Abnormal Condition Identiflcation and Self-Healing Control Scheme for the Electro-Fused Magnesia Smelting Process
-
摘要:
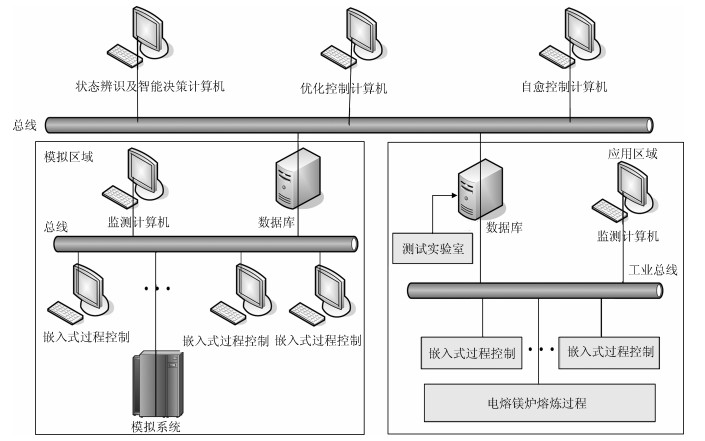
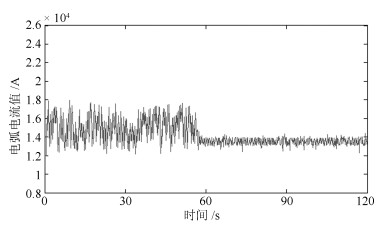
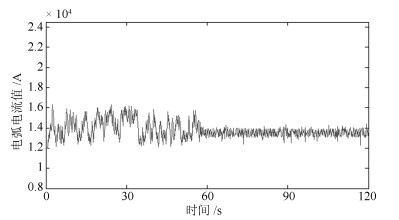
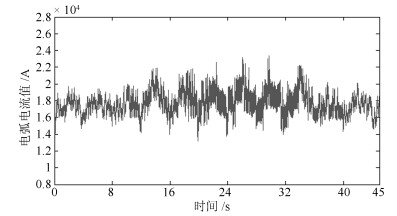
本文提出了基于多源信息融合的电熔镁炉异常工况识别及自愈控制方法.通过分析与三种异常相关的专家知识及操作经验, 本文提取了与异常工况相关的多源信息.通过融合多源信息, 建立了用于异常工况识别的贝叶斯网络模型.根据异常工况的识别结果, 利用剩余生命时间与控制变量调整量间的关系获得自愈控制措施.仿真结果表明提出的方法能够实现异常工况识别, 并且能够区分严重程度, 制定相应的自愈控制方案, 获得比现有方法更好的性能.
Abstract:In this paper, the abnormal condition identification and self-healing scheme is proposed based on the multi-source information fusion. By analyzing the expert knowledge and the experience of operators related with the abnormities, the related multi-source characteristics are extracted. The Bayesian networks are established to identify the abnormities by fusing the multi-source information. Based on the identification results, the self-healing control scheme can be obtained by the relationship between the remaining lifetime and the adjustment of control variables. The simulation results show that the proposed method is effective to identify the abnormal conditions and distinguish the abnormal degree. The corresponding self-healing control scheme can be made to remove the abnormal conditions. The proposed method owns the better performance than the existing research results.
-
Key words:
- Electro-fused magnesium furnace /
- multi-source information fusion /
- abnormal condition identification /
- Bayesian network /
- self-healing control
1) 本文责任编委 付俊 -
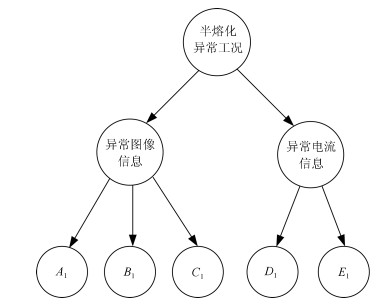
表 1 半熔化异常工况的典型事件
Table 1 The typical scenarios for the semimolten condition
事件编号 $A_1$ $B_1$ $C_1$ $D_1$ $E_1$ 1 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 3 1 3 1 1 1 2 2 4 1 1 1 2 3 5 2 2 2 2 3 6 2 2 2 2 4 7 3 3 3 2 3 8 3 3 3 2 4 表 2 过加热异常工况的典型事件
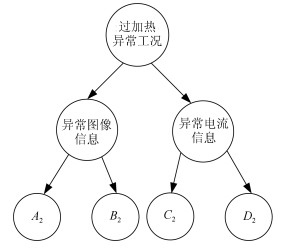
Table 2 The typical scenarios for the overheating condition
事件编号 $A_2$ $B_2$ $C_2$ $D_2$ 1 1 1 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 3 1 1 3 1 4 1 1 3 2 5 1 1 1 3 6 1 1 1 4 7 2 2 1 3 8 2 2 1 4 9 3 3 1 3 10 3 3 1 4 表 3 排气异常工况的典型事件
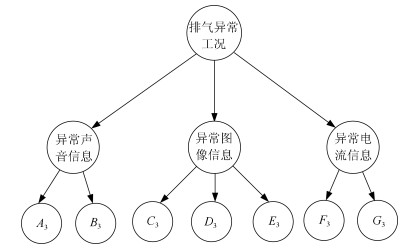
Table 3 The typical scenarios for the abnormal exhausting condition
事件编号 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 $A_3$ 1 2 2 3 3 3 3 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 $B_3$ 1 2 3 2 3 3 2 3 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 $C_3$ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 $D_3$ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 $E_3$ 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 3 3 3 3 2 2 2 2 2 $F_3$ 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 3 3 2 3 2 3 2 2 3 3 $G_3$ 1 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2 4 3 3 4 2 3 4 3 4 表 7 半熔化异常工况识别结果对比
Table 7 The identification results comparison for the semimolten condition
证据事件编号 3 4 5 6 7 8 正常 0.2654 0.2449 0.0009 0.0009 0.0002 0.0001 轻微异常 0.6032 0.3379 0.4639 0.1827 0.182 0.0438 中度异常 0.1073 0.2949 0.4565 0.6371 0.3401 0.2904 严重异常 0.0241 0.1222 0.0787 0.1793 0.4776 0.6656 表 8 过加热异常工况识别结果对比
Table 8 The identification results comparison for the overheating condition
证据事件编号 5 6 7 8 9 10 正常 0.13 0.1134 0.001 0.0008 0.0003 0.0002 轻微异常 0.475 0.37 0.5233 0.3935 0.2676 0.1698 中度异常 0.2931 0.3617 0.3347 0.3988 0.3274 0.3291 严重异常 0.1019 0.1548 0.141 0.2069 0.4047 0.5009 表 9 排气异常工况识别结果对比
Table 9 The identification results comparison for the abnormal exhausting condition
事件编号 1 2~5 6~8 9~18 本文方法辨识结果 1 2 3 4 传统方法辨识结果 1 1 1 4 -
[1] 张亚军, 柴天佑, 杨杰.一类非线性离散时间动态系统的交替辨识算法及应用.自动化学报, 2017, 43(1): 101-113 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150759Zhang Ya-Jun, Chai Tian-You, Yang Jie. Alternating identification algorithm and its application to a class of nonlinear discrete-time dynamical systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(1): 101-113 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2017.c150759 [2] Yang J, Chai T. Data-driven demand forecasting method for fused magnesium furnaces. In: Proceedings of the 12th World Congress on Intelligent Control and Automation. Guilin, China: IEEE, 2016. 2015-2022 [3] Wu Z, Wu Y, Chai T, Sun J. Data-driven abnormal condition identification and self-healing control system for fused magnesium furnace. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2015, 62(3): 1703-1715 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6880336/ [4] 吴志伟, 柴天佑, 吴永建.电熔镁砂产品单吨能耗混合预报模型.自动化学报, 2014, 39(12): 2002-2011 http://localhost:8080/article/id/18239Wu Zhi-Wei, Chai Tian-You, Wu Yong-Jian. A hybrid prediction model of energy consumption per ton for fused magnesia. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 39(12): 2002-2011 http://localhost:8080/article/id/18239 [5] Wu Z, Chai T, Sun J. Intelligent operational feedback control for fused magnesium furnace. In: Proceedings of the 19th World Congress The International Federation of Automatic Control. Cape Town, South Africa: IFAC, 2014. 8516-8521 [6] Ma W, Zhu S. Intelligent control algorithm of electric-fused magnesia furnace based on neural network. Unifying Electrical Engineering and Electronics Engineering. Springer, 2014. 1877-1886 [7] 孔维健, 柴天佑, 丁进良, 吴志伟.镁砂熔炼过程全厂电能分配实时多目标优化方法研究.自动化学报, 2014, 40(1): 51-61 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.00051Kong Wei-Jian, Chai Tian-You, Ding Jin-Liang, Wu Zhi-Wei. A real-time multiobjective electric energy allocation optimization approach for the smelting process of magnesia. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(1): 51-61 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.00051 [8] 吴志伟, 方正, 柴天佑, 张新海, 王超.电熔镁炉嵌入式专用控制器及其控制方法研究.仪器仪表学报, 2012, 33(6): 1261-1267 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YQXB201206009.htmWu Zhi-Wei, Fang Zheng, Chai Tian-You, Zhang Xin-Hai, Wang Chao. Research on special embedded controller and its control method for fused magnesium furnace. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2012, 33(6): 1261-1267 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-YQXB201206009.htm [9] 吴志伟, 柴天佑, 付俊, 闫占伟.电熔镁炉熔炼过程的智能设定值控制.控制与决策, 2011, 26(9): 1417-1420 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KZYC201109027.htmWu Zhi-Wei, Chai Tian-You, Fu Jun, Yan Zhan-Wei. Intelligent setpoints control of smelting process of fused magnesium furnace. Control and Decision, 2011, 26(9): 1417-1420 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-KZYC201109027.htm [10] Wu Y, Wu Z, Dong B, Zhang L, Chai T. The hybrid intelligent control for the fused magnesia production. In: Proceedings of joint 48th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control and 28th Chinese Control Conference. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2009. 3294-3299 [11] Dong B, Zhang L, Wu Y, Feng J, Chai T. The fuzzy control research on electrodes of electrical-fused magnesia furnace. In: Proceedings of Control and Decision Conference Chinese. Yantai, China: IEEE, 2008. 216-220 [12] 佟玉鹏, 张雄, 张化光.交流三相电熔镁炉的最佳运行分析.控制工程, 2007, 14(2): 205-208 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JZDF200702026.htmTong Yu-Peng, Zhang Xiong, Zhang Hua-Guang. Analysis of optimal operation about purifying magnesium oxide with three-phase AC electric smelting furnace. Control Engineering of China, 2007, 14(2): 205-208 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JZDF200702026.htm [13] Zhao C, Gao F. Fault subspace selection approach combined with analysis of relative changes for reconstruction modeling and multifault diagnosis. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2016, 24(3): 928-939 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7295568 [14] Zhao C, Gao F. Critical-to-fault-degradation variable analysis and direction extraction for online fault prognostic. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2017, 25(3): 842-854 https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?tp=&arnumber=7491337 [15] Qin Y, Zhao C, Gao F. An intelligent non-optimality self-recovery method based on reinforcement learning with small data in big data era. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2018, 176: 89-100 http://repository.ust.hk/ir/Record/1783.1-90416 [16] Zhang Y, Zhang P. Optimization of nonlinear process based on sequential extreme learning machine. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(20): 4702-4710 [17] Zhang Y, Ma C. Fault diagnosis of nonlinear processes using multiscale KPCA and multiscale KPLS. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011, 66(1): 64-72 [18] Zhang Y, Fan Y, Zhang P. Combining kernel partial least-squares modeling and iterative learning control for the batch-to-batch optimization of constrained nonlinear processes. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2010, 49(16): 7470-7477 doi: 10.1021/ie1004702 [19] 郑文博, 王坤峰, 王飞跃.基于贝叶斯生成对抗网络的背景消减算法.自动化学报, 2018, 44(5): 878-890 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170562Zheng Wen-Bo, Wang Kun-Feng, Wang Fei-Yue. Background subtraction algorithm with Bayesian generative adversarial networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(5): 878-890 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170562 [20] Li H, Wang F, Li H. A safe control scheme under the abnormity for the thickening process of gold hydrometallurgy based on Bayesian network. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 119: 10-19 [21] Liu Z, Liu Y, Cai B, Zheng C. An approach for developing diagnostic Bayesian network based on operation procedures. Expert Systems with Applications, 2015, 42(4): 1917-1926 [22] Diallo T M L, Henry S, Ouzrout Y. Bayesian network building for diagnosis in industrial domain based on expert knowledge and unitary traceability data. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2015, 48(3): 2411-2416 [23] Bhandari J, Abbassi R, Garaniya V, Khan F. Risk analysis of deepwater drilling operations using Bayesian network. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2015, 38: 11-23 [24] Sutrisnowati R A, Bae H, Park J. Bayesian network learning for port-logistics process knowledge discovery. International Journal of Industrial Engineering, 2014, 21(3): 141-152 [25] Bouejla A, Chaze X, Guarnieri F, Napoli A. A Bayesian network to manage risks of maritime piracy against offshore oil fields. Safety Science, 2014, 68: 222-230 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925753514000952 [26] Chen L, Arzaghi E, Abaei M M, Garaniya V, Abbassi R. Condition monitoring of subsea pipelines considering stress observation and structural deterioration. Journal of Loss Prevention in the Process Industries, 2018, 51: 178-185 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S095042301730863X [27] Lakehal A, Tachi F. Bayesian duval triangle method for fault prediction and assessment of oil immersed transformers. Measurement and Control, 2017, 50(4): 103-109 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0aa00a4eb0e4239c3932b41514b363f6 [28] Elmasry M, Hawari A, Zayed T. Defect based deterioration model for sewer pipelines using Bayesian belief networks. Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering, 2017, 44(9): 675-690 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=ec7e1e52d2579ae8cc420b06cf3a1e3b [29] Fu Y, Wang Z, Wang Z, Wang N, Wang X. Splattering suppression for three-phase AC electric arc furnace in fused magnesia production based on acoustic signal. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(6): 4772-4780 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=90ac12fb31232d2b0cc9bf0b334f3c35 [30] Li H, Wang F, Li H. Abnormal condition identification and safe control scheme for the electro-fused magnesia smelting process. ISA Transactions, 2018, 76: 178-187 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0cb72e4c6637e5700e3140a10c1b8e09 -




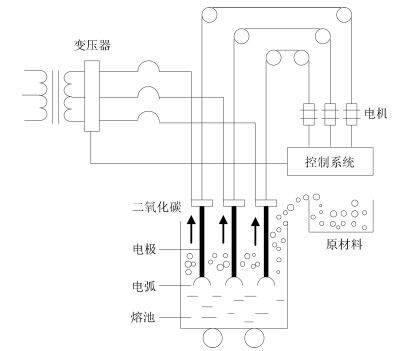
 下载:
下载: