Target Enclosing Control of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Swarm Based on Socialized Collaboration
-
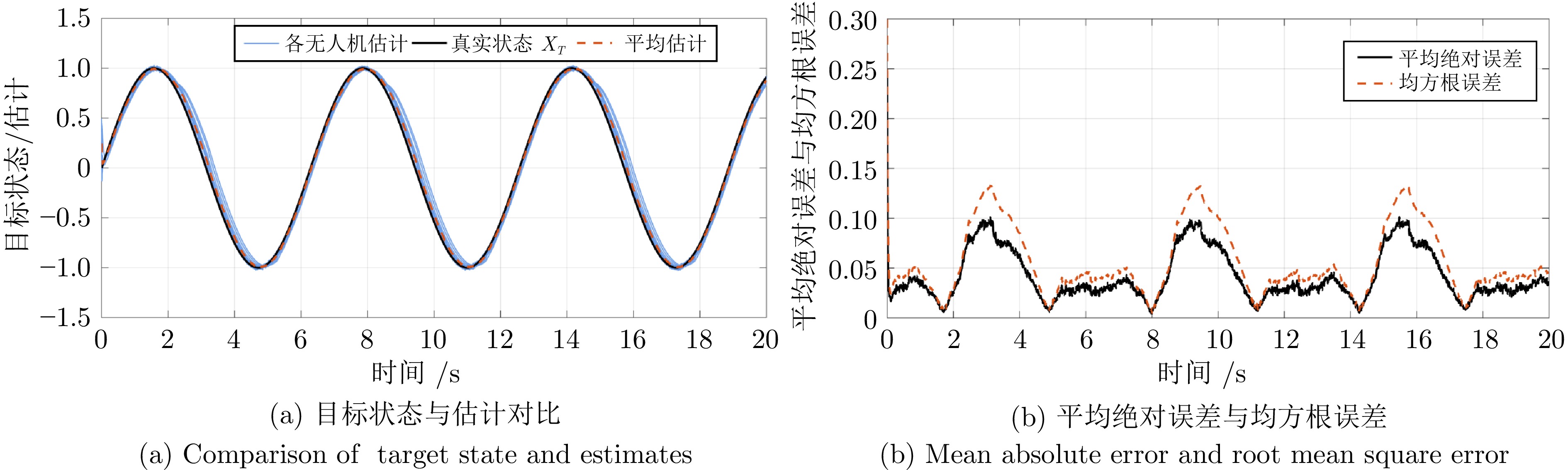
摘要: 面向感知、通信受限且存在环境障碍的移动目标合围控制, 提出一种基于社会化协同的控制策略. 首先, 借鉴生物集群社会化行为, 构建协同响应模型与层级交互机制; 在拓扑切换与丢包条件下, 显式建模受限信息流, 以驱动集群实现目标合围. 其次, 提出强引导式任务——避碰并行协同控制, 在优先保障飞行安全的前提下实现鲁棒合围控制. 再次, 设计一致性目标状态观测器, 对目标位置与速度进行稳健估计. 最后, 仿真结果表明, 所提方法在障碍环境以及感知、通信受限条件下能够实现稳定合围, 并表现出较好的鲁棒性.Abstract: A socialized collaboration-based control strategy is proposed for mobile-target enclosing under perception and communication constraints in the presence of environmental obstacles. First, inspired by socialized behaviors in biological swarms, a cooperative response model and a hierarchical interaction mechanism are established; under topology switching and packet-loss conditions, the constrained information flow is explicitly modeled to drive the swarm to achieve target enclosing. Second, a strongly guided task——Collision-avoidance parallel cooperative control scheme is proposed to realize robust enclosing control while prioritizing flight safety. Third, a consensus-based target-state observer is designed to robustly estimate the target position and velocity. Finally, simulation results demonstrate that the proposed method can achieve stable encirclement in obstacle-laden environments under perception and communication constraints, exhibiting favorable robustness.
-
表 1 仿真参数设置
Table 1 Settings of simulation parameters
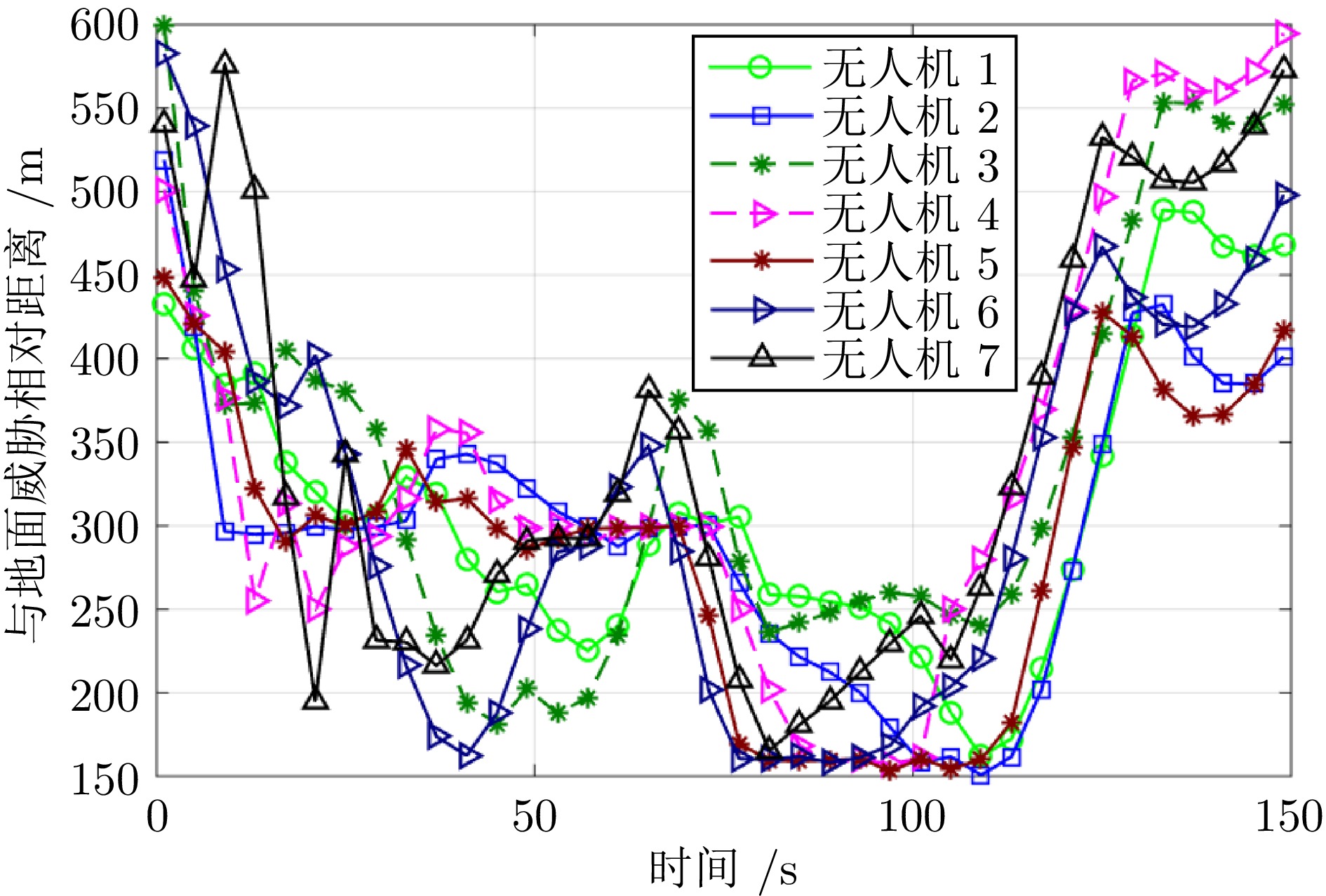
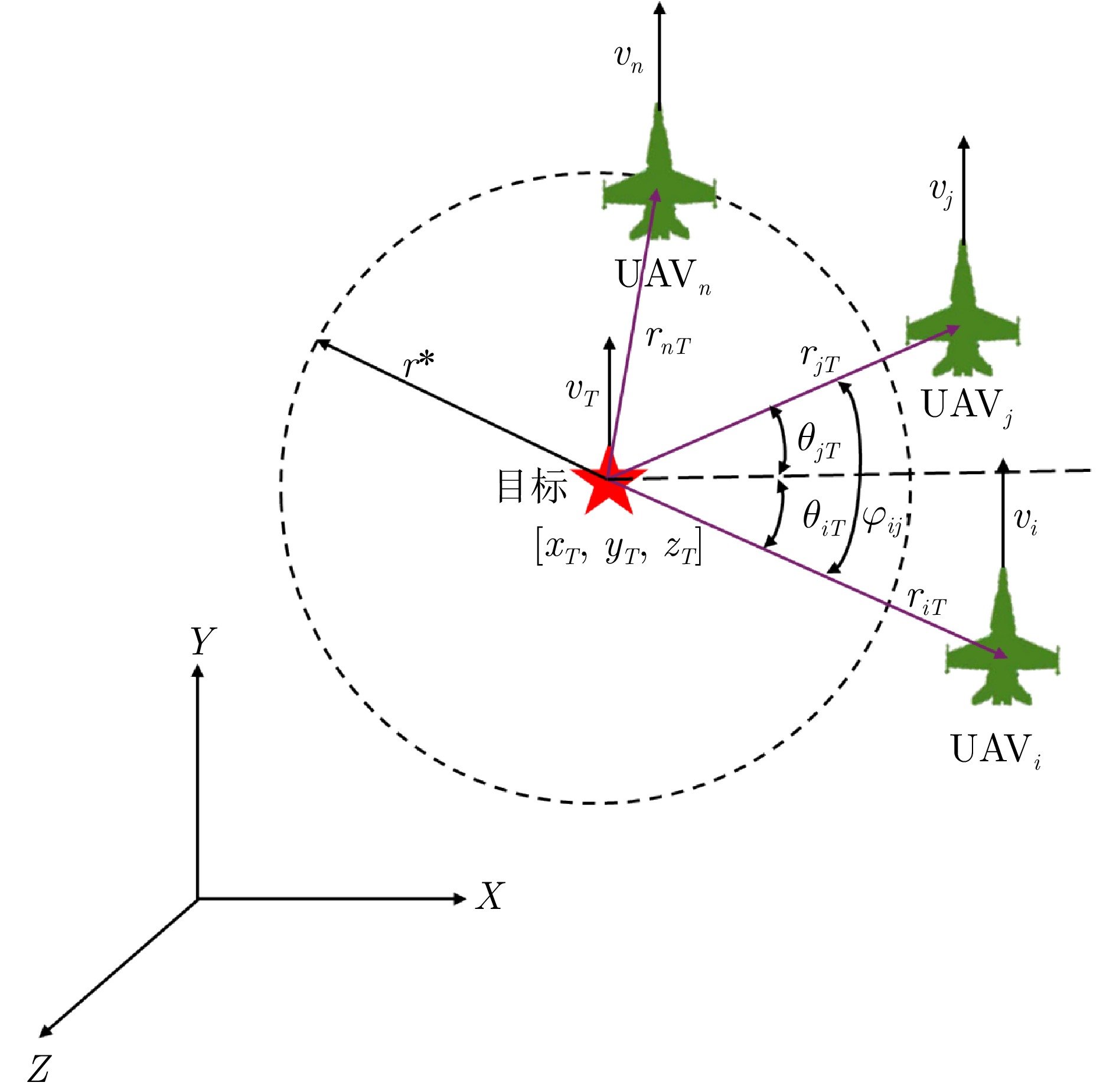
类别 符号 数值 无人机集群规模 $ N $ $ 7 $ 速度上下界 $ ({V}_{\min },\;{V}_{\max }) $ $ (10,\;80)\;\mathrm{m}/\mathrm{s} $ 最大过载 $ {n}_{\max } $ $ 6 $ 最大航迹角 $ {\gamma }_{\max } $ $ \pi /4 $ 自动驾驶仪时间常数 $ {\tau }_{v},\;{\tau }_{\chi },\;{\tau }_{\gamma } $ $ 2.5\;\mathrm{s} $, $ 2.5\;\mathrm{s},\;2.5\;\mathrm{s} $ 高度控制增益常数 $ {k}_{1},\;{k}_{2} $ $ 2,\;2 $ 感知半径 $ {r}_{d} $ $ 200\;\mathrm{m} $ 通信距离 $ {r}_{c} $ $ 200\;\mathrm{m} $ 期望合围半径 $ {r}^{\mathrm{*}} $ $ 100\;\mathrm{m} $ 期望角间距 $ \varphi _{iT}^{\mathrm{*}} $ $ -\pi $ 观测器收敛系数 $ \alpha $ $ 2 $ 排斥力系数 $ {\rho }_{a} $ $ 2 $ 安全距离 $ {d}_{s} $ $ 150\;\mathrm{m} $ 控制增益 $ {\gamma }_{1},\;{\gamma }_{2},\;{\gamma }_{3},\;{\gamma }_{4} $ $ 5,\;1,\;5,\;8 $ 社会力权重系数 $ {w}_{co},\;{w}_{T},\; $$ {w}_{d},\;{w}_{w} $ $ 0.40,\;0.40,\; $$ 0.15,\;0.05 $ 表 2 障碍物参数设置
Table 2 Settings of obstacle parameters
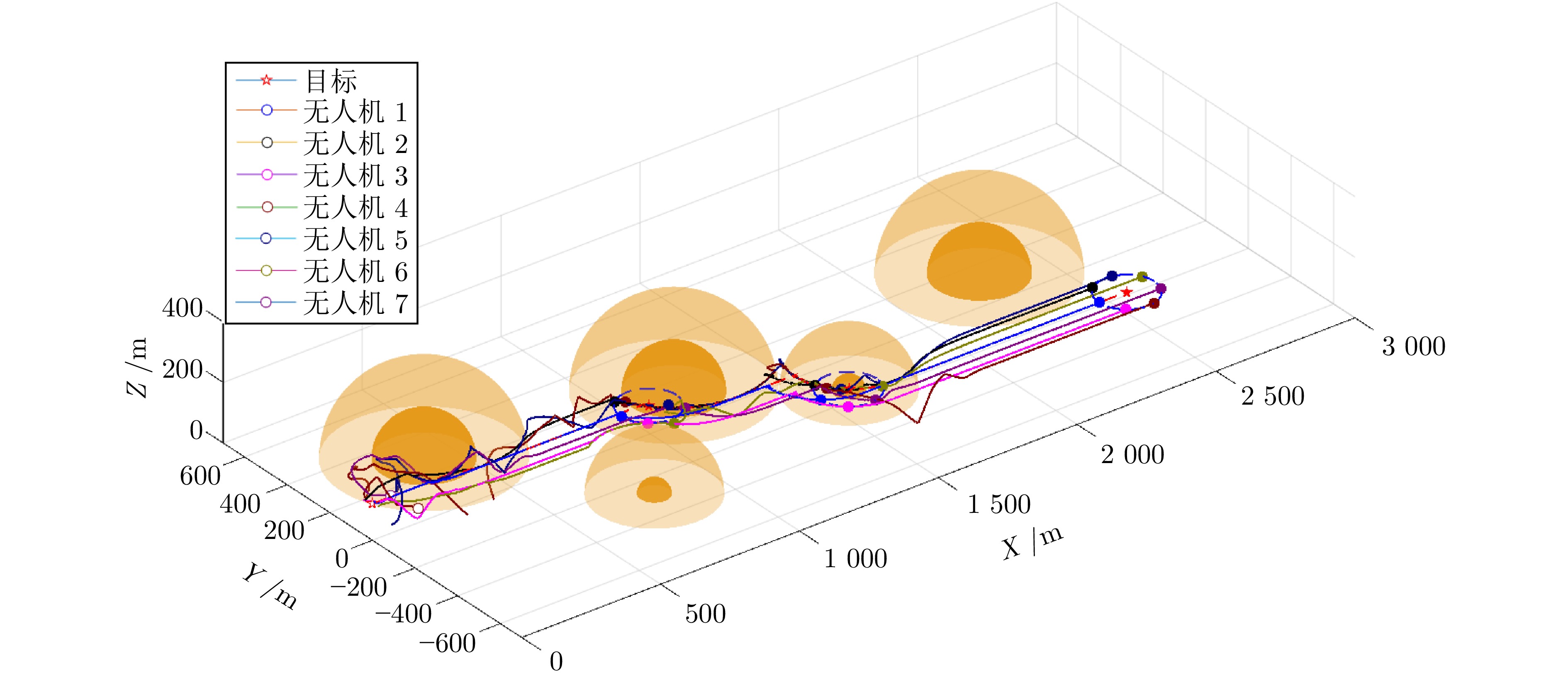
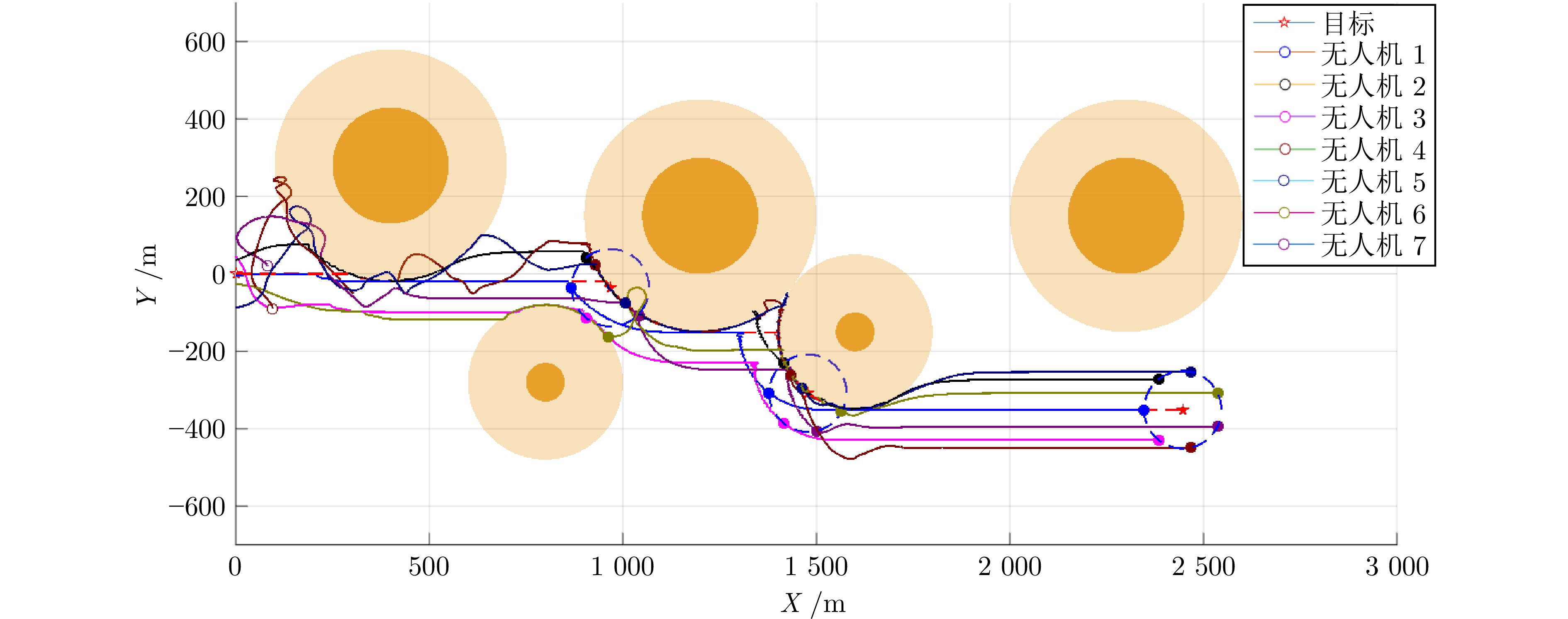
障碍物标号 中心点坐标 范围半径 1 (400, 280) 150 m 2 (800, −280) 50 m 3 ( 1200 , 150)150 m 4 ( 1600 , −150)50 m 5 ( 2300 , 150)150 m 表 3 三种算法对比仿真统计结果
Table 3 Simulation statistics results for three algorithms comparison
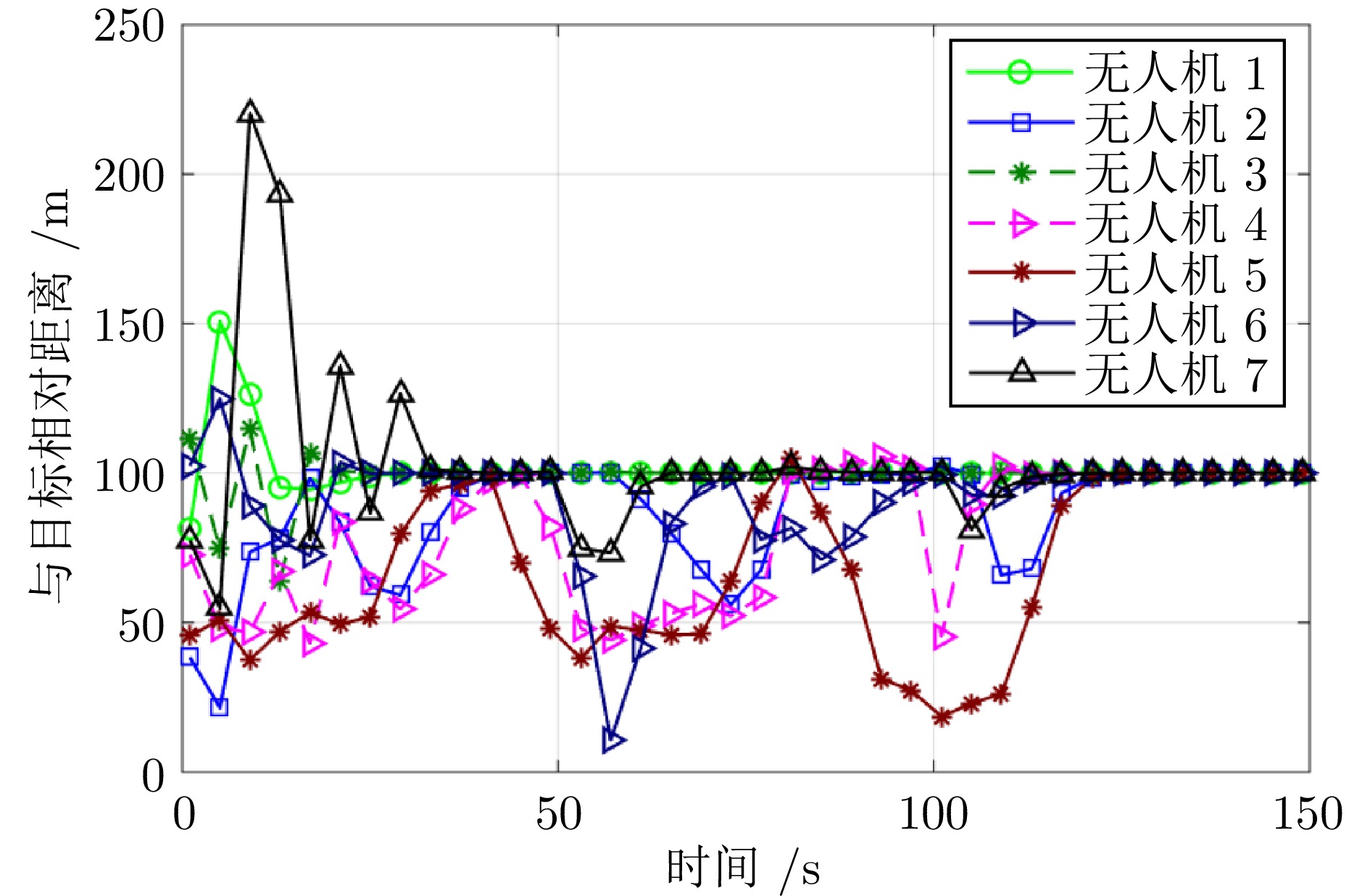
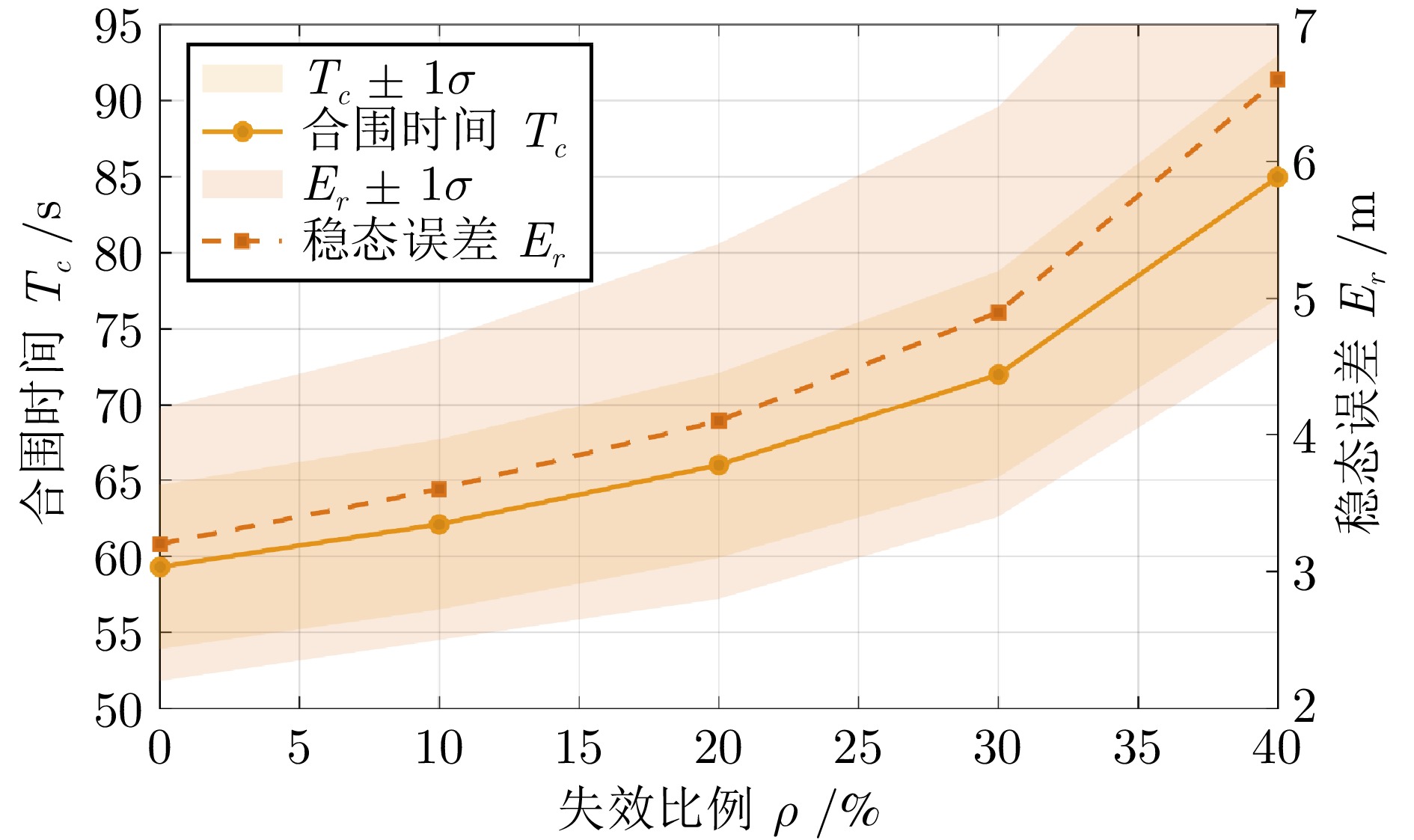
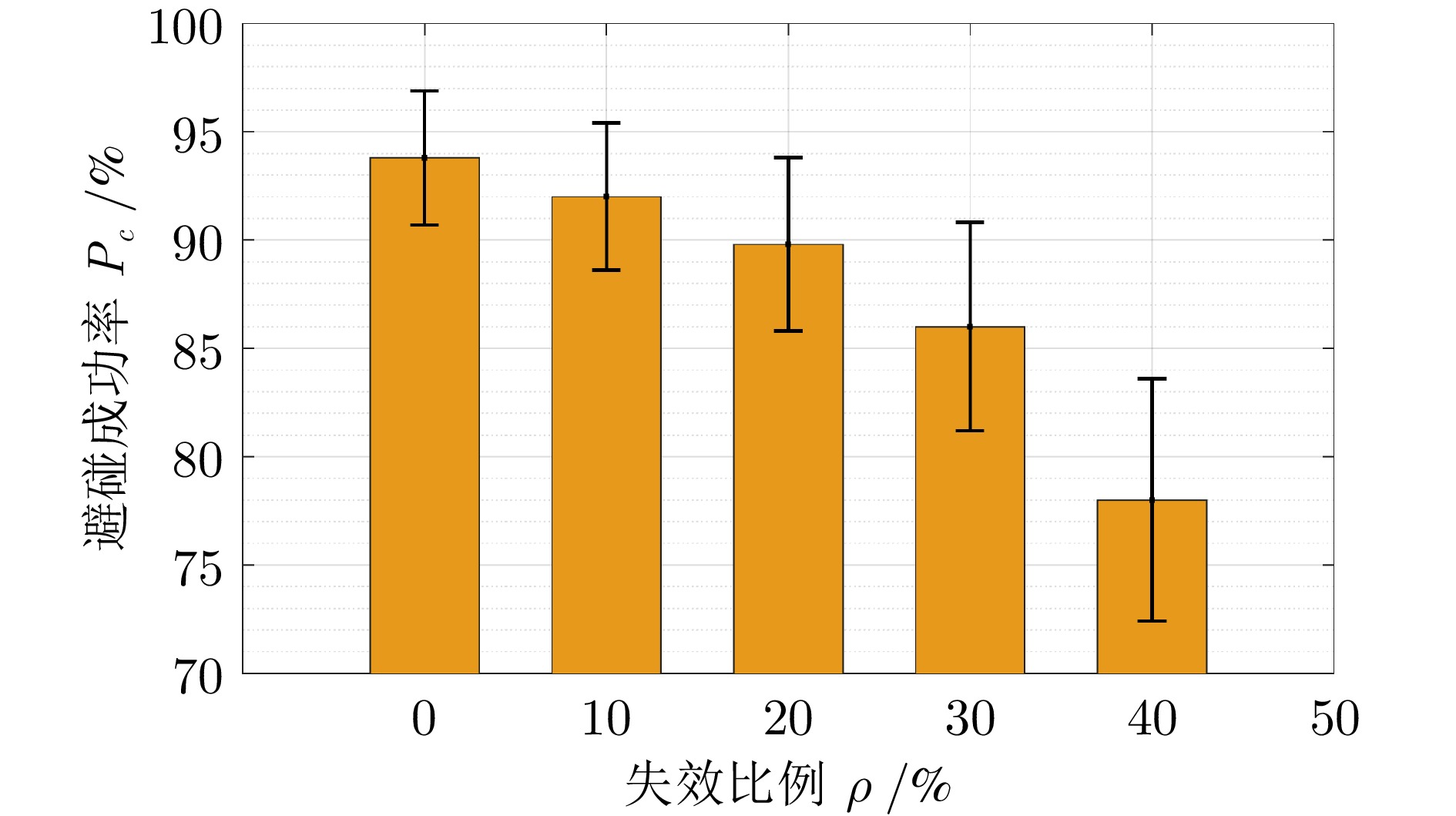
指标 VFM RFM 本文 合围时间$ {T}_{c}\;(\mathrm{s}) $ 82.4 ± 6.8 95.7 ± 9.3 59.3 ± 5.4 稳态半径均方误差$ {E}_{r}\left(\mathrm{m}\right) $ 5.1 ± 1.7 6.8 ± 2.1 3.2 ± 1.0 避碰成功率$ {P}_{c}\;(\% ) $ 71.2 ± 4.9 65.5 ± 6.3 93.8 ± 3.1 RMSE 3.5 ± 0.8 4.1 ± 1.0 2.4 ± 0.7 -
[1] Chung S J, Paranjape A A, Dames P, Shen S J, Kumar V. A survey on aerial swarm robotics. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(4): 837−855 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2857475 [2] Mei Z W, Shao X L, Xia Y, Liu J. Enhanced fixed-time collision-free elliptical circumnavigation coordination for UAVs. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 4257−4270 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3374708 [3] Zhang Q R, Liu H H T. Robust nonlinear close formation control of multiple fixed-wing aircraft. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2021, 44(3): 572−586 doi: 10.2514/1.G004592 [4] Raja G, Baskar Y, Dhanasekaran P, Nawaz R, Yu K P. An efficient formation control mechanism for multi-UAV navigation in remote surveillance. In: Proceedings of IEEE Globecom Workshops. Madrid, Spain: IEEE, 2021. 1−6 [5] Ranjan P K, Sinha A, Cao Y C, Tran D, Casbeer D, Weintraub I. Energy-efficient ring formation control with constrained inputs. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2023, 46(7): 1397−1407 doi: 10.2514/1.G007057 [6] Krátký V, Alcántara A, Capitán J, Štěpán P, Saska M, Ollero A. Autonomous aerial filming with distributed lighting by a team of unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2021, 6(4): 7580−7587 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3098811 [7] Sinha A, Cao Y C. 3-D nonlinear guidance law for target circumnavigation. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2023, 7: 655−660 doi: 10.1109/LCSYS.2022.3215609 [8] Kim T H, Sugie T. Cooperative control for target-capturing task based on a cyclic pursuit strategy. Automatica, 2007, 43(8): 1426−1431 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2007.01.018 [9] Pothen A A, Ratnoo A. Curvature-constrained Lyapunov vector field for standoff target tracking. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2017, 40(10): 2729−2736 doi: 10.2514/1.G002281 [10] Shao X L, Xia Y, Mei Z W, Zhang W D. Model-guided reinforcement learning enclosing for UAVs with collision-free and reinforced tracking capability. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2023, 142: Article No. 108609 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2023.108609 [11] Sinha A, Cao Y C. Three-dimensional guidance law for target enclosing within arbitrary smooth shapes. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2023, 46(11): 2224−2234 doi: 10.2514/1.G007539 [12] Dong F, You K Y, Song S J. Target encirclement with any smooth pattern using range-based measurements. Automatica, 2020, 116: Article No. 108932 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2020.108932 [13] Dong F, You K Y, Xie L H, Hu Q L. Coordinate-free circumnavigation of a moving target via a PD-like controller. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(3): 2012−2025 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3127858 [14] Jain P, Peterson C K, Beard R W. Encirclement of moving targets using noisy range and bearing measurements. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2022, 45(8): 1399−1414 doi: 10.2514/1.G006403 [15] Ranjan P K, Sinha A, Cao Y C. Robust UAV guidance law for safe target circumnavigation with limited information and autopilot lag considerations. In: Proceedings of AIAA SCITECH Forum. Orlando, USA: AIAA, 2024. Article No. 0124 [16] Ju S, Wang J, Dou L Y. Enclosing control for multiagent systems with a moving target of unknown bounded velocity. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(11): 11561−11570 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3072031 [17] Jiang Y, Peng Z H, Liu L, Wang D, Zhang F M. Safety-critical cooperative target enclosing control of autonomous surface vehicles based on finite-time fuzzy predictors and input-to-state safe high-order control barrier functions. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2024, 32(3): 816−830 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2023.3309706 [18] Dou L Y, Yu X, Liu L, Wang X F, Feng G. Moving-target enclosing control for mobile agents with collision avoidance. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2021, 8(4): 1669−1679 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2021.3078120 [19] Lu K, Dai S L, Jin X. Cooperative constrained enclosing control of multirobot systems in obstacle environments. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2024, 11(2): 718−730 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2023.3299151 [20] Olfati-Saber R, Murray R M. Consensus problems in networks of agents with switching topology and time-delays. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2004, 49(9): 1520−1533 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2004.834113 [21] Lian B S, Wan Y, Zhang Y, Liu M S, Lewis F L, Chai T Y. Distributed Kalman consensus filter for estimation with moving targets. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(6): 5242−5254 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3029007 [22] Li Y H, Li S Y. Self-localization for distributed systems based on the relative measurement information. In: Proceedings of the 41st Chinese Control Conference. Hefei, China: IEEE, 2022. 4778−4783 [23] Liu F, Guo C P, Meng W, Su R, Li H Y. Moving-target circumnavigation using adaptive neural anti-synchronization control via distance-only measurements. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(1): 308−318 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2023.3234366 [24] Li H L, Cai Y W, Hong J C, Xu P, Cheng H, Zhu X M, et al. VG-Swarm: A vision-based gene regulation network for UAVs swarm behavior emergence. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2023, 8(3): 1175−1182 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3236565 [25] Mirzaeinia A, Heppner F, Hassanalian M. An analytical study on leader and follower switching in V-shaped Canada goose flocks for energy management purposes. Swarm Intelligence, 2020, 14(2): 117−141 doi: 10.1007/s11721-020-00179-x [26] Pennisi E. How did cooperative behavior evolve? Science, 2005, 309(5731): 93 doi: 10.1126/science.309.5731.93 [27] Shanghai Jiao Tong University. 125 Questions: Exploration and Discovery. Science/AAAS Custom Publishing Office, 2021. [28] 蒲志强, 易建强, 刘振, 丘腾海, 孙金林, 李非墨. 知识和数据协同驱动的群体智能决策方法研究综述. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(3): 627−643Pu Zhi-Qiang, Yi Jian-Qiang, Liu Zhen, Qiu Teng-Hai, Sun Jin-Lin, Li Fei-Mo. Knowledge-based and data-driven integrating methodologies for collective intelligence decision making: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(3): 627−643 [29] Mogilner A, Edelstein-Keshet L, Bent L, Spiros A. Mutual interactions, potentials, and individual distance in a social aggregation. Journal of Mathematical Biology, 2003, 47(4): 353−389 doi: 10.1007/s00285-003-0209-7 [30] 陈波, 张辉, 江一鸣, 钟杭, 王耀南. 基于分层仿生神经网络的多机器人协同区域搜索算法. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(4): 890−902 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240458Chen Bo, Zhang Hui, Jiang Yi-Ming, Zhong Hang, Wang Yao-Nan. A hierarchical bio-inspired neural network based multi-robot cooperative area search algorithm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(4): 890−902 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240458 [31] Miao Z Q, Wang Y N, Fierro R. Cooperative circumnavigation of a moving target with multiple nonholonomic robots using backstepping design. Systems & Control Letters, 2017, 103: 58−65 doi: 10.1016/j.sysconle.2017.03.004 -




 下载:
下载: