Research on Coupled Co-firing Optimization Model for Segmented Planned Loads and Sulfur Constraint Boundary Adjustment
-
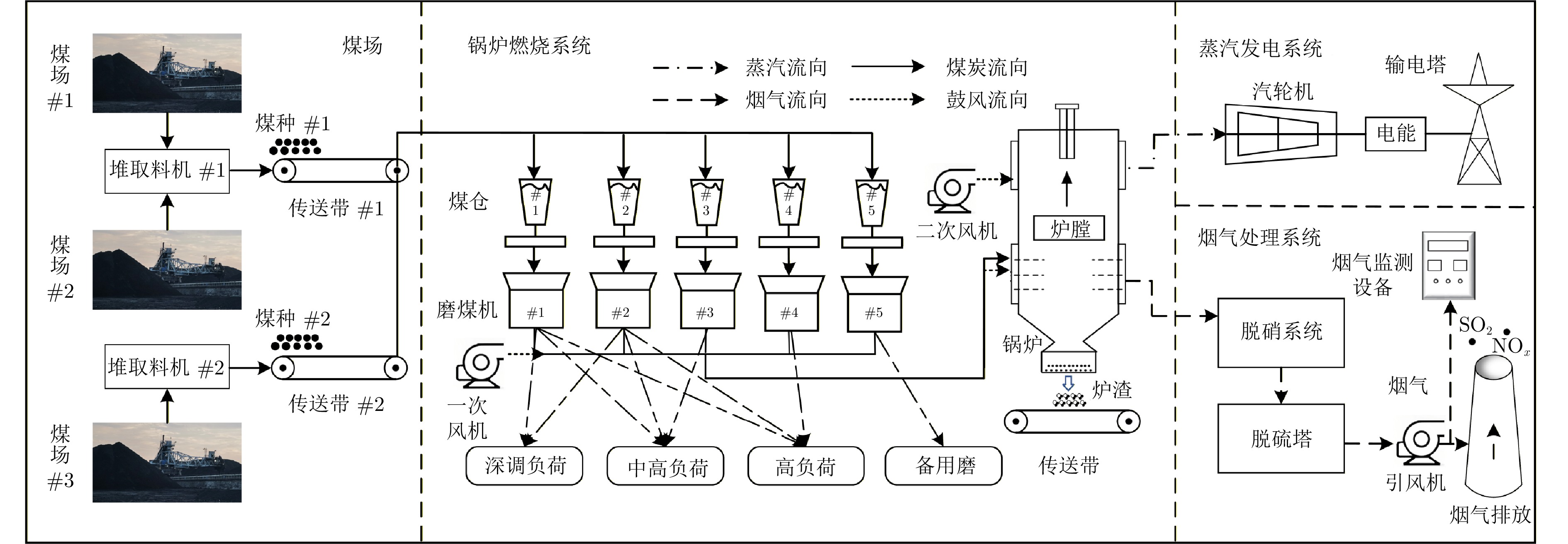
摘要: 针对火电企业人工配烧方案制定效率低、成本高的问题, 本文首次系统性开展面向分段计划负荷的耦合配烧优化模型与硫分约束界调整研究. 首先, 为保证更快速与更精准地制定配烧方案, 通过磨煤机组的切换磨向量建立分段计划负荷与配烧优化模型之间的耦合关系, 实现以计算机优化模型为主的数字化配烧. 然后, 针对耦合配烧优化模型中的硫分约束值受燃煤硫转化、脱硫等多重不确定性影响的问题, 在反演计算硫分约束界的基础上, 基于改进随机配置网络建立硫分约束界前馈补偿模型. 接下来, 为保证前馈补偿模型的历史训练样本案例数据库的最优性, 通过监测机组的实时生产数据全周期迭代动态更新案例数据库, 进而提升前馈补偿模型的全周期预测精准性. 基于该模型开发的软件系统应用结果表明: 配烧方案制定时间从原来的40分钟/次缩短至5分钟/次以内; 在满足环保要求的前提下, 优化后配烧成本较人工经验方案平均降低21 CNY/t, 取得显著的效率与经济效益.Abstract: In response to the issues of low efficiency and high cost in manual coal co-firing scheme formulation for thermal power plants, this paper systematically conducts a coupled blending optimization model and sulfur constraint boundary adjustment research for segmented planned loads for the first time. Firstly, in order to ensure faster and more accurate formulation of the blending scheme, a coupling relationship between segmented planned loads and blending optimization model is established through the switching of grinding vectors of the coal mill unit, achieving digital co-firing mainly based on computer optimization models. Then, to address the problem that the sulfur constraint in the coupled coal co-firing optimization model is subject to multiple uncertainties (e.g., coal sulfur conversion and desulfurization), a sulfur constraint boundary feedforward compensation model based on an improved stochastic configuration network is established on the basis of inverse calculation of the sulfur constraint boundary. Next, in order to ensure the optimality of the historical training sample case database for the feedforward compensation model, the case database is iteratively and dynamically updated throughout the entire cycle by monitoring the real-time production data of units, thereby improving the accuracy of the feedforward compensation model's full cycle prediction. Application results show the developed system cuts co-firing scheme formulation time from 40 to under 5 minutes per instance. Moreover, while meeting environmental standards, it lowers the cost by an average of 21 CNY/t compared to manual operations, yielding significant efficiency and economic gains.
-
Key words:
- co-firing /
- segmented loads /
- optimization model /
- model constraint boundary /
- dynamic compensation
-
表 1 计划负荷与煤耗关系数据
Table 1 Relationship data between planned loads and coal consumption
负荷(MW) 煤耗(g/(kWh)) 负荷(MW) 煤耗(g/(kWh)) 50 432.5 225 311.3 75 379.1 250 308.5 100 352.7 275 306.3 125 337.2 300 304.6 150 327.1 325 303.3 175 320.1 350 302.2 200 315.1 375 301.3 表 2 煤场存煤信息
Table 2 Coal yard storage information
煤种 编号 ${{{\boldsymbol{Q}}}}$ (kcal/kg) ${{{\boldsymbol{S}}}}$ (%) ${{V}}$ (%) ${{A}}$ (%) ${{M}}$ (%) ${{{\boldsymbol{P}}}}$ (CNY/t) 华能优 11 2976.00 0.35 26.34 2.95 46.24 1004.03 神混 12 4802.00 0.68 18.42 23.91 12.50 1046.20 印尼褐煤 13 2771.00 0.88 25.69 2.92 47.20 746.00 平混 21 4725.00 0.92 26.20 29.29 6.40 971.71 伊泰 22 4582.00 0.37 23.87 20.62 15.20 1070.00 印尼褐煤 23 4319.00 1.18 24.28 27.86 9.80 866.82 印尼烟煤 31 5562.00 0.76 39.77 15.05 9.20 1134.88 大友 32 5008.00 1.09 22.89 33.42 7.00 948.25 印尼褐煤 33 2733.00 0.37 24.38 6.37 47.14 877.79 表 4 磨煤机设置
Table 4 Configuration of coal mill
磨煤机编号 职能 ${R^{\max }}/{R^{\min }}$ (t/h) $v$ (t/h) #1磨煤机 深度调峰 50/25 0.2 #2磨煤机 深度调峰 50/25 0.2 #3磨煤机 中高 50/25 — #4磨煤机 高 50/25 — 表 3 配烧参数设置
Table 3 Co-firing parameters setting
负荷段名称 负荷 热值约束 环保约束 安全约束 $\angle_e$ (MW) $\angle_h$ (MW) $\angle_g$ (MW) $\angle_i$ (MW) $ \boldsymbol{Q}^{\rm{L}} $ (kcal/kg) $ S_i^{\rm{U}} $ (%) $M^{\rm{U}}$/ $M^{\rm{L}}$ (%) $V^{\rm{U}}$/$V^{\rm{L}}$ (%) $A^{\rm{U}}$/$A^{\rm{L}}$ (%) 深调负荷$\angle_1$ 70 15 5 90 2205 0.68 50/10 40/20 30/0 中高负荷$\angle_2$ 160 15 5 180 2681 0.45 50/10 40/20 30/0 高负荷$\angle_3$ 270 15 5 290 4130 0.45 50/10 40/20 30/0 表 5 人工配烧与模型配烧效益对比
Table 5 Comparison of benefits between manual co-firing and model co-firing
煤仓 煤种 比例(%) 热值(kcal/kg) 硫分(%) 价格(CNY/t) 人工 模型 人工 模型 人工 模型 人工 模型 人工 模型 #1煤仓 1D2/2D2 2D3/3D3 20/80 41/59 4626 3483 0.37 0.37 916.23 955.73 #2煤仓 1D3/2D2 2D2/2D3 35/65 70/30 3950 4699 0.45 0.61 1082.98 1009.80 #3煤仓 3D3 3D3 单烧 单烧 2733 2733 0.53 0.37 835.93 877.79 #4煤仓 2D2 2D2/3D3 单烧 80/20 4582 4212 0.37 0.60 1070.00 1031.56 深调 — — — — 4288 3426 0.49 0.37 1011.06 982.77$ \downarrow $28.29 中高 — — — — 3770 3468 0.45 0.45 966.64 947.77$ \downarrow $18.87 高 — — — — 4386 4131 0.45 0.45 1030.72 999.03 $ \downarrow $31.69 表 6 训练样本数据案例库
Table 6 Training sample data repository
负荷段 输入${\boldsymbol{U}}$ 输出${\boldsymbol{Y}}$ 评价指标 $\angle$ (MW) ${S^{\rm{U}}_i} $ (%) $\Delta {S^{\rm{U}}} $ (%) $E$ 深调 65 0.68 0.19 13.94 深调 88 0.68 0.21 14.51 深调 107 0.68 0.23 14.27 $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ 中高 136 0.45 0.19 14.22 中高 174 0.45 0.16 14.96 中高 220 0.45 0.15 14.66 $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ 高 260 0.45 0.17 15.02 高 300 0.45 0.15 13.15 $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ $ \cdots $ 高 350 0.45 0.16 13.73 表 7 硫分约束界迭代调整
Table 7 Sulfur constraint boundary iterative adjustment
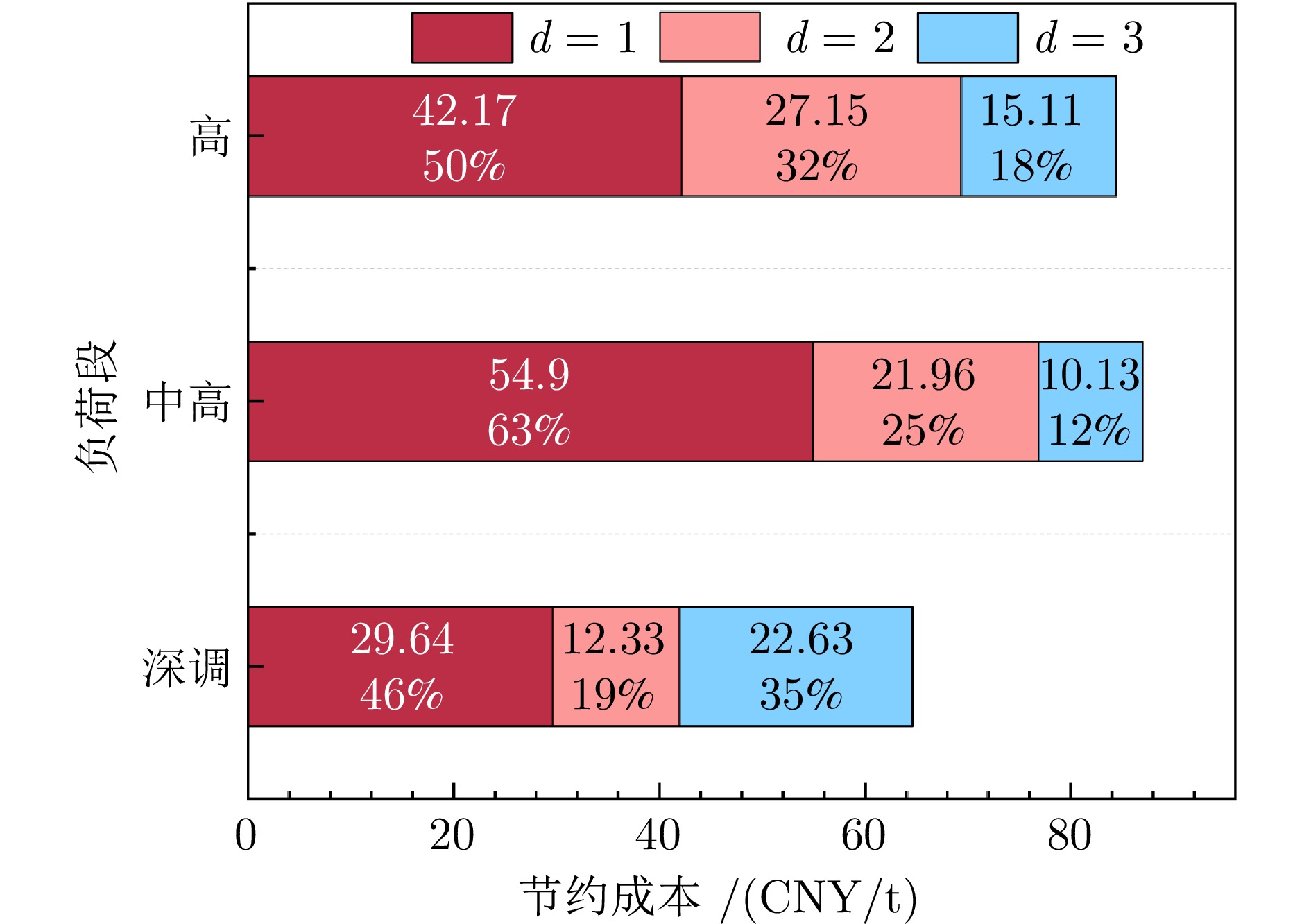
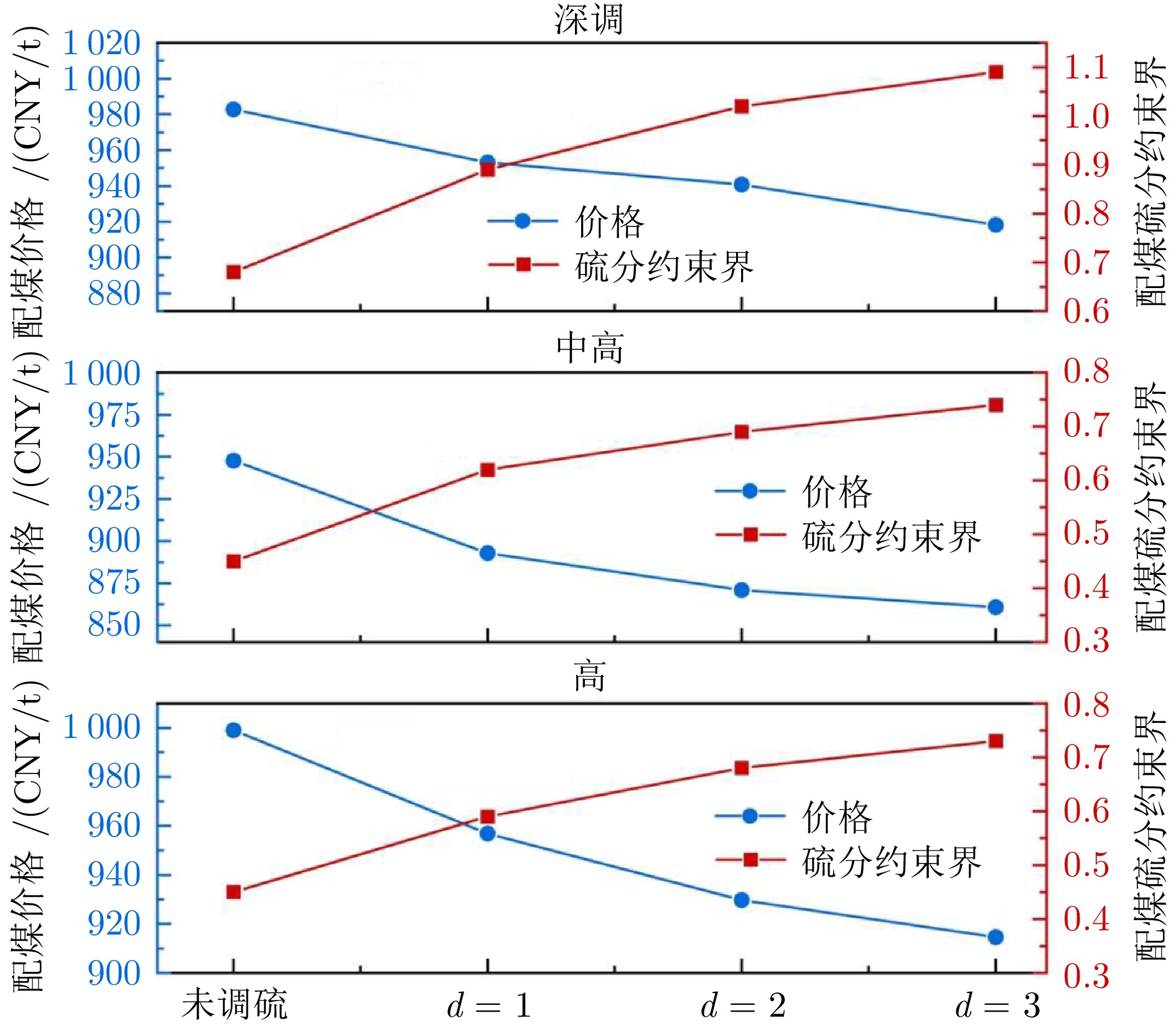
负荷段 参数 未调硫 $d=1$ $d=2$ $d=3$ 深调负荷段 $\angle$ (MW) 90 90 90 90 ${S^{\text{U}}_i} $ (%) 0.68 0.68 0.89 1.02 $\Delta \widehat S^{\rm{U}} $ (%) 0.00 0.21 0.13 0.07 $e^ {S{O_{2}}}$ ($\rm{mg/m^3}$) 11.89 6.82 5.27 4.83 价格 (CNY/t) 982.77 953.13 $\downarrow $29.64 940.80 $\downarrow $12.33 918.17 $\downarrow $22.63 中高负荷段 $\angle$ (MW) 180 180 180 180 ${S^{\text{U}}_i} $ (%) 0.45 0.45 0.62 0.69 $ \Delta \widehat S^{\rm{U}} $ (%) 0.00 0.17 0.07 0.05 $e^ {S{O_{2}}}$ ($\rm{mg/m^3}$) 13.18 7.47 5.57 4.32 价格 (CNY/t) 947.77 892.87 $\downarrow $54.90 870.91 $\downarrow $21.96 860.78 $\downarrow $10.13 高负荷段 $\angle$ (MW) 290 290 290 290 ${S^{\text{U}}_i} $ (%) 0.45 0.45 0.59 0.68 $\Delta \widehat S^{\rm{U}} $ (%) 0.00 0.14 0.09 0.05 $e^ {S{O_{2}}}$ ($\rm{mg/m^3}$) 11.42 7.56 6.02 4.76 价格 (CNY/t) 999.03 956.86 $\downarrow $42.17 929.71 $\downarrow $27.15 914.60 $\downarrow $15.11 表 8 模型配烧调硫分约束前后方案对比
Table 8 Comparison of schemes before and after sulfur constraint adjustment in model co-firing
煤仓 煤种 比例(%) 热值(kcal/kg) 硫分(%) 价格(CNY/t) 未调硫 调硫 未调硫 调硫 未调硫 调硫 未调硫 调硫 未调硫 调硫 #1煤仓 2D3/3D3 2D3/3D3 41/59 53/47 3483 3930 0.37 0.80 955.73 871.94 #2煤仓 2D2/2D3 2D2/3D3 70/30 45/55 4699 3566 0.61 0.37 1009.80 964.40 #3煤仓 3D3 1D3 单烧 单烧 2733 2771 0.37 0.88 877.79 746.00 #4煤仓 2D2/3D3 2D3/2D2 80/20 80/20 4212 4898 0.60 0.76 1031.56 907.46 深调 — — — — 3426 3748 0.37 0.59 982.77 918.17$\downarrow $64.60 中高 — — — — 3468 3422 0.45 0.68 947.77 860.78 $\downarrow $86.99 高 — — — — 4131 4131 0.45 0.73 999.03 914.60 $\downarrow $84.43 表 9 模型配煤调硫分约束前后方案对比(500 MW)
Table 9 Comparison of before and after schemes for model coal blending and sulfur constraint adjustment (500 MW)
煤仓 煤种 比例(%) 热值(kcal/kg) 硫分(%) 价格(CNY/t) 未调硫 调硫 未调硫 调硫 未调硫 调硫 未调硫 调硫 未调硫 调硫 #1煤仓 3D3 3D3 单烧 单烧 2733 2733 0.37 0.37 877.79 877.79 #2煤仓 3D3 1D3/3D3 单烧 41/59 2733 2749 0.37 0.58 877.79 845.74 #3煤仓 1D3/2D2 1D3/2D3 50/50 58/42 4073 3885 0.52 1.03 982.49 833.73 #4煤仓 1D3/3D3 1D3 39/61 单烧 2841 2771 0.54 0.88 847.68 800.00 #5煤仓 1D2/2D2 1D2/2D3 56/44 80/20 4706 4878 0.54 0.90 1056.52 967.84 深调 — — — — 2733 2741 0.37 0.48 877.79 861.76 $\downarrow $16.03 中高 — — — — 3095 3034 0.45 0.72 896.44 839.31 $\downarrow $57.13 高 — — — — 3561 3561 0.45 0.72 948.68 881.28 $\downarrow $67.40 表 10 不同模型配烧方案对比
Table 10 Comparison of co-firing schemes for different models
煤仓 煤种 比例(%) 热值(kcal/kg) 硫分(%) 价格(CNY/t) I II III I II III I II III I II III I II III #1煤仓 2D2/3D3 2D2/3D3 2D3/3D3 62/38 57/43 53/47 3877 3786 3930 0.37 0.37 0.80 996.70 987.24 871.94 #2煤仓 2D3/3D2 2D3/3D3 2D2/3D3 80/20 44/56 45/55 4983 3714 3566 1.16 0.72 0.37 883.11 873.00 964.40 #3煤仓 1D3/3D3 1D3/2D3 1D3 56/44 80/20 单烧 2754 3212 2771 0.66 0.94 0.88 803.37 770.16 746.00 #4煤仓 2D3/3D3 2D3/3D1 2D3/2D2 36/64 80/20 80/20 3531 5094 4898 0.66 1.10 0.76 873.89 920.43 907.46 深调 — — — — — — 4430 4015 3750 0.77 0.55 0.59 939.91 930.12 918.17 中高 — — — — — — 3872 3571 3422 0.73 0.68 0.68 894.39 876.80 860.78 高 — — — — — — 4131 4189 4131 0.73 0.73 0.73 917.90 926.89 914.60 -
[1] 国家能源局. 国家能源局发布2024年1−8月份全国电力工业统计数据. 电力勘测设计, 2024, 9: 39National Energy Administration. National Energy Administration releases national power industry statistics for 1−8 months of 2024. Electric Power Survey & Design, 2024, 9: 39 [2] Lin B Q, Shi F Y. Coal price, economic growth and electricity consumption in China under the background of energy transition. Energy Policy, 2024, 195: Article No. 114400 doi: 10.1016/j.enpol.2024.114400 [3] Song X H, Zhang B J. Study on the cost composition and control of coal power in China under the perspective of policy evolution. Heliyon, 2024, 10(16): Article No. e36098 doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e36098 [4] Prasad S K, Mangaraj B K. A multi-objective competitive-design framework for fuel procurement planning in coal-fired power plants for sustainable operations. Energy Economics, 2022, 108: Article No. 105914 doi: 10.1016/j.eneco.2022.105914 [5] Sherali H, Puri R. Models for a coal blending and distribution problem. Omega, 1993, 21(2): 235−243 doi: 10.1016/0305-0483(93)90056-Q [6] Li J, Jiang Y C, Li Q S, Wang Y F. Multi-stage stochastic programming for thermal power plant coal procurement considering long-term contract under uncertainties. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2025, 203: Article No. 109323 [7] Yan S Y, Lv C W, Yao L M, Hu Z N, Wang F J. Hybrid dynamic coal blending method to address multiple environmental objectives under a carbon emissions allocation mechanism. Energy, 2022, 254: Article No. 124297 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.124297 [8] Nakata E, Fujimoto H, Terazono K. Expert system for coal blending. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1992, 25: 109−114 [9] Guerras S L, Martín M. Optimal gas treatment and coal blending for reduced emissions in power plants: A case study in Northwest Spain. Energy, 2019, 169: 739−749 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.12.089 [10] Tillman D, Duong D. Managing slagging at Monroe power plant using on-line coal analysis and fuel blending. Fuel Processing Technology, 2007, 88(11−12): 1094−1098 doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2007.06.027 [11] 杨勇平, 杨志平, 徐钢, 王宁玲. 中国火力发电能耗状况及展望. 中国电机工程学报, 2013, 33(23): 1−11 doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2013.23.005Yang Yong-Ping, Yang Zhi-Ping, Xu Gang, Wang Ning-Ling. Situation and prospect of energy consumption for China's thermal power generation. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2013, 33(23): 1−11 doi: 10.13334/j.0258-8013.pcsee.2013.23.005 [12] Nawaz Z, Ali U. Techno-economic evaluation of different operating scenarios for indigenous and imported coal blends and biomass co-firing on supercritical coal fired power plant performance. Energy, 2020, 212: Article No. 118721 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.118721 [13] 李晗, 宋磊, 李鑫, 郑宇轩, 郑博聪, 王培键. 智能配煤技术的发展与应用. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2024, 3: 66−69Li Han, Song Lei, Li Xin, Zheng Yu-Xuan, Zheng Bo-Cong, Wang Pei-Jian. Review of the development of intelligent coal blending system. Cal Processing & Comprehensive Utlization, 2024, 3: 66−69 [14] Xia J, Chen G, Tan P, Zhang C. An online case-based reasoning system for coal blends combustion optimization of thermal power plant. International Journal of Electrical Power & Energy Systems, 2014, 62: 299−311 [15] 钟剑锋, 赵海宝, 赵晨, 楼亦刚, 傅文斌. 智慧环保技术在燃煤电厂中的研究和应用. 洁净煤技术, 2025, 31: 203−208Zhong Jian-Feng, Zhao Hai-Bao, Zhao Chen, Lou Yi-Gang, Fu Wen-Bin. Research and application of intelligent environmental protection technology in coal-fired power plants. Clean Coal Technology, 2025, 31: 203−208 [16] 华志刚, 郭荣, 崔希, 汪勇. 火电智慧电厂技术路线探讨与研究热力发电. 热力发电, 2019, 48(10): 8−14Hua Zhi-Gang, Guo Rong, Cui Xi, Wang Yong. Discussion and study on technical route of smart thermal power plant. Thermal Power Generation, 2019, 48(10): 8−14 [17] Zhou Z Y, Lu J Y, Feng Q, Liu W T. Review on occurrence, speciation, transition and fate of sulfur in typical ultra-low emission coal-fired power plants. Journal of the Energy Institute, 2022, 100: 259−276 doi: 10.1016/j.joei.2021.12.004 [18] Kang J, Su T, Jin H Y, Wang Y, Wu L Q, Fan X L. Risk analysis of boiler overpressure explosion based on complex network and fuzzy Bayesian inference. Engineering Failure Analysis, 2025, 170: Article No. 109261 doi: 10.1016/j.engfailanal.2025.109261 [19] Zhong Y X, Wang X, Xu G, Ning X Y, Zhou L, Tang W, et al. Investigation on slagging and high-temperature corrosion prevention and control of a 1 000 MW ultra supercritical double tangentially fired boiler. Energy, 2023, 275: Article No. 127455 doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.127455 [20] Wang D H, Li M. Stochastic configuration networks: Fundamentals and algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3466−3479 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2734043 [21] Dang G, Wang D H. An improved fuzzy recurrent stochastic configuration network for modeling nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2025, 33(4): 1265−1276 doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2024.3513394 [22] Dai W, Li D, Zhou P, Chai T Y. Stochastic configuration networks with block increments for data modeling in process industries. Information Sciences, 2019, 484: 367−386 doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.01.062 [23] 代伟, 张政煊, 杨春雨, 马小平. 基于SCN数据模型的SISO非线性自适应控制. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(10): 2002−2012Dai Wei, Zhang Zheng-Xuan, Yang Chun-Yu, Ma Xiao-Ping. Adaptive control of SISO nonlinear system using data-driven SCN model. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(10): 2002−2012 [24] Lu J, Ding J L, Liu C X, Chai T Y. Hierarchical-bayesian-based sparse stochastic configuration networks for construction of prediction intervals. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(8): 3560−3571 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3053306 [25] Jamal R, Khan N H, Ebeed M, Zeinoddini-Meymand H, Shahnia F. An improved pelican optimization algorithm for solving stochastic optimal power flow problem of power systems considering uncertainty of renewable energy resources. Results in Engineering, 2025, 26: Article No. 104553 doi: 10.1016/j.rineng.2025.104553 [26] 赵健, 刘士新. 火电厂动力配煤优化模型研究. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 36(10): 1388−1392Zhao Jian, Liu Shi-Xin. Optimization model of steam coal blending in coal-fired power plant. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2015, 36(10): 1388−1392 [27] 付轩熠, 茅大钧, 印琪民. 基于多种算法的火电厂配煤优化方法研究. 煤炭工程, 2018, 50(9): 150−154Fu Xuan-Yi, Mao Da-Jun, Yin Qi-Min. Research on coal blending optimization method based on multipe algorithms in thermal power plant. Coal Engineering, 2018, 50(9): 150−154 [28] Liu M, Yu Z Q, Li B R, Wang Q J, Ren H W, Xu D. Coal allocation optimization based on a hybrid residual prediction model with an improved genetic algorithm. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 137: Article No. 109072 doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2024.109072 [29] Xu W L, Zhong W Q, Zhou G W, Chen X, Liu X J. Optimization of air distribution and coal blending in pulverized coal boilers for high-temperature corrosion prevention based on POD reduced-order modeling. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2024, 255: Article No. 123705 doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2024.123705 [30] 孙庶. 动力配煤几个主要煤质指标可加性的论证. 煤炭技术, 2009, 28(5): 164−166Sun Shu. Some of the main driving force for coal blending coal quality indicators additive demonstration. Coal Technology, 2009, 28(5): 164−166 [31] 陶翔, 陈玲红, 蒋旭光, 吴学成, 岑可法. 动力配煤下入炉煤质参数快速计算分析. 能源工程, 2022, 42(5): 1−8Tao Xiang, Chen Ling-Hong, Jiang Xu-Guang, Wu Xue-Cheng, Cen Ke-Fa. Rapid calculation and analysis of furnace coal quality parameters under power coal blending. Energy Engineering, 2022, 42(5): 1−8 -




 下载:
下载: