An Improved Quantum Differential Evolution Algorithm for Optimization and Control in Power Systems Including DGs
-
摘要: 差分进化算法(DE)已被证明为解决无功优化问题的有效方法.随着越来越多的分布式电源并网,对配电网潮流、电压均有一定改变,同时也影响了DE的鲁棒性和性能.本文在研究DE基础上,针对其收敛过早、局部搜索能力较差的缺陷,分析了量子计算思想和人工蜂群算法的优势,提出改进量子差分进化混合算法(IQDE).通过量子编码思想提高了种群个体的多样性,人工蜂群算法的观察蜂加速进化操作和侦查蜂随机搜索操作分别提高了算法的局部搜索和全局搜索性能.建立以有功网损最小为目标的数学模型,将IQDE算法和DE算法分别用于14节点和30节点标准数据集进行大量仿真实验.实验结果表明,IQDE算法用更少的收敛时间、更小的种群规模便可以获得与DE算法相同甚至更佳的优化效果,并且可以很好的应用于解决难分布式电源的配电网无功优化问题.Abstract: Differential evolution algorithm (DE) has been proved to be an effective way for solving the optimal reactive power flow (ORPF) problem. As distributed generations (DGs) are introduced into the system, there is a certain impact on power flow and voltage of the power system, which affects the robustness and effectiveness of DE. On the basis of DE, aiming at its limitation of premature convergence and poor search ability, this paper discusses about how to improve it with quantum encoding and artificial bee colony (ABC) algorithm and proposes a hybrid algorithm, which is called improved quantum differential evolution algorithm (IQDE). The idea of quantum encoding increases the individual diversity while the accelerating evolution operation of the onlooker bees improves local search ability of DE. At the same time, the random search operation of the scout bees improves global search ability of DE. In the last, the effectiveness of IQDE is verified by simulations on the IEEE 14-bus system and 30-bus system including DGs. The experimental results show that with less convergence time and smaller population size, IQDE can obtain an even or better optimization effect compared with DE and can be applied to ORPF problem of power system including DGs.
-
Key words:
- Artificial bee colony /
- differential evolution /
- optimal reactive power flow /
- quantum /
- distributed generation (DG)
-
Table Ⅰ Number of Control Variables of IEEE 14-Bus System
Variable Number T 3 U 5 Q 2 SUM 10 Table Ⅱ Setting of Control Variables of IEEE 14-Bus System
Variable Min Max Step T 0.9 1.1 0.01 U 0.9 1.1 - Q 0 0.18 0.06 Table Ⅲ Constraints of The State Variables of IEEE 14-Bus
Node Min (MVar) Max (MVar) 1 0 10 2 -40 50 5 -40 40 8 -10 40 11 -6 24 13 -6 24 Table Ⅳ Statistics of Results for DE and IQDE (IEEE 14-Bus)
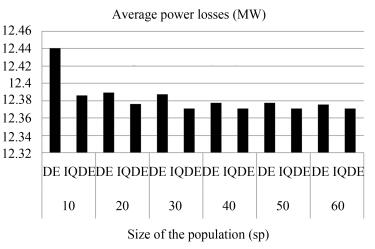
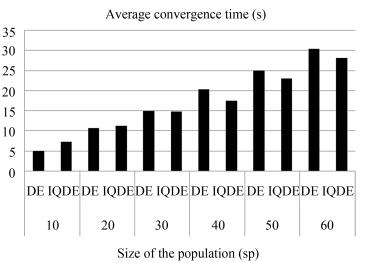
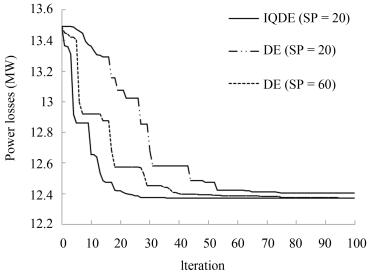
SP Algorithm Lossmin Lossmax Lossavg Timemin Timemax Timeavg 10 DE 12.3714 13.1578 12.4401 3.8977 5.3590 4.9267 IQDE 12.3712 12.5450 12.3858 4.9335 9.0550 7.2024 20 DE 12.3713 12.6364 12.3892 8.7948 9.9069 10.6250 IQDE 12.3712 12.4035 12.3761 7.8281 14.6796 11.2216 30 DE 12.3712 12.549 12.3876 12.569 15.7014 14.8099 IQDE 12.3712 12.3712 12.3712 12.1678 17.7190 14.7212 40 DE 12.3712 12.4463 12.3776 16.6632 21.4070 20.2090 IQDE 12.3712 12.3712 12.3712 15.2144 21.7840 17.3987 50 DE 12.3712 12.4319 12.3774 19.3238 26.4667 25.0056 IQDE 12.3712 12.3712 12.3712 19.0269 26.7894 22.9460 60 DE 12.3712 12.399 12.3754 25.2242 33.3440 30.3782 IQDE 12.3712 12.3712 12.3712 24.4536 33.4038 28.0544 Table Ⅴ Control Variable Setting and PLOSS Before and After Optimization for IEEE 14-Bus System
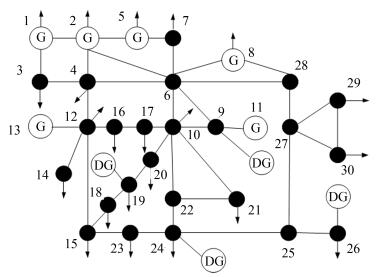
U1 U2 U3 U6 U8 T4 T5 T7 Q9 Q14 Ploss Before 1.06 1.045 1.01 1.07 1.09 0.978 0.969 0.932 18 18 13.393 After 1.1 1.0779 1.0465 1.1 1.1 1.06 0.9 1.03 18 6 12.3712 Table Ⅵ Number of Control Variables of IEEE 30-Bus System
Variable Number T 4 U 6 Q 2 SUM 12 Table Ⅶ Setting of Control Variables of IEEE 30-Bus System
Variable Minimum Maximum Step T 0.9 1.1 0.02 U 0.9 1.1 - Q9 0 0.2 0.05 Q24 0 0.04 0.01 Table Ⅷ Constraints of the State Variables of 30-Bus
Node Min (MVar) Max (MVar) 1 0 10 2 -40 50 5 -40 40 8 -10 40 11 -6 24 13 -6 24 Table Ⅸ Statistics of Results for DE and IQDE (IEEE 14-Bus)
Node Qout(MVar) Qlow Qup Pout (MW) Plow Pup 9 0.0137 -0.012 0.025 0.15 0.11 0.19 19 0.0554 -0.013 0.0689 0.25 0.1 0.45 24 0.01 -0.0069 0.02 0.09 0.05 0.15 26 0.0425 -0.15 0.0638 0.185 0.124 0.32 Table Ⅹ Statistics of Trial Results for IQDE in 30-Bus System Containing DGS
No. Ploss Time No. Ploss Time No. Ploss Time 1 16.2163 24.2024 11 16.2163 29.7159 21 16.2164 28.0426 2 16.2163 25.9639 12 16.2163 29.4342 22 16.2163 23.9344 3 16.2164 34.057 13 16.2163 27.2983 23 16.2166 33.3986 4 16.2163 28.0157 14 16.2163 29.5571 24 16.2163 28.6112 5 16.2163 30.1713 15 16.2166 34.6243 25 16.2164 23.7194 6 16.2163 26.3804 16 16.2163 30.1448 26 16.2163 24.2563 7 16.2165 31.7187 17 16.2164 25.1229 27 16.2164 32.3472 8 16.2163 29.4458 18 16.2163 25.7156 28 16.2163 24.8397 9 16.2163 25.2483 19 16.2164 33.2381 29 16.2164 28.5767 10 16.2165 33.7229 20 16.2163 25.9665 30 16.2166 33.8194 Table Ⅺ Statistics of Trial Results (IEEE 30-Bus)
Results Average Min Max Ploss 16.2164 16.2163 16.2166 Time 28.7097 23.7194 34.6243 Table Ⅻ Statistics of Trial Results for IQDE in 30-Bus System Containing DGS
U1 U2 U5 U8 U11 U13 T11 T12 T15 T36 Q10 Q24 P1 1.06 1.045 1.01 1.01 1.082 1.071 1.06 1.04 0.96 1.04 10 3 P2 1.1 1.0759 1.0431 1.0462 1.1 1.1 0.9 1 1.02 0.9 20 4 -
[1] X. Y. Yin, X. Yan, X, Liu, and C. L. Wang, "Reactive power optimization based on improved hybrid genetic algorithm, " J. Northeast Dianli Univ. , vol. 34, no. 3, pp. 48-53, Jun. 2014. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-CGCZ201101020.htm [2] T. Y. Xiang, Q. S. Zhou, F. P. Li, and Y. Wang, "Research on niche genetic algorithm for Reactive Power Optimization, " Proc. CSEE, vol. 25, no. 17, pp. 48-51, Sep. 2005. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-ZGDC200517010.htm [3] M. Varadarajan and K. S. Swarup, "Network loss minimization with voltage security using differential evolution, " Electr. Power Syst. Res. , vol. 78, no. 5, pp. 815-823, May2008. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/223544555_Network_loss_minimization_with_voltage_security_using_differential_evolution [4] M. Basu, "Optimal power flow with FACTS devices using differential evolution, " Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. , vol. 30, no. 2, pp. 150-156, Jan. 2008. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/222751245_Optimal_power_flow_with_FACTS_devices_using_differential_evolution [5] Y. T. Liu, L. Ma, and J. J. Zhang, "GA/SA/TS hybrid algorithms for reactive power optimization, " Proc. the IEEE Power Engineering Society Summer Meeting, Seattle, WA, USA, 2000, 245-249. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3862451_GASATS_hybrid_algorithms_for_reactive_power_optimization [6] B. Zhao, C. X. Guo, and Y. J. Cao, "A multiagent-based particle swarm optimization approach for optimal reactive power dispatch, " IEEE Trans. on Power Syst. , vol. 20, no. 2, pp. 1070-1078, 2005. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3267300_A_multiagent-based_particle_swarm_optimization_approach_for_optimal_reactive_power_dispatch [7] G. F. Fang, H. X. Wang, and X. S. Huang, "An improved genetic algorithm for reactive power optimization, " Proc. the EPSA, vol. 15, no. 4, pp. 15-18, Aug. 2003. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-DLZD200304004.htm [8] S. F. Wang, Z. P. Wan, H. Fan, C. Y. Xiang, and Y. G. Huang, "Reactive power optimization model and its hybrid algorithm based on bilevel programming, " Power Syst. Technol. , vol. 29, no. 9, pp. 22-25, May. 2005. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290751059_Reactive_power_optimization_modeland_its_hybrid_algorithm_based_on_bilevel_programming [9] W. Liu, X. L. Liang, and X. L. An, "Power system reactive power optimization based on BEMPSO, " Power Syst. Protect. Control, vol. 38, no. 7, pp. 16-21, Apr. 2010. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-JDQW201007006.htm [10] L. F. Zheng, J. Y. Chen, H. Lin, S. L. Le, and F. Chen, "Reactive power optimization based on quantum particle swarm optimization in electrical power system, " Central China Electr. Power, vol. 24, no. 2, pp. 16-19, 2011. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTOTAL-HZDL201102005.htm [11] B. Li, "Research of distribution reactive power optimization based on modified differential evolution algorithm, " M. S. thesis, North China Electr. Power Univ. , Beijing, China, 2012. [12] D. Devaraj and J. P. Roselyn, "Genetic algorithm based reactive power dispatch for voltage stability improvement, " Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. , vol. 32, no. 10, pp. 1151-1156, Dec. 2010. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229092065_Genetic_algorithm_based_reactive_power_dispatch_for_voltage_stability_improvement [13] Z. C. Hu, X. F. Wang, and G. Taylor, "Stochastic optimal reactive power dispatch: formulation and solution method, " Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. , vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 615-62, Jul. 2010. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/245214843_Stochastic_optimal_reactive_power_dispatch_Formulation_and_solution_method [14] T. Malakar and S. K. Goswami, "Active and reactive dispatch with minimum control movements, " Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 78-87, Jan. 2013. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256970308_Active_and_reactive_dispatch_with_minimum_control_movements [15] R. Storn and K. Price, "Differential evolution-a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces, " J. Glob. Optim. , vol. 11, no. 4, pp. 341-359, Dec. 1997. [16] W. F. Gao, S. Y. Liu, and L. L. Huang, "A novel artificial bee colony algorithm based on modified search equation and orthogonal learning, " IEEE Trans. Cybernet. , vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 1011-1024, Jun. 2013. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/232533895_A_Novel_Artificial_Bee_Colony_Algorithm_Based_on_Modified_Search_Equation_and_Orthogonal_Learning [17] F. S. Abu-Mouti and M. E. El-Hawary, "Optimal distributed generation allocation and sizing in distribution systems via artificial bee colony algorithm, " IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. , vol. 26, no. 4, pp. 2090-2101, Oct. 2011. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/252062867_Optimal_Distributed_Generation_Allocation_and_Sizing_in_Distribution_Systems_via_Artificial_Bee_Colony_Algorithm [18] R. W. Keyes, "Quantum computing and digital computing, " IEEE Trans. Electron Devices, vol. 57, no. 8, pp. 2041, Aug. 2010. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260512239_Quantum_Computing_and_Digital_Computing -




 下载:
下载: