Collaborative Optimization of Multiple Operating Parameters for Process Industries Based on Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning
-
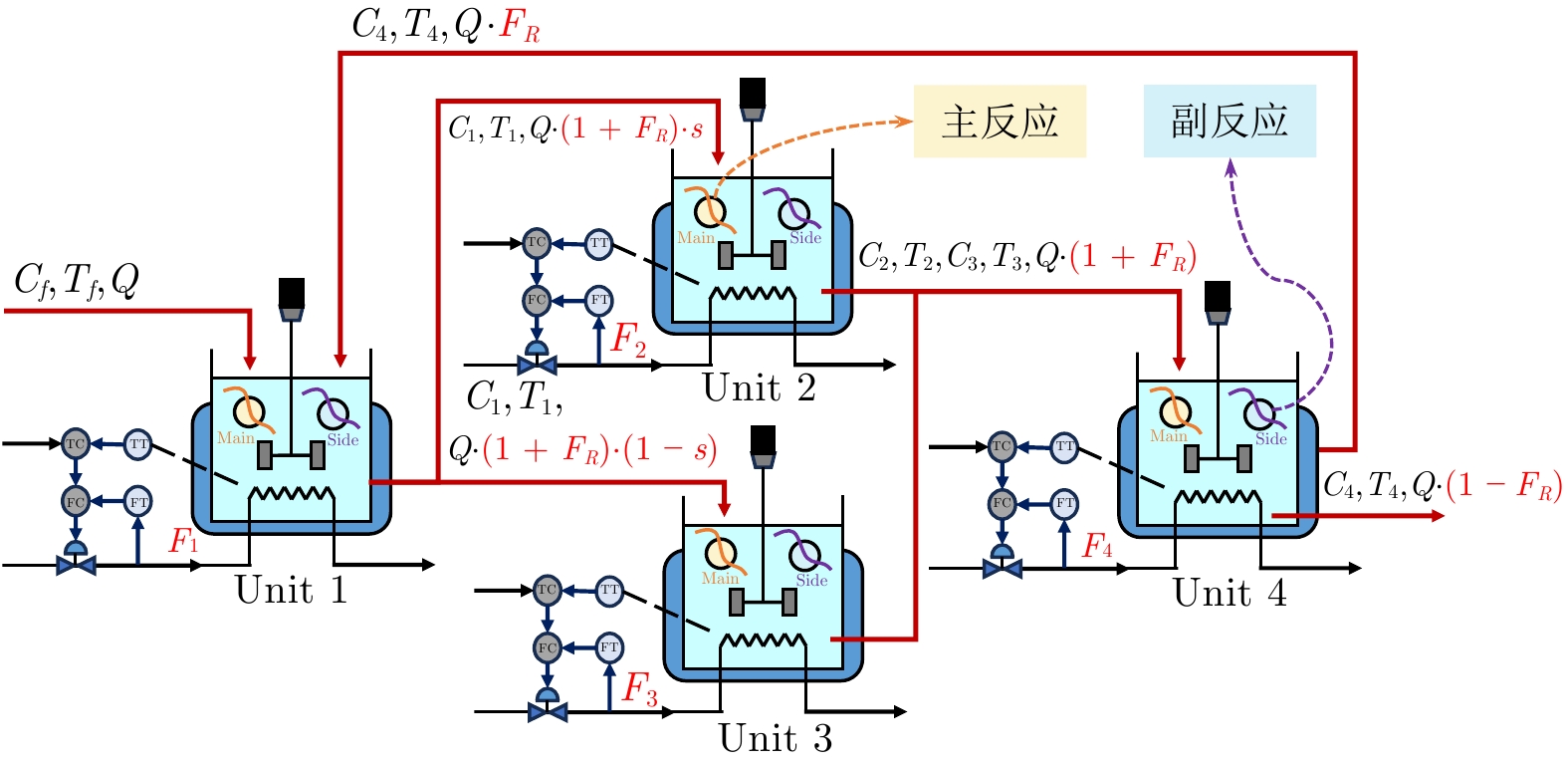
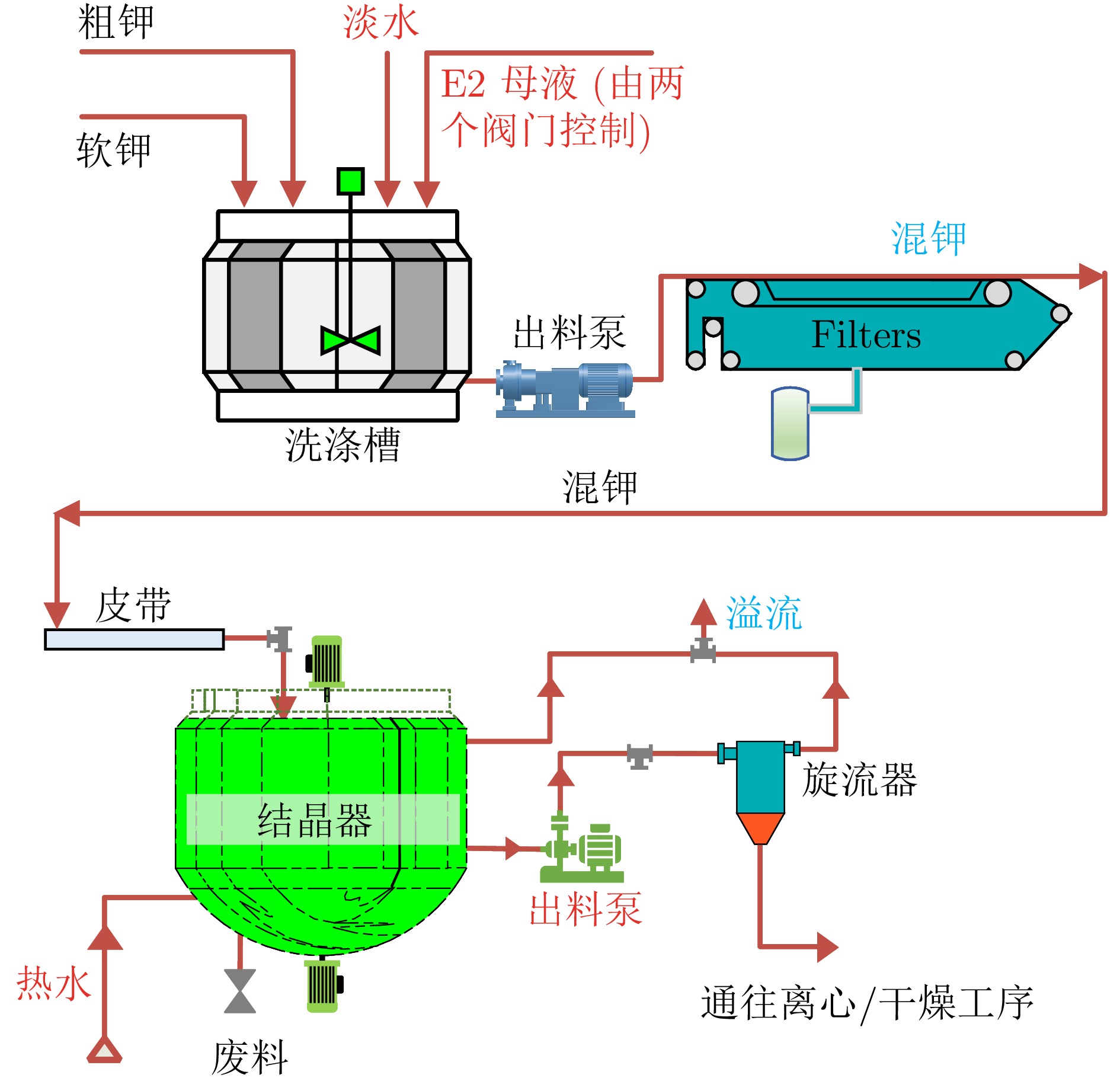
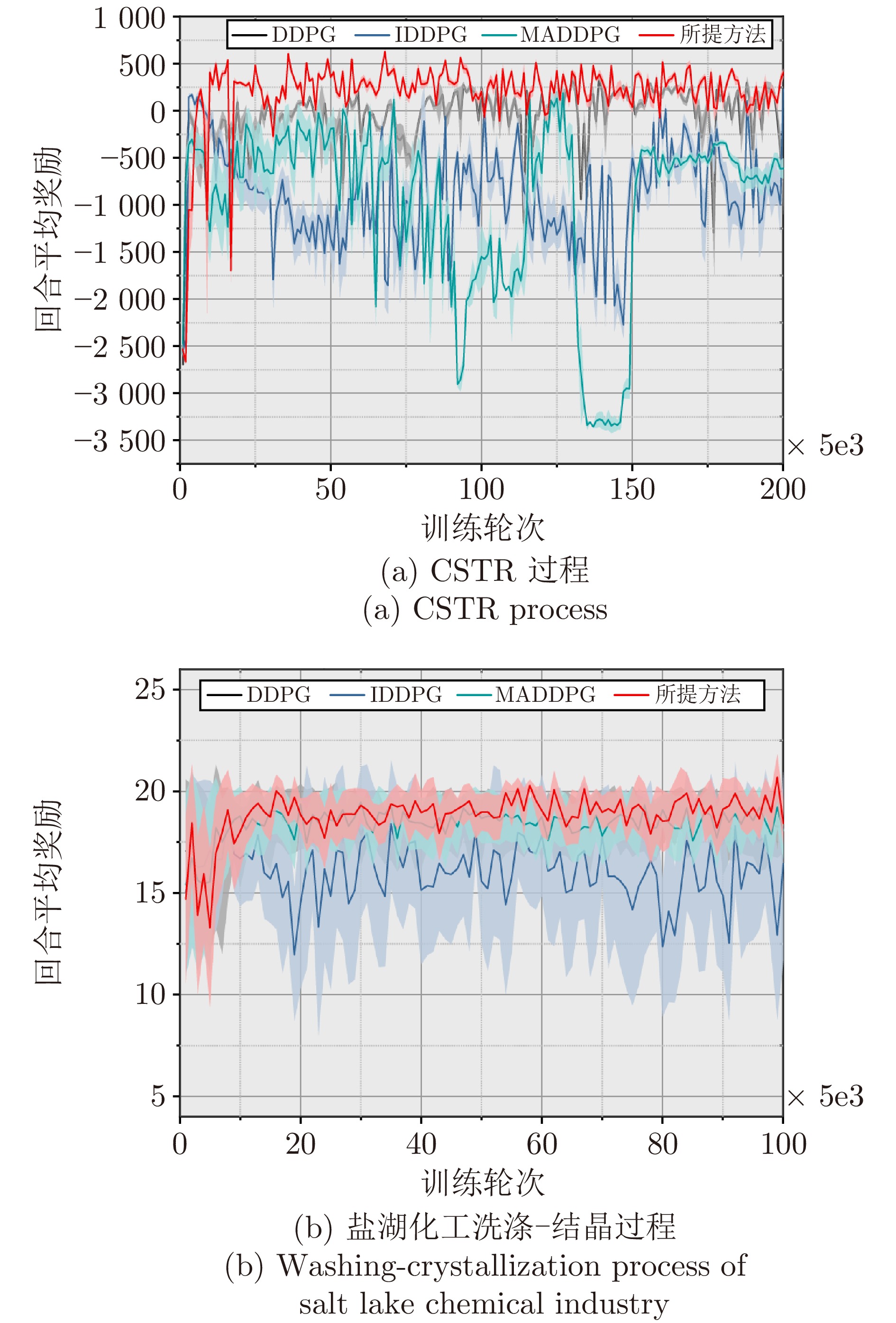
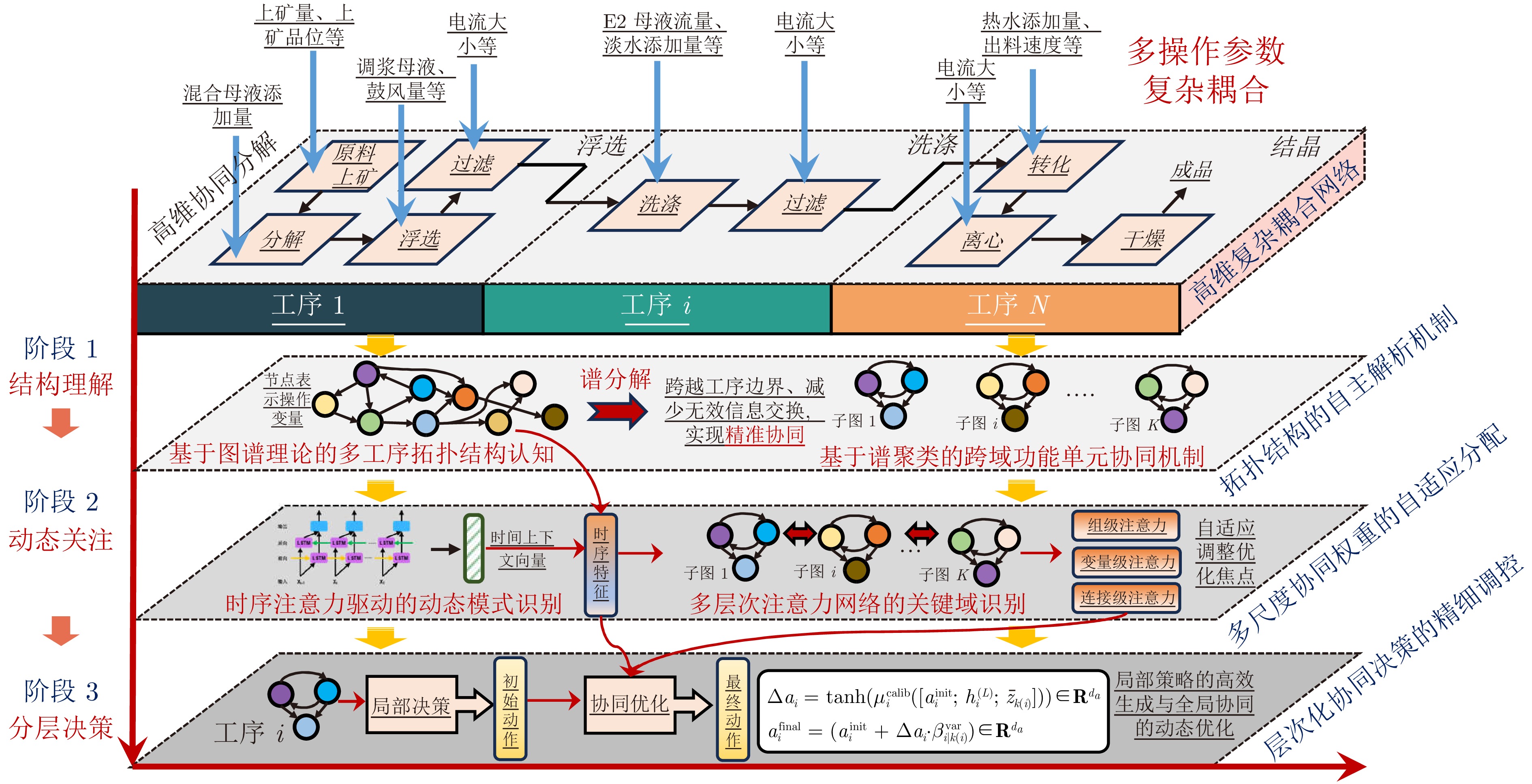
摘要: 流程工业普遍存在多操作参数强耦合、工艺拓扑复杂及多工序协同困难等问题, 传统局部优化方法难以实现全局最优运行. 针对上述挑战, 提出一种基于图谱理论的流程拓扑结构感知的多智能体强化学习协同优化方法, 以实现复杂拓扑流程工业的多操作参数协同优化. 首先, 构建基于拉普拉斯谱分析的拓扑结构解析框架, 刻画多操作参数间的耦合关系, 为智能体任务分配与协同决策提供支撑; 随后, 设计融合长短期记忆网络与多头注意机制的时序感知模块, 提取历史状态轨迹中的关键时间依赖特征; 进一步, 引入多层次空间注意力机制, 在组织层、变量层及连续控制域实现优化关注度的动态自适应调节; 在此基础上, 构建局部−全局协同的分层强化学习决策架构, 实现多智能体协调控制与策略优化. 基于连续搅拌釜反应器系统及盐湖化工典型流程工业数据开展仿真实验, 验证了所提方法的有效性. 实验结果表明, 该方法较传统方法性能提升41.2%, 在收敛速度与策略稳定性方面表现更优, 为流程工业多操作参数协同优化提供新的技术路径.Abstract: Process industries are often confronted with strong multi-operational parameter couplings, intricate process topologies, and difficulties in multi-stage coordination, which render conventional localized optimization methods inadequate for achieving global optimality. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a graph spectral theory-based process topology-aware multi-agent reinforcement learning collaborative optimization method for multiple operating parameter collaborative optimization in complex topological process industries. Specifically, a topology analysis framework based on Laplacian spectral analysis is developed to characterize structural coupling relationships among multiple operating parameters, thereby supporting agent task allocation and coordinated decision-making. Subsequently, a temporal perception module integrating long short-term memory networks with a multi-head attention mechanism is designed to extract key temporal dependencies from historical state trajectories. Furthermore, a hierarchical spatial attention mechanism is introduced to enable dynamic and adaptive regulation of optimization attention across organizational, variable, and continuous control domains. On this basis, a hierarchical reinforcement learning architecture is constructed to coordinate local and global policy optimization, facilitating cooperative control and strategy optimization among multiple agents. Simulation experiments using industrial data from a continuous stirred tank reactor system and a representative salt-lake chemical process validate the effectiveness of the proposed method. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves up to a 41.2% performance improvement over conventional approaches, exhibiting superior convergence behavior and policy stability, and providing a viable technical pathway for multiple operating parameter collaborative optimization in process industries.
-
表 1 超参数配置
Table 1 Hyperparameter configuration
组件 配置 actor网络 两层隐藏层(400, 300单元), ReLU激活 critic网络 两层隐藏层(400, 300单元), ReLU激活 图网络 隐藏维度: 64, GCN层数: 2, 循环维度: 64 优化器 Adam, 学习率: $ 3 \times 10^{-4} $ 训练配置 1 000 000 步, 回放缓冲:1 000 000 条转移折扣因子$ \gamma $ 0.99 软更新系数$ \tau $ 0.005 批处理大小 256 多头注意力头数$ M $ 8 历史窗口长度$ H $ CSTR: 24, 盐湖: 16 评估设置 10次随机种子, 报告均值和标准差 表 2 算法性能对比结果
Table 2 Algorithm performance comparison results
方法 CSTR过程 盐湖化工过程 DDPG 358.8030 ±30.2031 18.5837 ±1.3508 IDDPG 233.8783 ±29.5558 17.1829 ±2.4319 MADDPG 206.1738 ±69.6413 18.8161 ±1.1507 所提方法 506.5871 ±25.8564 19.2423 ±1.0250 -
[1] 阳春华, 孙备, 李勇刚, 黄科科, 桂卫华. 复杂生产流程协同优化与智能控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 528−539 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220737Yang Chun-Hua, Sun Bei, Li Yong-Gang, Huang Ke-Ke, Gui Wei-Hua. Cooperative optimization and intelligent control of complex production processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 528−539 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c220737 [2] 柴天佑. 工业人工智能发展方向. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(10): 2005−2012 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200796Chai Tian-You. Development directions of industrial artificial intelligence. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(10): 2005−2012 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200796 [3] Wang Y L, Tan X J, Liu C L, Huang P Q, Zhang Q, Yang C H. Exploring interpretable evolutionary optimization via significance of each constraint and population diversity. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2024, 91: Article No. 101679 doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2024.101679 [4] Han H G, Zhang L, Zhang L L, He Z, Qiao J F. Cooperative optimal controller and its application to activated sludge process. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2019, 51(8): 3938−3951 [5] Han H G, Tang Z C, Wu X L, Yang H Y, Qiao J F. Robust reconstructed neural network with spectral reshaping activation. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2025, 55(6): 2765−2778 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2025.3557397 [6] Liu D J, Wang Y L, Liu C L, Yuan X F, Wang K, Yang C H. Scope-free global multi-condition-aware industrial missing data imputation framework via diffusion transformer. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2024, 36(11): 6977−6988 doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2024.3392897 [7] Li L, Rong S M, Wang R, Yu S L. Recent advances in artificial intelligence and machine learning for nonlinear relationship analysis and process control in drinking water treatment: A review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 405: Article No. 126673 doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126673 [8] Zhao C. Perspectives on nonstationary process monitoring in the era of industrial artificial intelligence. Journal of Process Control, 2022, 116: 255−272 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2022.06.011 [9] Liu D J, Wang Y L, Liu C L, Luo B, Huang B. EKG-AC: A new paradigm for process industrial optimization based on offline reinforcement learning with expert knowledge guidance. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, DOI: 10.1109/TCYB.2025.3579361 [10] Ding J, Yang C, Chai T. Recent progress on data-based optimization for mineral processing plants. Engineering, 2017, 3(2): 183−187 doi: 10.1016/J.ENG.2017.02.015 [11] 李康, 王福利, 何大阔, 贾润达. 基于数据的湿法冶金全流程操作量优化设定补偿方法. 自动化学报, 2017, 43(6): 1047−1055Li Kang, Wang Fu-Li, He Da-Kuo, Jia Run-Da. A data-based compensation method for optimal setting of hydrometallurgical process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(6): 1047−1055 [12] Schwenzer M, Ay M, Bergs T, Abel D. Review on model predictive control: An engineering perspective. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2021, 117: 1327−1349 doi: 10.1007/s00170-021-07682-3 [13] Zhou P, Chai T, Wang H. Intelligent optimal-setting control for grinding circuits of mineral processing process. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2009, 6(4): 730−743 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2008.2011562 [14] 丁进良, 杨翠娥, 陈远东, 柴天佑. 复杂工业过程智能优化决策系统的现状与展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(11): 1931−1943 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c180550Ding Jin-Liang, Yang Cui-E, Chen Yuan-Dong, Chai Tian-You. Research progress and prospects of intelligent optimization decision making in complex industrial process. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11): 1931−1943 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c180550 [15] Sun B, Yang C H, Zhu H Q, Gui W H. Modeling, optimization, and control of solution purification process in zinc hydrometallurgy. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(2): 564−576 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510844 [16] Lattanzi L, Raffaeli R, Peruzzini M, Pellicciari M. Digital twin for smart manufacturing: A review of concepts towards a practical industrial implementation. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, 2021, 34(6): 567−597 doi: 10.1080/0951192X.2021.1911003 [17] 代伟, 陆文捷, 付俊, 马小平. 工业过程多速率分层运行优化控制. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(10): 1946−1959Dai Wei, Lu Wen-Jie, Fu Jun, Ma Xiao-Ping. Multi-rate layered optimal operational control of industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(10): 1946−1959 [18] 阳春华, 刘一顺, 黄科科, 孙备, 李勇刚, 陈晓方, 等. 有色金属工业智能模型库构建方法及应用. 中国工程科学, 2022, 24(4): 188−201Yang Chun-Hua, Liu Yi-Shun, Huang Ke-Ke, Sun Bei, Li Yong-Gang, Chen Xiao-Fang, et al. Intelligent model library for nonferrous metal industry: Construction method and application. Strategic Study of Chinese Academy of Engineering, 2022, 24(4): 188−201 [19] 刘强, 卓洁, 郎自强, 秦泗钊. 数据驱动的工业过程运行监控与自优化研究展望. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(11): 1944−1956 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c180207Liu Qiang, Zhuo Jie, Lang Zi-Qiang, Qin S. Joe. Perspectives on data-driven operation monitoring and self-optimization of industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(11): 1944−1956 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2018.c180207 [20] 周晓君, 阳春华, 桂卫华. 全局优化视角下的有色冶金过程建模与控制. 控制理论与应用, 2015, 32(9): 1158−1169Zhou Xiao-Jun, Yang Chun-Hua, Gui Wei-Hua. Modeling and control of nonferrous metallurgical processes on the perspective of global optimization. Control Theory & Applications, 2015, 32(9): 1158−1169 [21] Wei D, Ding S F, Zhang C L, Shi Z Z. Multiagent reinforcement learning with heterogeneous graph attention network. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2023, 34(10): 6851−6860 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3215774 [22] 朱美强, 程玉虎, 李明, 王雪松, 冯涣婷. 一类基于谱方法的强化学习混合迁移算法. 自动化学报, 2012, 38(11): 1765−1776 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01765Zhu Mei-Qiang, Cheng Yu-Hu, Li Ming, Wang Xue-Song, Feng Huan-Ting. A hybrid transfer algorithm for reinforcement learning based on spectral method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2012, 38(11): 1765−1776 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2012.01765 [23] Huang J, Su J, Chang Q. Graph neural network and multi-agent reinforcement learning for machine-process-system integrated control to optimize production yield. Journal of Manufacturing Systems, 2022, 64: 81−93 doi: 10.1016/j.jmsy.2022.05.018 [24] Jiang Y, Fan J L, Chai T Y, Li J N, Lewis F L. Data-driven flotation industrial process operational optimal control based on reinforcement learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2017, 14(5): 1974−1989 [25] 李金娜, 袁林, 丁进良. 不确定工业过程运行指标异步更新强化学习决策算法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(2): 461−472 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210983Li Jin-Na, Yuan Lin, Ding Jin-Liang. Asynchronous updating reinforcement learning algorithm for decision-making operational indices of uncertain industrial processes. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(2): 461−472 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210983 [26] Dogru O, Chiplunkar R, Huang B. Reinforcement learning with constrained uncertain reward function through particle filtering. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2022, 69(7): 7491−7499 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2021.3099234 [27] Yoo H, Byun H E, Han D, Lee J H. Reinforcement learning for batch process control: Review and perspectives. Annual Reviews in Control, 2021, 52: 108−119 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2021.10.006 [28] Shakya A K, Pillai G, Chakrabarty S. Reinforcement learning algorithms: A brief survey. Expert Systems With Applications, 2023, 231: Article No. 120495 doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2023.120495 [29] Liu D J, Wang Y L, Liu C L, Yuan X F, Yang C H, Gui W H. Data mode related interpretable transformer network for predictive modeling and key sample analysis in industrial processes. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(9): 9325−9336 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3227731 [30] Lillicrap T P, Hunt J J, Pritzel A, Heess N, Erez T, Tassa Y, et al. Continuous control with deep reinforcement learning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1509.02971, 2015. [31] Duan Y, Chen X, Houthooft R, Schulman J, Abbeel P. Benchmarking deep reinforcement learning for continuous control. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning. New York, USA: PMLR, 2016. 1329−1338 [32] Lowe R, Wu Y I, Tamar A, Harb J, Abbeel P, Mordatch I, et al. Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative-competitive environments. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 30: 1−12 -




 下载:
下载: