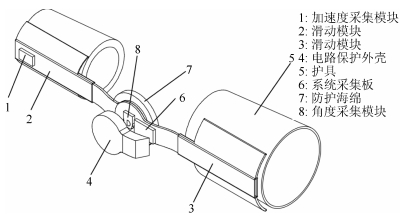
Upper Limb Spasticity Evaluation Based on Stretch Reflex Threshold: Method, Device, Validity and Reliability
-
摘要: 针对目前临床痉挛评定主观性大,信度与效度有待提高的问题,提出了一种新的基于牵张反射阈值的痉挛评定方法,利用关节角加速度变化判定牵张反射阈值,通过设计相应装置检验了牵张反射阈值在上肢痉挛评定中的信度与效度,并探讨了加速度变化在上肢痉挛评定中的信度与效度.4位检查者利用改良Ashworth量表(Modified Ashworth scale,MAS)及该痉挛检测装置对招募的22例伴随有上肢痉挛症状的受试者进行了痉挛评定.将评定过程中采集的牵张反射阈值以及加速度平均变化值(Acceleration mean variance,AMV)与MAS评分进行相关性分析,显示牵张反射阈值数据与MAS评分显著相关,相关性满足(r=-0.831~-0.953,P < 0.05),AMV与MAS评分相关性满足(r=0.665~0.900,P < 0.05).它们重测信度分别满足(r=0.890~0.962,P < 0.05)和(r=0.632~0.928,P < 0.05).实验结果表明该方法及装置可为痉挛评定提供一种实用的定量分析手段.
-
关键词:
- 痉挛 /
- 牵张反射阈值 /
- 加速度 /
- 改良Ashworth量表
Abstract: Clinical methods for spasticity evaluation are criticized as subjective, and their validity and reliability remain to improve. This study is to present a new evaluation method for accurate and reliable evaluation of spasticity based on a stretch reflex threshold which is obtained from the acceleration and angle data. A corresponding device is designed to test the validity and reliability of the stretch reflex threshold in spasticity assessment, and further study is conducted to discuss the validity and reliability of acceleration mean variance (AMV). Spasticity is evaluated in 22 subjects with upper limb spasticity using the constructed portable device and the modified Ashworth scale (MAS) by four evaluators. The results of correlation analysis show that there is a strong negative correlation (r=-0.831~-0.953, P < 0.05) between MAS and the stretch reflex threshold. Also, the correlation coefficient between the MAS and AMV is (r=0.665~0.900, P < 0.05). Their test-retest reliabilities are (r=0.890~0.962, P < 0.05) and (r=0.632~0.928, P < 0.05). These results demonstrate that the method and device may provide a quantitative and practical way for spasticity measurement.-
Key words:
- Spasticity /
- stretch reflex threshold /
- acceleration /
- modified Ashworth scale (MAS)
1) 本文责任编委 王卫群 -
表 1 受试者个人相关信息
Table 1 Demographic characteristics of the participants
病例 年龄 病程 性别 患侧 患病部位 痉挛肌群 ROM ($^{\circ})$ MAS Test MAS Retest Test Retest E1 E2 E1 E2 A S1 64 6月 男 右 左侧脑梗塞 屈肘肌群 96 104 0 0 0 0 S2 60 7月 女 右 左侧脑梗死 屈肘肌群 120 126 0 0 0 0 S3 66 3月 男 左 右侧脑梗死 伸肘肌群 100 104 2 2 2 2 S4 68 3月 男 左 右侧脑栓塞 屈肘肌群 132 124 1 1 1 1 S5 66 4月 女 左 右侧脑梗塞 屈肘肌群 113 114 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 S6 37 2月 男 左 右侧脑出血 屈肘肌群 114 117 1 1 1 1 S7 73 3月 男 右 左侧脑梗塞 屈肘肌群 105 113 0 0 0 0 S8 51 2月 男 左 右侧脑梗塞 屈肘肌群 94 99 1 1 1 1 S9 45 2月 女 左 右侧脑出血 屈肘肌群 100 101 2 2 2 2 S10 30 2月 女 左 右侧脑梗塞 屈肘肌群 106 106 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 S11 62 6月 男 左 右侧脑梗塞 伸肘肌群 130 135 3 3 3 3 S12 68 3月 男 左 右侧脑栓塞 伸肘肌群 123 125 3 3 3 3 S13 37 2月 男 左 右侧脑出血 伸肘肌群 114 117 2 2 2 2 S14 51 2月 男 左 右侧脑梗塞 伸肘肌群 98 100 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 Test Retest E3 E4 E3 E4 B S15 32 14月 男 左 右侧脑出血 屈肘肌群 128 129 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 S16 37 15月 男 右 左侧脑梗塞 屈肘肌群 118 120 2 2 2 2 S17 39 2年 男 右 左侧脑出血 屈肘肌群 103 106 0 0 0 0 S18 21 2年 男 右 左脑挫裂伤 屈肘肌群 110 110 3 3 3 3 S19 41 15天 男 左 右侧脑出血 屈肘肌群 101 100 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 S20 30 9月 男 左 右侧脑出血 屈肘肌群 110 115 1 1 1 1 S21 46 1年 男 右 左侧脑出血 屈肘肌群 143 145 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 S22 54 1月 男 右 左侧脑梗死 屈肘肌群 132 136 1 1 1 1 A:安徽省立医院, B:安徽中医药大学第一附属医院; ROM: range of motion; E1 $\sim$ E4: Evaluator1 $\sim$ 4, 检查者1 $\sim$ 4; S1 $\sim$ S22: Subject1 $\sim$ 22, 受试者1 $\sim$ 22; MAS Test:第一次MAS评分, MAS Retest:三天后MAS评分. 表 2 第一次以及三天后测试结果
Table 2 Experimental result at test and at retest
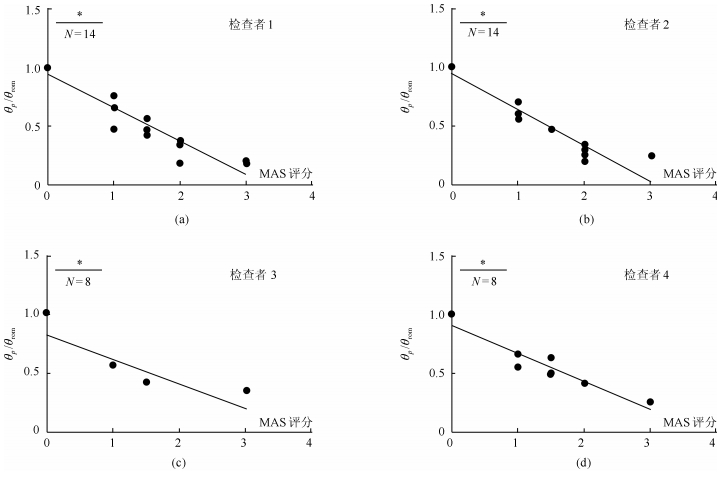
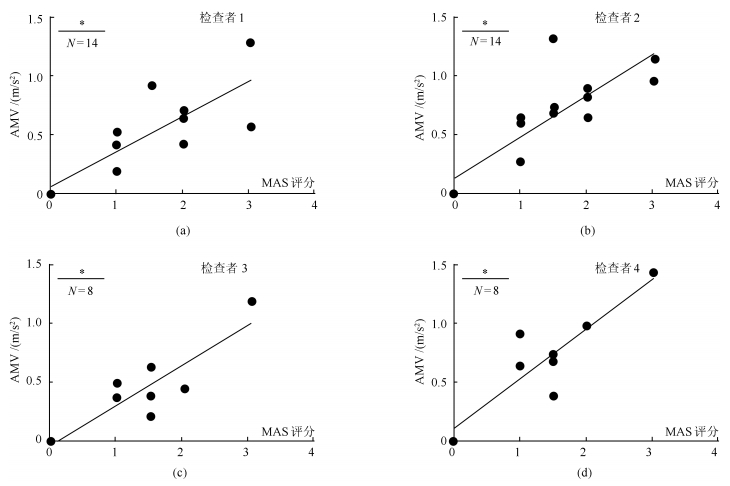
Test Retest 受试者 $\theta_{ p}$ $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ AMV $\theta_{ p}$ $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ AMV $\theta_{ p}$ $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ AMV $\theta_{ p}$ $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ AMV A E1 E2 E1 E2 S1 96 1.00 0 96 1.00 0 104 1.00 0 104 1.00 0 S2 120 1.00 0 120 1.00 0 126 1.00 0 126 1.00 0 S3 38 0.38 0.698 34 0.34 0.423 50 0.48 0.596 46 0.44 0.624 S4 64 0.48 0.412 93 0.70 0.392 70 0.56 0.321 80.63 0.65 0.469 S5 64 0.57 0.910 50 0.44 0.862 58 0.51 0.867 68 0.60 0.453 S6 75 0.66 0.192 64 0.56 0.182 62 0.53 0.260 75 0.64 0.175 S7 105 1.00 0 105 1.00 0 113 1.00 0 113 1.00 0 S8 71 0.76 0.526 56 0.60 0.421 54 0.55 1.501 47 0.47 0.479 S9 36 0.36 0.636 30 0.30 0.584 27 0.27 0.673 23 0.23 0.702 S10 50 0.47 0.498 44 0.42 0.455 53 0.50 0.426 55 0.52 0.452 S11 27 0.21 0.565 33 0.25 0.627 22 0.16 1.421 40 0.30 0.526 S12 23 0.19 1.268 25 0.20 0.746 46 0.37 0.837 29 0.23 1.105 S13 22 0.19 0.412 30 0.26 0.536 33 0.28 0.459 40 0.34 0.381 S14 42 0.43 0.526 46 0.47 0.469 49 0.49 0.450 55 0.55 0.502 B E3 E4 E3 E4 S15 54 0.42 0.380 80 0.63 0.485 64 0.50 0.325 65 0.50 0.416 S16 57 0.38 0.440 48 0.41 0.648 68 0.57 0.574 51 0.43 0.464 S17 103 1.00 0 103 1.00 0 106 1.00 0 106 1.00 0 S18 38 0.35 1.172 28 0.25 0.947 29 0.26 0.804 37 0.34 2.828 S19 42 0.42 0.206 50 0.50 0.258 55 0.55 0.249 37 0.37 0.225 S20 63 0.57 0.364 60 0.55 0.426 74 0.64 0.378 68 0.59 0.301 S21 60 0.42 0.628 70 0.49 0.450 53 0.37 0.459 50 0.34 0.416 S22 74 0.56 0.488 87 0.66 0.598 66 0.49 0.450 77 0.57 0.459 注: $\theta_{p}$($^{\circ}$); AMV(m/s$^{2}$). 表 3 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$及Amv与MAS的相关性
Table 3 The correlation between the MAS scores and $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta _{\rm rom}$ and between the MAS scores and AMV
相关性分析结果 装置数据 MAS评分 相关系数 $P$ Test Retest Test Retest E1 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ $-$0.944 $-$0.918 $P<$ 0.05 $P<$ 0.05 AMV 0.821 0.665 $P<$ 0.05 $P<$ 0.05 E2 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ $-$0.953 $-$0.931 $P<$ 0.05 $P<$ 0.05 AMV 0.841 0.864 $P<$ 0.05 $P<$ 0.05 E3 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ $-$0.855 $-$0.846 $P<$ 0.05 $P<$ 0.05 AMV 0.857 0.900 $P<$ 0.05 $P<$ 0.05 E4 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ $-$0.940 $-$0.831 $P<$ 0.05 $P<$ 0.05 AMV 0.873 0.813 $P<$ 0.05 $P<$ 0.05 表 4 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$及加速度重测相关系数
Table 4 The test-retest reliability of $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ and AMV
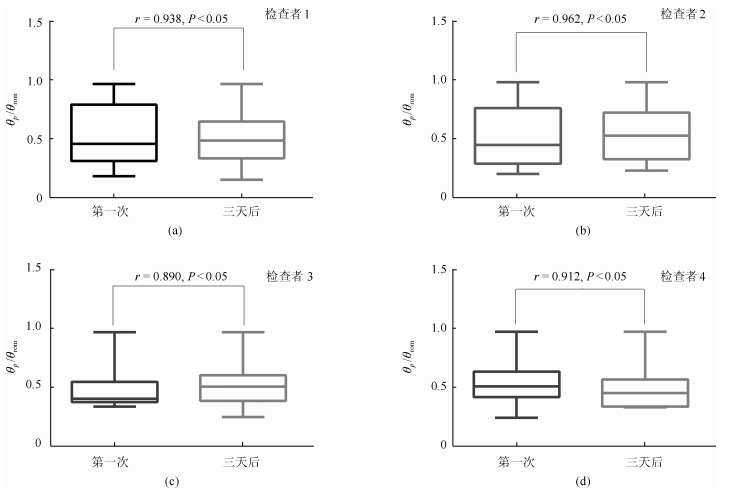
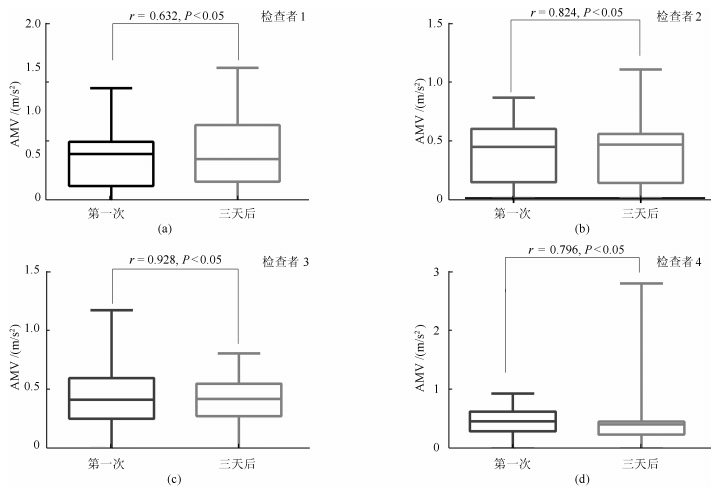
相关性分析结果 重测相关参数 相关系数 $P$值 E1 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ 0.938 $P<$ 0.05 AMV 0.632 $P<$ 0.05 E2 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ 0.962 $P<$ 0.05 AMV 0.824 $P<$ 0.05 E3 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ 0.890 $P<$ 0.05 AMV 0.928 $P<$ 0.05 E4 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ 0.912 $P<$ 0.05 AMV 0.796 $P<$ 0.05 表 5 装置结果验证
Table 5 Result validation of device
受试者 年龄
(岁)患病部位 患侧 装置结果 装置预测MAS MAS评分 $\theta_{ p}$/$\theta_{\rm rom}$ AMV $\sqrt{(\Delta \theta)^{2}}$ $\sqrt{\left({\Delta a} \right)^{2}}$ $\sqrt{(\Delta \theta)^{2}+\left({\Delta a} \right)^{2}}$ S1 57 右侧脑出血 左侧 0.65 0.320 1 1 1 1 S2 46 左侧脑干梗塞 右侧 0.49 0.435 1.5 2 1.5 1.5 -
[1] Bar-On L, Molenaers G, Aertbeliën E, Monari D, Feys H, Desloovere K. The relation between spasticity and muscle behavior during the swing phase of gait in children with cerebral palsy. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 2014, 35(12):3354-3364 doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2014.07.053 [2] 王广志.肌肉痉挛定量评估的研究进展.现代康复, 2000, 4(5):650-652 http://news.medlive.cn/ns/info-progress/show-131231_181.htmlWang Guang-Zhi. The advancing of quantitative assessment of spasticity. Modern Rehabilitation, 2000, 4(5):650-652 http://news.medlive.cn/ns/info-progress/show-131231_181.html [3] Feldman R G, Young R R, Koella W P. Spasticity: Disordered Motor Control. Chicago: Year Book Medical Publishers, 1980. 485-495 [4] Ishikawa S, Okamoto S, Isogai K, Akiyama Y, Yanagihara N, Yamada Y. Wearable dummy to simulate joint impairment: severity-based assessment of simulated spasticity of knee joint. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE/SICE International Symposium on System Integration. Kobe, Japan: IEEE, 2013. 300-305 [5] Gracies J M, Brashear A, Jech R, McAllister P, Banach M, Valkovic P, Walker H, Marciniak C, Deltombe T, Skoromets A, Khatkova S, Edgley S, Gul F, Catus F, De Fer Beatrice B, Vilain C, Picaut P. Safety and efficacy of abobotulinumtoxinA for hemiparesis in adults with upper limb spasticity after stroke or traumatic brain injury:a double-blind randomised controlled trial. The Lancet Neurology, 2015, 14(10):992-1001 doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00216-1 [6] Kim J-H, Park H-S, Damiano D L. Accuracy and reliability of haptic spasticity assessment using HESS (Haptic Elbow Spasticity Simulator). In: Proceedings of the 33rd Annual International Conference of the IEEE EMBS. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2001. 8527-8530 [7] 李雪萍, 程凯, 周俊, 杨婷, 于俊龙, 陈安亮, 张红飞.表面肌电联合等速测试评定肌痉挛的临床研究.中国现代医学杂志, 2010, 20(4):605-608, 611 http://www.docin.com/p-1694078342.htmlLi Xue-Ping, Cheng Kai, Zhou Jun, Yang Ting, Yu Jun-Long, Chen An-Liang, Zhang Hong-Fei. Clinical assessment of muscle spasticity in stroke patients with surface electromyography and isokinetic assessment. China Journal of Modern Medicine, 2010, 20(4):605-608, 611 http://www.docin.com/p-1694078342.html [8] Klingels K, De Cock P, Molenaers G, Desloovere K, Huenaerts C, Jaspers E, Feys H. Upper limb motor and sensory impairments in children with hemiplegic cerebral palsy. Can they be measured reliably? Disability and Rehabilitation, 2010, 32(5):409-416 doi: 10.3109/09638280903171469?needAccess=true [9] Fleuren J F M, Voerman G E, Erren-Wolters C V, Snoek G J, Rietman J S, Hermens H J, Nene A V. Stop using the Ashworth Scale for the assessment of spasticity. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry, 2010, 81(1):46-52 http://jnnp.bmj.com/content/jnnp/81/1/46.full.pdf [10] Mehrholz J, Wagner K, Meissner D, Grundmann K, Zange C, Koch R, Pohl M. Reliability of the modified Tardieu scale and the modified Ashworth scale in adult patients with severe brain injury:a comparison study. Clinical Rehabilitation, 2015, 19(7):751-759 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/7516824_Reliability_of_the_Modified_Tardieu_Scale_and_the_Modified_Ashworth_Scale_in_adult_patients_with_severe_brain_injury_A_comparison_study [11] Kaya T, Goksel K A, Gunaydin R, Koc A, Altundal E U. Inter-rater reliability of the modified Ashworth scale and modified modified Ashworth scale in assessing poststroke elbow flexor spasticity. International Journal of Rehabilitation Research, 2011, 34(1):59-64 doi: 10.1097/MRR.0b013e32833d6cdf [12] Kim K S, Seo J H, Song C G. Portable measurement system for the objective evaluation of the spasticity of hemiplegic patients based on the tonic stretch reflex threshold. Medical Engineering & Physics, 2011, 33(1):62-69 https://www.researchgate.net/publication/47382015_Portable_measurement_system_for_the_objective_evaluation_of_the_spasticity_of_hemiplegic_patients_based_on_the_tonic_stretch_reflex_threshold [13] Abdollahi I, Taghizadeh A, Shakeri H, Eivazi M, Jaberzadeh S. The relationship between isokinetic muscle strength and spasticity in the lower limbs of stroke patients. Journal of Bodywork and Movement Therapies, 2014, 19(2):284-290 https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1360859214001296 [14] Wu Y N, Park H-S, Ren Y P, Deborah G-S, Chen J J, Zhang L Q. Measurement of elbow spasticity in stroke patients using a manual spasticity evaluator. In: Proceedings of the 28th IEEE EMBS Annual International Conference. New York, USA: IEEE, 2006. 3974-3977 [15] 宋凡, 张峰, 朱玉连, 沈建, 白玉龙, 李放, 胡永善, 吴毅.等速测试指标与改良Ashworth法用于评定肌痉挛的相关性研究.中国康复医学杂志, 2008, 23(7):615-617 http://www.doc88.com/p-9425621312124.htmlSong Fan, Zhang Feng, Zhu Yu-Lian, Shen Jian, Bai Yu-Long, Li Fang, Hu Yong-Shan, Wu Yi. Research of the correlation between the isokinetic parameters and the modified Ashworth scores in spasticity measurement. Chinese Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 2008, 23(7):615-617 http://www.doc88.com/p-9425621312124.html [16] Fujisawa T, Takagi M, Takahashi Y, Inoue K, Terada T, Kawakami Y, Komeda T. Basic research on the upper limb patient simulator. In: Proceedings of the 10th IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics. Noordwijk, The Netherlands: IEEE, 2007. 48-51 [17] Park H-S, Kim J-H, Damiano D L. Development of a haptic elbow spasticity simulator (HESS) for improving accuracy and reliability of clinical assessment of spasticity. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2012, 20(3):361-370 doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2012.2195330 [18] Takhashi Y, Komeda T, Koyama H, Yamamoto S, Arimatsu T, Kawakami Y, Inoue K, Ito Y. Development of an upper limb patient simulator for physical therapy exercise. In: Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics. Zurich, Switzerland: IEEE, 2011. 1117-1120 [19] 李林, 纪仲秋, 李艳霞, 刘威彤.关节角度重置法、运动最小阈值测量法和力量重现法的相关性研究.天津体育学院学报, 2016, 31(1):36-40 http://c.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/tjtyxyxb/2016-1.aspxLi Lin, Ji Zhong-Qiu, Li Yan-Xia, Liu Wei-Tong. Correlation between joint position sense reproduce test, the threshold of detection of movement test and force sense reproduce test. Journal of TUS, 2016, 31(1):36-40 http://c.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/tjtyxyxb/2016-1.aspx [20] Calota A, Feldman A G, Levin M F. Spasticity measurement based on tonic stretch reflex threshold in stroke using a portable device. Clinical Neurophysiology, 2008, 119(10):2329-2337 doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2008.07.215 [21] Pandyan A D, Price C I M, Rodgers H, Barnes M P, Johnson G R. Biomechanical examination of a commonly used measure of spasticity. Clinical Biomechanics, 2001, 16(10):859-865 doi: 10.1016/S0268-0033(01)00084-5 [22] Pandyan A D, Price C I M, Barnes M P, Johnson G R. A biomechanical investigation into the validity of the modified Ashworth scale as a measure of elbow spasticity. Clinical Rehabilitation, 2003, 17(3):290-294 doi: 10.1191/0269215503cr610oa [23] McCrea P H, Eng J J, Hodgson A J. Linear spring-damper model of the hypertonic elbow:reliability and validity. Journal of Neuroscience Methods, 2003, 128(1-2):121-128 doi: 10.1016/S0165-0270(03)00169-9 [24] Grow D I, Wu M N, Locastro M J, Arora S K, Bastian A J, Okamura A M. Haptic simulation of elbow joint spasticity. In:Proceedings of the 2008 Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems. Nevada, USA:IEEE, 2008. 475-476 [25] 韩京清.从PID技术到"自抗扰控制"技术.控制工程, 2002, 9(3):13-18 http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/JZDF200203004.htmHan Jing-Qing. From PID technique to active disturbances rejection control technique. Control Engineering of China, 2002, 9(3):13-18 http://mall.cnki.net/magazine/Article/JZDF200203004.htm [26] 韩建达, 谈大龙, 蒋新松.直接驱动机器人关节加速度反馈解耦控制.自动化学报, 2000, 26(3):289-295 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16059.shtmlHan Jian-Da, Tan Da-Long, Jiang Xin-Song. Joint acceleration feedback control for direct-drive robot decoupling. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2000, 26(3):289-295 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract16059.shtml -




 下载:
下载: