A Gender Classification Model Based on Cross-connected Convolutional Neural Networks
-
摘要: 为提高性别分类准确率, 在传统卷积神经网络(Convolutional neural network, CNN)的基础上, 提出一个跨连卷积神经网络(Cross-connected CNN, CCNN)模型. 该模型是一个9层的网络结构, 包含输入层、6个由卷积层和池化层交错构成的隐含层、全连接层和输出层, 其中允许第2个池化层跨过两个层直接与全连接层相连接. 在10个人脸数据集上的性别分类实验结果表明, 跨连卷积网络的准确率均不低于传统卷积网络.Abstract: To improve gender classification accuracy, we propose a cross-connected convolutional neural network (CCNN) based on traditional convolutional neural networks (CNN). The proposed model is a 9-layer structure composed of an input layer, six hidden layers (i.e., three convolutional layers alternating with three pooling layers), a fully-connected layer and an output layer, where the second pooling layer is allowed to directly connect to the fully-connected layer across two layers. Experimental results in ten face datasets show that our model can achieve gender classification accuracies not lower than those of the convolutional neural networks.
-
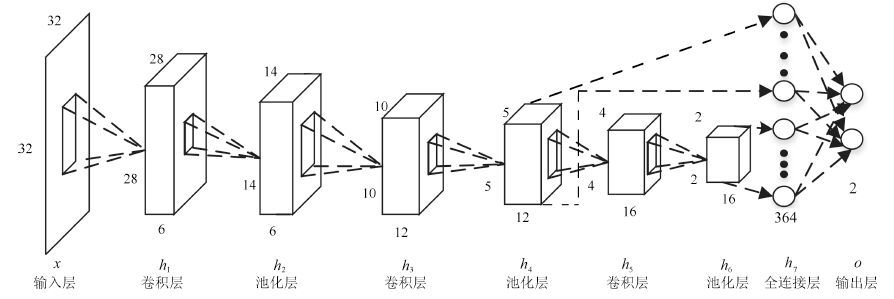
表 1 CCNN 的网络描述
Table 1 Description of the CCNN
Layer Type Patch size Stride Output size x Input 32×32 h1 Convolution 5×5 1 28×28×6 h2 Mean pooling 2×2 2 14×14×6 h3 Convolution 5×5 1 10×10×12 h4 Mean pooling 2×2 2 5×5×12 h5 Convolution 2×2 1 4×4×16 h6 Mean pooling 2×2 2 2×2×16 h7 Fully-connected 364 o Output 2 表 2 实验数据集的训练集和测试集信息描述
Table 2 Number of training samples and testing samples of the experiments
数据集 训练集 测试集 男 女 混合 男 女 混合 UMIST 209 57 266 95 19 114 ORL 320 30 350 40 10 50 Georgia Tech 450 75 525 195 30 225 FERET 658 532 1 190 105 105 Extended Yale B 1 280 384 1 664 576 192 768 AR 910 910 1 820 390 390 780 Faces94 2 000 400 2 400 660 20 680 LFW 8 000 1 900 9 900 2 000 800 2 800 MORPH 40 997 7 102 48 099 3 000 1 000 4 000 CelebFaces+ 27 887 37 113 65 000 2 500 2 500 5 000 表 3 CNN 和CCNN 在10 个数据集上的分类准确率(%)
Table 3 Classi¯cation accuracies of CNN and CCNN in ten datasets (%)
数据集 CNN CCNN UMIST 96.49 99.20 ORL 98 98.00 Georgia Tech 97.6 97.78 FERET 94.77 96.44 Extended Yale B 98.53 98.82 AR 98.71 98.71 Faces94 96.46 97.35 LFW 87 87.86 MORPH 92.73 94.56 CelebFaces+ 85.18 88.70 表 4 CNN 和CCNN 在4 个数据集上的分类准确率(%)
Table 4 Classi¯cation accuracies of CNN and CCNN in four datasets (%)
数据集 CNN CCNN 男 女 混合 男 女 混合 Georgia Tech 99.49 95.71 97.6 99.49 96.07 97.78 Extended Yale B 100 97.06 98.53 100 97.64 98.82 Faces94 98.48 94.44 96.46 100 94.7 97.35 LFW 95 79 87 96.8 78.92 87.86 表 5 CCNN 在不同跨连方式的分类准确率(%)
Table 5 Classif cation accuracies of the CCNN withdifferent cross-connections (%)
数据集 h2-h7 h3-h7 h4-h7 h5-h7 Georgia Tech 97.96 97.84 97.78 97.33 AR 98.85 98.85 98.71 98.59 Faces94 97.5 97.35 97.35 97.35 LFW 88.13 88.04 87.86 87.86 MORPH 94.63 94.63 94.56 94.45 -
[1] Golomb B A, Lawrence D T, Sejnowksi T J. SEXNET: a neural network identifies sex from human faces. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Colorado, USA: Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc., 1991. 572-579 [2] Brunelli R, Poggio T. HyberBF networks for gender classification. In: Proceedings of the 1992 DARPA Image Understanding Workshop. Detroit, USA, 1992. 311-314 [3] Tamura S, Kawai H, Mitsumoto H. Male/female identification from 8×6 very low resolution face images by neural network. Pattern Recognition, 1996, 29(2): 331-335 [4] Jiao Y B, Yang J C, Fang Z J, Xie S J, Park D S. Comparing studies of learning methods for human face gender recognition. In: Proceedings of the 7th Chinese Conference on Biometric Recognition (CCBR). Guangzhou, China: Springer, 2012. 67-74 [5] Verma A, Vig L. Using convolutional neural networks to discover cogntively validated features for gender classification. In: Proceedings of the 2014 International Conference on Soft Computing and Machine Intelligence (SCMI). New Delhi, India: IEEE, 2014. 33-37 [6] Hinton G E, Salakhutdinov R R. Reducing the dimensionality of data with neural networks. Science, 2006, 313(5786): 504-507 [7] 魏伟波, 洪丹枫, 潘振宽, 吴鑫. 基于区域特征映射的模糊掌纹识别方法. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(2): 386-395Wei Wei-Bo, Hong Dan-Feng, Pan Zhen-Kuan, Wu Xin. Blurred palmprint recognition algorithm based on region feature map. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(2): 386-395 [8] Tivive F H C, Bouzerdoum A. A gender recognition system using shunting inhibitory convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2006 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Vancouver, BC: IEEE, 2006. 5336-5341 [9] Ciresan D C, Meier U, Gambardella L M, Schmidhuber J. Convolutional neural network committees for handwritten character classification. In: Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition. Beijing, China: IEEE, 2011. 1135-1139 [10] Khalajzadeh H, Mansouri M, Teshnehlab M. Face recognition using convolutional neural network and simple logistic classifier. In: Proceedings of the 17th Online World Conference on Soft Computing in Industrial Applications. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2014. 197-207 [11] Fan J, Xu W, Wu Y, Gong Y H. Human tracking using convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 21(10): 1610-1623 [12] Jin J Q, Fu K, Zhang C S. Traffic sign recognition with hinge loss trained convolutional neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2014, 15(5): 1991-2000 [13] Xu C Y, Lu C Y, Liang X D, Gao J B, Zheng W, Wang T J, Yan S C. Multi-loss regularized deep neural network. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, DOI: 10.1109/TCSVT.2015.2477937 [14] Krizhevsky A, Sutshever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Lake Tahoe, USA: Curran Associates, Inc., 2012. 4-13 [15] Szegedy C, Liu W, Jia Y Q, Sermanet P, Reed S, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Vanhoucke V, Rabinovich A. Going deeper with convolutions. arXiv: 1409.4842, 2014. [16] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. arXiv: 1512.03385, 2015. [17] 随婷婷, 王晓峰. 一种基于CLMF的深度卷积神经网络模型. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(6): 875-882Sui Ting-Ting, Wang Xiao-Feng. Convolutional neural network with candidate location and multi-feature fusion. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(6): 875-882 [18] Zhong S H, Liu Y, Ren F F, Zhang J H, Ren T W. Video saliency detection via dynamic consistent spatio-temporal attention modelling. In: Proceedings of the 2013 AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Bellevue, USA: AAAI, 2013. 1063-1069 [19] 齐美彬, 檀胜顺, 王运侠, 刘皓, 蒋建国. 基于多特征子空间与核学习的行人再识别. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(2): 299-308Qi Mei-Bin, Tan Sheng-Shun, Wang Yun-Xia, Liu Hao, Jiang Jian-Guo. Multi-feature subspace and kernel learning for person re-identification. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(2): 299-308 [20] Sun Y, Wang X G, Tang X O. Deep learning face representation from predicting 10000 classes. In: Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Columbus, OH: IEEE. 2014. 1891-1898 [21] Hubel D H, Wiesel T N. Receptive fields, binocular interaction and functional architecture in the cat's visual cortex. Journal of Physiology, 1962, 160(1): 106-154 [22] Fukushima K, Miyake S, Ito T. Neocognitron: a neural network model for a mechanism of visual pattern recognition. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, 1983, SMC-13(5): 826-834 [23] LeCun Y, Bottou L, Bengio Y, Haffner P. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86(11): 2278-2324 [24] Graham D B, Allinson N M. Characterising virtual eigensignatures for general purpose face recognition. Face Recognition: from Theory to Applications. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 1998. 446-456 [25] Chen L, Man H, Nefian A V. Face recognition based on multi-class mapping of Fisher scores. Pattern Recognition, 2005, 38(6): 799-811 [26] Lee K C, Ho J, Kriegman D J. Acquiring linear subspaces for face recognition under variable lighting. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(5): 684-698 [27] Maetinez A M, Kak A C. PCA versus LDA. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2001, 23(2): 228-233 [28] Huang G B, Ramesh M, Berg T, Learned-Miller E. Labeled Faces in the Wild: a Database for Studying Face Recognition in Unconstrained Environment, Technical Report 07-49, University of Massachusetts, Amherst, USA, 2007. [29] Liu Z W, Luo P, Wang X G, Tang X O. Deep learning face attributes in the wild. In: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 3730-3738 -




 下载:
下载:


