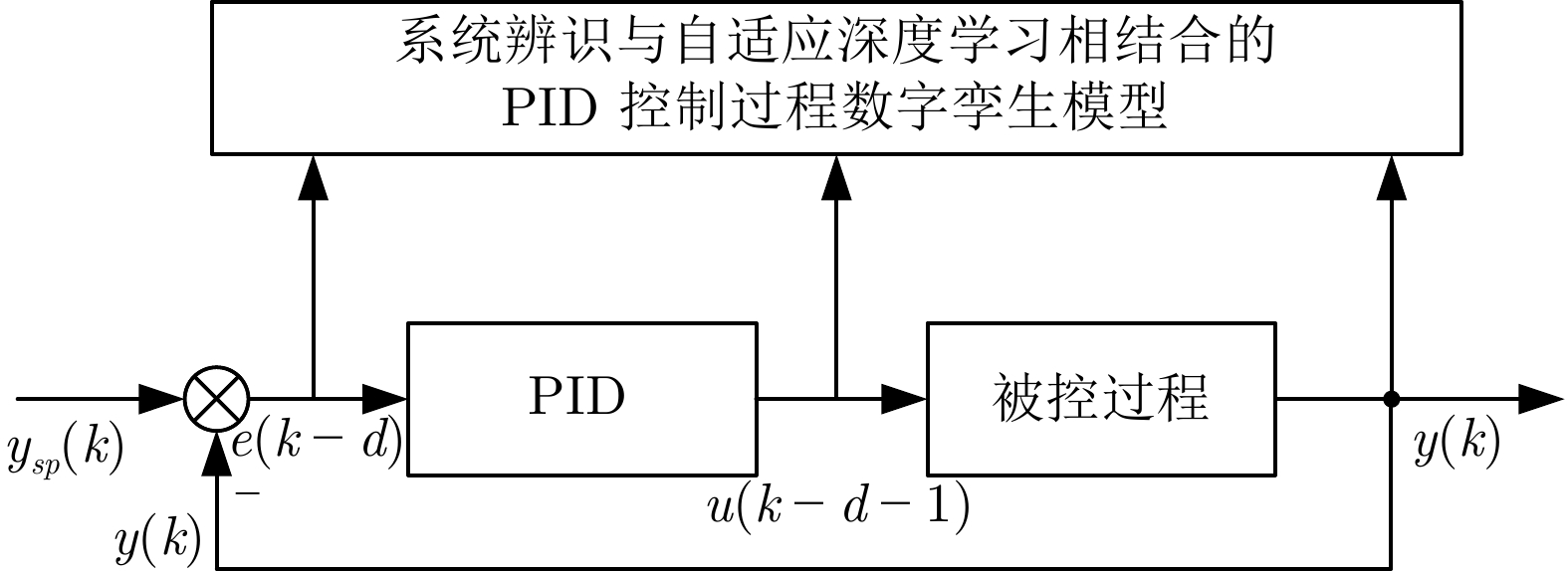
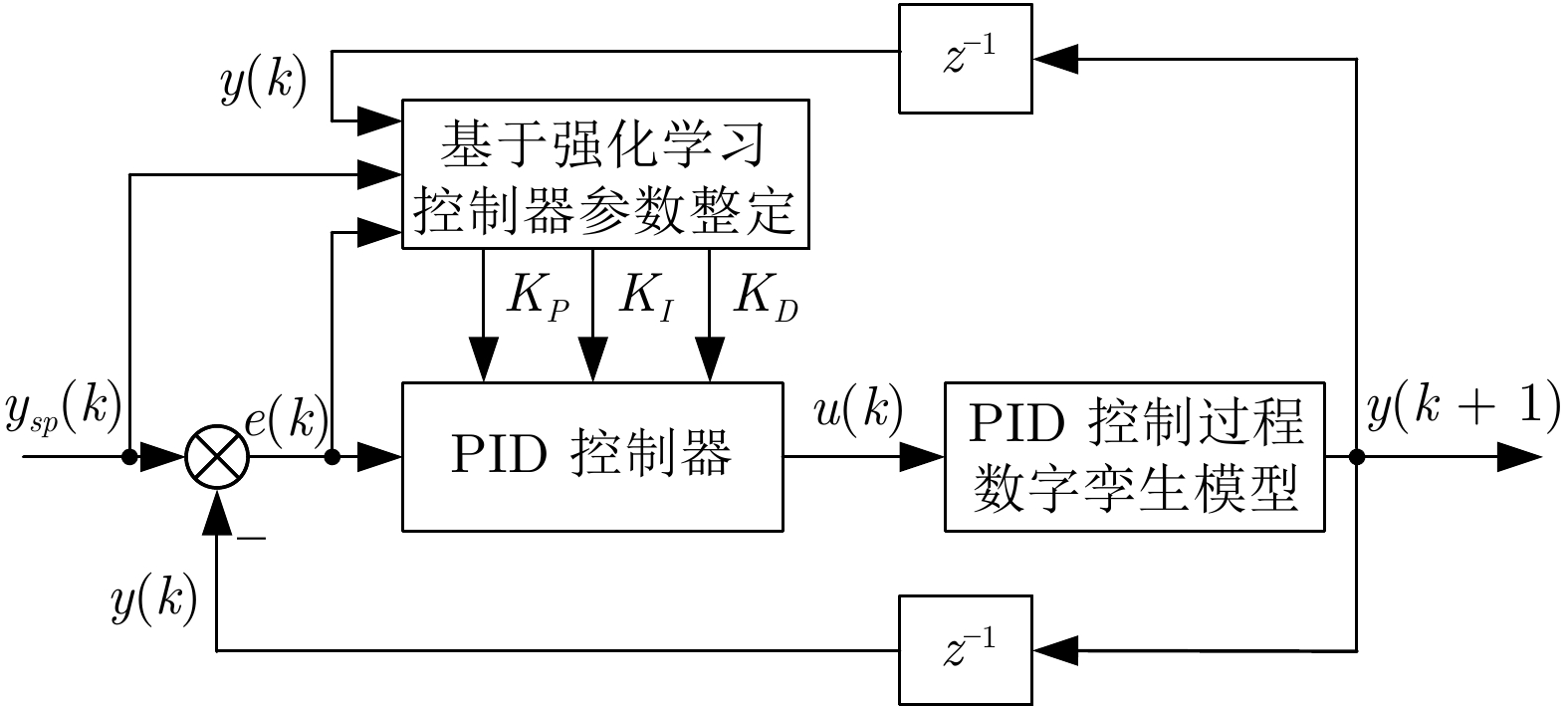
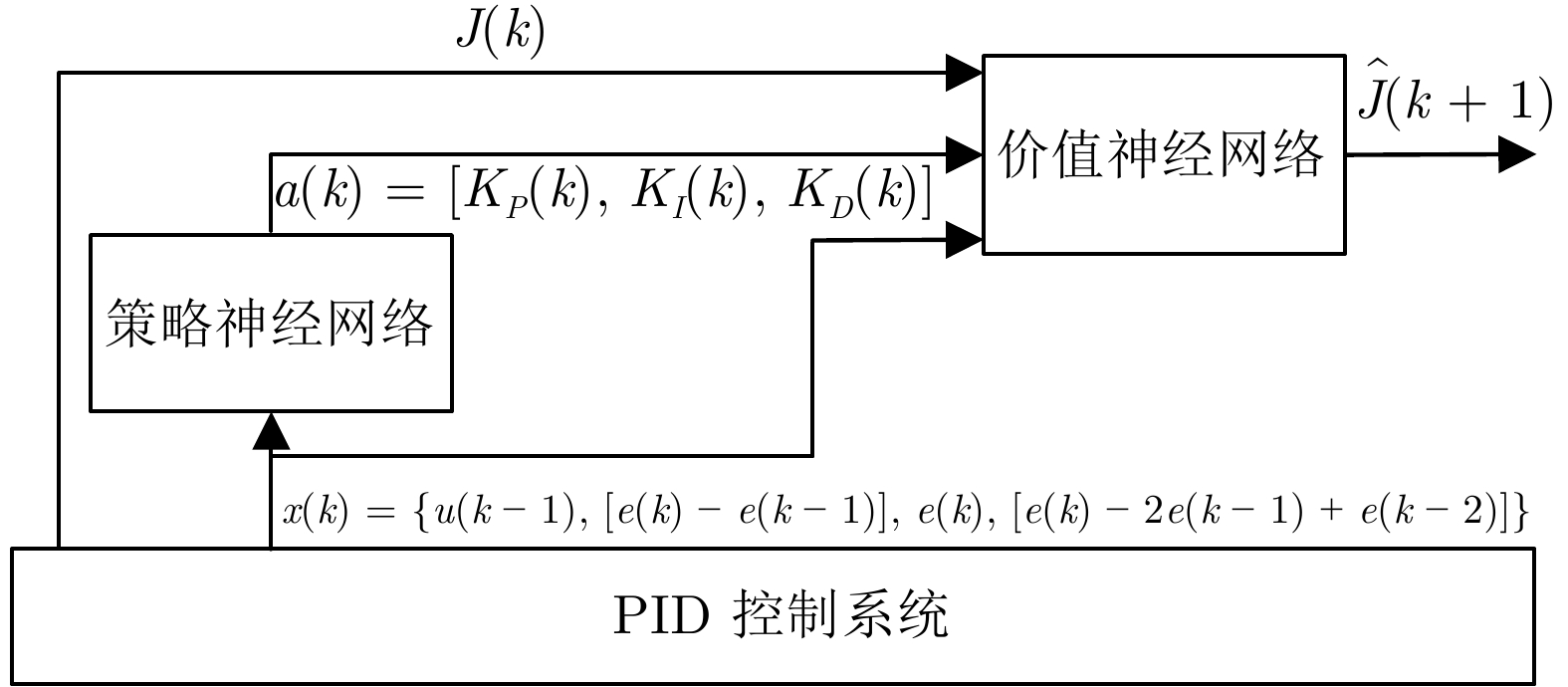
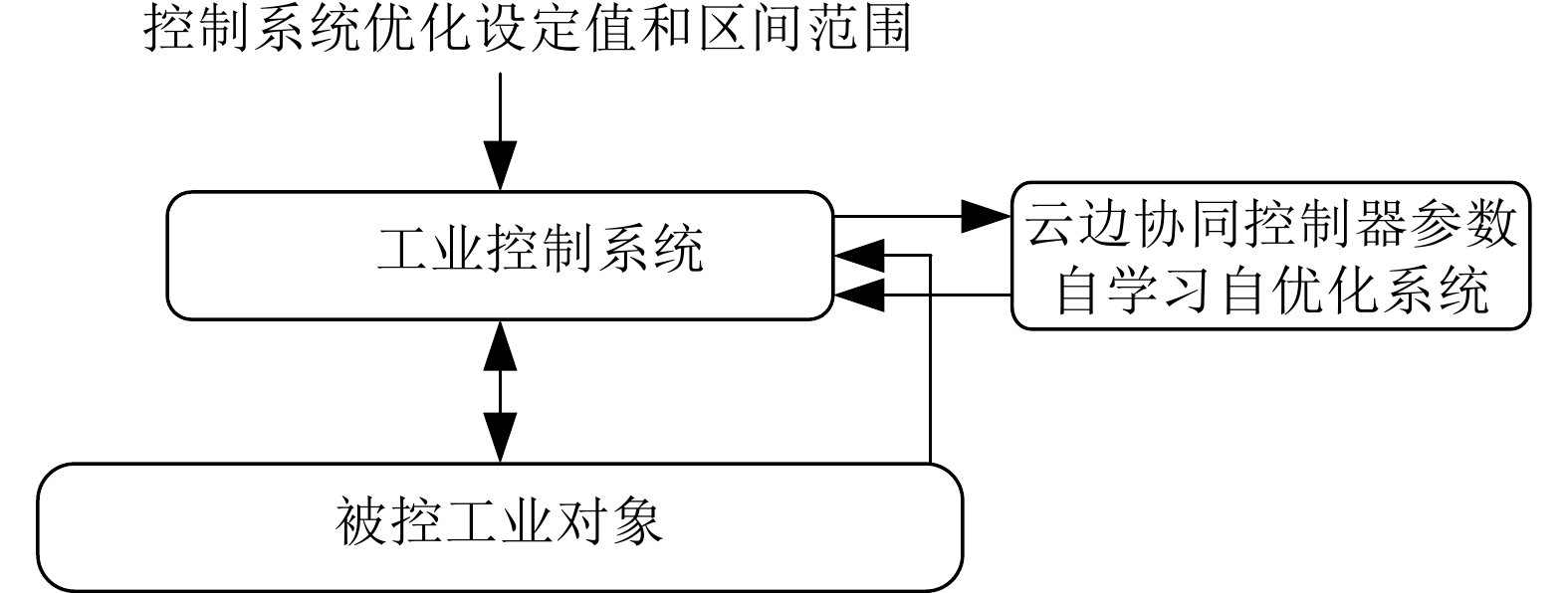
-
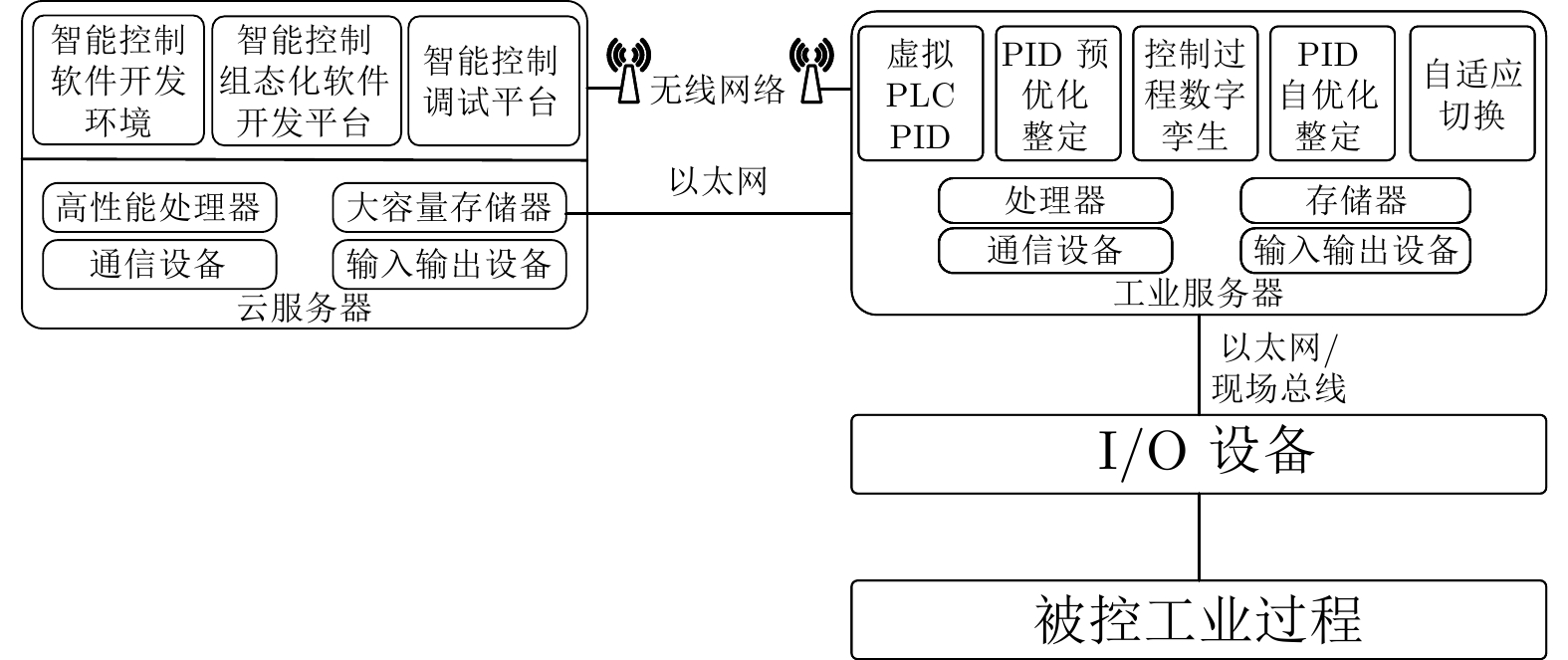
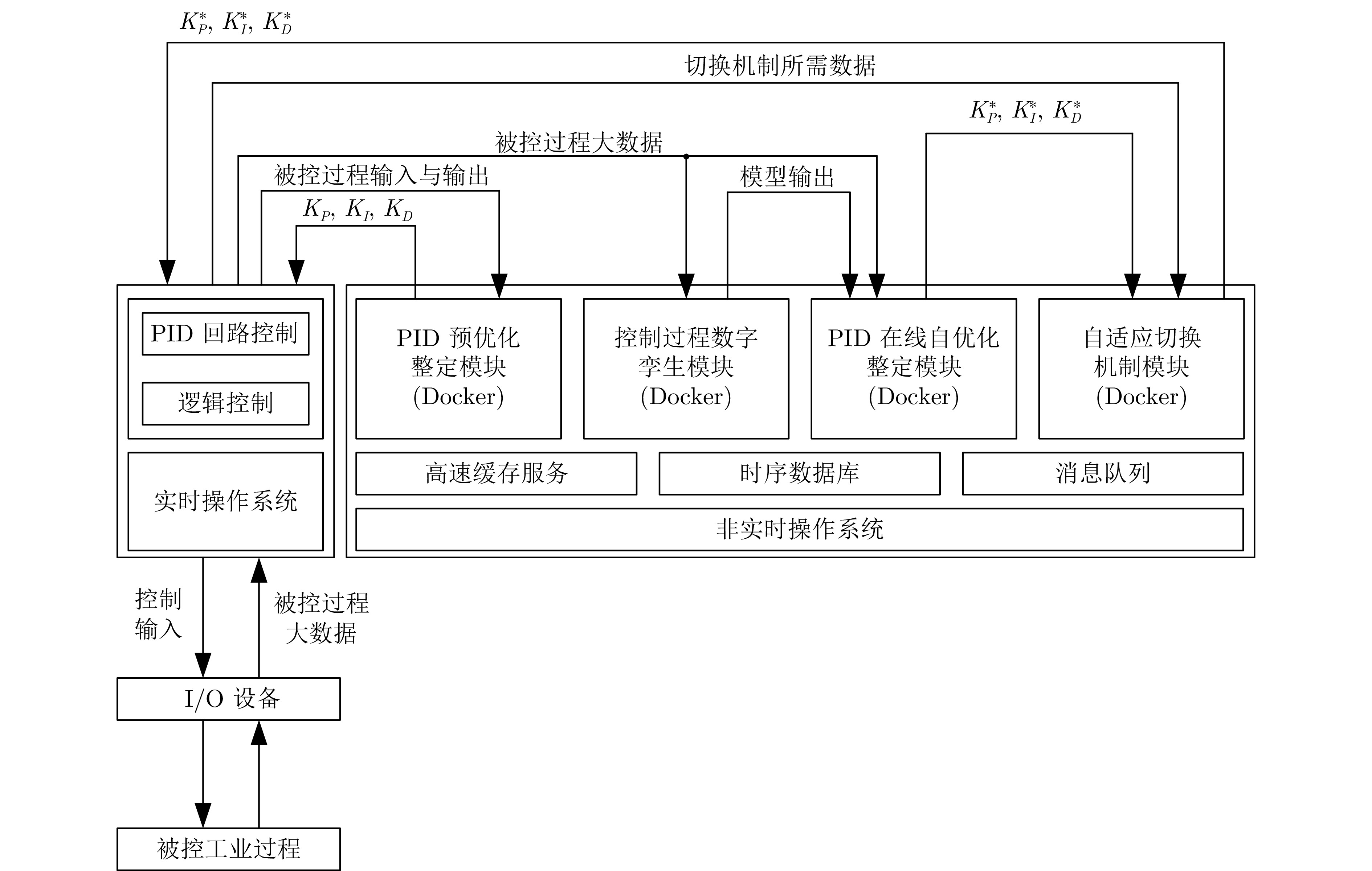
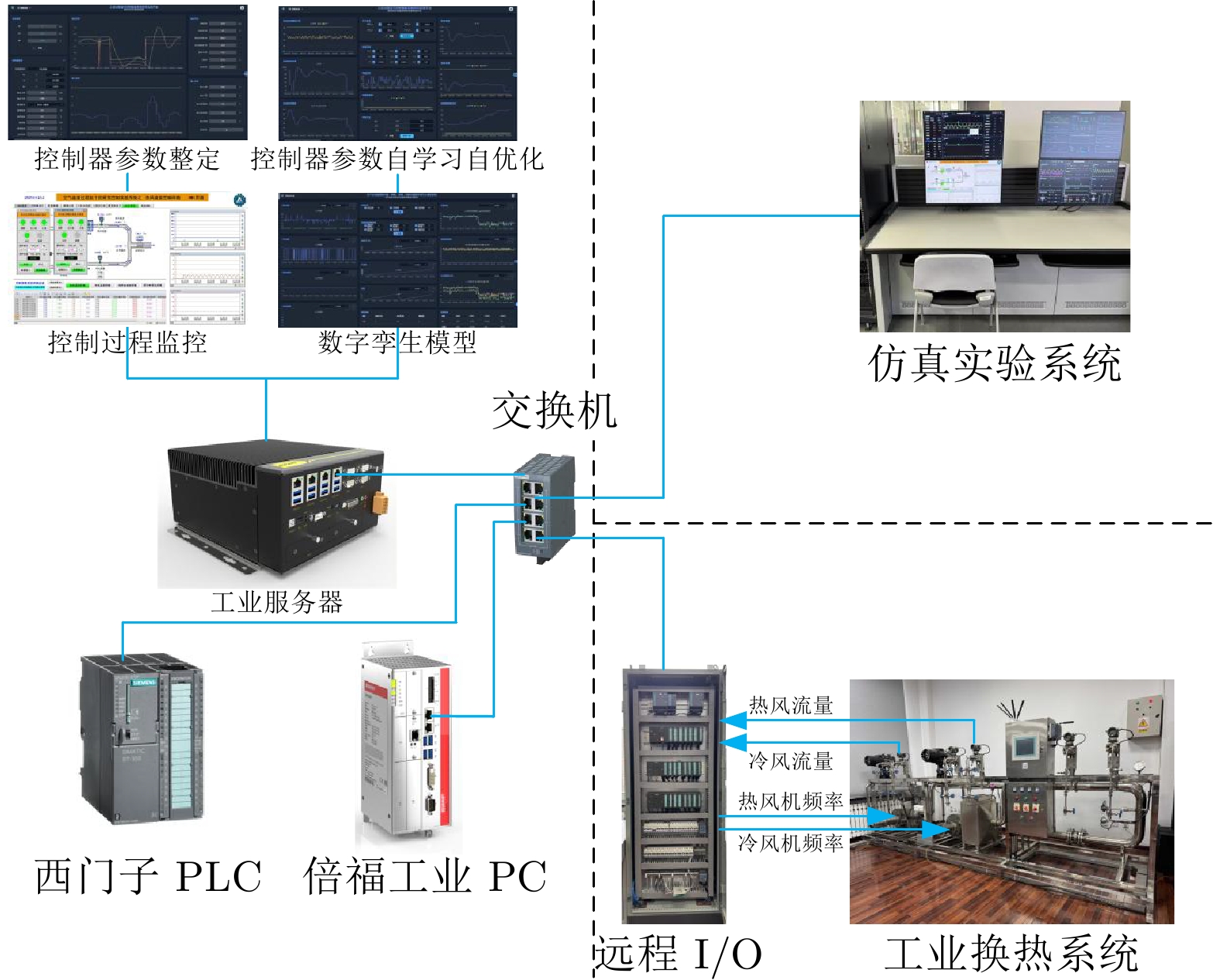
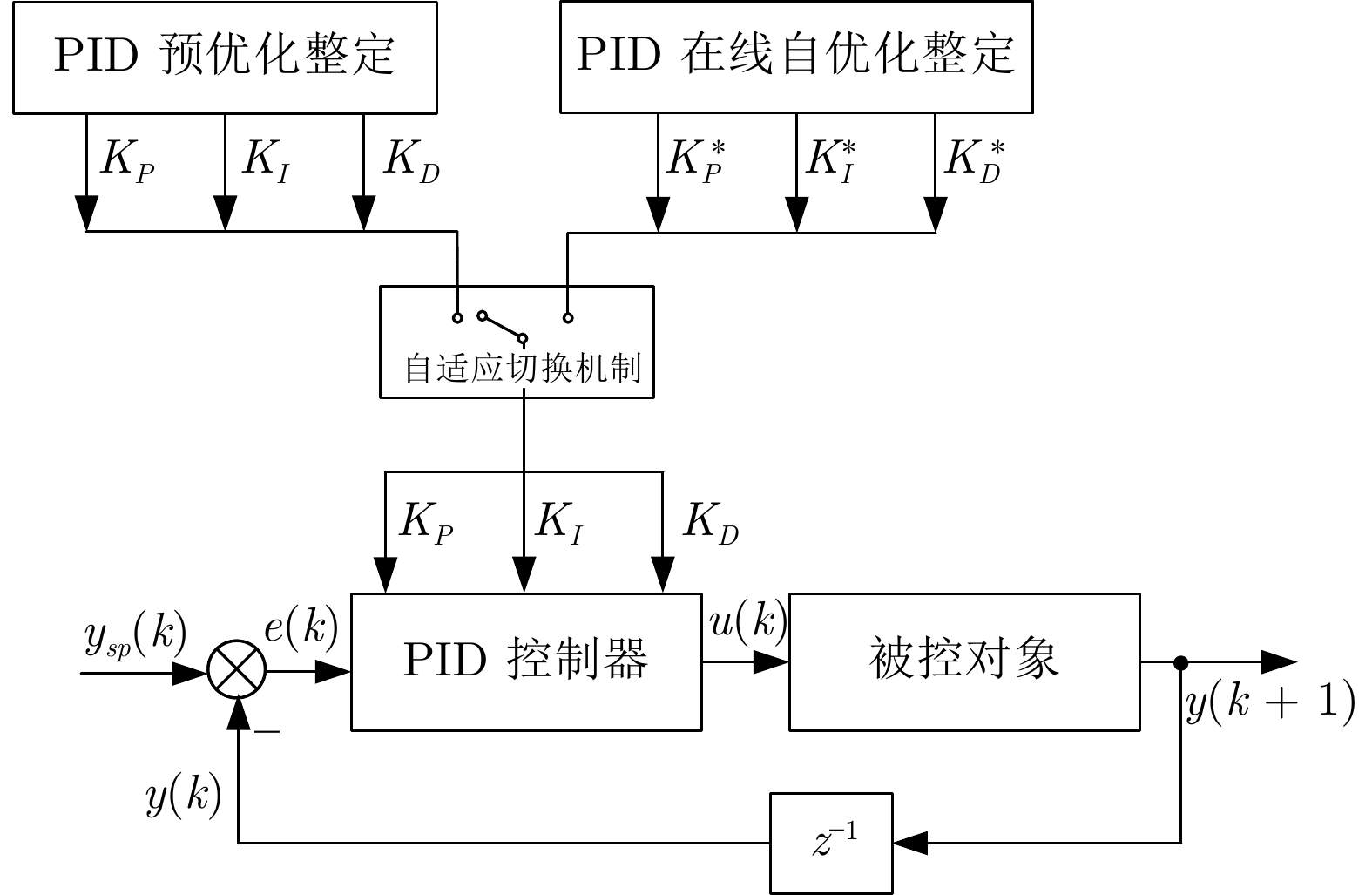
摘要: 针对可编程逻辑控制器(PLC)和虚拟PLC的PID难以优化整定的难题, 将建模、控制、优化和深度学习与强化学习相结合, 提出无模型PID在线自优化整定算法. 将工业云及边缘计算、软件定义实时及可靠保障机制的双通道通信架构与所提出的PID整定算法相结合, 提出云端协同的软件定义智能控制系统. 云为基于云服务器的智能控制软件开发平台;端为基于工业服务器的智能控制软件. 智能控制软件包括虚拟PLC PID、PID预优化整定和控制过程数字孪生以及在线自优化整定、自适应切换机制. 采用研制的软件定义智能控制系统研究实验平台, 进行所提出的控制系统与国外先进PLC和工业PC的无模型整定软件PID控制系统的仿真与物理对比实验. 实验结果表明本文的软件定义智能控制系统可进行控制器参数自优化整定, 控制性能显著优于国外无模型整定软件的PID控制系统.Abstract: To address the challenge of achieving optimal PID tuning in both physical programmable logic controller (PLC) and virtual PLC, a model-free PID online self-optimizing tuning algorithm is proposed by integrating modeling, control, optimization with deep learning and reinforcement learning. A cloud-edge collaborative software-defined intelligent control system is developed by combining the industrial cloud and edge computing as well as the proposed PID tuning algorithm and a software-defined dual-channel communication architecture based on real-time and reliability assurance mechanisms. In this system, the cloud serves as an intelligent control software development platform based on cloud servers, while the edge comprises intelligent control software deployed on industrial servers. The intelligent control software includes virtual PLC PID, pre-optimization PID tuning, digital twin of the control process, online self-optimizing tuning and an adaptive switching mechanism. Simulation and physical comparative experiments on the developed software-defined intelligent control system research experimental platform are conducted between the proposed control system and model-free PID tuning control systems on advanced foreign PLCs and industrial PCs. The experimental results indicate that the proposed software-defined intelligent control system is capable of self-optimizing controller parameter, and its control performance significantly outperforms that of advanced foreign model-free tuning PID control systems.
-
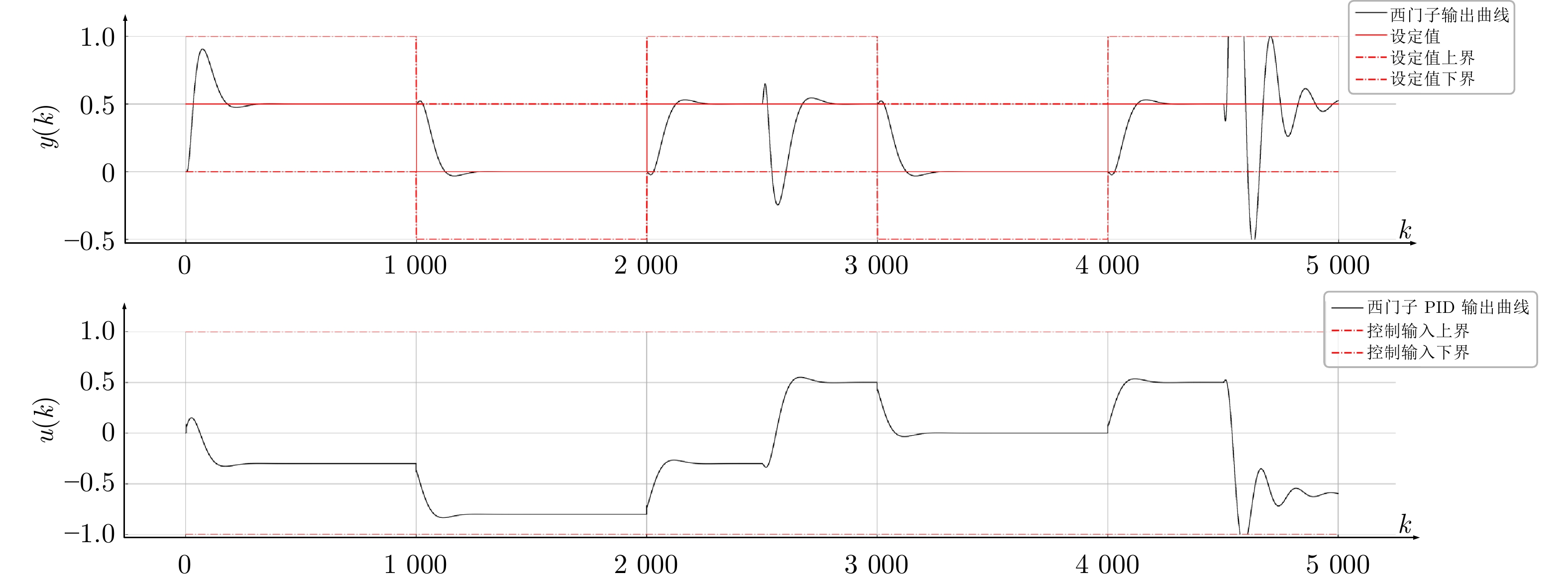
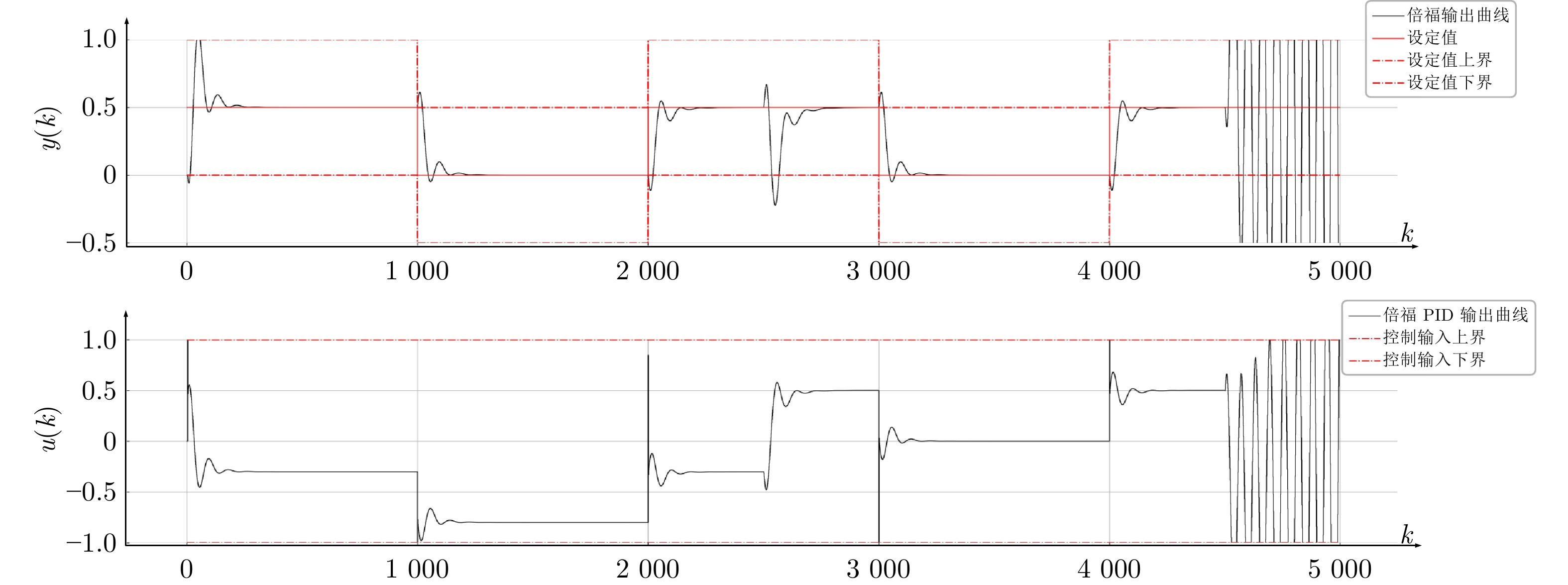
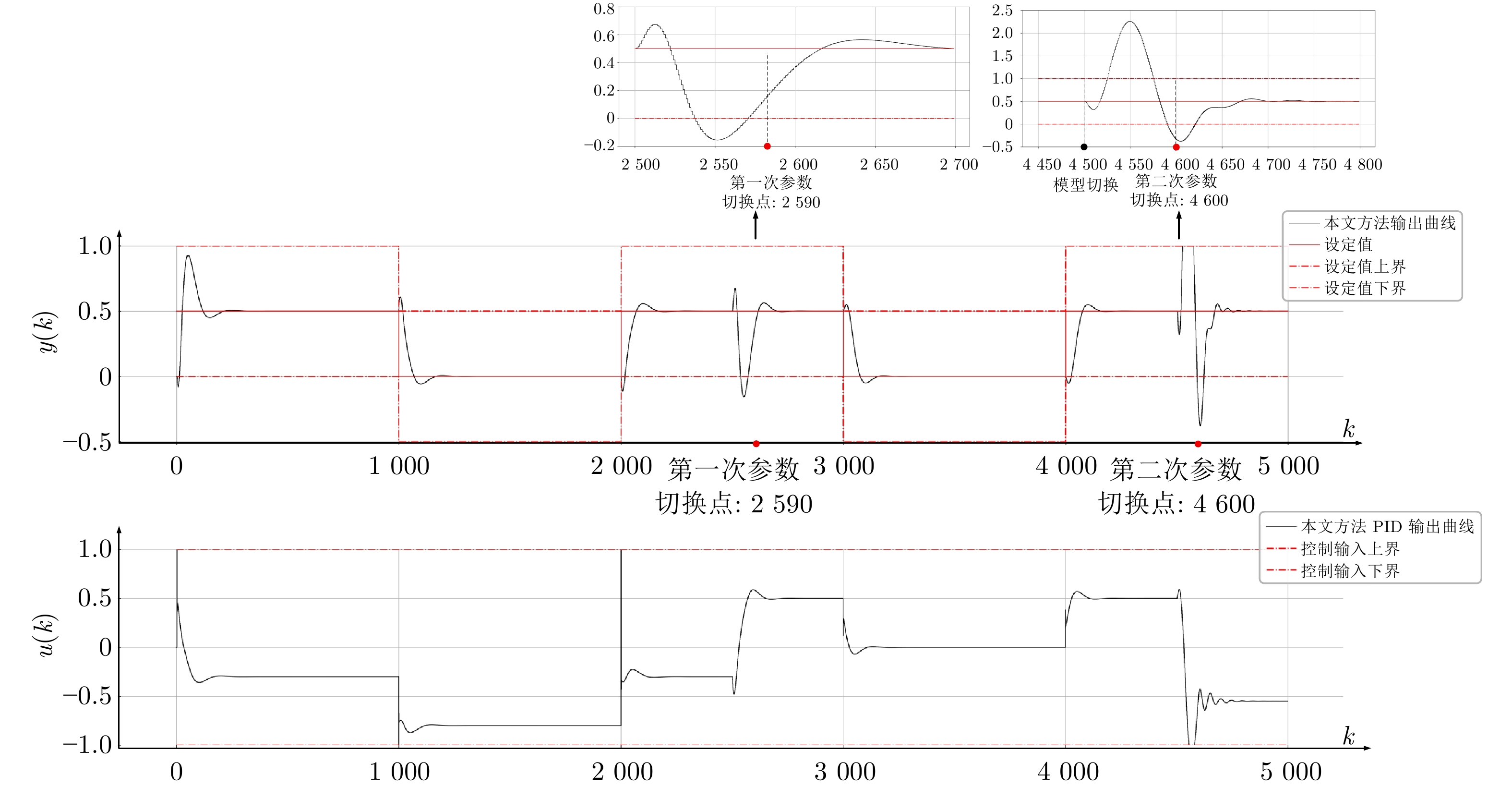
表 1 仿真被控模型西门子、倍福与本文控制性能指标对比
Table 1 Comparison of control performance indicators of the simulated controlled model among Siemens, Beckhoff, and this article
性能指标 $ 0 \leq k< 2\;590 $ $ 2\;590 \leq k< 4\;600 $ $ 4\;600 \leq k \leq 5\;000 $ $ J_e $ $ \bar{J}_e $ $ \bar{J}_u $ $ J_e $ $ \bar{J}_e $ $ \bar{J}_u $ $ J_e $ $ \bar{J}_e $ $ \bar{J}_u $ 西门子 0.026 0.041 0.000 0.112 0.067 0.013 0.132 0.135 0.018 倍福 0.019 0.039 0.000 0.063 0.053 0.017 3.181 0.848 0.620 本文 0.018 0.031 0.000 0.060 0.051 0.012 0.036 0.052 0.000 表 2 换热装置西门子、倍福与本文控制性能指标对比
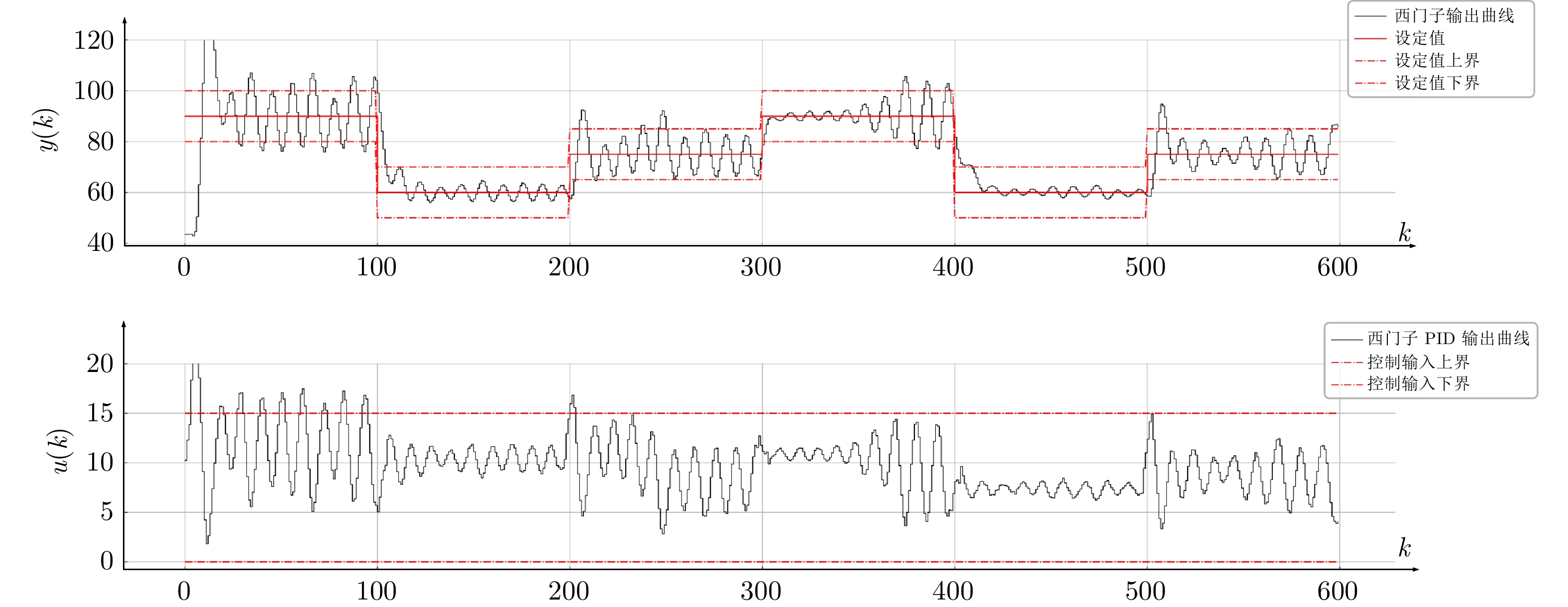
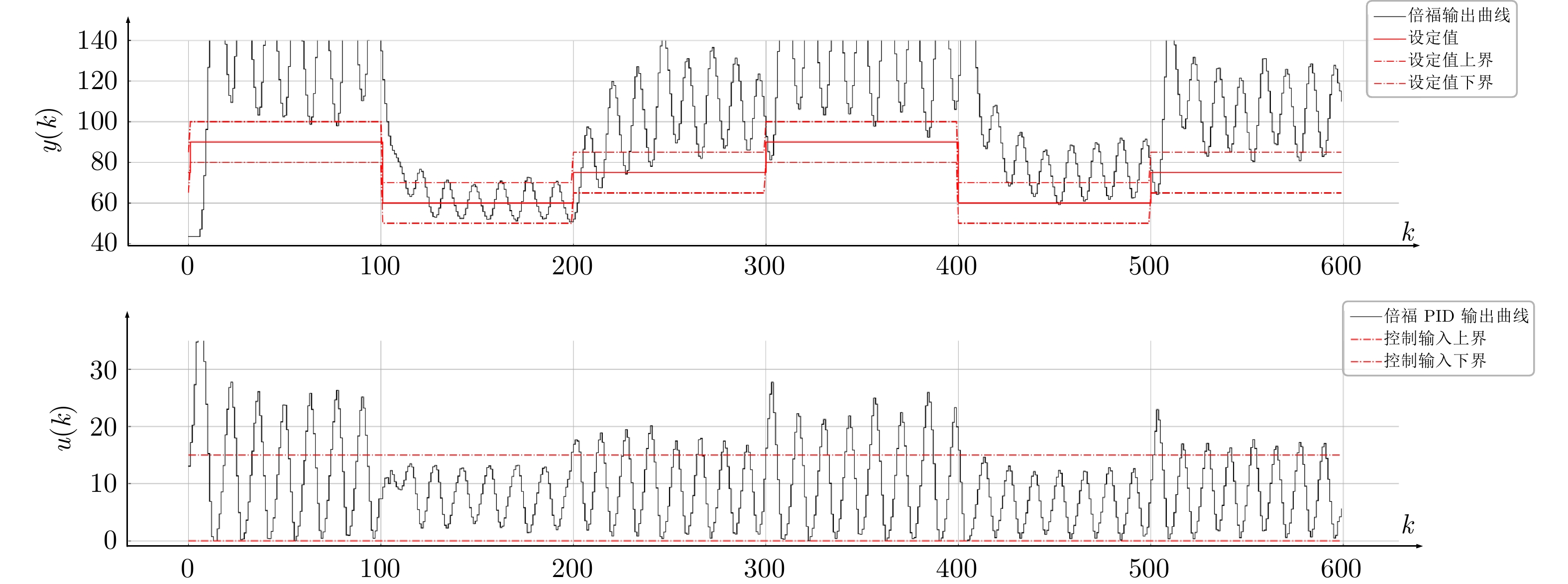
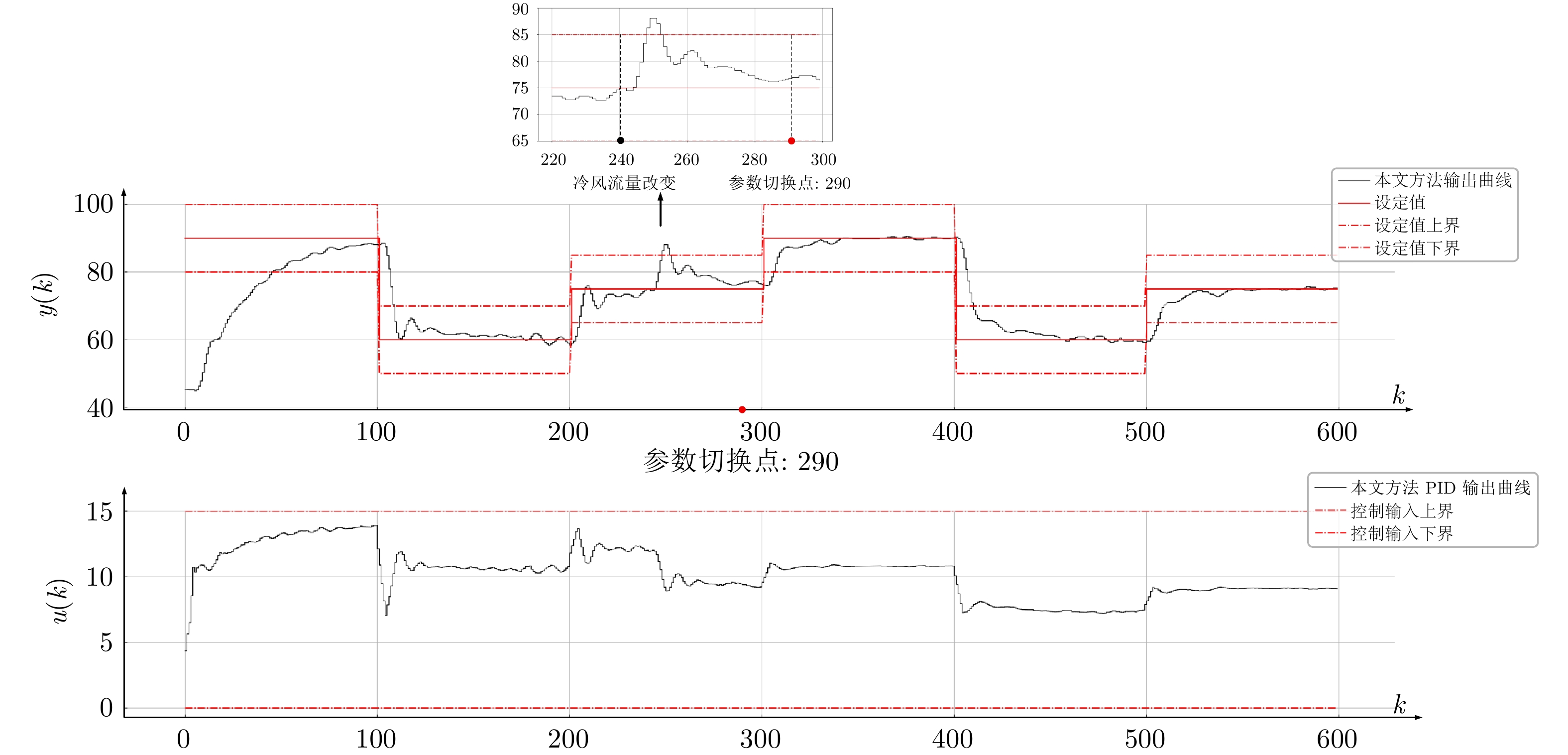
Table 2 Comparison of control performance indicators of the heat exchange device among Siemens, Beckhoff, and this article
性能指标 $ 0 \leq k< 290 $ $ 290 \leq k \leq 600 $ $ J_e $ $ \bar{J}_e $ $ \bar{J}_u $ $ J_e $ $ \bar{J}_e $ $ \bar{J}_u $ 西门子 215.18 0.379 0.17 56.45 0.177 0.04 倍福 1 915.88 0.651 0.26 2 118.48 0.765 0.25 本文 163.21 0.207 0.00 28.13 0.064 0.00 -
[1] Gaffurini M, Bellagente P, Depari A, Flammini A, Sisinni E, Ferrari P. Virtual PLC in industrial edge platform: Performance evaluation of supervision and control communication. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2024, 73: 1−10 [2] 柴天佑. 工业人工智能与工业互联网协同实现生产过程智能化及其未来展望. 控制工程, 2023, 30(8): 1378−1388Chai Tian-You. Industrial AI and industrial internet collaboratively achieving production process intelligence and its future perspectives. Control Engineering of China, 2023, 30(8): 1378−1388 [3] Perez D J, Waltl J, Prenzel L, Steinhorst S. How real (time) are virtual PLCs? In: Proceedings of the 27th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation. Stuttgart, Germany: IEEE, 2022. 1−8 [4] Cruz T, Simões P, Monteiro E. Virtualizing programmable logic controllers: Toward a convergent approach. IEEE Embedded Systems Letters, 2016, 8(4): 69−72 doi: 10.1109/LES.2016.2608418 [5] Hegazy T, Hefeeda M. Industrial automation as a cloud service. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 2014, 26(10): 2750−2763 [6] Xia Y Q, Zhang Y, Dai L, Zhan Y F, Guo Z H. A brief survey on recent advances in cloud control systems. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems II: Express Briefs, 2022, 69(7): 3108−3114 [7] Shi W S, Cao J, Zhang Q, Li Y H Z, Xu L Y. Edge computing: Vision and challenges. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(5): 637−646 doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2579198 [8] Sollfrank M, Loch F, Denteneer S, Vogel-Heuser B. Evaluating docker for lightweight virtualization of distributed and time-sensitive applications in industrial automation. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 17(5): 3566−3576 [9] Vyatkin V. IEC 61499 as enabler of distributed and intelligent automation: State-of-the-art review. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2011, 7(4): 768−781 doi: 10.1109/TII.2011.2166785 [10] Lyu G, Brennan R W. Towards IEC 61499-based distributed intelligent automation: A literature review. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 17(4): 2295−2306 [11] Dai W B, Zhang Y Y, Kong L B, Christensen J H, Huang D. Design of industrial edge applications based on IEC 61499 microservices and containers. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 19(7): 7925−7935 [12] Jin J, Pang Z B, Kua J, Zhu Q Y, Johansson K H, Marchenko N. Cloud-fog automation: The new paradigm towards autonomous industrial cyber-physical systems. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2025, 43(9): 2917−2937 doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2025.3574587 [13] 柴天佑, 郑锐, 贾瑶, 黄新宇, 宋延杰. 软件定义智能控制系统未来发展展望. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2025, 46(7): 1−10Chai Tian-You, Zheng Rui, Jia Yao, Huang Xin-Yu, Song Yan-Jie. Development and prospects for software-defined intelligent control systems. Journal of Northeastern University (Natural Science), 2025, 46(7): 1−10 [14] Guo L. Feedback and uncertainty: Some basic problems and results. Annual Reviews in Control, 2020, 49: 27−36 doi: 10.1016/j.arcontrol.2020.04.001 [15] Samad T. Technical activities: A survey on industry impact and challenges thereof. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2017, 37(1): 17−18 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2016.2621438 [16] Borase R P, Maghade D K, Sondkar S Y, Pawar S N. A review of PID control, tuning methods and applications. International Journal of Dynamics and Control, 2021, 9(2): 818−827 doi: 10.1007/s40435-020-00665-4 [17] Åström K J, Hägglund T. PID Controllers: Theory, Design and Tuning (Second Edition). Research Triangle Park: ISA, 1995. 64−69 [18] 柴天佑, 郑锐, 邢方新, 贾瑶, 郑秀萍. 工业过程控制智能化及未来发展展望. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2025, 55(7): 1555−1570 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2025-0108Chai Tian-You, Zheng Rui, Xing Fang-Xin, Jia Yao, Zheng Xiu-Ping. Intelligence for industrial process control: Development and prospects. Scientia Sinica (Informationis), 2025, 55(7): 1555−1570 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2025-0108 [19] Garpinger O, Hägglund T, Åström K J. Performance and robustness trade-offs in PID control. Journal of Process Control, 2014, 24(5): 568−577 doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2014.02.020 [20] Ortega R, Kelly R. PID self-tuners: Some theoretical and practical aspects. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2007, 31(4): 332−338 [21] Kim J H, Choi K K. Design of direct pole placement PID self-tuners. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 1987, 34(3): 351−356 [22] Wang Q G, Zhang Z P, Karl J A, Zhang Y, Zhang Y. Guaranteed dominant pole placement with PID controllers. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2008, 41(2): 5842−5845 doi: 10.3182/20080706-5-KR-1001.00985 [23] Ho W K, Lee T H, Han H P, Hong Y. Self-tuning IMC-PID control with interval gain and phase margins assignment. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2002, 9(3): 535−541 [24] Verma B, Padhy P K. Indirect IMC-PID controller design. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2019, 13(2): 297−305 [25] Åström K J, Panagopoulos H, Hägglund T. Design of PI controllers based on non-convex optimization. Automatica, 1998, 34(5): 585−601 doi: 10.1016/S0005-1098(98)00011-9 [26] Sekara T B, Matausek M R. Optimization of PID controller based on maximization of the proportional gain under constraints on robustness and sensitivity to measurement noise. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(1): 184−189 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2008.2008359 [27] Mercader P, Åström K J, Baños A, Hägglund T. Robust PID design based on QFT and convex-concave optimization. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2016, 25(2): 441−452 [28] 刘宁, 柴天佑. PID控制器参数的优化整定方法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(11): 2272−2285Liu Ning, Chai Tian-You. An optimal tuning method of PID controller parameters. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(11): 2272−2285 [29] Ziegler J G, Nichols N B. Optimum settings for automatic controllers. Transactions of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1942, 64(8): 759−765 doi: 10.1115/1.4019264 [30] Chien K L, Hrones J A, Reswick J B. On the automatic control of generalized passive systems. Transactions of the American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 1952, 74(2): 175−183 doi: 10.1115/1.4015724 [31] 柴天佑, 周正, 郑锐, 刘宁, 贾瑶. 端边云协同的PID整定智能系统. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(3): 514−527Chai Tian-You, Zhou Zheng, Zheng Rui, Liu Ning, Jia Yao. PID tuning intelligent system based on end-edge-cloud collaboration. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(3): 514−527 [32] Chai T Y, Xing F X, Zheng R, Jia Y, Song Y J. An anti-latency intelligent control for 5G wireless networks based on end-edge-cloud collaboration. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, DOI: 10.1109/JSAC.2025.3574593 [33] 柴天佑, 丁进良. 流程工业智能优化制造. 中国工程科学, 2018, 20(4): 51−58 doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2018.04.009Chai Tian-You, Ding Jin-Liang. Smart and optimal manufacturing for process industry. Strategic Study of CAE, 2018, 20(4): 51−58 doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2018.04.009 [34] 柴天佑, 刘强, 丁进良, 卢绍文, 宋延杰. 工业互联网驱动的流程工业智能优化制造新模式研究展望. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2022, 52(1): 14−25 doi: 10.1360/SST-2021-0405Chai Tian-You, Liu Qiang, Ding Jin-Liang, Lu Shao-Wen, Song Yan-Jie. Perspectives on industrial-internet-driven intelligent optimized manufacturing mode for process industries. Scientia Sinica (Technologica), 2022, 52(1): 14−25 doi: 10.1360/SST-2021-0405 [35] Rolf I. Digital Control Systems. Berlin Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag, 2013. [36] Chai T Y, Zhang J W, Yang T. Demand forecasting of the fused magnesia smelting process with system identification and deep learning. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2021, 17(12): 8387−8396 doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3065930 [37] Hochreiter S, Schmidhuber J. Long short-term memory. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735−1780 doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [38] Cavalieri S, Chiacchio F. Analysis of OPC UA performances. Computer Standards and Interfaces, 2013, 36(1): 165−177 [39] Nie Z Y, Li Z Y, Wang Q G, Gao Z Q, Luo J L. A unifying Ziegler-nichols tuning method based on active disturbance rejection. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2022, 32(18): 9525−9541 doi: 10.1002/rnc.5848 -




 下载:
下载: