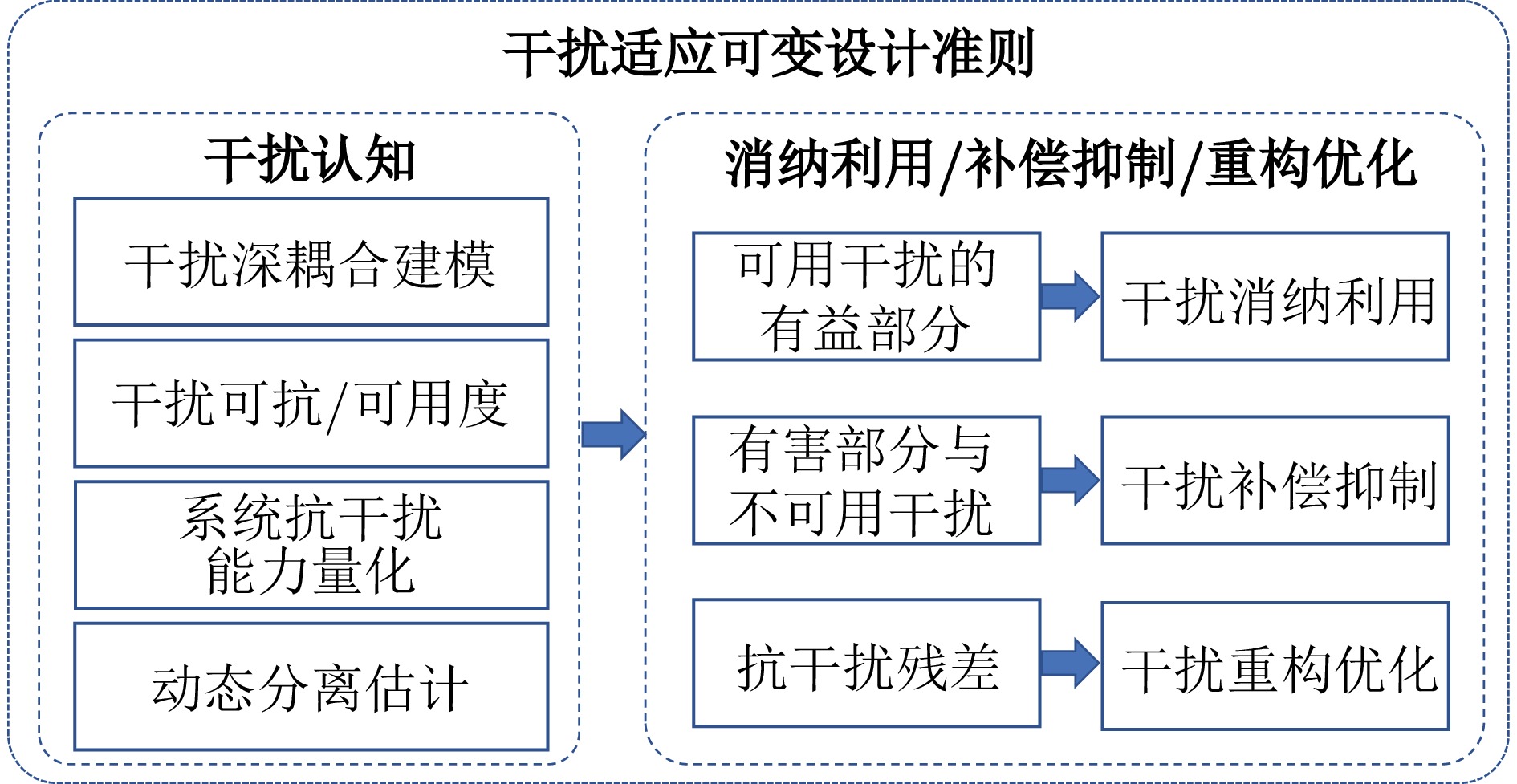
|
[1]
|
Schipanov G. Theory and methods of designing automatic regulators. Automatika in Telemekhanika, 1939, 4(1): 49−66
|
|
[2]
|
Luzin N N. Absolute invariance and ${\epsilon} $-invariance in the theory of differential equations. Dokl Akad Nauk SSSR, 1946, 51(4): 251−253
|
|
[3]
|
Petrov B N. The invariance principle and the conditions for its application during the calculation of linear and non-linear systems. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1960, 1(1): 127−135 doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)70045-6
|
|
[4]
|
Kulebakin V S. The theory of invariance of regulating and control systems. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1960, 1(1): 116−126 doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)70044-4
|
|
[5]
|
乌兰诺夫 [著], 胡保生 [译]. 扰动调节. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 1963.yJaHoB [Author], Hu Bao-Sheng [Translator]. Disturbance Adjusting. Shanghai: Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers, 1963.
|
|
[6]
|
Ashby W R. An Introduction to Cybernetics. New York: Wiley, 1956.
|
|
[7]
|
Preminger J, Rootenberg J. Some considerations relating to control systems employing the invariance principle. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1964, 9(3): 209−215 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1964.1105722
|
|
[8]
|
Prigogine I, Stengers I. The End of Certainty: Time, Chaos, and the New Laws of Nature. New York: Simon and Schuster, 1997.
|
|
[9]
|
冯纯伯. 鲁棒控制系统设计. 南京: 东南大学出版社, 1995.Feng Chun-Bo. Robust Control System Design. Nanjing: Southeast University Press, 1995.
|
|
[10]
|
陈翰馥, 郭雷. 现代控制理论的若干进展及展望. 科学通报, 1998, 43(1): 1−7Chen Han-Fu, Guo Lei. Progress and prospects of modern control theory. Chinese Science Bulletin, 1998, 43(1): 1−7
|
|
[11]
|
郭雷, 冯纯伯. 一类具有非线性不确定性系统的鲁棒H∞ 控制. 控制理论与应用, 1999, 16(4): 619−620Guo Lei, Feng Chun-Bo. Robust H∞ control for a class of systems with nonlinear uncertainties. Control Theory and Applications, 1999, 16(4): 619−620
|
|
[12]
|
黄琳, 段志生. 控制科学中的复杂性. 自动化学报, 2003, 29(5): 748−754Huang Lin, Duan Zhi-Sheng. Complexity in control science. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2003, 29(5): 748−754
|
|
[13]
|
郭雷. 不确定性动态系统的估计、控制与博弈. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2020, 50(9): 1327−1344 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0277Guo Lei. Estimation, control, and games of dynamical systems with uncertainty. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2020, 50(9): 1327−1344 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2020-0277
|
|
[14]
|
郭雷, 李文硕, 崔洋洋, 朱玉凯, 章健淳, 余翔, 等. 动态闭环不确定性量化理论与智能无人系统应用. 中国科学: 技术科学, 2025, 55(1): 1−13 doi: 10.1360/SST-2024-0155Guo Lei, Li Wen-Shuo, Cui Yang-Yang, Zhu Yu-Kai, Zhang Jian-Chun, Yu Xiang, et al. Dynamic closed-loop uncertainty quantification theory with intelligent unmanned systems applications. Scientia Sinica Technologica, 2025, 55(1): 1−13 doi: 10.1360/SST-2024-0155
|
|
[15]
|
郭雷, 朱玉凯, 乔建忠, 郭康, 包为民. 无人系统生存智能与安全、免疫、绿色控制技术. 航空学报, 2022, 43(10): Article No. 527129Guo Lei, Zhu Yu-Kai, Qiao Jian-Zhong, Guo Kang, Bao Wei-Min. Survival intelligence and safety, immunity and green control technologies for unmanned systems. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(10): Article No. 527129
|
|
[16]
|
Tian G, Gao Z Q. From Poncelet's invariance principle to active disturbance rejection. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference. St. Louis, USA: IEEE, 2009. 2451−2457
|
|
[17]
|
Guo L, Cao S Y. Anti-disturbance Control for Systems With Multiple Disturbances. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2014.
|
|
[18]
|
Guo L, Cao S Y. Anti-disturbance control theory for systems with multiple disturbances: A survey. ISA Transactions, 2014, 53(4): 846−849 doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2013.10.005
|
|
[19]
|
Chen W H, Yang J, Guo L, Li S H. Disturbance-observer-based control and related methods——An overview. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(2): 1083−1095 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2015.2478397
|
|
[20]
|
郭雷, 朱玉凯. 多源干扰系统复合自主抗干扰控制技术(中国科研信息化蓝皮书). 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2020. 210−220Guo Lei, Zhu Yu-Kai. Composite Autonomous Anti Disturbance Control for Systems With Multiple Disturbances (Chapter of Chinese E-Science Blue Book 2020). Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2020. 210−220
|
|
[21]
|
温婷, 何奎, 宋薇萍. 科技产业联动2023外滩大会“探路”可持续发展未来. 上海证券报, 2023-09-08 (004)Wen Ting, He Kui, Song Wei-Ping. Technology and industry collaborate at the 2023 inclusion conference on the bund to explore a sustainable future. Shanghai Securities News, 2023-09-08 (004
|
|
[22]
|
Jordan M I. Statistical contract theory [Online], available: https://www.emergentmind.com/topics/statistical-contract-theory, August 9, 2025
|
|
[23]
|
Bhattacharyyta S P. Disturbance rejection in linear systems. International Journal of Systems Science, 1974, 5(7): 633−637 doi: 10.1080/00207727408920129
|
|
[24]
|
Bhattacharyya S. Compensator design based on the invariance principle. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1975, 20(5): 708−711 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1975.1101044
|
|
[25]
|
Guo L, Li W S, Zhu Y K, Yu X, Wang Z D. Composite disturbance filtering: A novel state estimation scheme for systems with multisource, heterogeneous, and isomeric disturbances. IEEE Open Journal of the Industrial Electronics Society, 2023, 4: 387−400 doi: 10.1109/OJIES.2023.3317271
|
|
[26]
|
Davison E J, Smith H W. Pole assignment in linear time-invariant multivariable systems with constant disturbances. Automatica, 1971, 7(4): 489−498 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(71)90099-9
|
|
[27]
|
Davison E J. The output control of linear time-invariant multivariable systems with unmeasurable arbitrary disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1972, 17(5): 621−630 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1972.1100084
|
|
[28]
|
Johnson C. Optimal control of the linear regulator with constant disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1968, 13(4): 416−421 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1968.1098947
|
|
[29]
|
Johnson C. Accomodation of external disturbances in linear regulator and servomechanism problems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1971, 16(6): 635−644 doi: 10.1109/TAC.1971.1099830
|
|
[30]
|
Ohishi K, Ohnishi K, Miyachi K. Torque-speed regulation of DC motor based on load torque estimation method. In: Proceedings of the JIEE/International Power Electronics Conference. Tokyo, Japan: JIEE, 1983. 1209−1218
|
|
[31]
|
Chen W H, Ballance D J, Gawthrop P J, O'Reilly J. A nonlinear disturbance observer for robotic manipulators. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2000, 47(4): 932−938 doi: 10.1109/41.857974
|
|
[32]
|
Han J Q. From PID to active disturbance rejection control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(3): 900−906 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.2011621
|
|
[33]
|
Gao Z Q. Active disturbance rejection control: A paradigm shift in feedback control system design. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference. Minneapolis, USA: IEEE, 2006. 2399−2405
|
|
[34]
|
Guo B Z, Zhao Z L. On convergence of the nonlinear active disturbance rejection control for MIMO systems. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2013, 51(2): 1727−1757 doi: 10.1137/110856824
|
|
[35]
|
Cao M Y, Yang J, Li S H, Madonski R, Xue W C. Cascaded filter PID paradigm for error-based active disturbance rejection control: Equivalence, design, and implementation guidelines. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, DOI: 10.1109/TIE.2025.3559950
|
|
[36]
|
Deng J Q, Xue W C, Zhang L Y, Bao Q L, Mao Y. Disturbance-compression extended state observer with noise insensitivity: Application to electro-optical tracking system. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 17761−17777 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2025.3585348
|
|
[37]
|
Chen W H, Rhodes C, Liu C J. Dual control for exploitation and exploration (DCEE) in autonomous search. Automatica, 2021, 133: Article No. 109851 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109851
|
|
[38]
|
Li S H, Yang J, Iwasaki M, Chen W H. Hierarchical disturbance/uncertainty estimation and attenuation for integrated modeling and motion control: Overview and perspectives. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, DOI: 10.1109/TMECH.2024.3515084
|
|
[39]
|
Guo L, Chen W H. Disturbance attenuation for a class of nonlinear systems via disturbance-observer-based approach. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 2002, 35(1): 19−24
|
|
[40]
|
Guo L, Chen W H. Disturbance attenuation and rejection for systems with nonlinearity via DOBC approach. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2005, 15(3): 109−125 doi: 10.1002/rnc.978
|
|
[41]
|
Hurme E, Lenzi I, Wikelski M, Wild T A, Dechmann D K N. Bats surf storm fronts during spring migration. Science, 2025, 387(6729): 97−102 doi: 10.1126/science.ade7441
|
|
[42]
|
罗战虎. 地效飞行器发展综述. 科技创新导报, 2021, 18(9): 17−22Luo Zhan-Hu. A review of the development of wing-in-ground (WIG) aircraft. Science and Technology Innovation Herald, 2021, 18(9): 17−22
|
|
[43]
|
Benzi R, Sutera A, Vulpiani A. The mechanism of stochastic resonance. Journal of Physics A: Mathematical and General, 1981, 14(11): L453−L457 doi: 10.1088/0305-4470/14/11/006
|
|
[44]
|
Gammaitoni L, Hänggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F. Stochastic resonance. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1998, 70(1): 223−287 doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.70.223
|
|
[45]
|
Chapeau-Blondeau F. Noise-aided nonlinear Bayesian estimation. Physical Review E, 2002, 66(3): Article No. 032101
|
|
[46]
|
Chapeau-Blondeau F, Rousseau D. Noise-enhanced performance for an optimal Bayesian estimator. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2004, 52(5): 1327−1334 doi: 10.1109/TSP.2004.826176
|
|
[47]
|
Meissner P, Witrisal K. Multipath-assisted single-anchor indoor localization in an office environment. In: Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Systems, Signals and Image Processing (IWSSIP). Vienna, Austria: IEEE, 2012. 22−25
|
|
[48]
|
Witrisal K, Meissner P, Leitinger E, Shen Y, Gustafson C, Tufvesson F, et al. High-accuracy localization for assisted living: 5G systems will turn multipath channels from foe to friend. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2016, 33(2): 59−70 doi: 10.1109/MSP.2015.2504328
|
|
[49]
|
Wang T Y, Li Y X, Liu J C, Hu K K, Shen Y. Multipath-assisted single-anchor localization via deep variational learning. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2024, 23(8): 9113−9128 doi: 10.1109/TWC.2024.3359047
|
|
[50]
|
Gigi S, Tangirala A K. Quantification of interaction in multiloop control systems using directed spectral decomposition. Automatica, 2013, 49(5): 1174−1183 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.01.061
|
|
[51]
|
Guo Z Y, Zhou J, Guo J G, Cieslak J, Chang J. Coupling-characterization-based robust attitude control scheme for hypersonic vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2017, 64(8): 6350−6361 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2682031
|
|
[52]
|
Guo Z Y, Guo J G, Zhou J, Chang J. Robust tracking for hypersonic reentry vehicles via disturbance estimation-triggered control. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1279−1289 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2928605
|
|
[53]
|
Zhang M H, Jing X J. Energy-saving robust saturated control for active suspension systems via employing beneficial nonlinearity and disturbance. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(10): 10089−10100 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3069632
|
|
[54]
|
Huang Z G, Chen M, Shi P. Disturbance utilization-based tracking control for the fixed-wing UAV with disturbance estimation. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, 2023, 70(3): 1337−1349 doi: 10.1109/TCSI.2022.3229169
|
|
[55]
|
Jia J D, Guo K X, Yu X, Zhao W H, Guo L. Accurate high-maneuvering trajectory tracking for quadrotors: A drag utilization method. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(3): 6966−6973 doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3176449
|
|
[56]
|
Teng H, Lu Y K, Xia P F, Qiao J Z, Guo L. Refined disturbance utilization-based green control for spacecraft with composite actuator disturbances. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, DOI: 10.1109/TMECH.2025.3563132
|
|
[57]
|
Zhou X B, Yu X, Guo K X, Zhou S C, Guo L, Zhang Y M, et al. Safety flight control design of a quadrotor UAV with capability analysis. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2023, 53(3): 1738−1751 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3113168
|
|
[58]
|
Gu Y P, Guo K X, Zhao C L, Yu X, Guo L. Fast reactive mechanism for desired trajectory attacks on unmanned aerial vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(8): 8976−8984 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3224980
|
|
[59]
|
Meng Y, Qiao J Z, Zhu Y K, Teng H, Zhang J C. Remaining useful life prediction for spacecraft actuator based on multiplicative fault observer. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(6): 8489−8501 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2023.3306332
|
|
[60]
|
Zhang J C, Liu T Y, Qiao J Z. Solving a reliability-performance balancing problem for control systems with degrading actuators under model predictive control framework. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2022, 359(9): 4260−4287 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2022.04.007
|
|
[61]
|
Bian J, Zhang J C, Guo K X, Li W S, Yu X, Guo L. Risk-aware path planning using CVaR for quadrotors. In: Proceedings of the 6th International Symposium on Autonomous Systems (ISAS). Nanjing, China: IEEE, 2023. 1−6
|
|
[62]
|
Guo L, Zhu Y K, Qiao J Z, Wang C L. Composite anti-disturbance dynamic regulation for systems with multiple disturbances: From stability to balance. In: Proceedings of the 33rd Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC). Kunming, China: IEEE, 2021. 5685−5690
|
|
[63]
|
Zhou S C, Wang M, Jia J D, Guo K X, Yu X, Zhang Y M, et al. Fault separation based on an excitation operator with application to a quadrotor UAV. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2024, 60(4): 4010−4022 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2024.3371967
|
|
[64]
|
Jia J D, Zhang W Y, Guo K X, Wang J L, Yu X, Shi Y, et al. EVOLVER: Online learning and prediction of disturbances for robot control. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2024, 40: 382−402 doi: 10.1109/TRO.2023.3326318
|
|
[65]
|
Yang Y J, Bao Z Y, Qiao J Z, Zhu Y K, Guo L. Refined metamodel disturbance observer-based control for coarse pointing assembly under constraints. Guidance, Navigation and Control, 2024, 4(4): Article No. 2450017 doi: 10.1142/S2737480724500171
|
|
[66]
|
谭铁牛. 加强国际治理与合作推动人工智能向善向好. 当代世界, 2025(5): 4−9Tan Tie-Niu. Promoting AI for good through intensified global governance and cooperation. Contemporary World, 2025(5): 4−9
|
|
[67]
|
曾凯, 王耀南, 谭浩然, 方遒, 汪渊, 袁礼伟. AI大模型驱动的具身智能人形机器人技术与展望. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2025, 55(5): 967−992 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2024-0350Zeng Kai, Wang Yao-Nan, Tan Hao-Ran, Fang Qiu, Wang Yuan, Yuan Li-Wei. Prospects and technology of embodied intelligent humanoid robots driven by AI large models. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2025, 55(5): 967−992 doi: 10.1360/SSI-2024-0350
|




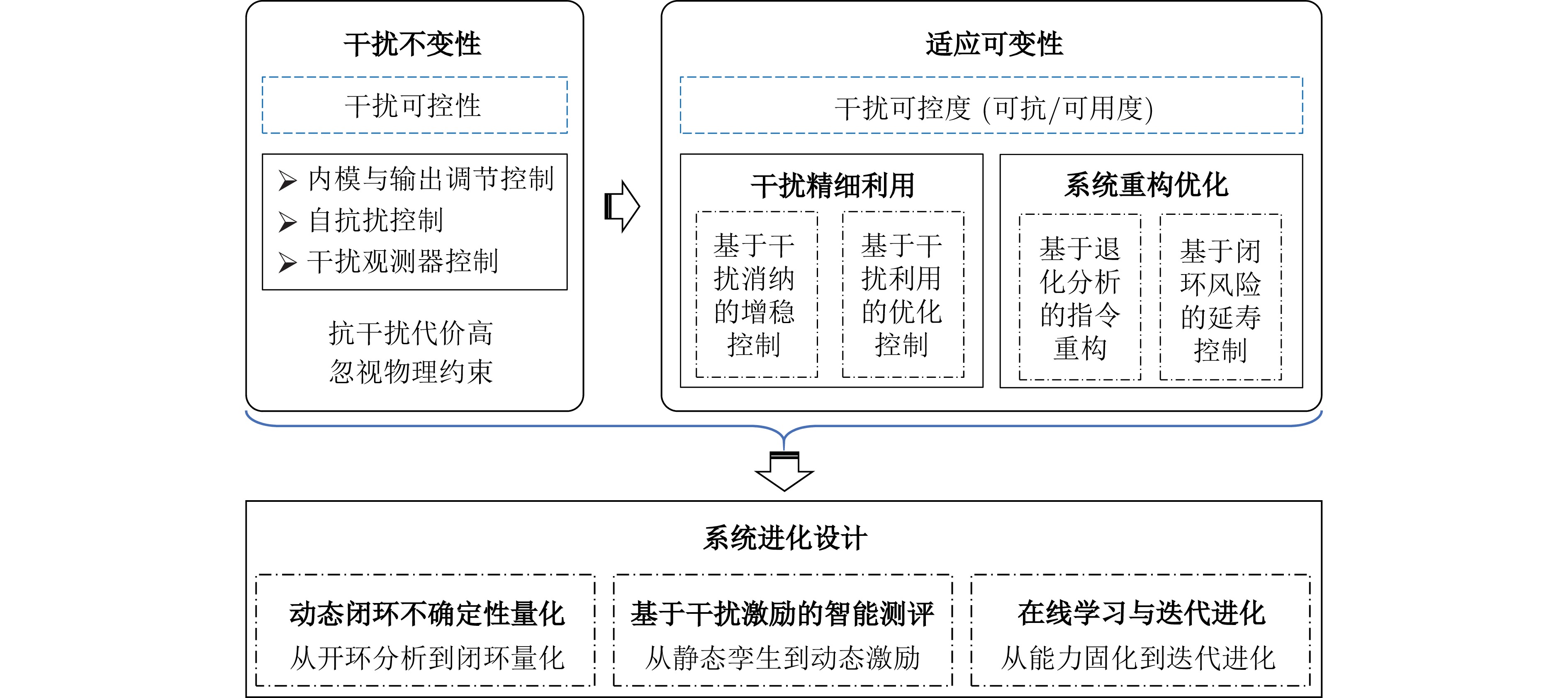
 下载:
下载: