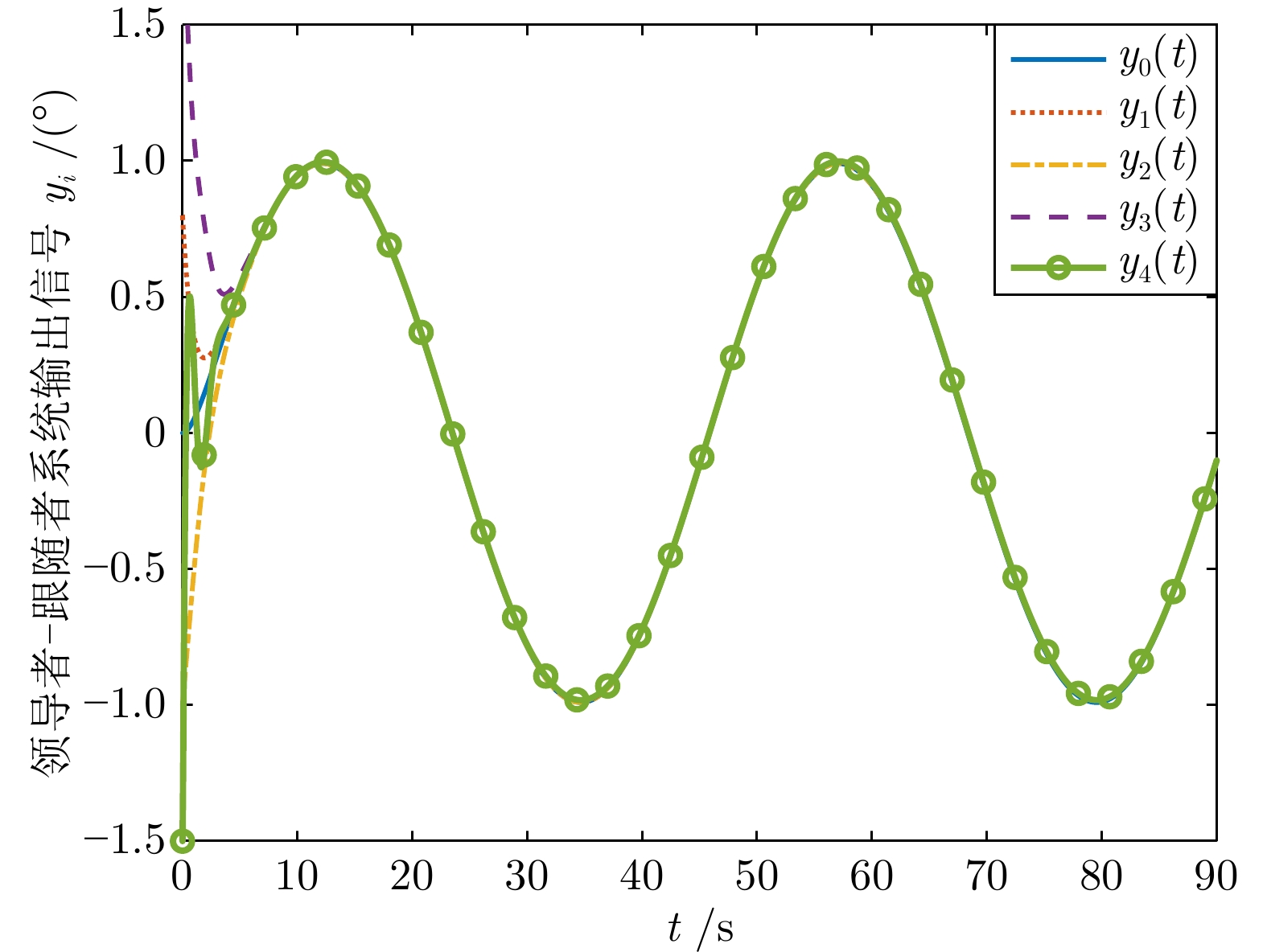
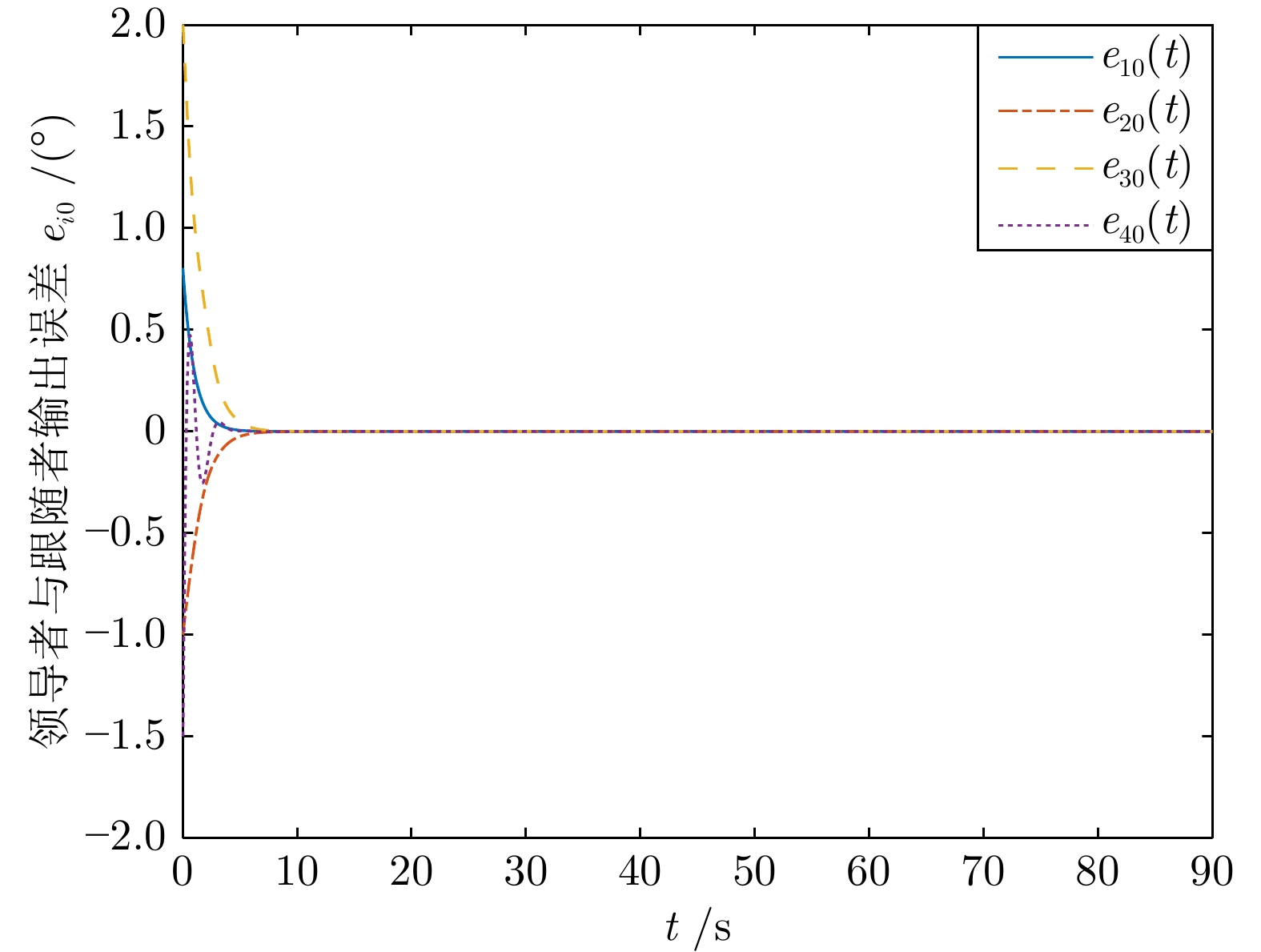
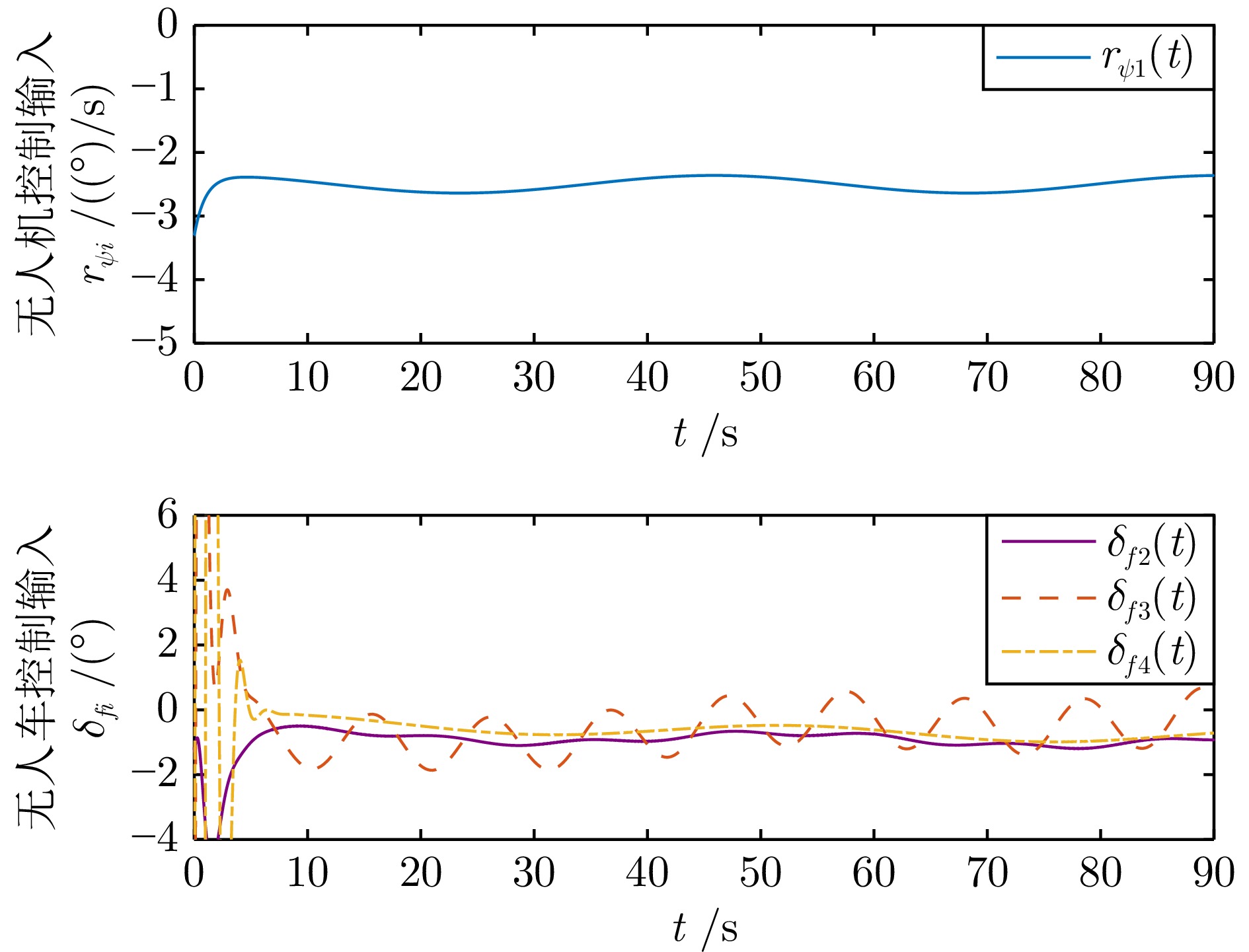
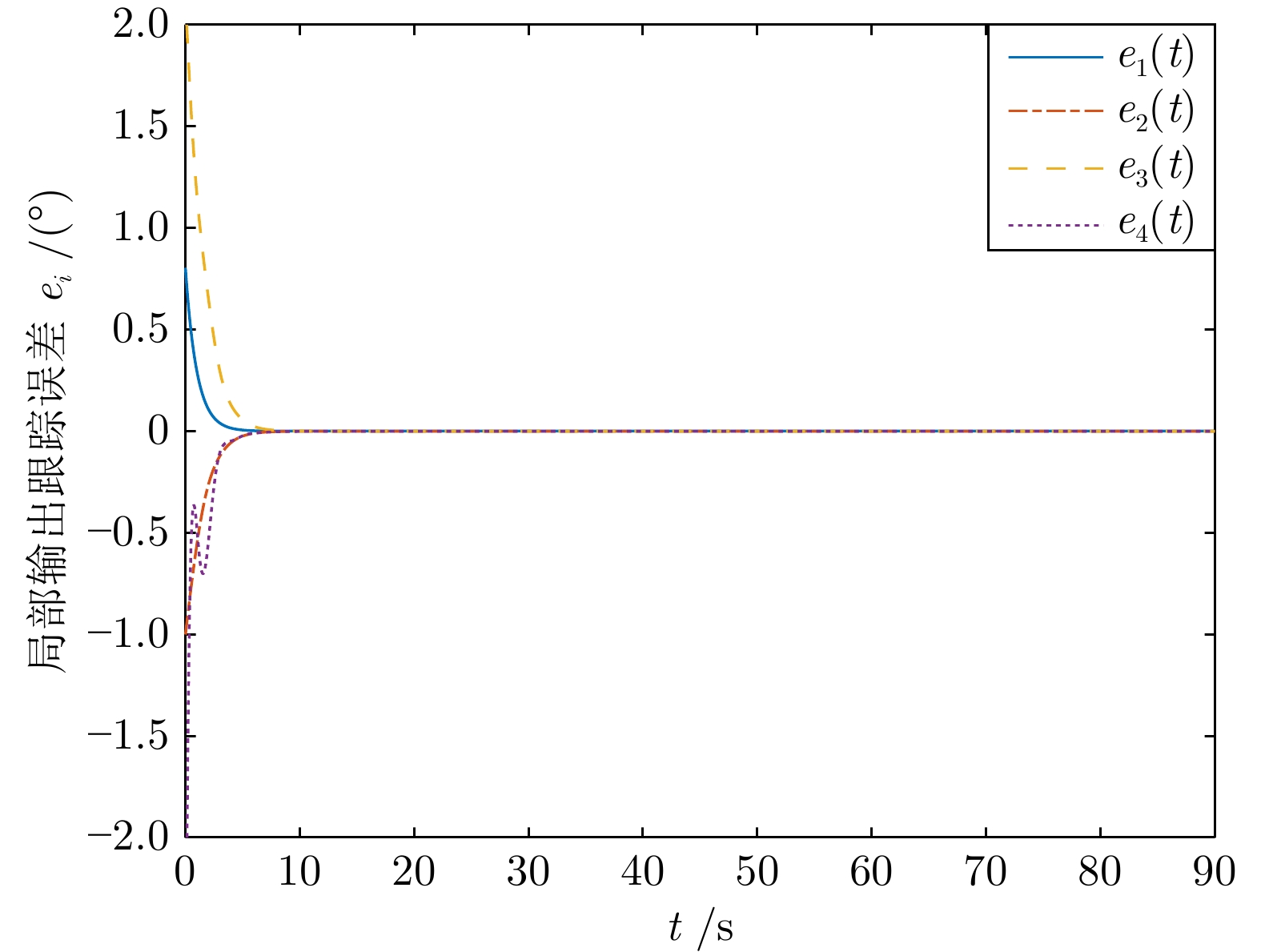
|
[1]
|
Bao G, Ma L, Yi X. Recent advances on cooperative control of heterogeneous multi-agent systems subject to constraints: A survey. Systems Science and Control Engineering, 2022, 10(1): 539−551 doi: 10.1080/21642583.2022.2074169
|
|
[2]
|
Ma Y J, Jiang B, Wang J, Gong J Y. Adaptive fault-tolerant formation control for heterogeneous UAVs-UGVs systems with multiple actuator faults. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(5): 6705−6716
|
|
[3]
|
Canese L, Cardarilli G C, Di N L, Fazzolari R, Giardino D, Re M, et al. Multi-agent reinforcement learning: A review of challenges and applications. Applied Sciences, 2021, 11(11): 1−25
|
|
[4]
|
Amirkhani A, Barshool A H. Consensus in multi-agent systems: A review. Artificial Intelligence Review, 2022, 22(5): 3897−3935
|
|
[5]
|
Bhusal R, Subbarao K. Consensus of cooperative unmanned systems with nonuniform time-varying delays. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2022, 45(9): 1724−1731 doi: 10.2514/1.G006703
|
|
[6]
|
Wei H L, Liu C X, Shi Y. A robust distributed MPC framework for multi-agent consensus with communication delays. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(11): 7418−7432 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2024.3389075
|
|
[7]
|
Liang H J, Yang S F, Li T S, Zhang H G. Distributed adaptive cooperative control for human-in-the-loop heterogeneous UAV-UGV systems with prescribed performance. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(11): 6915−6925
|
|
[8]
|
刘建刚, 杨胜杰. 具有容性负载的直流微电网系统分布式协同控制. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(4): 1283−1290 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190018Liu Jian-Gang, Yang Sheng-Jie. Distributed cooperative control of DC micro-grid systems with capacitive loads. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(4): 1283−1290 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190018
|
|
[9]
|
Yang R H, Liu L, Feng G. Cooperative output tracking of unknown heterogeneous linear systems by distributed event-triggered adaptive control. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 52(1): 3−15
|
|
[10]
|
Zadeh H N, Naseri R, Menhaj M B, Suratgar A A. Heterogeneous unknown multiagent systems of different relative degrees: A distributed optimal coordination design. IEEE Systems Journal, 2024, 18(3): 1570−1580 doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2024.3417255
|
|
[11]
|
Cao X Y, Zhang C H, Zhao D D, Sun B, Li Y. Event-triggered consensus control of continuous-time stochastic multi-agent systems. Automatica, 2022, 137(3): 22−29
|
|
[12]
|
Lin W L, Peng G S, Fu Z W, Chen T, Gu Z H. Consensus of fractional-order multi-agent systems via event-triggered pinning impulsive control. Neurocomputing, 2022, 494(10): 409−417
|
|
[13]
|
Leng H, Wu Z Y, Zhao Y. Group consensus in second-order multi-agent systems with nonlinear dynamics. International Journal of Modern Physics, 2021, 32(5): Article No. 2150071 doi: 10.1142/S0129183121500716
|
|
[14]
|
Yi J, Li J, Zhang Z. Fixed-time connectivity-preserving consensus of periodically disturbed nonlinear multi-agent systems with limited communication ranges. ISA Transactions, 2023, 138(6): 291−300
|
|
[15]
|
Zhang Z, Chen S M, Zheng Y S. Fully distributed scaled consensus tracking of high-order multiagent systems with time delays and disturbances. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2022, 18(1): 305−314 doi: 10.1109/TII.2021.3069207
|
|
[16]
|
Wang G, Wang X, Li S. Sliding-mode consensus algorithms for disturbed second-order multi-agent systems. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2018, 355(15): 7443−7465 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2018.07.027
|
|
[17]
|
Du C L, Li F B, Yang C H. An improved homogeneous polynomial approach for adaptive sliding-mode control of Markov jump systems with actuator faults. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 65(3): 955−969
|
|
[18]
|
Li Z K, Duan Z S, Xie L H, Liu X D. Distributed robust control of linear multi-agent systems with parameter uncertainties. International Journal of Control, 2012, 85(8): 1039−1050 doi: 10.1080/00207179.2012.674644
|
|
[19]
|
Li X, Soh Y C, Xie L H. Output-feedback protocols without controller interaction for consensus of homogeneous multi-agent systems: A unified robust control view. Automatica, 2017, 81: 37−45 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.03.001
|
|
[20]
|
Valcher M E, Misra P. On the stabilizability and consensus of positive homogeneous multi-agent dynamical systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2014, 59(7): 1936−1941 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2013.2294621
|
|
[21]
|
张冬梅, 欧琳琳, 孟莉, 王辛刚. 具有多图拓扑结构的同类智能体LQR控制. 自动化学报, 2013, 39(6): 913−919 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60059-2Zhang Dong-Mei, Ou Lin-Lin, Meng Li, Wang Xin-Gang. LQR control for homogeneous agents with multi-graph topology. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2013, 39(6): 913−919 doi: 10.1016/S1874-1029(13)60059-2
|
|
[22]
|
王澄, 刘德荣, 魏庆来, 赵冬斌, 夏振超. 带有储能设备的智能电网电能迭代自适应动态规划最优控制. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(9): 1984−1990 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.01984Wang Cheng, Liu De-Rong, Wei Qing-Lai, Zhao Dong-Bin, Xia Zhen-Chao. Iterative adaptive dynamic programming approach to power optimal control for smart grid with energy storage devices. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(9): 1984−1990 doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2014.01984
|
|
[23]
|
Zhang L P, Zhang H S, Xie L H. Distributed leaderless optimal output consensus of heterogeneous multi-agent systems. Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, 2025, 38(2): 671−690 doi: 10.1007/s11424-025-4528-2
|
|
[24]
|
Ren Y X, Wang Q S, Duan Z S. Optimal leader-following consensus control of multi-agent systems: A neural network based graphical game approach. IEEE Transactions on Network Science and Engineering, 2022, 9(5): 3590−3601 doi: 10.1109/TNSE.2022.3185019
|
|
[25]
|
Goel R, Grag T, Roy S B. Closed-loop reference model based distributed MRAC using cooperative initial excitation and distributed reference input estimation. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2022, 9(1): 37−49 doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3141015
|
|
[26]
|
Peng Z H, Dan W, Zhang H W, Sun G, Wang H. Distributed model reference adaptive control for cooperative tracking of uncertain dynamical multi-agent systems. IET Control Theory and Applications, 2013, 7(8): 1079−1087 doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2012.0765
|
|
[27]
|
Gong J Y, Ma Y J, Jiang B, Zhang Y M, Guo L. An adaptive fault-tolerant control scheme for heterogeneous multiagent systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2025, 55(2): 1264−1276
|
|
[28]
|
Ren Y H, Zhou W N, Li Z W, Liu L, Sun Y Q. Prescribed-time leader-following consensus for stochastic second-order multi-agent systems subject to actuator failures via sliding mode control strategy. Neurocomputing, 2021, 425: 82−95 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.10.103
|
|
[29]
|
Su Y, Huang J. Cooperative output regulation of linear multi-agent systems by output feedback. Systems and Control Letters, 2012, 61(12): 1248−1253 doi: 10.1016/j.sysconle.2012.09.005
|
|
[30]
|
Li G Q, Wang L. Adaptive output consensus of heterogeneous nonlinear multiagent systems: A distributed dynamic compensator approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 68(4): 2483−2489
|
|
[31]
|
Guo J, Zhang Y J, Zhang J F. Distributed output feedback indirect MRAC of continuous-time multiagent linear systems. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2025, 63(3): 1616−1640 doi: 10.1137/23M1620107
|
|
[32]
|
陈世明, 化俞新, 祝振敏, 赖强. 邻域交互结构优化的多智能体快速蜂拥控制算法. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(12): 2092−2099 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c150254Chen Shi-Ming, Hua Yu-Xin, Zhu Zhen-Min, Lai Qiang. Fast flocking algorithm for multi-agent systems by optimizing local interactive topology. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(12): 2092−2099 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.2015.c150254
|
|
[33]
|
Gohokar V N, Khedkar M K, Dhole G M. Formulation of distribution reconfiguration problem using network topology: A generalized approach. Electric Power Systems Research, 2004, 69(2): 304−310
|
|
[34]
|
Valcher M E, Zorzan I. On the consensus of homogeneous multi-agent systems with arbitrarily switching topology. Automatica, 2017, 84(1): 79−85
|
|
[35]
|
Zhang H G, Cai Y L, Wang Y C, Su H G. Adaptive bipartite event-triggered output consensus of heterogeneous linear multiagent systems under fixed and switching topologies. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(11): 4816−4830 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2958107
|
|
[36]
|
Tang W Y, Wu J, Liu N, Mo H H. Distributed data driven control for multi-agent consensus with unknown system dynamics. Journal of the Franlin Institute, 2021, 358(14): 7013−7031 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.07.017
|
|
[37]
|
Hu H, Huo S, Zhang Y. Adaptive fully distributed anti-disturbance containment control for heterogeneous multi-agent systems. International Journal of Systems Science, 2023, 54(1): 73−86 doi: 10.1080/00207721.2022.2103199
|
|
[38]
|
Stepanyan V, Hovakimyan N. Adaptive disturbance rejection controller for visual tracking of a maneuvering target. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2007, 30(4): 1090−1106 doi: 10.2514/1.25034
|
|
[39]
|
Wen L Y, Tao G, Yang H, Yang Y. Aircraft turbulence compensation using adaptive multivariable disturbance rejection techniques. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2015, 38(5): 954−963 doi: 10.2514/1.G000658
|
|
[40]
|
Dong M, Tao G, Wen L Y, Jiang B. Adaptive sensor fault detection for rail vehicle suspension systems. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(8): 7552−7565 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2926225
|
|
[41]
|
Tao G. Adaptive Control Design and Analysis. New York: John Wiley and Sons, 2003.
|
|
[42]
|
文利燕, 陶钢, 姜斌, 杨杰. 非线性动态突变系统的多模型自适应执行器故障补偿设计. 自动化学报, 2022, 48(1): 207−222 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200318Wen Li-Yan, Tao Gang, Jiang Bin, Yang Jie. A multiple-model based adaptive actuator failure compensation scheme for nonlinear systems with dynamic mutations. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2022, 48(1): 207−222 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200318
|
|
[43]
|
Baldi S, Yuan S, Paolo F. Output synchronizaiton of unknown heterogeneous agents via distributed model reference adaptation. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2018, 6(2): 515−525
|
|
[44]
|
Rosa M R. Adaptive synchronization for heterogeneous multi-agent systems with switching topologies. Machines, 2018, 6(1): 1−18 doi: 10.3390/machines6010001
|
|
[45]
|
Song G, Tao G. Adaptive leader-following state consensus of multiagent systems with switching topology. International Journal of Adaptive Control and Signal Processing, 2018, 32(10): 1508−1528 doi: 10.1002/acs.2926
|
|
[46]
|
刘宇, 文利燕, 姜斌, 马亚杰, 崔玉康. 切换拓扑下异构多智能体系统自适应输出一致性. 上海交通大学学报, 2024, 58(11): 1805−1815 doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2024.221Liu Yu, Wen Li-Yan, Jiang Bin, Ma Ya-Jie, Cui Yu-Kang. Adaptive output consencus of heterogeneous multi-agent system with switching topology. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2024, 58(11): 1805−1815 doi: 10.16183/j.cnki.jsjtu.2024.221
|
|
[47]
|
Levant A. Higher-order sliding modes, differentiation and output-feedback control. International Journal of Control, 2003, 76(9): 924−941
|




 下载:
下载: