Model-free Policy Gradient-based Reinforcement Learning Algorithms for Optimal Control of Unknown Stochastic Systems
-
摘要: 针对一类未知动力学马尔科夫随机系统的最优控制问题, 提出两种无模型策略梯度强化学习算法. 首先, 针对模型信息部分未知的马尔科夫随机系统, 基于系统采样数据和耦合李雅普诺夫方程推导出无模型策略梯度的解析形式, 并提出一种部分无模型策略梯度强化学习最优控制算法, 实现对预设性能指标的直接最小化. 由于求解耦合李雅普诺夫方程和计算策略梯度的必要数据均可从系统采样数据同一轨迹提取, 而无需再额外收集采样数据, 降低了算法的采样复杂度. 进一步地, 为完全解除对马尔科夫随机系统模型信息的依赖, 通过随机摄动反馈增益估计策略梯度, 并提出一种完全无模型策略梯度强化学习算法, 实现了马尔科夫随机系统动力学完全未知情况下的最优控制. 最后, 通过仿真结果证明了本文所提两种无模型策略梯度强化学习最优控制算法的高效性与优越性.Abstract: This paper investigates the optimal control problem of a class of Markov stochastic jump systems (MSJSs) with unknown dynamics by two novel model-free policy gradient (PG)-based reinforcement learning (RL) algorithms. Firstly, for MSJSs with partially unknown model information, an analytical form of model-free PG is derived based on the sampling data of MSJSs and the solutions to coupled Lyapunov equations, and a partially model-free PG-based RL optimal control algorithm is proposed, where the predefined performance index is directly minimized. As the fact that the necessary data for solving the coupled Lyapunov equations and calculating the PG can be extracted from the same trajectory of the system sampling data, without the need to collect additional sampling data, the sampling complexity of the algorithm is significantly reduced. Furthermore, in order to completely eliminate the dependence on the model information of MSJSs, the PG is estimated through random perturbation feedback gain, and a completely model-free PG-based RL algorithm is proposed to achieve optimal control of MSJSs with completely unknown dynamics. Finally, simulation results are presented to demonstrate the efficiency and superiority of the proposed two model-free PG-based RL optimal control algorithms.
-
Key words:
- Stochastic systems /
- optimal control /
- unknown dynamics /
- policy gradient /
- reinforcement learning
-
表 1 符号说明
Table 1 Notations explanation
符号 说明 ${\bf{R}}^{m}$, ${\bf{R}}^{m\times n}$ 实数向量, 实数矩阵 ${\rm{E}}\{\cdot\}$ 数学统计期望 $\otimes$ 克罗内克(Kronecker)积 ${\bf{Z}}$, ${\bf{Z}}_{\ge 0}$ 整数集, 非负整数集 $X> {\bf{0}}$, $X\geq{\bf{0}}$ 正定矩阵$X$, 半正定矩阵$X$ $I_{n}$, ${\bf{0}}$ 单位矩阵, 零矩阵 ${\rm{vec}}(X)$ $[x_{1}^{{\mathrm{T}}},\; \cdots,\; x_{m}^{{\mathrm{T}}}]^{{\mathrm{T}}}\in {\bf{R}}^{n\times m}$, $X\in {\bf{R}}^{n\times m}$ ${\rm{vecs}}(X)$ $[x_{11},\; \cdots,\; x_{1n},\; x_{22},\; \cdots,\; x_{2n},\; \cdots,\; x_{nn}]^{{\mathrm{T}}}\in$
${\bf{R}}^{\frac{n(n+1)}{2}}$, $X\in{\bf{R}}^{n\times n}$$\bar{x}$ $[x_{1}^{2},\; \cdots,\; 2x_{1}x_{n},\; x_{2}^{2},\; \cdots,\; 2x_{2}x_{n},\; \cdots,\; x_{n}^{2}]^{{\mathrm{T}}}\in$
$ {\bf{R}}^{\frac{n(n+1)}{2}}$, $x=[x_{1},\; \cdots,\; x_{n}]^{{\mathrm{T}}}\in{\bf{R}}^{n}$表 2 算法1和算法2在采样效率方面的比较
Table 2 Comparison between algorithm 1 and algorithm 2 in sampling efficiency
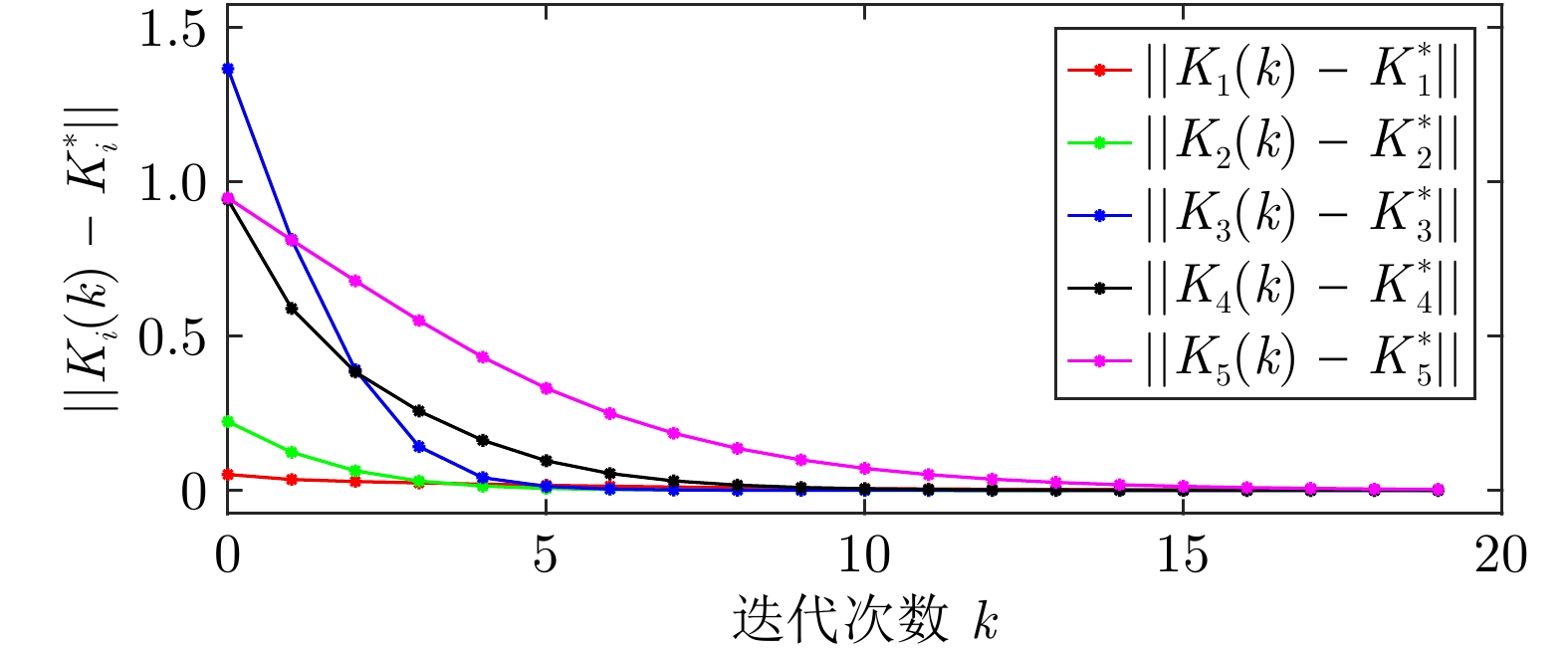
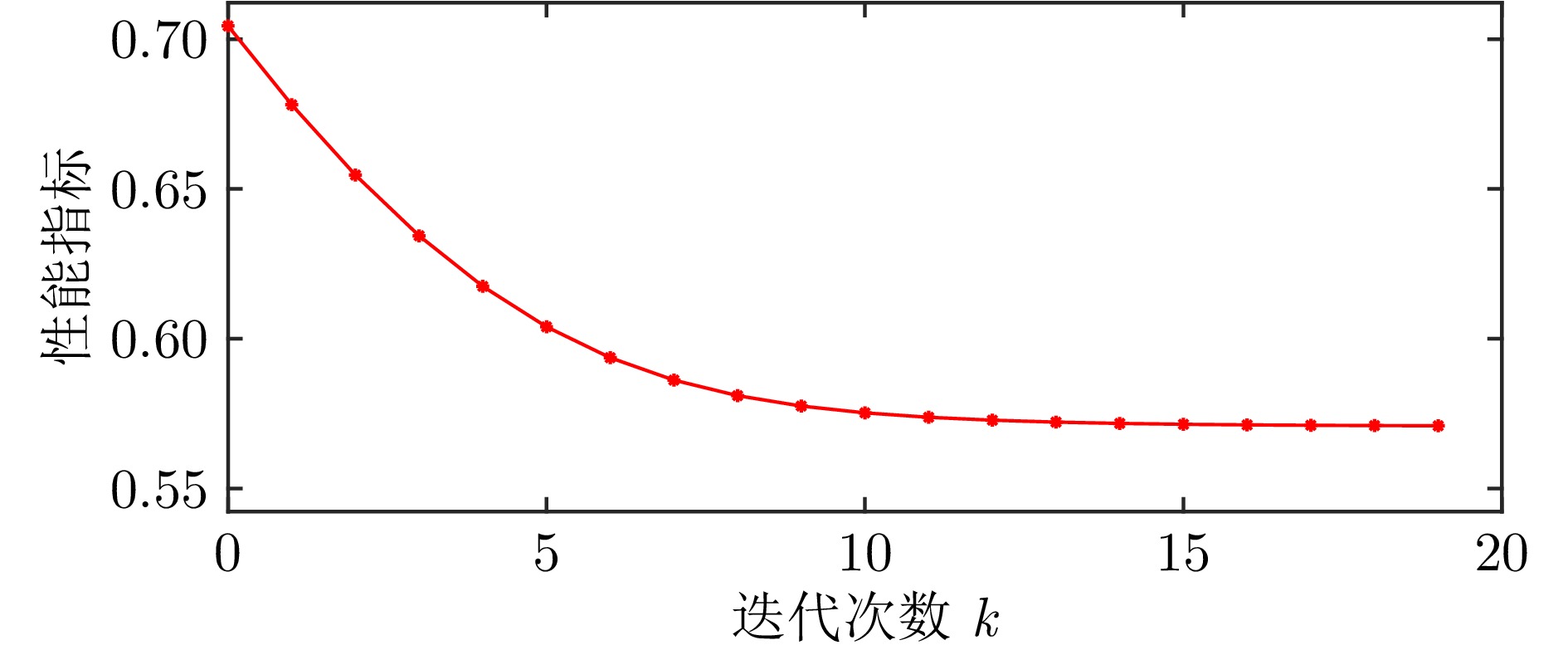
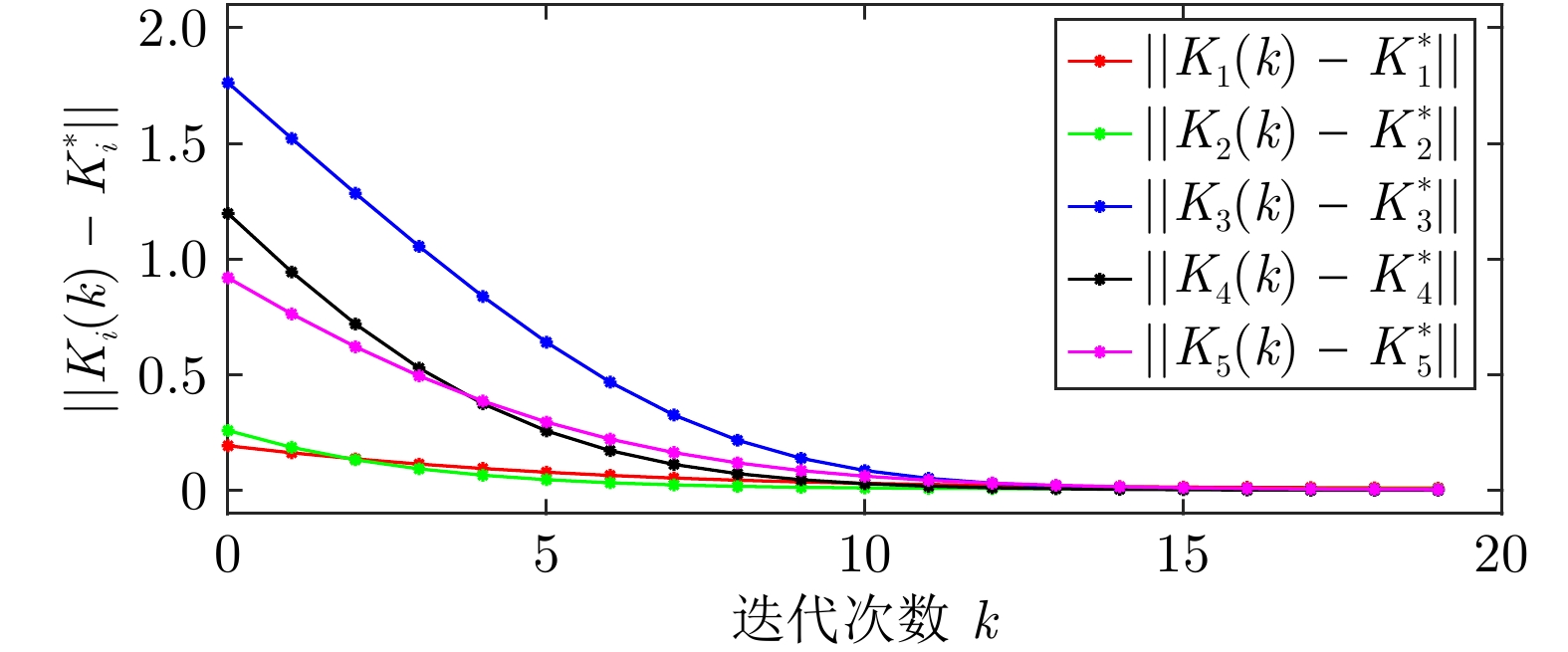
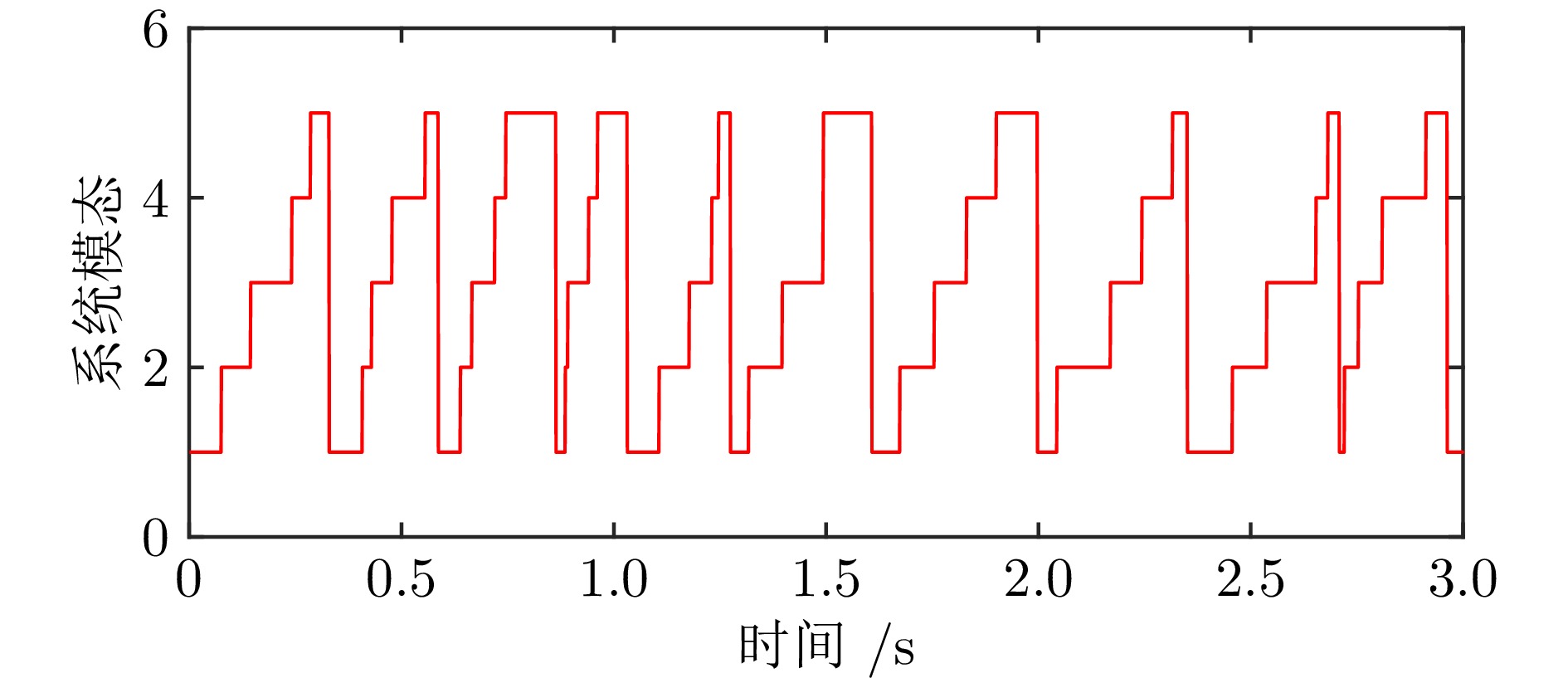
算法 算法1 算法2 采样数量$N_{{{s}}}$ $10$ $10$ 单条轨迹仿真时间$T_{t}\; ({\rm{s}})$ $10 $ $10 $ 采样周期$T_{s}\; ({\rm{s}})$ $0. 001 $ $0. 001 $ 总仿真时间$({\rm{s}})$ $N_{s}T_{t}=100$ $N_{s}T_{t}\frac{2T_{t}}{T_{s}}=2\;000\;000$ -
[1] 王鼎, 王将宇, 乔俊飞. 融合自适应评判的随机系统数据驱动策略优化. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(5): 980−990Wang Ding, Wang Jiang-Yu, Qiao Jun-Fei. Data-driven policy optimization for stochastic systems involving adaptive critic. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(5): 980−990 [2] 宋秀兰, 李洋阳, 何德峰. 外部干扰和随机DoS攻击下的网联车安全H∞ 队列控制. 自动化学报, 2024, 50(2): 348−355Song Xiu-Lan, Li Yang-Yang, He De-Feng. Secure H∞ platooning control for connected vehicles subject to external disturbance and random DoS attacks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2024, 50(2): 348−355 [3] Kuppusamy S, Joo Y H, Kim H S. Asynchronous control for discrete-time hidden Markov jump power systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(9): 9943−9948 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3062672 [4] 满景涛, 曾志刚, 盛银, 来金钢. 基于ODE-PDE的大规模多智能体系统有限时间编队. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(3): 631−642Man Jing-Tao, Zeng Zhi-Gang, Sheng Yin, Lai Jin-Gang. Finite-time formation of large-scale multi-agent systems based on an ODE-PDE approach. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(3): 631−642 [5] Cui R H, Xie X J. Finite-time stochastic integral input-to-state stability and its applications. Automatica, 2023, 158: Article No. 111311 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2023.111311 [6] 王乐, 崔凯, 蒋秀珊, 赵东亚, 张维海. 线性Markov跳变随机系统的Pareto最优控制. 控制理论与应用, 2025, 42(1): 59−66Wang Le, Cui Kai, Jiang Xiu-Shan, Zhao Dong-Ya, Zhang Wei-Hai. Pareto optimal control of linear Markov jump stochastic systems. Control Theory & Applications, 2025, 42(1): 59−66 [7] Li F B, Du C L, Yang C H, Gui W H. Passivity-based asynchronous sliding mode control for delayed singular Markovian jump systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(8): 2715−2721 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2017.2776747 [8] 李桂林, 王传锐, 季海波. 具有Markov跳跃参数的一类随机非线性系统逆最优增益设计. 自动化学报, 2014, 40(7): 1285−1294Li Gui-Lin, Wang Chuan-Rui, Ji Hai-Bo. Inverse optimal gain assignment control for a class of stochastic nonlinear systems with Markovian jump parameters. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2014, 40(7): 1285−1294 [9] 刘越, 周平. 马尔可夫跳变线性系统最优控制的研究现状与进展. 信息与控制, 2022, 51(1): 54−68Liu Yue, Zhou Ping. Recent status and progress in optimal control of Markov jump linear systems. Information and Control, 2022, 51(1): 54−68 [10] Xiong J L, Lam J, Gao H J, Ho D W C. On robust stabilization of Markovian jump systems with uncertain switching probabilities. Automatica, 2005, 41(5): 897−903 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2004.12.001 [11] Zhang Y, He Y, Wu M, Zhang J. Stabilization for Markovian jump systems with partial information on transition probability based on free-connection weighting matrices. Automatica, 2011, 47(1): 79−84 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2010.09.009 [12] Zhang K, Su R, Zhang H G. A novel resilient control scheme for a class of Markovian jump systems with partially unknown information. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(8): 8191−8200 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3050619 [13] Tian E G, Yue D, Wei G L. Robust control for Markovian jump systems with partially known transition probabilities and nonlinearities. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2013, 350(8): 2069−2083 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2013.05.011 [14] Qi W H, Hou Y K, Park J H, Zong G D, Cao J D, Cheng J. SMC for discrete-time networked semi-Markovian switching systems with random DoS attacks and applications. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2023, 53(3): 1982−1993 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2022.3211322 [15] 王国庆, 姚凤麒. 具有有界时滞的脉冲随机泛函微分系统的有限时间稳定. 控制理论与应用, 2023, 40(9): 1569−1575Wang Guo-Qing, Yao Feng-Qi. Finite-time stability of impulsive stochastic functional differential systems with bounded delays. Control Theory & Applications, 2023, 40(9): 1569−1575 [16] Wei Y L, Park J H, Qiu J B, Wu L G, Jung H Y. Sliding mode control for semi-Markovian jump systems via output feedback. Automatica, 2017, 81: 133−141 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.03.032 [17] Wu L G, Ho D W C. Sliding mode control of singular stochastic hybrid systems. Automatica, 2010, 46(4): 779−783 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2010.01.010 [18] Liu M, Zhang L X, Shi P, Zhao Y X. Sliding mode control of continuous-time Markovian jump systems with digital data transmission. Automatica, 2017, 80: 200−209 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.02.002 [19] Li F B, Du C L, Yang C H, Wu L G, Gui W H. Finite-time asynchronous sliding mode control for Markovian jump systems. Automatica, 2019, 109: Article No. 108503 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.108503 [20] Du C L, Yang C H, Li F B, Gui W H. A novel asynchronous control for artificial delayed Markovian jump systems via output feedback sliding mode approach. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2019, 49(2): 364−374 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2815032 [21] Li Z, Zhang Y, Wu A G. An inversion-free iterative algorithm for Riccati matrix equations in discrete-time Markov jump systems. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(9): 4754−4761 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3172266 [22] Dong S L, Liu L, Feng G, Liu M Q, Wu Z G, Zheng R H. Cooperative output regulation quadratic control for discrete-time heterogeneous multiagent Markov jump systems. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(9): 9882−9892 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3110792 [23] Jansch-Porto J P, Hu B, Dullerud G E. Policy optimization for Markovian jump linear quadratic control: Gradient method and global convergence. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(4): 2475−2482 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3176439 [24] Jansch-Porto J P, Hu B, Dullerud G E. Convergence guarantees of policy optimization methods for Markovian jump linear systems. In: Proceedings of the American Control Conference (ACC). Denver, USA: IEEE, 2020. 2882−2887 [25] Chávez-Fuentes J R, Costa E F, Terra M H, Rocha K D T. The linear quadratic optimal control problem for discrete-time Markov jump linear singular systems. Automatica, 2021, 127: Article No. 109506 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109506 [26] Lai J, Xiong J L, Shu Z. Model-free optimal control of discrete-time systems with additive and multiplicative noises. Automatica, 2023, 147: Article No. 110685 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2022.110685 [27] Mohammadi H, Zare A, Soltanolkotabi M, Jovanović M R. Convergence and sample complexity of gradient methods for the model-free linear-quadratic regulator problem. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(5): 2435−2450 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2021.3087455 [28] Bian T, Jiang Z P. Value iteration and adaptive dynamic programming for data-driven adaptive optimal control design. Automatica, 2016, 71: 348−360 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.05.003 [29] 李艺春, 刘泽娇, 洪艺天, 王继超, 王健瑞, 李毅, 等. 基于多智能体强化学习的博弈综述. 自动化学报, 2025, 51(3): 540−558Li Yi-Chun, Liu Ze-Jiao, Hong Yi-Tian, Wang Ji-Chao, Wang Jian-Rui, Li Yi, et al. Multi-agent reinforcement learning based game: A survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2025, 51(3): 540−558 [30] 袁雷, 张子谦, 李立和, 管聪, 俞扬. 开放环境下的协作多智能体强化学习进展. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2025, 55(2): 217−268Yuan Lei, Zhang Zi-Qian, Li Li-He, Guan Cong, Yu Yang. Progress on cooperative multi-agent reinforcement learning in open environment. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2025, 55(2): 217−268 [31] Wang J, Zhao W, Cao J D, Park J H, Shen H. Reinforcement learning-based predefined-time tracking control for nonlinear systems under identifier-critic-actor structure. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2024, 54(11): 6345−6357 doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2024.3431670 [32] Zhang Z Y, Mo Z B, Chen Y T, Huang J. Reinforcement learning behavioral control for nonlinear autonomous system. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 9(9): 1561−1573 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2022.105797 [33] Gravell B, Esfahani P M, Summers T. Learning optimal controllers for linear systems with multiplicative noise via policy gradient. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(11): 5283−5298 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3037046 [34] Ji Y D, Chizeck H J. Controllability, stabilizability, and continuous-time Markovian jump linear quadratic control. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1990, 35(7): 777−788 doi: 10.1109/9.57016 [35] Qian Y Y, Pang W J. An implicit sequential algorithm for solving coupled Lyapunov equations of continuous-time Markovian jump systems. Automatica, 2015, 60: 245−250 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2015.07.011 [36] Konda V R, Tsitsiklis J N. Actor-critic algorithms. In: Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS). Denver, USA: MIT Press, 1999. 1008−1014 [37] Gao W N, Mynuddin M, Wunsch D C, Jiang Z P. Reinforcement learning-based cooperative optimal output regulation via distributed adaptive internal model. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2022, 33(10): 5229−5240 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3069728 [38] Borno I. Parallel computation of the solutions of coupled algebraic Lyapunov equations. Automatica, 1995, 31(9): 1345−1347 doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(95)00037-W -




 下载:
下载: