Adaptive Constant Pressure Control for the Influent Process of Municipal Wastewater Treatment
-
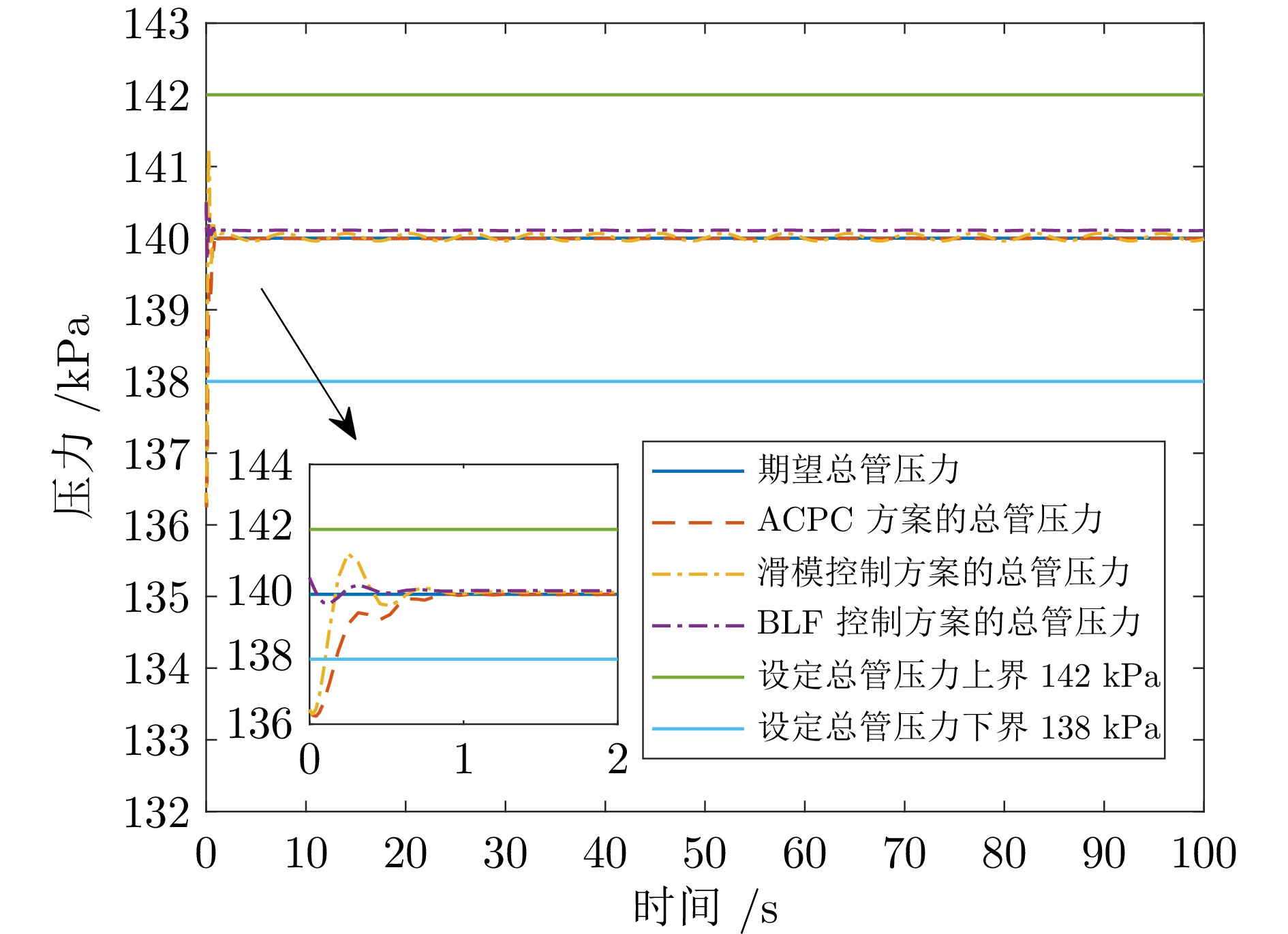
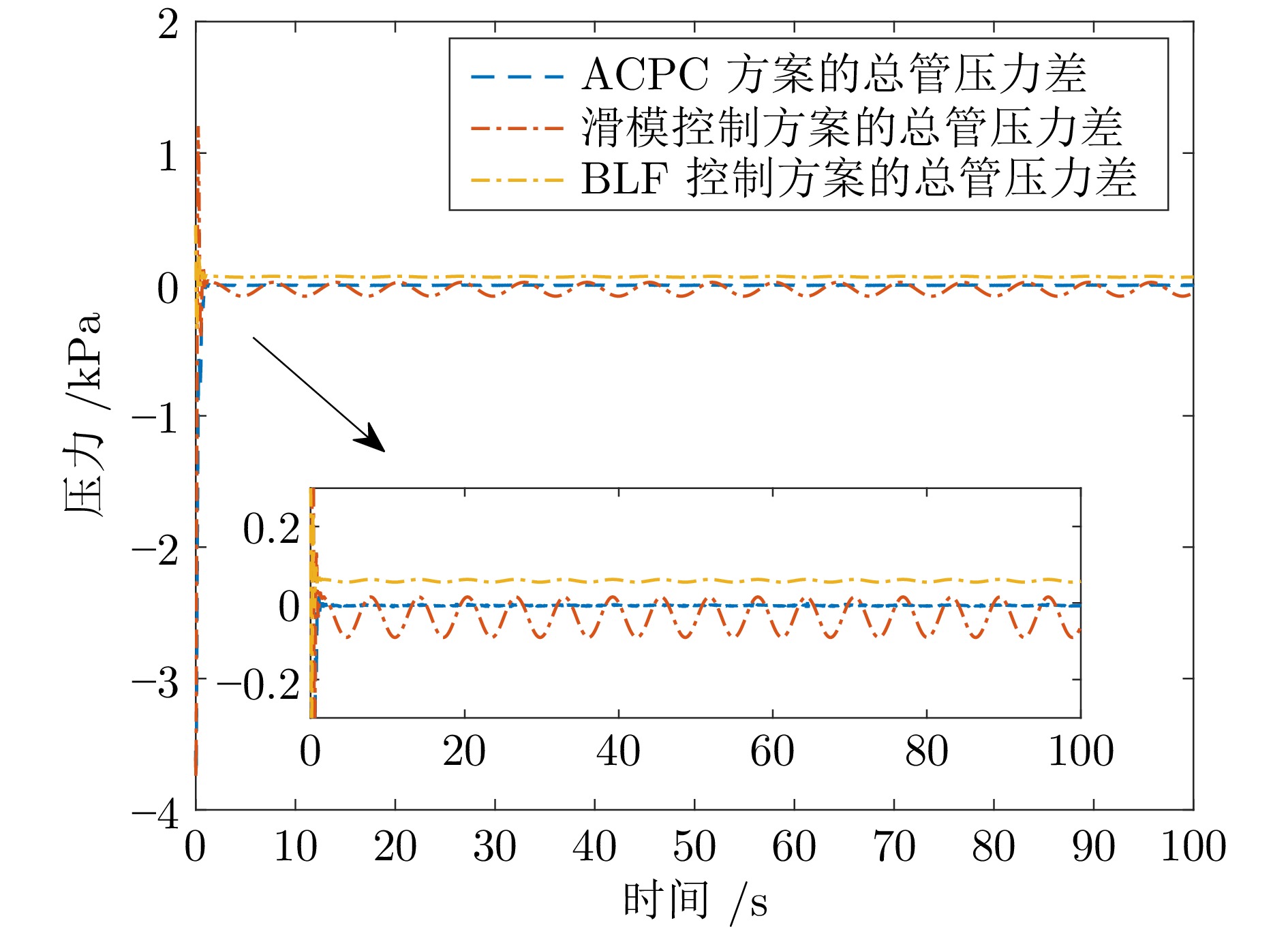
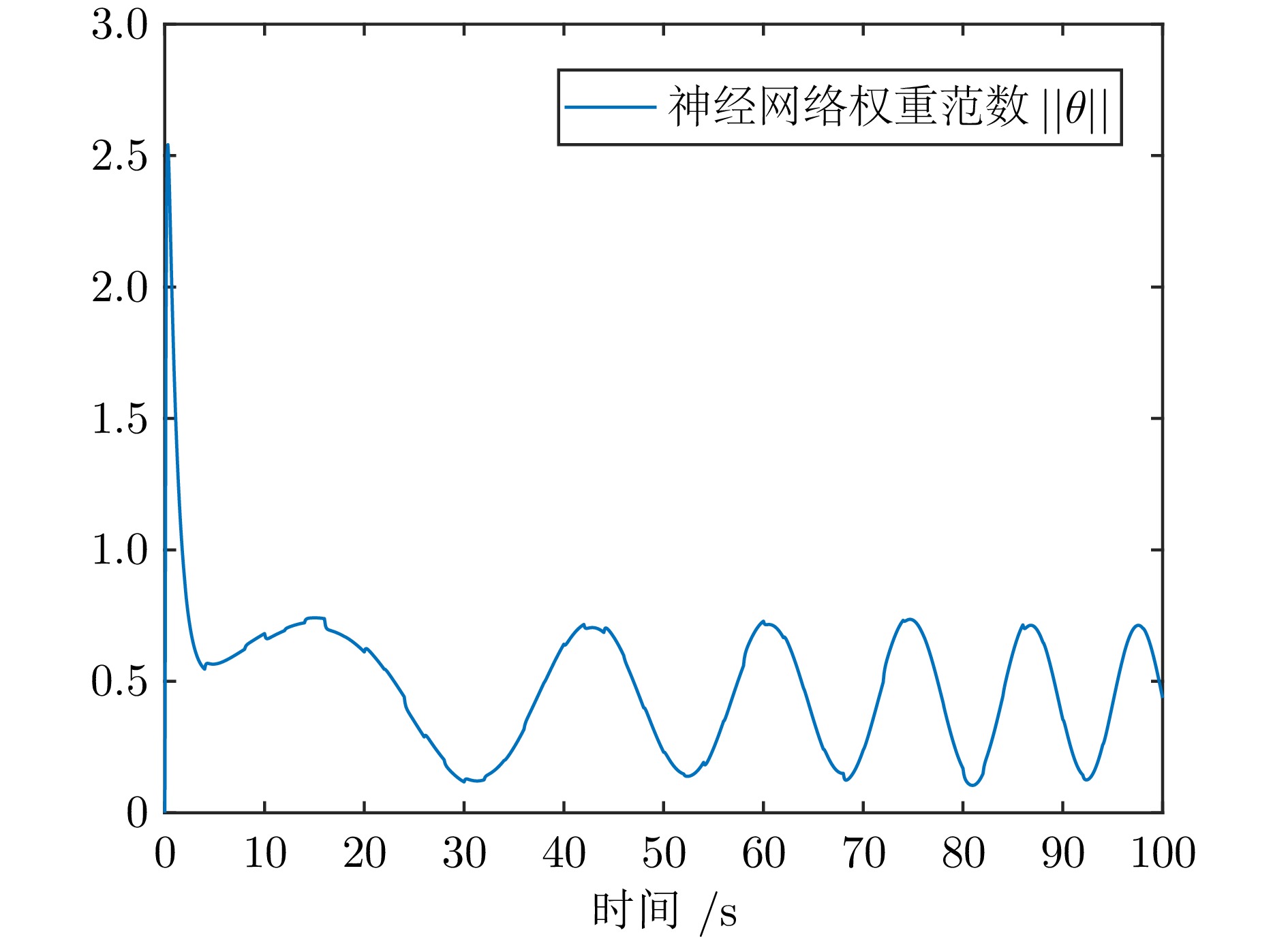
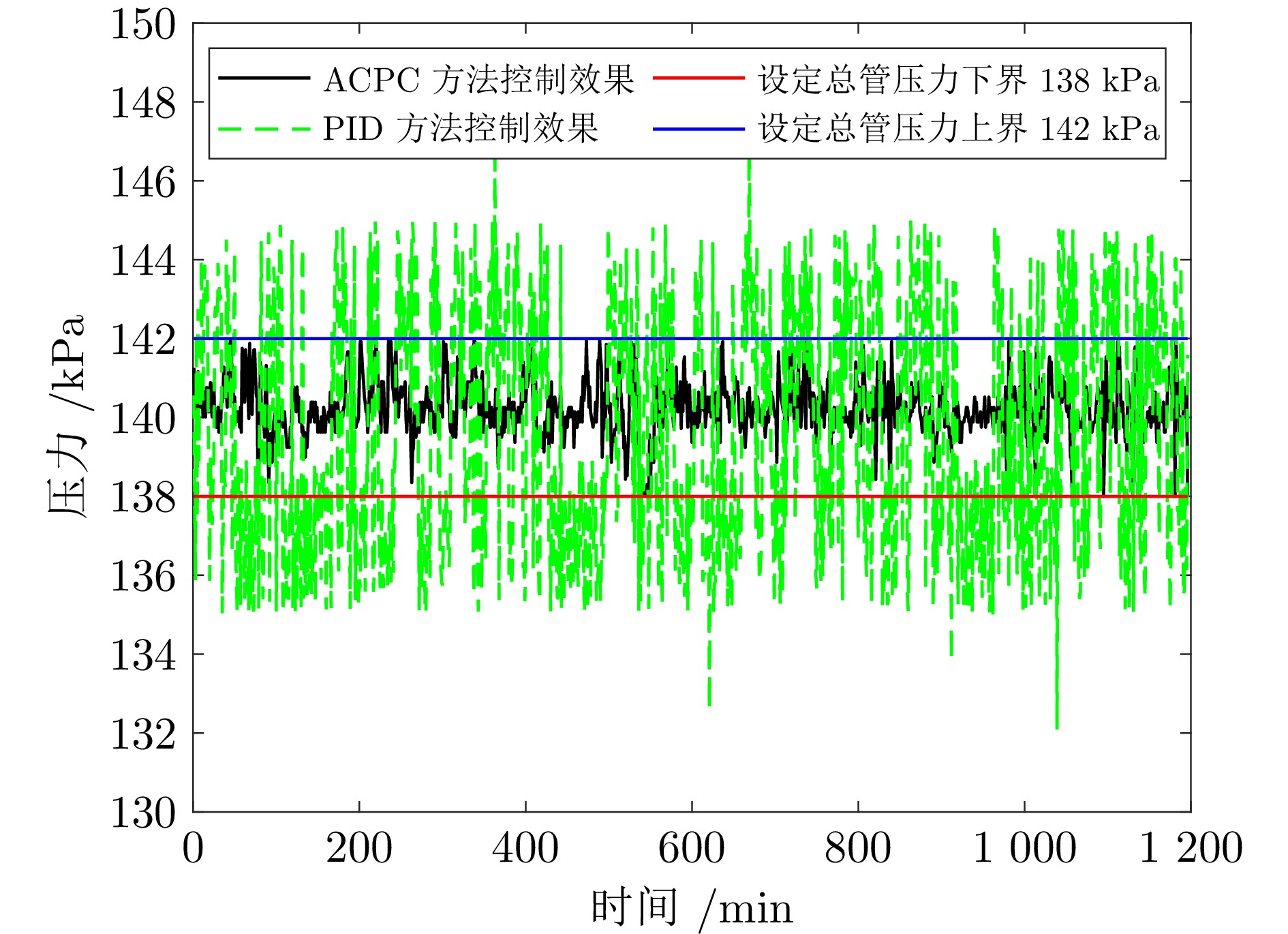
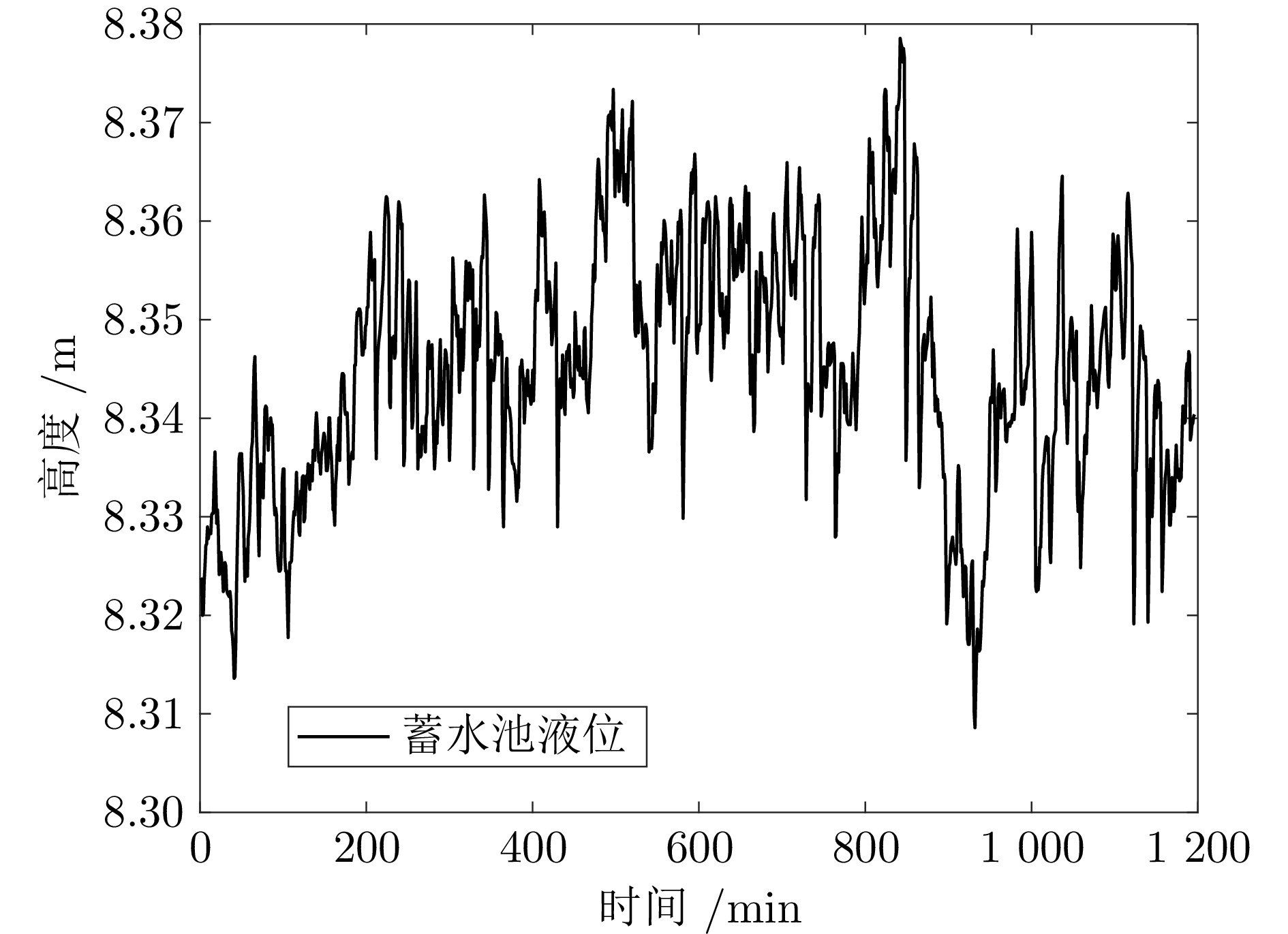
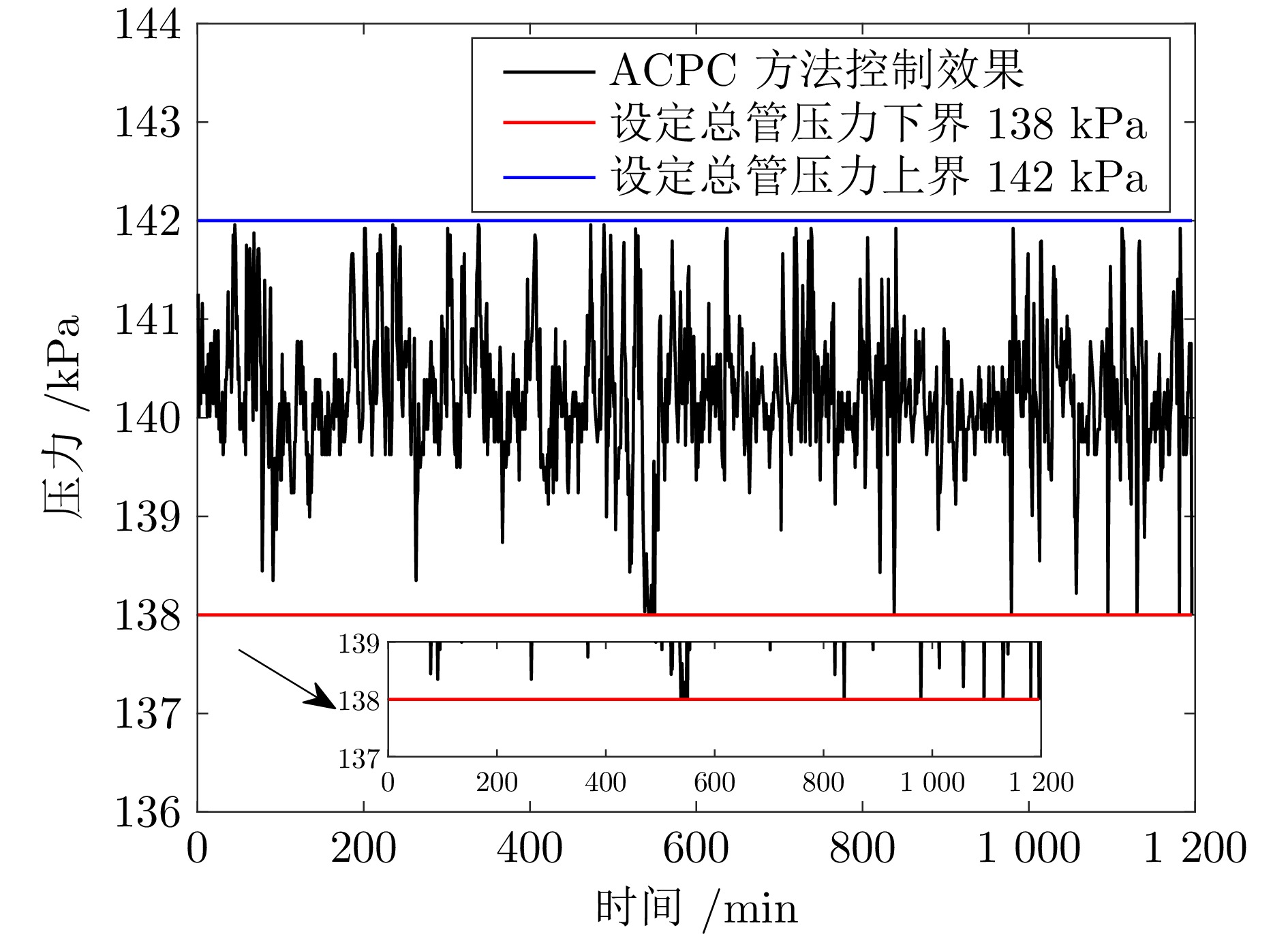
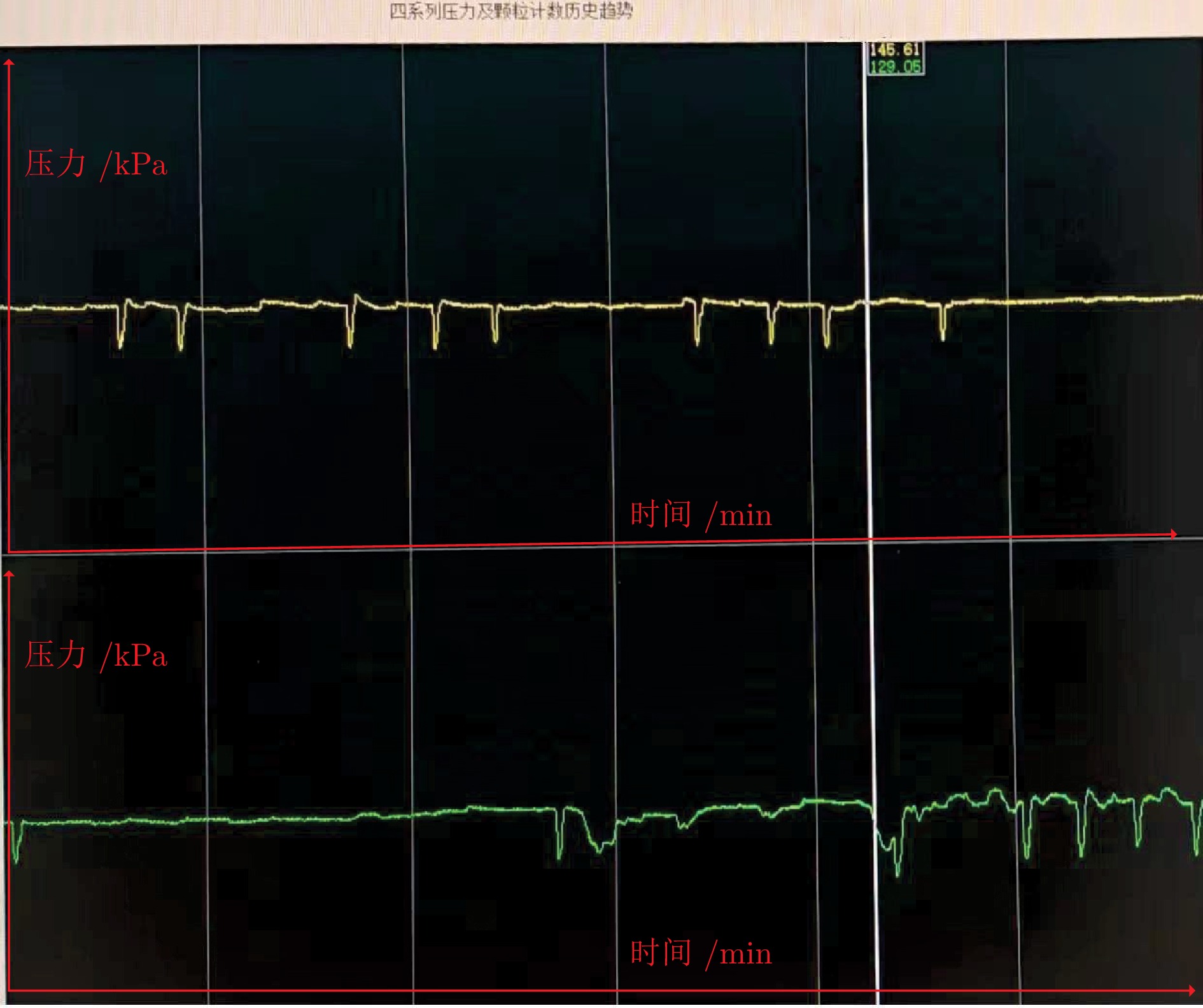
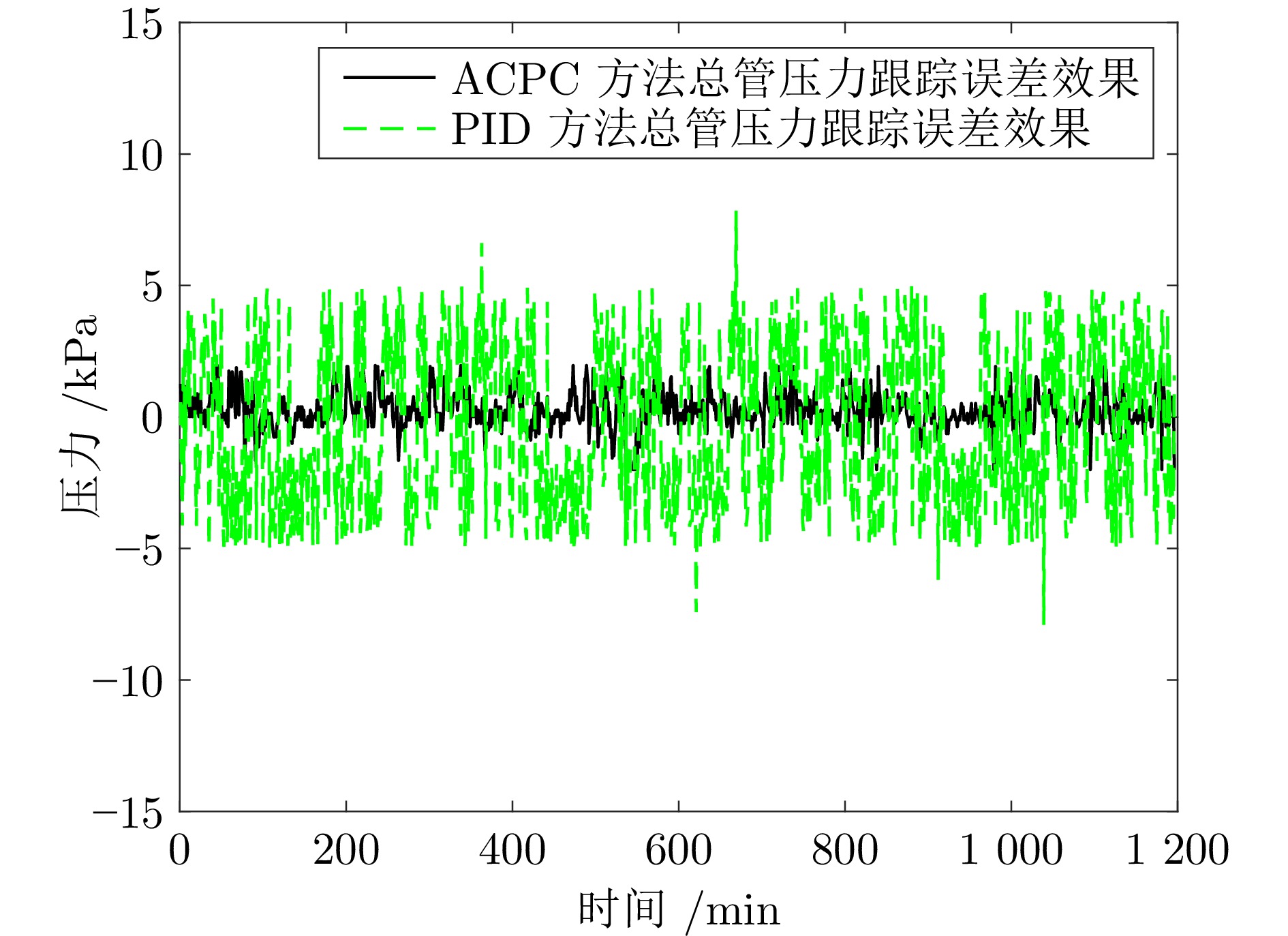
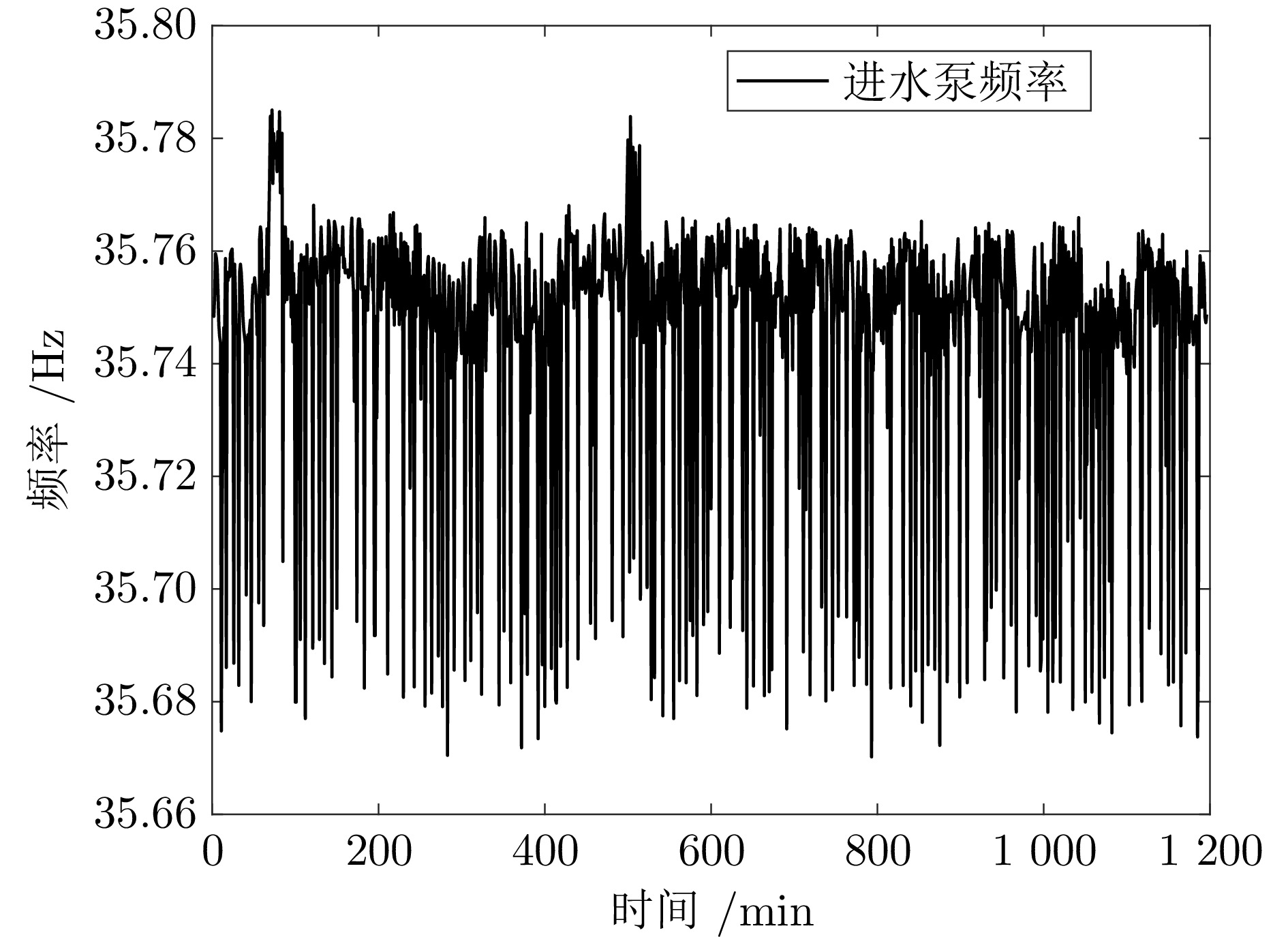
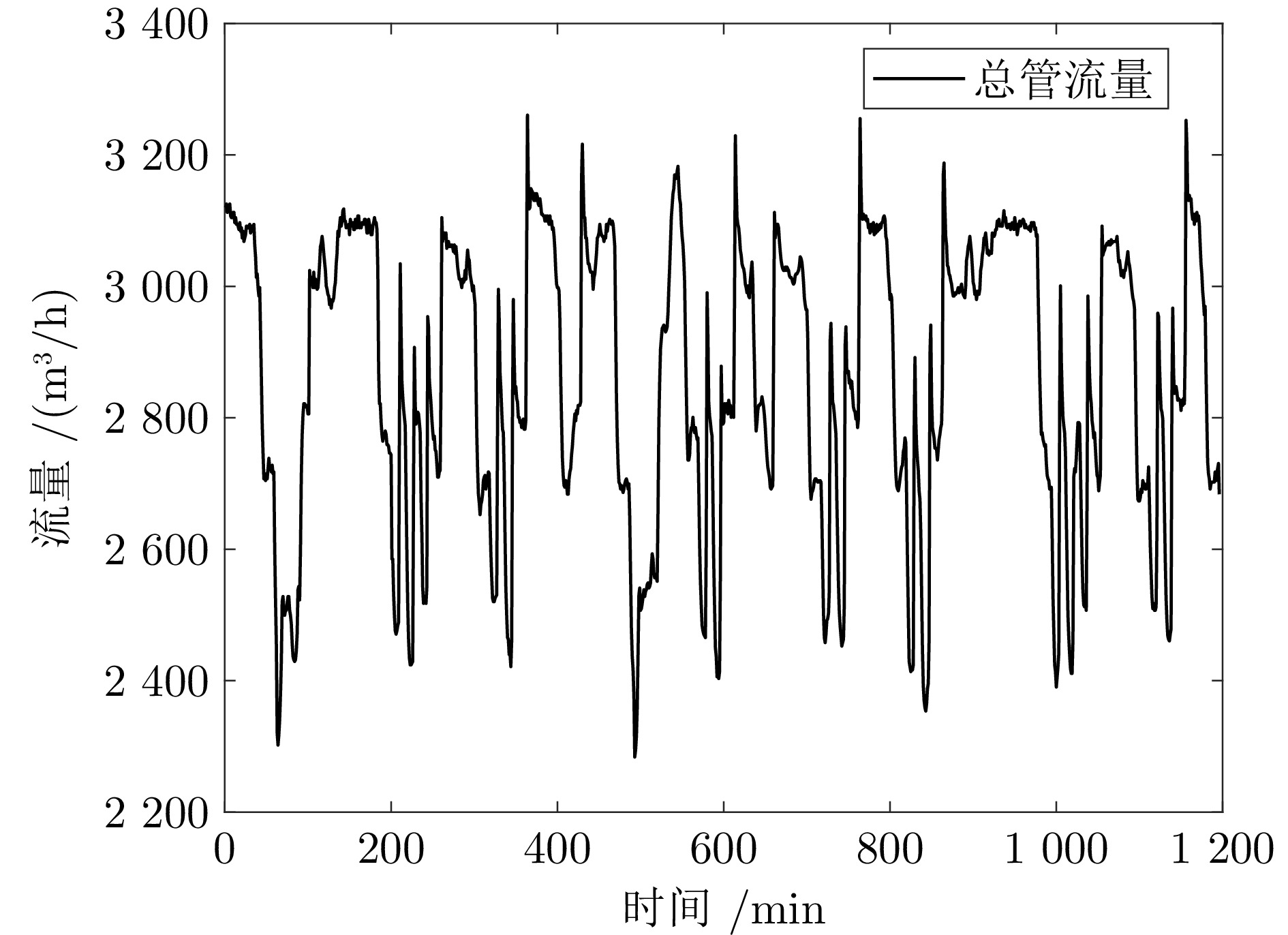
摘要: 针对城市污水处理进水过程总管压力难以稳定控制, 导致污水处理过程运行不稳定的问题, 提出一种自适应恒压控制(ACPC)方法. 首先, 建立基于时滞特性的城市污水处理进水过程控制模型, 设计基于帕德逼近的等效变换模型, 动态补偿运行过程滞后的影响. 其次, 提出基于障碍李雅普诺夫函数的ACPC方法, 设计转移策略放宽初始总管压力对控制器的约束, 保障进水过程在规定压力范围内运行. 然后, 提出神经网络自适应动态调整算法, 根据进水过程运行状态实时调整控制参数, 降低膜组器清洗操作导致的总管压力波动, 提升进水过程的稳定性. 最后, 给出控制器稳定性分析, 证明进水过程中所有变量是半全局最终有界的, 实现总管压力的稳定控制. 实验结果表明, 该方法能够保证城市污水处理进水过程稳定运行.
-
关键词:
- 城市污水处理进水过程 /
- 帕德逼近方法 /
- 障碍李雅普诺夫函数 /
- 自适应恒压控制
Abstract: To address the problem that the main pipe pressure of the influent process in municipal wastewater treatment is difficult to be stably controlled, which leads to the unstable operation of the wastewater treatment process, an adaptive constant pressure control (ACPC) method is proposed. Firstly, a control model for the influent process of municipal wastewater treatment is established based on time-delay characteristics. A Pade approximation-based equivalent transformation model is designed to dynamically compensate for the influence caused by time-delay in the operation process. Secondly, a barrier Lyapunov function-based ACPC method is proposed, and a transfer strategy is designed to relieve the constraint imposed by the initial main pipe pressure on the controller. This ensures that the influent process operates within the specified pressure range. Then, a neural network-based adaptive dynamic adjustment algorithm is proposed to adjust control parameters in real time according to the operation status, reducing the main pipe pressure fluctuations caused by cleaning operations of the membrane module and improving the stability of the influent process. Finally, the stability analysis of the controller is provided, proving that all variables in the influent process are semi-globally ultimately bounded. This confirms the realization of stable control over the main pipe pressure. Simulation tests and practical verification results show that this method can ensure the stable operation of the influent process in municipal wastewater treatment. -
表 1 控制性能对比 (kPa)
Table 1 Comparison of the control performances (kPa)
方法 IAE ISE MaxDev ACPC 0.5359 0.5374 1.9265 PID 9.7240 2.8241 7.9069 -
[1] 韩红桂, 王玉爽, 刘峥, 孙浩源, 乔俊飞. 知识和数据驱动的污水处理反硝化脱氮过程协同优化控制. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(6): 1221−1233Han Hong-Gui, Wang Yu-Shuang, Liu Zheng, Sun Hao-Yuan, Qiao Jun-Fei. Knowledge-data-driven cooperative optimal control for wastewater treatment denitrification process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(6): 1221−1233 [2] Han H G, Ji W Y, Liu Z, Sun H Y, Qiao J F. Predefined-time adaptive neural control for nonlinear systems with unknown interconnection. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2025, 55(6): 2608−2620 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2025.3552926 [3] Han H G, Liu Z, Lu W, Hou Y, Qiao J F. Dynamic MOPSO-based optimal control for wastewater treatment process. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(5): 2518−2528 [4] Borja S, Albert G, Xavier F, Ulf J, Juan A B. A plant-widemodel describing GHG emissions and nutrient recovery options for water resource recovery facilities. Water Research, 2022, 215: Article No. 118223 doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2022.118223 [5] 刘玉发, 刘勇华, 苏春翌, 鲁仁全. 一类具有未知幂次的高阶不确定非线性系统的自适应控制. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(8): 2018−2027Liu Yu-Fa, Liu Yong-Hua, Su Chun-Yi, Lu Ren-Quan. Adaptive control for a class of high-order uncertain nonlinear systems with unknown powers. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(8): 2018−2027 [6] Zhu Z Z, Lin Y L, Zhang Y. Adaptive quasi-fixed-time integral terminal sliding mode control for nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2024, 71(3): 1366−1370 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2023.3327629 [7] Wan X B, Wang Z Q, Wei F, Jin L, Zhang C K, Wu M. Hybrid variables-dependent event-based efficient model predictive load frequency control for power systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20(11): 12771−12782 doi: 10.1109/TII.2024.3424490 [8] You S, Kim W. Adaptive learning gain-based control for nonlinear systems with external disturbances: Application to PMSM. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2023, 31(3): 1427−1434 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2022.3208446 [9] 韩红桂, 秦晨辉, 孙浩源, 乔俊飞. 城市污水处理过程自适应滑模控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(5): 1010−1018Han Hong-Gui, Qin Chen-Hui, Sun Hao-Yuan, Qiao Jun-Fei. Adaptive sliding mode control for municipal wastewater treat ment process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(5): 1010−1018 [10] Wu X L, Han W H, Yang H Y, Li X, Han H G. Robust soft constrained model predictive control and its application in wastewater treatment processes. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 13198−13211 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2025.3552421 [11] Li D P, Han H G, Qiao J F. Composite boundary structure-based tracking control for nonlinear state-dependent constrained systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(8): 5686−5693 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3372888 [12] Hou Q H, Dong J X. Dynamic event-triggered fixed-time tracking control for state-constrained nonlinear systems with dead zone based on fast fixed-time filters. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2024, 54(1): 634−643 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2023.3317406 [13] Wang W, Li Y M. Distributed fuzzy optimal consensus control of state-constrained nonlinear strict-feedback systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(5): 2914−2929 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3140104 [14] Qiu J B, Sun K K, Rudas I J, Gao H J. Command filter-based adaptive NN control for MIMO nonlinear systems with full-state constraints and actuator hysteresis. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(7): 2905−2915 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2944761 [15] Zhao L, Liu G Q. Adaptive finite-time attitude tracking control for state constrained rigid spacecraft systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems Ⅱ: Express Briefs, 2021, 68(12): 3552−3556 doi: 10.1109/TCSII.2021.3070799 [16] Jin X. Adaptive fixed-time control for MIMO nonlinear systems with asymmetric output constraints using universal barrier functions. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(7): 3046−3053 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2874877 [17] Zhang Y H, Xie L P, Xie X P, Sun Z Y, Zhang K J. Fuzzy adaptive control for stochastic nonstrict feedback systems with multiple time-delays: A novel Lyapunov-Krasovskii method. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2024, 32(6): 3815−3824 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2024.3384588 [18] Xu K, Wang H Q, Liu P X P. Adaptive fixed-time control for high-order stochastic nonlinear time-delay systems: An improved Lyapunov-Krasovskii function. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(2): 776−786 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2023.3337792 [19] Peng Y R, Xu S Y, Park J H. Adaptive fuzzy control for stochastic nonlinear systems with delayed input and delayed state via improved Lyapunov-Krasovskii function. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2025, 33(2): 570−579 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2024.3486574 [20] Ma J L, Xu S Y, Ma Q, Zhang Z Q. Event-triggered adaptive neural network control for nonstrict-feedback nonlinear time-delay systems with unknown control directions. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(10): 4196−4205 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2952709 [21] 杨彬, 周琪, 曹亮, 鲁仁全. 具有指定性能和全状态约束的多智能体系统事件触发控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(8): 1527−1535Yang Bin, Zhou Qi, Cao Liang, Lu Ren-Quan. Event-triggered control for multi-agent systems with prescribed performance and full state constraints. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(8): 1527−1535 [22] Kim G, Lee H, Won D, Tomizuka M, Kim W. Singularity-free nonlinear position control using time-varying barrier Lyapunov function for permanent magnet synchronous motors. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2025, 11(1): 3454−3465 doi: 10.1109/TTE.2024.3441832 [23] Li D P, Han H G, Qiao J F. Deterministic learning-based adaptive neural control for nonlinear full-state constrained systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(8): 5002−5011 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3126320 [24] 毛艳岭, 富月. 非线性系统自适应最优切换控制方法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(10): 2122−2135Mao Yan-Ling, Fu Yue. Adaptive optimal switching control of nonlinear systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(10): 2122−2135 [25] Lv J X, Ju X Z, Wang C H. Neural network-based nonconservative predefined-time backstepping control for uncertain strict-feedback nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(11): 16562−16573 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3296194 [26] 赵光同, 曹亮, 周琪, 李鸿一. 具有未建模动态的互联大系统事件触发自适应模糊控制. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(8): 1932−1942Zhao Guang-Tong, Cao Liang, Zhou Qi, Li Hong-Yi. Event-triggered adaptive fuzzy control for interconnected large-scale systems with unmodeled dynamics. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(8): 1932−1942 [27] 王祚, 朱延正, 陈新开, 杨帆, 苏春翌. 双端切换拓扑下基于二值通信的多智能体系统容错控制. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(6): 1347−1358Wang Zuo, Zhu Yan-Zheng, Chen Xin-Kai, Yang Fan, Su Chun-Yi. Fault-tolerant control for multi-agent systems based on binary-valued communication under dual-terminal switching topologies. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(6): 1347−1358 [28] 李冬妮, 孙佳月, 闫宇晴, 张化光. 基于混合双端事件触发机制的协同控制策略研究. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(4): 792−803Li Dong-Ni, Sun Jia-Yue, Yan Yu-Qing, Zhang Hua-Guang. Cooperative control strategy research based on hybrid dual-terminal event-triggered mechanism. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(4): 792−803 -





 下载:
下载: