The Autonomous Decision-making Method for Beyond Visual Range Air Combat Driven by Deep Reinforcement Learning
-
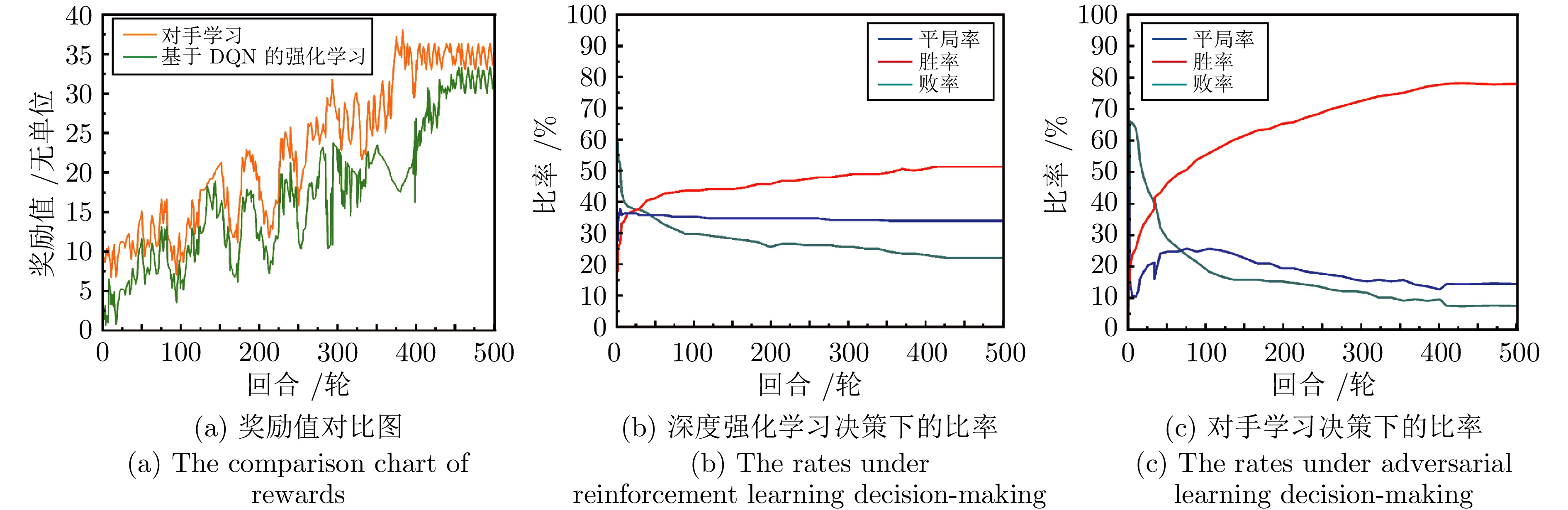
摘要: 随着机载传感器和中远距空空导弹技术的快速发展, 超视距空战已经成为现代空战的主流形式. 在这种复杂多变的作战环境中, 开发能够实时掌握战场态势并制定合理机动决策的智能化技术, 已成为军事技术研究领域的热点问题. 首先, 构建一个涵盖飞机六自由度动力学模型、导弹制导系统模型和雷达传感器系统的高保真仿真环境. 接着, 融合模仿学习和自博弈方法, 提出基于对手学习的空战决策框架, 以解决深度强化学习在空战中适应性和泛化性差的缺点, 提升智能体在复杂多变战场环境中快速适应和策略优化能力. 最后, 构建具有战术差异性的专家系统, 在高保真空战仿真平台中与智能体进行博弈对抗. 结果表明, 在收敛速度和胜率等关键指标上, 所提出的空战决策框架优于传统深度强化学习决策策略, 有效性和泛化性强, 可为复杂超视距空战态势下快速生成可靠策略提供技术支持.Abstract: With the rapid development of airborne sensor technologies and medium-to-long-range air-to-air missile technologies, Beyond Visual Range air combat has become the dominant form of modern air warfare. In such a complex and dynamic operational environment, the development of intelligent technologies capable of real-time battlefield situation awareness and rational maneuver decision-making has emerged as a research hotspot in the field of military technology. First, a high-fidelity simulation environment is constructed, encompassing a six-degree-of-freedom aircraft dynamics model, a missile guidance system model, and a radar sensor system. Subsequently, integrating imitation learning and self-play methods, an opponent-learning-based air combat decision-making framework is proposed to address the poor adaptability and generalization of deep reinforcement learning in aerial combat, thereby enhancing the agent's ability to rapidly adapt and optimize strategies in complex and variable battlefield environments. Finally, ten expert systems with significant tactical differences are developed to engage in game-based confrontations with the agent within the high-fidelity air combat simulation platform. The results demonstrate that the proposed decision-making framework significantly traditional deep reinforcement learning strategies in key metrics such as convergence speed and winning rate, exhibiting strong effectiveness and generalization. This work can provide technical support for the rapid generation of reliable strategies in complex Beyond Visual Range air combat scenarios.1)
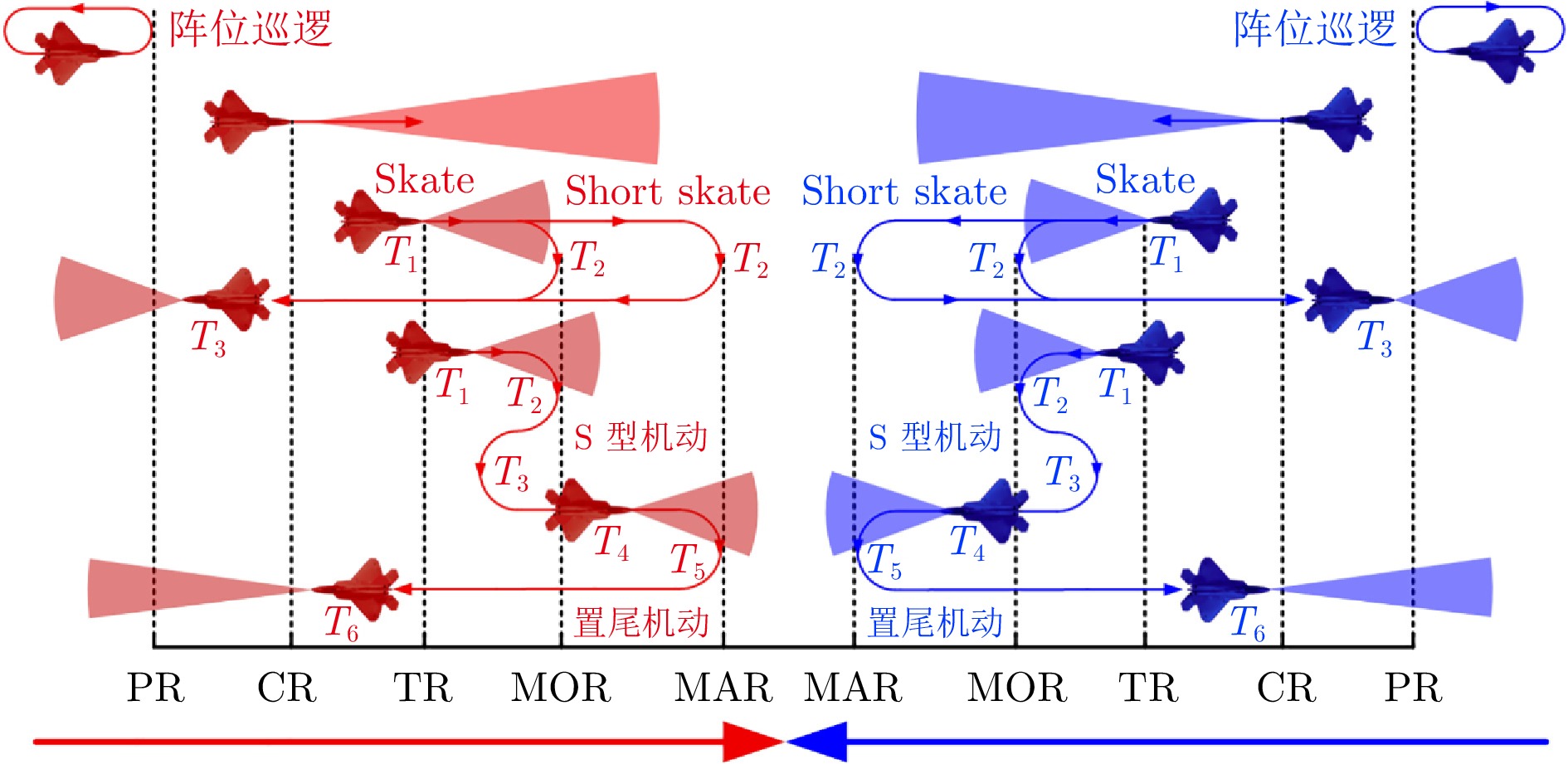
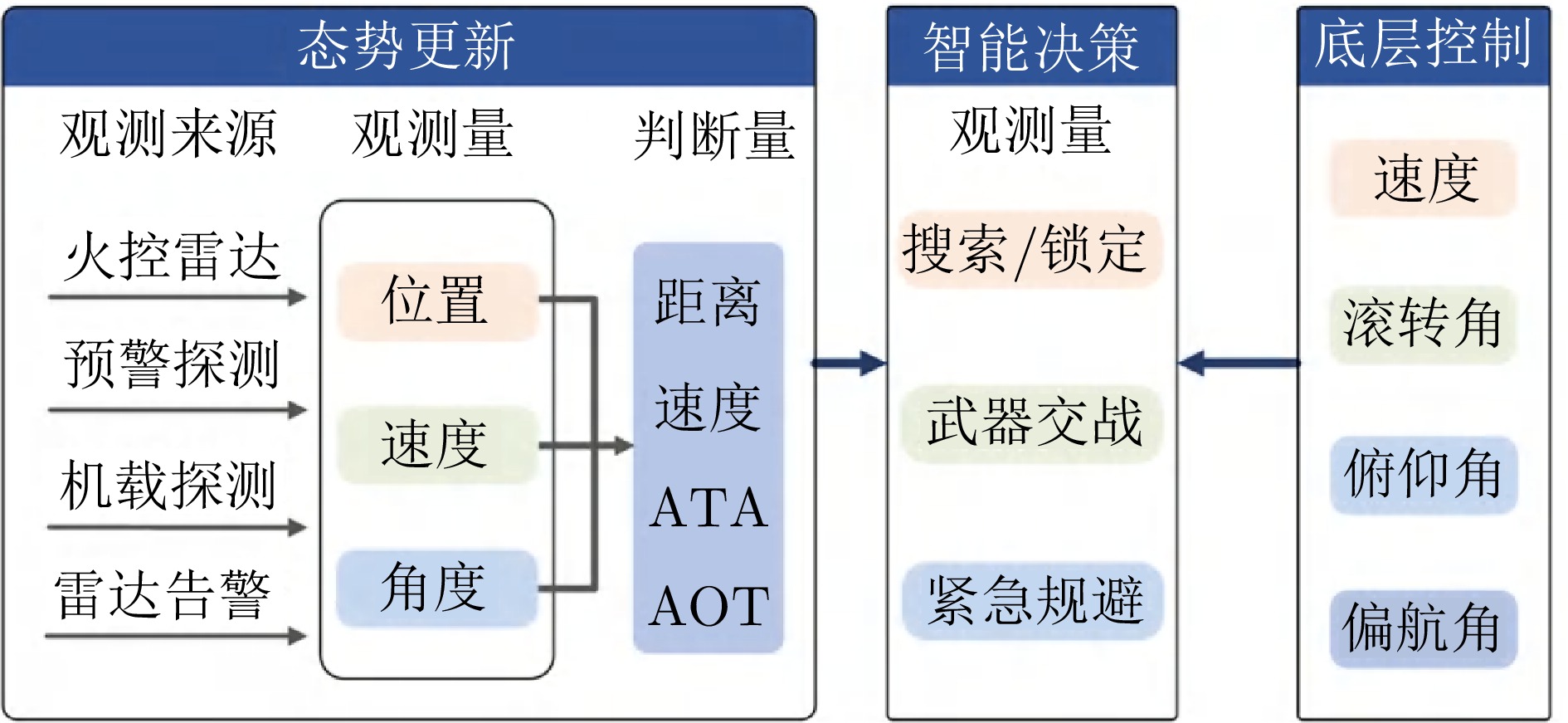
1 1 MAR: Minimum Abort Range. 2 MOR: Minimum Out Range. 3 TR: Target Range. 4 CR: Commit Range. 5PR: Picture Range. -
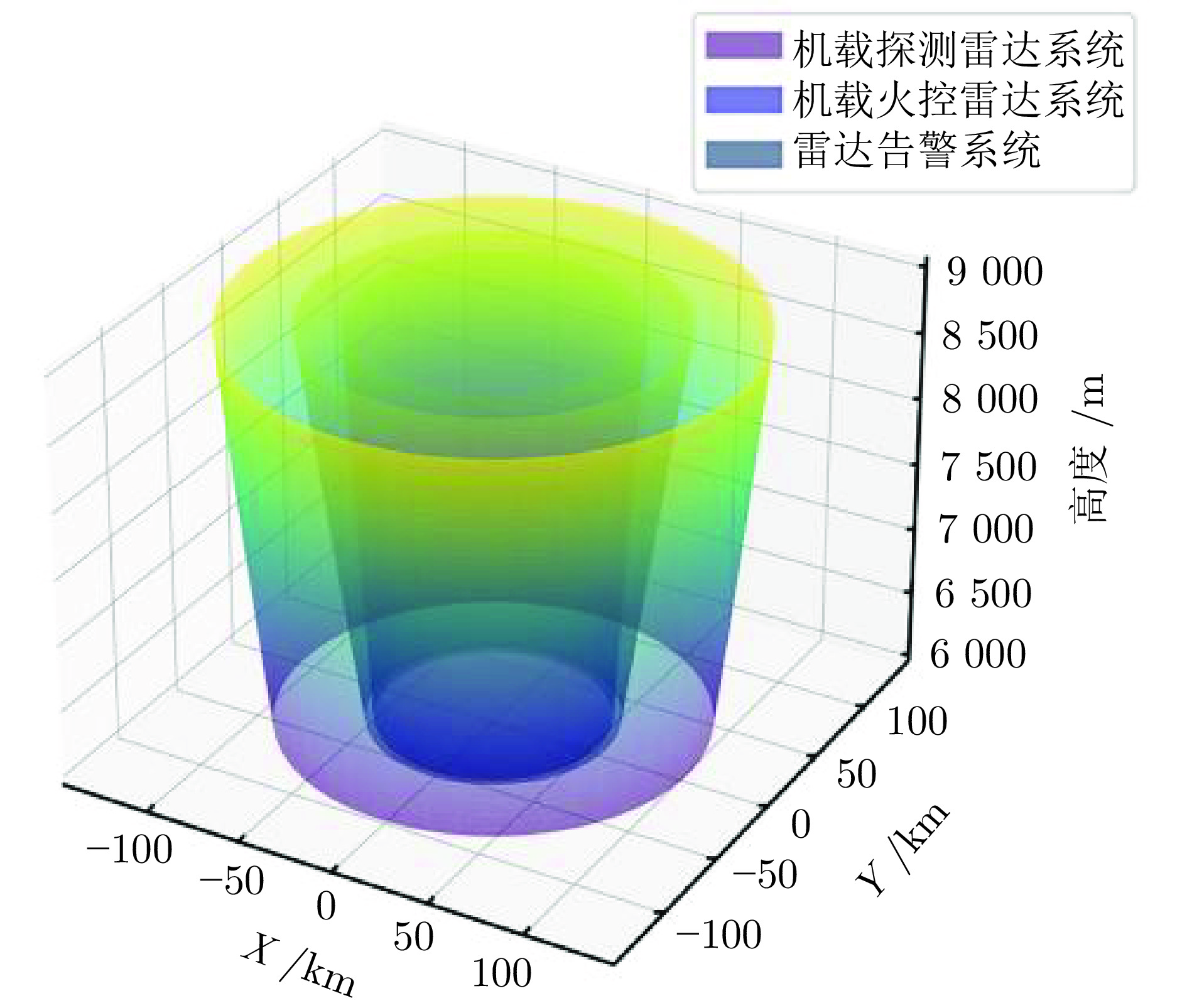
表 1 雷达传感器参数
Table 1 Parameters of radar sensors
参数名称 机载探测雷达
系统机载火控雷达
系统雷达告警
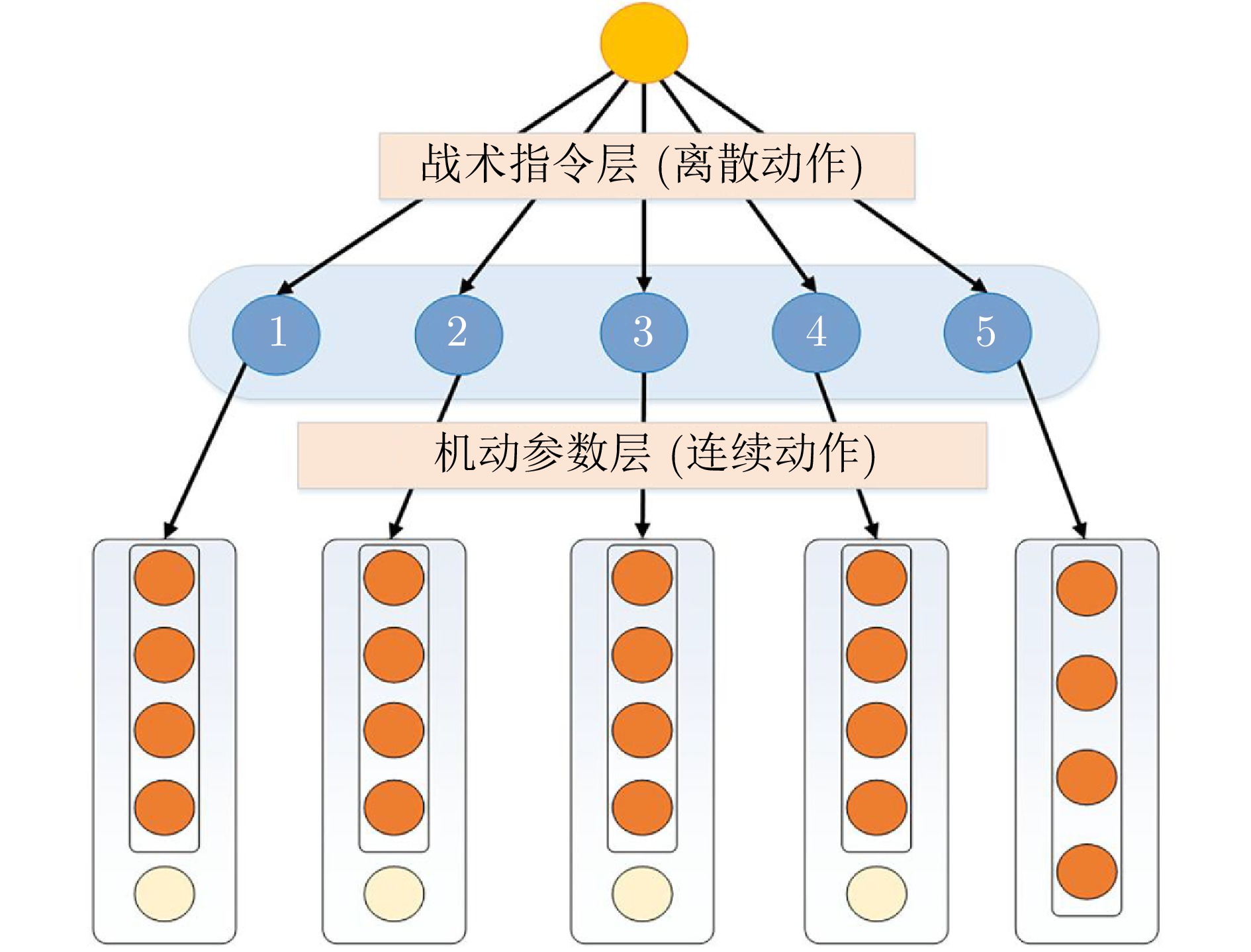
系统飞机发射功率(kw) 30 22 \ 导弹发射功率(kw) \ \ 1 双方雷达反射截面积($ m^2 $) 4 4 \ 发射天线增益(dBi) 42 38 20 接收天线增益(dBi) 42 38 30 信号波长($ m $) 0.037 0.032 0.024 方位角(°) [−120, 120] [−60, 60] [−180, 180] 俯仰角(°) [−60, 60] [−15, 15] [−90, 90] 表 2 战术指令层动作集
Table 2 Tactical command layer action set
序号 战术指令 机动参数 1 搜索 四种基本参数、探测雷达开机参数 2 锁定 四种基本参数、火控雷达开机参数 3 攻击 四种基本参数、发射导弹参数 4 规避 四种基本参数、告警雷达开机参数 5 脱离 四种基本参数 表 3 奖励事件及取值设计
Table 3 Reward event and value design
类型 名称 数值 关键事件奖励 击落 50 平局 −20 被击落 −50 锁定 10 被锁定 −10 发射导弹 −5 状态奖励 危险飞行 $ R_{\rm{df}} $ 威胁 $ R_{\rm{th}} $ 优势 $ R_{\rm{ad}} $ 时间步 $ R_{\rm{ts}} $ 表 4 超视距空战时间线
Table 4 Timeline of BVR
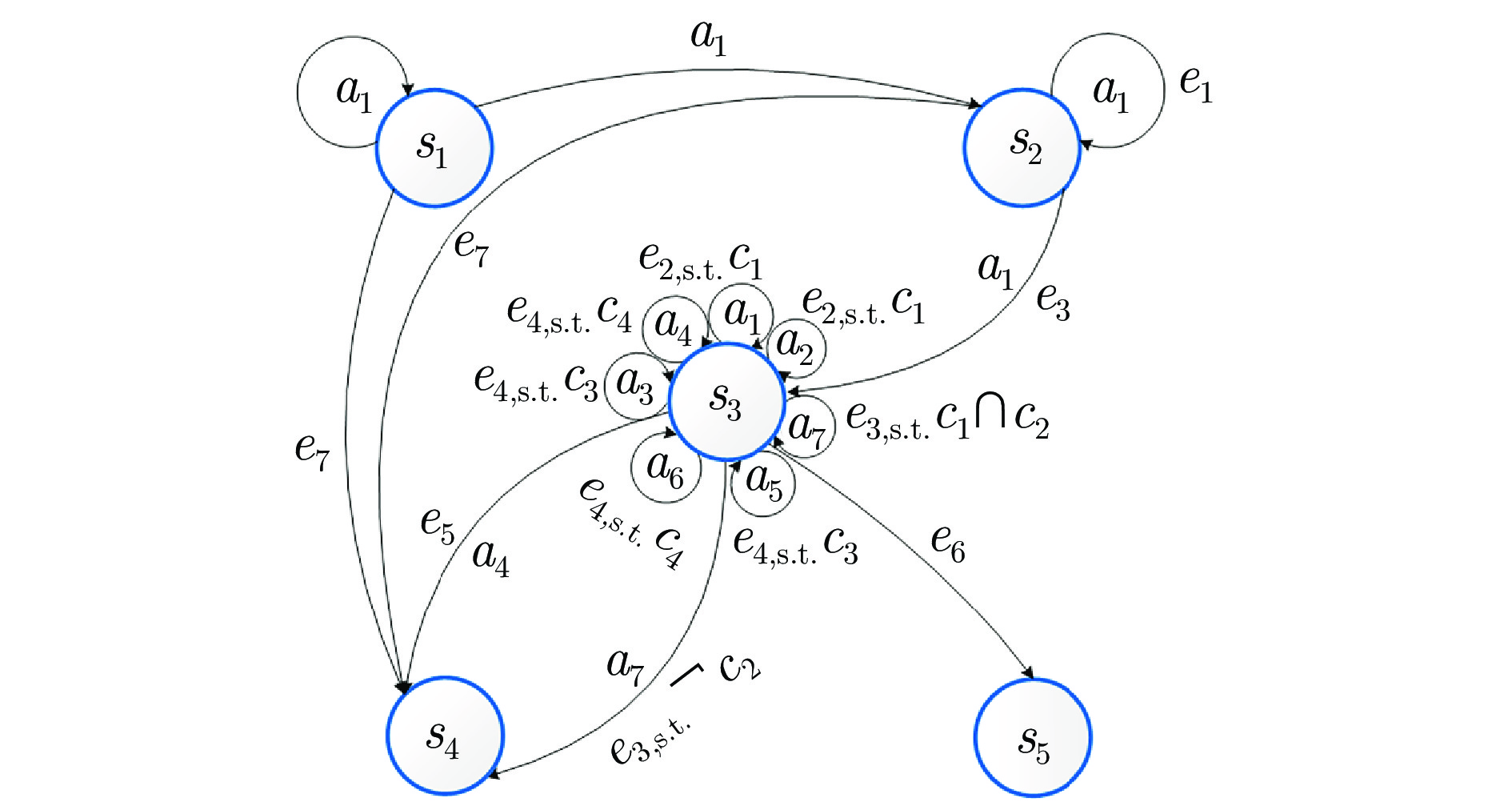
表 5 基于规则的超视距空战决策框架典型态势
Table 5 Typical situation of Rule-based BVR decision-making framework
态势$ S $ 描述 战术分类 $ s_1 $ 在PR外前出 基础状态 $ s_2 $ 在TR$ \sim $PR之间前出 进攻性 $ s_3 $ 在MAR$ \sim $TR之间前出 进攻性+防御性 $ s_4 $ 返航 基础状态 $ s_5 $ 任务失败 基础状态 表 6 基于规则的超视距空战决策框架典型事件
Table 6 Typical events of Rule-based BVR decision-making framework
事件$ E $ 描述 战术分类 $ e_1 $ 目标雷达开机 基础状态 $ e_2 $ 目标进入武器攻击区 进攻性 $ e_3 $ 锁定目标 进攻性 $ e_4 $ 被目标锁定 防御性 $ e_5 $ 击杀目标 基础状态 $ e_6 $ 被目标击杀 基础状态 $ e_7 $ 目标逃逸 基础状态 表 7 基于规则的超视距空战决策框架典型条件
Table 7 Typical conditions of Rule-based BVR decision-making framework
条件$ C $ 描述 战术分类 $ c_1 $ 在MAR$ \sim $TR之间内 进攻性 $ c_2 $ 导弹剩余数量大于0 进攻性 $ c_3 $ 在MOR外被攻击 进攻性 $ c_4 $ 在MAR内被攻击 防御性 表 8 基于规则的超视距空战决策框架基础机动动作
Table 8 Basic maneuvers of Rule-based BVR decision-making framework
动作$ A $ 动作名称 描述 战术分类 $ a_1 $ 匀速前飞 适用于巡航和搜索阶段 基础状态 $ a_2 $ 爬升 提升高度以获得高度优势 基础状态 $ a_3 $ 俯冲 降低高度以获得速度优势 基础状态 $ a_4 $ 置尾机动 180°转弯机动 防御性 $ a_5 $ Skate机动 在MOR外发射后脱离 进攻性 $ a_6 $ Short Skate机动 在MAR外发射后脱离 进攻性 $ a_7 $ 发射 发射导弹 进攻性 表 9 基于规则的超视距空战决策框架规则集
Table 9 Rule set of Rule-based BVR decision-making framework
规则
编号当前
状态S触发
事件E满足
条件C执行
动作A下一
状态S'战术类别 1 $ s_1 $ − − $ a_1 $ $ s_1 $ 基础状态 2 $ s_1 $ − − $ a_1 $ $ s_2 $ 基础状态 3 $ s_1 $ $ e_7 $ − − $ s_4 $ 基础状态 4 $ s_2 $ $ e_7 $ − − $ s_4 $ 基础状态 5 $ s_2 $ $ e_1 $ − $ a_1 $ $ s_2 $ 进攻性 6 $ s_2 $ $ e_3 $ − $ a_1 $ $ s_3 $ 进攻性 7 $ s_3 $ $ e_2 $ $ c_1 $ $ a_1 $ $ s_3 $ 进攻性 8 $ s_3 $ $ e_2 $ $ c_1 $ $ a_2 $ $ s_3 $ 进攻性 9 $ s_3 $ $ e_3 $ $ {c_1} \cap {c_2} $ $ a_7 $ $ s_3 $ 进攻性 10 $ s_3 $ $ e_3 $ $ \neg {c_2} $ $ a_7 $ $ s_4 $ 防御性 11 $ s_3 $ $ e_5 $ − $ a_4 $ $ s_4 $ 基础状态 12 $ s_3 $ $ e_4 $ $ c_3 $ $ a_5 $ $ s_3 $ 防御性+进攻性 13 $ s_3 $ $ e_4 $ $ c_4 $ $ a_6 $ $ s_3 $ 防御性+进攻性 14 $ s_3 $ $ e_4 $ $ c_3 $ $ a_3 $ $ s_3 $ 防御性 15 $ s_3 $ $ e_4 $ $ c_4 $ $ a_4 $ $ s_3 $ 防御性 16 $ s_3 $ $ e_6 $ − − $ s_5 $ 基础状态 表 10 10种空战专家系统设计
Table 10 Ten designs of expert system for air combat
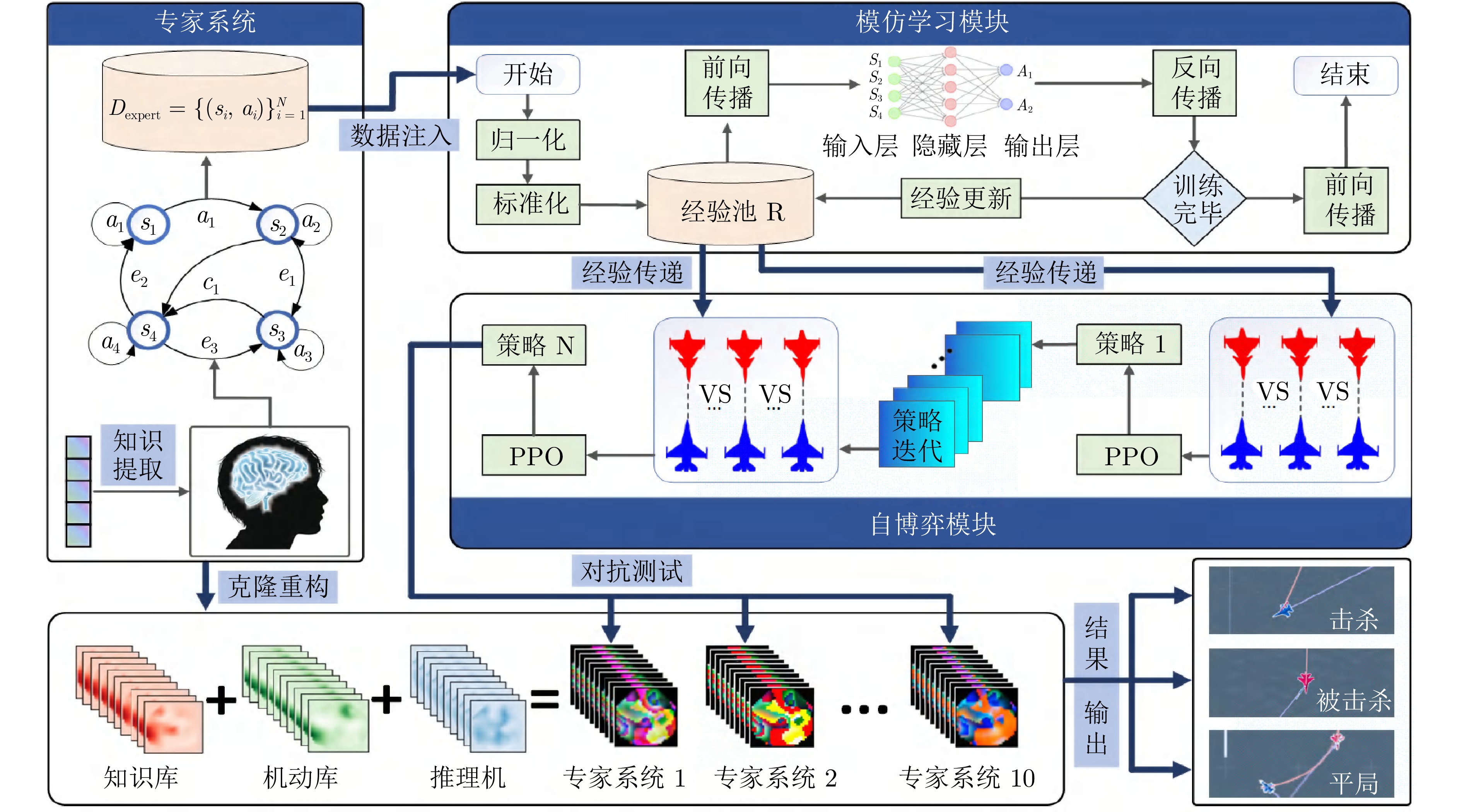
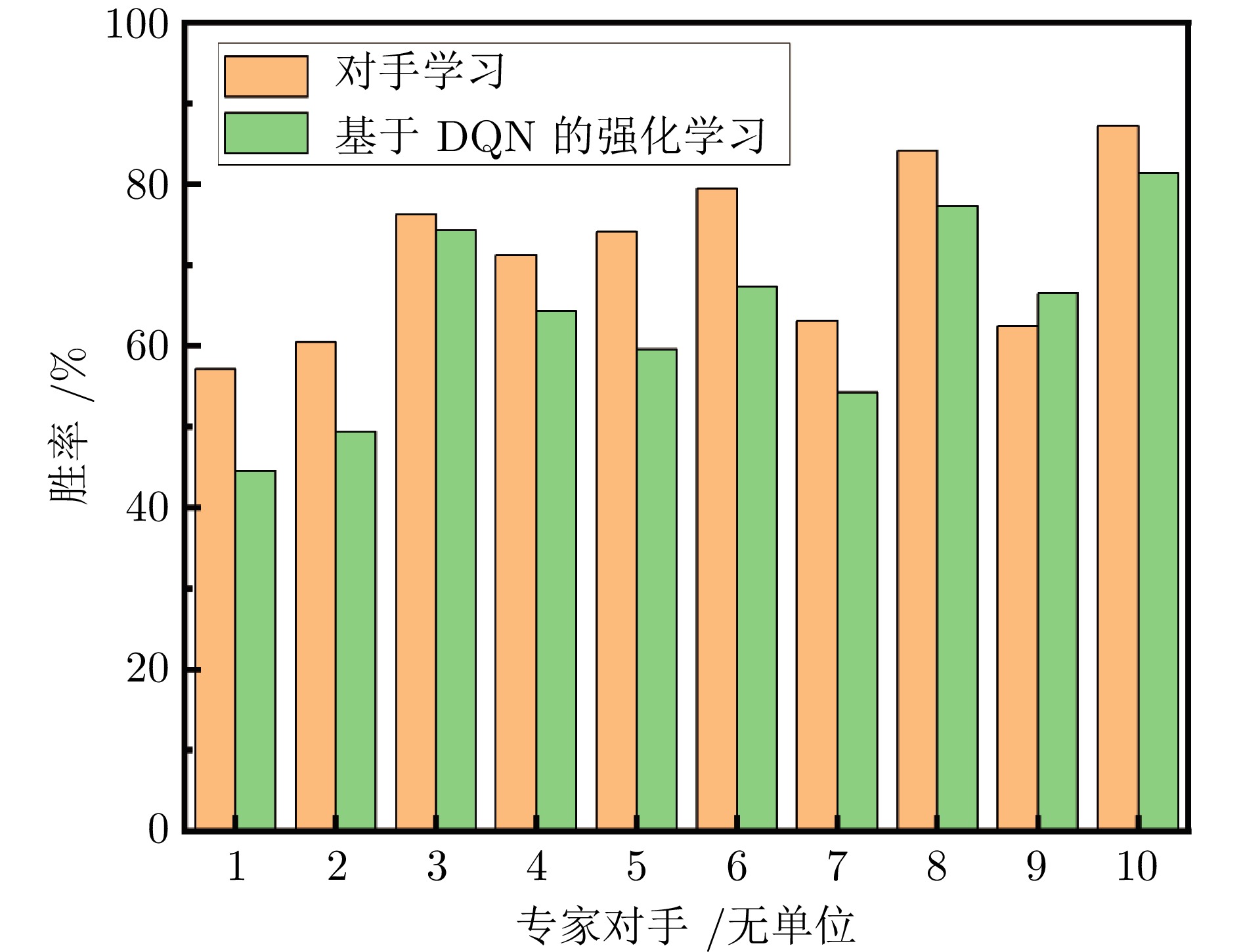
类型 名称 功能特点 偏好攻击型 对手1 首轮双弹打击 对手2 高速接近突袭 对手3 保持高位压制 攻防均衡型 对手4 能量−射程均衡 对手5 雷达扫描−锁定优化 对手6 高度−速度攻防转换 对手7 多弹压制−复合规避 偏好防御型 对手8 TR巡逻规避 对手9 MOR巡逻规避 对手10 持续转冷规避 -
[1] 环球时报. 印巴冲突折射未来战争特征[Online], available: https://www.news.cn/milpro/20250512/904cb51918044b828f16d82da7964ac7/c.html, 2025-09-11.Global Times. The India-Pakistan conflict reflects the characteristics of future warfare[Online], available: https://www.news.cn/milpro/20250512/904cb51918044b828f16d82da7964ac7/c.html, September 11, 2025 [2] 孙智孝, 杨晟琦, 朴海音, 白成超, 葛俊. 未来智能空战发展综述. 航空学报, 2021, 42(08): 35−49Sun Zhi-Xiao, Yang Sheng-Qi, Piao Hai-Yin, Bai Cheng-Chao, Ge Jun. A survey of air combat artificial intelligence. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(08): 35−49 [3] 任好, 马亚杰, 姜斌, 刘成瑞. 基于零和微分博弈的航天器编队通信链路故障容错控制. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(01): 174−185Ren Hao, Ma Ya-Jie, Jiang Bin, Liu Chen-Rui. Research on application of differential game in attack and defense of UAV swarms. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(01): 174−185 [4] Herrala O, Terho T, Oliveira F. Risk-averse decision strategies for influence diagrams using rooted junction trees. Operations Research Letters, DOI: 10.1016/J.ORL.2025.107308 [5] 史桐雨, 王昊, 王酉琨, 吕茂隆. 无人作战飞机超视距空战博弈对抗决策仿真. 现代防御技术, 20251−11Shi Tong-Yu, Wang Hao, Wang You-Kun, Lv Mao-Long. Simulation of Game-Theoretic Decision-Making for Beyond-Visual-Range Combat with UCAVs. Modern Defence Technology, 20251−11 [6] 吕茂隆, 丁晨博, 韩浩然, 段海滨. 基于深度强化学习的无人机自主感知-规划-控制策略. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(05): 1092-1106Lv Mao-Long, Ding Chen-Bo, Han Hao-Ran, Duan Hai-Bin: Autonomous perception-planning-control strategy based on deep reinforcement learning for unmanned aerial vehicles, vol. 51, no. 12, pp. 1092-1106(2025) (in Chinese). doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240639 Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(05): 1092-1106 [7] 施伟, 冯旸赫, 程光权, 黄红蓝, 黄金才, 刘忠, 等. 基于深度强化学习的多机协同空战方法研究. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(07): 1610−1623 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c201059Shi Wei, Feng Yang-He, Cheng Guang-Quan, Huang Hong-Lan, Huang Jin-Cai, Liu Zhong, et al. Survey on multi-agent reinforcement learning for control and decision-making. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(07): 1610−1623 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c201059 [8] 罗彪, 胡天萌, 周育豪, 黄廷文, 阳春华, 桂卫华. 多智能体强化学习控制与决策研究综述. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(03): 510−539Luo Bin, Hu Tian-Meng, Zhou Yu-Hao, Huang Ting-Wen, Yang Chun-Hua, Gui Wei-Hua. Survey on multi-agent reinforcement learning for control and decision-making. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(03): 510−539 [9] 郭万春, 解武杰, 尹晖, 董文瀚. 基于改进双延迟深度确定性策略梯度法的无人机反追击机动决策. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 22(04): 15−21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2021.04.003Guo Wan-Chun, Xie Wu-Jie, Yin Hui, Dong Wen-Han. Research on UAV anti-pursing maneuvering decision based on improved twin delayed deep deterministic policy gradient method. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 22(04): 15−21 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3516.2021.04.003 [10] 孙世彬, 王庆领. 基于改进多智能体强化学习的大规模无人机集群博弈对抗. 海军航空大学学报, 2025, 40(04): 528−538Sun Shi-Bin, Wang Qing-Ling. Large scale UAV cluster game confrontation based on improved multi-agent reinforcement learning. Journal of Naval Aviation University, 2025, 40(04): 528−538 [11] 欧洋, 徐扬, 张金鹏, 罗德林. 无人机空战的竞争与双重深度强化学习机动对抗决策. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 61(06): 975−985 doi: 10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.202204056Ou Yang, Xu Yang, Zhang Jin-Peng, Luo De-Lin. UAV air combat dueling and double deep reinforcement learning maneuver adversarial decision making. Journal of Xiamen University (Natural Science), 2022, 61(06): 975−985 doi: 10.6043/j.issn.0438-0479.202204056 [12] 吴宜珈, 赖俊, 陈希亮, 曹雷, 徐鹏. 强化学习算法在超视距空战辅助决策上的应用研究. 航空兵器, 2021, 28(02): 55−61Wu Yi-Jia, Lai Jun, Chen Xi-Liang, Cao Lei, Xu Peng. Research on the application of reinforcement learning algorithm in decision support of beyond-visual-range air combat. Aero Weaponry, 2021, 28(02): 55−61 [13] 孔维仁, 周德云, 赵艺阳, 杨婉莎. 基于深度强化学习与自学习的多无人机近距空战机动策略生成算法. 控制理论与应用, 2022, 39(02): 352−362Kong Wei-ren, Zhou De-yun, Zhao Yi-yang, Yang Wan-sha. Maneuvering strategy generation algorithm for multi-UAV in close-range air combat based on deep reinforcement learning and self-play. Control Theory & Applications, 2022, 39(02): 352−362 [14] 王臆淞, 张鹏翼, 顾启佳, 赵铭慧, 张雪波. ASM2:面向海空联合场景的多对 手多智能体博弈算法. 控制理论与应用, 2025, 42(07): 1275−1284 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2024.30220Wang Yi-Song, Zhang Peng-Yi, Gu Qi-Jia, Zhao Ming-Hui, Zhang Xue-Bo. ASM2: multi-agent multi-opponent game algorithm for joint sea-air scenarios. Control Theory & Applications, 2025, 42(07): 1275−1284 doi: 10.7641/CTA.2024.30220 [15] Piao H Y, Sun Z X, Meng G L, Chen H C, Qu B H, Lang K J. Beyond-visual-range air combat tactics auto-generation by reinforcement learning. In: 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Glasgow, UK: IEEE, 2020. 1-8 [16] 单圣哲, 张伟伟. 基于自博弈深度强化学习的空战智能决策方法. 航空学报, 2024, 45(04): 200−212Shan Sheng-Zhe, Zhang Wei-Wei. Air combat intelligent decision-making method based on self-play and deep reinforcement learning. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2024, 45(04): 200−212 [17] 周攀, 黄江涛, 章胜, 刘刚, 舒博文, 唐骥罡. 基于深度强化学习的智能空战决策与仿真. 航空学报, 2023, 44(04): 99−112Zhou Pan, Huang Jiang-Tao, Zhang Sheng, Liu Gang, Shu Bo-Wen, Tang Ji-Gang. Intelligent air combat decision making and simulation based on deep reinforcement learning. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2023, 44(04): 99−112 [18] 李银通, 韩统, 孙楚, 魏政磊. 基于逆强化学习的空战态势评估函数优化方法. 火力与指挥控制, 2019, 44(08): 101−106Li Yin-Tong, Han Tong, Sun Chu, Wei Zheng-Lei. An optimization method of air combat situation assessment function based on inverse reinforcement learning. Fire Control & Command Control, 2019, 44(08): 101−106 [19] Shi Y Y, Li J, Lv M L, Wang N, Zhang B Y. Distributed consensus control for 6-DOF fixed-wing multi-UAVs in asynchronously switching topologies, IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3520141 [20] 梁玉峰, 赵景朝, 刘旺魁, 王雷, 王世鹏, 阮仕龙. 基于顶层滚动优化和底层跟踪的空战导引方法. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(09): 2866−2872 doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.09.26Liang Yu-Feng, Zhao Jing-Chao, Liu Wang-Kui, Wang Lei, Wang Shi-Peng, Ruan Shi-Long. Air combat guidance method based on top rolling optimization and bottom tracking. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(09): 2866−2872 doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.09.26 [21] Wang W F, Ru L, Lv M L, Hou Y Q, Yin H. Exploring hierarchical hybrid autonomous maneuvering decision-making architecture in Beyond Visual Range air combat. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2025.3568377 [22] Wang W F, Ru L, Lv M L, Mo L. Dynamic and adaptive learning for autonomous decision-making in Beyond Visual Range air combat. Aerospace Science and Technology, DOI: 10.1016/J.AST.2025.110327 [23] Xu Y H, Wei Y R, Jiang K Y, Chen L, Wang D, Deng H B. Action decoupled SAC reinforcement learning with discrete-continuous hybrid action spaces. Neurocomputing, DOI: 10.1016/j.neucom.2023.03.054 [24] Han H R, Cheng J, Lv M L, Duan H B. Augmenting the robustness of tactical maneuver decision-making in unmanned aerial combat vehicles during dogfights via prioritized population play with diversified partners. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3578294 [25] Jiang C R, Wang H, Ai J L. Autonomous maneuver decision-making algorithm for UCAV based on generative adversarial imitation learning. Aerospace Science and Technology, DOI: 10.1016/j.ast.2025.110313 [26] Hou Y Q, Liang X L, Zhang J Q, Lv M L, Yang A W. Hierarchical decision-making framework for multiple UCAVs autonomous confrontation. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, DOI: 10.1109/TVT.2023.3285223 [27] Chen C, Song T, Mo L, Lv M L, Lin D F. Autonomous dogfight decision-making for air combat based on reinforcement learning with automatic opponent sampling. Aerospace, DOI: 10.3390/aerospace12030265 [28] 陈灿, 莫雳, 郑多, 程子恒, 林德福. 非对称机动能力多无人机智能协同攻防对抗. 航空学报, 2020, 41(12): 342−354Chen Can, Mo Li, Zheng Duo, Cheng Zi-Heng, Lin De-Fu. Cooperative attack-defense game of multiple UAVs with asymmetric maneuverability. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(12): 342−354 [29] Chen C, Song T, Mo L, Lv M L, Yu Y N. Scalable cooperative decision-making in multi-UAV confrontations: an attention-based multi-agent actor-critic approach. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, DOI: 10.1109/TAES.2025.3571405 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 135
- HTML全文浏览量: 116
- 被引次数: 0



 下载:
下载: