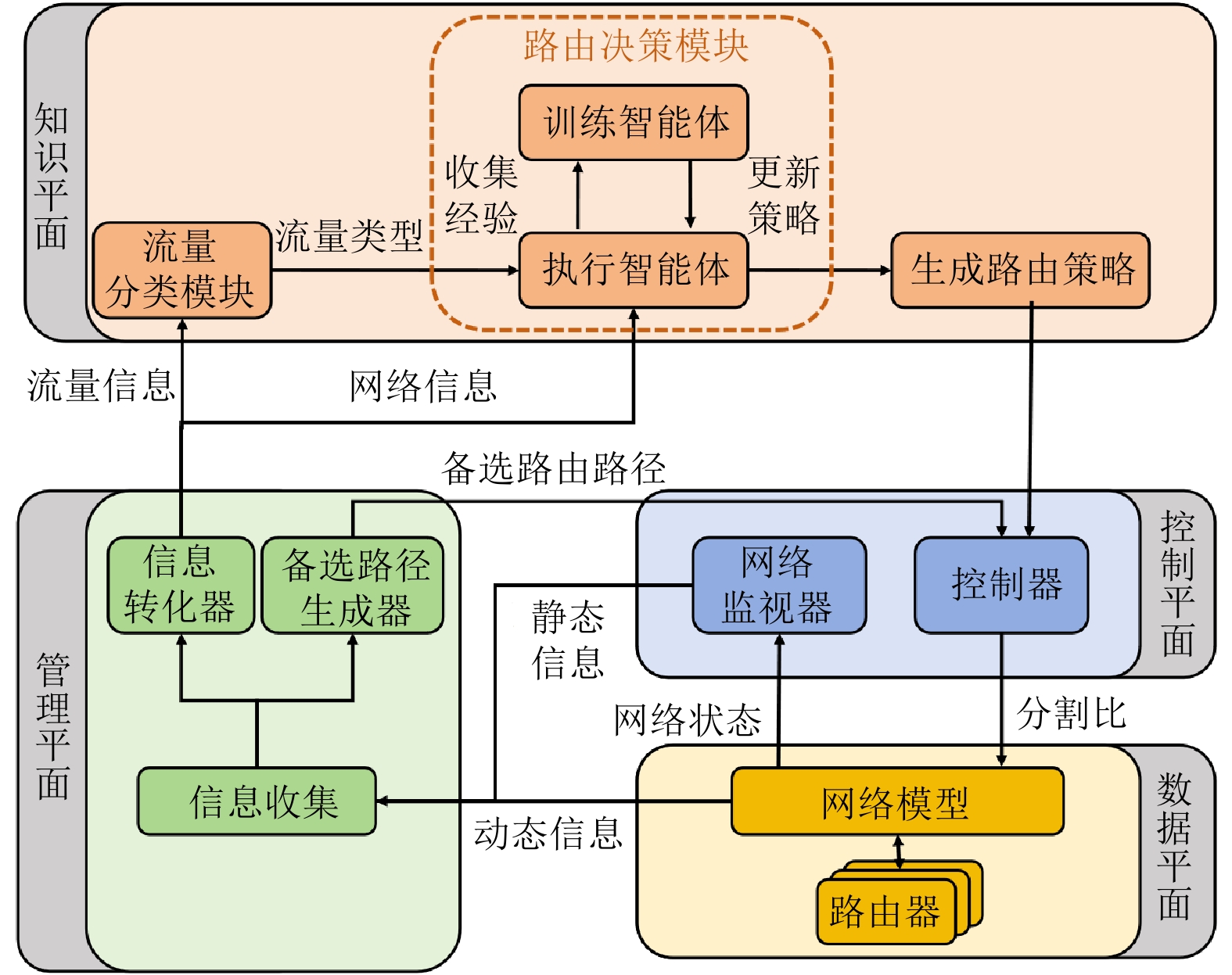
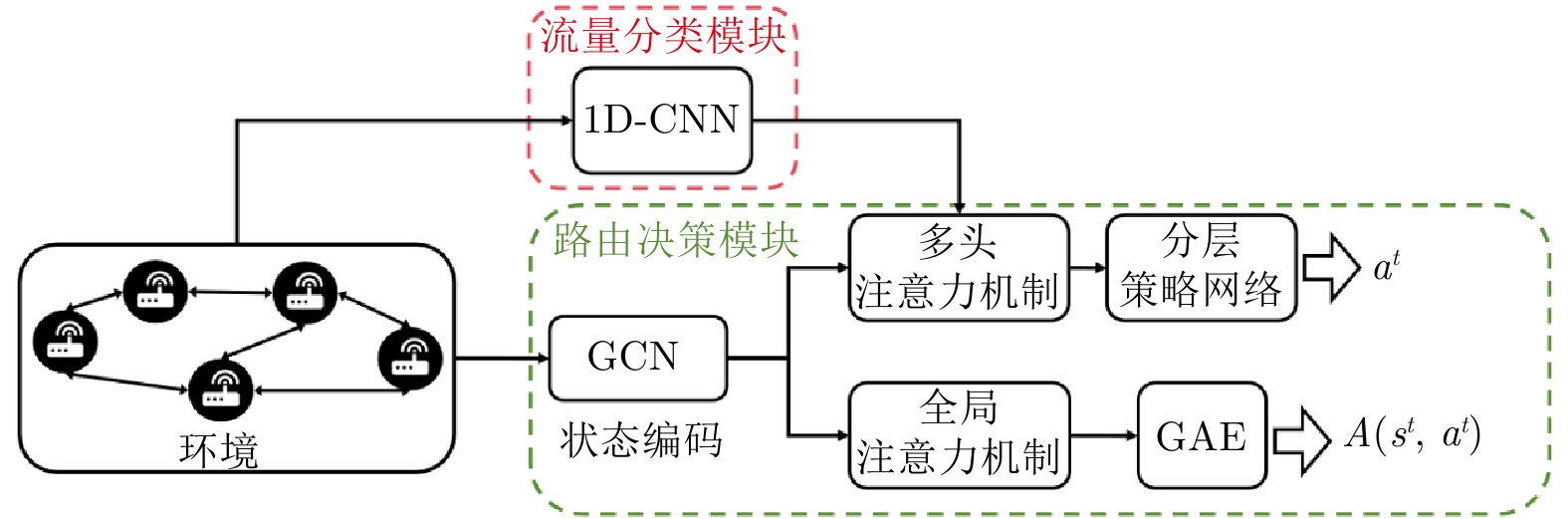
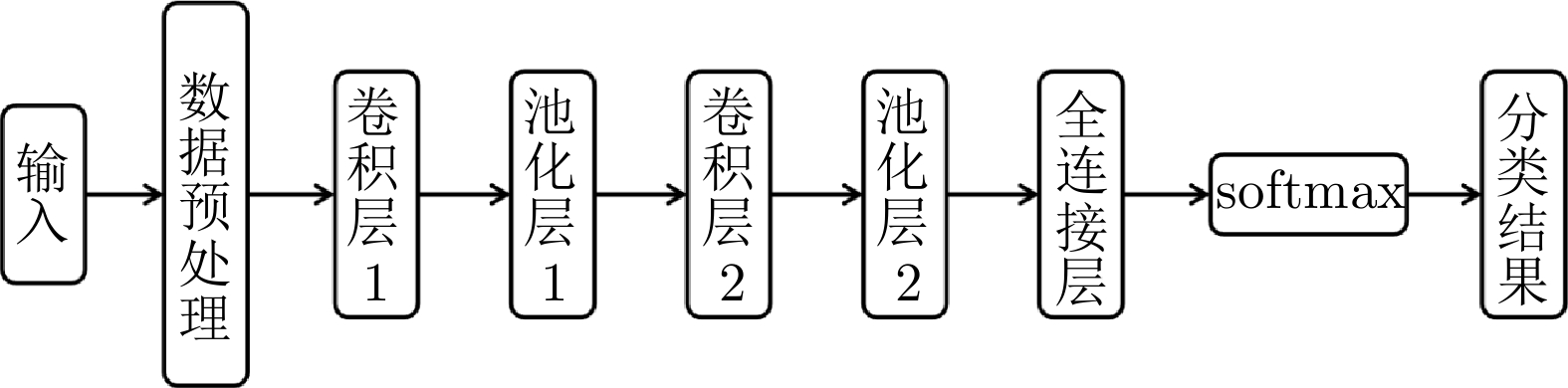
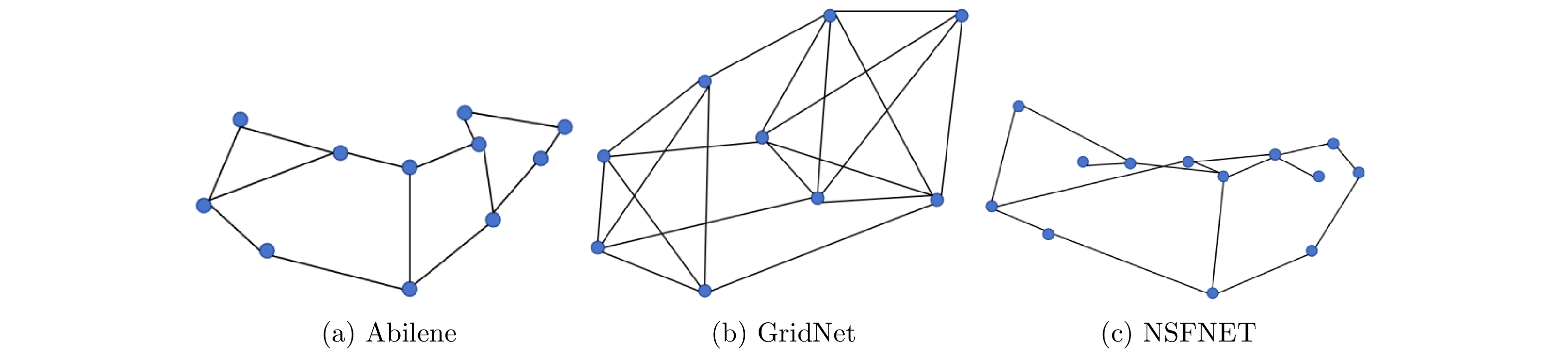
Differentiated Routing Optimization for Multi-type Traffic Based on Hierarchical Policy Reinforcement Learning
-
摘要: 路由是优化网络资源分配的重要方法. 然而, 传统路由算法依赖静态策略优化单一服务质量指标, 难以应对多类型流量爆发性增长下的差异化需求. 尽管深度强化学习为动态网络环境下的路由优化提供了新思路, 现有方法仍缺乏对流量类型的精细化感知能力, 无法灵活调整路由策略. 为此, 本文针对不同类型流量的差异化路由需求, 设计一种基于分层策略强化学习的流量感知路由算法. 首先, 引入流量分类模块, 实现对不同流量差异化业务需求的精细感知. 其次, 利用图卷积网络对网络拓扑进行高效建模, 并在此基础上设计分层决策网络以及差异化奖励函数, 引导智能体生成自适应路由决策, 实现对各流量类别路由策略的动态调整. 同时, 在演员-评论家框架中引入全局注意力机制, 增强智能体对网络状态时空依赖关系的建模能力, 并通过广义优势估计和近端策略优化算法提升训练的效率与稳定性. 最后, 在多种拓扑网络上验证了所提算法的有效性.Abstract: Routing is an important method for optimizing network resource allocation. However, traditional routing algorithms rely on static strategies to optimize single quality of service metrics, making it difficult to address the differentiated requirements of explosive growth in multi-type traffic. Although deep reinforcement learning has provided new ideas for routing optimization in dynamic network environments, existing methods still lack fine-grained perception of traffic types and cannot flexibly adjust routing strategies. To this end, this paper designs a traffic-aware routing algorithm based on hierarchical policy reinforcement learning for the differentiated routing requirements of different traffic types. First, a traffic classification module is introduced to achieve fine-grained perception of the differentiated service requirements of different traffic. Second, graph convolutional networks are used to efficiently model the network topology, based on which a hierarchical decision network and a differentiated reward function are designed to guide the agent to generate adaptive routing decisions and realize dynamic adjustment of routing strategies for each traffic category. Meanwhile, a global attention mechanism is introduced into the actor-critic framework to enhance the agent's ability to model the spatio-temporal dependency of network states, and the training efficiency and stability are improved through generalized advantage estimation and proximal policy optimization algorithms. Finally, the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm is verified on various network topologies.
-
表 1 主要符号及其含义
Table 1 Main notations and their meanings
符号 含义 $ G $ 网络拓扑 $ {\cal{V}} $ 节点集合 $ {\cal{E}} $ 有向链路集合 $ N $、$ M $ 节点与链路的数量 $ \lambda $ 流的到达速率 $ \varphi $ 节点的服务速率 $ \alpha $ 流量分割比 $ \rho $ 节点利用率 $ P $ 节点丢包率 $ D $ 节点/路径延迟 $ U_{QoS} $ QoS感知效用函数 $ {\cal{S}} $ 马尔科夫决策过程(Markov decision process, MDP)状态空间 $ {\cal{A}} $ MDP中动作空间 $ {\cal{R}} $ MDP中奖励函数 $ \gamma $ 折扣因子 $ \eta $ 流量类型 表 2 服务类型分类
Table 2 Service type classification
类别 类型应用 主要特征 延迟敏感型 网络电话、在线聊天和音频流 对实时性要求较高 丢包敏感型 视频流、点对点传输和文件传输 需要较高带宽传输 容错型 电子邮件和网页浏览 对QoS要求不明显或
介于上述两者之间表 3 缩放因子默认值
Table 3 Default values of scaling factors
类别 $ \beta_{P, \delta_{n}} $ $ \beta_{D, \delta_{n}} $ 延迟敏感 0.2 0.8 丢包敏感 0.8 0.2 容错型 0.5 0.5 表 4 流量分类结果
Table 4 Results of traffic classification
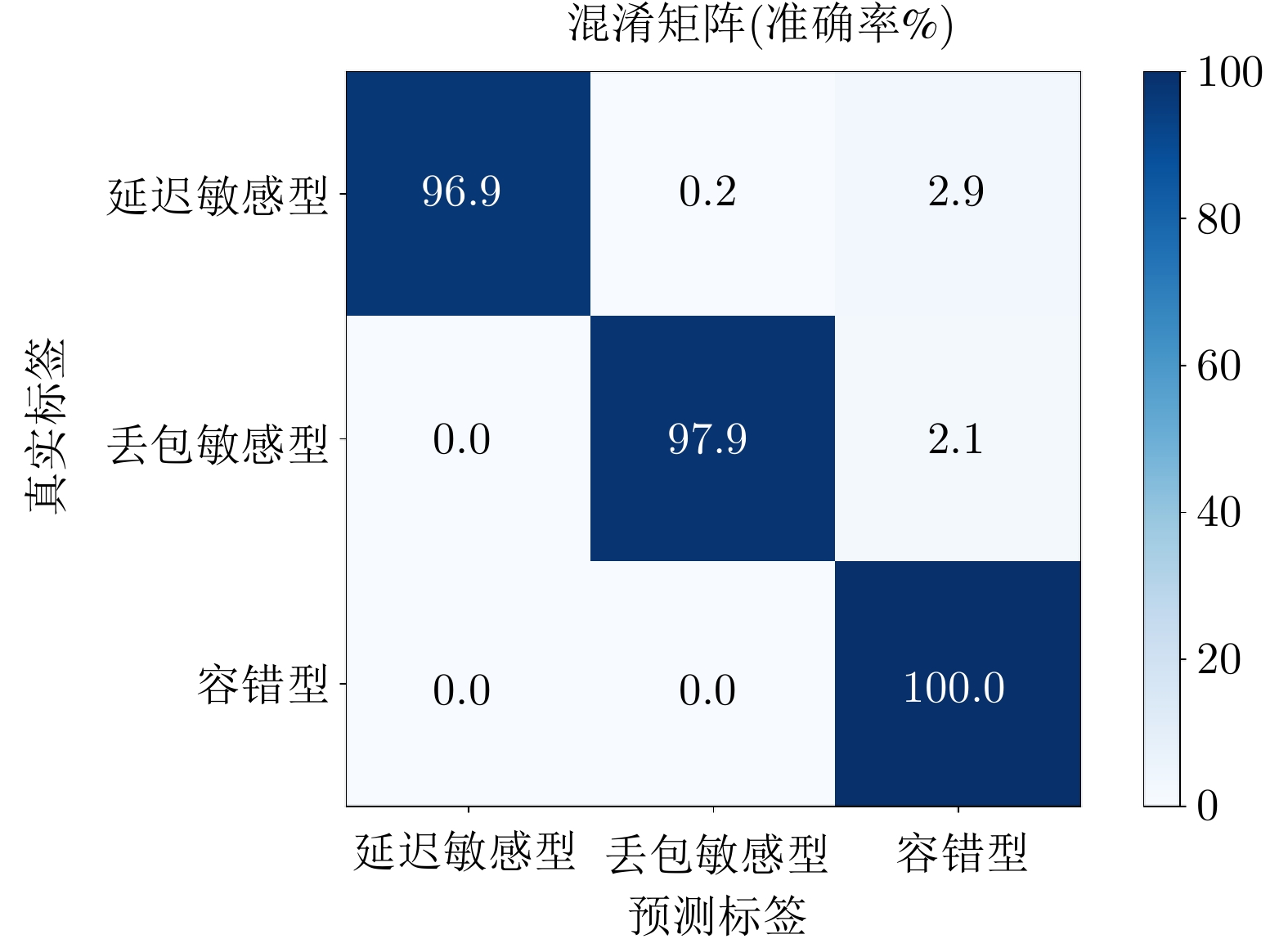
类别 $ Pr $ $ Rc $ 延迟敏感型 1.00 0.97 丢包敏感型 0.99 0.98 容错型 0.95 1.00 表 5 算法模块消融实验结果
Table 5 Results of algorithm module
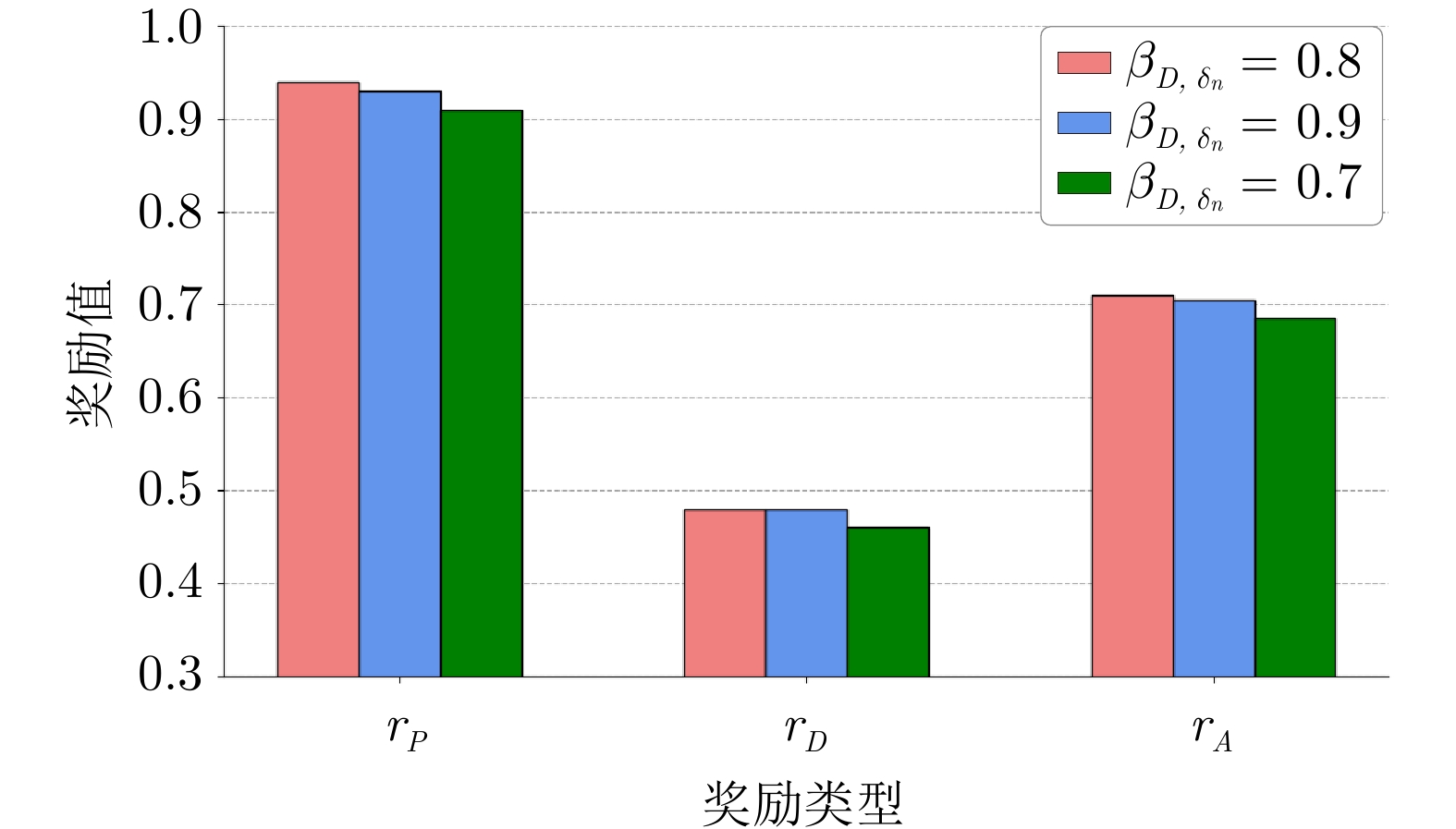
算法模型 $ r_P $ $ r_D $ TR-RL 0.88 0.42 R-HPRL 0.92 0.45 TR-HPRL $ \underline{0.94} $ $ \underline{0.48} $ -
[1] 第55次《中国互联网络发展状况统计报告》发布. 传媒论坛, 2025: 121 [2] 2024年通信业统计公报. 通信企业管理, 2025: 22-26 [3] 中国信息通信研究院. 中国数字经济发展研究报告(2024年). 2024. [4] 蔡岳平, 姚宗辰, 李天驰. 时间敏感网络标准与研究综述. 计算机学报, 2021, 44(07): 1378−1397 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.01378Cai Yue-Ping, Yao Zong-Chen, Li Tian-Chi. A Survey on Time-Sensitive Networking: Standards and State-of-the-Art. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2021, 44(07): 1378−1397 doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2021.01378 [5] 李永福, 何昌鹏, 朱浩, 郑太雄. 通信延时环境下异质网联车辆队列非线性纵向控制. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(12): 2841−2856 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190442Li Yong-Fu, He Chang-Peng, Zhu Hao, Zheng Tai-Xiong. Nonlinear longitudinal control for heterogeneous connected vehicle platoon in the presence of communication delays. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(12): 2841−2856 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190442 [6] Moy J. OSPF version 2. 1997. [7] Zhang H, Guo X, Yan J, Liu B, Shuai Q J. SDN-based ECMPalgorithm for data center networks. In: Proceedings of the 1st IEEE Computers, Communications and IT Applications Conference. Beijing, China, 2014: 13-18 [8] Mestres A, Rodriguez-Natal A, Carner J, Barlet-Ros P, Alarcón E, Solé M, et al. Knowledge-defined networking. ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2017, 47(3): 2−10 doi: 10.1145/3138808.3138810 [9] Ashtari S, Zhou I, Abolhasan M, Shariati N, Lipman J, Ni W. Knowledge-defined networking: Applications, challenges and future work. Array, 2022, 14: 100136 doi: 10.1016/j.array.2022.100136 [10] Akyildiz I F, Lee A, Wang P, Luo M, Chou W. A roadmap for traffic engineering in SDN-OpenFlow networks. Computer Networks, 2014, 71: 1−30 doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2014.06.002 [11] Singh S, Jha R K. A Survey on Software Defined Networking: Architecture for Next Generation Network. Journal of Network and Systems Management, 2017, 25(2): 321−374 doi: 10.1007/s10922-016-9393-9 [12] 夏元清. 云控制系统及其面临的挑战. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(1): 1−12Xia Yuan-Qing. Cloud control systems and their challenges. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(1): 1−12 [13] Rusek K, Suárez-Varela J, Almasan P, Barlet-Ros P, Cabellos-Aparicio A. RouteNet: Leveraging graph neural networks for network modeling and optimization in SDN. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(10): 2260−2270 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000405 [14] Azzouni A, Pujolle G. NeuTM: A neural network-based framework for traffic matrix prediction in SDN. In: Proceedings of the 37th IEEE/IFIP Network Operations and Management Symposium(NOMS). Taipei, Taiwan: IEEE, 2018: 1-5. [15] Xu Z Y, Tang J, Meng J S, Zhang W Y, Wang Y Z, Liu C H. Experience-driven networking: A deep reinforcement learning based approach. In: Proceedings of the 37th IEEE International Conference on Computer Communications. Honolulu, HI, USA, 2018: 1871-1879 [16] Dai B, Cao Y Y, Wu Z L, Xu Y. IQoR-LSE: an intelligent QoS on-demand routing algorithm with link state estimation. IEEE Systems Journal, 2022, 16(4): 5821−5830 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2022.3149990 [17] Yin X, Wu D, Wang Z L, Shi X G, Wu J P. DIMR: Disjoint interdomain multipath routing. Computer Networks, 2015, 91: 356−375 doi: 10.1016/j.comnet.2015.08.028 [18] Li J, Giotsas V, Wang Y Y, Zhou S. Bgp-multipath routing in the internet. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2022, 19(3): 2812−2826 doi: 10.1109/tnsm.2022.3177471 [19] Singh R, Singh Y N, Yadav A. Loop free multipath routing algorithm. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1601.01245, 2016. [20] Lutimath N M, Suresh L, Naikodi C. Efficient power aware multipath routing protocol for MANETs. In: Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Circuits, Controls, Communications and Computing. Bangalore, India, 2016: 1-4 [21] Chen C, Xue F F, Lu Z Y, Tang Z Y, Li C H. Rlmr: Reinforcement learning based multipath routing for sdn. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2022, 2022(1): 5124960 doi: 10.1155/2022/5124960 [22] Gurusamy U, Hariharan K, Manikandan M. Path optimization of box-covering based routing to minimize average packet delay in software defined network. Peer-to-Peer Networking and Applications, 2020, 13: 932−939 doi: 10.1007/s12083-019-00855-8 [23] Prabhavat S, Nishiyama H, Ansari N, Kato N. On load distribution over multipath networks. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2011, 14(3): 662−680 doi: 10.1109/surv.2011.082511.00013 [24] He J Y, Rexford J. Toward internet-wide multipath routing. IEEE Network, 2008, 22(2): 16−21 doi: 10.1109/MNET.2008.4476066 [25] Deng G C, Wang K C. An application-aware QoS routing algorithm for SDN-based IoT networking. In: Proceedings of the 23rd IEEE Symposium on Computers and Communications. Natal, Brazil, 2018: 186-191 [26] Lin X J, Shroff N B. Utility maximization for communication networks with multipath routing. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2006, 51(5): 766−781 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2006.875032 [27] 李凯文, 张涛, 王锐, 覃伟健, 贺惠晖, 黄鸿. 基于深度强化学习的组合优化研究进展. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(11): 2521−2537 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200551Li Kai-Wen, Zhang Tao, Wang Rui, Qin Wei-Jian, He Hui-Hui, Huang Hong. Research reviews of combinatorial optimization methods based on deep reinforcement learning. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(11): 2521−2537 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200551 [28] Bao K, Matyjas J D, Hu F, Kumar S. Intelligent software-defined mesh networks with link-failure adaptive traffic balancing. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking, 2018, 4(2): 266−276 doi: 10.1109/TCCN.2018.2790974 [29] Zou G B, Li T F, Jiang M, Hu S X, Cao C H, Zhang B F, et al. DeepTSQP: Temporal-aware service QoS prediction via deep ne Bural network and feature integration. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2022, 241: 108062 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2021.108062 [30] De Assis M V, Carvalho L F, Rodrigues J J, Lloret J, Proença Jr M L. Near real-time security system applied to SDN environments in IoT networks using convolutional neural network. Computers and Electrical Engineering, 2020, 86: 106738 doi: 10.1016/j.compeleceng.2020.106738 [31] Arulkumaran K, Deisenroth M P, Brundage M, Bharath A A. Deep reinforcement learning: A brief survey. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(6): 26−38 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2743240 [32] Tang J Q, Mihailovic A, Aghvami H. Constructing a DRL decision making scheme for multi-path routing in all-IP access network. In: Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Global Communications Conference. Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2022: 3623-3628 [33] Altamirano J C, Guitouni M, Hassan H, Drira K. Routing optimization based on DRL and Generative Adversarial Networks for SDN environments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Network Operations and Management Symposium. Athens, Greece, 2024: 1-5 [34] Casas-Velasco D M, Rendon O M C, da Fonseca N L. Intelligent routing based on reinforcement learning for software-defined networking. IEEE Transactions on Network and Service Management, 2020, 18(1): 870−881 doi: 10.47749/t/unicamp.2020.1157788 [35] Ye M H, Zhang J J, Guo Z H, Chao H J. Date: Disturbance-aware traffic engineering with reinforcement learning in software-defined networks. In: Proceedings of the 29th IEEE/ACM International Symposium on Quality of Service. Toronto, Canada, 2021: 1−10 [36] Zhang J J, Ye M H, Guo Z H, Yen C Y, Chao H J. CFR-RL: Traffic engineering with reinforcement learning in SDN. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2020, 38(10): 2249−2259 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2020.3000371 [37] Rezaei S, Liu X. Multitask learning for network traffic classification. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Computer Communications and Networks. Honolulu, HI, USA, 2020: 1−9 [38] Zhang Y, Qiu L X, Xu Y Z, Wang X J, Wang S J, Paul A, et al. Multi-Path Routing Algorithm Based on Deep Reinforcement Learning for SDN. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(22): 12520 doi: 10.3390/app132212520 [39] He N, Yang S, Li F, Trajanovski S, Zhu L H, Wang Y. Leveraging Deep Reinforcement Learning With Attention Mechanism for Virtual Network Function Placement and Routing. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2023, 34(4): 1186−1201 doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2023.3240404 [40] He Q, Wang Y, Wang X W, Xu W Q, Li F L, Yang K Q. Routing optimization with deep reinforcement learning in knowledge defined networking. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(2): 1444−1455 doi: 10.1109/TMC.2023.3235446 [41] Ding M J, Guo Y Y, Huang Z B, Lin B, Luo H. GROM: A generalized routing optimization method with graph neural network and deep reinforcement learning. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2024, 229: 103927 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2024.103927 [42] Xu Z Y, Yan F Y, Singh R, Chiu J T, Rush A M, Yu M L. Teal: Learning-Accelerated Optimization of WAN Traffic Engineering. Proceedings of the ACM SIGCOMM 2023 Conference, 2023378−393 [43] Lin B, Guo Y Y, Luo H, Ding M J. TITE: A transformer-based deep reinforcement learning approach for traffic engineering in hybrid SDN with dynamic traffic. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2024, 161: 95−105 doi: 10.1016/j.future.2024.07.006 [44] Hu F, Hao Q, Bao K. A survey on software-defined network and openflow: From concept to implementation. IEEE Communications Surveys and Tutorials, 2014, 16(4): 2181−2206 doi: 10.1109/COMST.2014.2326417 [45] Richardson L, Ruby S. RESTful web services. ” O'Reilly Media, Inc.”, 2008. [46] Draper-Gil G, Lashkari A H, Mamun M S I, Ghorbani A A. Characterization of encrypted and VPN traffic using time-related. In: Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Information Systems Security and Privacy. Rome, Italy, 2016: 407−414 [47] Hagberg A, Swart P, Schult D. Exploring network structure, dynamics, and function using NetworkX. Proceedings of the 7th Python in Science Conference, 2008. -

计量
- 文章访问数: 194
- HTML全文浏览量: 225
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: