Type-2 Adaptive Fuzzy Modeling and Oxygen Excess Ratio Control for PEMFC Air Supply System
-
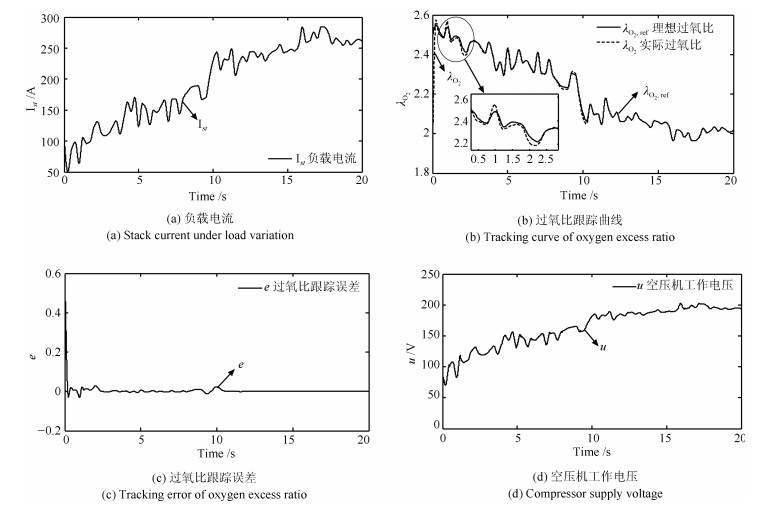
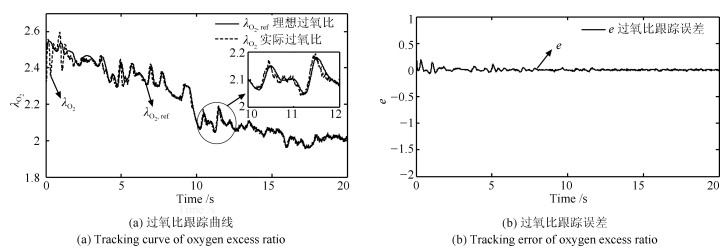
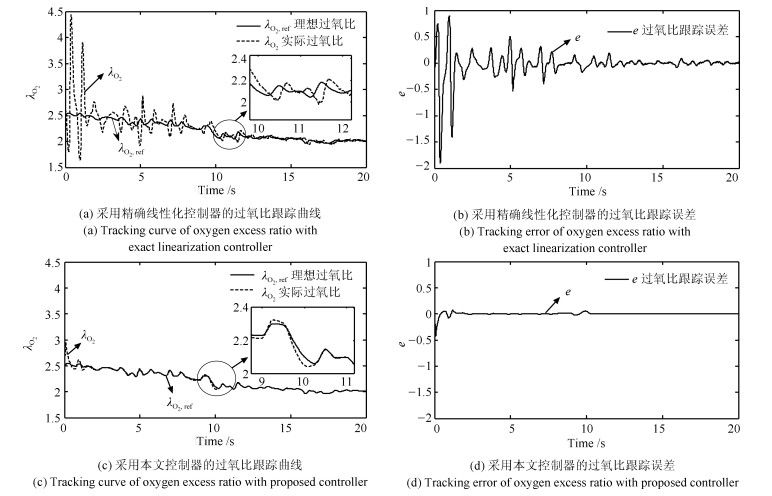
摘要: 质子交换膜燃料电池(Proton exchange membrane fuel cell,PEMFC)空气供给系统存在外部扰动和参数不确定等动态特性,难以实现精准建模和控制.本文结合精确线性化和二型模糊逻辑系统,提出一种自适应控制器实现PEMFC空气供给系统的建模与过氧比控制.该控制器不需要PEMFC空气供给系统模型结构和参数完全已知的条件,而是通过二型模糊逻辑系统在线逼近PEMFC空气供给系统中的未建模动态并从Lyapunov函数中导出自适应参数,从而保证系统收敛性与稳定性.通过稳定性分析证明了该控制器作用下系统跟踪误差的有界性,仿真实验进一步验证了该控制器的有效性与实用性.
-
关键词:
- 二型模糊逻辑系统 /
- 自适应控制 /
- 精确线性化 /
- Lyapunov稳定性 /
- 过氧比
Abstract: Proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) air supply system has the characteristics of external disturbances and uncertain parameters, which make it difficult to achieve accurate modeling and stability control. In this paper, an adaptive controller is proposed to control the oxygen excess ratio of PEMFC air supply system by using the type-2 fuzzy logic systems. The controller does not need the known conditions of PEMFC system model but approximates unmodeled dynamics in the system by the adaptive fuzzy system whose the parameter adjustment is derived based on the Lyapunov theory. The stability analysis shows that the system is stable under the control of the controller. Simulation results demonstrate the usefulness and effectiveness of our proposed control strategy.1) 本文责任编委 赵旭东 -
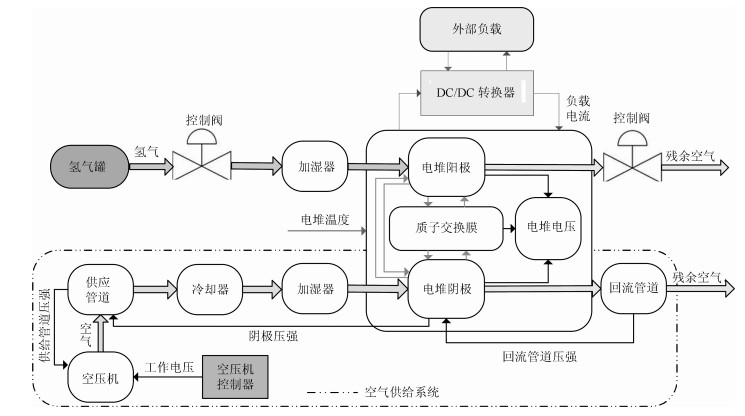
表 1 PEMFC空气供给系统状态变量
Table 1 State variables of PEMFC air supply system
状态变量 符号 单位 空压机转速 $x_{1}=\omega_{cp}$ rad/s 供给管道内空气压强 $x_{2}=P_{sm}$ Pa 供给管道内空气质量 $x_{3}=m_{sm}$ kg 阴极内氧气质量 $x_{4}=m_{{\rm O_{2}}}$ kg 阴极内氮气质量 $x_{5}=m_{{\rm N_{2}}}$ kg 回流管道内空气压强 $x_{6}=P_{rm}$ Pa A1 原公式和修正后公式的对比
A1 Comparison of original formulas and revised formulas
物理意义 原公式 修正后公式 注入阴极氧气流量 $\begin{array}{c}W_{{\rm O_{2}}, \rm in}(x_{2}, x_{3}, x_{4})=((x_{2}-B_{32}-B_{33}-\\x_{5}B_{34}-x_{4}B_{35})\times(x_{2}-x_{2}B_{6})^{-1}+ \\(x_{2}B_{36}-B_{37}-x_{5}B_{38}-\\x_{4}B_{39}))e(x_{2})k(x_{2})\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{c}W_{{\rm O_{2}}, \rm in}(x_{2}, x_{4}, x_{5})=((x_{2}B_{32}-B_{33}-\\x_{5}B_{34}-x_{4}B_{35})\times(x_{2}-x_{2}B_{6})^{-1}+\\(x_{2}B_{36}-K_{sm, \rm out}B_{37}-x_{5}K_{sm, \rm out}B_{38}-\\x_{4}K_{sm, \rm out}B_{39}))e(x_{2})k(x_{2})\end{array}$ 流出阴极空气流量 $\begin{array}{c}W_{ca, \rm out}(x_{4}, x_{5}, x_{6})=B_{47}+x_{5}B_{48}+\\x_{4}B_{49}-x_{6}B_{46} \end{array}$ $\begin{array}{c}W_{ca, \rm out}(x_{4}, x_{5}, x_{6})=B_{20}+x_{5}B_{21}+\\ x_{4}B_{22}-x_{6}B_{19}\end{array}$ 注入阴极氮气流量 $\begin{array}{c}W_{{\rm N_{2}}, \rm in}(x_{2}, x_{3}, x_{4})=((x_{2}B_{23}-B_{24}-\\x_{5}B_{25}-x_{4}B_{26})\times(x_{2}-x_{2}B_{6})^{-1}+\\(x_{2}B_{27}-B_{28}-x_{5}B_{29}-\\x_{4}B_{30}))e(x_{2})k(x_{2})\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{c}W_{{\rm N_{2}}, \rm in}(x_{2}, x_{4}, x_{5})=((x_{2}B_{23}-B_{24}-\\x_{5}B_{25}-x_{4}B_{26})\times(x_{2}-x_{2}B_{6})^{-1}+\\(x_{2}B_{27}-K_{sm, \rm out}B_{28}-x_{5}K_{sm, \rm out}B_{29}-\\x_{4}K_{sm, \rm out}B_{30}))e(x_{2})k(x_{2})\end{array}$ 流出阴极氧气流量 $\begin{array}{c} W_{{\rm O_{2}}, \rm out}(x_{4}, x_{5}, x_{6})=-x_{4}(B_{10}-x_{5}B_{11} +\\ x_{4}B_{12}-x_{6}B_{9})\times j(x_{4}, x_{5})x_{4 }^{-1} \times\\(j(x_{4}, x_{5})B_{40}-M_{N_{2}})^{-1} \times m(x_{4}, x_{5})\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{c}W_{{\rm O_{2}}, \rm out}(x_{4}, x_{5}, x_{6})=x_{4}(B_{10}+x_{5}B_{11} +\\x_{4}B_{12}-x_{6}B_{9}) \times j(x_{4}, x_{5})x_{4 }^{-1} \times\\(j(x_{4}, x_{5})B_{40}+M_{N_{2}})^{-1} \times m(x_{4}, x_{5})\end{array}$ 空压机驱动力矩 $\begin{array}{c}\tau_{cm}(u, x_{1})=\frac{\eta_{cm}K_{t}(u-K_{v}x_{1})}{R_{cm}J_{cp}}\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{c}\tau_{cm}(u, x_{1})=\frac{\eta_{cm}K_{t}(u-K_{v}x_{1})}{R_{cm}}\end{array} $ 空压机负载力矩 $\begin{array}{c}\tau_{cp}(x_{1}, x_{2})=\frac{C_{p}T_{atm}n(x_{2})W_{cp}(x_{1}, x_{2})}{\eta_{cp}J_{cp}x_{1}}\end{array}$ $\begin{array}{c}\tau_{cp}(x_{1}, x_{2})=\frac{C_{p}T_{atm}n(x_{2})W_{cp}(x_{1}, x_{2})}{\eta_{cp}x_{1}}\end{array}$ -
[1] Gruber J K, Bordons C, Oliva A. Nonlinear MPC for the airflow in a PEM fuel cell using a volterra series model. Control Engineering Practice, 2012, 20(2):205-217 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2011.10.014 [2] Ramos-Paja C A, Giral R, Martinez-Salamero L, Romano J, Romero A, Spagnuolo G. A PEM fuel-cell model featuring oxygen-excess-ratio estimation and power-electronics interaction. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 57(6):1914-1924 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2026363 [3] Hayati M R, Khayatian A, Dehghani M. Simultaneous optimization of net power and enhancement of PEM fuel cell lifespan using extremum seeking and sliding mode control techniques. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2016, 31(2):688-696 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c0aa01670a3a8ef4e16917ce0adf032a [4] Jayakumar A, Chalmers A, Lie T T. Review of prospects for adoption of fuel cell electric vehicles in New Zealand. IET Electrical Systems in Transportation, 2017, 7(4):259-266 doi: 10.1049/iet-est.2016.0078 [5] Pilloni A, Pisano A, Usai E. Observer-based air excess ratio control of a PEM fuel cell system via high-order sliding mode. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(8):5236-5246 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2412520 [6] Zhou D M, Gao F, Breaz E, Ravey A, Miraoui A, Zhang K. Dynamic phenomena coupling analysis and modeling of proton exchange membrane fuel cells. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2016, 31(4):1399-1412 doi: 10.1109/TEC.2016.2587162 [7] Pukrushpan J T, Stefanopoulou A G, Peng H. Control of Fuel Cell Power Systems:Principles, Modeling, Analysis and Feedback Design. London:Springer-Verlag, 2004. [8] Matraji I, Laghrouche S, Jemei S, Wack M. Robust control of the PEM fuel cell air-feed system via sub-optimal second order sliding mode. Applied Energy, 2013, 104:945-957 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2012.12.012 [9] Ki Na W, Gou B. Feedback-linearization-based nonlinear control for PEM fuel cells. IEEE Transactions on Energy Conversion, 2008, 23(1):179-190 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=f9367cef535a36276ef8eb9f13f31baf [10] Laghrouche S, Liu J X, Ahmed F S, Harmouche M, Wack M. Adaptive second-order sliding mode observer-based fault reconstruction for PEM fuel cell air-feed system. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 23(3):1098-1109 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2014.2361869 [11] Talj R J, Hissel D, Ortega R, Becherif M, Hilairet M. Experimental validation of a PEM fuel-cell reduced-order model and a moto-compressor higher order sliding-mode control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 57(6):1906-1913 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2029588 [12] Xu L F, Hu J M, Cheng S L, Fang C, Li J Q, Ouyang M G, et al. Robust control of internal states in a polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell air-feed system by considering actuator properties. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(18):13171-13191 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.03.191 [13] 莫红, 王飞跃, 肖志权, 陈茜.基于区间二型模糊集合的语言动力系统稳定性.自动化学报, 2011, 37(8):1018-1024 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17522.shtmlMo Hong, Wang Fei-Yue, Xiao Zhi-Quan, Chen Qian. Stabilities of linguistic dynamic systems based on interval type-2 fuzzy sets. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2011, 37(8):1018-1024 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17522.shtml [14] Saha A, Konar A, Nagar A K. EEG analysis for cognitive failure detection in driving using type-2 fuzzy classifiers. IEEE Transactions on Emerging Topics in Computational Intelligence, 2017, 1(6):437-453 doi: 10.1109/TETCI.2017.2750761 [15] Sun D, Liao Q F, Ren H L. Type-2 fuzzy modeling and control for bilateral teleoperation system with dynamic uncertainties and time-varying delays. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(1):447-459 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2719604 [16] Sarabakha A, Fu C H, Kayacan E, Kumbasar T. Type-2 fuzzy logic controllers made even simpler:from design to deployment for UAVs. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(6):5069-5077 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2767546 [17] Andreu-Perez J, Cao F, Hagras H, Yang G Z. A self-adaptive online brain-machine interface of a humanoid robot through a general type-2 fuzzy inference system. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(1):101-116 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2637403 [18] Wang L X. A new look at type-2 fuzzy sets and type-2 fuzzy logic systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(3):693-706 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2543746 [19] 王飞跃, 莫红.关于二型模糊集合的一些基本问题.自动化学报, 2017, 43(7):1114-1141 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19087.shtmlWang Fei-Yue, Mo Hong. Some fundamental issues on type-2 fuzzy sets. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(7):1114-1141 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract19087.shtml [20] Wang L X. Stable adaptive fuzzy control of nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 1993, 1(2):146-155 doi: 10.1109/91.227383 [21] 王永富, 王殿辉, 柴天佑.一个具有完备性和鲁棒性的模糊规则提取算法.自动化学报, 2010, 36(9):1337-1342 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17330.shtmlWang Yong-Fu, Wang Dian-Hui, Chai Tian-You. Extraction of fuzzy rules with completeness and robustness. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2010, 36(9):1337-1342 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract17330.shtml [22] Wang Y F, Wang D H, Chai T Y. Extraction and adaptation of fuzzy rules for friction modeling and control compensation. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2011, 19(4):682-693 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2011.2134104 [23] Wu T S, Karkoub M, Wang H W, Chen H S, Chen T H. Robust tracking control of MIMO underactuated nonlinear systems with dead-zone band and delayed uncertainty using an adaptive fuzzy control. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(4):905-918 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2586970 [24] Cervantes J, Yu W, Salazar S, Chairez I. Takagi-Sugeno dynamic neuro-fuzzy controller of uncertain nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2017, 25(6):1601-1615 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2016.2612697 [25] Zhang X Y, Xu Z S, Su C Y, Li Z, Li X M, Xiong C H, et al. Fuzzy approximator based adaptive dynamic surface control for unknown time delay nonlinear systems with input asymmetric hysteresis nonlinearities. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2017, 47(8):2218-2232 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2016.2641926 [26] Mendel J M. On KM algorithms for solving type-2 fuzzy set problems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2013, 21(3):426-446 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2012.2227488 [27] Liang Q L, Mendel J M. MPEG VBR video traffic modeling and classification using fuzzy technique. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2001, 9(1):183-193 doi: 10.1109/91.917124 [28] Mendel J M, John R I B. Type-2 fuzzy sets made simple. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2002, 10(2):117-127 doi: 10.1109/91.995115 [29] Mendel J M, John R I, Liu F L. Interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems made simple. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2006, 14(6):808-821 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2006.879986 [30] Mo H, Wang F Y, Zhou M, Li R M, Xiao Z Q. Footprint of uncertainty for type-2 fuzzy sets. Information Sciences, 2014, 272:96-110 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.02.092 -




 下载:
下载: