A Hierarchical Control Scheme for Formation Transportation of Multiple Quadrotors With Propeller Speed Constraints
-
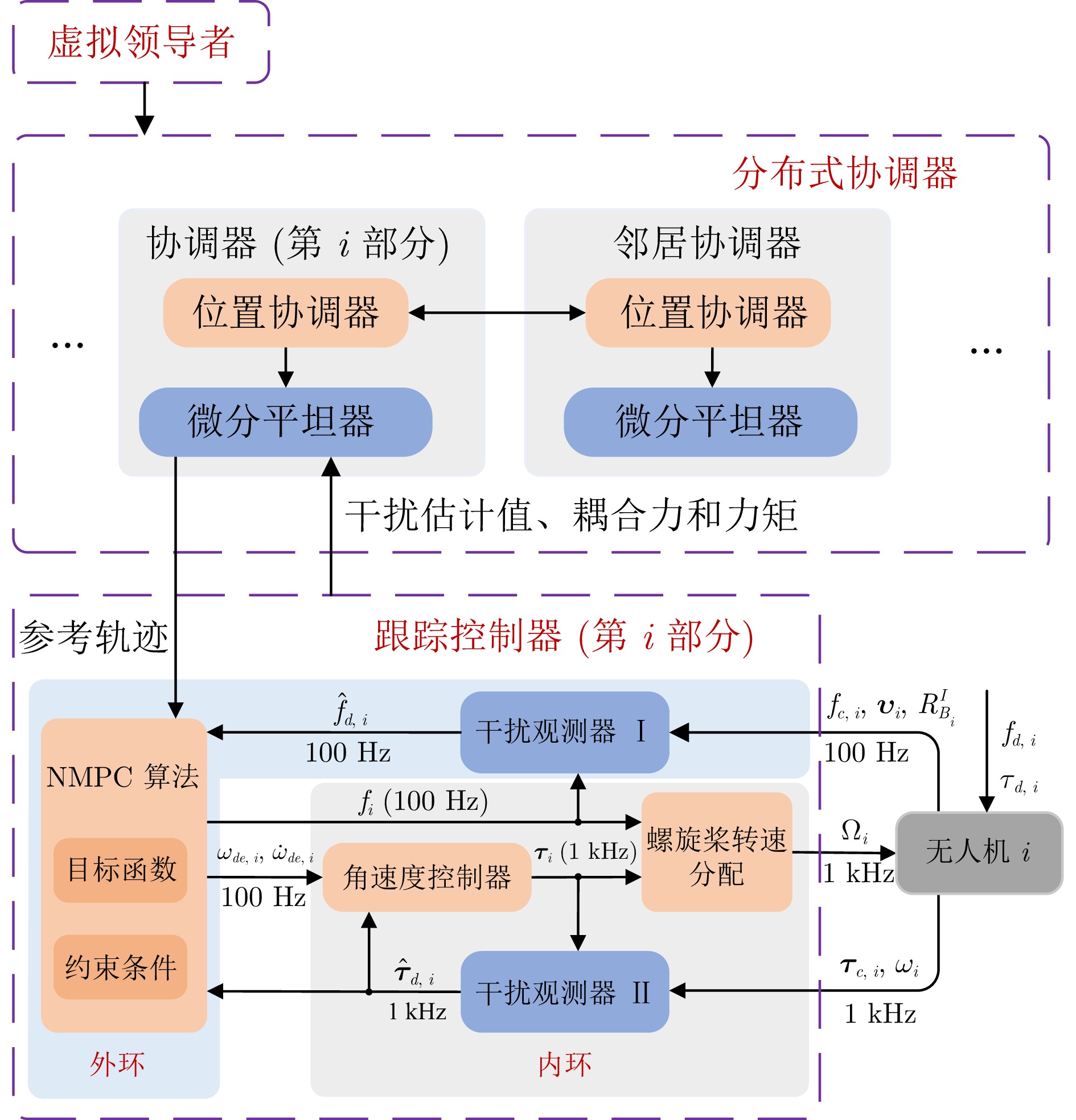
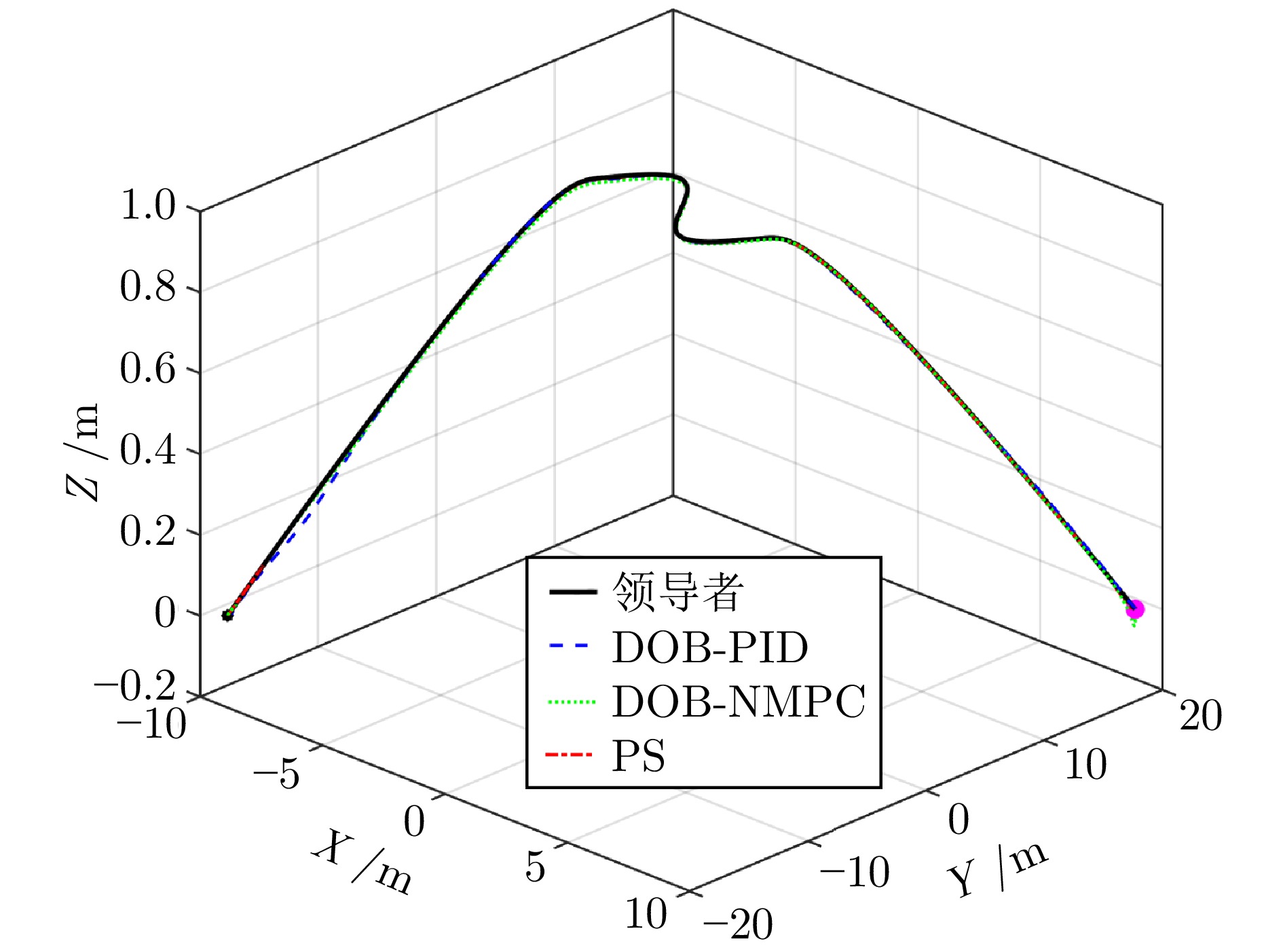
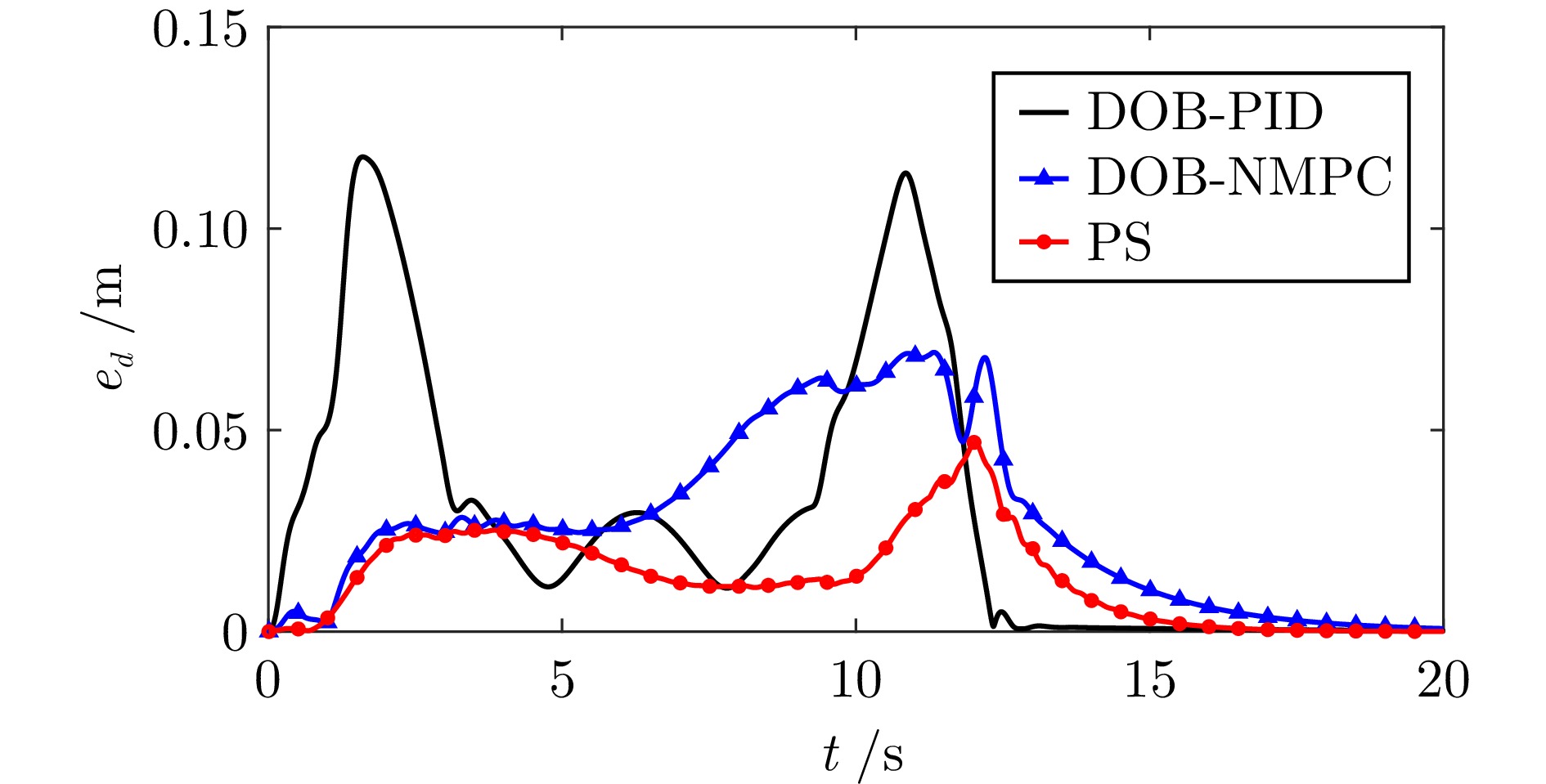
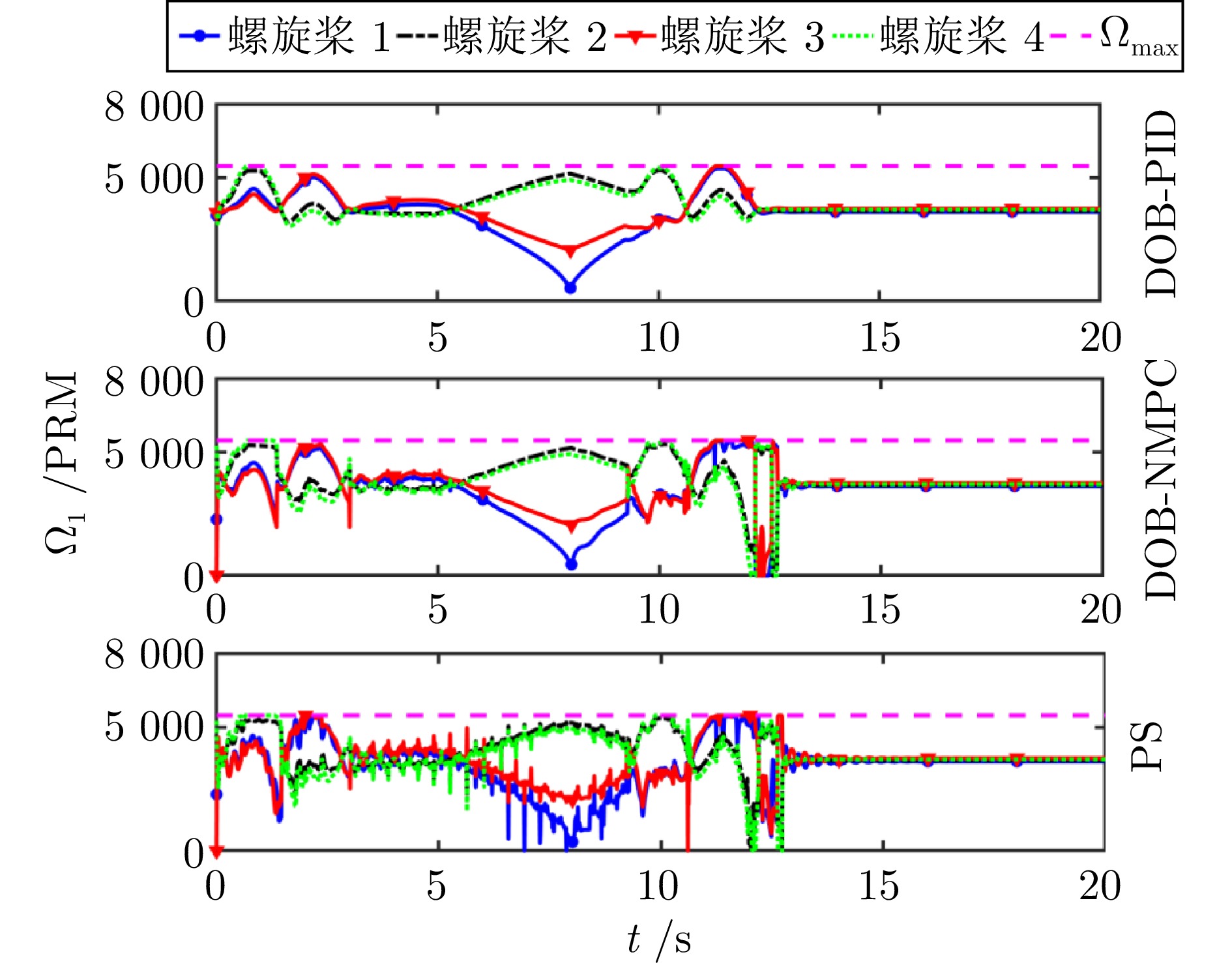
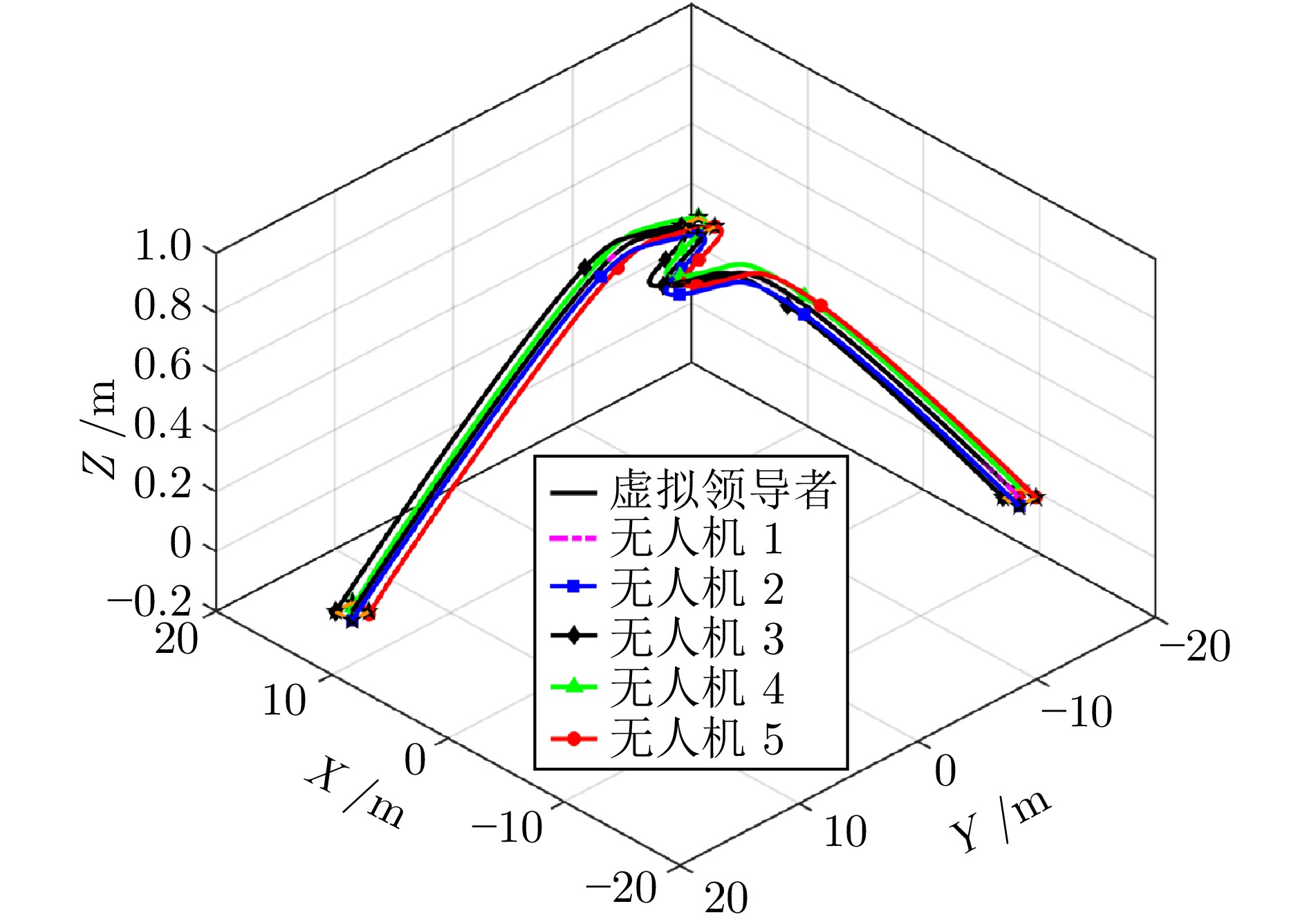
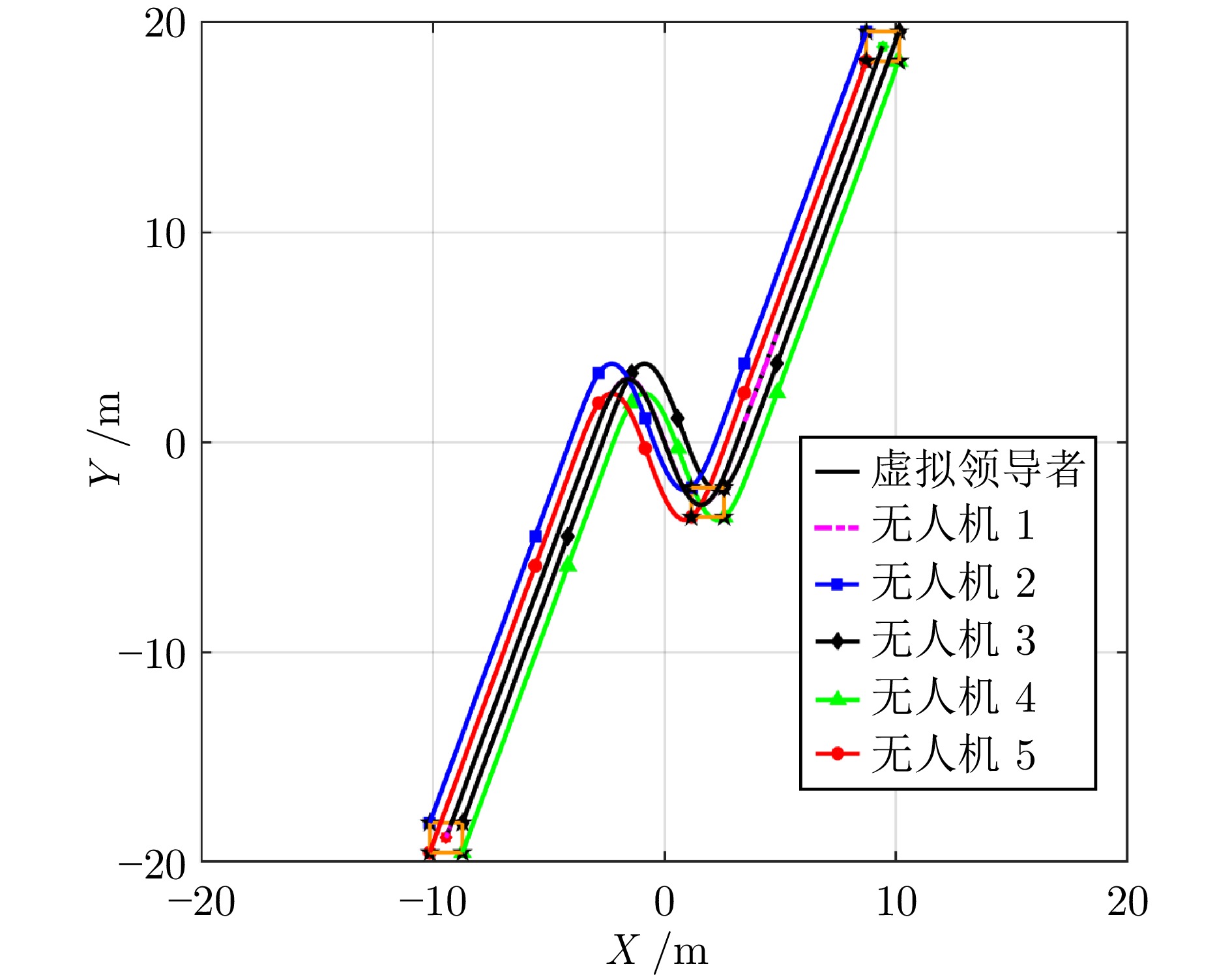
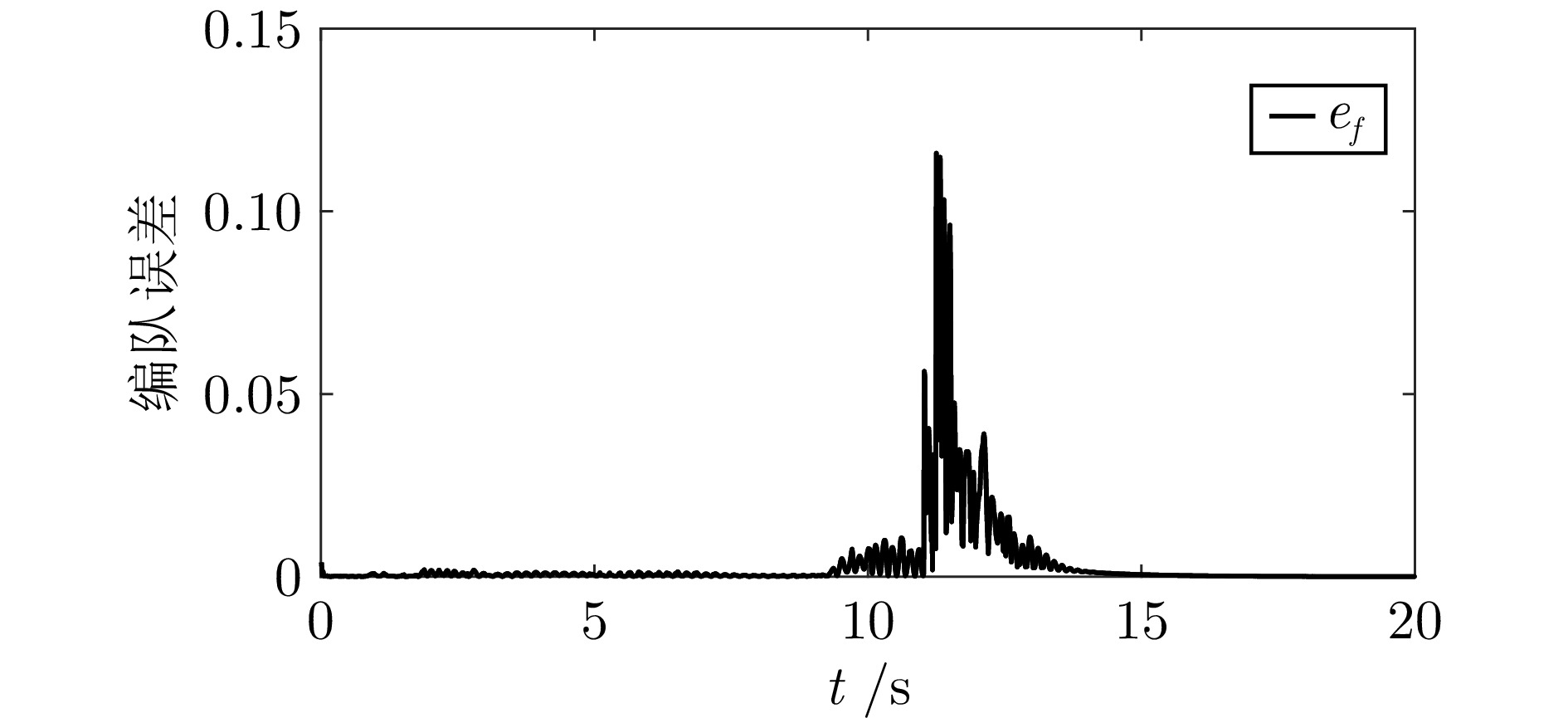
摘要: 多四旋翼无人机协同编队运输技术因其高容错性和强灵活性等特点, 近年来受到广泛关注. 针对受到螺旋桨转速约束和外界环境干扰影响的多四旋翼无人机系统, 提出一种分层控制方案以实现多无人机协同编队运输. 该方案设计主要包含分布式协调器设计和跟踪控制器设计. 在分布式协调器中, 位置协调器基于虚拟领导者的位置、速度等信息生成各带载无人机的期望位置, 然后微分平坦器输出无人机的期望无偏轨迹; 跟踪控制器采用非线性模型预测控制、角速度控制以及螺旋桨转速分配算法相结合的策略, 为各带载无人机生成合理的螺旋桨转速指令, 确保无人机精确跟踪其期望轨迹. 在所提方案作用下, 多带载无人机能维持期望编队队形并跟踪虚拟领导者, 从而实现多无人机协同编队运输. 特别地, 当省略位置协调器时, 该方案可简化为单无人机轨迹跟踪控制器. 数值仿真包括单机轨迹跟踪和多机协同运输两个场景, 结果表明: 在单机跟踪任务中, 所提方案展现出良好的跟踪精度; 在多机运输场景下, 多无人机能够有效实现协同编队运输.Abstract: The cooperative formation transportation technology of multiple quadrotors has attracted widespread attention in recent years due to its high fault tolerance and remarkable flexibility. This paper proposes a hierarchical control scheme for multiple quadrotors subject to propeller speed constraints and external disturbances to achieve cooperative formation transportation. The design of the proposed scheme primarily consists developing a distributed coordinator and some tracking controllers. In the distributed coordinator, position coordinators generate the desired positions for all quadrotors with payload using information such as the position and velocity of a virtual leader. This is followed by differential flatness-based trajectory planners, which further derive the desired offset-free trajectories. The tracking controllers combine the nonlinear model predictive control, angular velocity control, and a propeller speed allocation algorithm to generate appropriate propeller speed commands for all quadrotors, ensuring accurate trajectory tracking. Under the proposed scheme, multiple quadrotors with payload maintain the desired formation while tracking the virtual leader, thereby achieving cooperative formation transportation. Notably, when the position coordinators are omitted, the scheme simplifies to a single-quadrotor trajectory tracking controller. Numerical simulation results, including both single-quadrotor trajectory tracking and multiple quadrotors cooperative transportation scenarios, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme. Specifically, it achieves remarkable tracking performance in single-quadrotor operations, while enabling cooperative formation transportation in multiple quadrotors systems.
-
表 1 变量符号表
Table 1 Nomenclature
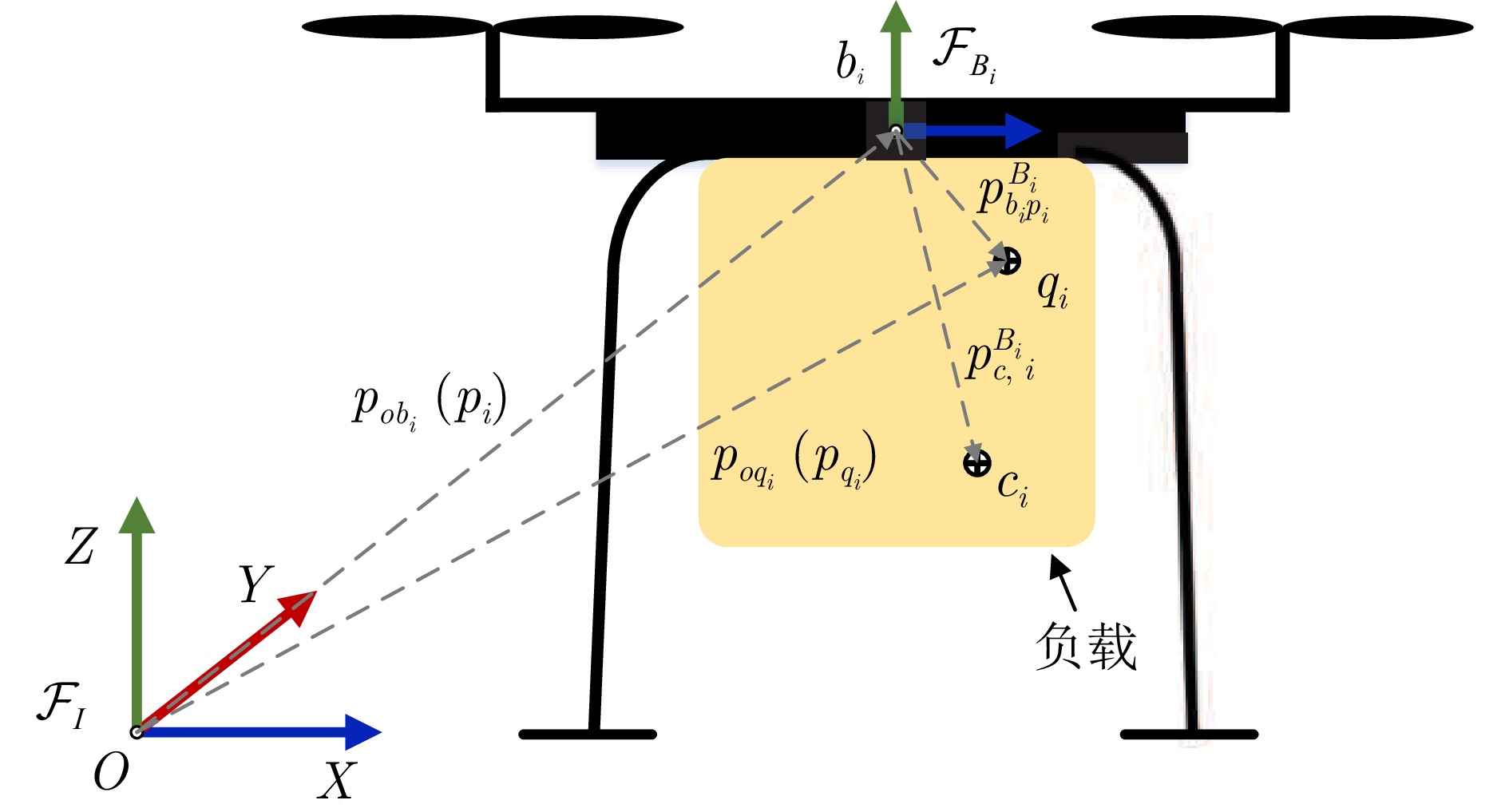
符号 物理意义 $ \boldsymbol{p}_{0},\;\boldsymbol{v}_{0},\; \boldsymbol{a}_{0},\; \boldsymbol{j}_{0} \in \mathbf{R}^{3} $ 虚拟领导者在惯性系$ \mathcal{F}_{I} $下的位置, 速度, 加速度, 加加速度 $ \boldsymbol{p}_{r,\;i},\; \boldsymbol{v}_{r,\;i},\; \boldsymbol{a}_{r,\;i},\; \boldsymbol{j}_{r,\;i} \in \mathbf{R}^{3} $ 无人机$ i $参考轨迹在惯性系 $ \mathcal{F}_{I} $下的位置, 速度, 加速度, 加加速度 $ \boldsymbol{\Theta}_{r,\;i},\; \boldsymbol{\omega}_{r,\;i} $ 无人机$ i $参考轨迹的姿态和角速度 $ f_{r,\;i},\; \boldsymbol{\tau}_{r,\;i} $ 无人机$ i $参考轨迹的推力和力矩 $ \boldsymbol{p}_{i},\;\boldsymbol{v}_{i},\; \boldsymbol{a}_{i},\; \boldsymbol{j}_{i} \in \mathbf{R}^{3} $ 无人机$ i $在惯性系$ \mathcal{F}_{I} $下的位置, 速度, 加速度, 加加速度 $ \boldsymbol{\Theta}_{i} = [\psi_{i},\; \theta_{i},\; \phi_{i}]^{\mathrm{T}},\; \boldsymbol{\omega}_{i} $ 无人机$ i $的姿态和角速度 $ \boldsymbol{\omega}_{de,\;i}\in \mathbf{R}^{3} $ 无人机$ i $NMPC算法输出的角速度信号 $ \boldsymbol{f}_{c,\;i},\; \boldsymbol{\tau}_{c,\;i}\in \mathbf{R}^{3} $ 无人机$ i $受到来自负载的耦合力和力矩 $ \boldsymbol{f}_{d,\;i},\; \boldsymbol{\tau}_{d,\;i}\in \mathbf{R}^{3} $ 无人机$ i $受到的外部力干扰和力矩干扰 $ \boldsymbol{p}_{c,\;i}^{B_{i}} $ 在体坐标系$ \mathcal{F}_{B_{i}} $下, 无人机$ i $负载的质心 $ J_{b,\;i}\in \mathbf{R}^{3\times 3} $ 在体坐标系$ \mathcal{F}_{B_{i}} $下, 无人机$ i $的惯量张量 $ J_{c,\;i}\in \mathbf{R}^{3\times 3} $ 在体坐标系$ \mathcal{F}_{B_{i}} $下, 无人机$ i $负载的惯量张量 $ m_{b,\;i},\; m_{c,\;i} $ 无人机$ i $的质量和其负载的质量 $ f_{i},\; \boldsymbol{\tau}_{i} $ 无人机$ i $的推力和力矩 $ \Omega_{i,\;j} $ 无人机$ i $的第$ j $个螺旋桨的转速 $ R_{B,\;i}^{I}\in \mathbf{R}^{3\times 3} $ 从惯性系$ \mathcal{F}_{I} $到体坐标系$ \mathcal{F}_{B_{i}} $的旋转矩阵 表 2 无人机参数
Table 2 Quadrotor parameters
参数 数值 参数 数值 $ m_{b,\; i} $ 1.0 kg $ d $ 0.3 m $ J_x $ $ 2.64 \times 10^{-3}\,\; \text{kg}\cdot\text{m}^2 $ $ c_T $ $ 1.984 \times 10^{-7}\,\; \text{N/PRM}^{2} $ $ J_y $ $ 2.64 \times 10^{-3}\,\; \text{kg}\cdot\text{m}^2 $ $ c_M $ $ 3.733 \times 10^{-9}\,\; \text{N/PRM}^{2} $ $ J_z $ $ 4.96 \times 10^{-3}\,\; \text{kg}\cdot\text{m}^2 $ 表 3 各方案对比
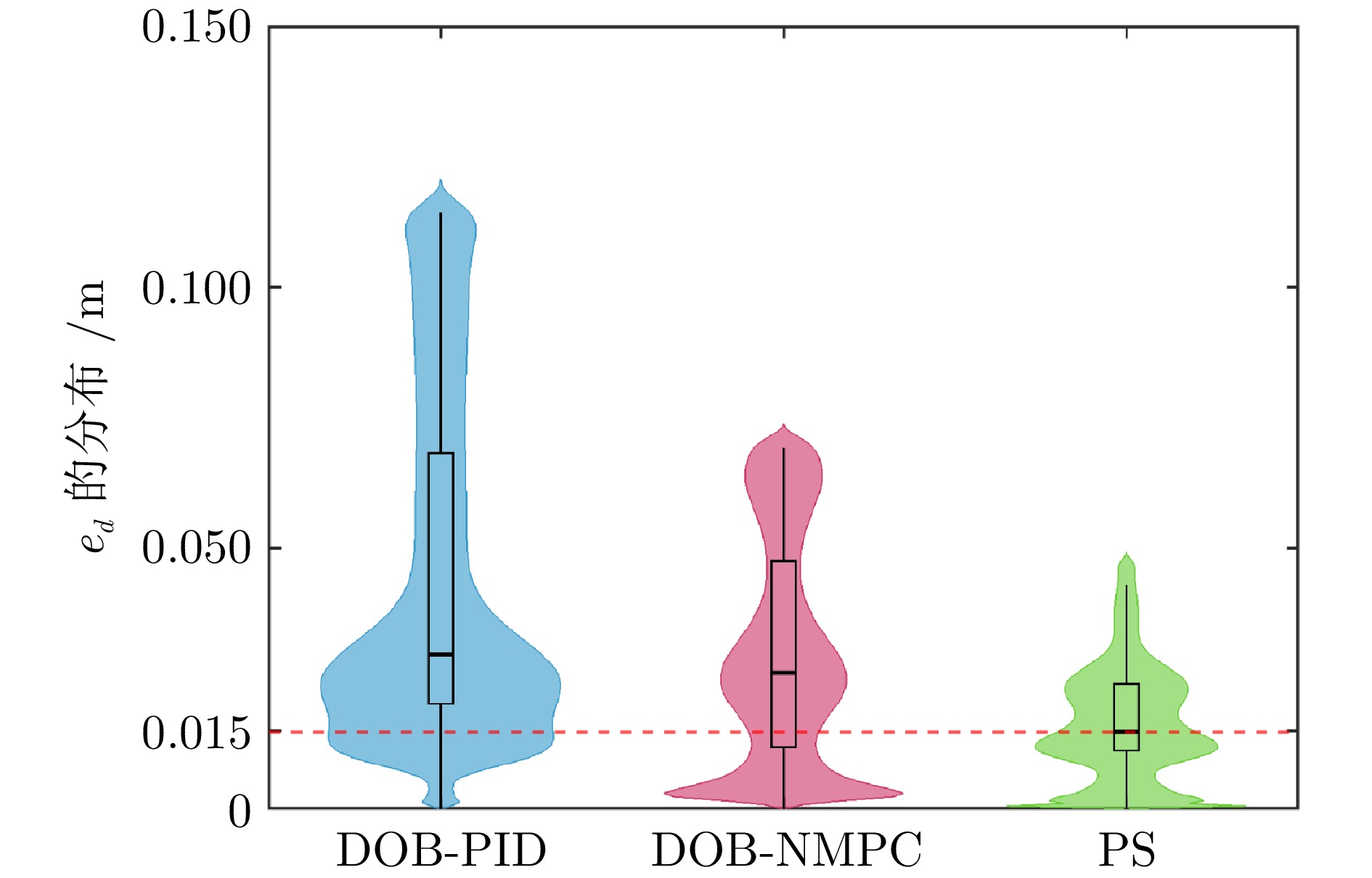
Table 3 Comparison of various schemes
方案 分布式协调器是
否考虑干扰动态(1a) $ \sim $ (1c)的控制算法 DOB-PID $ - $ PID DOB-NMPC $ - $ NMPC 所提方案
(Proposed scheme, PS)$ \checkmark $ NMPC 表 4 各无人机携带负载
Table 4 The payloads carried by quadrotors
无人机 负载质量 负载质心 负载惯量张量 $ 1,\;2,\;3 $ 0.10 kg $ {\begin{bmatrix} -0.05\\ 0.03\\ -0.10 \end{bmatrix}} $ m $ {\begin{bmatrix} 0.01083& 0.00500& -0.00500\\ 0.00500& 0.01083& 0.00500\\ -0.00500& 0.00500& 0.01083 \end{bmatrix}} $ kg·m $ ^{2} $ $ 4,\;5 $ 0.13 kg $ {\begin{bmatrix} -0.05\\ 0.05\\ -0.12 \end{bmatrix}} $ m $ {\begin{bmatrix} 0.01470& 0.00700& -0.00700\\ 0.00700& 0.0147& 0.00700\\ -0.00700& 0.00700& 0.01470 \end{bmatrix} }$ kg·m $ ^{2} $ -
[1] 王诗章, 鲜斌, 杨森. 无人机吊挂飞行系统的减摆控制设计. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1771−1780 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170413Wang Shi-Zhang, Xian Bin, Yang Sen. Anti-swing controller design for an unmanned aerial vehicle with a slung-load. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1771−1780 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170413 [2] Khosravi M, Enayati S, Saeedi H, Pishro-Nik H. Multi-purpose drones for coverage and transport applications. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20(6): 3974−3987 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3054748 [3] Li G R, Ge R D, Loianno G. Cooperative transportation of cable suspended payloads with MAVs using monocular vision and inertial sensing. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(3): 5316−5323 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3065286 [4] Zhang Y, Xu J, Zhao C, Dong J X. IF-based trajectory planning and cooperative control for transportation system of cable suspended payload with multi UAVs. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Detroit, USA: IEEE, 2023. 635-642 [5] Lee H, Kim H, Kim H J. Planning and control for collision-free cooperative aerial transportation. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(1): 189−201 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2016.2605707 [6] Tagliabue A, Kamel M S, Siegwart R, Nieto J. Robust collaborative object transportation using multiple MAVs. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2019, 38(9): 1020−1044 doi: 10.1177/0278364919854131 [7] Wang Z J, Hu T F, Long L J. Multi-UAV safe collaborative transportation based on adaptive control barrier function. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(11): 6975−6983 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3292810 [8] Dong X W, Zhou Yan, Ren Z, Zhong Y. Time-varying formation tracking for second-order multi-agent systems subjected to switching topologies with application to quadrotor formation flying. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(6): 5014−5024 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2593656 [9] 方浩, 赵欣悦, 陈杰. 无人飞行器集群自主控制: 预设性能驱动的安全编队控制. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(5): 931−941 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240603Fang Hao, Zhao Xin-Yue, Chen Jie. Autonomous control of unmanned aerial vehicle swarms: Prescribed performance driven safety formation control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(5): 931−941 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240603 [10] Abdessameud A, Tayebi A. Formation control of VTOL unmanned aerial vehicles with communication delays. Automatica, 2011, 47(11): 2383−2394 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.08.042 [11] 王耀南, 华和安, 张辉, 钟杭, 樊叶心, 梁鸿涛, 等. 性能函数引导的无人机集群深度强化学习控制方法. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(5): 905−916 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240519Wang Yao-Nan, Hua He-An, Zhang Hui, Zhong Hang, Fan Ye-Xin, Liang Hong-Tao, et al. Performance function-guided deep reinforcement learning control for UAV swarm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(5): 905−916 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240519 [12] Jasim W, Gu D B. Robust team formation control for quadrotors. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2018, 26(4): 1516−1523 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2017.2705072 [13] Ai X L, Yu J Q. Flatness-based finite-time leader-follower formation control of multiple quadrotors with external disturbances. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 92: 20−33 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.05.060 [14] Guo K X, Liu C, Zhang X, Yu X, Zhang Y M, Xie L H, et al. A bio-inspired safety control system for UAVs in confined environment with disturbance. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(2): 1308−1320 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2022.3217982 [15] Eliker K, Grouni S, Tadjine M, Zhang W D. Quadcopter nonsingular finite-time adaptive robust saturated command-filtered control system under the presence of uncertainties and input saturation. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2021, 104: 1363−1387 doi: 10.1007/s11071-021-06332-3 [16] Gao Z Y, Guo G. A novel strategy to solve communication constraints for formation control of multi-AUVs. Science China Information Sciences, 2021, 64: Article No. 179204 doi: 10.1007/s11432-018-9672-1 [17] Fu J J, Wen G H, Yu W W, Huang T W, Yu X H. Consensus of second-order multiagent systems with both velocity and input constraints. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2019, 66(10): 7946−7955 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2018.2879292 [18] Wang Z X, Liu T F, Jiang Z P. Cooperative formation control under switching topology: an experimental case study in multirotors. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(12): 6141−6153 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2967844 [19] Xu H, Cui G, Ma Q, Li Z. Event-triggered distributed adaptive fixed-time formation control of QUAVs with input constraints. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(5): 6357−6367 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3345925 [20] Shao X Y, Sun G H, Yao W R, Liu J X, Wu L G. Adaptive sliding mode control for quadrotor UAVs with onput saturation. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2022, 27(3): 1498−1509 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2021.3094575 [21] Dimitrios H V, William S L. Handbook of networked and embedded control systems. Boston: Birkhäuser, 2005. [22] Wang X Y, Xu Y J, Cao Y, Li S H. A hierarchical design framework for distributed control of multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2024, 160: Article No. 111402 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111402 [23] Tang Y T, Deng Z H, Hong Y G. Optimal output consensus of high-order multiagent systems with embedded technique. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 49(5): 1768−1779 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2813431 [24] Wu Q W, Wang X Y, Qiu X C. Embedded technique-based formation control of multiple wheeled mobile robots with application to cooperative transportation. Control Engineering Practice, 2024, 150: Article No. 106002 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2024.106002 [25] Zadeh H N, Naseri R, Menhaj M B, Suratgar A A. Heterogeneous unknown multiagent systems of different relative degrees: A distributed optimal coordination design. IEEE Systems Journal, 2024, 18(3): 1570−1580 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2024.3417255 [26] Guo G, Kang J. Distributed optimization of multiagent systems against unmatched disturbances: A hierarchical integral control framework. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(6): 3556−3567 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2021.3071307 [27] Guerrero J M, Vasquez J C, Matas J, de Vicuna L G, Castilla M. Hierarchical control of droop-controlled AC and DC microgrids—a general approach toward standardization. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2011, 58(1): 158−172 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2010.2066534 [28] Wu Q W, Wang G D, Wang X Y. A Formation strategy relying on monotrajectory planning for velocity-constrained wheeled mobile robots with application to cooperative transportation. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2025, 33(6): 2080−2091 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2025.3573888 [29] Faessler M, Franchi A, Scaramuzza D. Differential flatness of quadrotor dynamics subject to rotor drag for accurate tracking of high-speed trajectories. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(2): 620−626 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2017.2776353 [30] Xu L W, Tian B L, Wang C, Lu J J, Wang D D, Li Z Y, et al. Fixed-time disturbance observer-based MPC robust trajectory tracking control of quadrotor. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2025, 30(6): 4272−4282 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2024.3503062 [31] Olfati-Saber R, Murray R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1520−1533 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834113 [32] Bhat S P, Bernstein D S. Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2000, 38(3): 751−766 doi: 10.1137/S0363012997321358 [33] Monteiro J C, Lizarralde F, Liu H. Optimal control allocation of quadrotor UAVs subject to actuator constraints. In Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC). Boston, USA: IEEE, 2016. 500-505 [34] 王浩坤, 徐祖华, 赵均, 江爱朋. 无偏模型预测控制综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(5): 858−877 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180415Wang Hao-Kun, Xu Zu-Hua, Zhao Jun, Jiang Ai-Peng. A survey on ofiset-free model predictive control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(5): 858−877 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180415 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 19
- HTML全文浏览量: 15
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: