Conditional Diffusion Model-based Imputation Method for Missing Satellite Telemetry Data
-
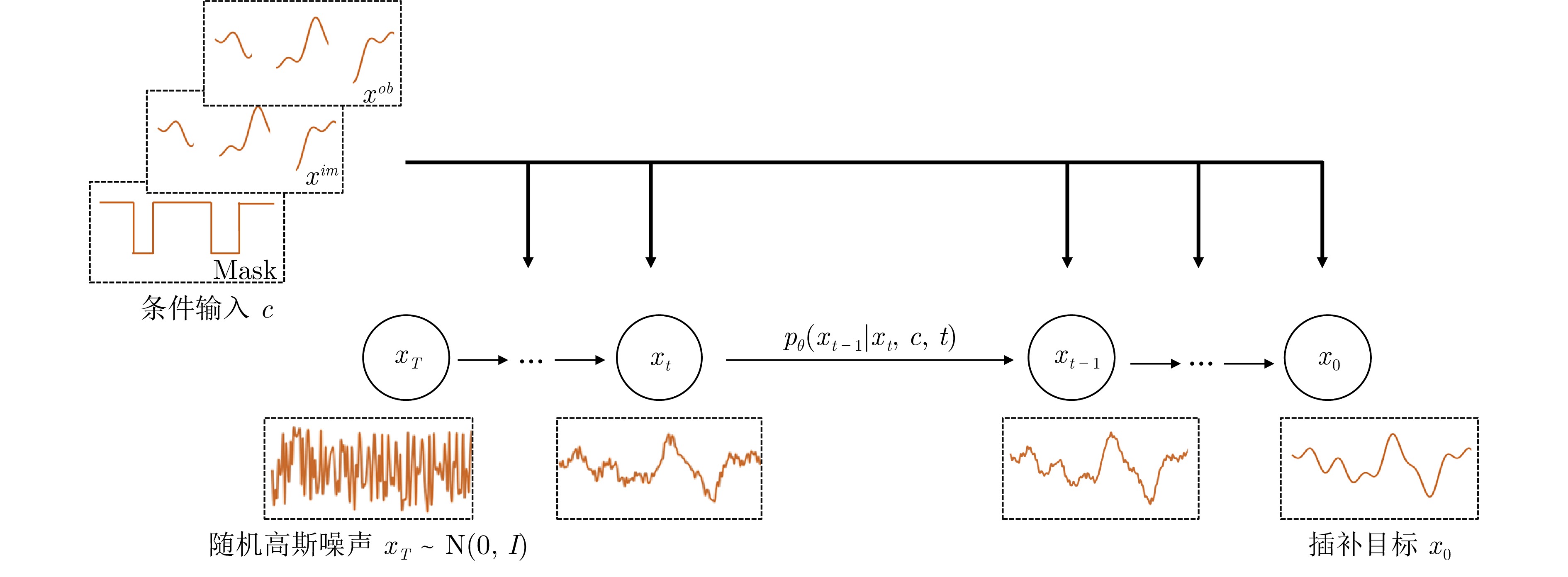
摘要: 卫星遥测时间序列数据在遥感监测、导航定位等领域具有重要应用价值, 同时也能有效监控卫星的健康状态. 然而, 这些数据常常因传感器故障、数据传输错误等复杂因素出现缺失, 严重影响数据的完整性和可用性, 甚至可能导致决策失误. 对此, 提出基于多变量条件扩散模型的卫星时间序列补全方法, 旨在提高卫星遥测数据缺失值插补的准确性. 首先, 通过引入条件扩散方法, 将观测到的卫星数据作为条件输入, 通过建模缺失值的后验分布来生成数据, 并在生成过程中对该残缺样本进行初步的线性插补, 从而提高模型的稳定性. 其次, 设计由时间注意力层和门控激活单元组成的残差模块作为主干预测网络, 对多维遥测数据中的时间依赖关系进行充分捕捉, 实现对缺失数据的精准重构. 最后, 在某通信卫星的动量轮遥测数据集以及公开的时间序列数据集上进行广泛实验. 实验结果表明, 所提方法在不同缺失率下均表现出良好的性能和泛化能力, 与现有方法相比, 展现出更高的准确性和稳定性.Abstract: Satellite telemetry time-series data is critically valuable for applications like remote sensing monitoring and navigation positioning, and is also effective for monitoring satellite health status. However, these data often suffer from missing values caused by complex factors such as sensor malfunctions and data transmission errors, which severely impair data integrity and usability, potentially leading to erroneous decisions. To address this, a satellite time-series completion method based on multivariate conditional diffusion model is proposed to improve the accuracy of missing value imputation in satellite telemetry data. The method first incorporates a conditional diffusion method that uses observed satellite data as conditional input to generate data by modeling the posterior distribution of the missing values. Preliminary linear imputation is applied to the incomplete samples during generation to enhance the stability of the model. Furthermore, a residual module integrating a temporal attention layer and a gated activation unit serves as the core prediction network, effectively capturing temporal dependencies in the multivariate telemetry data for precise reconstruction of missing values. Finally, Extensive experiments were conducted on a momentum wheel telemetry dataset from a communications satellite and on public time-series datasets. The experimental results show that the proposed method delivers robust performance and generalization ability across varying missing rates, outperforming existing methods in both accuracy and stability.
-
Key words:
- Diffusion models /
- satellite telemetry data /
- time-series imputation /
- deep learning
-
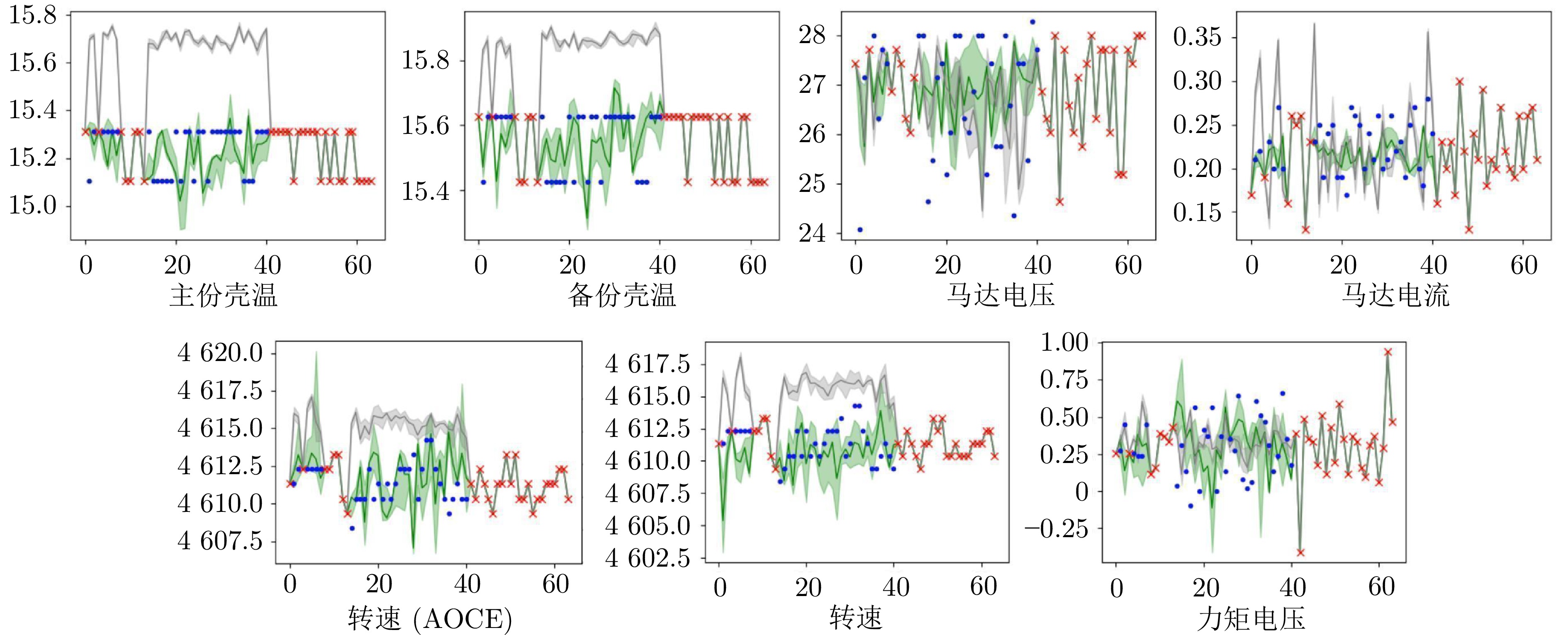
表 1 动量轮数据集
Table 1 Momentum wheel dataset
序号 具体信息 $ \dfrac{均值}{标准差}$ 1 主份壳温 $ \dfrac{15.81}{\;\;3.55}$ 2 备份壳温 $ \dfrac{15.80}{\;\;3.47}$ 3 马达电压 $ \dfrac{26.96}{\;\;1.20}$ 4 马达电流 $ \dfrac{0.23}{0.07}$ 5 转速(AOCE) $ \dfrac{4\;836.45}{\;\;\;113.49}$ 6 转速 $ \dfrac{4\;836.71}{\;\;\;125.53}$ 7 力矩电压 $ \dfrac{0.22}{0.50}$ 表 2 数据集A与数据集B具体细节
Table 2 Specific details of dataset A and dataset B
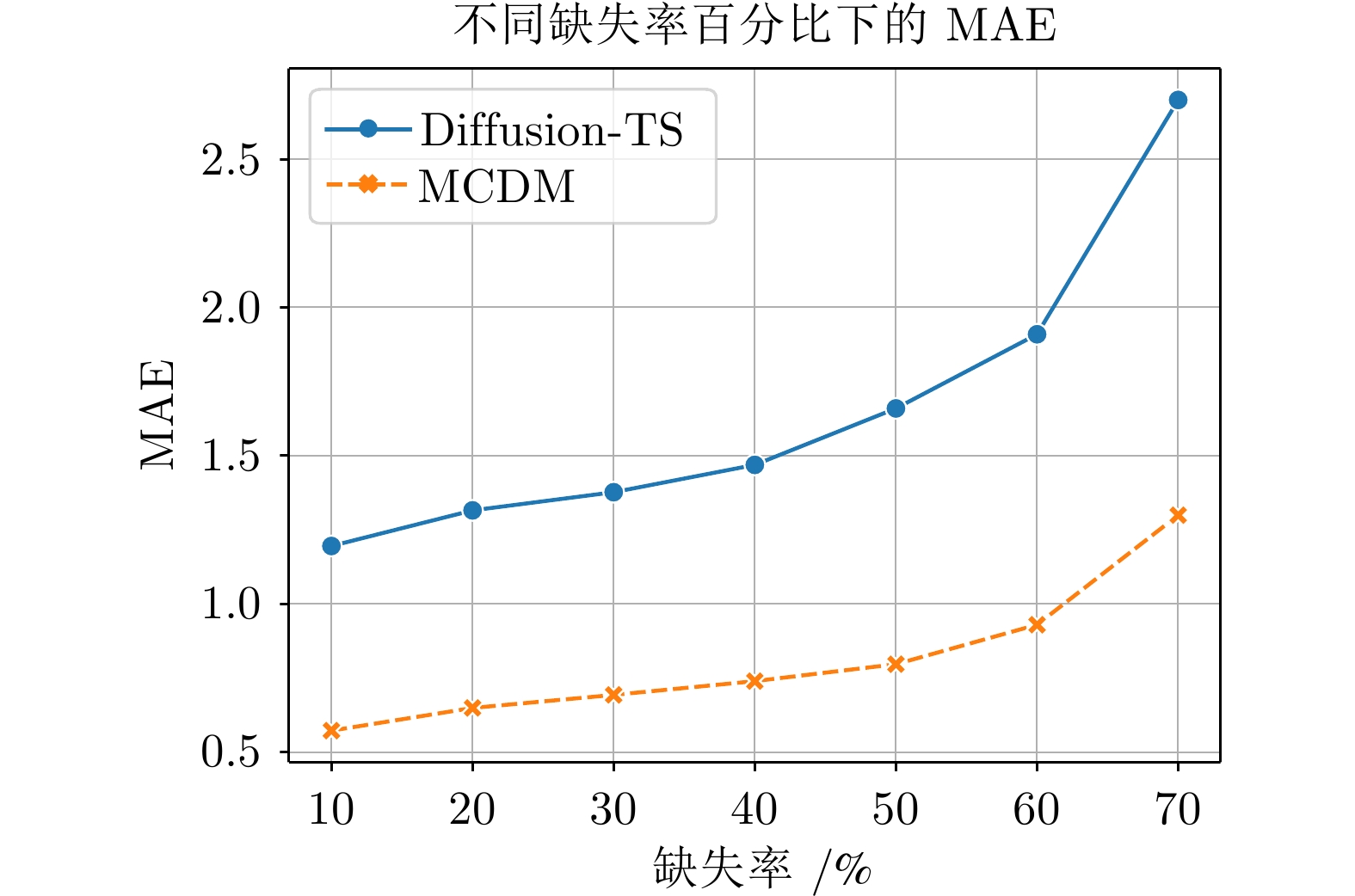
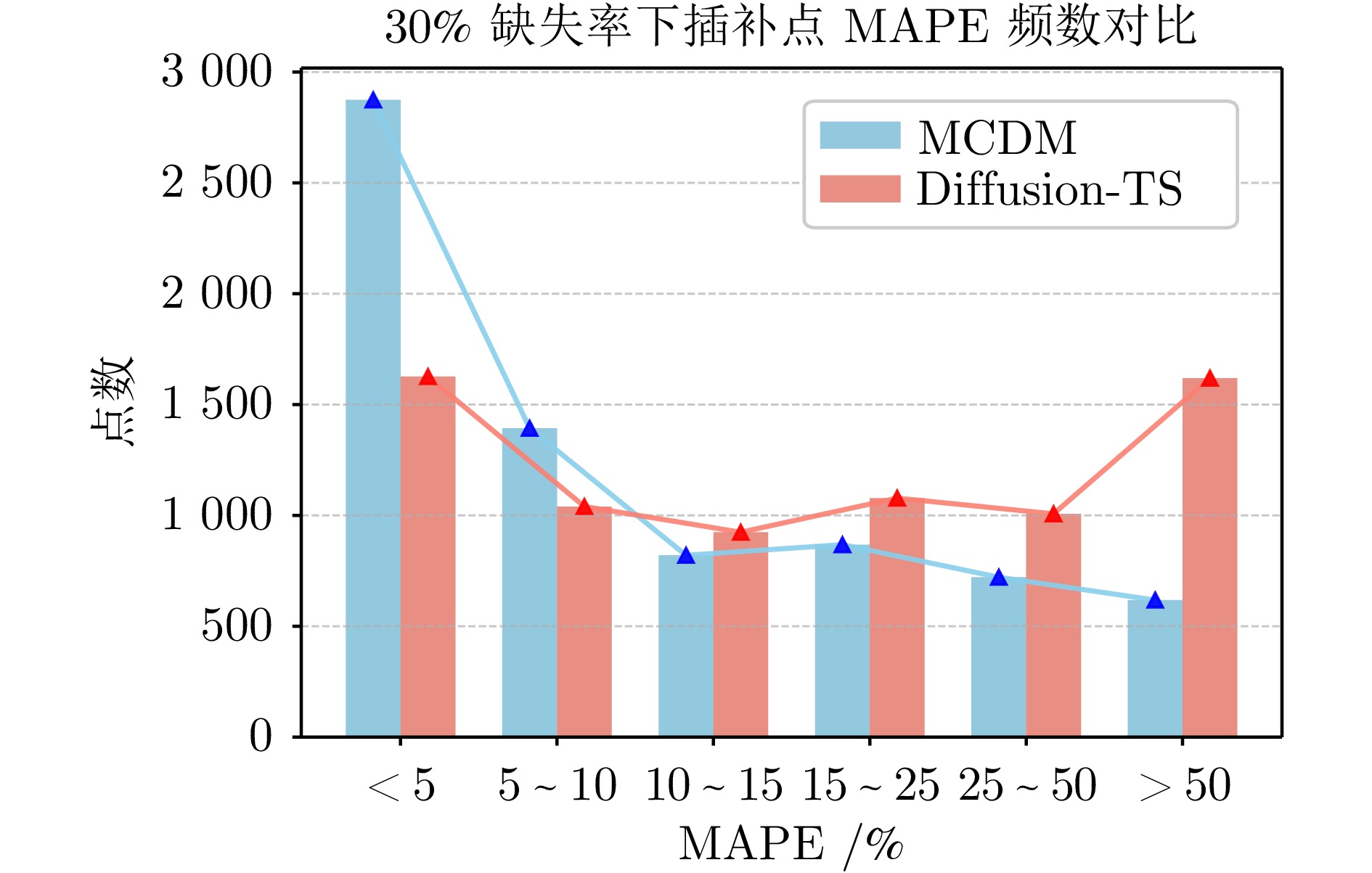
数据集A 数据集B 训练样本集 400 8000 验证和测试样本集 100 2000 总计样本集 500 10000 单个样本序列长度 64 100 样本特征维度 7 14 表 3 MCDM和Diffusion-TS在不同缺失率下的实验结果对比(MAE)
Table 3 Experimental results comparison of MCDM and Diffusion-TS under different missing rates (MAE)
缺失率 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% Diffusion-TS[34] 1.19 1.31 1.37 1.46 1.66 MCDM 0.57 0.66 0.68 0.73 0.80 表 4 在数据集B (MuJoCo)中, 不同缺失率下的插补 结果均方误差(MSE), 所有结果均乘以1e−3
Table 4 In dataset B (MuJoCo), the mean squared error (MSE) of imputation results under different missing rates, with all results multiplied by 1e−3
-
[1] 袁利, 王淑一. 航天器控制系统智能健康管理技术发展综述. 航空学报, 2021, 42(4): 122−136Yuan Li, Wang Shu-Yi. A review on development of intelligent health management technology for space-craft control systems. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(4): 122−136 [2] Yairi T, Takeisi N, Oda T, Nakajima Y, Nishimura N, Takata N. A data-driven health monitoring method for satellite housekeeping data based on probabilistic clustering and dimensionality reduction. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2017, 53(3): 1384−1401 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2017.2671247 [3] 刘切, 李嘉玺, 王泽煜, 陈小龙. 基于遥测数据特征预测的轻量化航天器异常检测. 宇航学报, 2025, 46(2): 232−243Liu Qie, Li Jia-Xi, Wang Ze-Yu, Chen Xiao-Long. Lightweight spacecraft anomaly detection based on telemetry data feature prediction. Journal of Astronautics, 2025, 46(2): 232−243 [4] 詹兆康, 胡旭光, 赵浩然, 张思琪, 张峻凯, 马大中. 基于多变量时空融合网络的风机数据缺失值插补研究. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(6): 1171−1184Zhan Zhao-Kang, Hu Xu-Guang, Zhao Hao-Ran, Zhang Si-Qi, Zhang Jun-Kai, Ma Da-Zhong. Study of missingvalue imputation in wind turbine data based on multivariate spatiotemporal integration network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(6): 1171−1184 [5] 许美玲, 邢通, 韩敏. 基于时空Kriging方法的时空数据插值研究. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(8): 1681−1688Xu Mei-Ling, Xing Tong, Han Min. Spatial-temporal data interpolation based on spatial-temporal Kriging method. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1681−1688 [6] Wu H, Xu J, Wang J, Long M. Autoformer: Decomposition transformers with auto-correlation for long-term series forecasting. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Virtual Event: Curran Associates, 2021. 22419−22430 [7] Zhou H, Zhang S, Peng J, Zhang S, Li J, Xiong H, et al. Informer: Beyond efficient Transformer for long sequence time-series forecasting. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Virtual Event: AAAI Press, 2021. 11106−11115 [8] Box G E P, Jenkins G M, Reinsel G C, Ljung G M. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2015. [9] 马友, 贾树泽, 赵现纲, 冯小虎, 范存群, 朱爱军. 基于张量分解的卫星遥测缺失数据预测算法. 电子与信息学报, 2020, 42(2): 403−409 doi: 10.11999/JEIT180728Ma You, Jia Shu-Ze, Zhao Xian-Gang, Feng Xiao-Hu, Fan Cun-Qun, Zhu Ai-Jun. Missing telemetry data prediction algorithm via tensor factorization. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2020, 42(2): 403−409 doi: 10.11999/JEIT180728 [10] 蒋珂, 蒋朝辉, 谢永芳, 潘冬, 桂卫华. 基于动态注意力深度迁移网络的高炉铁水硅含量在线预测方法. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(5): 949−963Jiang Ke, Jiang Zhao-Hui, Xie Yong-Fang, Pan Dong, Gui Wei-Hua. Online prediction method for silicon content of molten iron in blast furnace based on dynamic attention deep transfer network. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(5): 949−963 [11] 刘雨蒙, 郑旭, 田玲, 王宏安. 基于时序图推理的设备剩余使用寿命预测. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(1): 76−88Liu Yu-Meng, Zheng Xu, Tian Ling, Wang Hong-An. Remaining useful life estimation of facilities based on reasoning over temporal graphs. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(1): 76−88 [12] Li T, Baireddy S, Comer M, Delp E, Desai S R, Foster R H, et al. Multichannel anomaly detection for spacecraft time series using MAP estimation. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(5): 5842−5855 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3400943 [13] Zhang J, Huang C, Chow M Y, Li X, Tian J, Luo H, et al. A data-model interactive remaining useful life prediction approach of lithium-ion batteries based on PF-BiGRU-TSAM. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 20(2): 1144−1154 [14] Hundman K, Constantinou V, Laporte C, Colwell I, Soderstrom T. Detecting spacecraft anomalies using LSTMs and nonparametric dynamic thresholding. In: Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining. London, UK: ACM, 2018. 387−395 [15] Lin L, Wu J, Fu S, Zhang S, Tong C, Zu L. Channel attention & temporal attention based temporal convolutional network: A dual attention framework for remaining useful life prediction of the aircraft engines. Advanced Engineering Informatics, 2024, 60: Article No. 102372 doi: 10.1016/j.aei.2024.102372 [16] Ahmadzadeh F, Lundberg J. Remaining useful life estimation: Review. International Journal of System Assurance Engineering and Management, 2014, 5(4): 461−474 [17] 许凯凯, 张锐. 基于SE-TCN的一维低采样卫星帆板温度遥测数据插补方法. 中国科学院大学学报, 2023, 40(6): 810−820Xu Kai-Kai, Zhang Rui. An interpolation method for temperature telemetry data of one-dimensional low-sampling satellite panel based on SE-TCN. Journal of University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2023, 40(6): 810−820 [18] 张博玮, 郑建飞, 胡昌华, 裴洪, 董青. 基于流模型的缺失数据生成方法在剩余寿命预测中的应用. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(1): 185−196Zhang Bo-Wei, Zheng Jian-Fei, Hu Chang-Hua, Pei Hong, Dong Qing. Missing data generation method based on flow model and its application in remaining life prediction. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(1): 185−196 [19] Li X, Tian Y, Ye P, Duan H, Wang F. A novel scenarios engineering methodology for foundation models in metaverse. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 53(4): 2148−2159 [20] Li X, Duan H, Liu B, Wang X, Wang F. A novel framework to generate synthetic video for foreground detection in highway surveillance scenarios. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(6): 5958−5970 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3253919 [21] Yoon J, Jarrett D, Schaar M. Time-series generative adversarial networks. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates, 2019. 1−11 [22] Qi M, Qin J, Wu Y, Yang Y. Imitative non-autoregressive modeling for trajectory forecasting and imputation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Virtual Event: IEEE Computer Society, 2020. 12736−12745 [23] Kingma D P, Welling M. Auto-encoding variational bayes. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.6114, 2013. [24] Goodfellow I J, Pouget-Abadie J, Mirza M, Xu B, Warde-Farley D, Ozair S, et al. Generative adversarial nets. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Montreal, Canada: Curran Associates, 2014. 1−9 [25] Ho J, Jain A, Abbeel P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates, 2020. 6840−6851 [26] Yang Y, Jin M, Wen H, Zhang C, Liang Y, Ma L, et al. A survey on diffusion models for time series and spatio-temporal data. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2404.18886, 2024. [27] 赵浩天, 邱实, 刘明, 盖琦超, 曹喜滨. 基于全生命周期数据驱动的通讯卫星行波管退化评估方法. 航空学报, 2025, 46(9): 262−279Zhao Hao-Tian, Qiu Shi, Liu Ming, Gai Qi-Chao, Cao Xi-Bin. Degradation evaluation method for communication satellite traveling wave tubes based on full life cycle data. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2025, 46(9): 262−279 [28] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez A, et al. Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates, 2017. 1−11 [29] Kong Z, Ping W, Huang J, Zhao K, Catanzaro B. Diffwave: A versatile diffusion model for audio synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2009.09761, 2020. [30] Rubanova Y, Chen R T Q, Duvenaud D K. Latent ordinary differential equations for irregularly-sampled time series. In: Proceedings of Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates, 2019. [31] Che Z, Purushotham S, Cho K, Sontag D, Liu Y. Recurrent neural networks for multivariate time series with missing values. Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1): Article No. 6085 doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24271-9 [32] Shan S, Li Y, Oliva J B. NRTSI: Non-recurrent time series imputation. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Rhodes Island, Greece: IEEE, 2023. 1−5 [33] Alcaraz J M L, Strodthoff N. Diffusion-based time series imputation and forecasting with structured state space models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2208.09399, 2022. [34] Yuan X, Qiao Y. Diffusion-TS: Interpretable diffusion for general time series generation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2403.01742, 2024. -




 下载:
下载: