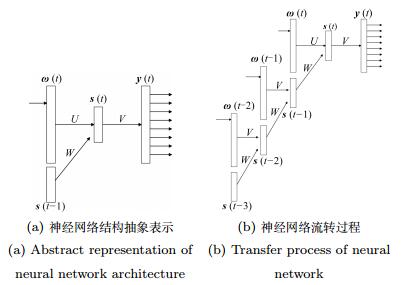
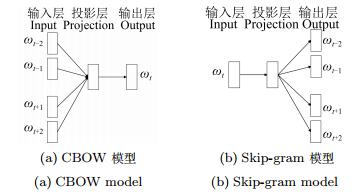
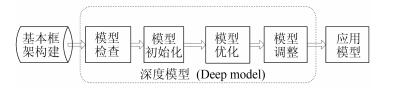
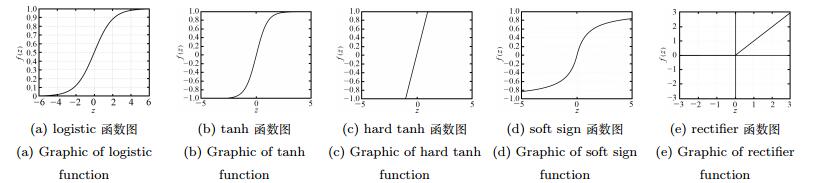
|
[1]
|
Erhan D, Bengio Y, Couville A, Manzagol P A, Vincent P, Samy B. Why does unsupervised pre-training help deep learning? Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2010, 11:625-660 http://research.google.com/pubs/archive/35536.pdf
|
|
[2]
|
孙志军, 薛磊, 许阳明, 王正.深度学习研究综述.计算机应用研究, 2012, 29(8):2806-2810 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD201501011.htmSun Zhi-Jun, Xue Lei, Xu Yang-Ming, Wang Zheng. Overview of deep learning. Application Research of Computers, 2012, 29(8):2806-2810 http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJGD201501011.htm
|
|
[3]
|
Bengio Y. Learning deep architectures for AI. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2009, 2(1):1-127 doi: 10.1561/2200000006
|
|
[4]
|
Hinton G E, Osindero S, Teh Y W. A fast learning algorithm for deep belief nets. Neural Computation, 2006, 18(7):1527-1554 doi: 10.1162/neco.2006.18.7.1527
|
|
[5]
|
Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313(5786):504-507 doi: 10.1126/science.1127647
|
|
[6]
|
Bengio Y, Lamblin P, Popovici D, Larochelle H. Greedy layer-wise training of deep networks. In:Proceedings of the 2007 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19(NIPS'06). Vancouver, Canada:MIT Press, 2007. 153-160
|
|
[7]
|
Ranzato M A, Poultney C, Chopra S, LeCun Y. Efficient learning of sparse representations with an energy-based model. In:Proceedings of the 2007 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 19(NIPS'06). Vancouver, Canada:MIT Press, 2007. 1137-1144
|
|
[8]
|
Weston J, Ratle F, Collobert R. Deep learning via semi-supervised embedding. In:Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML'08). New York, USA:ACM Press, 2008. 1168-1175
|
|
[9]
|
Srivastava N, Mansimov E, Salakhutdinov R. Unsupervised learning of video representations using LSTMs. In:Proceedings of the 32nd International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML'15). Lille, France:Omni Press, 2015. 843-852
|
|
[10]
|
Jia K, Sun L, Gao S H, Song Z, Shi B E. Laplacian auto-encoders:an explicit learning of nonlinear data manifold. Neurocomputing, 2015, 160:250-260 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.02.023
|
|
[11]
|
Chan T H, Jia K, Gao S H, Lu J W, Zeng Z N, Ma Y. PCANet:a simple deep learning baseline for image classification? IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(12):5017-5032 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2475625
|
|
[12]
|
Alain G, Bengio Y. What regularized auto-encoders learn from the data-generating distribution? The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1):3563-3593 http://www.taodocs.com/p-61696734.html
|
|
[13]
|
Srivastava N, Hinton G, Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Salakhutdinov R. Dropout:a simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1):1929-1958 http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~rsalakhu/papers/srivastava14a.pdf
|
|
[14]
|
Dosovitskiy A, Springenberg J T, Riedmiller M, Brox T. Discriminative unsupervised feature learning with convolutional neural networks. In:Proceedings of the 2014 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27(NIPS'14). Montréal, Quebec, Canada:MIT Press, 2014. 766-774
|
|
[15]
|
Sun Y, Wang X G, Tang X O. Deep learning face representation from predicting 10000 classes. In:Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, Ohio, USA:IEEE, 2014. 1891-1898
|
|
[16]
|
乔俊飞, 潘广源, 韩红桂.一种连续型深度信念网的设计与应用.自动化学报, 2015, 41(12):2138-2146 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18786.shtmlQiao Jun-Fei, Pan Guang-Yuan, Han Hong-Gui. Design and application of continuous deep belief network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12):2138-2146 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18786.shtml
|
|
[17]
|
Längkvist M, Karlsson L, Loutfi A. A review of unsupervised feature learning and deep learning for time-series modeling. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2014, 42:11-24 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2014.01.008
|
|
[18]
|
Han X F, Leung T, Jia Y Q, Sukthankar R, Berg A C. MatchNet:unifying feature and metric learning for patch-based matching. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'15). Boston, Massachusetts, USA:IEEE Press, 2015. 3279-3286
|
|
[19]
|
Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A. Going deeper with convolutions. In:Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'15). Boston, Massachusetts, USA:IEEE, 2015. 1-9
|
|
[20]
|
Denton E L, Chintala S, Szlam A, Fergus R. Deep generative image models using a Laplacian pyramid of adversarial networks. In:Proceedings of the 2015 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28(NIPS'15). Montreal, Canada:MIT Press, 2015. 1486-1494
|
|
[21]
|
Dong C, Loy C C, He K M, Tang X O. Learning a deep convolutional network for image super-resolution. In:Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV'14). Zurich, Switzerland:Springer International Publishing, 2014. 184-199
|
|
[22]
|
Nie S Q, Wang Z H, Ji Q. A generative restricted Boltzmann machine based method for high-dimensional motion data modeling. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2015, 136:14-22 doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2014.12.005
|
|
[23]
|
Jain A, Tompson J, LeCun Y, Bregler C. Modeep:a deep learning framework using motion features for human pose estimation. In:Proceedings of the 12th Asian Conference on Computer Vision (ACCV'2014). Singapore:Springer International Publishing, 2015. 302-315
|
|
[24]
|
耿杰, 范剑超, 初佳兰, 王洪玉.基于深度协同稀疏编码网络的海洋浮筏SAR图像目标识别.自动化学报, 2016, 42(4):593-604 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18846.shtmlGeng Jie, Fan Jian-Chao, Chu Jia-Lan, Wang Hong-Yu. Research on marine floating raft aquaculture SAR image target recognition based on deep collaborative sparse coding network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4):593-604 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18846.shtml
|
|
[25]
|
Erhan D, Szegedy C, Toshev A, Anguelov D. Scalable object detection using deep neural networks. In:Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR'14). Columbus, Ohio, USA:IEEE, 2014. 2155-2162
|
|
[26]
|
Qi Y J, Das S G, Collobert R, Weston J. Deep learning for character-based information extraction. In:Proceedings of the 36th European Conference on IR Research on Advances in Information Retrieval. Amsterdam, The Netherland:Springer International Publishing, 2014. 668-674
|
|
[27]
|
Nie L Q, Wang M, Zhang L M, Yan S C, Zhang B, Chua T S. Disease inference from health-related questions via sparse deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2015, 27(8):2107-2119 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2015.2399298
|
|
[28]
|
Collobert R, Weston J, Bottou L, Karlen M, Kavukcuoglu K, Kuksa P. Natural language processing (almost) from scratch. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2011, 12:2493-2537 http://jmlr.org/papers/volume12/collobert11a/collobert11a.pdf
|
|
[29]
|
Mnih A, Hinton G E. A scalable hierarchical distributed language model. In:Proceedings of the 2009 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 21(NIPS'08). Vancouver, Canada:MIT Press, 2009. 1081-1088
|
|
[30]
|
Collobert R, Weston J. A unified architecture for natural language processing:deep neural networks with multitask learning. In:Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML'08). Helsinki, Finland:ACM Press, 2008. 160-167
|
|
[31]
|
Olshausen B A, Field D J. Emergence of simple-cell receptive field properties by learning a sparse code for natural images. Nature, 1996, 381(6583):607-609 doi: 10.1038/381607a0
|
|
[32]
|
Overview of deep learning and parallel implementation, available:http://djt.qq.com/article/view/1245, June20, 2016
|
|
[33]
|
Hastad J. Computational Limitations for Small Depth Circuits. Cambridge, MA, USA:Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1987
|
|
[34]
|
Serre C, Mellot-Draznieks C, Surblé S, Audebrand N, Filinchuk Y, Férey G. Role of solvent-host interactions that lead to very large swelling of hybrid frameworks. Science, 2007, 315(5820):1828-1831 doi: 10.1126/science.1137975
|
|
[35]
|
Salakhutdinov R R, Hinton G. Deep Boltzmann machines. In:Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS'09). Florida, USA:Omni Press, 2009. 448-455
|
|
[36]
|
Bengio Y, Ducharme R, Vincent P, Jauvin C. A neural probabilistic language model. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2003, 3:1137-1155 http://www.academia.edu/7327284/A_Neural_Probabilistic_Language_Model
|
|
[37]
|
Mikolov T, Deoras A, Kombrink S, Burget L, Černocký J H. Empirical evaluation and combination of advanced language modeling techniques. In:Proceedings of the 2011 Conference of the International Speech Communication Association (INTERSPEECH'2011). Florence, Italy:ISCA Press, 2011. 605-608
|
|
[38]
|
Schwenk H, Rousseau A, Attik M. Large, pruned or continuous space language models on a GPU for statistical machine translation. In:Proceedings of the NAACL-HLT 2012 Workshop:Will We ever Really Replace the N-gram Model? on the Future of Language Modeling for HLT. Montréal, Canada:ACL Press, 2012. 11-19
|
|
[39]
|
Socher R, Huang E H, Pennington J, Ng A Y, Manning C D. Dynamic pooling and unfolding recursive autoencoders for paraphrase detection. In:Proceedings of the 2011 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 24(NIPS'11). Granada, Spain:MIT Press, 2011. 801-809
|
|
[40]
|
Socher R, Huval B, Manning C D, Ng A Y. Semantic compositionality through recursive matrix-vector spaces. In:Proceedings of the 2012 Joint Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing and Computational Natural Language Learning. Jeju Island, Korea:ACL Press, 2012. 1201-1211
|
|
[41]
|
Le Q, Mikolov T. Distributed representations of sentences and documents. In:Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML'14). Beijing, China:ACM Press, 2014. 1188-1196
|
|
[42]
|
Kim Y. Convolutional neural networks for sentence classification. In:Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'2014). Doha, Qatar:ACL Press, 2014. 1746-1751
|
|
[43]
|
Dahl G E, Yu D, Deng L, Acero A. Context-dependent pre-trained deep neural networks for large vocabulary speech recognition. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2012, 20(1):30-42 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2011.2134090
|
|
[44]
|
Mohamed A R, Dahl G E, Hinton G. Acoustic modeling using deep belief networks. IEEE Transactions on Audio, Speech, and Language Processing, 2012, 20(1):14-22 doi: 10.1109/TASL.2011.2109382
|
|
[45]
|
Mikolov T, Yih W T, Zweig G. Linguistic regularities in continuous space word representations. In:Proceedings of the 2013 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL-HLT'2013). Atlanta, Georgia:ACL Press, 2013. 746-751
|
|
[46]
|
Mikolov T, Sutskever I, Chen K, Corrado G S, Dean J. Distributed representations of words and phrases and their compositionality. In:Proceedings of the 2013 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 26(NIPS'13). Nevada, USA:MIT Press, 2013. 3111-3119
|
|
[47]
|
Mikolov T, Karafiát M, Burget L, Černocký, Khudanpur S. Recurrent neural network based language model. In:Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP'2010). Chiba, Japan:Speech Communication Press, 2010. 1045-1048
|
|
[48]
|
Mikolov T, Kombrink S, Burget L, Černocký J H, Khudanpur S. Extensions of recurrent neural network language model. In:Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP). Prague, Czech Republic:IEEE, 2011. 5528-5531
|
|
[49]
|
Mikolov T, Deoras A, Povey D, Burget L, Černocký J H. Strategies for training large scale neural network language models. In:Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Workshop on Automatic Speech Recognition and Understanding (ASRU). Waikoloa, Hawaii, USA:IEEE Press, 2011. 196-201
|
|
[50]
|
Mikolov T, Zweig G. Context dependent recurrent neural network language model. In:Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE Conference on Spoken Language Technology (SLT). Miami, Florida, USA:IEEE, 2012. 234-239
|
|
[51]
|
Socher R, Perelygin A, Wu J Y, Chuang J, Manning C D, Ng A Y, Potts C. Recursive deep models for semantic compositionality over a sentiment treebank. In:Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'2013). Seattle, USA:ACL Press, 2013. 1631-1642
|
|
[52]
|
Turian J, Ratinov L, Bengio Y. Word representations:a simple and general method for semi-supervised learning. In:Proceedings of the 48th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL'2010). Uppsala, Sweden:ACL Press, 2010. 384-394
|
|
[53]
|
Firth J R. A synopsis of linguistic theory 1930-55. Studies in Linguistic Analysis. Oxford:Philological Society, 1957. 1-32
|
|
[54]
|
Hinton G E. Learning distributed representations of concepts. In:Proceedings of the 8th Annual Conference of the Cognitive Science Society. Amherst, Massachusetts:Cognitive Science Society Press, 1986. 1-12
|
|
[55]
|
Salton G. Automatic processing of foreign language documents. Journal of the American Society for Information Science, 1970, 21(3):187-194 doi: 10.1002/(ISSN)1097-4571
|
|
[56]
|
Rapp R. Word sense discovery based on sense descriptor dissimilarity. In:Proceedings of the 9th Conference on Machine Translation Summit. New Orleans, USA:IAMT Press, 2003. 315-322
|
|
[57]
|
Turney P D. Expressing implicit semantic relations without supervision. In:Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Computational Linguistics and the 44th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (COLING and ACL 2006). Sydney, Australia:ACL Press, 2006. 313-320
|
|
[58]
|
Manning C D, Raghavan P, Schütze H. Introduction to Information Retrieval. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2008.
|
|
[59]
|
Zheng X Q, Chen H Y, Xu T Y. Deep learning for Chinese word segmentation and POS tagging. In:Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'2013). Seattle, Washington, USA:ACL Press, 2013. 647-657
|
|
[60]
|
Xu W, Rudnicky A I. Can artificial neural networks learn language models? In:Proceedings of 2000 International Conference on Spoken Language Processing (ICSLP'2000). Beijing, China:Speech Communication Press, 2000. 202-205
|
|
[61]
|
Mnih A, Hinton G. Three new graphical models for statistical language modelling. In:Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML'07). Corvallis, Oregon:ACM Press, 2007. 641-648
|
|
[62]
|
Morin F, Bengio Y. Hierarchical probabilistic neural network language model. In:Proceedings of the 10th International Workshop on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS'2005). Barbados:Omni Press, 2005. 246-252
|
|
[63]
|
Bordes A, Usunier N, Garcia-Durán A, Weston J, Yakhnenko O. Translating embeddings for modeling multi-relational data. In:Proceedings of the 2013 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 26(NIPS'13). Nevada, USA:MIT Press, 2013. 2787-2795
|
|
[64]
|
Bengio Y. Deep learning of representations for unsupervised and transfer learning. In:Proceedings of the ICML2011 Unsupervised and Transfer Learning Workshop. Bellevue, Washington, USA:ACM Press, 2012. 17-37
|
|
[65]
|
Le Q V, Ngiam J, Coates A, Lahiri A, Prochnow B, Ng A Y. On optimization methods for deep learning. In:Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML'11). Bellevue, Washington, USA:ACM Press, 2011. 67-105
|
|
[66]
|
Henderson J. Neural network probability estimation for broad coverage parsing. In:Proceedings of the 10th Conference on European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics (EACL'03). Budapest, Hungary:ACL Press, 2003. 131-138
|
|
[67]
|
Henderson J. Discriminative training of a neural network statistical parser. In:Proceedings of the 42nd Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL'2004). Barcelona, Spain:ACL Press, 2004. 95-102
|
|
[68]
|
Titov I, Henderson J. Porting statistical parsers with data-defined kernels. In:Proceedings of the 10th Conference on Computational Natural Language Learning (CoNLL-2006). New York, USA:ACL Press, 2006. 6-13
|
|
[69]
|
Titov I, Henderson J. Constituent parsing with incremental sigmoid belief networks. In:Proceedings of the 45th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL'2007). Prague, Czech Republic:ACL Press, 2007. 632-639
|
|
[70]
|
Collobert R. Deep learning for efficient discriminative parsing. In:Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics (AISTATS'2011). Fort Lauderdale, Florida, USA:Omni Press, 2011. 224-232
|
|
[71]
|
Costa F, Frasconi P, Lombardo V, Soda G. Towards incremental parsing of natural language using recursive neural networks. Applied Intelligence, 2003, 19(1-2):9-25 https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/f570/6d576037dcf6d412c65373e9c787060cd64f.pdf
|
|
[72]
|
Menchetti S, Costa F, Frasconi P, Pontil M. Wide coverage natural language processing using kernel methods and neural networks for structured data. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2005, 26(12):1896-1906 doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2005.03.011
|
|
[73]
|
Collins M. Head-driven statistical models for natural language parsing. Computational linguistics, 2003, 29(4):589-637 doi: 10.1162/089120103322753356
|
|
[74]
|
Socher R, Bauer J, Manning C D, Ng A Y. Parsing with compositional vector grammars. In:Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL'2013). Sofia, Bulgaria:ACL Press, 2013. 455-465
|
|
[75]
|
Legrand J, Collobert R. Recurrent greedy parsing with neural networks. In:Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases. Nancy, France:Springer Press, 2014. 130-144
|
|
[76]
|
Huang E H, Socher R, Manning C D, Ng A Y. Improving word representations via global context and multiple word prototypes. In:Proceedings of the 50th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL'2012). Jeju Island, Korea:ACL Press, 2012. 873-882
|
|
[77]
|
Zhou S S, Chen Q C, Wang X L. Active deep networks for semi-supervised sentiment classification. In:Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Computational Linguistics (COLING'2010). Beijing, China:ACL Press, 2010. 1515-1523
|
|
[78]
|
Glorot X, Bordes A, Bengio Y. Domain adaptation for large-scale sentiment classification:a deep learning approach. In:Proceedings of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML'11). Bellevue, Washington, USA:Omni Press, 2011. 513-520
|
|
[79]
|
Socher R, Pennington J, Huang E H, Ng A Y, Manning C D. Semi-supervised recursive autoencoders for predicting sentiment distributions. In:Proceedings of the 2011 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'2011). Edinburgh, UK:ACL Press, 2011. 151-161
|
|
[80]
|
Liu L M, Watanabe T, Sumita E, Zhao T J. Additive neural networks for statistical machine translation. In:Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL'2013). Sofa, Bulgaria:ACL Press, 2013. 791-801
|
|
[81]
|
Yang N, Liu S J, Li M, Zhou M, Yu N H. Word alignment modeling with context dependent deep neural network. In:Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL'2013). Sofa, Bulgaria:ACL Press, 2013. 166-175
|
|
[82]
|
Kalchbrenner N, Blunsom P. Recurrent continuous translation models. In:Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'2013). Seattle, Washington, USA:ACL Press, 2013. 1700-1709
|
|
[83]
|
Sutskever I, Vinyals O, Le Q V. Sequence to sequence learning with neural networks. In:Proceedings of the 2014 Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 27(NIPS'14). Montréal, Quebec, Canada:MIT Press, 2014. 3104-3112
|
|
[84]
|
Cho K, van Merriënboer B, Gulcehre C, Bahdanau D, Bougares F, Schwenk H, Bengio Y. Learning phrase representations using RNN encoder-decoder for statistical machine translation. In:Proceedings of the 2014 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP'2014). Doha, Qatar:ACL Press, 2014. 1724-1734
|
|
[85]
|
Cho K, van Merriënboer B, Bahdanau D, Bengio Y. On the properties of neural machine translation:encoder-decoder approaches. In:Proceedings of the 8th Workshop on Syntax, Semantics and Structure in Statistical Translation (SSST-8). Doha, Qatar:ACL Press, 2014. 103-111
|
|
[86]
|
Bahdanau D, Cho K, Bengio Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate. In:Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR'2015). San Diego, California, USA:arXiv Press, 2015. 1409.0473V7
|
|
[87]
|
Dong D X, Wu H, He W, Yu D H, Wang H F. Multi-task learning for multiple language translation. In:Proceedings of the 53rd Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics and the 7th International Joint Conference on Natural Language Processing. Beijing, China:ACL Press, 2015. 1723-1732
|
|
[88]
|
Pinheiro P O, Collobert R. Recurrent convolutional neural networks for scene labeling. In:Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML'14). Beijing, China, 2014. 82-90 http://wenku.baidu.com/view/b6cc3becccbff121dc368336.html
|
|
[89]
|
Le Q V. Building high-level features using large scale unsupervised learning. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Vancouver, BC:IEEE, 2013. 8595-8598
|
|
[90]
|
田渊栋.阿法狗围棋系统的简要分析.自动化学报, 2016, 42(5):671-675 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18856.shtmlTian Yuan-Dong. A simple analysis of AlphaGo. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5):671-675 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18856.shtml
|




 下载:
下载: