-
摘要: 图实现(Graph realization)问题研究基于节点间全部或部分距离关系测量, 在$d$维空间中计算图的顶点坐标, 使得在所实现图中各节点之间实现距离与测量距离尽可能一致.图实现问题是一个典型的优化问题, 在传感器网络定位、蛋白质结构重建、数据可视化、社交网络分析、机器人同步定位与构图等领域有着广泛应用.图实现的研究同图刚性理论有着紧密的联系, 图的刚性与全局刚性决定图的可实现性.在可实现图中, 现有工作提出几类典型的代表性图实现算法, 包括: 1)基于三边测距类方法; 2)求解距离方程类方法; 3)基于全局优化类方法; 4)基于模块拼合类方法.本文对图实现的刚性理论, 四类图实现算法的设计思想、适用条件、算法流程等进行综述分析, 通过实验对算法进行准确性、计算复杂度、可靠性等方面的比较和分析.Abstract: The graph realization problem is to calculate vertex coordinates in d-dimensional space based on all or parts of distance measurements between the vertexes, so that the Euclidean distance between any two neighboring nodes in the realized graph is consistent with the measured distance. The graph realization problem is widely used in the fields of sensor network location, protein structure reconstruction, social network analysis and robot simultaneous localization and mapping. Graph realization is closely related to rigidity theory. The rigidity and global rigidity properties determine the realizability of the graph. A series of algorithms were presented to address the graph realization problem, including: 1) trilateration-based algorithm, 2) distance equation based, 3) global optimization based, and 4) module embedding based methods. This paper introduces the representative algorithms in details with their design ideas, applicable conditions. In particular, in sensor network localization applications, we conduct a series of experiments to compare and analyze these algorithms in terms of accuracy, computational complexity and robustness.
-
Key words:
- Graph realization /
- network localization /
- optimization /
- component stitching /
- survey /
- rigidity /
- global rigidity
1) 本文责任编委 段书凯 -
表 1 算法分类表
Table 1 Algorithm classification
方法类型 算法 算法特点 三边测量类方法 Trilateration 基于几何性质, 增量式求解结果 距离方程类方法 MDS 求解完全图的实现方法 SDP 以半正定规划求解问题 全局优化类方法 $g^2o$ 基于最小二乘法的迭代搜索方法 SMACOF 基于构造辅助函数的迭代搜索方法 模块拼合类方法 AAAP 将部分模块变形, 以仿射变换拼合模块 ARAP 以迭代搜索的策略, 优化拼合后结果的形状偏差 ASAP 以矩阵特征向量求解模块拼合结果 表 2 计算符号说明表
Table 2 Notation list
符号 定义 $n$ 节点数量, $|V|=n$ $m$ 图中边的数量, $|E|=m$ $t$ 迭代次数 $g $ 节点最大度数 $N $ 模块中节点数最大值 表 3 算法时间复杂度
Table 3 Time complexity of different algorithms
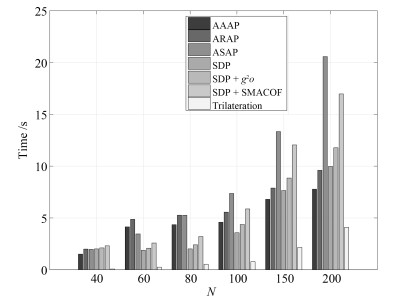
算法名称 时间复杂度 Trilateration ${\rm O}(n^2)$ MDS ${\rm O}(n^2)$ SDP ${\rm O}(n^2m^{2.5}+m^{3.5})$ $g^2o$ ${\rm O}(n^2t)$ SMACOF ${\rm O}(n^2t)$ AAAP ${\rm O}(mn^2)$ ARAP ${\rm O}(mn^2+n^3t)$ ASAP ${\rm O}(nN^2t+mn^2)$ 表 4 算法比较表
Table 4 Algorithm comparison
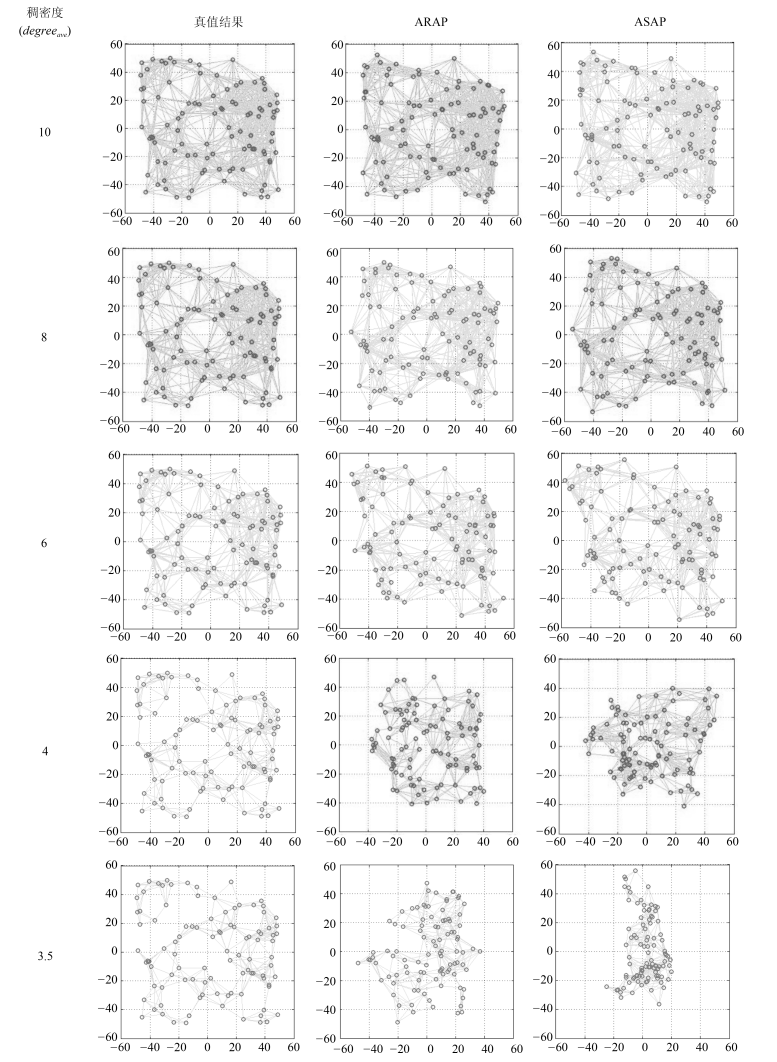
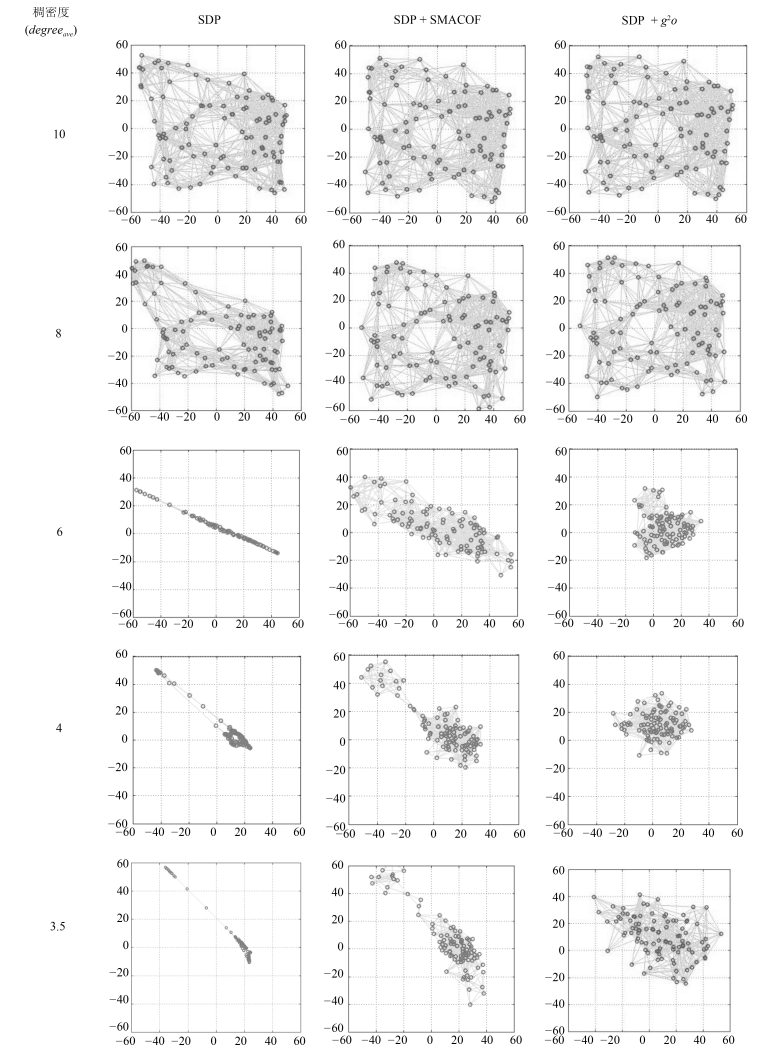
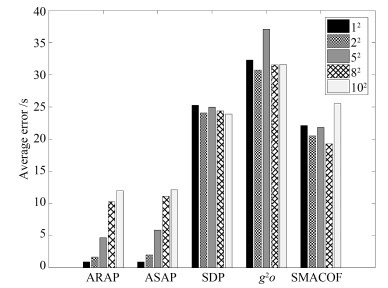
方法类型 算法 准确性 计算效率 鲁棒性(稠密度) 鲁棒性(噪声) 三边测量类方法 Trilateration $\bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar$ 距离方程类方法 MDS $\bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar$ SDP $\bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ 全局优化类方法 $g^2o$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ SMACOF $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ 模块拼合类方法 AAAP $\bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar$ ARAP $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ ASAP $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ $\bigstar \bigstar \bigstar \bigstar$ -
[1] Bulusu N, Heidemann J, Estrin D. GPS-less low-cost outdoor localization for very small devices. IEEE Personal Communications, 2000, 7(5): 28-34 doi: 10.1109/98.878533 [2] Doherty L, Pister K S J, El Ghaoui L. Convex position estimation in wireless sensor networks. In: IEEE INFOCOM, Twentieth Annual Joint Conference of the IEEE Computer and Communications Societies. Anchorage, United States: IEEE, 2001. 1655-1663 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3893900_Convex_position_estimation_in_wireless_sensor_networks [3] Hightower J, Borriello G. Location systems for ubiquitous computing. Computer, 2001, 34(8): 57-66 doi: 10.1109/2.940014 [4] Savvides A, Han C C, Strivastava M B. Dynamic fine-grained localization in Ad-Hoc networks of sensors. In: Proceedings of the 7th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking. Rome, Italy: ACM, 2001. 166-179 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220926176_Srivastava_Dynamic_Fine-grained_Localization_in_Ad-Hoc_Networks_of_Sensors [5] Savarese C, Rabaey J M, Langendoen K. Robust positioning algorithms for distributed Ad-Hoc wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the General Track of the Annual Conference on USENIX Annual Technical Conference. Monterey, USA: USENIX Association, 2002. 317-327 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2529202_Robust_Positioning_Algorithms_for_Distributed_Ad-Hoc_Wireless_Sensor_Networks [6] Hays P A. Proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (NMR) methods for determining the purity of reference drug standards and illicit forensic drug seizures. Journal of Forensic Sciences, 2005, 50(6): 1342-1360 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=3517aaf1c734242ab4ed9eeb65736e5c&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [7] Kaufmann K W, Lemmon G H, DeLuca S L, Sheehan J H, Meiler J. Practically useful: what the Rosetta protein modeling suite can do for you. Biochemistry, 2010, 49(14): 2987-2998 doi: 10.1021/bi902153g [8] Sit A, Wu Z J, Yuan Y X. A geometric buildup algorithm for the solution of the distance geometry problem using least-squares approximation. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 2009, 71(8): 1914-1933 doi: 10.1007/s11538-009-9431-9 [9] Sit A, Wu Z J. Solving a generalized distance geometry problem for protein structure determination. Bulletin of Mathematical Biology, 2011, 73(12): 2809-2836 doi: 10.1007/s11538-011-9644-6 [10] 刘勘, 周晓峥, 周洞汝.数据可视化的研究与发展.计算机工程, 2002, 28(8): 1-2, 63 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjgc200208001Liu Kan, Zhou Xiao-Zheng, Zhou Dong-Ru. Data visualization research and development. Computer Engineering, 2002, 28(8): 1-2, 63 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjgc200208001 [11] Wilkinson L. SYSTAT: the System for Statistics. Evanston, IL: SYSTAT, Inc., 1986. [12] Kümmerle R, Grisetti G, Strasdat H, Konolige K, Burgard W. $G.2o$: a general framework for graph optimization. In: IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2011. 3607-3613 [13] Li Z, Trappe W, Zhang Y, Nath B. Robust statistical methods for securing wireless localization in sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Symposium on Information Processing in Sensor Networks. Boise, USA: IEEE, 2005. 91-98 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4149846_Robust_statistical_methods_for_securing_wireless_localization_in_sensor_networks [14] Saxe J B. Embeddability of Weighted Graphs in K-Space is Strongly NP-Hard. Qatar: Carnegie-Mellon University, 1980. [15] Yemini Y. Some theoretical aspects of position-location problems. In: Proceedings of the 20th Annual Symposium on Foundations of Computer Science. Washington D. C., USA: IEEE, 1979. 1-8 http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/001457938680151X [16] Jackson B, Jordán T. Connected rigidity matroids and unique realizations of graphs. Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B, 2005, 94(1): 1-29 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=593b97de641132c7f040a84dc72841fa [17] Thomas F, Ros L. Revisiting trilateration for robot localization. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2005, 21(1): 93-101 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2004.833793 [18] Čapkun S, Buttyán L, Hubaux J P. SECTOR: secure tracking of node encounters in multi-hop wireless networks. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM Workshop on Security of Ad Hoc and Sensor Networks. Fairfax, Virginia: ACM, 2003. 21-32 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/37402492_SECTOR_Secure_Tracking_of_Node_Encounters_in_Multi-hop_Wireless_Networks [19] Lazos L, Poovendran R. SeRLoc: secure range-independent localization for wireless sensor networks. In: Proceedings of the 3rd ACM Workshop on Wireless Security. Philadelphia, PA, USA: ACM, 2004. 21-30 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221005650_SeRLoc_Secure_Range-Independent_Localization_for_Wireless_Sensor_Networks [20] Kusy B, Ledeczi A, Maroti M, Meertens L. Node-density independent localization. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Information Processing in Sensor Networks. Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2006. 441-448 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224642430_Node-density_independent_localization [21] Hendrickson B. The molecule problem: exploiting structure in global optimization. Siam Journal on Optimization, 1995, 5(4): 835-857 doi: 10.1137/0805040 [22] Shang Y, Ruml W, Zhang Y, Fromherz M P J. Localization from mere connectivity. In: Proceedings of the 4th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing. Annapolis, Maryland, USA: ACM, 2003. 201-212 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2892241_Localization_from_Mere_Connectivity [23] Shang Y, Ruml W. Improved MDS-based localization. In: EEE INFOCOM 2004. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2004. 2640-2651 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4102894_Improved_MDS-based_localization [24] Shang Y, Ruml W, Zhang Y, Fromherz M. Localization from connectivity in sensor networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2004, 15(11): 961-974 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2004.67 [25] Biswas P, Lian T C, Wang T C, Ye Y Y. Semidefinite programming based algorithms for sensor network localization. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 2006, 2(2): 188-220 doi: 10.1145/1149283.1149286 [26] Biswas P, Aghajan H, Ye Y Y. Semidefinite programming algorithms for sensor network localization using angle information. In: Proceedings of the Conference Record of the Thirty-Ninth Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers. Pacific Grove, CA, USA: IEEE, 2005. 220-224 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/4225543_Semidefinite_Programming_Algorithms_for_Sensor_Network_Localization_using_Angle_Information [27] Biswas P, Liang T C, Toh K C, Ye Y, Wang T C. Semidefinite programming approaches for sensor network localization with noisy distance measurements. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2006, 3(4): 360-371 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2006.877401 [28] Zhu Z S, So A M C, Ye Y Y. Universal rigidity: towards accurate and efficient localization of wireless networks. In: Proceedings IEEE INFOCOM. San Diego, USA: IEEE, 2010. 1-9 [29] Boyd S, El Ghaoui L, Feron E, Balakrishnan V. Linear Matrix Inequalities in System and Control Theory. Philadelphia: Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 1994. http://library.wur.nl/WebQuery/clc/1669445 [30] Liang T C, Wang T C, Ye Y Y. A Gradient Search Method to Round the Semidefinite Programming Relaxation Solution for Ad Hoc Wireless Sensor Network Localization, Technical Report, Department of Management Science and Engineering, Stanford University, 2004. [31] Cox T F, Cox M A A. Multidimensional Scaling (Second Edition). London: Chapman Hall/CRC, 2000. [32] Savvides A, Park H, Srivastava M B. The bits and flops of the n-hop multilateration primitive for node localization problems. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Workshop on Wireless Sensor Networks and Applications. Atlanta, USA: ACM, 2002. 112-121 [33] Costa J A, Patwari N, Hero A O Ⅲ. Distributed weighted-multidimensional scaling for node localization in sensor networks. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 2006, 2(1): 39-64 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_doaj-articles_1757e346002855db37f97718c6d6e3b1 [34] Groenen P J F. The Majorization Approach to Multidimensional Scaling: Some Problems and Extensions[Ph.D. dissertation], Leiden University, Leiden, The Netherlands, 1993 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/243785955_The_majorization_approach_to_multidimensional_scaling_some_problems_and_extensions [35] Press W H, Teukolsky S A, Vetterling W T, Flannery B P. Numerical Recipes (Second Edition). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 1992. [36] Lourakis M I A, Argyros A A. SBA: a software package for generic sparse bundle adjustment. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 2009, 36(1): Article No. 2 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/wjclxb200304024 [37] Endres F, Hess J, Engelhard N, Sturm J, Cremers D, Burgard W. An evaluation of the RGB-D SLAM system. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Saint Paul, MN, USA: IEEE, 2012. 1691-1696 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/254041427_An_evaluation_of_the_RGB-D_SLAM_system [38] Sturm J, Engelhard N, Endres F, Burgard W, Cremers D. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Vilamoura, Portugal: IEEE, 2012. 573-580 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/261353760_A_benchmark_for_the_evaluation_of_RGB-D_SLAM_systems?ev=auth_pub [39] Engel J, Schōps T, Cremers D. LSD-SLAM: large-scale direct monocular SLAM. In: European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 834-849 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/290620817_LSD-SLAM_Large-Scale_Direct_Monocular_SLAM [40] Forster C, Pizzoli M, Scaramuzza D. SVO: fast semi-direct monocular visual odometry. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2014. 15-22 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/262378002_SVO_Fast_Semi-Direct_Monocular_Visual_Odometry [41] Fraundorfer F, Heng L, Honegger D, Lee G H, Meier L, Tanskanen P, et al. Vision-based autonomous mapping and exploration using a quadrotor MAV. In: Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Vilamoura, Portugal: IEEE, 2012. 4557-4564 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/261353707_Vision-based_autonomous_mapping_and_exploration_using_a_quadrotor_MAV [42] De Leeuw J. Applications of convex analysis to multidimensional scaling. Department of Statistics, UCLA, 2005. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/239417876_APPLICATIONS_OF_CONVEX_ANALYSIS_TO_MULTIDIMENSIONAL_SCALING [43] Borg I, Groenen P J F. Modern Multidimensional Scaling: Theory and Applications (Second Edition). New York, NY: Springer, 2005. [44] Moore D C. Robust distribution sensor network localization with noisy range measurements. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 2005. 50-61 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/35943813_Robust_distribution_sensor_network_localization_with_noisy_range_measurements [45] Koren Y, Gotsman C, Ben-Chen M. PATCHWORK: efficient localization for sensor networks by distributed global optimization. Technical Report, 2005. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/254039773_PATCHWORK_Efficient_Localization_for_Sensor_Networks_by_Distributed_Global_Optimization [46] Roweis S T, Saul L K. Nonlinear dimensionality reduction by locally linear embedding. Science, 2000, 290(5500): 2323-2326 doi: 10.1126/science.290.5500.2323 [47] Shi J B, Malik J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2000, 22(8): 888-905 doi: 10.1109/34.868688 [48] Zhang L, Liu L G, Gotsman C, Gortler S J. An as-rigid-as-possible approach to sensor network localization. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 2010, 6(4): Article No. 35 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=fa857a82ca6af6ecf09b9cba6458a2e5 [49] Sorkine O, Alexa M. As-rigid-as-possible surface modeling. In: Proceedings of the 5th Eurographics Symposium on Geometry Processing. Barcelona, Spain, 2007. 109-116 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221316589_As-Rigid-As-Possible_Surface_Modeling [50] Alexa M, Cohen-Or D, Levin D. As-rigid-as-possible shape interpolation. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques. New Orleans, USA: ACM, 2000. 157-164 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/2538876_As-Rigid-As-Possible_Shape_Interpolation [51] Press W H, Teukolsky S A, Vetterling W T, Flannery B P. Numerical Recipes: The Art of Scientific Computing (3rd Edition). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2007. [52] Cornilescu G, Marquardt J L, Ottiger M, Bax A. Validation of protein structure from anisotropic carbonyl chemical shifts in a dilute liquid crystalline phase. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1998, 120(27): 6836-6837 doi: 10.1021/ja9812610 [53] Hendrickson B. Conditions for unique graph realizations. SIAM Journal on Computing, 1992, 21(1): 65-84 doi: 10.1137/0221008 [54] Gower J C, Dijksterhuis G B. Procrustes Problems. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2004. [55] Golub G H, Van Loan C F. Matrix Computations (4th Edition). Baltimore, MD: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2012. [56] Gortler S J, Healy A D, Thurston D P. Characterizing generic global rigidity. American Journal of Mathematics, 2010, 132(4): 897-939 doi: 10.1353/ajm.0.0132 [57] Cucuringu M, Lipman Y, Singer A. Sensor network localization by eigenvector synchronization over the euclidean group. ACM Transactions on Sensor Networks, 2012, 8(3): Article No. 19 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=51a43c69302e35adee96e330ee6450b8 [58] Sobeih A, Hack M, Liu Z, Zhang L. Almost peer-to-peer clock synchronization. In: Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Parallel and Distributed Processing Symposium. Rome: IEEE, 2007. 1-10 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/220951841_Almost_Peer-to-Peer_Clock_Synchronization?ev=prf_cit [59] Mainwaring A, Culler D, Polastre J, Szewczyk R, Anderson J. Wireless sensor networks for habitat monitoring. In: Proceedings of the 1st ACM International Workshop on Wireless Sensor Networks and Applications. Atlanta, USA: ACM, 2002. 88-97 [60] Brust M R, Akbaș M I, Turgut D. Multi-hop localization system for environmental monitoring in wireless sensor and actor networks. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 2013, 25(5): 701-717 doi: 10.1002/cpe.1812 [61] Wang X P, Liu Y H, Yang Z, Lu K, Luo J. Robust component-based localizationin sparse networks. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 25(5): 1317-1327 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2013.85 [62] Korniienko A, Khan U A, Scorletti G. Robust sensor localization with locally-computed, global $H_\infty$-design. In: Proceedings of the 2016 American Control Conference. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2016. 6375-6380 [63] Khan U A, Kar S, Moura J M F. DILAND: an algorithm for distributed sensor localization with noisy distance measurements. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2010, 58(3): 1940-1947 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2038423 [64] Lin Z Y, Fu M Y, Diao Y F. Distributed self localization for relative position sensing networks in 2D space. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2015, 63(14): 3751-3761 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2015.2432739 [65] Hubbell W L, Cafiso D S, Altenbach C. Identifying conformational changes with site-directed spin labeling. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology, 2000, 7(9): 735-739 doi: 10.1038/78956 [66] Oh K J, Altenbach C, Collier R J, Hubbell W L. Site-directed spin labeling of proteins. Bacterial Toxins: Methods and Protocols. New York: Humana Press, 2000. 147-169 [67] Dong Q F, Wu Z J. A linear-time algorithm for solving the molecular distance geometry problem with exact inter-atomic distances. Journal of Global Optimization, 2002, 22(1-4): 365-375 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/227120408_A_linear-time_algorithm_for_solving_the_molecular_distance_geometry_problem_with_exact_inter-atomic_distances [68] Wu D, Wu Z J. An updated geometric build-up algorithm for solving the molecular distance geometry problems with sparse distance data. Journal of Global Optimization, 2007, 37(4): 661-673 doi: 10.1007/s10898-006-9080-6 [69] Lavor C, Liberti L, Donald B, Worley B, Bardiaux B, Malliavin T E, Nilges M. Minimal NMR distance information for rigidity of protein graphs. Discrete Applied Mathematics, 2019, 256: 91-104 doi: 10.1016/j.dam.2018.03.071 [70] Blumenthal L M. Theory and Applications of Distance Geometry. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1953. [71] Moré J J, Wu Z J. Distance geometry optimization for protein structures. Journal of Global Optimization, 1999, 15(3): 219-234 doi: 10.1023/A:1008380219900 [72] Cleveland W S, McGill M E. Dynamic Graphics for Statistics. Belmont, California: Wadsworth, 1988. [73] Littlefield R J. Using the glyph concept to create user-definable display formats. Pacific Northwest Lab, Richland, USA, 1983. [74] 柳萌萌, 赵书良, 韩玉辉, 苏东海, 李晓超, 陈敏.多尺度数据挖掘方法.软件学报, 2016, 27(12): 3030-3050 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjkx201904009Liu Meng-Meng, Zhao Shu-Liang, Han Yu-Hui, Su Dong-Hai, Li Xiao-Chao, Chen Min. Research on multi-scale data mining method. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(12): 3030-3050 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjkx201904009 [75] Levy S. A cross-cultural analysis of the structure and levels of attitudes towards acts of political protest. Social Indicators Research, 1983, 12(3): 281-309 doi: 10.1007/BF00319806 [76] Castellanos J A, Montiel J M M, Neira J, Tardos J D. The SPmap: a probabilistic framework for simultaneous localization and map building. IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1999, 15(5): 948-952 doi: 10.1109/70.795798 [77] Paz L M, Tardos J D, Neira J. Divide and conquer: EKF SLAM in O($n$). IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2008, 24(5): 1107-1120 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2008.2004639 [78] Montemerlo M, Thrun S, Koller D, Wegbreit B. FastSLAM: a factored solution to the simultaneous localization and mapping problem. In: Proceedings of the AAAI National Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco: AAAI, 2002. 593-598 [79] Hahnel D, Burgard W, Fox D, Thrun S. An efficient fastSLAM algorithm for generating maps of large-scale cyclic environments from raw laser range measurements. In: IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2003. 206-211 [80] Eustice R M, Singh H, Leonard J J. Exactly sparse delayed-state filters. In: Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2005. 2417-2424 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/221077974_Exactly_Sparse_Delayed-State_Filters [81] Thrun S, Liu Y F, Koller D, Ng A Y, Ghahramani Z, Durrant-Whyte H. Simultaneous localization and mapping with sparse extended information filters. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2004, 23(7-8): 693-716 doi: 10.1177/0278364904045479 [82] Grisetti G, Kummerle R, Stachniss C, Burgard W. A tutorial on graph-based SLAM. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2010, 2(4): 31-43 doi: 10.1109/MITS.2010.939925 [83] Saez J M, Hogue A, Escolano F, Jenkin M. Underwater 3D SLAM through entropy minimization. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Orlando, USA: IEEE, 2006. 3562-3567 http://www.researchgate.net/publication/221069355_Underwater_3D_SLAM_through_Entropy_Minimization [84] Kümmerle R, Steder B, Dornhege C, Kleiner A, Grisetti G, Burgard W. Large scale graph-based SLAM using aerial images as prior information. Autonomous Robots, 2011, 30(1): 25-39 doi: 10.1007/s10514-010-9204-1 [85] 张毅, 汪龙峰, 余佳航.基于深度信息的移动机器人室内环境三维地图创建.计算机应用, 2014, 34(12): 3438-3440 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjyy201412015Zhang Yi, Wang Long-Feng, Yu Jia-Hang. Depth-image based 3D map reconstruction of indoor environment for mobile robots. Journal of Computer Applications, 2014, 34(12): 3438-3440 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=jsjyy201412015 [86] Levi Z, Gotsman C. Smooth rotation enhanced As-Rigid-As-Possible mesh animation. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2015, 21(2): 264-277 doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2014.2359463 [87] Parashar S, Pizarro D, Bartoli A, Collins T. As-rigid-as-possible volumetric shape-from-template. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 891-899 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/300408305_As-Rigid-as-Possible_Volumetric_Shape-from-Template?ev=auth_pub [88] Jacobs D J, Hendrickson B. An algorithm for two-dimensional rigidity percolation: the pebble game. Journal of Computational Physics, 1997, 137(2): 346-365 doi: 10.1006/jcph.1997.5809 [89] Connelly R. Generic global rigidity. Discrete & Computational Geometry, 2005, 33(4): 549-563 http://www.researchgate.net/profile/R_Connelly/publication/220453469_Generic_Global_Rigidity/links/5447b0890cf2f14fb8121c28?ev=pub_ext_doc_dl_meta -




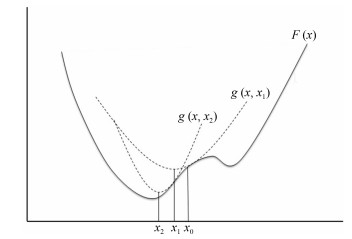
 下载:
下载: