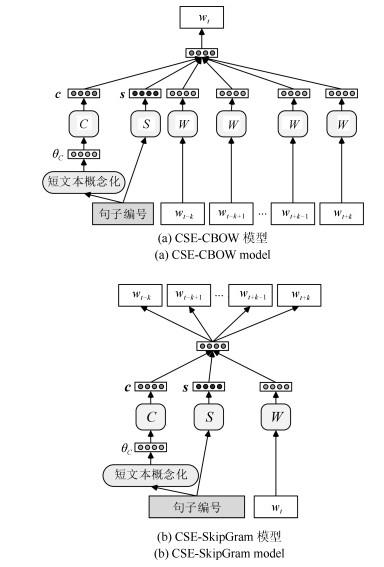
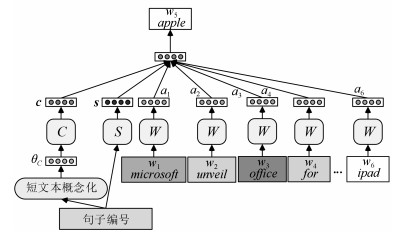
-
摘要: 大多数句嵌模型仅利用文本字面信息来完成句子向量化表示, 导致这些模型对普遍存在的一词多义现象缺乏甄别能力.为了增强句子的语义表达能力, 本文使用短文本概念化算法为语料库中的每个句子赋予相关概念, 然后学习概念化句嵌入(Conceptual sentence embedding, CSE).因此, 由于引入了概念信息, 这种语义表示比目前广泛使用的句嵌入模型更具表达能力.此外, 我们通过引入注意力机制进一步扩展概念化句嵌入模型, 使模型能够有区别地选择上下文语境中的相关词语以实现更高效的预测.本文通过文本分类和信息检索等语言理解任务来验证所提出的概念化句嵌入模型的性能, 实验结果证明本文所提出的模型性能优于其他句嵌入模型.Abstract: Most sentence embedding models typically represent each sentence only using word surface, which makes these models indiscriminative for ubiquitous homonymy and polysemy. In order to enhance representation capability of sentence, we employ short-text conceptualization algorithm to assign associated concepts for each sentence in the text corpus, and then learn conceptual sentence embedding (CSE). Hence, this semantic representation is more expressive than some widely-used text representation models such as latent topic model, especially for short-text. Moreover, we further extend CSE models by utilizing an attention mechanism that select relevant words within the context to make more efficient prediction. In the experiments, we evaluate the CSE models on three tasks, text classification and information retrieval. The experimental results show that the proposed models outperform typical sentence embed-ding models.
-
Key words:
- Sentence embedding /
- short-text conceptualization /
- attention mechanism /
- word embedding /
- semantic representation
1) 本文责任编委 赵铁军 -
表 1 文本分类任务实验结果
Table 1 Evaluation results of text classification task
数据集 NewsTitle Twitter TREC 模型 P R F P R F P R F BOW 0.731 0.719 0.725 0.397 0.415 0.406 0.822 0.820 0.821 LDA 0.720 0.706 0.713 0.340 0.312 0.325 0.815 0.811 0.813 PV-DBOW 0.726 0.721 0.723 0.409 0.410 0.409 0.825 0.817 0.821 PV-DM 0.745 0.738 0.741 0.424 0.423 0.423 0.837 0.824 0.830 TWE 0.810 0.805 0.807 0.454 0.438 0.446 0.894 0.885 0.885 SCBOW 0.812$^\beta$ 0.805$^\beta$ 0.809$^\beta$ 0.455$^\beta$ 0.439 0.449$^\beta$ 0.897$^\beta$ 0.887$^\beta$ 0.892$^\beta$ CSE-CBOW 0.814 0.811 0.812 0.458 0.450 0.454 0.895 0.891 0.893 CSE-SkipGram 0.827 0.819 0.823 0.477 0.447 0.462 0.899 0.894 0.896 aCSE-SUR 0.828 0.822 0.825 0.469 0.453 0.462 0.906 0.897 0.901 aCSE-TYPE 0.838 0.830 0.834 0.483 0.455 0.468 0.911 0.903 0.907 aCSE-ALL 0.845$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.832$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.838$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.485$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.462$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.473$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.917$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.914$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.915$^{\alpha\beta}$ 表 2 信息检索任务实验结果
Table 2 Evaluation results of information retrieval
查询项集合 TMB2011 TMB2012 模型 MAP P@30 MAP P@30 BOW 0.304 0.412 0.321 0.494 LDA 0.281 0.409 0.311 0.486 PV-DBOW 0.285 0.412 0.324 0.491 PV-DM 0.327 0.431 0.340 0.524 TWE 0.331 0.446 0.347 0.509 SCBOW 0.333 0.448$^{\beta}$ 0.349$^{\beta}$ 0.511 CSE-CBOW 0.337 0.451 0.344 0.512 CSE-SkipGram 0.367 0.461 0.360 0.517 aCSE-SUR 0.342 0.458 0.349 0.520 aCSE-TYPE 0.373 0.466 0.365 0.525 aCSE-ALL 0.376$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.471$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.369$^{\alpha\beta}$ 0.530$^{\alpha\beta}$ -
[1] Harris Z S. Distributional Structure. Word, 1954, 10: 146-162 doi: 10.1080/00437956.1954.11659520 [2] Palangi H, Deng L, Shen Y, Gao J, He X, Chen J, Song X, Ward R. Deep Sentence Embedding Using Long Short-Term Memory Networks: Analysis and Application to Information Retrieval. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2016, 24: 694-707 doi: 10.1109/TASLP.2016.2520371 [3] Le Q, Mikolov T. Distributed Representations of Sentences and Documents. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, NY, USA: ACM, 2014. 1188-1196 [4] Liu Y, Liu Z, Chua T S, Sun M. Topical Word Embeddings. In: Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, CA, USA: AAAI, 2015. 2418-2424 [5] Mikolov T, Corrado G, Chen K, Dean J. Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1301.3781, 2015. http://arxiv.org/abs/1301.3781 [6] Wang Z, Zhao K, Wang H, Dean J. Query Understanding through Knowledge-Based Conceptualization. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, CA, USA: Morgan Kaufmann, 2015. 3264-3270 [7] Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y. Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1409.0473, 2015. http://arxiv.org/abs/1409.0473 [8] Lin Y, Shen S, Liu Z, Luan H, Sun M. Neural Relation Extraction with Selective Attention over Instances. In: Proceedings of the 54th Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016. 2124-2133 [9] Wang Y, Huang H, Feng C, Zhou Q, Gu J, Gao X. CSE: Conceptual Sentence Embeddings based on Attention Model. In: Proceedings of the 54th Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016. 505-515 [10] Rayner K. Eye movements in Reading and Information Processing: 20 Years of Research. Psychological Bulletin, 1998, 124: 372-422 doi: 10.1037/0033-2909.124.3.372 [11] Nilsson M, Nivre J. Learning where to look: Modeling eye movements in reading. In: Proceedings of the 13th Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2009. 93-101 [12] Lai S, Xu L, Liu K, Zhao J. Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks for Text Classification. In: Proceedings of the 29th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto, CA, USA: AAAI, 2015. 2267-2273 [13] Kenter T, Borisov A, De Rijke M. Siamese CBOW: Optimizing Word Embeddings for Sentence Representations. In: Proceedings of the 54th Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016. 941-951 [14] Xiong C, Merity S, Socher R. Dynamic Memory Networks for Visual and Textual Question Answering. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, NY. USA: ACM, 2016. 1230-1239 [15] Yu J. Learning Sentence Embeddings with Auxiliary Tasks for Cross-Domain Sentiment Classification. In: Proceedings of the 2016 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016. 236-246 [16] Yong Z, Meng J E, Ning W, Pratama M. Attention Pooling-based Convolutional Neural Network for Sentence Modelling. Information Sciences, 2016, 373: 388-403 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2016.08.084 [17] Wang S, Zhang J, Zong C. Learning sentence representation with guidance of human attention. In: Proceedings of IJCAI International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, CA, USA: Morgan Kaufmann, 2017. 4137-4143 [18] Lang Z, Gu X, Zhou Q, Xu T. Combining statistics-based and CNN-based information for sentence classification. In: Proceedings of the 28th IEEE International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence. New York, NY. USA: IEEE, 2017. 1012-1018 [19] Wieting J, Gimpel K. Revisiting Recurrent Networks for Paraphrastic Sentence Embeddings. In: Proceedings of the 55th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017. 2078-2088 [20] Nicosia M, Moschitti A. Learning Contextual Embeddings for Structural Semantic Similarity using Categorical Information. In: Proceedings of the 21st Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2017. 260-270 [21] Peng W, Wang J, Zhao B, Wang L. Identification of Protein Complexes Using Weighted PageRank-Nibble Algorithm and Core-Attachment Structure. IEEE/ACM Transactions on Computational Biology & Bioinformatics, 2015, 12: 179-192 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=abeae9028ba365cfcf0b6aadc978a058 [22] Hua W, Wang Z, Wang H, Zheng K, Zhou X. Short text understanding through lexical-semantic analysis. In: Proceedings of the 31st IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering. New York, NY. USA: IEEE, 2015. 495-506 [23] Song Y, Wang H. Open Domain Short Text Conceptualization: A Generative + Descriptive Modeling Approach. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. San Francisco, CA, USA: Morgan Kaufmann, 2015. 3820-3826 [24] Wang F, Wang Z, Li Z, Wen J R. Concept-based Short Text Classification and Ranking. In: Proceedings of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management. New York, NY. USA: ACM, 2014. 1069-1078 [25] Wang Y, Huang H, Feng C. Query Expansion Based on a Feedback Concept Model for Microblog Retrieval. In: Proceedings of the 26th International Conference on World Wide Web. New York, NY. USA: ACM, 2017. 559-568 [26] Wu W, Li H, Wang H, Zhu K Q. Probase: A probabilistic taxonomy for text understanding. In: Proceedings of the 2012 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data. New York, NY. USA: ACM, 2012. 481-492 [27] Yu Z, Wang H, Lin X, Wang M. Understanding Short Texts through Semantic Enrichment and Hashing. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2016, 28: 566-579 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2015.2485224 [28] Itti L, Koch C, Niebur E. A Model of Saliency Based Visual Attention for Rapid Scene Analysis. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1998, 20: 1254-1259 doi: 10.1109/34.730558 [29] Hahn M, Keller F. Modeling Human Reading with Neural Attention. Psychological Bulletin, 2016, 85: 618-627 http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=Arxiv000001371070 [30] Narayanan S, Jurafsky D. A Bayesian Model Predicts Human Parse Preference and Reading Times in Sentence Processing. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2001, 14: 59-65 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=295791b42c4db2c7f0cea418567b841e&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [31] Demberg V, Keller F. Data from eye-tracking corpora as evidence for theories of syntactic processing complexity. Cognition, 2016, 109: 193-210 http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=8f52c0a66bab4fbea159c968896ec065&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn [32] Barrett M, Sogaard A. Reading behavior predicts syntactic categories. In: Proceedings of the 2015 SIGNLL Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2015. 345-349 [33] Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado G, Dean J. Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality. In: Proceedings of the 27th Annual Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge, MA, USA: MIT Press, 2013. 1-9 [34] Fernandez-Carbajales V, García M A, MartU.S.A.nez J M. Visual attention based on a joint perceptual space of color and brightness for improved video tracking. Pattern Recognit, 2016, 60: 571-584 [35] Attneave F. Applications of information theory to psychology: a summary of basic concepts, methods, and results. American Journal of Psychology, 1961, 74(2): 319-324 doi: 10.2307/1419430 [36] Hale J. A probabilistic earley parser as a psycholinguistic model. In: Proceedings of the 2nd meeting of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics on Language technologies. Stroudsburg, PA, USA: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2001. 1-8 [37] Ounis I, Macdonald C, Lin J. Overview of the trec-2011 microblog track. In: Proceedings of the 2011 Text REtrieval Conference. Gaithersburg, MD, USA: NIST, 2001. 1-9 [38] Blei D M, Ng A Y, Jordan M I. Latent Dirichlet Allocation. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2003, 3: 993-1022 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/jsjyy201306024 [39] Fan R E, Chang K W, Hsieh C J, Wang X R, Lin C J. LIBLINEAR: A Library for Large Linear Classification. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2008, 9: 1871-1874 http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dzjs201506001 -




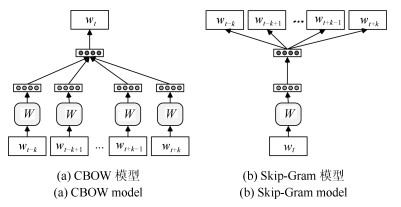
 下载:
下载: