-
摘要: 视觉作为强化学习智能体感知环境的主要途径, 能够提供丰富的细节信息, 从而支持智能体实现更复杂、精准的决策. 然而, 视觉数据的高维特性易导致信息冗余与样本效率低下, 成为强化学习应用中的关键挑战. 如何在有限交互数据中高效提取关键视觉表征, 提升智能体决策能力, 已成为当前研究热点. 为此, 系统梳理视觉强化学习方法, 依据核心思想与实现机制, 将其归纳为五类: 图像增强型、模型增强型、任务辅助型、知识迁移型以及离线视觉强化学习, 深入分析各类方法的研究进展及代表性工作的优势与局限. 同时, 综述DMControl、DMControl-GB、Distracting Control Suite 和RL-ViGen四大主流基准平台, 总结视觉强化学习在机器人控制、自动驾驶以及多模态大模型等典型场景中的应用实践. 最后, 结合当前研究瓶颈, 探讨未来发展趋势与潜在研究方向, 以期为该领域提供清晰的技术脉络与研究参考.Abstract: Vision, as the primary means for reinforcement learning agents to perceive their environment, provides rich and detailed information that supports agents in making more complex and precise decisions. However, the high-dimensional nature of visual data often leads to information redundancy and low sample efficiency, posing a key challenge in the application of reinforcement learning. How to efficiently extract key visual representations from limited interaction data to enhance agents' decision-making capabilities has become a current research focus. To address this, this paper systematically reviews visual reinforcement learning methods, categorizing them into five categories based on their core ideas and implementation mechanisms: Image-enhanced, model-enhanced, task-assisted, knowledge-transferred, and offline visual reinforcement learning approaches. It provides an in-depth analysis of the research progress in each category, as well as the strengths and limitations of representative works. Meanwhile, the paper reviews four major benchmark platforms: DMControl, DMControl-GB, Distracting Control Suite, and RL-ViGen, and summarizes the applications of visual reinforcement learning in typical scenarios such as robotic control, autonomous driving, and multimodal large models. Finally, based on current research bottlenecks, this paper discusses future development trends and potential research directions, aiming to offer a clear technical framework and research reference for this field.
-
Key words:
- reinforcement learning /
- visual representation /
- visual reinforcement learning /
- agent
-
表 1 与已有综述对比
Table 1 Comparison with existing reviews
综述 覆盖范围 分类框架 基准平台 应用场景 文献[12] 图像增强型与任务辅助型VRL 基于数据增强在VRL中的使用方式:
生成增强数据与利用增强数据主要涵盖: Atari游戏、DMControl及其变体; 简要提及: OpenAI Procgen、DeepMind Lab、CARLA 涵盖无模型方法; 适用于在线VRL环境 文献[13] 图像增强型与任务辅助型VRL 基于状态表征学习方法: 基于度量、辅助任务、数据增强、对比学习、非对比学习和基于注意力的方法 未明确讨论或比较基准平台 涵盖无模型方法; 适用于在线VRL环境 本文 五种类型全覆盖 基于方法的核心思想与实现机制: 图像增强型、模型增强型、任务辅助型、知识迁移型以及离线视觉强化学习 DMControl、DMControl-GB、DCS和RL-ViGen 涵盖无模型与基于模型方
法; 适用于在线与离线VRL
环境表 2 视觉强化学习方法对比
Table 2 Comparison of visual reinforcement learning methods
方法
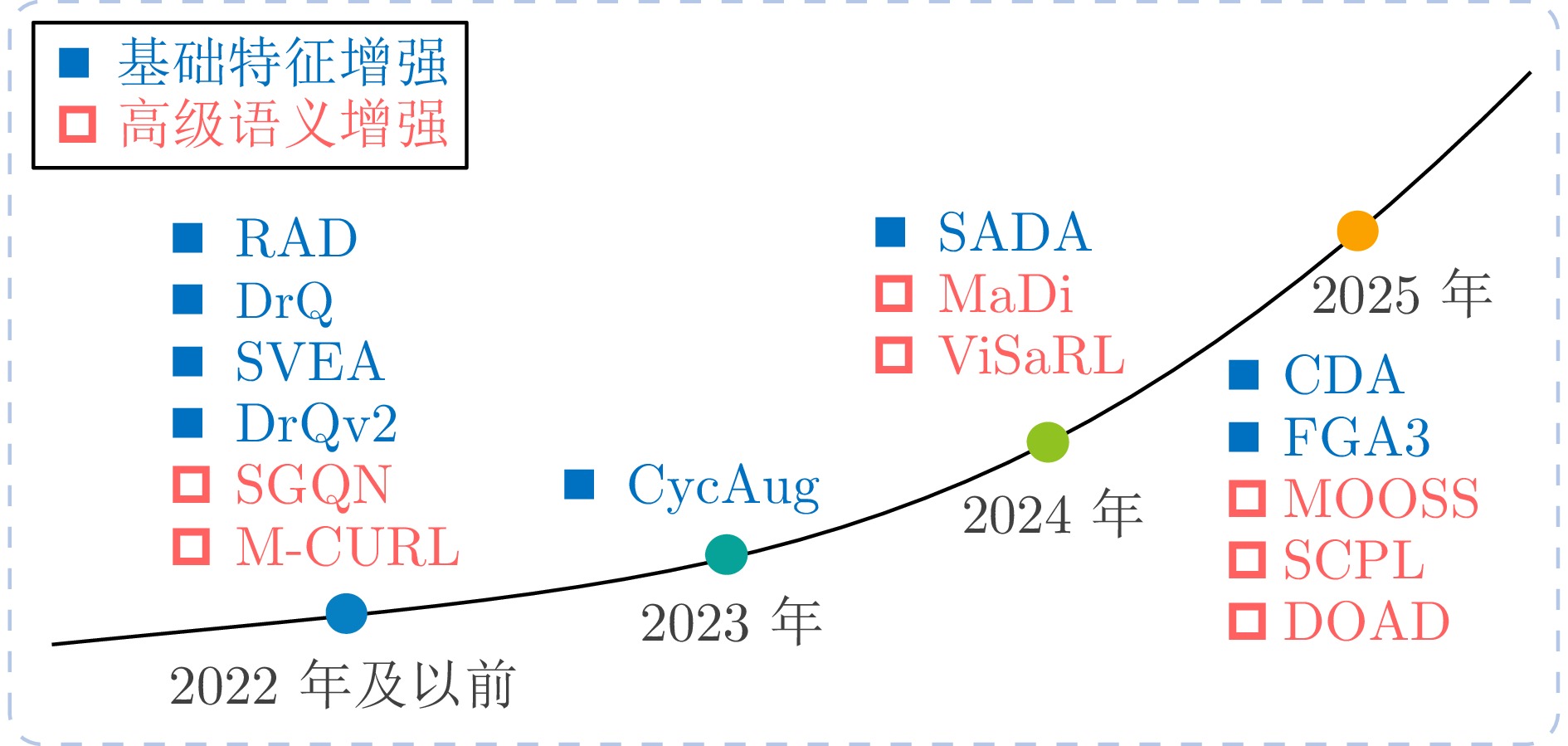
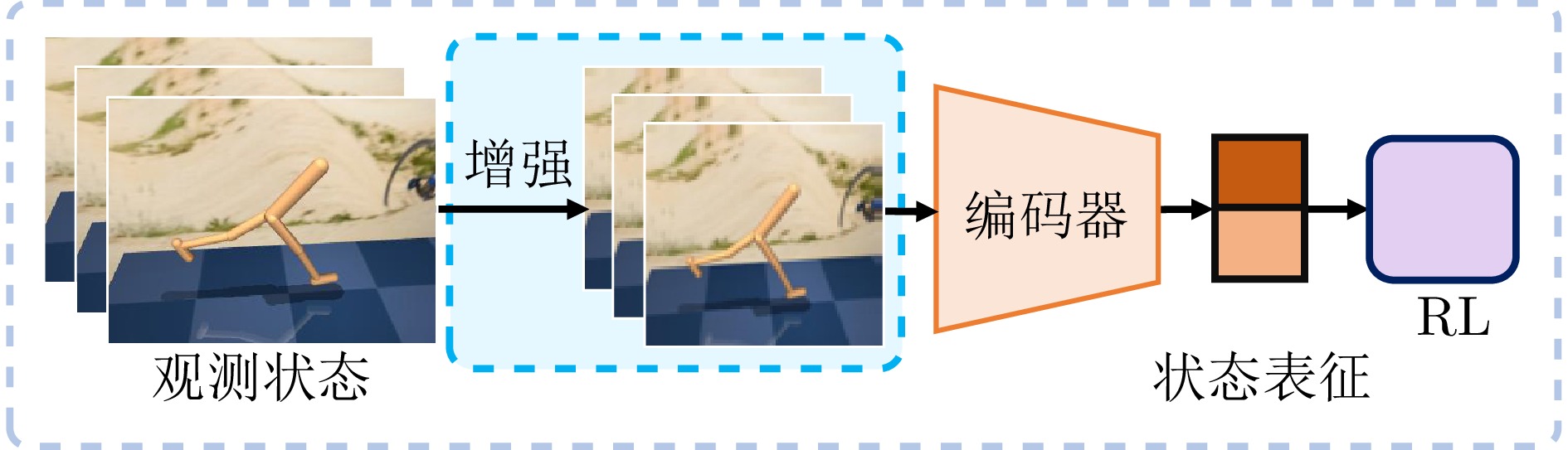
类别子类 总体目标 核心思想 优势 劣势 适用场景 图像增强型VRL 基础特征增强 提升数据利用率 直接修改像素值或
频谱信息实现简单、计算开销低、通用性强 易破坏关键语义信息, 误导策略学习 通用视觉任务 高级语义增强 优化关键区域学习 基于语义显著性进行
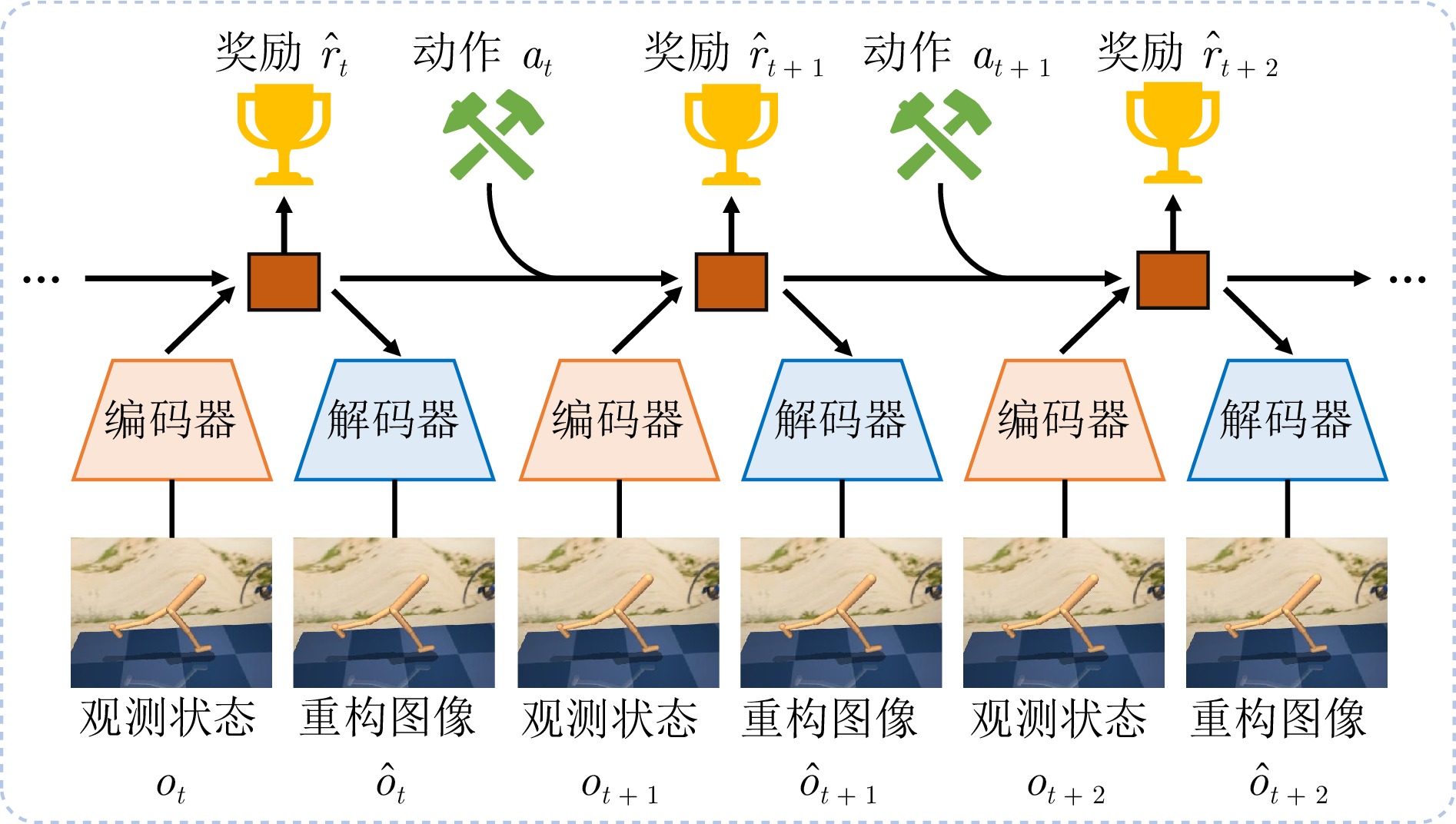
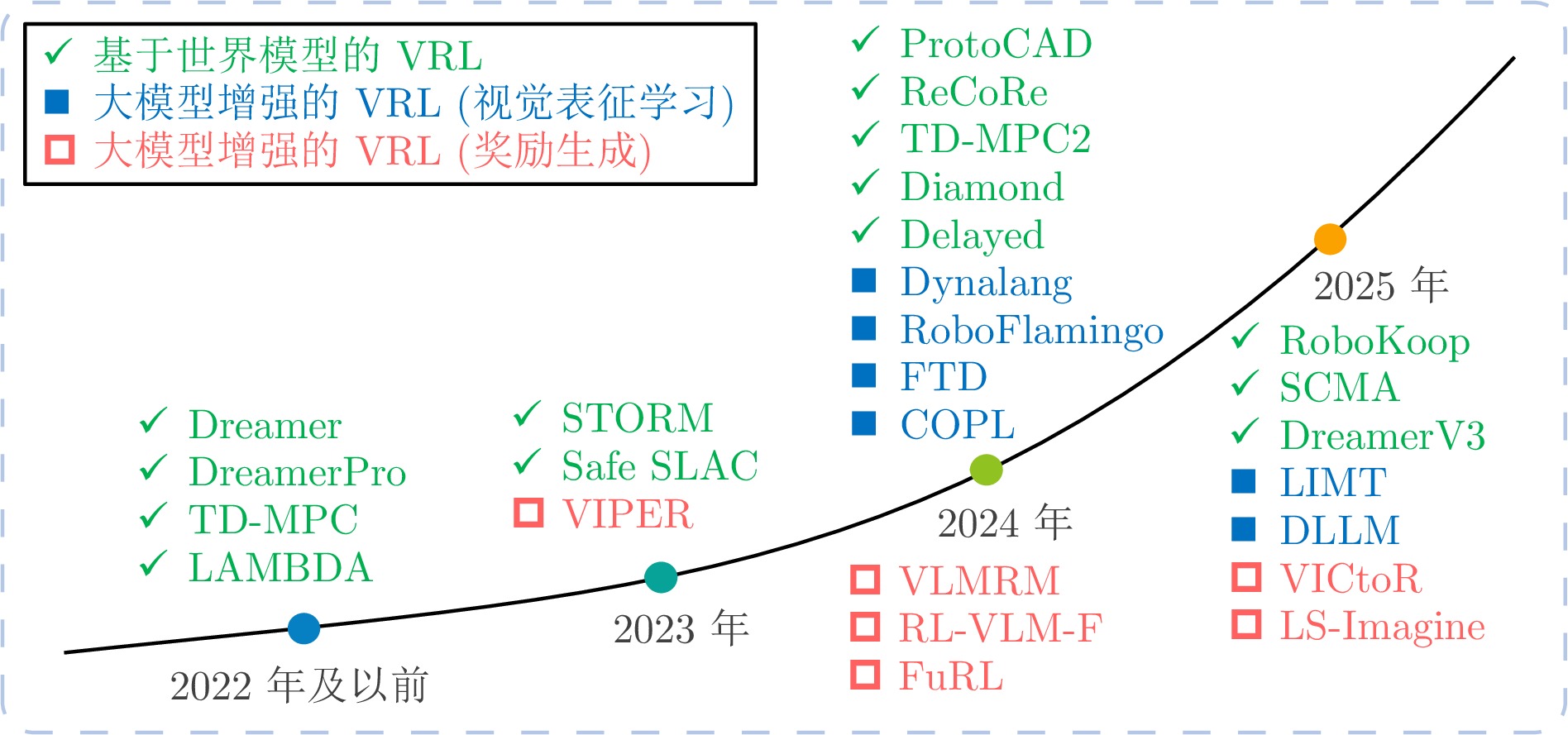
针对性增强保留并强化关键区域, 提升语义理解能力 依赖显著性检测精度, 实现复杂 需精细感知的任务 模型增强型VRL 基于世界模型的VRL 减少环境交互, 提升
推理能力构建内部环境动力学模型,
预测状态转移可在模拟中规划, 减少真实交互 模型偏差易导致策略
退化复杂动力学环境、长视野任务 大模型增强的VRL 视觉表征学习 提升视觉理解能力 利用预训练大模型提取低维语义特征 特征提取能力强, 泛化性好 存在领域差异, 计算资源消耗大 复杂视觉理解任务 奖励生成 解决奖励稀疏问题 利用大模型生成密集、语义
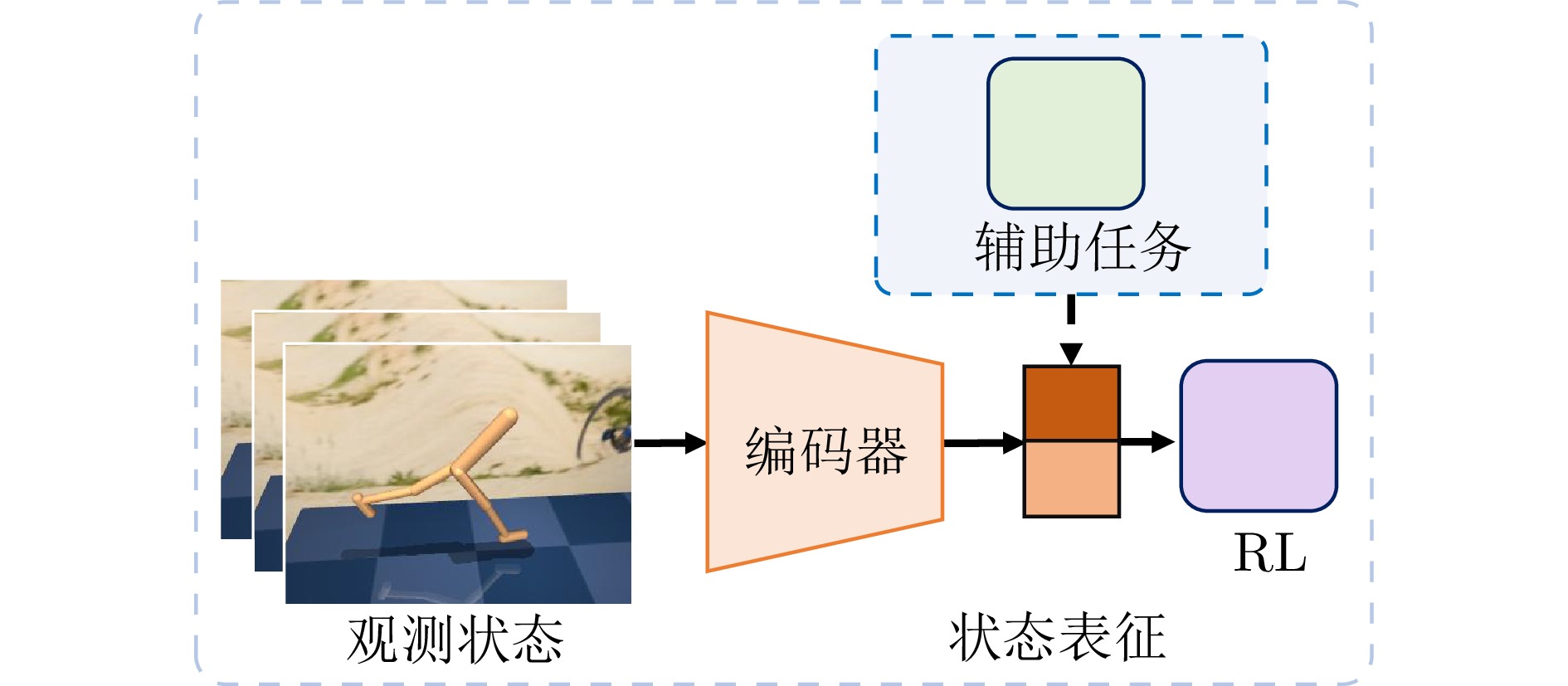
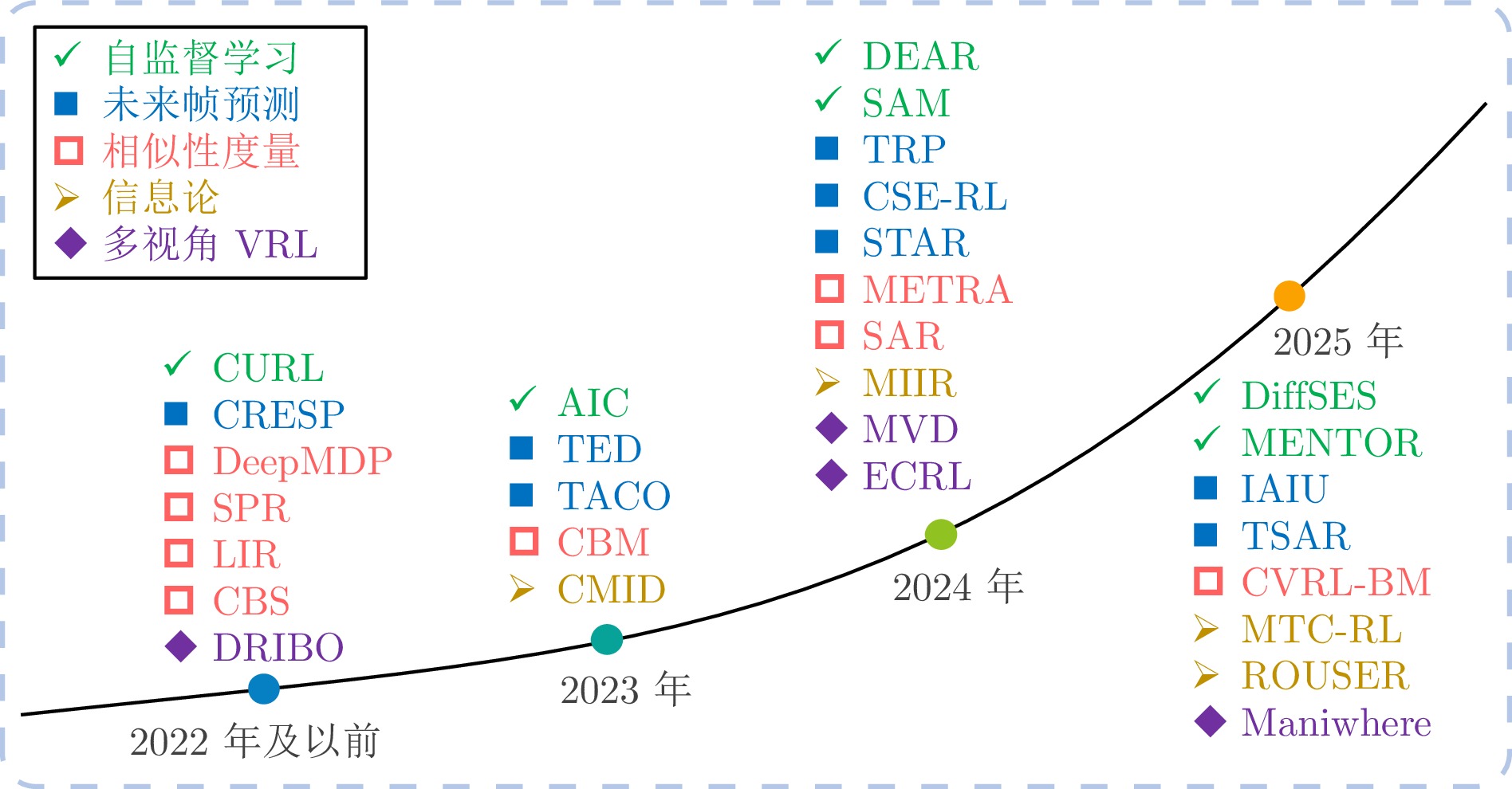
合理的奖励信号减少人工设计成本, 缓解稀疏奖励 存在幻觉风险, 奖励可能不准确 奖励设计困难的任务 任务辅助型VRL 辅助任务引导的VRL 自监督学习 提升表征学习效率 设计自监督任务促进特征
学习提升智能体提取特征能力, 增强对环境理解 可能与主任务冲突, 增加训练复杂度 需丰富表征的任务 未来帧预测 学习环境动态 预测未来图像帧来学习
状态表征相似性度量 提升状态一致性 通过相似性度量增强状态表征一致性 信息论 学习稳健表征, 提升
泛化力压缩无关信息, 保留任务相关信息 多视角VRL 克服遮挡与盲区 融合多个视角图像信息 提升环境感知完
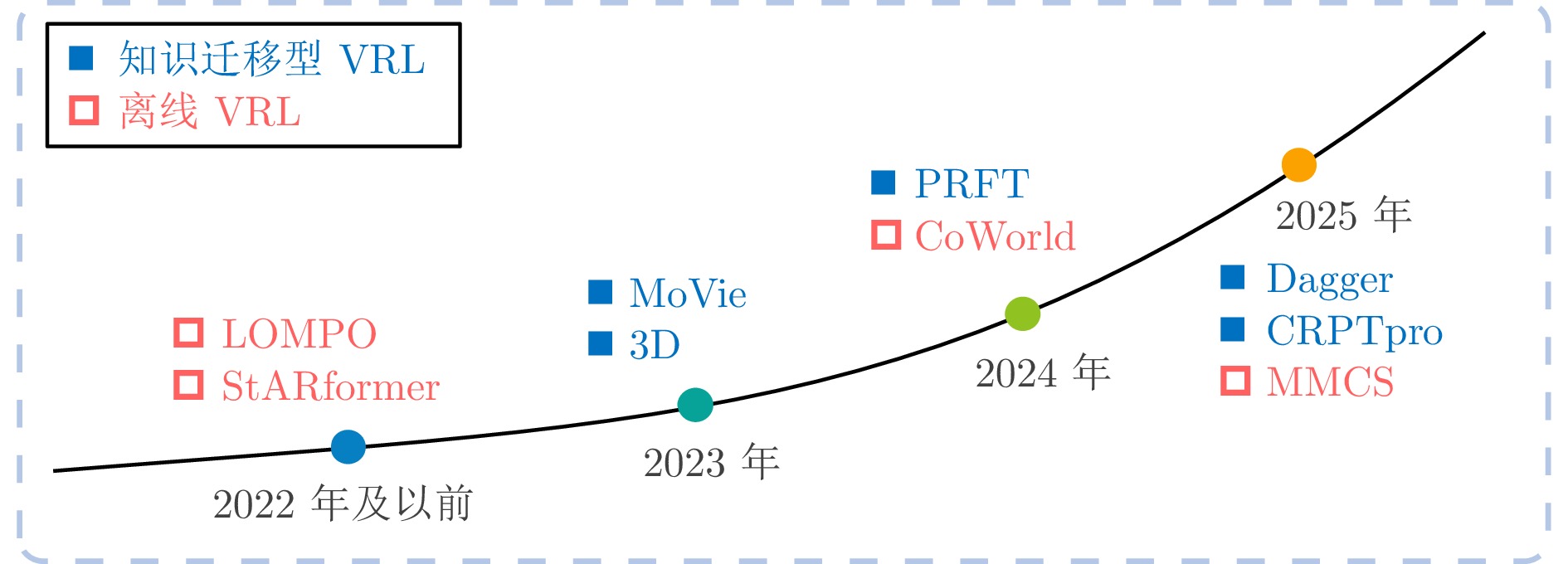
整性视角缺失或质量差时性能下降 多摄像头环境 知识迁移型VRL - 提升跨域泛化能力 迁移已有知识至新环境 加速适应, 提升泛化 领域差异大时可能负
迁移跨环境、跨任务迁移 离线VRL - 从静态图像数据集中学习策略 利用历史数据集训练, 无需环境交互 安全性高, 避免在线试错风险 易受数据分布偏移影响, 泛化能力受限 数据集丰富但交互受限场景 表 3 基准平台对比
Table 3 Comparison of benchmark platforms
基准平台 DMControl DMControl-GB DCS RL-ViGen 核心目标 基础连续控制任务评估 视觉泛化能力评估 抗视觉干扰能力评估 全面视觉泛化评估 基础环境 MuJoCo 基于DMControl 基于DMControl 融合多个仿真平台 任务类型 连续控制 同DMControl, 但增加泛化
测试同DMControl, 但增加视觉
干扰多样化(运动控制、自动驾驶、灵巧操作、桌面操作、
室内导航)视觉观测 固定视角、简单背景 支持视觉变化
(颜色、背景)动态干扰
(相机位姿、颜色、背景)高保真、多视角、动态光照、复杂场景、跨形态 泛化能力评估 不支持 支持背景变化下的泛化 支持干扰下的零样本泛化 支持多种泛化类型, 强调跨任务、跨形态、跨视角的
综合泛化能力环境复杂度 低
(简单物理仿真)中等
(视觉变化但任务单一)中等
(动态干扰但任务单一)高
(真实仿真、多样化任务) -
[1] Sutton R S, Barto A G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction (Second edition). Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018. [2] Li B Y, Zhang Z N, Zheng G Z, Cai C R, Zhang J Q, Chen L. Cooperation in public goods games: Leveraging other-regarding reinforcement learning on hypergraphs. Physical Review E, 2025, 111(1): Article No. 014304 doi: 10.1103/physreve.111.014304 [3] Haarnoja T, Moran B, Lever G, Huang S H, Tirumala D, Humplik J, et al. Learning agile soccer skills for a bipedal robot with deep reinforcement learning. Science Robotics, 2024, 9(89): Article No. eadi8022 doi: 10.1126/scirobotics.adi8022 [4] 高宇宁, 王安成, 赵华凯, 罗豪龙, 杨子迪, 李建胜. 基于深度强化学习的视觉导航方法综述. 计算机工程与应用, 2025, 61(10): 66−78 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2409-0215Gao Yu-Ning, Wang An-Cheng, Zhao Hua-Kai, Luo Hao-Long, Yang Zi-Di, Li Jian-Sheng. Review on visual navigation methods based on deep reinforcement learning. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2025, 61(10): 66−78 doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2409-0215 [5] He X K, Huang W H, Lv C. Trustworthy autonomous driving via defense-aware robust reinforcement learning against worst-case observational perturbations. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2024, 163: Article No. 104632 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2024.104632 [6] 国务院关于印发新一代人工智能发展规划的通知. 中华人民共和国国务院公报, 2017, (22): 7−21 Notice of the state council on issuing the development plan on the new generation of artificial intelligence. Gazette of the State Council of the People's Republic of China, 2017, (22): 7−21 [7] 国家人工智能产业综合标准化体系建设指南(2024版). 中小企业管理与科技, 2024, (12): 1−5 Guidelines for the construction of a comprehensive standardization system for the national artificial intelligence industry (2024 Edition). Management & Technology of SME, 2024, (12): 1−5 [8] Mnih V, Kavukcuoglu K, Silver D, Rusu A A, Veness J, Bellemare M G, et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature, 2015, 518(7540): 529−533 doi: 10.1038/nature14236 [9] Haarnoja T, Zhou A, Abbeel P, Levine S. Soft actor-critic: Off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. 1861−1870 [10] Schulman J, Wolski F, Dhariwal P, Radford A, Klimov O. Proximal policy optimization algorithms. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1707.06347, 2017. [11] 李家宁, 田永鸿. 神经形态视觉传感器的研究进展及应用综述. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(6): 1258−1286 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.01258Li Jia-Ning, Tian Yong-Hong. Recent advances in neuromorphic vision sensors: A survey. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(6): 1258−1286 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.01258 [12] Ma G Z, Wang Z, Yuan Z C, Wang X Q, Yuan B, Tao D C. A comprehensive survey of data augmentation in visual reinforcement learning. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2025, 133(10): 7368−7405 doi: 10.1007/s11263-025-02472-w [13] Echchahed A, Castro P S. A survey of state representation learning for deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2506.17518, 2025. [14] Yarats D, Fergus R, Lazaric A, Pinto L. Reinforcement learning with prototypical representations. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. Virtual Event: PMLR, 2021. 11920−11931 [15] Laskin M, Lee K, Stooke A, Pinto L, Abbeel P, Srinivas A. Reinforcement learning with augmented data. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 1669 [16] Yarats D, Kostrikov I, Fergus R. Image augmentation is all you need: Regularizing deep reinforcement learning from pixels. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Learning Representations. Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2021. Article No. 121 [17] Yarats D, Fergus R, Lazaric A, Pinto L. Mastering visual continuous control: Improved data-augmented reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2022. Article No. 113 (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版地和页码, 请确认) [18] Lillicrap T P, Hunt J J, Pritzel A, Heess N, Erez T, Tassa Y, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). San Juan, Puerto Rico: ICLR, 2016. [19] Hansen N, Su H, Wang X L. Stabilizing deep Q-learning with ConvNets and vision transformers under data augmentation. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Virtual Event: Curran Associates Inc., 2021. Article No. 281 (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版地, 请确认) [20] Almuzairee A, Hansen N, Christensen H I. A recipe for unbounded data augmentation in visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of Reinforcement Learning Conference (RLC). Amherst, USA: RLJ, 2024. 130−157 (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版信息, 请确认) [21] Xiong X, Shen C, Wu J H, Lv S, Zhang X D. Combined data augmentation framework for generalizing deep reinforcement learning from pixels. Expert Systems With Applications, 2025, 264: Article No. 125810 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.125810 [22] Ma G Z, Zhang L R, Wang H Y, Li L, Wang Z L, Wang Z, et al. Learning better with less: Effective augmentation for sample-efficient visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 2614 [23] Lee J W, Hwang H. Fourier guided adaptive adversarial augmentation for generalization in visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Philadelphia, USA: AAAI Press, 2025. 18110−18118 [24] Grooten B, Tomilin T, Vasan G, Taylor M E, Mahmood A R, Fang M, et al. MaDi: Learning to mask distractions for generalization in visual deep reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. Auckland, New Zealand: International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, 2024. 733−742 [25] Bertoin D, Zouitine A, Zouitine M, Rachelson E. Look where you look! Saliency-guided q-networks for generalization in visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 2225 [26] Zhu J H, Xia Y C, Wu L J, Deng J J, Zhou W G, Qin T, et al. Masked contrastive representation learning for reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2023, 45(3): 3421−3433 [27] Grill J B, Strub F, Altché F, Tallec C, Richemond P H, Buchatskaya E, et al. Bootstrap your own latent a new approach to self-supervised learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 1786 [28] Sun J R, Akcal M U, Chowdhary G, Zhang W. MOOSS: Mask-enhanced temporal contrastive learning for smooth state evolution in visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Tucson, USA: IEEE, 2025. 6719−6729 [29] Liang A, Thomason J, Biyik E. ViSaRL: Visual reinforcement learning guided by human saliency. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: IEEE, 2024. 2907−2912 [30] Sun J B, Tu S J, Zhang Q C, Chen K, Zhao D B. Salience-invariant consistent policy learning for generalization in visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems. Detroit, USA: International Foundation for Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, 2025. 1987−1995 [31] Ma J L, Li C, Feng Z Q, Xiao L M, He C D, Zhang Y. Don't overlook any detail: Data-efficient reinforcement learning with visual attention. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2025, 310: Article No. 112869 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2024.112869 [32] Hafner D, Lillicrap T, Ba J, Norouzi M. Dream to control: Learning behaviors by latent imagination. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: OpenReview.net, 2020. Article No. 120 [33] 胡铭菲, 左信, 刘建伟. 深度生成模型综述. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 40−74 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190866Hu Ming-Fei, Zuo Xin, Liu Jian-Wei. Survey on deep generative model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 40−74 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190866 [34] Zhang W P, Wang G, Sun J, Yuan Y T, Huang G. STORM: Efficient stochastic transformer based world models for reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 1182 [35] Wang J J, Zhang Q C, Mu Y, Li D, Zhao D B, Zhuang Y Z, et al. Prototypical context-aware dynamics for generalization in visual control with model-based reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(9): 10717−10727 doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3396525 [36] Poudel R P K, Pandya H, Liwicki S, Cipolla R. ReCoRe: Regularized contrastive representation learning of world model. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 22904−22913 [37] Deng F, Jang I, Ahn S. DreamerPro: Reconstruction-free model-based reinforcement learning with prototypical representations. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 4956−4975 [38] Eyüboğlu M, Powell N, Karimi A. Data-driven control synthesis using Koopman operator: A robust approach. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC). Toronto, Canada: IEEE, 2024. 1879−1884 [39] Kumawat H, Chakraborty B, Mukhopadhyay S. RoboKoop: Efficient control conditioned representations from visual input in robotics using Koopman operator. In: Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Robot Learning. Seoul, Korea: PMLR, 2025. 3474−3499 [40] Hansen N, Su H, Wang X L. Temporal difference learning for model predictive control. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 8387−8406 [41] Hansen N, Su H, Wang X L. TD-MPC2: Scalable, robust world models for continuous control. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. Article No. 130 [42] Alonso E, Jelley A, Micheli V, Kanervisto A, Storkey A, Pearce T, et al. Diffusion for world modeling: Visual details matter in Atari. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2024. Article No. 1873 [43] Zhou X X, Ying C Y, Feng Y, Su H, Zhu J. Self-consistent model-based adaptation for visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI). Montreal, Canada: IJCAI, 2025. 7191−7199 [44] Hafner D, Pasukonis J, Ba J, Lillicrap T. Mastering diverse control tasks through world models. Nature, 2025, 640(8059): 647−653 doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08744-2 [45] Karamzade A, Kim K, Kalsi M, Fox R. Reinforcement learning from delayed observations via world models. In: Proceedings of the Reinforcement Learning Conference (RLC). Amherst, USA: RLJ, 2024. 2123−2139 [46] 王雪松, 王荣荣, 程玉虎. 安全强化学习综述. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(9): 1813−1835 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220631Wang Xue-Song, Wang Rong-Rong, Cheng Yu-Hu. Safe reinforcement learning: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(9): 1813−1835 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220631 [47] As Y, Usmanova I, Curi S, Krause A. Constrained policy optimization via Bayesian world models. In: Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Virtual Event: OpenReview.net, 2022. Article No. 124 (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版地信息, 请确认) [48] Hogewind Y, Simão T D, Kachman T, Jansen N. Safe reinforcement learning from pixels using a stochastic latent representation. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). TBD: OpenReview.net, 2023. Article No. 114 (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版地信息, 请确认) [49] Lee A X, Nagabandi A, Abbeel P, Levine S. Stochastic latent actor-critic: Deep reinforcement learning with a latent variable model. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. Article No. 63 [50] Radford A, Kim J W, Hallacy C, Ramesh A, Goh G, Agarwal S, et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning. Virtual Event: PMLR, 2021. 8748−8763 (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版地, 请确认) [51] Doroudian E, Taghavifar H. CLIP-RLDrive: Human-aligned autonomous driving via CLIP-based reward shaping in reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2412.16201, 2024. [52] Alayrac J B, Donahue J, Luc P, Miech A, Barr I, Hasson Y, et al. Flamingo: A visual language model for few-shot learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. Article No. 1723 [53] Lin J, Du Y Q, Watkins O, Hafner D, Abbeel P, Klein D, et al. Learning to model the world with language. In: Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: PMLR, 2024. 29992−30017 [54] Aljalbout E, Sotirakis N, van der Smagt P, Karl M, Chen N. LIMT: Language-informed multi-task visual world models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Atlanta, USA: IEEE, 2025. 8226−8233 [55] Liu Z Y, Huan Z Y, Wang X Y, Lv J F, Tao J, Li X, et al. World models with hints of large language models for goal achieving. In: Proceedings of the 2025 Conference of the Nations of the Americas Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies. Albuquerque, New Mexico: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2025. 50−72 [56] Chen C, Xu J C, Liao W J, Ding H, Zhang Z Z, Yu Y, et al. Focus-then-decide: Segmentation-assisted reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2024. 11240−11248 [57] Jiang H B, Lu Z Q. Visual grounding for object-level generalization in reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Milan, Italy: Springer, 2024. 55−72 [58] Li X H, Liu M H, Zhang H B, Yu C J, Xu J, Wu H T, et al. Vision-language foundation models as effective robot imitators. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. Article No. 119 [59] Ma H Z, Sima K K, Vo T V, Fu D, Leong T Y. Reward shaping for reinforcement learning with an assistant reward agent. In: Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: PMLR, 2024. 33925−33939 [60] Escontrela A, Adeniji A, Yan W, Jain A, Peng X B, Goldberg K, et al. Video prediction models as rewards for reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 3009 [61] Hung K H, Lo P C, Yeh J F, Hsu H Y, Chen Y T, Hsu W H. VICtoR: Learning hierarchical vision-instruction correlation rewards for long-horizon manipulation. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Singapore, Singapore: OpenReview.net, 2025. Article No. 128 [62] Rocamonde J, Montesinos V, Nava E, Perez E, Lindner D. Vision-language models are zero-shot reward models for reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. Article No. 118 [63] Wang Y F, Sun Z Y, Zhang J, Xian Z, Biyik E, Held D, et al. RL-VLM-F: Reinforcement learning from vision language foundation model feedback. In: Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: PMLR, 2024. 51484−51501 [64] Fu Y W, Zhang H C, Wu D, Xu W, Boulet B. FuRL: Visual-language models as fuzzy rewards for reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 41st International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: PMLR, 2024. 14256−14274 [65] Yu T H, Quillen D, He Z P, Julian R, Hausman K, Finn C, et al. Meta-world: A benchmark and evaluation for multi-task and meta reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning. Osaka, Japan: PMLR, 2020. 1094−1100 [66] Li J J, Wang Q, Wang Y B, Jin X, Li Y, Zeng W J, et al. Open-world reinforcement learning over long short-term imagination. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Singapore, Singapore: OpenReview.net, 2025. Article No. 123 [67] Laskin M, Srinivas A, Abbeel P. CURL: Contrastive unsupervised representations for reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning. Vienna, Austria: PMLR, 2020. 5639−5650 [68] 张重生, 陈杰, 李岐龙, 邓斌权, 王杰, 陈承功. 深度对比学习综述. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 15−39 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220421Zhang Chong-Sheng, Chen Jie, Li Qi-Long, Deng Bin-Quan, Wang Jie, Chen Cheng-Gong. Deep contrastive learning: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 15−39 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220421 [69] Pore A, Muradore R, Dall'Alba D. DEAR: Disentangled environment and agent representations for reinforcement learning without reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates: IEEE, 2024. 650−655 [70] Zheng W Q, Sharan S P, Fan Z W, Wang K, Xi Y H, Wang Z Y. Symbolic visual reinforcement learning: A scalable framework with object-level abstraction and differentiable expression search. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2025, 47(1): 400−412 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3469053 [71] Zhai Y P, Peng P X, Zhao Y F, Huang Y R, Tian Y H. Stabilizing visual reinforcement learning via asymmetric interactive cooperation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Paris, France: IEEE, 2023. 207−216 [72] 刘宇昕, 项刘宇, 何召锋, 魏运, 吴惠甲, 王永钢. 基于状态-动作联合掩码的自监督学习算法. 计算机技术与发展, 2024, 34(11): 125−132 doi: 10.20165/j.cnki.ISSN1673-629X.2024.0255Liu Yu-Xin, Xiang Liu-Yu, He Zhao-Feng, Wei Yun, Wu Hui-Jia, Wang Yong-Gang. State-action joint mask-based self-supervised learning algorithm. Computer Technology and Development, 2024, 34(11): 125−132 doi: 10.20165/j.cnki.ISSN1673-629X.2024.0255 [73] Huang S N, Zhang Z A, Liang T H, Xu Y H, Kou Z H, Lu C H, et al. MENTOR: Mixture-of-experts network with task-oriented perturbation for visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Vancouver, Canada: PMLR, 2025. 26143−26161 [74] Shi W J, Huang G, Song S J, Wu C. Temporal-spatial causal interpretations for vision-based reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(12): 10222−10235 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3133717 [75] Yang R, Wang J, Geng Z J, Ye M X, Ji S W, Li B, et al. Learning task-relevant representations for generalization via characteristic functions of reward sequence distributions. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. Washington, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2022. 2242−2252 [76] Wang S, Wu Z H, Hu X B, Wang J W, Lin Y F, Lv K. What effects the generalization in visual reinforcement learning: Policy consistency with truncated return prediction. In: Proceedings of the 38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, Canada: AAAI Press, 2024. 5590−5598 [77] Dunion M, McInroe T, Luck K S, Hanna J P, Albrecht S V. Temporal disentanglement of representations for improved generalisation in reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). TBD: OpenReview.net, 2023. Article No. 116 (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版地信息, 请确认) [78] Wang R R, Cheng Y H, Wang X S. Clustering-driven state embedding for reinforcement learning under visual distractions. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(12): 7382−7395 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2024.3449294 [79] Wang R R, Cheng Y H, Wang X S. Visual reinforcement learning control with instance-reweighted alignment and instance-dimension uniformity. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2025, 36(6): 9905−9918 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2025.3556838 [80] Zheng R J, Wang X Y, Sun Y C, Ma S, Zhao J Y, Xu H Z, et al. TACO: Temporal latent action-driven contrastive loss for visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 2092 [81] Yan M B, Lv J F, Li X. Enhancing visual reinforcement learning with state-action representation. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2024, 304: Article No. 112487 [82] 刘民颂, 朱圆恒, 赵冬斌. 基于Transformer的状态-动作-奖赏预测表征学习. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(1): 117−132 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240230Liu Min-Song, Zhu Yuan-Heng, Zhao Dong-Bin. State-action-reward prediction representation learning based on Transformer. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(1): 117−132 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240230 [83] Choi H, Lee H, Song W, Jeon S, Sohn K, Min D B. Local-guided global: Paired similarity representation for visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 15072−15082 [84] Schwarzer M, Anand A, Goel R, Hjelm R D, Courville A, Bachman P. Data-efficient reinforcement learning with self-predictive representations. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2021. Article No. 118 [85] Park S, Rybkin O, Levine S. METRA: Scalable unsupervised RL with metric-aware abstraction. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. Article No. 125 [86] Liang D Y, Chen Q H, Liu Y L. Sequential action-induced invariant representation for reinforcement learning. Neural Networks, 2024, 179: Article No. 106579 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2024.106579 [87] Cai F Z, Kwietniak D, Li J, Pourmand H. On the properties of the mean orbital pseudo-metric. Journal of Differential Equations, 2022, 318: 1−19 doi: 10.1016/j.jde.2022.02.019 [88] Ferns N, Panangaden P, Precup D. Metrics for finite Markov decision processes. In: Proceedings of the 20th Conference on Uncertainty in Artificial Intelligence. Banff, Canada: AUAI Press, 2004. 162−169 [89] Gelada C, Kumar S, Buckman J, Nachum O, Bellemare M G. DeepMDP: Learning continuous latent space models for representation learning. In: Proceedings of the 36th International Conference on Machine Learning. Long Beach, USA: PMLR, 2019. 2170−2179 [90] Zhang A, McAllister R T, Calandra R, Gal Y, Levine S. Learning invariant representations for reinforcement learning without reconstruction. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2021. Article No. 117 [91] Agarwal R, Machado M C, Castro P S, Bellemare M G. Contrastive behavioral similarity embeddings for generalization in reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2021. Article No. 130 [92] Liu Q Y, Zhou Q, Yang R, Wang J. Robust representation learning by clustering with bisimulation metrics for visual reinforcement learning with distractions. In: Proceedings of the 37th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Washington, USA: AAAI Press, 2023. 8843−8851 [93] Wang R R, Cheng Y H, Wang X S. Constrained visual representation learning with bisimulation metrics for safe reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2025, 34: 379−393 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2024.3523798 [94] Dunion M, McInroe T, Luck K S, Hanna J P, Albrecht S V. Conditional mutual information for disentangled representations in reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 3509 [95] Wang S, Wu Z H, Wang J W, Hu X B, Lin Y F, Lv K. How to learn domain-invariant representations for visual reinforcement learning: An information-theoretical perspective. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI). Jeju, South Korea: IJCAI, 2024. 1389−1397 [96] You B, Liu P Z, Liu H P, Peters J, Arenz O. Maximum total correlation reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 42nd International Conference on Machine Learning. Vancouver, Canada: PMLR, 2025. 72677−72699 (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版地, 请确认) [97] Yang R, Wang J, Peng Q J, Guo R B, Wu G P, Li B. Learning robust representations with long-term information for generalization in visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Singapore, Singapore: OpenReview.net, 2025. Article No. 129 [98] Fan J M, Li W C. DRIBO: Robust deep reinforcement learning via multi-view information bottleneck. In: Proceedings of the 39th International Conference on Machine Learning. Baltimore, USA: PMLR, 2022. 6074−6102 [99] Yuan Z C, Wei T M, Cheng S Q, Zhang G, Chen Y P, Xu H Z. Learning to manipulate anywhere: A visual generalizable framework for reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Robot Learning. Munich, Germany: PMLR, 2025. 1815−1833 [100] Dunion M, Albrecht S V. Multi-view disentanglement for reinforcement learning with multiple cameras. In: Proceedings of the Reinforcement Learning Conference (RLC). Amherst, USA: RLJ, 2024. 498−515 [101] Haramati D, Daniel T, Tamar A. Entity-centric reinforcement learning for object manipulation from pixels. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vienna, Austria: OpenReview.net, 2024. Article No. 135 [102] Yang S Z, Ze Y J, Xu H Z. MoVie: Visual model-based policy adaptation for view generalization. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 940 [103] Mu T Z, Li Z Y, Strzelecki S W, Yuan X, Yao Y C, Liang L T, et al. When should we prefer state-to-visual dagger over visual reinforcement learning?. In: Proceedings of the 39th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Philadelphia, Pennsylvania: AAAI Press, 2025. 14637−14645 [104] Wang W Y, Fang X Y, Hager G. Adapting image-based RL policies via predicted rewards. In: Proceedings of the 6th Annual Learning for Dynamics & Control Conference. Oxford, UK: PMLR, 2024. 324−336 [105] Liu X, Chen Y R, Li H R, Li B Y, Zhao D B. Cross-domain random pretraining with prototypes for reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2025, 55(5): 3601−3613 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2025.3541926 [106] Ze Y J, Hansen N, Chen Y B, Jain M, Wang X L. Visual reinforcement learning with self-supervised 3D representations. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023, 8(5): 2890−2897 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3259681 [107] 王雪松, 王荣荣, 程玉虎. 基于表征学习的离线强化学习方法研究综述. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(6): 1104−1128 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230546Wang Xue-Song, Wang Rong-Rong, Cheng Yu-Hu. A review of offline reinforcement learning based on representation learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(6): 1104−1128 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230546 [108] Rafailov R, Yu T H, Rajeswaran A, Finn C. Offline reinforcement learning from images with latent space models. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Conference on Learning for Dynamics and Control. Virtual Event, Switzerland: PMLR, 2021. 1154−1168 (查阅网上资料, 未找到本条文献出版地, 请确认) [109] Shang J H, Kahatapitiya K, Li X, Ryoo M S. StARformer: Transformer with state-action-reward representations for visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 17th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Tel Aviv, Israel: Springer, 2022. 462−479 [110] Zhang Y R, Chen K Z, Liu Y L. Causal representation learning in offline visual reinforcement learning. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2025, 320: Article No. 113565 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2025.113565 [111] Wang Q, Yang J M, Wang Y B, Jin X, Zeng W J, Yang X K. Making offline RL online: Collaborative world models for offline visual reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2024. 97203−97230 [112] Tassa Y, Doron Y, Muldal A, Erez T, Li Y Z, de Las Casas D, et al. DeepMind control suite. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1801.00690, 2018. [113] Hansen N, Wang X L. Generalization in reinforcement learning by soft data augmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2021. 13611−13617 [114] Stone A, Ramirez O, Konolige K, Jonschkowski R. The distracting control suite-a challenging benchmark for reinforcement learning from pixels. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2101.02722, 2021. [115] Yuan Z C, Yang S Z, Hua P, Chang C, Hu K Z, Xu H Z. RL-ViGen: A reinforcement learning benchmark for visual generalization. In: Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. Article No. 295 [116] Jiang J H, Yang Y X, Deng Y Q, Ma C L, Zhang J. BEVNav: Robot autonomous navigation via spatial-temporal contrastive learning in bird's-eye view. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024, 9(12): 10796−10802 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3482190 [117] Chen W, Rojas N. TraKDis: A transformer-based knowledge distillation approach for visual reinforcement learning with application to cloth manipulation. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024, 9(3): 2455−2462 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3358750 [118] 赵静, 裴子楠, 姜斌, 陆宁云, 赵斐, 陈树峰. 基于深度强化学习的无人机虚拟管道视觉避障. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(11): 2245−2258 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230728Zhao Jing, Pei Zi-Nan, Jiang Bin, Lu Ning-Yun, Zhao Fei, Chen Shu-Feng. Virtual tube visual obstacle avoidance for UAV based on deep reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(11): 2245−2258 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230728 [119] 杨蕾, 雷为民, 张伟. 融合时空特征的视觉自动驾驶强化学习算法. 小型微型计算机系统, 2023, 44(2): 356−362 doi: 10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/TP.2022-0597Yang Lei, Lei Wei-Min, Zhang Wei. Reinforcement learning algorithm for visual auto-driving based space-time features. Journal of Chinese Computer Systems, 2023, 44(2): 356−362 doi: 10.20009/j.cnki.21-1106/TP.2022-0597 [120] Jiang B, Chen S Y, Zhang Q, Liu W Y, Wang X G. AlphaDrive: Unleashing the power of VLMs in autonomous driving via reinforcement learning and reasoning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2503.07608, 2025. [121] Liu Y Q, Qu T Y, Zhong Z S, Peng B H, Liu S, Yu B, et al. VisionReasoner: Unified reasoning-integrated visual perception via reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2505.12081, 2025. [122] Li W Q, Zhang X Y, Zhao S J, Zhang Y B, Li J L, Zhang L, et al. Q-insight: Understanding image quality via visual reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2503.22679, 2025. [123] Miao Z C, Wang J, Wang Z, Yang Z Y, Wang L J, Qiu Q, et al. Training diffusion models towards diverse image generation with reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 10844−10853 [124] Kondrotas K, Zhang L, Lim C P, Asadi H, Yu Y H. Audio-visual emotion classification using reinforcement learning-enhanced particle swarm optimisation. IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, 2025, 16(4): 3434−3451 doi: 10.1109/TAFFC.2025.3591356 [125] 徐樊丰, 仝明磊. 基于视觉强化学习的数字芯片全局布局方法. 计算机应用研究, 2024, 41(4): 1270−1274 doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2023.08.0385Xu Fan-Feng, Tong Ming-Lei. Visual-based reinforcement learning for digital chip global placement. Application Research of Computers, 2024, 41(4): 1270−1274 doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2023.08.0385 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 434
- HTML全文浏览量: 282
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: