Full Coverage Test Cases Generating Method for Automated Driving System in Logical Scenario
-
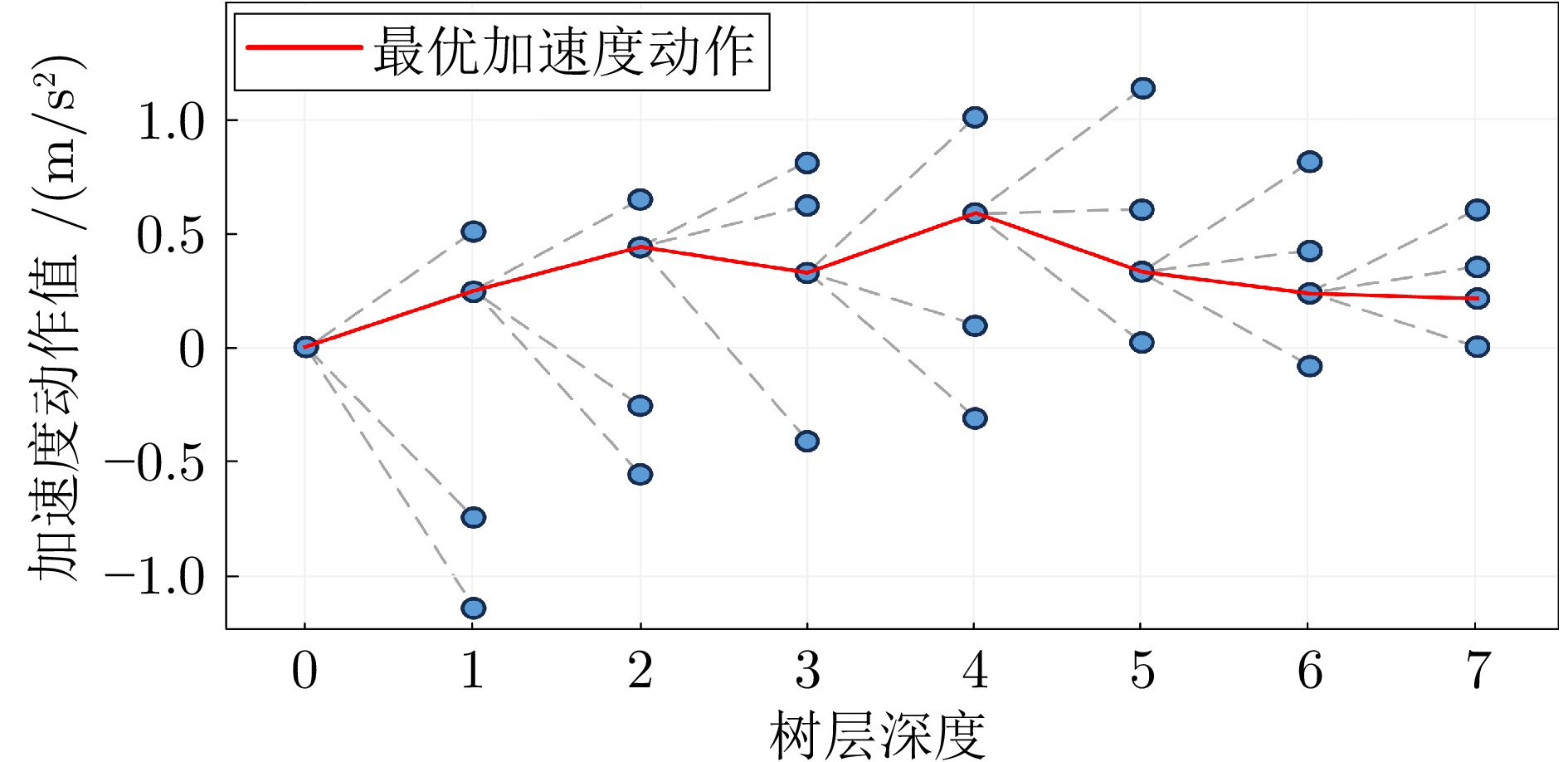
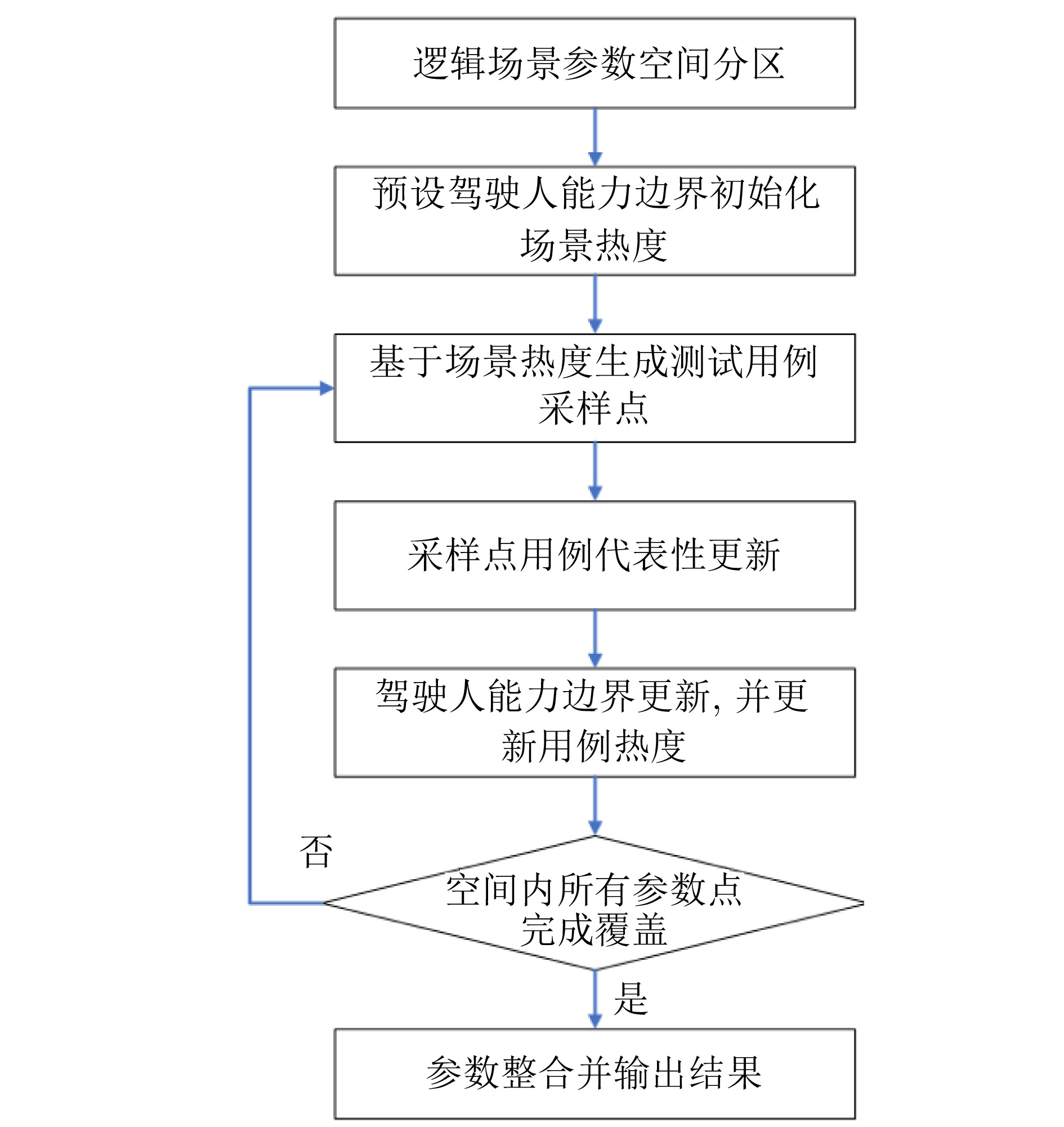
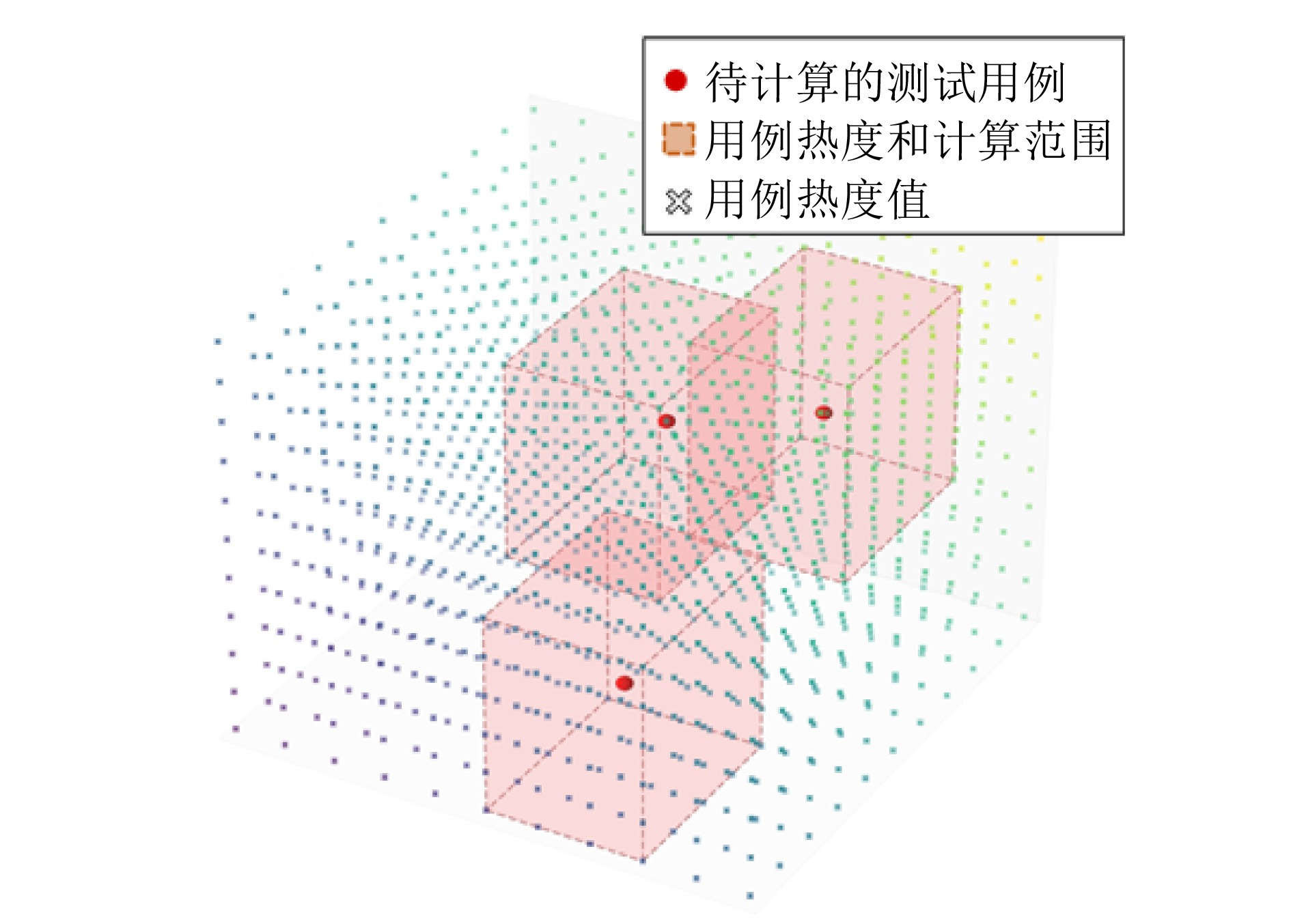
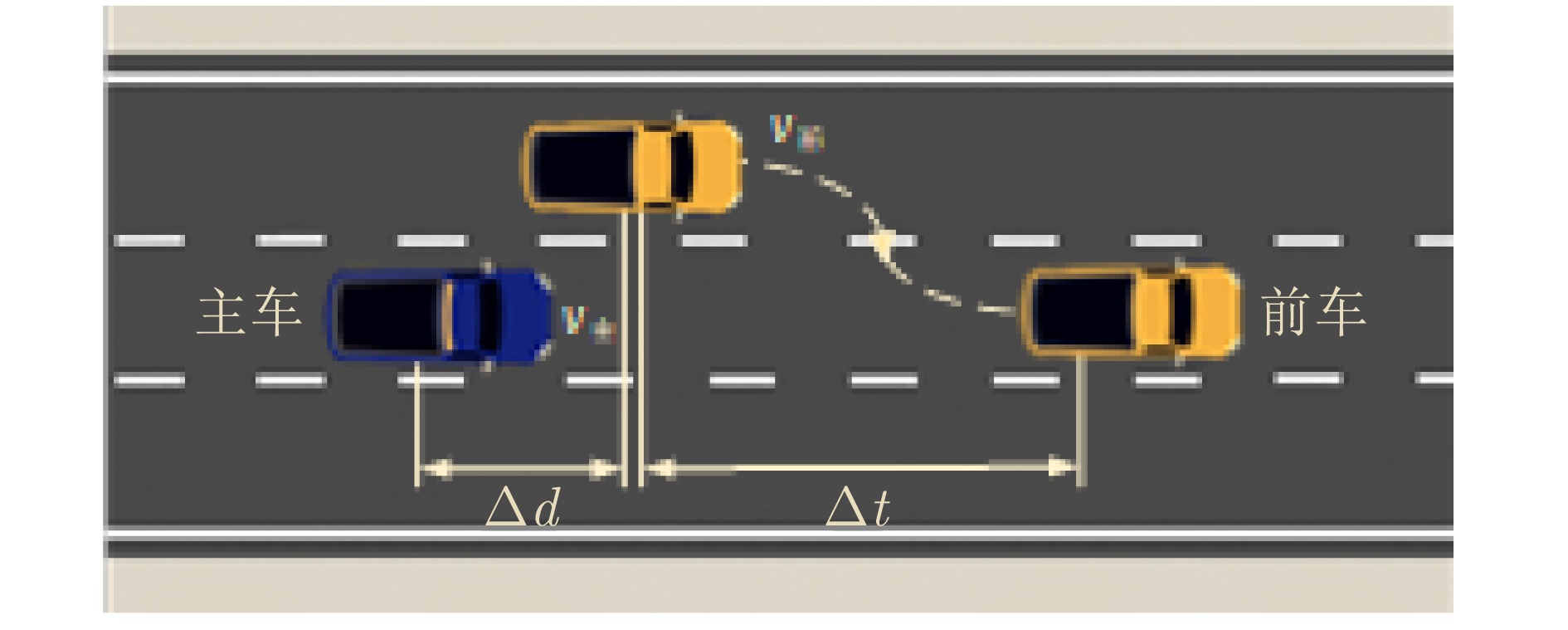
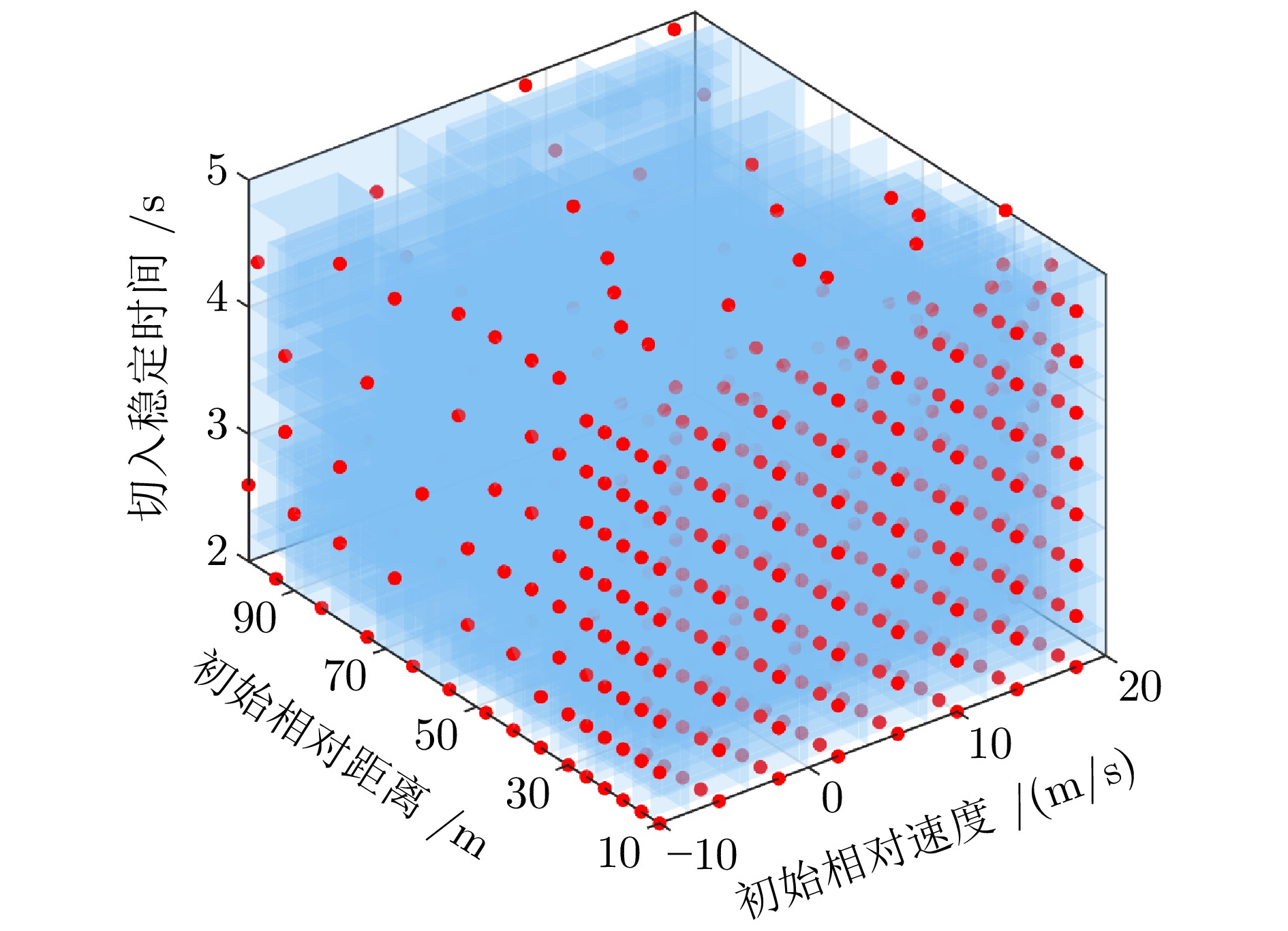
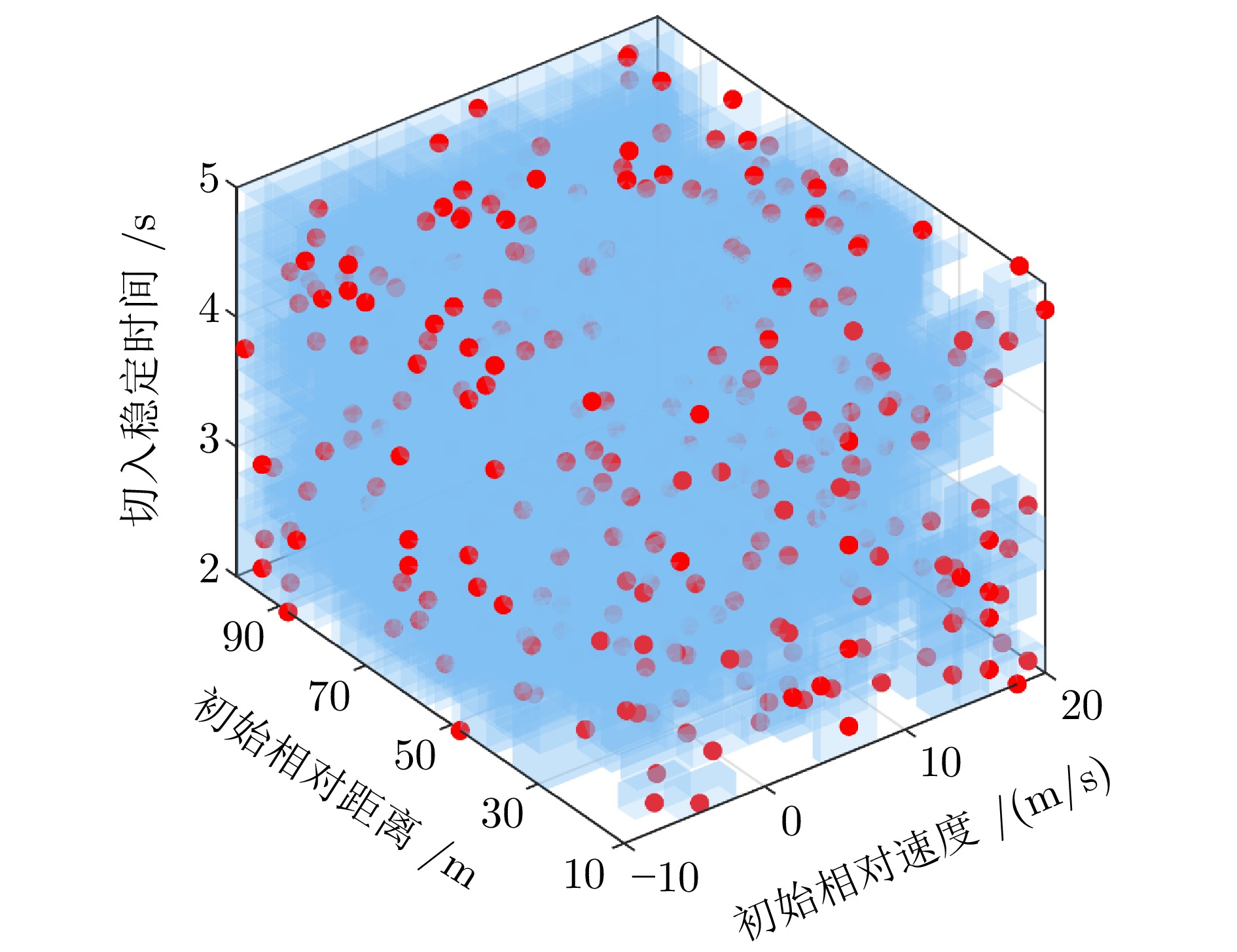
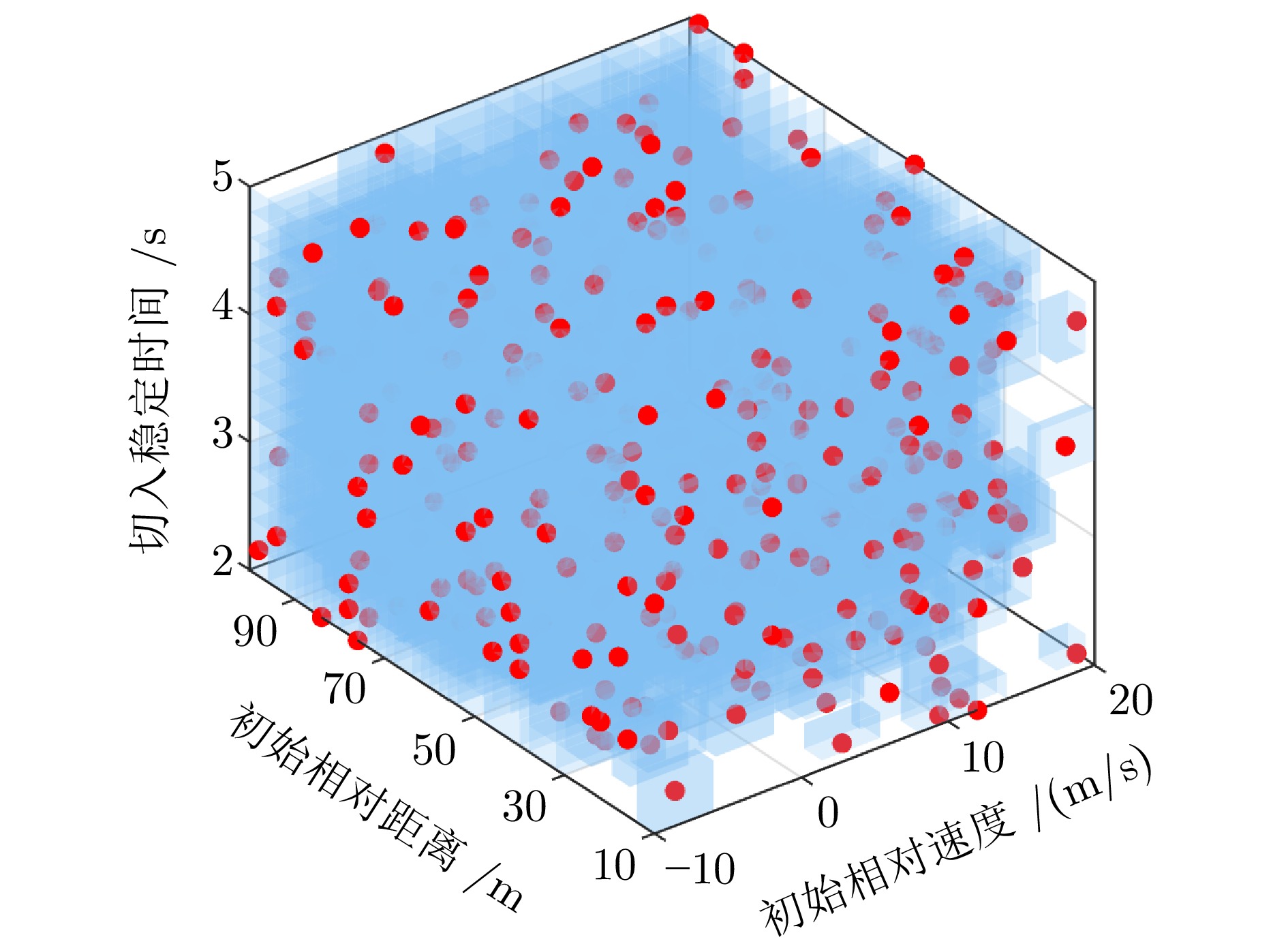
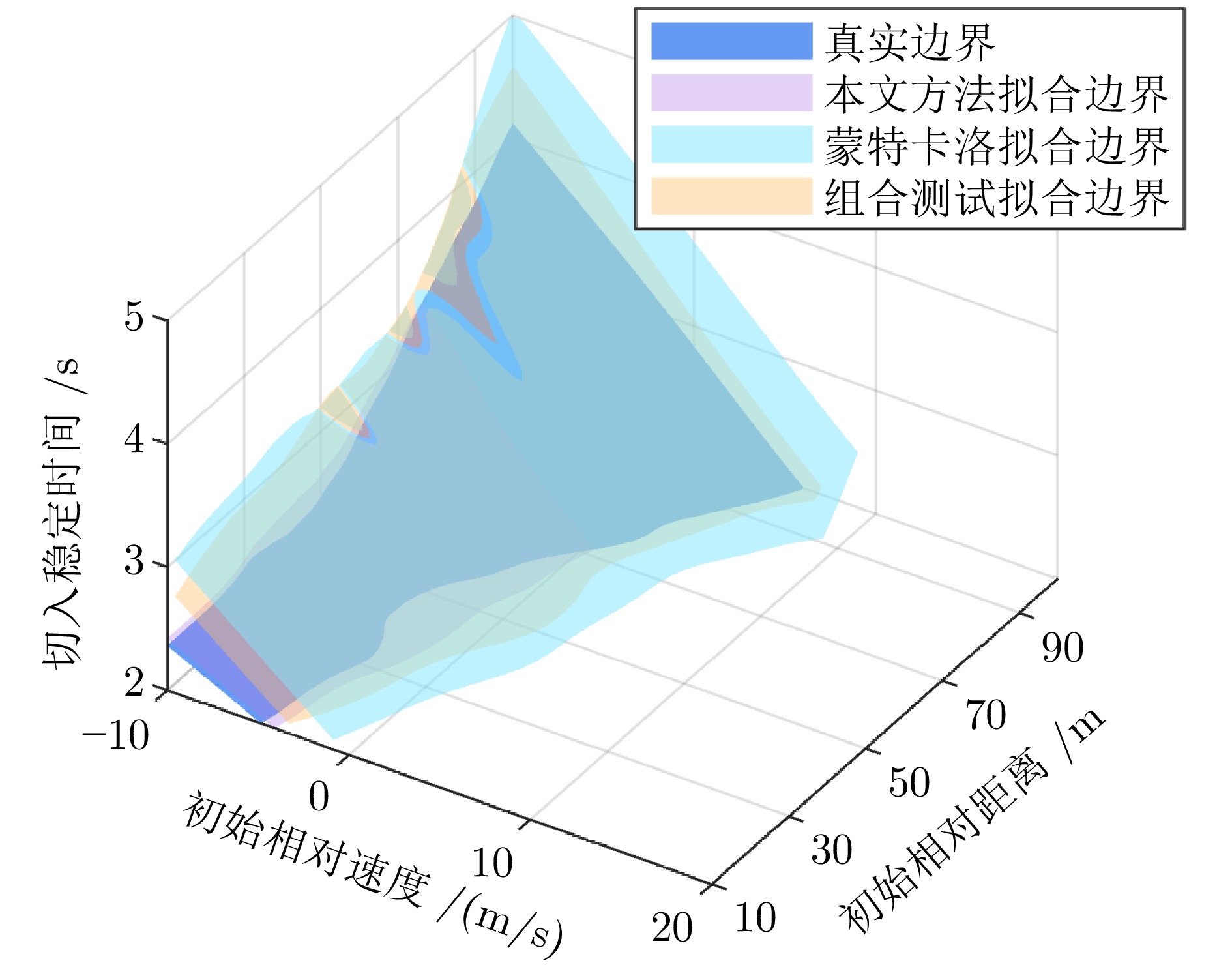
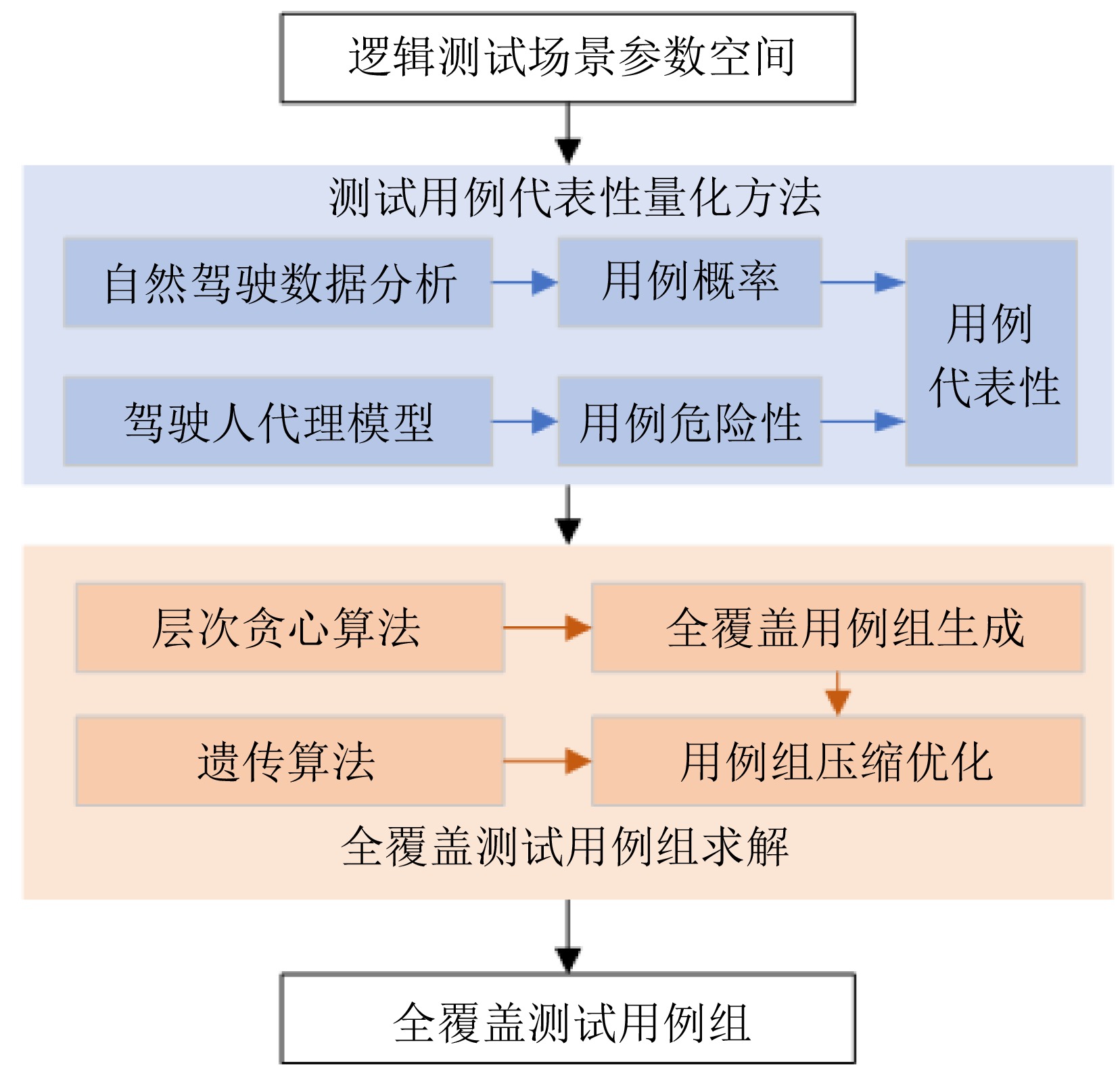
摘要: 基于场景的测试方法是验证自动驾驶系统安全性的主流手段, 然而逻辑场景使用参数空间的形式对场景进行描述, 当被测系统性能存在差异时, 第三方检测机构难以使用同样的测试用例在保证测试公平性的同时兼顾测试覆盖率. 为此, 提出一种基于测试用例代表性的自动驾驶系统逻辑场景全覆盖测试用例生成方法. 首先建立了自动驾驶系统全覆盖测试用例生成框架; 提出综合分析自然驾驶概率分布及危险情况的测试用例代表性量化评价方法; 开发了一种基于热度驱动层次贪心算法和遗传算法的差异化样本组合空间全覆盖问题优化求解方法, 获取测试用例参数组合实现逻辑场景参数空间全覆盖. 使用前车切入场景对本文提出的方法进行了验证. 结果表明, 本文提出的方法在逻辑场景参数空间覆盖率(100%)、测试边界拟合误差(8%)均显著高于当前主流的蒙特卡洛方法(覆盖率84.3%、拟合误差19%)与组合测试方法(覆盖率86.5%、拟合误差14%), 可有效帮助检测机构建设公平、高效的测试场景生成体系.Abstract: The scenario-based testing method is the mainstream means to verify the safety of the automated driving system (ADS). However, the logical scenario uses the form of parameter space to describe the scenario, it is difficult for the third-party detection organizations to use the same test case to ensure the test fairness and test coverage when the systems under test are different. For this reason, this paper proposes a full coverage test cases generating method for ADS in logical scenario based on the test case representativeness. First, a systematic full-coverage testing framework tailored for ADS is established. Subsequently, a quantitative evaluation method is introduced to assess the representativeness of test cases by jointly analyzing naturalistic driving probability distributions and hazardous event characteristics. To solve the resulting non-uniform full-coverage optimization problem, a hybrid algorithm combining heatmap-guided hierarchical greedy search with genetic optimization is developed, enabling the efficient acquisition of representative parameter combinations that achieve full coverage of the logical scenario parameter space. The proposed approach is empirically validated using a lead-vehicle cut-in scenario. The results indicate that the proposed method achieves a logical scenario parameter space coverage rate of 100% and a boundary fitting error of 8%, both of which significantly outperform current mainstream approaches, including the monte carlo method (coverage rate: 84.3%, fitting error: 19%) and combinatorial testing (coverage rate: 86.5%, fitting error: 14%). These findings demonstrate the method's potential to effectively support testing organizations in developing a fair and efficient scenario generation framework.
-
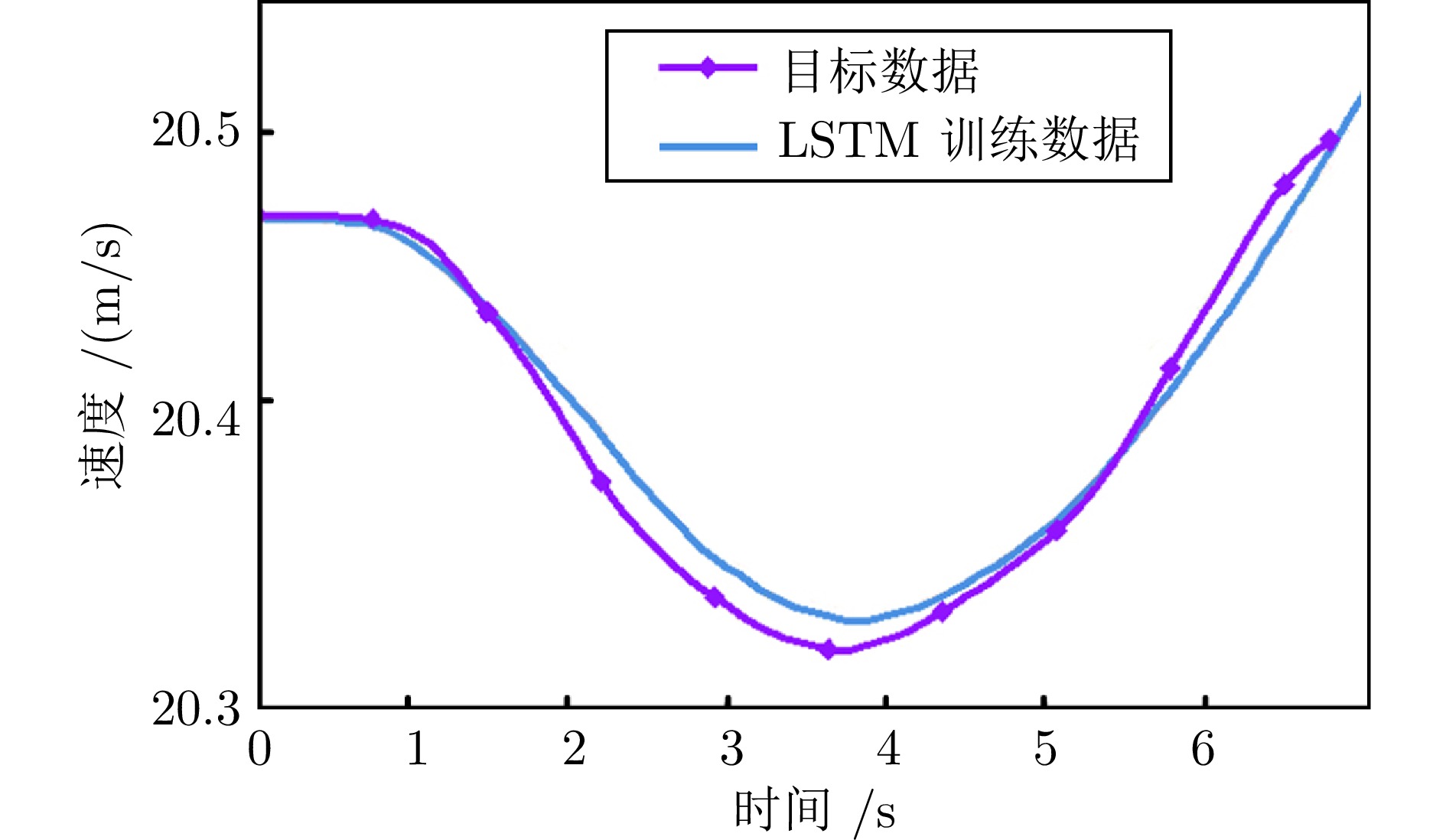
表 1 LSTM模型训练参数
Table 1 Training parameters of the LSTM model
参数 LSTM 输入特征维度 5 输出特征维度 1 LSTM隐藏层单元 64 LSTM层数 3 学习率 0.001 Dropout 0.1 迭代次数 20 Batch Size 8 Attention类型 / 表 2 不同方法的覆盖率对比
Table 2 Comparison of coverage for different methods
用例生成方法 用例数量 参数空间覆盖率 本文方法 482 100% 蒙特卡洛方法 482 84.3% 组合测试方法 482 86.5% 表 3 不同方法性能边界拟合均方根误差
Table 3 RMSE of performance boundary fitting for different methods
测试用例生成方法 均方根误差 本文方法 0.08 蒙特卡洛方法 0.19 组合测试方法 0.14 -
[1] 赵祥模, 赵玉钰, 景首才, 惠飞, 刘建蓓. 面向自动驾驶测试的危险变道场景泛化生成. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(10): 2211−2223 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220772Zhao Xiang-Mo, Zhao Yu-Yu, Jing Shou-Cai, Hui Fei, Liu Jian-Bei. Generalization generation of hazardous lane-changing scenarios for automated vehicle testing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(10): 2211−2223 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220772 [2] 王晓, 张翔宇, 周锐, 田永林, 王建功, 陈龙, 等. 基于平行测试的认知自动驾驶智能架构研究. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(2): 356−371Wang Xiao, Zhang Xiang-Yu, Zhou Rui, Tian Yong-Lin, Wang Jian-Gong, Cheng Long, et al. An intelligent architecture for cognitive autonomous driving based on parallel testing. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(2): 356−371 [3] 林粤彤, 王飞跃, 肖靖, 王知学. 基于模糊神经元网络的智能车辆个性自动驾驶系统的设计与实现. 自动化学报, 2001, 27(4): 531−542 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2001.04.008Lin Yue-Tong, Wang Fei-Yue, Xiao Jing, Wang Zhi-Xue. Design and implementation of a neruo-fuzzy based control system intelligent vehicles. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2001, 27(4): 531−542 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2001.04.008 [4] Riedmaier S, Ponn T, Ludwig D, Schick B, Diermeyer F. Survey on scenario-based safety assessment of automated vehicles. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 87456−87477 doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2993730 [5] 邢星宇, 吴旭阳, 刘力豪, 陈君毅, 余卓平. 基于目标优化的自动驾驶决策规划系统自动化测试方法. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(08): 1162−1169 doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.21004Xing Xing-Yu, Wu Xu-Yang, Liu Li-Hao, Chen Jun-Yi, Yu Zhuo-Ping. Automatic testing method based on optimization algorithms for the decision and planning system of autonomous vehicles. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2021, 49(08): 1162−1169 doi: 10.11908/j.issn.0253-374x.21004 [6] Mullins G, Stankiewicz P, Gupta S. Automated generation of diverse and challenging scenarios for test and evaluation of autonomous vehicles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). New York, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1443–1450 [7] Zhao D, Huang X, Peng H, Lam H, LeBlanc D J. Accelerated evaluation of automated vehicles in car-following maneuvers. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(3): 733−744 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2701846 [8] Liu H, Zhang L, Sastry S K, Zhao J. Safety-critical scenario generation via reinforcement learning based editing. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. New York, USA: IEEE, 2024. 14405–14412 [9] Cai J, Yang S, Guang H. A review on scenario generation for testing autonomous vehicles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. Jeju Island, South Korea: IEEE, 2024. 3371-3376 [10] 赵文博. 智能汽车行人避撞系统相机在环测试方法研究. 长春: 吉林大学, 2021Zhao Wen-Bo. Research on camera-in-the-loop test method for pedestrian collision avoidance system of intelligent vehicle. Changchun: Jilin University, 2021 [11] Duan J, Gao F, He Y. Test scenario generation and optimization technology for intelligent driving systems. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2022, 14(1): 115−127 doi: 10.1109/MITS.2019.2926269 [12] Gambi A, Mueller M, Fraser G. Automatically testing self-driving cars with search-based procedural content generation. In: Proceedings of the 28th ACM SIGSOFT International Symposium on Software Testing and Analysis. Beijing, China: Association for Computing Machinery, 2019. 318-328 [13] Li S, Li W, Li P, Ma P, Yang M. Novel test scenario generation technology for performance evaluation of automated vehicle. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2023, 24(6): 1691−1694 doi: 10.1007/s12239-022-0113-z [14] Zhu B, Zhang P, Zhao J, Deng W. Hazardous scenario enhanced generation for automated vehicle testing based on optimization searching method. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 7321−7331 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3068784 [15] Liu R, Zhao X, Zhu X, Ma J. Statistical characteristics of driver acceleration behaviour and its probability model. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2022, 236: 395−406 doi: 10.1177/09544070211018039 [16] 朱冰, 范天昕, 赵健, 张培兴, 孙宇航. 基于危险边界搜索的自动驾驶系统加速测试方法. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2023, 53(3): 704−712 doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211177Zhu Bing, Fan Tian-Xin, Zhao Jian, Zhang Pei-Xing, Sun Yu-Hang. Accelerated test method of automated driving system based on hazardous boundary search. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2023, 53(3): 704−712 doi: 10.13229/j.cnki.jdxbgxb.20211177 [17] Quante L, Zhang M, Preuk K, Schiebl C. Human performance in critical scenarios as a benchmark for highly automated vehicles. Automotive Innovation, 2021, 4(3): 274−283 doi: 10.1007/s42154-021-00152-2 [18] Sun J, Zhou H, Xi H, Zhang H, Tian Y. Adaptive design of experiments for safety evaluation of automated vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(9): 14497−14508 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3130040 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 6
- HTML全文浏览量: 4
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: