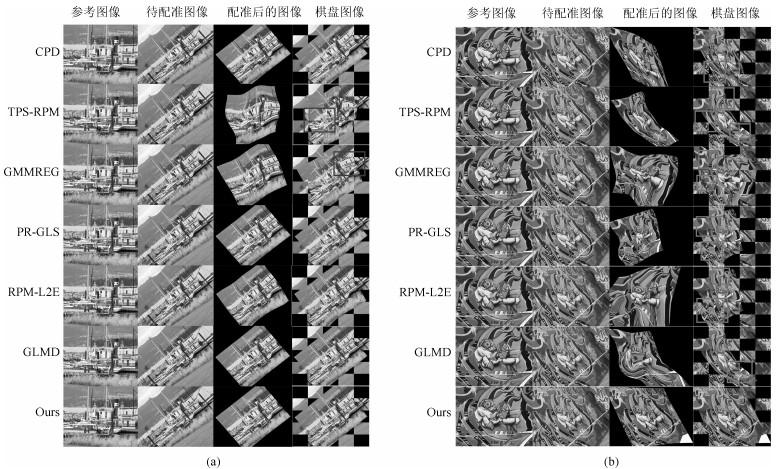
表 4 “boat”图像配准结果的误差展示
Table 4 Registration error of boat image
算法 RMSE MAE MEE CPD 1.4513 1.8151 0.2486 GMMREG 12.0899 4.2977 16.513 RPM-L2E 1.9918 0.8515 2.4792 TPS-RPM 42.3288 14.9059 53.4349 GLMD 1.6392 2.0807 0.495 PR-GLS 1.9291 0.8609 2.0807 Ours 1.0799 0.8523 0.134 表 5 “graf”图像配准结果的误差展示
Table 5 Registration error of graf image
算法 RMSE MAE MEE CPD 74.9729 94.3400 24.8849 GMMREG 41.6075 53.4556 17.0273 RPM-L2E 47.7672 64.1356 22.5171 TPS-RPM 97.4394 125.3333 21.2458 GLMD 38.2704 48.5050 17.4508 PR-GLS 75.0847 90.4167 46.5821 Ours 1.5312 1.7801 0.5905 -
[1] Yang J L, Li H D, Campbell D, Jia Y D. Go-ICP: a globally optimal solution to 3D ICP point-set registration. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(11): 2241-2254 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2513405 [2] Qu H B, Wang J Q, Li B, Yu M. Probabilistic model for robust affine and non-rigid point set matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(2): 371-384 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2545659 [3] Kolesov I, Lee J, Sharp G, Vela P, Tannenbaum A. A stochastic approach to diffeomorphic point set registration with landmark constraints. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(2): 238-251 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2448102 [4] Zeng Y, Wang C H, Gu X F, Samaras D, Paragios N. Higher-order graph principles towards non-rigid surface registration. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(12): 2416-2429 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2528240 [5] Serradell E, Pinheiro M A, Sznitman R, Kybic J, Moreno-Noguer F, Fua P. Non-rigid graph registration using active testing search. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 625-638 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2343235 [6] Tao W B, Sun K. Robust point sets matching by fusing feature and spatial information using nonuniform gaussian mixture models. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3754-3767 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2449559 [7] 薛鹏, 杨佩, 曹祝楼, 贾大宇, 董恩清.基于平衡系数的Active Demons非刚性配准算法.自动化学报, 2016, 42(9): 1389-1400 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150186Xue Peng, Yang Pei, Cao Zhu-Lou, Jia Da-Yu, Dong En-Qing. Active demons non-rigid registration algorithm based on balance coefficient. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(9): 1389-1400 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150186 [8] Dan T T, Yang Y, Xing L, Yang K, Zhang Y Y, Ong S H, et al. Multifeature energy optimization framework and parameter adjustment-based nonrigid point set registration. Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2018, 12(3): Article No. 035006 [9] Maron H, Dym N, Kezurer I, Kovalsky S, Lipman Y. Point registration via efficient convex relaxation. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2016, 35(4): Article No. 73 [10] Lipman Y, Yagev S, Poranne R, Jacobs D W, Basri R. Feature matching with bounded distortion. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2014, 33(3): Article No. 26 [11] Haring M T, Liv N, Zonnevylle A C, Narvaez A C, Voortman L M, Kruit P, et al. Automated sub-5 nm image registration in integrated correlative fluorescence and electron microscopy using cathodoluminescence pointers. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7: Article No. 43621 doi: 10.1038/srep43621 [12] Nguyen T M, Wu Q M J. Multiple kernel point set registration. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2016, 35(6): 1381-1394 doi: 10.1109/TMI.2015.2511063 [13] 陆雪松, 涂圣贤, 张素.一种面向医学图像非刚性配准的多维特征度量方法.自动化学报, 2016, 42(9): 1413-1420 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150608Lu Xue-Song, Tu Sheng-Xian, Zhang Su. A metric method using multidimensional features for nonrigid registration of medical images. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(9): 1413-1420 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150608 [14] Li H G, Ding W R, Cao X B, Liu C L. Image registration and fusion of visible and infrared integrated camera for medium-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle remote sensing. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(5): Article No. 441 doi: 10.3390/rs9050441 [15] Zhao M, An B W, Wu Y P, Van Luong H, Kaup A. Rfvtm: a recovery and filtering vertex trichotomy matching for remote sensing image registration. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(1): 375-391 doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2016.2606899 [16] Yang Z Q, Dan T T, Yang Y. Multi-temporal remote sensing image registration using deep convolutional features. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 38544-38555 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2853100 [17] Yang K, Pan A N, Yang Y, Zhang S, Ong S H, Tang H L. Remote sensing image registration using multiple image features. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(6): Article No. 581 doi: 10.3390/rs9060581 [18] Chui H L, Rangarajan A. A new point matching algorithm for non-rigid registration. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2003, 89(2-3): 114-141 doi: 10.1016/S1077-3142(03)00009-2 [19] Zheng Y F, Doermann D. Robust point matching for nonrigid shapes by preserving local neighborhood structures. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2006, 28(4): 643-649 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2006.81 [20] Schölkopf B, Platt J, Hofmann T. Non-rigid Point Set Registration: Coherent Point Drift. In: Proceedings of the 2007 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press, 2007. 1009-1016 [21] Myronenko A, Song X B. Point set registration: coherent point drift. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(12): 2262-2275 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.46 [22] Jian B, Vemuri B C. Robust point set registration using gaussian mixture models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2011, 33(8): 1633-1645 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.223 [23] Ma J Y, Zhao J, Tian J W, Tu Z W, Yuille A L. Robust estimation of nonrigid transformation for point set registration. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA: IEEE, 2013. 2147-2154 [24] Yang Y, Ong S H, Foong K W C. A robust global and local mixture distance based non-rigid point set registration. Pattern Recognition, 2015, 48(1): 156-173 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2014.06.017 [25] Wang G, Wang Z C, Chen Y F, Zhao W D. A robust non-rigid point set registration method based on asymmetric gaussian representation. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2015, 141: 67-80 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2015.05.014 [26] Ma J Y, Zhao J, Yuille A L. Non-rigid point set registration by preserving global and local structures. IEEE Transactions on image Processing, 2016, 25(1): 53-64 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2467217 [27] 汤昊林, 杨扬, 杨昆, 罗毅, 张雅莹, 张芳瑜.基于混合特征的非刚性点阵配准算法.自动化学报, 2016, 42(11): 1732-1743 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150618Tang Hao-Lin, Yang Yang, Yang Kun, Luo Yi, Zhang Ya-Ying, Zhang Fang-Yu. Non-rigid point set registration with mixed features. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(11): 1732-1743 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2016.c150618 [28] Rangarajan A, Chui H L, Bookstein F L. The softassign Procrustes matching algorithm. In: Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging. Poultney, Vermont, USA: Springer, 1997. 29-42 [29] Chui H L, Rambo J, Duncan J, Schultz R, Rangarajan A. Registration of cortical anatomical structures via robust 3D point matching. In: Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Information Processing in Medical Imaging. Visegrád, Hungary: Springer, 1999. 168-181 [30] Gold S, Rangarajan A, Lu C P, Pappu S, Mjolsness E. New algorithms for 2D and 3D point matching: pose estimation and correspondence. Pattern Recognition, 1998, 31(8): 1019-1031 doi: 10.1016/S0031-3203(98)80010-1 [31] Yuille A L. Generalized deformable models, statistical physics, and matching problems. Neural Computation, 1990, 2(1): 1-24 doi: 10.1162/neco.1990.2.1.1 [32] Belongie S, Malik J, Puzicha J. Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(4): 509-522 doi: 10.1109/34.993558 [33] Körtgen M, Park G J, Novotni M, Klein R. 3D shape matching with 3D shape contexts. In: Proceedings of the 7th Central European Seminar on Computer Graphics. Vienna, Austria: Vienna University of Technlonogy Press, 2003. 5-17 [34] Bookstein F L. Principal warps: thin-plate splines and the decomposition of deformations. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1989, 11(6): 567-585 doi: 10.1109/34.24792 [35] Yuille A L, Grzywacz N M. A mathematical analysis of the motion coherence theory. International Journal of Computer Vision, 1989, 3(2): 155-175 [36] Basu A, Harris I R, Hjort N L, Jones M C. Robust and efficient estimation by minimising a density power divergence. Biometrika, 1998, 85(3): 549-559 doi: 10.1093/biomet/85.3.549 [37] Scott D W. Parametric statistical modeling by minimum integrated square error. Technometrics, 2001, 43(3): 274-285 doi: 10.1198/004017001316975880 [38] Balakrishnan V K. Schaum's Outline of Graph Theory: Including Hundreds of Solved Problems. New York: McGraw-Hill Professional, 1997 [39] Sundar H, Silver D, Gagvani N, Dickinson S. Skeleton based shape matching and retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 2003 Shape Modeling International. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2003. 130-139 [40] Markovsky I, Usevich K. Low Rank Approximation. London: Springer, 2012. 116-132 [41] Ma J Y, Zhao J, Tian J W, Bai X, Tu Z W. Regularized vector field learning with sparse approximation for mismatch removal. Pattern Recognition, 2013, 46(12): 3519-3532 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2013.05.017 [42] Rifkin R, Yeo G, Poggio T. Regularized least-squares classification. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2007, 190(1): 93-104 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/rjxb201004002 [43] Carcassoni M, Hancock E R. Correspondence matching with modal clusters. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(12): 361-369 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=076d9c1fc18551ea15e1416ab99d32b8 [44] Caetano T S, McAuley J J, Cheng L, Le Q V, Smola A J. Learning graph matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 31(6): 1048-1058 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.28 [45] Leordeanu M, Sukthankar R, Hebert M. Unsupervised learning for graph matching. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2012, 96(1): 28-45 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=e952ad833ca3d54292160d0b26045a22 [46] Mikolajczyk K, Schmid C. A performance evaluation of local descriptors. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(10): 1615-1630 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.188 [47] Caetano T S, Cheng L, Le Q V, Smola A J. Learning graph matching. In Proceedings of the 11th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil: IEEE, 2007. 1-8 [48] Torresani L, Kolmogorov V, Rother C. A dual decomposition approach to feature correspondence. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(2): 259-271 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.105 [49] Zhou F, De la Torre F. Factorized graph matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(9): 1774-1789 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2501802 [50] Latecki L J, Lakamper R, Eckhardt T. Shape descriptors for non-rigid shapes with a single closed contour. In: Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hilton Head Island, USA: IEEE, 2000. 424-429 [51] Mokhtarian F, Abbasi S, Kittler J. Efficient and robust retrieval by shape content through curvature scale space. Image Databases and Multi-Media Search. River Edge, NJ: World Scientific Publishing Co Pte Ltd, 1997. 51-58 [52] Mokhtarian F, Mackworth A K. A theory of multiscale, curvature-based shape representation for planar curves. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1992, 14(8): 789-805 doi: 10.1109/34.149591 [53] Yang K, Pan A N, Yang Y, Zhang S, Ong S H. Remote sensing image registration using multiple image features. Remote Sensing, 2017, 9(6): 581-595 doi: 10.3390/rs9060581 -




 下载:
下载: