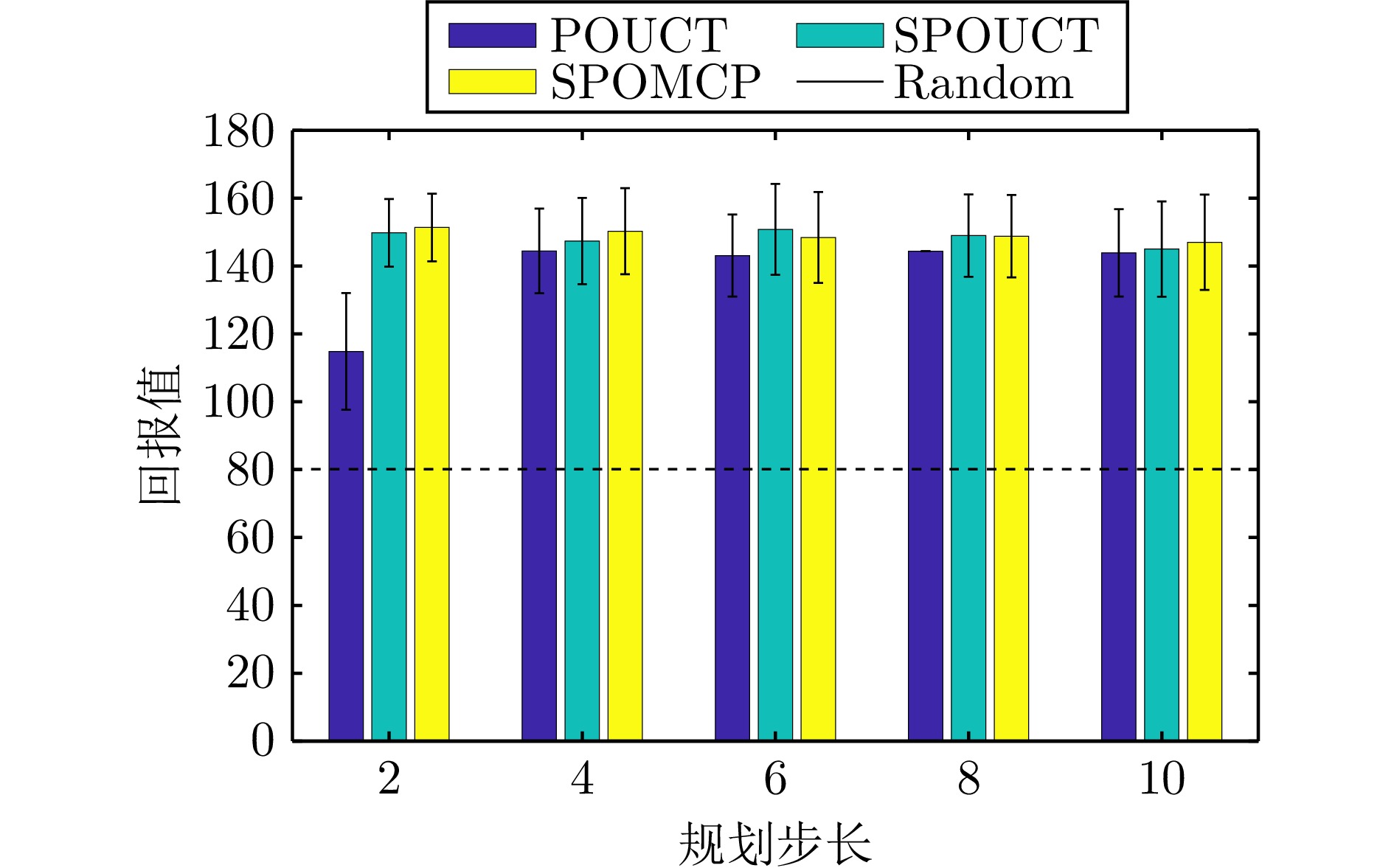
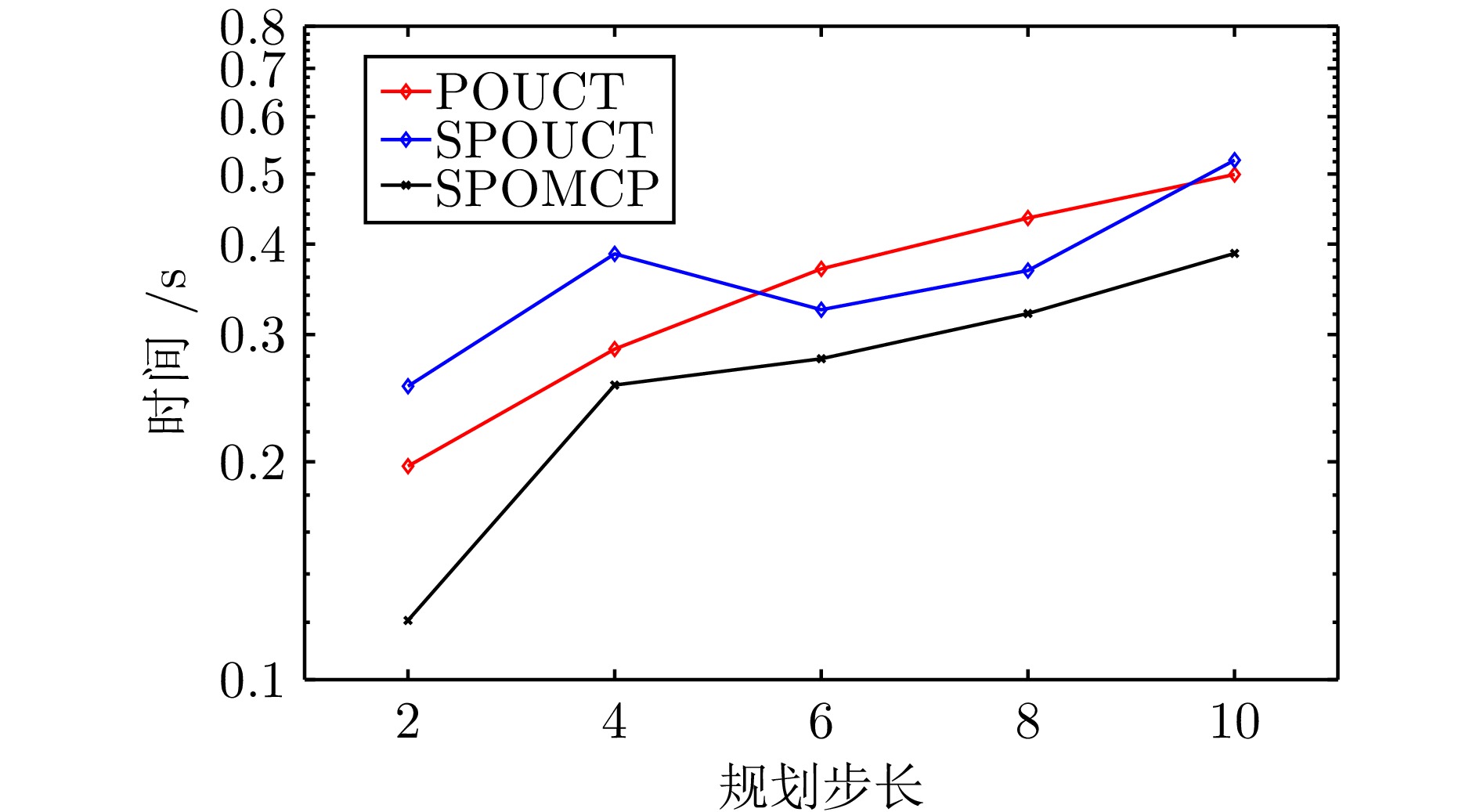
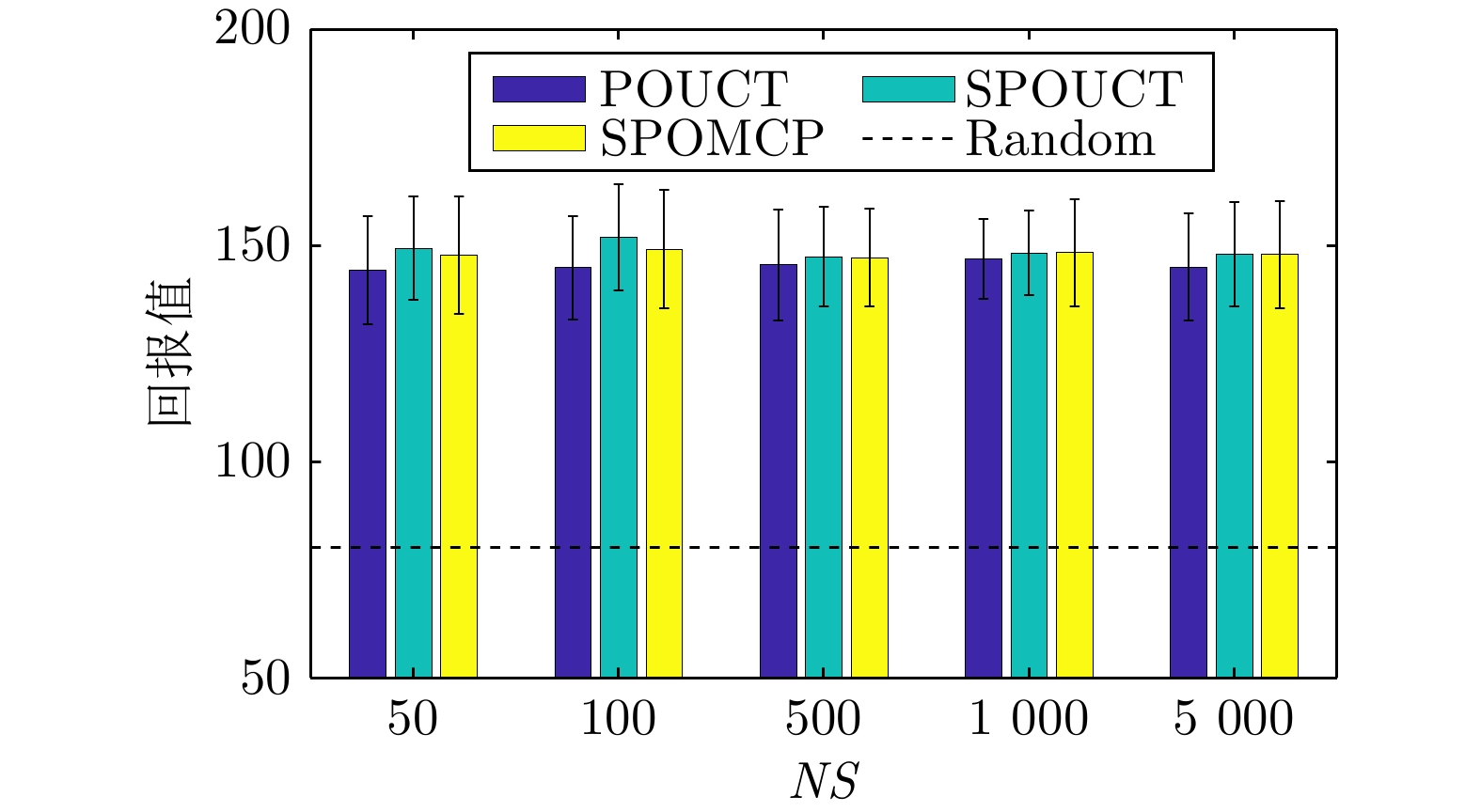
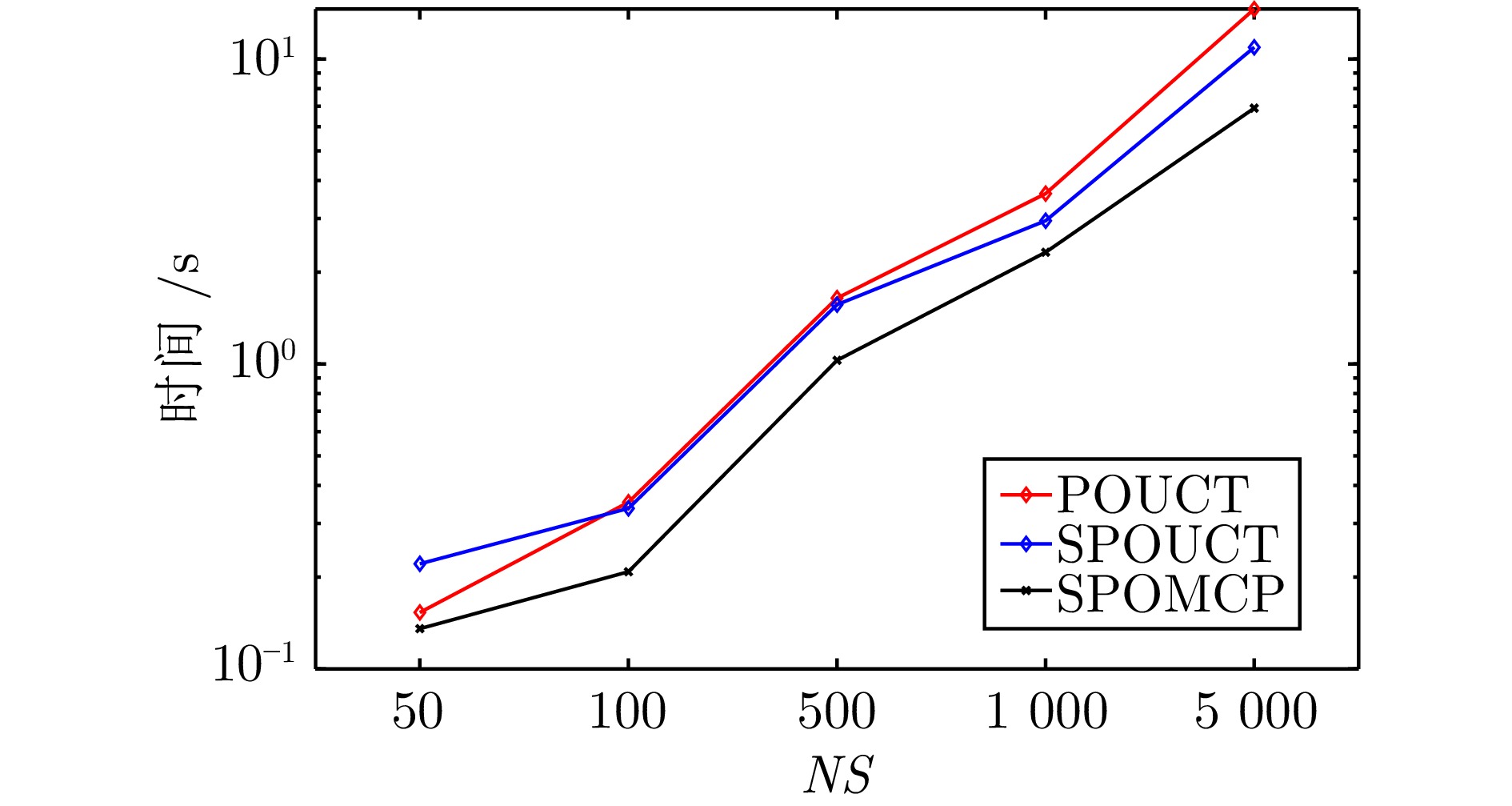
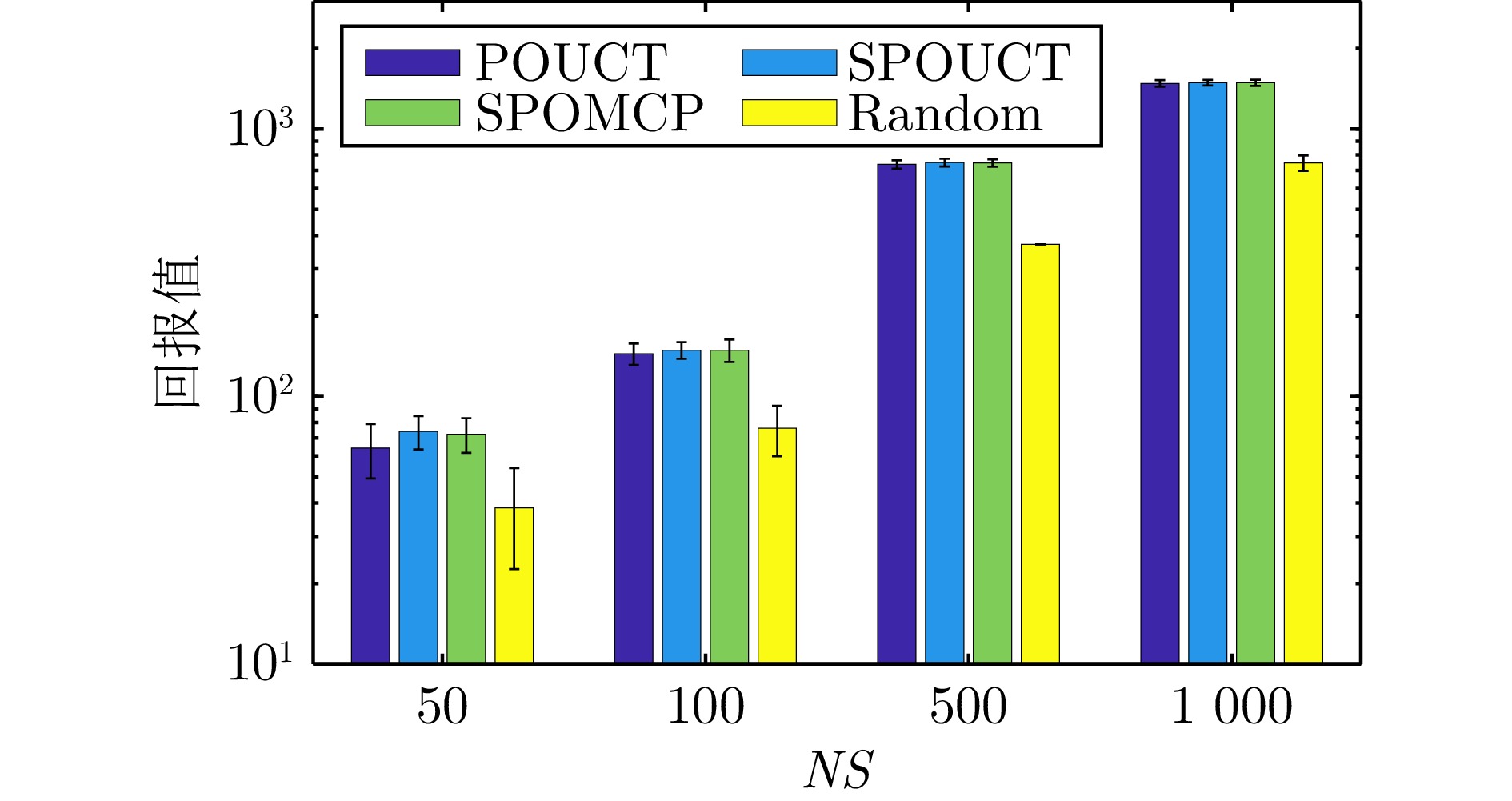
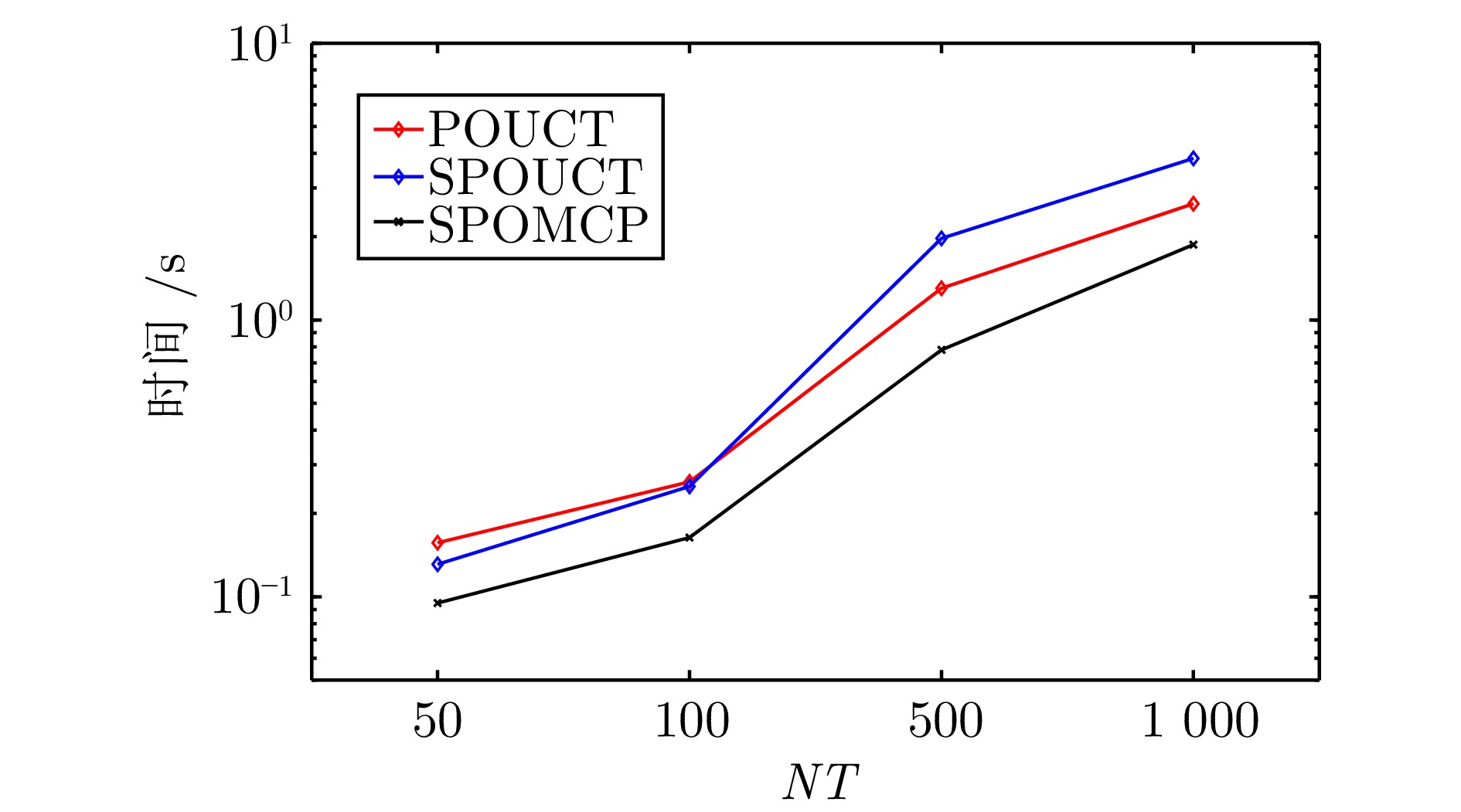
|
[1]
|
杨松, 王涛, 李小波, 何华, 孙吉东. 异构无人集群杀伤网任务路径生成建模与评估. 系统工程与电子技术, 2025, 47(10): 3278−3287 doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.10.15Yang Song, Wang Tao, Li Xiao-Bo, He Hua, Sun Ji-Dong. Modelingeneous unmanned swarm kill-web. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(10): 3278−3287 doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.10.15
|
|
[2]
|
孙鹏耀. 面向体系破击行动的无人机集群任务规划研究[Ph.D. dissertation]. 南京理工大学, 中国, 2024.Sun Yao-peng. Mission planning of UAV swarm oriented to combat system paralysis action [Ph.D. dissertation]. Nanjing University of Science and Technology, China, 2024.
|
|
[3]
|
袁媛, 孙柏, 刘赶超. 景象匹配无人机视觉定位. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(2): 287−311 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230778Yuan Yuan, Sun Bo, Liu Gan-Chao. Drone-based scene matching visual geo-localization. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(2): 287−311 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c230778
|
|
[4]
|
罗彪, 胡天萌, 周育豪. 多智能体强化学习控制与决策研究综述. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(3): 510−539 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240392Luo Biao, Hu Tian-Meng, Zhou Yu-Hao. Survey on multi-agent reinforcement learning for control and decision-making. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(3): 510−539 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240392
|
|
[5]
|
王冰洁, 徐磊, 林宗利, 施阳, 杨涛. 基于自适应动态规划的量化通信下协同最优输出调节. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(4): 813−823 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240494Wang Bing-jie, Xu Lei, Lin Zong-li, Shi Yang, Yang Tao. Cooperative optimal output regulation under quantized communication based on adaptive dynamic programming. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(4): 813−823 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240494
|
|
[6]
|
Zhou X, Chen Z Y, Huang M G, Zhu Z, Wang T. A collaborative evolution algorithm for unmanned equipment project distributed scheduling optimization with grouping and due window constraints. Expert Systems with Applications, 2026, 296(D): 129143
|
|
[7]
|
Ivan M, Jesus C, Luis M. Multi-UAV cooperation. Encyclopedia of Aerospace Engineering, DOI: 10.1002/9780470686652.eae1130
|
|
[8]
|
Zhao Y, Wang X, Wang C, Cong Y, Shen L. Systemic design of distributed multi-UAV cooperative decision-making for multi-target tracking. Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 2019, 33(1-2): 1−27 doi: 10.1007/s10458-018-9397-9
|
|
[9]
|
Messias J. Decision-making under uncertainty for real robot teams [Ph.D. dissertation]. Institute for Systems and Robotics, Instituto Superior Técnico, Portugal, 2014.
|
|
[10]
|
Chen S, Wu F, Shen L, Chen J, Ramchurn S. Multi-agent patrolling under uncertainty and threats. PloS one, 2015, 10(6): Article No. e0130154 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130154
|
|
[11]
|
Nguyen, T T, Ngoc D N, Saeid N. Deep reinforcement learning for multiagent systems: A review of challenges, solutions, and applications. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(9): 3826−3839 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.2977374
|
|
[12]
|
Xiaoning J, Hongxu H, Nier W. Low-resource machine translation based on asynchronous dynamic programming. In: Proceedings of the 20th Chinese National Conference on Computational Linguistics. Virtual, Online: EI, 2021. 886-894
|
|
[13]
|
Zhou X, Ling G D, Yu J Y, Zhou T, Wang R. Balanced multi-objective evolution algorithm for unmanned systems project scheduling with preventive maintenance and order grouping constraints. Expert Systems with Applications, 2026, 299(A): 130006
|
|
[14]
|
Ming F, Gong W, Wang L, Jin Y. Constrained multi-objective optimization with deep reinforcement learning assisted operator selection. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(4): 919−931 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123687
|
|
[15]
|
Ming F, Gong W, Wang L. Even search in a promising region for constrained multi-objective optimization. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(2): 474−486 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123792
|
|
[16]
|
Silver D, Veness J. Monte-carlo planning in large POMDPs. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, CA: 2010.
|
|
[17]
|
Amato C, Oliehoek F A. Scalable planning and learning for multiagent POMDPs. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Austin, Texas, USA: 2015.
|
|
[18]
|
Pfrommer J. Graphical partially observable Monte-Carlo planning. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: 2016.
|
|
[19]
|
Fischer J, Tas Ö S. Information particle filter Tree: An online algorithm for POMDPs with belief-based rewards on continuous domains. In: Proceedings of International Conference on Machine Learning. US: proceedings.mlr.press, 2020. 3177-3187
|
|
[20]
|
满景涛, 曾志刚, 盛银, 来金钢. 基于ODE-PDE的大规模多智能体系统有限时间编队. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(3): 631−642 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240426Man Jing-tao, Zeng Zhi-gang, Sheng Yin, Lai Jin-gang. Finite-time formation of large-scale multi-agent systems based on an ODE-PDE approach. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(3): 631−642 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c240426
|
|
[21]
|
Guo C, Liang Z. Predictive inspection and maintenance optimization for partially observable semi-Markov deteriorating systems. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22(1): 10893−10904
|
|
[22]
|
Wang Wei-zheng, Mao Le, Wang Rui-qi, Min Byung-Cheol. Multi-robot cooperative socially-aware navigation using multi-agent reinforcement learning. In: Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Nishi-ku, Yokohama, Japan: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc, 2024: 12353-12360
|
|
[23]
|
Wang T, Zhu Z, Zhou X, Jing T, Chen W. A function-based behavioral modeling method for air combat simulation. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 35(4): 945−954 doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2024.000068
|
|
[24]
|
陈人龙, 陈嘉礼, 李善琦, 谭营. 多智能体强化学习方法综述. 信息对抗技术, 2024, 3(1): 18−32Chen Ren-Long, Chen Jia-Li, Li Shan-Qi, Tan Ying. A survey of multi-agent reinforcement learning methods. Information Counter measure Technology, 2024, 3(1): 18−32
|
|
[25]
|
He W, Xu W, Ge X, Han Q, Du W, Qian F. Secure control of multiagent systems against malicious attacks: A brief survey. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 18(6): 3595−3608
|
|
[26]
|
Zhou X, Jing T, Wang T, Huang Z J, Wu D. A human-supported robot swarm information gathering task planning method. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 20231−8
|
|
[27]
|
Lev-Yehudi I, Barenboim M, Indelman V. Simplifying complex observation models in continuous POMDP planning with probabilistic guarantees and practice. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, BC, Canada: Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence, 2024.
|
|
[28]
|
Zhang M, Revie M. Continuous-observation partially observable semi-Markov decision processes for machine maintenance. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2016, 66(1): 202−218
|
|
[29]
|
Yu H. Approximate Solution Methods for Partially Observable Markov and Semi-Markov Decision Processes[Ph.D. dissertation]. Massachusetts Institute of Technology, US, 2006.
|
|
[30]
|
Xing Y, Zhang G, Li J. Adaptive fuzzy quantized control for a cooperative USV-UAV system based on asynchronous separate guidance. Journal of Marine Science and Engineering, 2023, 11(12): Article No. 2331 doi: 10.3390/jmse11122331
|
|
[31]
|
Seiler K M, Kong F H, Fitch R. Multi-horizon multi-agent planning using decentralised Monte Carlo Tree Search. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2024, 9(9): 7715−7722 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3426273
|
|
[32]
|
Skrynnik A, Andreychuk A, Yakovlev K, Panov A. Decentralized Monte Carlo tree search for partially observable multi-agent pathfinding. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Vancouver, BC, Canada: Association for the Advancement of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 38(16): 17531-17540
|
|
[33]
|
李晓辉, 苏家楠, 吕思婷, 张鹏. 基于SMDP模型的车路协同任务智能卸载算法. 北京邮电大学学报, 2023, 46(2): 15−21 doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2022-066Li Xiao-Hui, Su Jia-Nan, Lyu Si-Ting, Zhang Peng. Intelligent offloading algorithm for road collaborative tasks based on SMDP model. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2023, 46(2): 15−21 doi: 10.13190/j.jbupt.2022-066
|




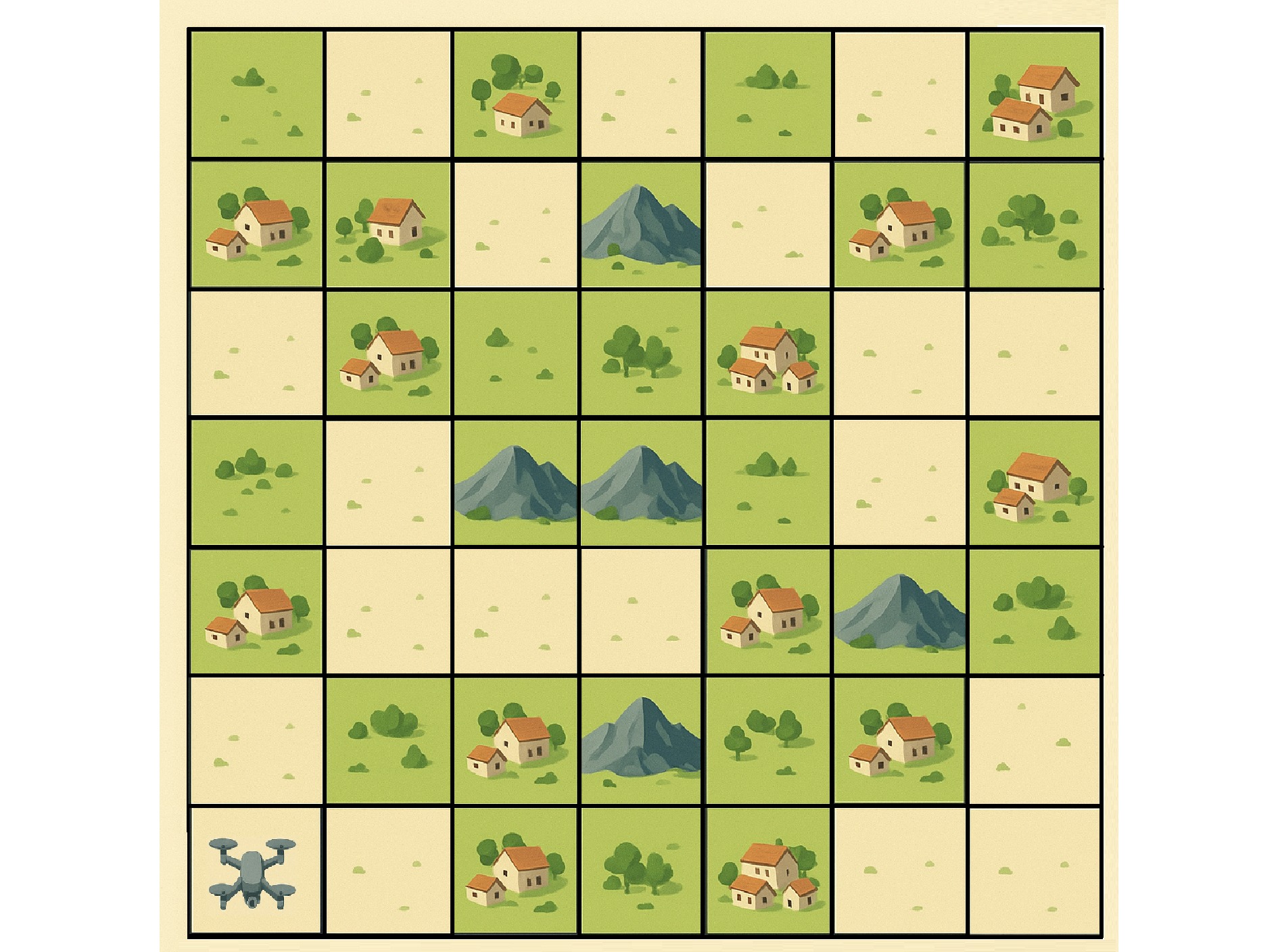
 下载:
下载: