-
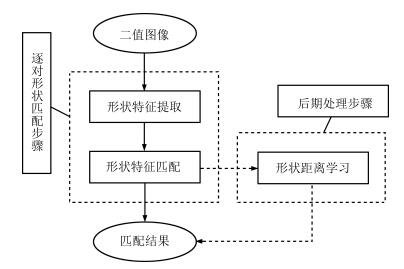
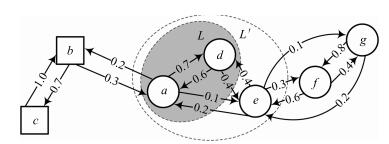
摘要: 形状距离学习是形状匹配框架中引入的后处理步骤, 能够有效改善逐对计算得到的形状间距离.利用期望首达时间分析形状间相似度可能导致距离更新不准确, 针对这一问题提出了一种基于广义期望首达时间 (Generalized mean first-passage time, GMFPT) 的形状距离学习方法.将形状样本集合视作状态空间, 广义期望首达时间表示质点由一个状态转移至指定状态集合所需的平均时间步长, 本文将其视作更新后的形状间距离.通过引入广义期望首达时间, 形状距离学习方法能够有效地分析上下文相关的形状相似度, 显式地挖掘样本空间流形中的最短路径, 并消除冗余上下文形状信息的影响.将所提出的方法应用到不同形状数据集中进行仿真实验, 本文方法比其他方法能够得到更准确的形状检索结果.Abstract: With the help of shape distance learning introduced into shape matching framework as a post-processing procedure, shape distances obtained by pairwise shape similarity analysis can be improved effectively. A novel shape distance learning method based on generalized mean first-passage time (GMFPT) is proposed to solve the problem of inaccurate matching results caused by mean first-passage time. Given a set of shapes as the state space, the generalized mean first-passage time, which is regarded as the updated shape distance, is used to represent the average time step from one state to a certain set of states. With the generalized mean first-passage time introduced into the distance learning algorithms, context-sensitive similarities can be evaluated effectively, and the shortest paths on the distance manifold can be explicitly captured without redundant context. Simulation experiments are carried out on different shape datasets with the proposed method, and the results demonstrate that the retrieval score can be improved significantly.
-
表 1 Kimia-216数据集在不同方法下检索结果比较
Table 1 Comparison of retrieval rates for different algorithms tested on Kimia-216 database
方法 1st 2nd 3rd 4th 5th 6th 7th 8th 9th 10th 11th 全部 SC 216 216 215 210 210 209 208 204 200 191 175 2 254 IDSC 216 216 215 211 211 210 211 207 203 198 185 2 283 SC + LP 216 216 214 212 211 211 215 209 209 206 197 2 316 IDSC + LP 216 216 214 211 213 213 212 210 207 208 203 2 323 SC + MD 215 215 215 213 212 212 214 211 211 209 208 2 335 IDSC + MD 215 215 215 211 212 213 212 212 207 209 209 2 330 SC + MFPT 216 216 216 212 212 212 212 212 212 211 212 2 343 IDSC + MFPT 216 216 216 212 212 212 212 212 212 212 212 2 344 SC + GMFPT 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 2 376 IDSC + GMFPT 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 216 2 376 表 2 Tari-1000数据集在不同方法下的结果比较
Table 2 Comparison of results for different algorithms tested on Tari-1000 database
方法 检索精度 (%) SC 88.01 IDSC 90.43 SC + LP 94.22 IDSC + LP 96.44 SC + MD 94.98 IDSC + MD 98.49 SC + MFPT 97.02 IDSC + MFPT 99.11 SC + GMFPT 97.15 IDSC + GMFPT 99.27 表 3 MPEG-7数据集在不同方法下的结果比较
Table 3 Comparison of results for different algorithms tested on MPEG-7 database
方法 检索精度 (Bullseye) (%) IDSC + LP[5] 91.61 SC + GM + Meta Descriptor[10] 92.51 IDSC + LCDP[6] 93.32 IDSC + Mutual Graph[22] 93.40 SC + MFPT[13] 94.04 ASC + LCDP[8] 95.96 ASC + TPG Diffusion[11] 96.47 SC + IDSC + Co-transduction[23] 97.72 IDSC + SSC+LCDP[9] 98.85 AIR + TPG Diffusion[11] 99.99 AIR + Generic Diffusion Framework[12] 100.00 AIR + GMFPT 100.00 表 4 不同方法下的时间复杂度比较
Table 4 Comparison of the time complexities for different algorithms
-
[1] Hu R X, Jia W, Ling H B, Zhao Y, Gui J. Angular pattern and binary angular pattern for shape retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2014, 23(3):1118-1127 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2286330 [2] Hong B W, Soatto S. Shape matching using multiscale integral invariants. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(1):151-160 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2342215 [3] 周瑜, 刘俊涛, 白翔.形状匹配方法研究与展望.自动化学报, 2012, 38(6):889-910 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00889Zhou Yu, Liu Jun-Tao, Bai Xiang. Research and perspective on shape matching. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(6):889-910 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.00889 [4] Hasanbelliu E, Sanchez G L, Principe J C. Information theoretic shape matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(12):2436-2451 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2324585 [5] Bai X, Yang X W, Latecki L J, Liu W Y, Tu Z W. Learning context-sensitive shape similarity by graph transduction. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(5):861-874 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.85 [6] Yang X W, Koknar-Tezel S, Latecki L J. Locally constrained diffusion process on locally densified distance spaces with applications to shape retrieval. In:Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, USA:IEEE, 2009. 357-364 [7] Yang X W, Bai X, Latecki L J, Tu Z W. Improving shape retrieval by learning graph transduction. In:Proceedings of the 10th European Conference on Computer Vision. Marseille, France:Springer, 2008. 788-801 [8] Ling H B, Yang X W, Latecki L J. Balancing deformability and discriminability for shape matching. In:Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision. Crete, Greece:Springer, 2010. 411-424 [9] Premachandran V, Kakarala R. Perceptually motivated shape context which uses shape interiors. Pattern Recognition, 2013, 46(8):2092-2102 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2013.01.030 [10] Egozi A, Keller Y, Guterman H. Improving shape retrieval by spectral matching and meta similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2010, 19(5):1319-1327 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2040448 [11] Yang X W, Prasad L, Latecki L J. Affinity learning with diffusion on tensor product graph. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(1):28-38 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2012.60 [12] Donoser M, Bischof H. Diffusion processes for retrieval revisited. In:Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Portland, USA:IEEE, 2013. 1320-1327 [13] 郑丹晨, 韩敏.基于期望首达时间的形状距离学习算法.自动化学报, 2014, 40(1):92-99 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18270.shtmlZheng Dan-Chen, Han Min. Learning shape distance based on mean first-passage time. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(1):92-99 http://www.aas.net.cn/CN/abstract/abstract18270.shtml [14] Wang J Y, Li Y P, Bai X, Zhang Y, Wang C, Tang N. Learning context-sensitive similarity by shortest path propagation. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44(10-11):2367-2374 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.02.007 [15] Hopcroft J, Tarjan R. Efficient algorithms for graph manipulation. Communications of the ACM, 1973, 16(6):372-378 doi: 10.1145/362248.362272 [16] Belongie S, Malik J, Puzicha J. Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(4):509-522 doi: 10.1109/34.993558 [17] Ling H B, Jacobs D W. Shape classification using the inner-distance. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(2):286-299 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.41 [18] Gopalan R, Turaga P, Chellappa R. Articulation-invariant representation of non-planar shapes. In:Proceedings of the 11th European Conference on Computer Vision. Crete, Greece:Springer, 2010. 286-299 [19] Sebastian T B, Klein P N, Kimia B B. Recognition of shapes by editing their shock graphs. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2004, 26(5):550-571 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2004.1273924 [20] Baseski E, Erdem A, Tari S. Dissimilarity between two skeletal trees in a context. Pattern Recognition, 2009, 42(3):370-385 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2008.05.022 [21] Latecki L J, Lakamper R, Eckhardt T. Shape descriptors for non-rigid shapes with a single closed contour. In:Proceedings of the 2000 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hilton Head, USA:IEEE, 2000, 1:424-429 [22] Kontschieder P, Donoser M, Bischof H. Beyond pairwise shape similarity analysis. In:Proceedings of the 9th Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Xi'an, China:Springer, 2010. 655-666 [23] Bai X, Wang B, Yao C, Liu W Y, Tu Z W. Co-transduction for shape retrieval. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(5):2747-2757 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2011.2170082 -




 下载:
下载: