Coordinated Sliding Mode Control of Fuel Cell Systems Based on Partial State Feedback
-
摘要: 质子交换膜燃料电池因其高效清洁的特性, 成为替代传统内燃机的理想选择. 在质子交换膜燃料电池系统中, 空气供给子系统的氧气过量比与阴极压力是影响其性能和寿命的关键变量. 然而, 这些变量在实际应用中通常难以直接测量, 且系统模型存在参数不确定性. 为应对上述挑战, 提出一种部分状态反馈预设时间协同控制策略. 该策略的核心在于, 首先创新性地设计仅依赖于可测状态与目标设定值的“引导变量”, 并借助输入−状态稳定性理论, 将原控制问题转化为“引导变量”的镇定问题. 随后, 选取“引导变量”及其导数的线性组合来构建滑模面, 并提出一种基于障碍李雅普诺夫函数的自适应滑模控制律, 确保滑动变量在预设时间内收敛至指定小邻域内, 从而间接实现对氧气过量比和阴极压力的精确控制, 同时抑制测量噪声的干扰. 该方法规避了对关键状态的直接测量需求, 且不依赖于精确的系统模型参数. 仿真与硬件在环实验结果验证了所提策略具有优异的动态响应性能和对参数不确定性的鲁棒性.Abstract: Proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) has emerged as an ideal alternative to traditional internal combustion engines due to their high efficiency and clean characteristics. Within PEMFC systems, the oxygen excess ratio and cathode pressure in the air supply subsystem are critical variables that affect performance and durability. However, these variables are often not directly measurable in practical applications, and the system model is subject to parameter uncertainties. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a partial state feedback coordinated control strategy with a prescribed time. The core of this strategy is the innovative design of “guidance variables”, which depend solely on measurable states and target setpoints. By leveraging input-to-state stability theory, the original control problem is transformed into a stabilization problem for “guidance variables”. Subsequently, a sliding surface is constructed as a linear combination of “guidance variables” and their derivatives. Building upon this, an adaptive sliding mode control law based on a barrier Lyapunov function is proposed. This ensures that the sliding variable converges to a specified small neighborhood within a prescribed time, thereby achieving indirectly precise control of the oxygen excess ratio and cathode pressure while the measurement noise vanishes. This method circumvents the need for direct measurement of critical states and does not rely on an exact system model parameter. Both simulation and hardware-in-the-loop experimental results validate that the proposed strategy exhibits excellent dynamic response and strong robustness against parameter uncertainties.
-
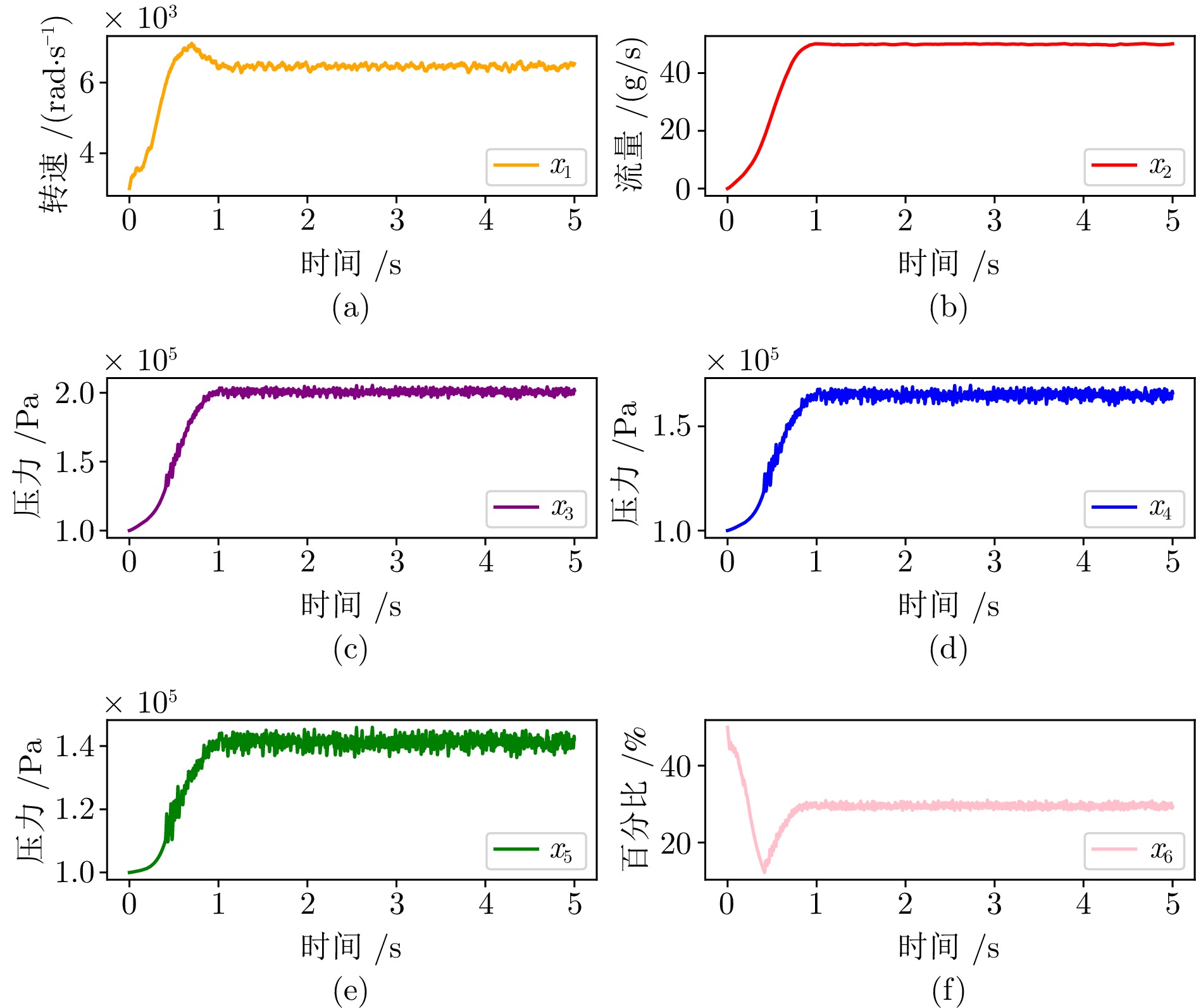
图 12 实验中系统状态变化((a)空压机转速; (b)空压机出口流量; (c)供气歧管压力; (d)阴极压力; (e)排气歧管压力; (f)背压阀开度)
Fig. 12 Variation of system states in the experiment ((a) Compressor speed; (b) Compressor outlet flow rate; (c) Supply manifold pressure; (d) Cathode pressure; (e) Exhaust manifold pressure; (f) Backpressure valve opening)
表 1 系统状态方程中的参数$ a_i $和$ c_i $
Table 1 Parameters $ a_i $ and $ c_i $ in the system state equations
参数 表达式 确定性 $ a_1 $ $ p_{atm} $ $ \checkmark $ $ a_2 $ $ \frac{\gamma-1}{\gamma} $ $ \checkmark $ $ a_3 $ $ k_{ca,\; in} $ $ \checkmark $ $ a_4 $ $ k_{ca,\; out} $ $ \checkmark $ $ a_5 $ $ \frac{R_{O_2} n_{cell} M_{O_2}}{4R_a F} $ $ \checkmark $ $ a_6 $ $ \frac{n_{cell} M_{O_2}}{4F \omega_{O_2}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ c_1 $ $ \frac{1}{J_{cp}} \left(\frac{k_t \eta_{cm} k_{cm,\; p}}{R_{cm}} + f\right) $ $ \times $ $ c_2 $ $ \frac{C_p T_{atm}}{J_{cp} \eta_{cp}} $ $ \times $ $ c_3 $ $ \frac{k_t \eta_{cm} k_{cm,\; p}}{J_{cp} R_{cm}} $ $ \times $ $ c_4 $ $ \frac{k_t \eta_{cm} k_{cm,\; i}}{J_{cp} R_{cm}} $ $ \times $ $ c_5 $ $ \frac{A_{cp}}{L_{cp}} $ $ \times $ $ c_6 $ $ \frac{R_a T_{atm}}{V_{sm}} $ $ \times $ $ c_7 $ $ \frac{1}{\eta_{cp}} $ $ \times $ $ c_8 $ $ \frac{R_a T_{st}}{V_{ca}} $ $ \times $ $ c_9 $ $ \frac{R_a T_{st}}{V_{rm}} $ $ \times $ $ c_{10} $ $ \frac{C_{D} A_{T}}{\sqrt{R_a T_{st}}} \gamma^{\frac{1}{2}} \left(\frac{2}{\gamma +1}\right)^{\frac{\gamma +1}{2\gamma - 1}} $ $ \times $ $ c_{11} $ $ \frac{1}{\tau_{rm}} $ $ \times $ 表 2 模拟参数表
Table 2 Simulation parameter table
参数 含义 数值 确定性 物理
系统
参数$ J_{{{cp}}} $ 空压机转动惯量 $ 4.8 \times 10^{-5} \,\; {\rm{kg\cdot m}}^2 $ $ \checkmark $ $ \eta_{{{cm}}} $ 电机效率 $ 0.85 $ $ \times $ $ R_{{{cm}}} $ 电机内阻 $ 0.7 \,\; \Omega $ $ \times $ $ k_t $ 电机转矩常数 $ 0.016 \;1 \,\; {\rm{N m/A}} $ $ \times $ $ k_{cm,\; p} $ 电机比例系数 $ 0.005 \,\; {\rm{V/({rad \cdot s}^{-1})}} $ $ \times $ $ k_{cm,\; i} $ 电机积分系数 $ 0.005 \,\; {\rm{V/({rad \cdot s}^{-1})}} $ $ \times $ $ C_p $ 定压空气比热容 $ 1 00\;4 \,\; {\rm{J/(kg \cdot K)}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ T_{{{atm}}} $ 大气温度 $ 298.15 \,\; {\rm{K}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ \eta_{{{cp}}} $ 空压机效率 $ 0.7 $ $ \times $ $ p_{{{atm}}} $ 大气压力 $ 101.315 \,\; {\rm{kPa}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ \gamma $ 绝热常数 $ 1.4 $ $ \checkmark $ $ f $ 摩擦系数 $ 3 \times 10^{-4} \,\; {\rm{N m/({rad \cdot s}^{-1})}} $ $ \times $ $ A_{{{cp}}} $ 空压机流通面积 $ 0.03 \,\; {\rm{m}}^2 $ $ \times $ $ L_{{{cp}}} $ 空压机腔体长度 $ 0.5 \,\; {\rm{m}} $ $ \times $ $ R_a $ 空气气体常数 $ 287 \,\; {\rm{J/(kg \cdot K)}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ V_{{{sm}}} $ 进气歧管容积 $ 0.004 \;3 \,\; {\rm{m}}^3 $ $ \times $ $ k_{{{ca,\; in}}} $ 阴极入口流通系数 $ 1.4 \times 10^{-6} \,\; {\rm{kg/(Pa \cdot s)}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ T_{{{st}}} $ 电堆温度 $ 349 \,\; {\rm{K}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ V_{{{ca}}} $ 电堆阴极容积 $ 0.005 \,\; {\rm{m}}^3 $ $ \times $ $ R_{{{O}}_2} $ 氧气气体常数 $ 259 \,\; {\rm{J/(kg \cdot K)}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ n_{{{cell}}} $ 电堆单元数量 $ 280 $ $ \checkmark $ $ M_{{{O}}_2} $ 氧气摩尔质量 $ 0.032 \,\; {\rm{kg/mol}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ F $ 法拉第常数 $ 96\; 485 \,\; {\rm{C/mol}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ \omega_{{{O}}_2} $ 空气中氧气质量分数 $ 0.233 $ $ \checkmark $ $ k_{{{ca,\; out}}} $ 阴极出口流通系数 $ 2.1 \times 10^{-6} \,\; {\rm{kg/(Pa \cdot s)}} $ $ \checkmark $ $ V_{{{rm}}} $ 排气歧管容积 $ 0.001 \,\; {\rm{m}}^3 $ $ \times $ $ A_T $ 背压阀最大开口面积 $ 0.002\;5 \,\; {\rm{m}}^2 $ $ \times $ $ C_D $ 流速常数 $ 0.025 $ $ \times $ $ \tau_{{{rm}}} $ 时间常数 $ 0.2 \,\; {\rm{s}} $ $ \times $ 运行
条件
与设
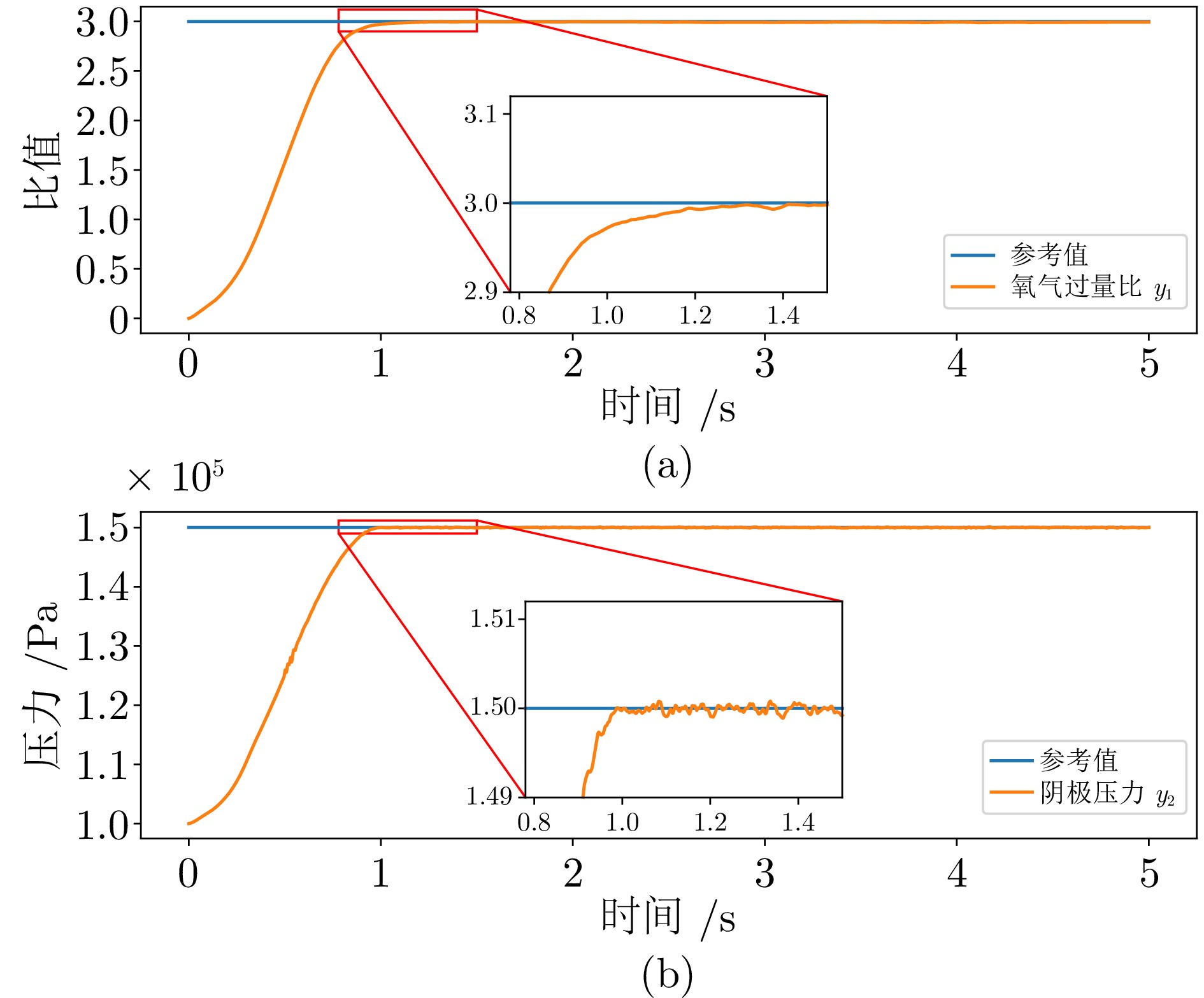
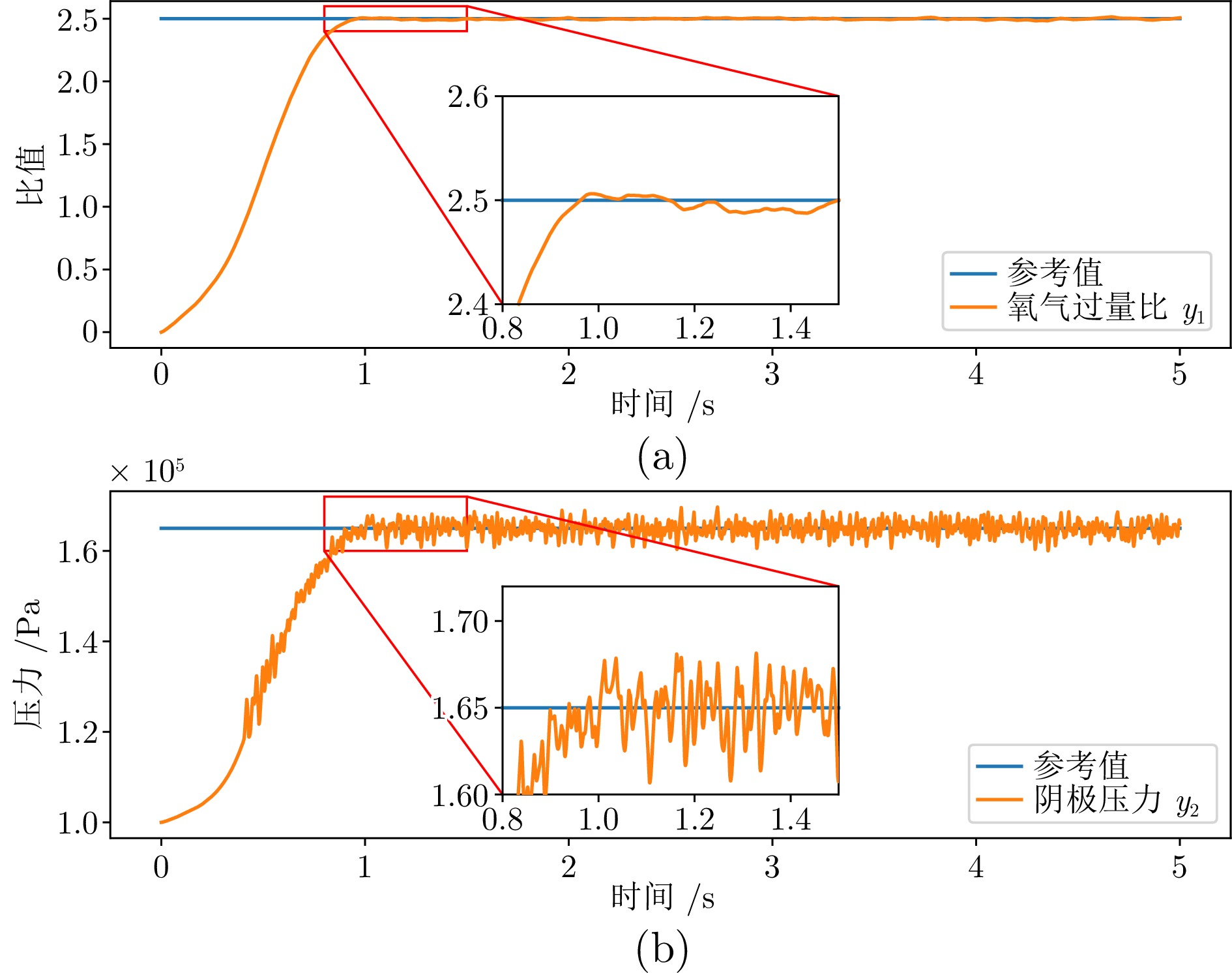
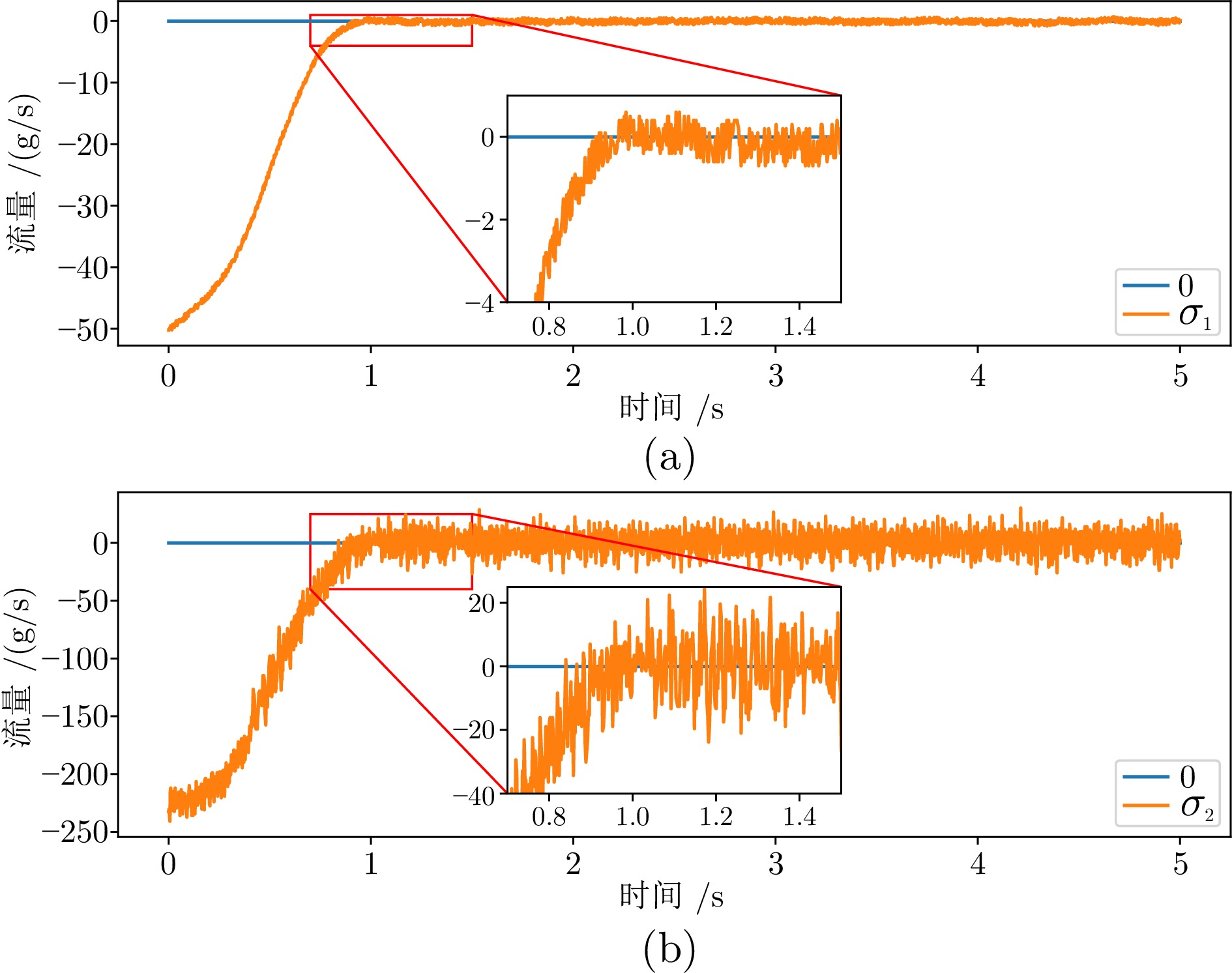
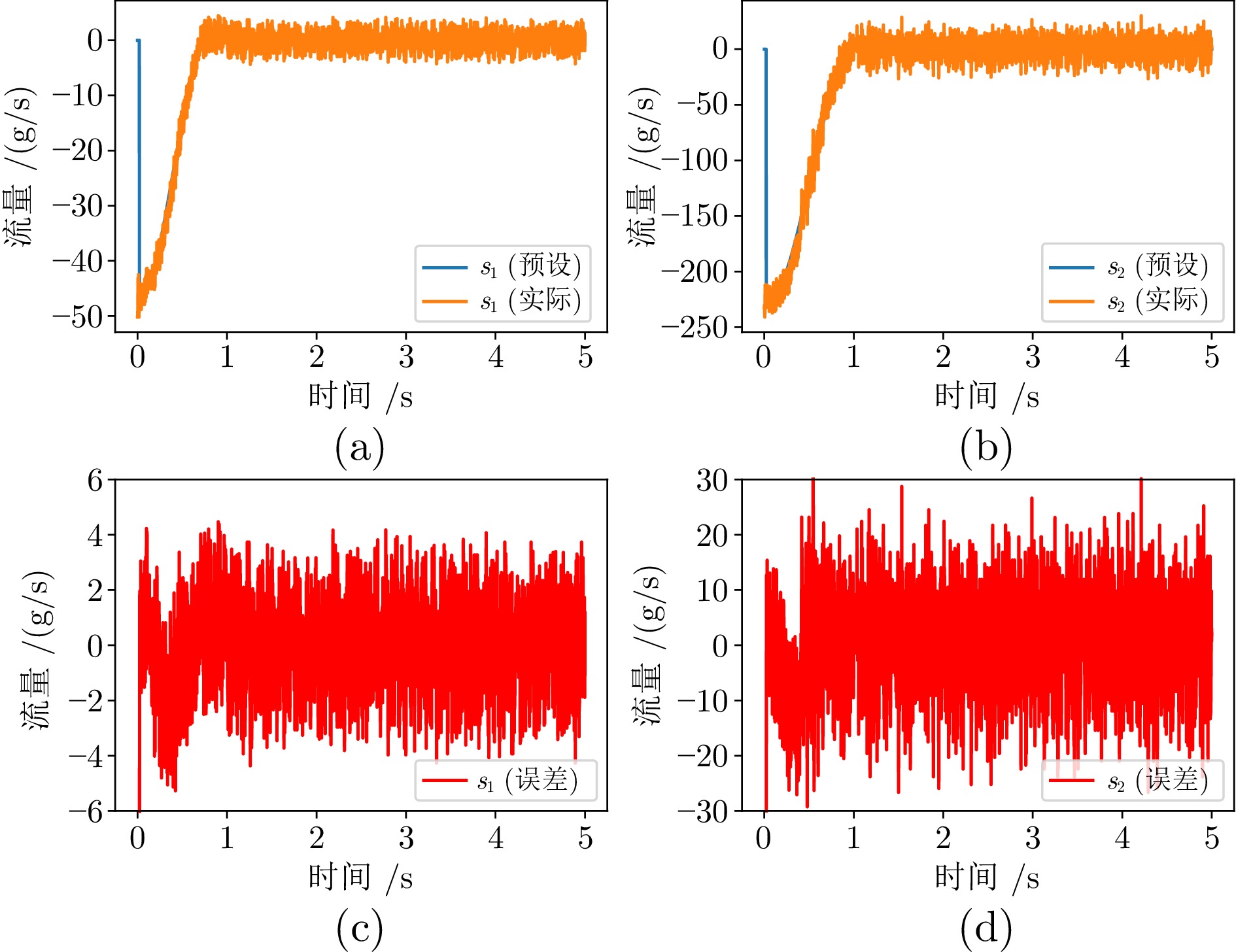
定值$ I_{{{st}}} $ 电堆负载电流 200 A $ \checkmark $ $ y_{1,\; {{ref}}} $ 氧气过量比设定值 3 $ \checkmark $ $ y_{2,\; {{ref}}} $ 阴极压力设定值 $ 150 \,\; {\rm{kPa}} $ $ \checkmark $ -
[1] 张博, 郭戈, 王丽媛, 王琼. 基于信号灯状态的燃油最优车速规划与控制. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(3): 461−470 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c160684Zhang Bo, Guo Ge, Wang Li-Yuan, Wang Qiong. Vehicle speed planning and control for fuel consumption optimization with traffic light state. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(3): 461−470 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c160684 [2] 原豪男, 郭戈. 交通信息物理系统中的车辆协同运行优化调度. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(1): 143−152 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180354Yuan Hao-Nan, Guo Ge. Vehicle cooperative optimization scheduling in transportation cyber physical systems. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(1): 143−152 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180354 [3] 张晗, 杨继斌, 张继业, 宋鹏云, 徐晓惠. 燃料电池有轨电车能量管理Pareto多目标优化. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(12): 2378−2392 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190044Zhang Han, Yang Ji-Bin, Zhang Ji-Ye, Song Peng-Yun, Xu Xiao-Hui. Pareto-based multi-objective optimization of energy management for fuel cell tramway. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(12): 2378−2392 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190044 [4] Xie S Q, Li Q, Yin L Z, Huo S S, Wang T H, Chen W R. Multivariable cooperative control for performance guarantee of PEMFC system in high-altitude environment. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(12): 15846−15857 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2024.3390742 [5] Peng C, Xie C, Zou J X, Jiang X Y, Zhu Y. A feedback linearization sliding mode decoupling and fuzzy anti-surge compensation based coordinated control approach for PEMFC air supply system. Renewable Energy, 2024, 237: Article No. 121760 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2024.121760 [6] Meng J W, Guo Q H, Yue M L, Diallo D. A Lyapunov-based adaptive control strategy with fault-tolerant objectives for proton exchange membrane fuel cell air supply systems. Applied Energy, 2024, 376: Article No. 124275 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.124275 [7] Jiang F F, Wei Z B, Zhang C Z, He H W, Song R Y, Gao F. Cathodic supply optimization of PEMFC system under variable altitude. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(11): 14298−14307 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2024.3368097 [8] Ajanovic A, Haas R. Prospects and impediments for hydrogen and fuel cell vehicles in the transport sector. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2021, 46(16): 10049−10058 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.03.122 [9] Yin L Z, Li Q, Breaz E, Chen W R, Gao F. Net power enhancement of PEMFC system based on dual loop multivariable coordinated management. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2023, 70(11): 11216−11230 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3234144 [10] Liu Z M, Chang G F, Jiang S F, Wei X Z, Yuan H, Xie J P, et al. Adaptive anti-surge control strategy for PEM fuel cell vehicle with online surge detection. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2024, 10(1): 844−858 doi: 10.1109/TTE.2023.3287539 [11] Pukrushpan J T, Peng H E, Stefanopoulou A G. Control-oriented modeling and analysis for automotive fuel cell systems. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2004, 126(1): 14−25 doi: 10.1115/1.1648308 [12] Suh K W. Modeling, Analysis and Control of Fuel Cell Hybrid Power Systems [Ph.D. dissertation], University of Michigan, United States, 2006. [13] Talj R J, Hissel D, Ortega R, Becherif M, Hilairet M. Experimental validation of a PEM fuel-cell reduced-order model and a moto-compressor higher order sliding-mode control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2010, 57(6): 1906−1913 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2009.2029588 [14] Liu J X, Gao Y B, Su X J, Wack M, Wu L G. Disturbance-observer-based control for air management of PEM fuel cell systems via sliding mode technique. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2019, 27(3): 1129−1138 doi: 10.1109/TCST.2018.2802467 [15] Derakhshannia M, Moosapour S S. RBFNN based fixed time sliding mode control for PEMFC air supply system with input delay. Renewable Energy, 2024, 237: Article No. 121772 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2024.121772 [16] Beirami H, Shabestari A Z, Zerafat M M. Optimal PID plus fuzzy controller design for a PEM fuel cell air feed system using the self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015, 40(30): 9422−9434 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.05.114 [17] Guo X Y, Fan N N, Dong Z, Wang C L. Adaptive prescribed performance control for PEM fuel cell air supply systems with unknown air compressor faults. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2024, 71(7): 7664−7672 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2023.3312416 [18] Neisen V, Mannhardt J, Abel D. Dynamic tracking of power demand for integrated fuel cell systems using nonlinear model predictive control. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2020, 53(2): 13216−13223 doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2020.12.148 [19] Sobhani B, Rahmani Z. A novel controller based on the sum of squares relaxation for the uncertain model of the PEMFC considering external disturbances and actuator saturation. ISA Transactions, 2023, 137: 419−435 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2022.12.004 [20] 王永富, 马冰心, 柴天佑, 张晓宇. PEMFC空气供给系统的二型自适应模糊建模与过氧比控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(5): 853−865 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180047Wang Yong-Fu, Ma Bing-Xin, Chai Tian-You, Zhang Xiao-Yu. Type-2 adaptive fuzzy modeling and oxygen excess ratio control for PEMFC air supply system. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(5): 853−865 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c180047 [21] Luo G, Ma B X, Wang Z Z, Yin L, Wang Y F. Model-free adaptive control for the PEMFC air supply system based on interval type-2 fuzzy logic systems. Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, 2020, 12(6): Article No. 064301 [22] Li S, Qiu Y B, Yin L Z, Li R R, Gan R, Li Q, et al. Net power optimization based on extremum search and model-free adaptive control of PEMFC power generation system for high altitude. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2023, 9(4): 5151−5164 doi: 10.1109/TTE.2022.3222970 [23] Deng Z H, Chen M, Wang H J, Chen Q H. Performance-oriented model learning and model predictive control for PEMFC air supply system. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 64: 339−348 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.01.351 [24] Su Q Q, Zhou J M, Yi F Y, Hu D H, Lu D G, Wu G P, et al. An intelligent control method for PEMFC air supply subsystem to optimize dynamic response performance. Fuel, 2024, 361: Article No. 130697 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.130697 [25] Zhang C, Hu Y F, Gong X, Huang Y J, Chen H. Design and experimental verification of model-free adaptive sliding controller for air supply system of PEMFCs. Control Engineering Practice, 2022, 128: Article No. 105336 doi: 10.1016/j.conengprac.2022.105336 [26] Wang Y L, Wang Y F. Pressure and oxygen excess ratio control of PEMFC air management system based on neural network and prescribed performance. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2023, 121: Article No. 105850 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.105850 [27] Wang L F, Wang L, Liu Z Y, Su H Y. Robust regulation of oxygen excess ratio and cathode pressure for PEMFC air supply systems with centrifugal compressor. In: Proceedings of the 49th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society. Singapore: IEEE, 2023. 1−6 [28] Zhang X, Zhang C L, Zhang Z J, Gao S, Li H. Coordinated management of oxygen excess ratio and cathode pressure for PEMFC based on synthesis variable-gain robust predictive control. Applied Energy, 2024, 367: Article No. 123415 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2024.123415 [29] Wang L F, Wang L, Liu Z Y, Su H Y. Constrained adaptive simultaneous control of oxygen excess ratio and cathode pressure for PEMFC air supply system. In: Proceedings of the China Automation Congress (CAC). Qingdao, China: IEEE, 2024. 5565−5570 [30] Fan N N, Guo X Y, Wang C L, Dong Z, Liu L, Yang J. Adaptive coordinated control for nonlinear PEM fuel cell air supply systems. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2025, 72(5): 5312−5321 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2024.3468708 [31] Yuan H, Dai H F, Wei X Z, Ming P W. A novel model-based internal state observer of a fuel cell system for electric vehicles using improved Kalman filter approach. Applied Energy, 2020, 268: Article No. 115009 doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2020.115009 [32] Yue H W, He H W, Han M, Gong S K. Active disturbance rejection control strategy for PEMFC oxygen excess ratio based on adaptive internal state estimation using unscented Kalman filter. Fuel, 2024, 356: Article No. 129619 doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2023.129619 [33] el Aoumari A, Ouadi H, El-Bakkouri J, Giri F. Adaptive filtered high-gain observer for PEMFC systems in electric vehi-cles. Renewable Energy, 2024, 231: Article No. 120996 doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2024.120996 [34] Zhang C L, Zhang Z J, Li H, Li M X. Switching threshold event-triggered estimation and control for unmeasured oxygen excess ratio of automotive PEMFC air feeding system with input and prescribed performance constraints. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2023, 111(15): 14027−14054 doi: 10.1007/s11071-023-08559-8 [35] Kuang J Y, Lv J F, Hao W B, Lin X P, Zhao D D, Matraji I, et al. Oxygen excess ratio control of PEM fuel cell systems with prescribed regulation time. ISA Transactions, 2023, 142: 683−692 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2023.07.026 [36] Wang Z X, Guo X Y, Dong Z, Fan N N, Cao S Y. Fixed time adaptive fault tolerant sliding mode control of PEMFC air supply system. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 55: 1434−1444 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2023.11.264 [37] Zhang C L, Li H. Fixed-time observation and predefined performance regulation for oxygen excess ratio of vehicular fuel cells under input saturation. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 69: 1022−1035 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.04.342 [38] Greitzer E M. Surge and rotating stall in axial flow compressors——Part I: Theoretical compression system model. Journal of Engineering for Power, 1976, 98(2): 190−198 doi: 10.1115/1.3446138 [39] Wei L, Zhu X C, Wang X H, Hu Z Z, Wang M Q. Research on the coordinated control of oxygen excess ratio and air pressure for PEMFC's air supply system. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2024, 69: 122−133 doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2024.04.361 [40] Isidori A. Nonlinear Control Systems II. London: Springer-Verlag, 1999. 1−35 [41] Song J W, Zuo Z Y, Basin M. New class $ \kappa_\infty$ function-based adaptive sliding mode control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(12): 7840−7847 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3247465 [42] Ning B D, Han Q L, Zuo Z Y. Practical fixed-time consensus for integrator-type multi-agent systems: A time base generator approach. Automatica, 2019, 105: 406−414 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.04.013 -





 下载:
下载: