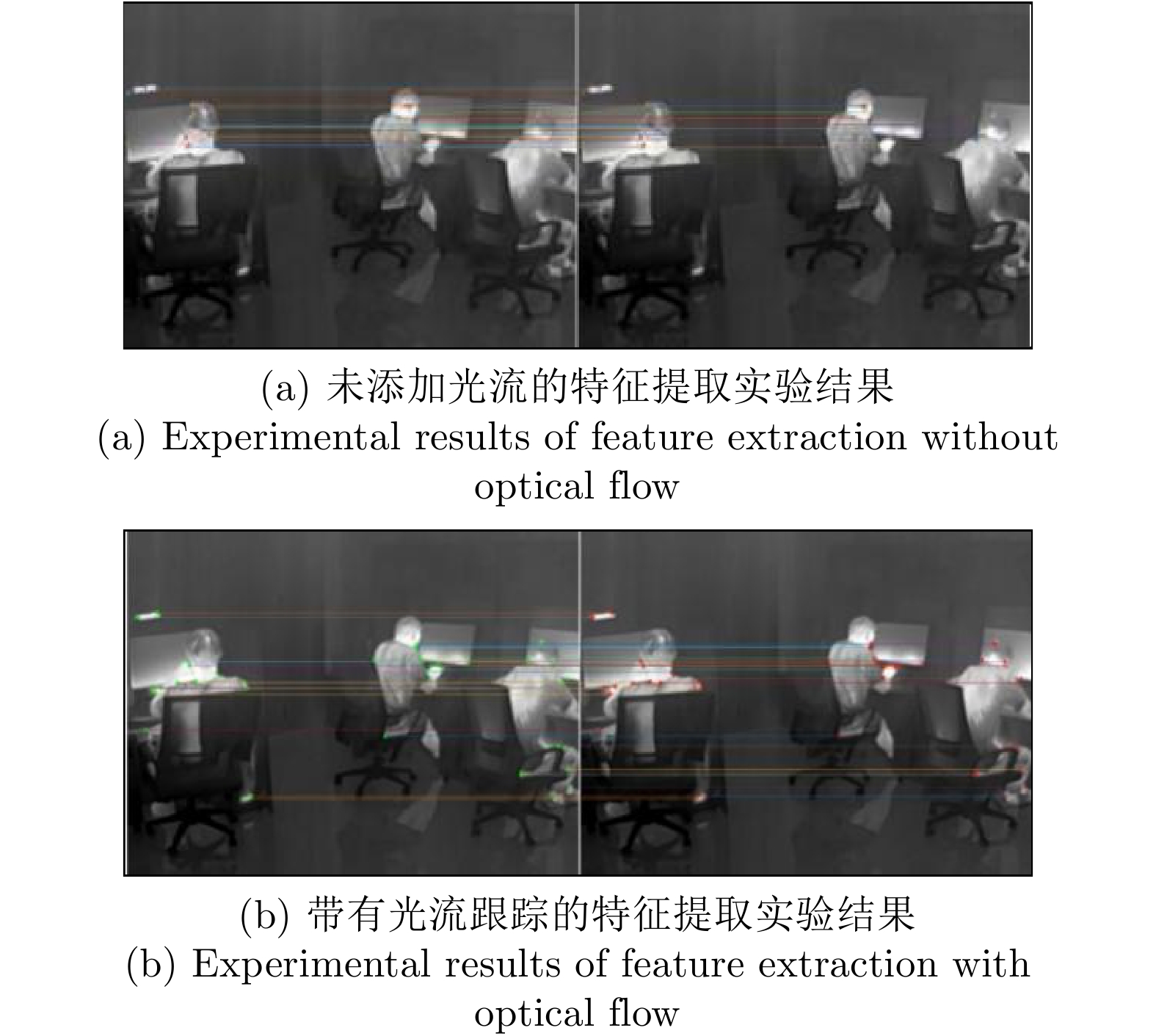
-
摘要: 作为移动机器人与自动驾驶领域的关键基础技术, 视觉同时定位与地图构建(V-SLAM)在动态环境中面临严峻挑战. 由动态物体引起的特征匹配错误常常导致定位偏差、地图失真以及系统鲁棒性受损. 运动分割技术是提高V-SLAM性能的重要手段, 但在复杂动态场景中准确区分静态和动态元素仍极具挑战性. 本文系统梳理V-SLAM运动分割研究进展, 根据对环境的潜在假设, 将现有方法分为三个主要研究范式, 并给出各范式的技术原理, 代表性策略的核心优势、本质局限及适用边界. 最后展望未来的研究方向.Abstract: As a critical foundational technology in the fields of mobile robotics and autonomous driving, visual simultaneous localization and mapping (V-SLAM) faces severe challenges in dynamic environments. Feature mismatches induced by dynamic objects frequently lead to localization drift, map distortion, and degradation of system robustness. Motion segmentation technology is an important means of enhancing V-SLAM performance, but accurate discrimination between static and dynamic elements in complex dynamic scenarios remains highly challenging. This paper systematically reviews the research progress on motion segmentation techniques for V-SLAM. Taxonomically categorizing existing methods into three primary research paradigms based on underlying environmental assumptions, we present the technical principles of each paradigm, along with the core strengths, inherent limitations, and applicability boundaries of representative strategies. Finally, future research directions are prospected.
-
Key words:
- visual SLAM /
- dynamic environments /
- motion segmentation /
- motion understanding /
- multi-sensor fusion /
- mobile robot
-
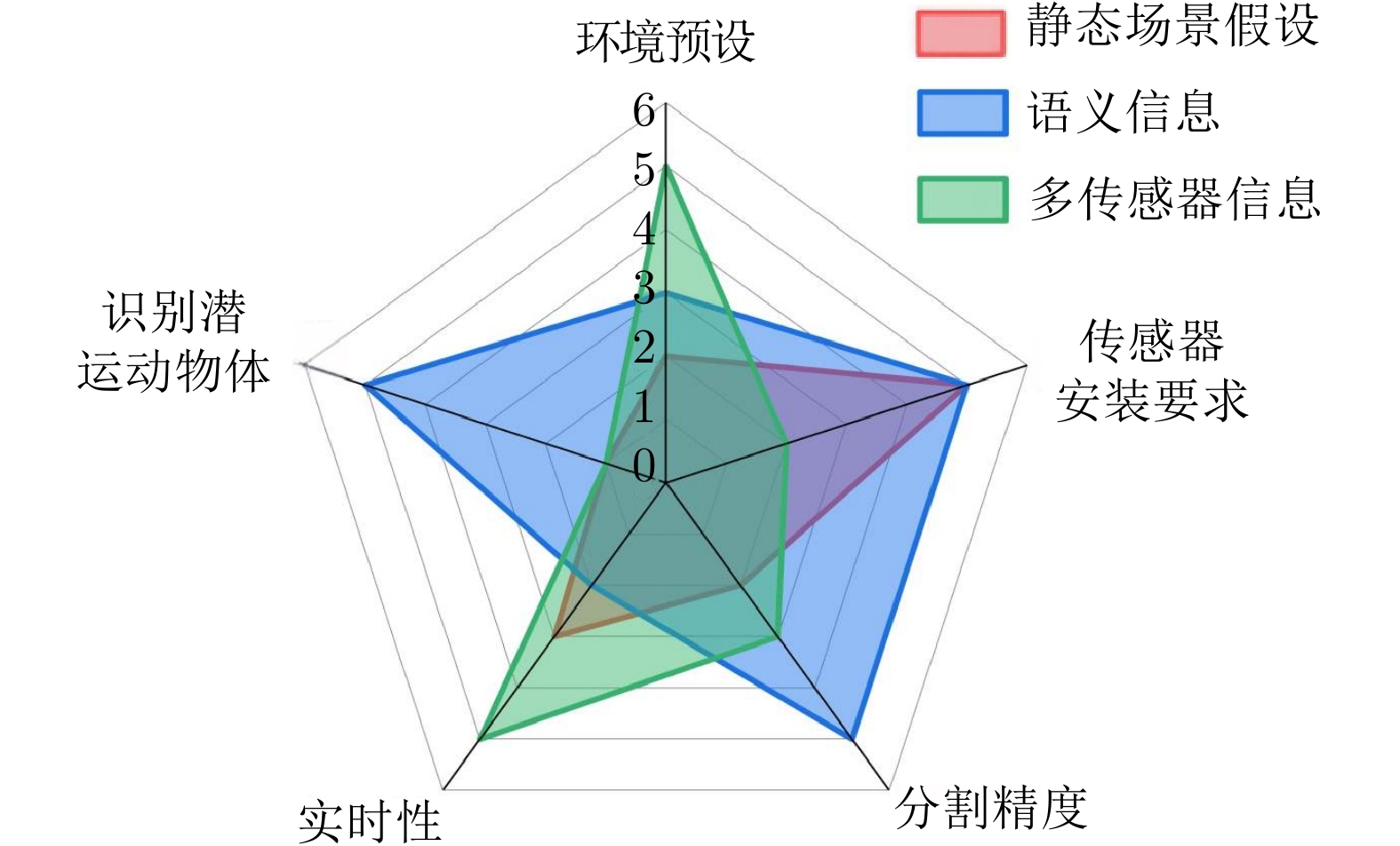
表 3 部分基于静态场景假设的运动分割方法
方法 绝对轨迹均方根误差(m) 相机类型 运行环境 基础框架 单帧跟踪时间(ms) Dou等[54] 0.01138 RGB-D i7-12700K + 32GB ORB-SLAM3 14.153 SamSLAM[55] 0.19870 RGB-D i7-12850HX + 32GB ORB-SLAM3 — DZ-SLAM[56] 0.01300 RGB-D i7-12700K + 32GB ORB-SLAM3 231 GMP-SLAM[57] 0.01300 RGB-D i7-9750H + 16GB ORB-SLAM2 50 Wang等[58] 0.01480 RGB-D i5-7500HQ + 16GB ORB-SLAM3 54 RED-SLAM[59] 0.01480 RGB-D i7-12700KF + 16GB ORB-SLAM3 26.88 Zhang等[60] 0.01300 RGB-D i7 13700K + 64GB ORB-SLAM2 169 DyGS-SLAM[61] 0.01400 RGB-D i7-9750H + 16GB ORB-SLAM3 50 FD-SLAM[62] 0.01620 RGB-D i7 + 16GB ORB-SLAM3 355.18 FND-SLAM[63] 0.01300 RGB-D i7-13650HX ESLAM 812.32 PLFF-SLAM[64] 0.08600 RGB-D i7-13650HX ORB-SLAM3 — Qi等[65] 0.01470 RGB-D i7- 12700 + RTX 4060TiORB-SLAM2 117.8 Cheng等[66] 0.01300 RGB-D i7-13700K + 64GB Manhattan-SLAM 169 Li等[67] 0.01490 RGB-D R9 + RTX3060 ORB-SLAM3 86 表 1 常用的动态环境下视觉SLAM数据集
Table 1 Common visual SLAM datasets in dynamic environments
数据集名称 场景 采集平台 LiDAR RGB MONO (单色) Stereo IMU Event GNSS TUM[39] 室内 手持/机器人 √ √ Bonn[40] 室内 手持 √ OpenLORIS[41] 室内 机器人 √ √ √ √ ADVIO[48] 室内/室外 手持 √ √ KITTI[44] 室外道路 汽车 √ √ √ √ √ Oxford[45] 室外道路 汽车 √ √ √ √ √ ICL-NUIM[42] 室内 手持 √ Augmented ICL-NUIM[43] 室内 手持 √ M2DGR[49] 室内/室外 机器人 √ √ √ √ √ √ RAWSEEDS[50] 室内/室外 机器人 √ √ √ √ EuRoC MAV[51] 室内/室外 飞行器 √ √ √ Mapillary Vistas[46] 室外 手持/机器人 √ √ Apollo Scape[47] 室外 汽车 √ √ Fusion PortableV2[52] 室内/室外 手持/机器人/汽车 √ √ √ √ √ M3DGR[53] 室内/室外 机器人 √ √ √ √ 表 2 静态场景假设方法的分类及特点
Table 2 Categories and characteristics of static scene assumption methods
类别 优点 缺点 基于相机运动的几何约束方法 通过几何约束区分静态与动态特征, 在低动态环境下精度较好 高动态环境下精度显著下降 基于直接几何约束的方法 无需估计相机运动, 计算量小且实时性高 动态特征占比高时分割精度低 基于静态背景构建方法 高动态场景精度较好 计算复杂 表 4 代表性计算机视觉算法
Table 4 Representative computer vision algorithms
领域 方法模型 年份 贡献 目标检测 R-CNN[88] 2014 首次将CNN引入目标检测领域. Fast R-CNN[89] 2015 引入感兴趣区域池化层实现特征共享, 结合多任务损失端到端训练. Faster R-CNN[90] 2016 提出区域建议网络替代选择性搜索, 实现候选框生成与检测一体化. SSD[91] 2016 结合多尺度特征图预测与预设锚框机制. YOLO[78] 2016 开创单阶段检测范式. YOLOv5[92] 2022 集成自适应锚框计算、Mosaic自适应数据增强及自适应图片缩放. RT-DETRv3[93] 2025 设计了层次密集正监督方法, 通过CNN辅助分支和自注意力扰动策略. YOLOv13[94] 2025 引入超图自适应相关增强机制, 通过自适应超图计算建模高阶视觉相关性. 图像分割 FCN[95] 2015 首创全卷积网络结构. SegNet[79] 2017 利用最大池化索引实现高效上采样. Mask R-CNN[80] 2017 在Faster R-CNN基础上添加掩码分支并设计RoIAlign层消除量化误差. DeepLabv3 2018 改进空洞空间金字塔池化并引入图像级特征. YOLACT[81] 2019 提出原型掩码生成与掩码系数预测的并行分支结构. SegFormer[96] 2021 结合无位置编码的分层Transformer编码器和全MLP解码器. Mask2Former[97] 2022 提出通用图像分割架构, 通过掩码注意力机制和高效多尺度策略. Segment Anything[98] 2023 定义可提示分割任务, 支持点/框/文本等任意提示输入. MagNet[99] 2024 设计跨模态对齐损失和模块, 缩小语言—图像模态差距. OMG-Seg[100] 2024 整合多领域分割任务, 降低计算和参数开销. GleSAM[101] 2025 利用生成式潜在空间增强提高对低质量图像的鲁棒性. 表 5 部分基于语义信息的动态SLAM方法
Table 5 Partially semantic-information-based dynamic SLAM methods
方法 语义帧选择 运动分割方法 相机类型 年份 运行环境 单帧跟踪时间/(ms) DS-SLAM[82] 每帧 SegNet RGB-D 2018 i7 + P4000 59 DynaSLAM[83] 每帧 MaskR-CNN+几何约束 单、双目及RGB-D 2018 TeslaM40 195 DynamicSLAM[103] 每帧 SSD 单目 2019 i5-7300HQ + GTX1050Ti 45 YPL-SLAM[110] 每帧 YOLOv5s RGB-D 2024 i7- 12700 + RTX206050~100 SDD-SLAM[112] 关键帧滑动窗口 GroundingDINO+SAM-Track RGB-D 2025 NVIDIA RTX3080 — HMC-SLAM[107] 每帧 YOLOv5 RGB-D 2025 i5 + RTX4070Ti 51.02 DOA-SLAM[104] 每帧 FastInst实例分割 立体相机 2025 — — DYMRO-SLAM[108] 关键帧 MaskR-CNN 双目 2025 — 64.89 DYR-SLAM[109] 每帧 YOLOv8 RGB-D 2025 i7-12700K + RTX3080 57.82 DEG-SLAM[105] 每帧 YOLOv5 RGB-D 2025 i5-8300H + GTX1050Ti 57.82 DHP-SLAM[106] 每帧 SOLOv2 RGB-D/双目 2025 i7-9750H + RTX2070 76.09 YOLO-SLAM[113] 每帧 Darknet19-YOLOv3 RGB-D 2021 Intel Core i5-4288U 696.09 RDS-SLAM[114] 双向关键帧 Mask R-CNN或SegNet RGB-D 2021 RTX2080Ti 22~30 RDMO-SLAM[115] 关键帧 Mask R-CNN RGB-D 2021 RTX 2080Ti 22~35 Jiang等[116] 每帧 RT-DETR with PP-LCNet RGB-D 2025 i7-12650H + RTX4060 29.86 Cheng等[117] 每帧 YOLOX RGB-D/双目 2024 E5-2686v4 + RTX3080 37.43 Huang等[118] 每帧 YOLOv5s RGB-D 2024 R7-6800H + RTX3050Ti 29.86 DFE-SLAM[119] 每帧 YOLOv5s RGB-D 2024 — — YLS-SLAM[120] 每帧 YOLOv5s-seg 单目/RGB-D 2025 i5 + RTX3060 17 UE-SLAM[122] 每帧 DINOv2 单目 2025 i7-12700K + RTX3090Ti — 表 6 部分基于多传感器信息的SLAM方法
Table 6 Partially multi-sensor-information-based SLAM methods
方法 年份 传感器 绝对轨迹均方根
误差/(m)分割方法 运行环境 MSCKF[124] 2007 单目相机 + IMU − 多状态约束Kalman滤波、特征点跟踪与三角测量 T7200 VINS-Mono[123] 2018 单目相机 + IMU 0.12 0.22 关键帧选择 + 滑动窗口优化 + 特征点跟踪 i7- 4790 VINS-Fusion[157] 2022 RGB(单目/双目)+ IMU + GPS 0.06 滑动窗口优化 + 因子图优化 + 多传感器因子融合 − R3LIVE[144] 2021 LiDAR + RGB + IMU 0.085 基于点云运动一致性与视觉语义融合 i7-8550U + 8GB PLD-VINS[129] 2019 RGB-D相机 + IMU 0.731866 改进EDLines检测线特征, 光流法跟踪线特征 XeonE5645 + 48GB VA-fusion[147] 2023 RGB-D相机 + 麦克风阵列+IMU 0.301 声源方向投影至图像平面, 直接标记动态区域 i7 + 64GB DP-VINS[130] 2023 立体相机 + IMU 0.092 通过光流场聚类和残差计算估计运动状态 i7-9700K + 16GB FMSCKF[132] 2024 单目相机 + IMU 0.151 基于关键帧特征跟踪阈值, 结合IMU预积分预测匹配 i7-11800H + 32GB RDynaSLAM[143] 2024 4D毫米波雷达 + 相机 0.233 通过RANSAC提取动态簇并生成动态掩码, 以过滤动态点 E3-1270V2 + 8GB PSMD-SLAM[148] 2024 LiDAR + 相机 + IMU 2.87 概率传播 + PCA聚类 + 全景分割辅助动态检测 5950X + RTX3090 Ground-Fusion[158] 2024 RGB-D相机 + IMU + 轮速计 + GNSS 0.1 运动一致性检查、深度验证 + 传感器异常检测 E3-1270V2 + 8GB SFCI[136] 2025 单目相机 + IMU 0.22 IMU预积分预测位姿生成对极几何约束, 直接剔除动态点 i9 + 16GB RAM EN-SLAM[150] 2024 RGB-D + 事件相机 0.1597 利用事件数据的高动态范围和时序特性 RTX 4090 WTI-SLAM[155] 2025 热红外相机 + IMU 0.059 多尺度相位一致性特征提取 + 光流前后向跟踪 i5-12450H + 32GB Hybrid-VINS[159] 2025 UBSL + 单目相机 + IMU 0.11 基于深度一致性过滤动态物体 − DVI-SLAM[160] 2025 单目/stereo相机 + IMU 0.148 动态融合视觉 + 惯性因子优化位姿 RTX3090 -
[1] Cadena C, Carlone L, Carrillo H, Latif Y, Scaramuzza D, Neira J, et al. Past, present, and future of simultaneous localization and mapping: Toward the robust-perception age. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2016, 32(6): 1309−1332 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2016.2624754 [2] 王金科, 左星星, 赵祥瑞, 吕佳俊, 刘勇. 多源融合SLAM的现状与挑战. 中国图象图形学报, 2022, 27(2): 368−389Wang Jin-Ke, Zuo Xing-Xing, Zhao Xiang-Rui, Lv Jia-Jun, Liu Yong. Review of multi-source fusion SLAM: Current status and challenges. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2022, 27(2): 368−389 [3] Fuentes-Pacheco J, Ruiz-Ascencio J, Rendón-Mancha J M. Visual simultaneous localization and mapping: A survey. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2015, 43(1): 55−81 doi: 10.1007/s10462-012-9365-8 [4] 张峻宁, 苏群星, 刘鹏远, 朱庆, 张凯. 一种自适应特征地图匹配的改进VSLAM算法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(3): 553−565 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c170608Zhang Jun-Ning, Su Qun-Xing, Liu Peng-Yuan, Zhu Qing, Zhang Kai. An improved VSLAM algorithm based on adaptive feature map. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(3): 553−565 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c170608 [5] Nguyen T M, Wu Q J. A consensus model for motion segmentation in dynamic scenes. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2016, 26(12): 2240−2249 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2015.2511479 [6] Xia L L, Cui J S, Shen R, Xu X, Gao Y P, Li X Y. A survey of image semantics-based visual simultaneous localization and mapping: Application-Oriented solutions to autonomous navigation of mobile robots. International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems, 2020, 17(3): 1−17 doi: 10.1177/1729881420919185 [7] Wang Y N, Tian Y B, Chen J W, Xu K, Ding X L. A survey of visual slam in dynamic environment: The evolution from geometric to semantic approaches. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: Article No. 2523221 doi: 10.1109/tim.2024.3420374 [8] Xu Z W, Rong Z, Wu Y H. A survey: Which features are required for dynamic visual simultaneous localization and mapping?. Visual Computing for Industry, Biomedicine, and Art, 2021, 4(1): Article No. 20 doi: 10.1186/s42492-021-00086-w [9] Azzam R, Taha T, Huang S D, Zweiri Y. Feature-based visual simultaneous localization and mapping: A survey. SN Applied Sciences, 2020, 2(2): Article No. 224 doi: 10.1007/s42452-020-2001-3 [10] Mur-Artal R, Montiel J M M, Tardós J D. ORB-SLAM: A versatile and accurate monocular SLAM system. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2015, 31(5): 1147−1163 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671 [11] Mur-Artal R, Tardós J D. ORB-SLAM2: An open-source SLAM system for monocular, stereo, and RGB-D cameras. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2017, 33(5): 1255−1262 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2017.2705103 [12] Campos C, Elvira R, Rodríguez J J G, Montiel J M M, Tardós J D. ORB-SLAM3: An accurate open-source library for visual, visual-inertial, and multimap SLAM. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2021, 37(6): 1874−1890 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2021.3075644 [13] Caruso D, Engel J, Cremers D. Large-scale direct SLAM for omnidirectional cameras. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Hamburg, Germany: IEEE, 2015. 141−148 [14] Engel J, Koltun V, Cremers D. Direct sparse odometry. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(3): 611−625 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2658577 [15] Xu S Y, Wang T, Lang C Y, Feng S H, Jin Y. Graph-based visual odometry for VSLAM. Industrial Robot, 2018, 45(5): 679−687 doi: 10.1108/IR-04-2018-0061 [16] Xu B, Yang G C. Interpretability research of deep learning: A literature survey. Information Fusion, 2025, 115: Article No. 102721 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2024.102721 [17] Qu H Z, Hu Z H, Zhao Y C, Lu J L, Ding K K, Liu G F, et al. Point-Line feature-based vSLAM systems: A survey. Expert Systems With Applications, 2025, 289: Article No. 127574 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2025.127574 [18] 罗元, 沈吉祥, 李方宇. 动态环境下基于深度学习的视觉SLAM研究综述. 半导体光电, 2024, 45(1): 1−10 doi: 10.16818/j.issn1001-5868.2023112202Yuan Luan, Shen Ji-Xiang, Li Fang-Yu. Review of visual slam research based on deep learning in dynamic environments. Semiconductor Optoelectronics, 2024, 45(1): 1−10 doi: 10.16818/j.issn1001-5868.2023112202 [19] Lai T. A review on visual-slam: Advancements from geometric modelling to learning-based semantic scene understanding using multi-modal sensor fusion. Sensors, 2022, 22(19): Article No. 7265 doi: 10.3390/s22197265 [20] 赵洋, 刘国良, 田国会, 罗勇, 王梓任, 张威, 等. 基于深度学习的视觉SLAM综述. 机器人, 2017, 39(6): 889−896 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.220426Zhao Yang, Liu Guo-Liang, Tian Guo-Hui, Luo Yong, Wang Zi-Ren, Zhang Wei, et al. A survey of visual slam based on deep learning. Robot, 2017, 39(6): 889−896 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.220426 [21] 黄泽霞, 邵春莉. 深度学习下的视觉SLAM综述. 机器人, 2023, 45(6): 756−768 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.220426Huang Ze-Xia, Shao Chun-Li. Survey of visual SLAM based on deep learning. Robot, 2023, 45(6): 756−768 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.220426 [22] 张荣芬, 袁文昊, 李景玉, 刘宇红. 融入语义信息的VSLAM研究综述. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 39(5): 81−87 doi: 10.15958/j.cnki.gdxbzrb.2022.05.12Zhang Rong-Fen, Yuan Wen-Hao, Li Jing-Yu, Liu Yu-Hong. Review of VSLAM research with semantic information. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 2022, 39(5): 81−87 doi: 10.15958/j.cnki.gdxbzrb.2022.05.12 [23] Fan Z, Zhang L L, Wang X Y, Shen Y L, Deng F. LiDAR, IMU, and camera fusion for simultaneous localization and mapping: A systematic review. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2025, 58(6): Article No. 174 doi: 10.1007/s10462-025-11187-w [24] Li X D, Dunkin F, Dezert J. Multi-source information fusion: Progress and future. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2024, 37(7): 24−58 doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2023.12.009 [25] 高强, 陆科帆, 吉月辉, 刘俊杰, 许亮, 魏光睿. 多传感器融合SLAM研究综述. 现代雷达, 2024, 46(8): 29−39 doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2024.08.005Gao Qiang, Lu Ke-Fan, Ji Yue-Hui, Liu Jun-Jie, Xu Liang, Wei Guang-Rui. Survey on the research of multi-sensor fusion SLAM. Modern Radar, 2024, 46(8): 29−39 doi: 10.16592/j.cnki.1004-7859.2024.08.005 [26] Qiu Z Y, Martínez-Sánchez J, Arias-Sánchez P, Rashdi R. External multi-modal imaging sensor calibration for sensor fusion: A review. Information Fusion, 2023, 97: Article No. 101806 doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2023.101806 [27] 谭臻, 牛中颜, 张津浦, 陈谢沅澧, 胡德文. SLAM新机遇-高斯溅射技术. 中国图象图形学报, 2025, 30(6): 1792−1807 doi: 10.11834/jig.240443Tan Zhen, Niu Zhong-Yan, Zhang Jin-Pu, Chen Xie-Yuan-Li, Hu De-Wen. New opportunities in SLAM-Gaussian splatting technology. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2025, 30(6): 1792−1807 doi: 10.11834/jig.240443 [28] 喻伟东, 鲁静, 程晗蕾. 基于NeRF的SLAM研究综述. 计算机系统应用, 2025, 34(4): 18−33 doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.009865Yu Wei-Dong, Lu Jing, Cheng Han-Lei. Review of NeRF-based SLAM research. Computer Systems & Applications, 2025, 34(4): 18−33 doi: 10.15888/j.cnki.csa.009865 [29] 韩开, 徐娟. 3D场景渲染技术——神经辐射场的研究. 计算机应用研究, 2024, 41(8): 2252−2260 doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2023.11.0551Han Kai, Xu Juan. Comprehensive review of 3D scene rendering technique-neural radiance fields. Application Research of Computers, 2024, 41(8): 2252−2260 doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2023.11.0551 [30] Mildenhall B, Srinivasan P P, Tancik M, Barron J T, Ramamoorthi R, Ng R. NeRF: Representing scenes as neural radiance fields for view synthesis. Communications of the ACM, 2022, 65(1): 99−106 doi: 10.1145/3503250 [31] Kerbl B, Kopanas G, Leimkühler T, Drettakis G. 3D Gaussian splatting for real-time radiance field rendering. ACM Transactions on Graphics (TOG), 2023, 42(4): Article No. 139 doi: 10.1145/3592433 [32] Cai Z P, Müller M. CLNeRF: Continual learning meets NeRF. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Paris, France: IEEE, 2023. 23185−23194 [33] Li B C, Yan Z K, Wu D, Jiang H Q, Zha H B. Learn to memorize and to forget: A continual learning perspective of dynamic SLAM. In: Proceedings of the 18th European Conference on Computer Vision. Milan, Italy: Springer, 2024. 41−57 [34] Anthwal S, Ganotra D. An overview of optical flow-based approaches for motion segmentation. The Imaging Science Journal, 2019, 67(5): 284−294 doi: 10.1080/13682199.2019.1641316 [35] 王柯赛, 姚锡凡, 黄宇, 刘敏, 陆玉前. 动态环境下的视觉SLAM研究评述. 机器人, 2021, 43(6): 715−732 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.200468Wang Ke-Sai, Yao Xi-Fan, Huang Yu, Liu Min, Lu Yu-Qian. Review of visual SLAM in dynamic environment. Robot, 2021, 43(6): 715−732 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.200468 [36] Kazerouni I A, Fitzgerald L, Dooly G, Toal D. A survey of state-of-the-art on visual SLAM. Expert Systems With Applications, 2022, 205: Article No. 117734 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117734 [37] 朱东莹, 钟勇, 杨观赐, 李杨. 动态环境下视觉定位与建图的运动分割研究进展. 计算机应用, 2023, 43(8): 2537−2545 doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022070972Zhu Dong-Ying, Zhong Yong, Yang Guan-Ci, Li Yang. Research progress on motion segmentation of visual localization and mapping in dynamic environment. Journal of Computer Applications, 2023, 43(8): 2537−2545 doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2022070972 [38] Saputra M R U, Markham A, Trigoni N. Visual SLAM and structure from motion in dynamic environments: A survey. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 2019, 51(2): Article No. 37 doi: 10.1145/3177853 [39] Sturm J, Engelhard N, Endres F, Burgard W, Cremers D. A benchmark for the evaluation of RGB-D SLAM systems. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Vilamoura-Algarve, Portugal: IEEE, 2012. 573−580 [40] Palazzolo E, Behley J, Lottes P, Giguère P, Stachniss C. ReFusion: 3D reconstruction in dynamic environments for RGB-D cameras exploiting residuals. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Macau, China: IEEE, 2019. 7855−7862 [41] Shi X S, Li D J, Zhao P P, Tian Q B, Tian Y X, Long Q W, et al. Are we ready for service robots? The OpenLORIS-scene datasets for lifelong SLAM. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, France: IEEE, 2020. 3139−3145 [42] Handa A, Whelan T, McDonald J, Davison A J. A benchmark for RGB-D visual odometry, 3D reconstruction and SLAM. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Hong Kong, China: IEEE, 2014. 1524−1531 [43] Choi S, Zhou Q Y, Koltun V. Robust reconstruction of indoor scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 5556−5565 [44] Geiger A, Lenz P, Urtasun R. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Providence, USA: IEEE, 2012. 3354−3361 [45] Barnes D, Gadd M, Murcutt P, Newman P, Posner I. The oxford radar RobotCar dataset: A radar extension to the oxford RobotCar dataset. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Paris, France: IEEE, 2020. 6433−6438 [46] Neuhold G, Ollmann T, Rota Bulò S, Kontschieder P. The mapillary vistas dataset for semantic understanding of street scenes. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4990−4999 [47] Huang X Y, Cheng X J, Geng Q C, Cao B B, Zhou D F, Wang P, et al. The ApolloScape dataset for autonomous driving. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops. Salt Lake City: IEEE, 2018. 954−960 [48] Cortés S, Solin A, Rahtu E, Kannala J. ADVIO: An authentic dataset for visual-inertial odometry. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 419−434 [49] Yin J, Li A, Li T, Yu W X, Zou D P. M2DGR: A multi-sensor and multi-scenario SLAM dataset for ground robots. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(2): 2266−2273 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2021.3138527 [50] Amigoni F, Schiaffonati V. Methods and Experimental Techniques in Computer Engineering. Cham Springer, 2013. [51] Burri M, Nikolic J, Gohl P, Schneider T, Rehder J, Omari S, et al. The EuRoC micro aerial vehicle datasets. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2016, 35(10): 1157−1163 doi: 10.1177/0278364915620033 [52] Wei H X, Jiao J H, Hu X C, Yu J W, Xie X P, Wu J, et al. FusionPortableV2: A unified multi-sensor dataset for generalized slam across diverse platforms and scalable environments. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2025, 44(7): 1093−1116 doi: 10.1177/02783649241303525 [53] Zhang D T, Zhang J J, Sun Y, Li T, Yin H, Xie H Z, et al. Towards robust sensor-fusion ground SLAM: A comprehensive benchmark and a resilient framework. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2507.08364, 2025. [54] Dou H X, Liu B, Jia Y H, Wang C H. Monocular initialization for real-time feature-based SLAM in dynamic environments with multiple frames. Sensors, 2025, 25(8): Article No. 2404 doi: 10.3390/s25082404 [55] Chen X H, Wang T Y, Mai H N, Yang L J. SamSLAM: A visual SLAM based on segment anything model for dynamic environment. In: Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Robotics, Control and Automation (ICRCA). Shanghai, China: IEEE, 2024. 91−97 [56] Chen Z, Zang Q Y, Zhang K H. DZ-SLAM: A SAM-based slam algorithm oriented to dynamic environments. Displays, 2024, 85: Article No. 102846 doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2024.102846 [57] Hu Z M, Fang H, Zhong R, Wei S Z, Xu B C, Dou L H. GMP-SLAM: A real-time RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments using GPU dynamic points detection method. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2023, 56(2): 5033−5040 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2023.10.1282 [58] Wang K S, Yao X F, Ma N F, Jing X. Real-Time motion removal based on point correlations for RGB-D SLAM in indoor dynamic environments. Neural Computing and Applications, 2023, 35(12): 8707−8722 doi: 10.1007/s00521-022-07879-x [59] Liu H L, Tian L F, Du Q L, Duan R X. RED-SLAM: Real-time and effective RGB-D SLAM with spatial-geometric observations and fast semantic perception for dynamic environments. Measurement Science and Technology, 2025, 36(3): Article No. 036303 doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ada4c4 [60] Zhang L X, Xu B L, Chen S W, Nener B, Zhou X, Lu M L, et al. An inpainting SLAM approach for detecting and recovering regions with dynamic objects. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2025, 111(1): Article No. 29 doi: 10.1007/s10846-025-02234-3 [61] Zhu F, Zhao Y F, Chen Z Y, Jiang C M, Zhu H, Hu X X. DyGS-SLAM: Realistic map reconstruction in dynamic scenes based on double-constrained visual SLAM. Remote Sensing, 2025, 17(4): Article No. 625 doi: 10.3390/rs17040625 [62] Luo Y, Rao Z R, Wu R S. FD-SLAM: A semantic SLAM based on enhanced fast-SCNN dynamic region detection and DeepFillv2-driven background inpainting. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 110615−110626 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3322453 [63] Yang X B, Wang T, Wang Y Y, Lang C Y, Jin Y, Li Y D. FND-SLAM: A Slam system using feature points and NeRF in dynamic environments based on RGB-D sensors. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2025, 25(5): 8598−8610 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2025.3527558 [64] Huang S C, Ren W H, Li M X. PLFF-SLAM: A point and line feature fused visual SLAM algorithm for dynamic illumination environments. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 34946−34953 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3540563 [65] Qi H B, Chen X C, Yu Z G, Li C, Shi Y L, Zhao Q R, et al. Semantic-Independent dynamic SLAM based on geometric re-clustering and optical flow residuals. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2025, 35(3): 2244−2259 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3496489 [66] 程鹏, 王珂, 邓甘霖, 李炎隆, 李鹏. 改进几何约束的多特征视觉Manhattan-SLAM. 导航定位学报, 2025, 13(2): 172−178 doi: 10.16547/j.cnki.10-1096.20250221Cheng Peng, Wang Ke, Deng Gan-Lin, Li Yan-Long, Li Peng. Multi-feature visual Manhattan-SLAM with improved geometric constraints. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2025, 13(2): 172−178 doi: 10.16547/j.cnki.10-1096.20250221 [67] 李泳, 刘宏杰, 周永录, 余映. 一种室内动态场景下RGB-D SLAM的前端优化方法. 计算机应用研究, 2023, 40(4): 991−995 doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2022.09.0459Li Yong, Liu Hong-Jie, Zhou Yong-Lu, Yu Ying. Front end optimization method of RGB-D SLAM in indoor dynamic scenes. Application Research of Computers, 2023, 40(4): 991−995 doi: 10.19734/j.issn.1001-3695.2022.09.0459 [68] 谢颖, 石永康. 融合投影变换与光流的双目视觉SLAM研究. 电光与控制, 2024, 31(9): 98−103 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2024.09.017Xie Ying, Shi Yong-Kang. Binocular slam based on projection transformation and optical flow. Electronics Optics & Control, 2024, 31(9): 98−103 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2024.09.017 [69] He W Z, Lu Z K, Liu X, Xu Z W, Zhang J S, Yang C, et al. A real-time and high precision hardware implementation of RANSAC algorithm for visual SLAM achieving mismatched feature point pair elimination. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2024, 71(11): 5102−5114 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2024.3422082 [70] Li T, Yu Z B, Guan B L, Han J L, Lv W M, Fraundorfer F. Trifocal tensor and relative pose estimation with known vertical direction. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2025, 10(2): 1305−1312 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3521181 [71] Yang Z Y, He Y, Zhao K, Lang Q, Duan H, Xiong Y H, et al. Research on inter-frame feature mismatch removal method of VSLAM in dynamic scenes. Sensors, 2024, 24(3): Article No. 1007 doi: 10.3390/s24031007 [72] 杨永刚, 武楚健, 杨正全. 基于融合改进RANSAC光流法的无人机视觉SLAM研究. 半导体光电, 2023, 44(2): 277−283 doi: 10.16818/j.issn1001-5868.2022112901Yang Yong-Gang, Wu Chu-Jian, Yang Zheng-Quan. Research on UAV visual SLAM based on fusing improved RANSAC optical flow method. Semiconductor Optoelectronics, 2023, 44(2): 277−283 doi: 10.16818/j.issn1001-5868.2022112901 [73] Zhao X, Ding W C, An Y Q, Du Y L, Yu T, Li M, et al. Fast segment anything. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2306.12156, 2023. [74] 李嘉辉, 范馨月, 张干, 张阔. 基于背景修复的动态SLAM. 数据采集与处理, 2024, 39(5): 1204−1213 doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2024.05.012Li Jia-Hui, Fan Xin-Yue, Zhang Gan, Zhang Guo. Dynamic SLAM based on background restoration. Journal of Data Acquisition and Processing, 2024, 39(5): 1204−1213 doi: 10.16337/j.1004-9037.2024.05.012 [75] Ruan C Y, Zang Q Y, Zhang K H, Huang K. DN-SLAM: A visual SLAM with ORB features and NeRF mapping in dynamic environments. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(4): 5279−5287 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3345877 [76] Xu Z H, Niu J W, Li Q F, Ren T, Chen C. NID-SLAM: Neural implicit representation-based RGB-D SLAM in dynamic environments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Niagara Falls, Canada: IEEE, 2024. 1−6 [77] Li M R, Guo Z T, Deng T C, Zhou Y M, Ren Y X, Wang H Y. DDN-SLAM: Real time dense dynamic neural implicit SLAM. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2025, 10(5): 4300−4307 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2025.3546130 [78] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788 [79] Badrinarayanan V, Kendall A, Cipolla R. SegNet: A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12): 2481−2495 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [80] He K M, Gkioxari G, Dollár P, Girshick R. Mask R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 2961−2969 [81] Bolya D, Zhou C, Xiao F Y, Lee Y J. YOLACT: Real-Time instance segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 9157−9166 [82] Yu C, Liu Z X, Liu X J, Xie F G, Yang Y, Wei Q, et al. DS-SLAM: A semantic visual SLAM towards dynamic environments. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Madrid, Spain: IEEE, 2018. 1168−1174 [83] Bescos B, Fácil J M, Civera J, Neira J. DynaSLAM: Tracking, mapping, and inpainting in dynamic scenes. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(4): 4076−4083 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2860039 [84] Zhong F W, Wang S, Zhang Z Q, Chen C N, Wang Y Z. Detect-SLAM: Making object detection and SLAM mutually beneficial. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Lake Tahoe, USA: IEEE, 2018. 1001−1010 [85] Long X D, Zhang W W, Zhao B. PSPNet-SLAM: A semantic slam detect dynamic object by pyramid scene parsing network. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 214685−214695 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3041038 [86] Cheng S H, Sun C H, Zhang S J, Zhang D F. SG-SLAM: A real-time RGB-D visual SLAM toward dynamic scenes with semantic and geometric information. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: Article No. 7501012 [87] Wei W H, Huang K Z, Liu X, Zhou Y F. GSL-VO: A geometric-semantic information enhanced lightweight visual odometry in dynamic environments. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2023, 72: Article No. 2522513 doi: 10.1109/tim.2023.3300446 [88] Girshick R, Donahue J, Darrell T, Malik J. Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Columbus, USA: IEEE, 2014. 580−587 [89] Girshick R. Fast R-CNN. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1440−1448 [90] Ren S Q, He K M, Girshick R, Sun J. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. In: Proceedings of the 29th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: MIT Press, 2015. 91−99 [91] Liu W, Anguelov D, Erhan D, Szegedy C, Reed S, Fu C Y, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 21−37 [92] Jocher G, Chaurasia A, Stoken A, Borovec J, NanoCode012, Kwon Y, et al. Ultralytics/Yolov5: v7.0-YOLOv5 SOTA Realtime Instance Segmentation, Zenodo, 2022. (查阅网上资料, 未找到对应的出版地信息, 请确认) [93] Wang S, Xia C L, Lv F, Shi Y F. RT-DETRv3: Real-time end-to-end object detection with hierarchical dense positive supervision. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Tucson, USA: IEEE, 2025. 1628−1636 [94] Lei M Q, Li S Q, Wu Y H, Hu H, Zhou Y, Zheng X H, et al. YOLOv13: Real-Time object detection with hypergraph-enhanced adaptive visual perception. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2506.17733, 2025. [95] Long J, Shelhamer E, Darrell T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 3431−3440 [96] Xie E Z, Wang W H, Yu Z D, Anandkumar A, Alvarez J M, Luo P. SegFormer: Simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Curran Associates Inc., 2021. Article No. 924 (查阅网上资料, 未找到对应的出版地信息, 请确认) [97] Cheng B W, Misra I, Schwing A G, Kirillov A, Girdhar R. Masked-Attention mask transformer for universal image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 1290−1299 [98] Kirillov A, Mintun E, Ravi N, Mao H Z, Rolland C, Gustafson L, et al. Segment anything. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Paris, France: IEEE, 2023. 4015−4026 [99] Chng Y X, Zheng H, Han Y Z, Qiu X C, Huang G. Mask grounding for referring image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 26573−26583 [100] Li X T, Yuan H B, Li W, Ding H H, Wu S Z, Zhang W W, et al. OMG-Seg: Is one model good enough for all segmentation?. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 27948−27959 [101] Guo G Q, Guo Y, Yu X H, Li W B, Wang Y X, Gao S. Segment any-quality images with generative latent space enhancement. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2025. 2366−2376 [102] 张玮奇, 王嘉, 张琳, 马宗方. SUI-SLAM: 一种面向室内动态环境的融合语义和不确定度的视觉SLAM方法. 机器人, 2024, 46(6): 732−742 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.230195Zhang Wei-Qi, Wang Jia, Zhang Lin, Ma Zong-Fang. SUI-SLAM: A semantics and uncertainty incorporated visual SLAM algorithm towards dynamic indoor environments. Robot, 2024, 46(6): 732−742 doi: 10.13973/j.cnki.robot.230195 [103] Xiao L H, Wang J G, Qiu X S, Rong Z, Zou X D. Dynamic-SLAM: Semantic monocular visual localization and mapping based on deep learning in dynamic environment. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2019, 117: 1−16 doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2019.03.012 [104] Jia Z Q, Ma Y X, Lai J W, Wang Z G. DOA-SLAM: An efficient stereo visual SLAM system in dynamic environment. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2025, 23(4): 1181−1198 doi: 10.1007/s12555-024-0180-1 [105] Pan G G, Cao S Y, Lv S, Yi Y. DEG-SLAM: A dynamic visual RGB-D SLAM based on object detection and geometric constraints for degenerate motion. Measurement Science and Technology, 2025, 36(2): Article No. 026302 doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ada39c [106] Yang J M, Wang Y T, Tan X, Fang M E, Ma L Z. DHP-SLAM: A real-time visual slam system with high positioning accuracy under dynamic environment. Displays, 2025, 89: Article No. 103067 doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2025.103067 [107] Xu B W, Zheng Z X, Pan Z H, Yu L. HMC-SLAM: A robust VSLAM based on RGB-D camera in dynamic environment combined hierarchical multidimensional clustering algorithm. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2025, 74: Article No. 5020311 doi: 10.1109/tim.2025.3551451 [108] Cui H J, Zhao X, Luo G Y. DYMRO-SLAM: A robust stereo visual SLAM for dynamic environments leveraging mask R-CNN and optical flow. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 54240−54253 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3555156 [109] Li C, Jiang S, Zhou K Q. DYR-SLAM: Enhanced dynamic visual SLAM with YOLOv8 and RTAB-Map. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2025, 81(5): Article No. 718 doi: 10.1007/s11227-025-07191-0 [110] Du X W, Zhang C L, Gao K H, Liu J, Yu X F, Wang S S. YPL-SLAM: A simultaneous localization and mapping algorithm for point-line fusion in dynamic environments. Sensors, 2024, 24(14): Article No. 4517 [111] Zhu S T, Qin R J, Wang G M, Liu J M, Wang H S. SemGauss-SLAM: Dense semantic Gaussian splatting SLAM. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2403.07494, 2024. [112] Liu H S, Wang L, Luo H Y, Zhao F, Chen R Z, Chen Y S, et al. SDD-SLAM: Semantic-driven dynamic slam with Gaussian splatting. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2025, 10(6): 5721−5728 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2025.3561565 [113] Wu W X, Guo L, Gao H L, You Z C, Liu Y K, Chen Z Q. YOLO-SLAM: A semantic SLAM system towards dynamic environment with geometric constraint. Neural Computing and Applications, 2022, 34(8): 6011−6026 doi: 10.1007/s00521-021-06764-3 [114] Liu Y B, Miura J. RDS-SLAM: Real-Time dynamic SLAM using semantic segmentation methods. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 23772−23785 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3050617 [115] Liu Y B, Miura J. RDMO-SLAM: Real-Time visual SLAM for dynamic environments using semantic label prediction with optical flow. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 106981−106997 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3100426 [116] 姜丽梅, 陈信威. 动态场景下基于特征点筛选的视觉SLAM算法. 系统仿真学报, 2025, 37(3): 753−762 doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.23-1406Jiang Li-Mei, Chen Xin-Wei. Visual slam algorithm based on feature point selection in dynamic scenes. Journal of System Simulation, 2025, 37(3): 753−762 doi: 10.16182/j.issn1004731x.joss.23-1406 [117] 程强, 张友兵, 周奎. 基于改进YOLOX的动态视觉SLAM方法. 电子测量技术, 2024, 47(23): 123−133 doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2416875Cheng Qiang, Zhang You-Bing, Zhou Kui. Dynamic visual SLAM method based on improved YOLOX. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2024, 47(23): 123−133 doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2416875 [118] 黄友锐, 王照锋, 韩涛, 宋红萍. 结合轻量化YOLOv5s的动态视觉SLAM算法. 电子测量技术, 2024, 47(11): 59−68 doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2416024Huang You-Rui, Wang Zhao-Feng, Han Tao, Song Hong-Ping. Dynamic visual slam algorithm combined with lightweight YOLOv5s. Electronic Measurement Technology, 2024, 47(11): 59−68 doi: 10.19651/j.cnki.emt.2416024 [119] Cheng G Y, Jia J F, Pang X Q, Wen J, Shi Y H, Zeng J C. DFE-SLAM: Dynamic SLAM based on improved feature extraction. In: Proceedings of the China Automation Congress (CAC). Qingdao, China: IEEE, 2024. 4584−4589 [120] Feng D, Yin Z Y, Wang X H, Zhang F Q, Wang Z S. YLS-SLAM: A real-time dynamic visual slam based on semantic segmentation. Industrial Robot, 2025, 52(1): 106−115 doi: 10.1108/IR-04-2024-0160 [121] Lian X F, Kang M M, Tan L, Sun X, Wang Y L. LSSMask: A lightweight semantic segmentation network for dynamic object. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2025, 19(3): Article No. 216 doi: 10.1007/s11760-024-03751-8 [122] Zhang Y Q, Jiang G G, Li M R, Feng G S. UE-SLAM: Monocular neural radiance field slam with semantic mapping capabilities. Symmetry, 2025, 17(4): Article No. 508 doi: 10.3390/sym17040508 [123] Qin T, Li P L, Shen S J. VINS-Mono: A robust and versatile monocular visual-inertial state estimator. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(4): 1004−1020 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2853729 [124] Mourikis A I, Roumeliotis S I. A multi-state constraint Kalman filter for vision-aided inertial navigation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Rome, Italy: IEEE, 2007. 3565−3572 [125] 杨观赐, 王霄远, 蒋亚汶, 李杨. 视觉与惯性传感器融合的SLAM技术综述. 贵州大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 37(6): 1−12 doi: 10.15958/j.cnki.gdxbzrb.2020.06.01Yang Guan-Ci, Wang Xiao-Yuan, Jiang Ya-Wen, Li Yang. Review of SLAM technologies based on visual and inertial sensor fusion. Journal of Guizhou University (Natural Sciences), 2020, 37(6): 1−12 doi: 10.15958/j.cnki.gdxbzrb.2020.06.01 [126] Bloesch M, Omari S, Hutter M, Siegwart R. Robust visual inertial odometry using a direct EKF-based approach. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Hamburg, Germany: IEEE, 2015. 298−304 [127] Wu K Z, Zhang T, Su D, Huang S D, Dissanayake G. An invariant-EKF VINS algorithm for improving consistency. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2017. 1578−1585 [128] Chen S M, Frémont V. A loosely coupled vision-LiDAR odometry using covariance intersection filtering. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV). Nagoya, Japan: IEEE, 2021. 1102−1107 [129] Zhu Y Q, Jin R, Lou T S, Zhao L Y. PLD-VINS: RGBD visual-inertial SLAM with point and line features. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 119: Article No. 107185 doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.107185 [130] Zhang L C, Yin H L, Ye W, Betz J. DP-VINS: Dynamics adaptive plane-based visual-inertial SLAM for autonomous vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: Article No. 5036516 doi: 10.1109/tim.2024.3476615 [131] Yin H S, Li S M, Tao Y, Guo J L, Huang B. Dynam-SLAM: An accurate, robust stereo visual-inertial SLAM method in dynamic environments. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2023, 39(1): 289−308 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2022.3199087 [132] Abdollahi M R, Pourtakdoust S H, Nooshabadi M H Y, Pishkenari H N. An improved multi-state constraint Kalman filter for visual-inertial odometry. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2024, 361(15): Article No. 107130 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2024.107130 [133] Jung K, Song J, Seong S, Myung H. MSCKF-DVIO: Multi-State constraint Kalman filter based RGB-D visual-inertial odometry with spline interpolation and nonholonomic constraint. In: Proceedings of the 21st International Conference on Ubiquitous Robots (UR). New York: IEEE, 2024. 558−565 [134] Fornasier A, van Goor P, Allak E, Mahony R, Weiss S. MSCeqF: A multi state constraint equivariant filter for vision-aided inertial navigation. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024, 9(1): 731−738 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2023.3335775 [135] Cao L, Liu J B, Lei J T, Zhang W, Chen Y S, Hyyppä J. Real-Time motion state estimation of feature points based on optical flow field for robust monocular visual-inertial odometry in dynamic scenes. Expert Systems With Applications, 2025, 274: Article No. 126813 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2025.126813 [136] Yu Z L. A self-adaptation feature correspondences identification algorithm in terms of IMU-aided information fusion for VINS. Applied Intelligence, 2025, 55(3): Article No. 202 doi: 10.1007/s10489-024-06120-7 [137] 李阳铭, 宋全军, 刘海, 葛运建. 用于移动机器人导航的通用激光雷达特征提取. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 41(S1): 280−283Li Yang-Ming, Song Quan-Jun, Liu Hai, Ge Yun-Jian. General purpose LIDAR feature extractor for mobile robot navigation. Journal of Huazhong University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(S1): 280−283 [138] Du K Y, Meng J, Meng X H, Xiang Z H, Wang S F, Yang J H. Projection mapping segmentation block: A fusion approach of pointcloud and image for multi-objects classification. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 77802−77809 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3299220 [139] Tan M K, Zhuang Z W, Chen S T, Li R, Jia K, Wang Q C, et al. EPMF: Efficient perception-aware multi-sensor fusion for 3D semantic segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(12): 8258−8273 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3402232 [140] Song H M, Cho J, Ha J S, Park J, Jo K. Panoptic-FusionNet: Camera-LiDAR fusion-based point cloud panoptic segmentation for autonomous driving. Expert Systems With Applications, 2024, 251: Article No. 123950 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2024.123950 [141] Shi H S, Wang X, Zhao J H, Hua X N. A cross-modal attention-driven multi-sensor fusion method for semantic segmentation of point clouds. Sensors, 2025, 25(8): Article No. 2474 doi: 10.3390/s25082474 [142] Sánchez-García F, Montiel-Marín S, Antunes-García M, Gutiérrez-Moreno R, Llamazares Á L, Bergasa L M. SalsaNext+: A multimodal-based point cloud semantic segmentation with range and RGB images. IEEE Access, 2025, 13: 64133−64147 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2025.3559580 [143] Zhu D Y, Yang G C. RDynaSLAM: Fusing 4D radar point clouds to visual SLAM in dynamic environments. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2025, 111(1): Article No. 11 doi: 10.1007/s10846-024-02204-1 [144] Lin J R, Zhang F. R.3LIVE: A robust, real-time, RGB-colored, LiDAR-inertial-visual tightly-coupled state estimation and mapping package. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Philadelphia, USA: IEEE, 2022. 10672−10678 [145] Li X X, Wang X B, Liao J C, Li X, Li S Y, Lv H B. Semi-tightly coupled integration of multi-GNSS PPP and S-VINS for precise positioning in GNSS-challenged environments. Satellite Navigation, 2021, 2(1): Article No. 1 doi: 10.1186/s43020-020-00033-9 [146] Cao S Z, Lu X Y, Shen S J. GVINS: Tightly coupled GNSS-visual-inertial fusion for smooth and consistent state estimation. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2022, 38(4): 2004−2021 [147] Zhang T W, Zhang H Y, Li X F. Vision-audio fusion SLAM in dynamic environments. CAAI Transactions on Intelligence Technology, 2023, 8(4): 1364−1373 [148] Song C Q, Zeng B, Cheng J, Wu F X, Hao F S. PSMD-SLAM: Panoptic segmentation-aided multi-sensor fusion simultaneous localization and mapping in dynamic scenes. Applied Sciences, 2024, 14(9): Article No. 3843 doi: 10.3390/app14093843 [149] Lang X L, Li L J, Wu C M, Zhao C, Liu L N, Liu Y, et al. Gaussian-LIC: Real-time photorealistic SLAM with Gaussian splatting and LiDAR-inertial-camera fusion. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Atlanta: IEEE, 2025. 8500−8507 [150] Qu D L, Yan C, Wang D, Yin J, Chen Q Z, Xu D, et al. Implicit event-RGBD neural SLAM. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 19584−19594 [151] Vidas S, Sridharan S. Hand-held monocular SLAM in thermal-infrared. In: Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Control Automation Robotics & Vision (ICARCV). Guangzhou, China: IEEE, 2012. 859−864 [152] Vidas S, Moghadam P, Bosse M. 3D thermal mapping of building interiors using an RGB-D and thermal camera. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Karlsruhe, Germany: IEEE, 2013. 2311−2318 [153] Mouats T, Aouf N, Sappa A D, Aguilera C, Toledo R. Multispectral stereo odometry. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2015, 16(3): 1210−1224 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2014.2354731 [154] Qin L, Wu C, Kong X T, You Y, Zhao Z Q. BVT-SLAM: A binocular visible-thermal sensors SLAM system in low-light environments. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24(7): 11599−11609 doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3341068 [155] Li S, Ma X F, He R, Shen Y R, Guan H, Liu H Z, Li F. WTI-SLAM: A novel thermal infrared visual SLAM algorithm for weak texture thermal infrared images. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2025, 11(6): Article No. 242 doi: 10.1007/s40747-025-01858-0 [156] 陈鹏宇, 聂秀山, 李南君, 李拓. 基于时空解耦和区域鲁棒性增强的半监督视频目标分割方法. 计算机应用, 2025, 45(5): 1379−1386 doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2024060802Chen Peng-Yu, Nie Xiu-Shan, Li Nan-Jun, Li Tuo. Semi-supervised video object segmentation method based on spatio-temporal decoupling and regional robustness enhancement. Journal of Computer Applications, 2025, 45(5): 1379−1386 doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2024060802 [157] Qin T, Cao S Z, Pan J, Shen S J. A general optimization-based framework for global pose estimation with multiple sensors. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1901.03642, 2019. [158] Yin J, Li A, Xi W, Yu W X, Zou D P. Ground-fusion: A low-cost ground SLAM system robust to corner cases. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Yokohama, Japan: IEEE, 2024. 8603−8609 [159] Ou Y M, Fan J F, Zhou C, Zhang P J, Zeng G. Hybrid-VINS: Underwater tightly coupled hybrid visual inertial dense SLAM for AUV. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2025, 72(3): 2821−2831 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2024.3440515 [160] Peng X F, Liu Z H, Li W M, Tan P, Cho S Y, Wang Q. DVI-SLAM: A dual visual inertial SLAM network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Yokohama, Japan: IEEE, 2024. 12020−12026 [161] 杨观赐, 杨静, 苏志东, 陈占杰. 改进的YOLO特征提取算法及其在服务机器人隐私情境检测中的应用. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(12): 2238−2249 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170265Yang Guan-Ci, Yang Jing, Su Zhi-Dong, Chen Zhan-Jie. An improved YOLO feature extraction algorithm and its application to privacy situation detection of social robots. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(12): 2238−2249 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c170265 [162] Zhou Y H, Sun M L. A visual SLAM loop closure detection method based on lightweight Siamese capsule network. Scientific Reports, 2025, 15(1): Article No. 7644 doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-90511-4 [163] 张晓东, 张朝昆, 赵继军. 边缘智能研究进展. 计算机研究与发展, 2023, 60(12): 2749−2769 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.202440385Zhang Xiao-Dong, Zhang Chao-Kun, Zhao Ji-Jun. State-of-the-art survey on edge intelligence. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2023, 60(12): 2749−2769 doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.202440385 [164] Satyanarayanan M. The emergence of edge computing. Computer, 2017, 50(1): 30−39 [165] 何高湘, 朱斌, 解博, 陈熠. 基于神经辐射场的新视角合成研究进展. 激光与光电子学进展, 2024, 61(12): Article No. 1200005 doi: 10.3788/LOP231578He Gao-Xiang, Zhu Bin, Xie Bo, Chen Yi. Progress in novel view synthesis using neural radiance fields. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2024, 61(12): Article No. 1200005 doi: 10.3788/LOP231578 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 316
- HTML全文浏览量: 430
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: