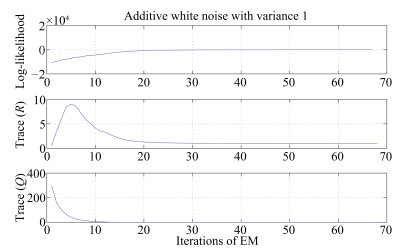
-
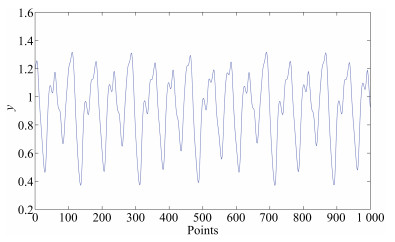
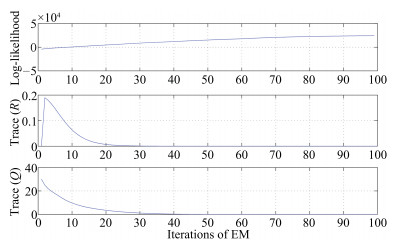
摘要: 为了利用EKF(extended Kalman filter)算法对RBF-AR(radial basis function network-based autoregressive)模型进行参数估计,重构了RBF-AR模型的网络结构,将其变换成一种新型的广义径向基函数(radial basis function,RBF)神经网络.与典型三层RBF网络结构相比,该广义RBF网络增加了线性输出加权层.为了克服基于EKF神经网络学习算法由于噪声统计特性未知导致滤波发散或者滤波精度不高的问题,利用EM(expectation maximization)算法对RBF-AR模型噪声协方差矩阵进行估计.同时,通过EKF滤波实时估计RBF-AR模型参数(系统状态),EKF平滑过程得到了更加准确的期望估计.仿真结果显示,该方法用在此变形的RBF-AR模型结构中是有效的,特别在信噪比低的情况下,估计效果比SNPOM(structured nonlinear parameter optimization method)方法好,而且还能估计出噪声方差.F检验显示了两方法估计得到的标准偏差有显著性差异.Abstract: RBF-AR (radial basis function network-based autoregressive) model is reconstructed as a new type of general radial basis function (RBF) neural network, which has additional linear output weight layer in comparison with the traditional three-layer RBF network. The extended Kalman filter (EKF) algorithm for RBF training has low filtering accuracy and divergence because of unknown prior knowledge, such as noise covariance and initial states. To overcome the drawback, the expectation maximization (EM) algorithm is used to estimate the covariance matrices of noises and the initial states. The proposed method, called the EM-EKF (expectation-maximization extended Kalman filter) algorithm, which combines the expectation maximization, extended Kalman filtering and smoothing process, is developed to estimate the parameters of the RBF-AR model, the initial conditions and the noise variances simultaneously. It is shown by the simulation tests that the EM-EKF method for the reconstructed RBF-AR network provides better results than structured nonlinear parameter optimization method (SNPOM) and the EKF, especially in low SNR (signal noise ratio). Moreover, the EM-EKF method can accurately estimate the noise variance. F test indicates there is significant difference between results obtained by the SNPOM and the EM-EKF.
-
Table Ⅰ COMPARISON RESULTS FOR MACKEY-GLASS TIME SERIES
Method MSE (Training) MSE (Testing) $R$ SNPOM 1.0800E-7 1.2600E-7 unknown EKF 1.9560E-7 2.1786E-7 0.002 (given) EKF 1.2559E-7 1.9793E-7 0.0002 (given) EM-EKF 7.1765E-8 1.2008E-7 1.8146E-7 Table Ⅱ COMPARISON RESULTS FOR MACKEY-GLASS TIME SERIES CORRUPTES BY ADDITIVE WHITE NOISE
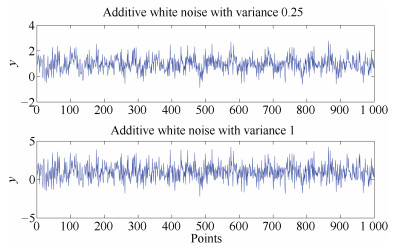
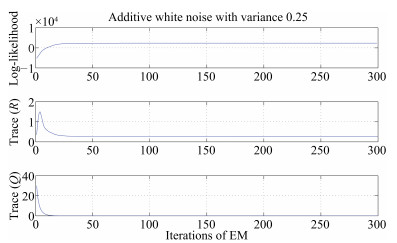
Noise variance Method MSE (Training) MSE (Testing) R 0.25 SNPOM 0.26606 0.28120 unknown EKF 0.26577 0.28082 0.2 (given) EKF 0.27343 0.28825 0.1 (given) EM-EKF 0.25750 0.27825 0.25950 1 SNPOM 0.97452 1.1644 unknown EKF 0.97215 1.1512 0.8 (given) EKF 0.98262 1.1785 0.6 (given) EM-EKF 0.96590 1.13907 1.0589 Table Ⅲ THE RESULTS OF STATISTICAL F TEST AT LEVEL 0.05
Case $F_{\alpha=0.05}$ $F$ Results Case 1 (Training) 1.16 1.4642 Reject; Difference Case 1 (Testing) 1.16 1.0105 No reject; No difference Case 2 (Training) 1.16 14.1212 Reject; Significant difference Case 2 (Testing) 1.16 9.2984 Reject; Significant difference Case 3 (Training) 1.16 37.8297 Reject; Significant difference Case 3 (Testing) 1.16 15.5751 Reject; Significant difference Table Ⅳ THE COMPUTATION TIME OF DIFFERENT METHODS (S)
Method Time SNPOM 10.690 EKF 0.40572 EM-EKF 30.766 -
[1] Z. Y. Shi, Y. Tamura, and T. Ozaki, "Nonlinear time series modelling with the radial basis function-based state-dependent autoregressive model, "Int. J. Syst. Sci. , vol. 30, no. 7, pp. 717-727, Jul. 1999. doi: 10.1080/002077299292038 [2] H. Peng, T. Ozaki, V. Haggan-Ozaki, and Y. Toyoda, "A parameter optimization method for radial basis function type models, "IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. , vol. 14, no. 2, pp. 432-438, Mar. 2003. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/18238025 [3] M. Gan, H. Peng, X. Y. Peng, X. H. Chen, and G. Inoussa, "A locally linear RBF network-based state-dependent AR model for nonlinear time series modeling, "Inform. Sci. , vol. 180, no. 22, pp. 4370-4380, Nov. 2010. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025510003300 [4] M. Gan, C. L. P. Chen, H. X. Li, and L. Chen, "Gradient radial basis function based varying-coefficient Autoregressive model for nonlinear and nonstationary time series, "IEEE Signal Proc. Lett. , vol. 22, no. 7, pp. 809-812, Jul. 2015. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6953131/ [5] H. Peng, J. Wu, G. Inoussa, Q. L. Deng, and K. Nakano, "Nonlinear system modeling and predictive control using the RBF nets-based quasi-linear ARX model, "Control Eng. Pract. , vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 59-66, Jan. 2009. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0967066108000993 [6] H. Peng, G. Kitagawa, J. Wu, and K. Ohtsu, "Multivariable RBF-ARX model-based robust MPC approach and application to thermal power plant, "Appl. Math. Model. , vol. 35, no. 7, pp. 3541-3551, Jul. 2011. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0307904X11000151 [7] M. Gan, H. Peng, and L. Y. Chen, "A global-local optimization approach to parameter estimation of RBF-type models, "Inform. Sci. , vol. 197, pp. 144-160, Aug. 2012. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0020025512000679 [8] M. Gan, H. X. Li, and H. Peng, "A variable projection approach for efficient estimation of RBF-ARX model, "IEEE Trans. Cybern. , vol. 45, no. 3, pp. 462-471, Mar. 2015. http://europepmc.org/abstract/med/24988599 [9] H. K. Wei and S. I. Amari, "Dynamics of learning near singularities in radial basis function networks, "Neural Netw. , vol. 21, no. 7, pp. 989-1005, Sep. 2008. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1411874 [10] J. S. Kim and S. Jung, "Implementation of the RBF neural chip with the back-propagation algorithm for on-line learning, "Appl. Soft Comput. , vol. 29, pp. 233-244, Apr. 2015. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568494614006620 [11] F. P. Härter and H. F. de Campos Velho, "New approach to applying neural network in nonlinear dynamic model, "Appl. Math. Model. , vol. 32, no. 12, pp. 2621-2633, Dec. 2008. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0307904X07002296 [12] H. Z. Yang, J. Li, and F. Ding, "A neural network learning algorithm of chemical process modeling based on the extended Kalman filter, "Neurocomputing, vol. 70, no. 4-6, pp. 625-632, Jan. 2007. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=1224059&CFID=448466066&CFTOKEN=67010250 [13] K. Salahshoor, S. Zakeri, and M. H. Sefat, "Stabilization of gas-lift oil wells by a nonlinear model predictive control scheme based on adaptive neural network models, "Eng. Appl. Artif. Intel. , vol. 26, no. 8, pp. 1902-1910, Sep. 2013. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2508322 [14] N. Y. Zeng, Z. D. Wang, Y. R. Li, M. Du, and X. H. Liu, "Inference of nonlinear state-space models for sandwich-type lateral flow immunoassay using extended Kalman filtering, "IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. , vol. 58, no. 7, pp. 1959-1966, Jul. 2011. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21245000 [15] J. F. G. de Freitas, M. Niranjan, and A. H. Gee, "Hierarchical Bayesian models for regularization in sequential learning, "Neural Comput. , vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 933-953, Apr. 2000. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpls/abs_all.jsp?arnumber=6789428 [16] Y. S. T. Hong, "Dynamic nonlinear state-space model with a neural network via improved sequential learning algorithm for an online real-time hydrological modeling, "J. Hydrol. , vol. 468-469, pp. 11-21, Oct. 2012. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022169412006658 [17] Y. H. Xi, H. Peng, and X. H. Chen, "A sequential learning algorithm based on adaptive particle filtering for RBF networks, "Neural Comput. Appl. , vol. 25, no. 3-4, pp. 807-814, Sep. 2014. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2662643 [18] N. Y. Zeng, Z. D. Wang, Y. R. Li, M. Du, and X. H. Liu, "A hybrid EKF and switching PSO algorithm for joint state and parameter estimation of lateral flow immunoassay models, "IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinform. , vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 321-329, Mar. -Apr. 2012. [19] N. Y. Zeng, Z. D. Wang, Y. R. Li, M. Du, and X. H. Liu, "Identification of nonlinear lateral flow immunoassay state-space models via particle filter approach, "IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. , vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 321-327, Mar. 2012. http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/6081979/ [20] M. Hürzeler and H. R. Künsch, "Approximating and maximising the likelihood for a general state-space model, "in Sequential Monte Carlo Methods in Practice, A. Doucet, N. de Freitas, and N. Gordon, Eds. New York: Springer, 2001, pp. 159-175. http://www.ams.org/mathscinet-getitem?mr=1847791 [21] N. Y. Zeng, Z. D. Wang, Y. R. Li, M. Du, J. Cao, and X. H. Liu, "Time series modeling of nano-gold immunochromatographic assay via expectation maximization algorithm, "IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. , vol. 60, no. 12, pp. 3418-3424, Dec. 2013. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23629840 [22] M. Lázaro, I. Santamaría, and C. Pantaleón, "A new EM-based training algorithm for RBF networks, "Neural Netw. , vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 69-77, Jan. 2003. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=776140 [23] C. Constantinopoulos and A. Likas, "Semi-supervised and active learning with the probabilistic RBF classifier, "Neurocomputing, vol. 71, no. 13-15, pp. 2489-2498, Aug. 2008. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0925231208002117 -




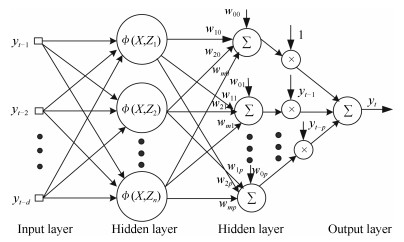
 下载:
下载: