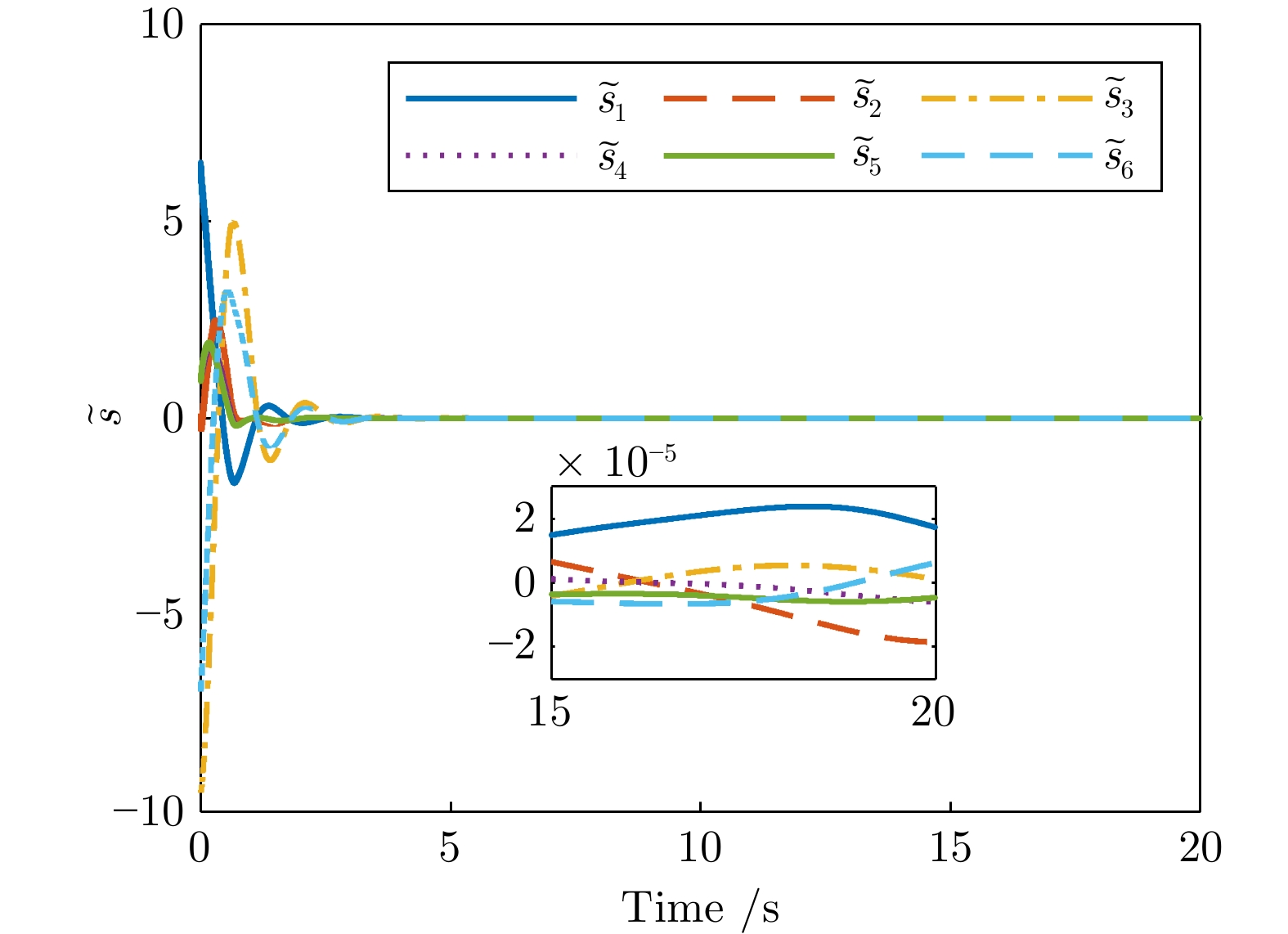
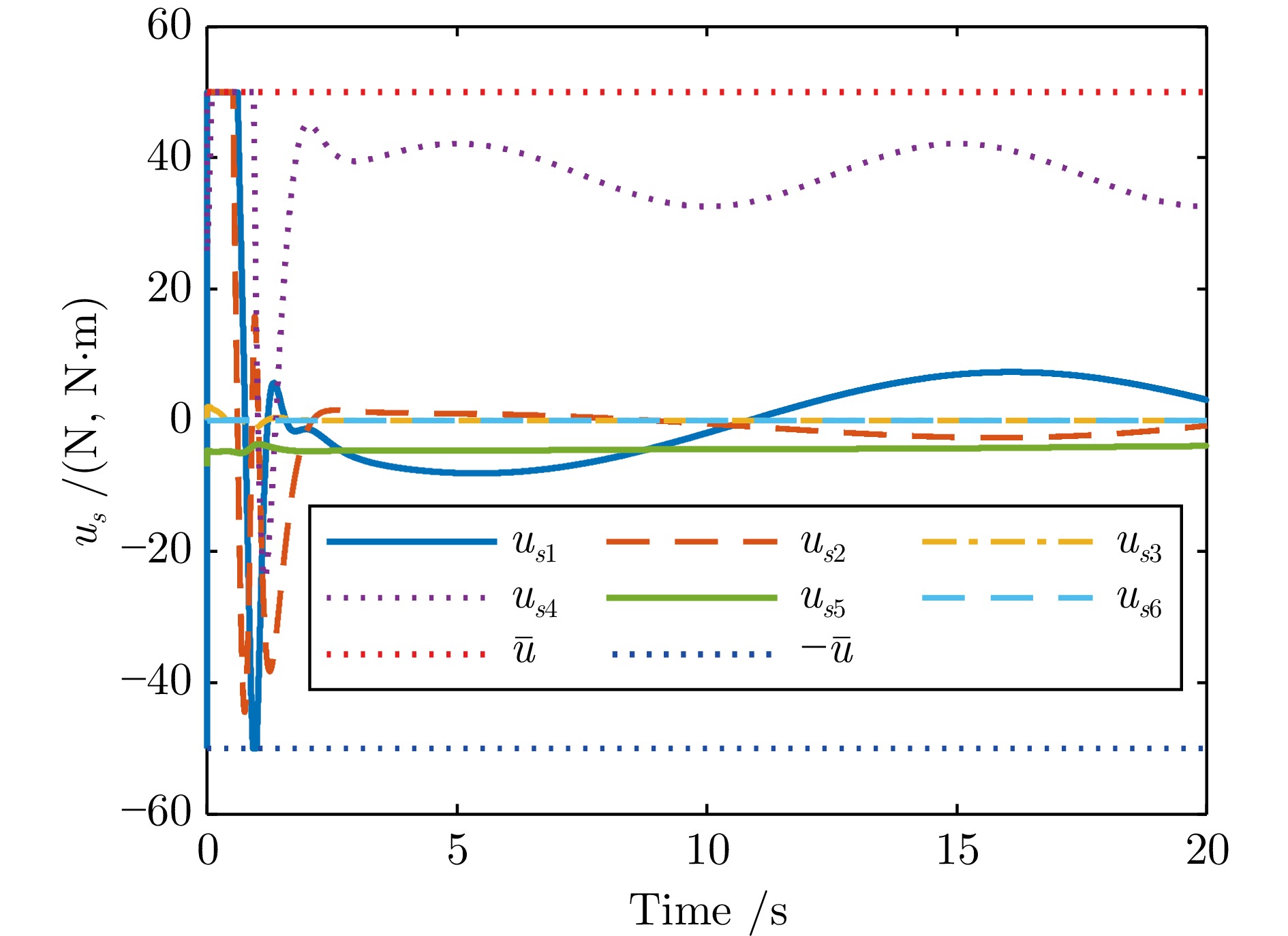
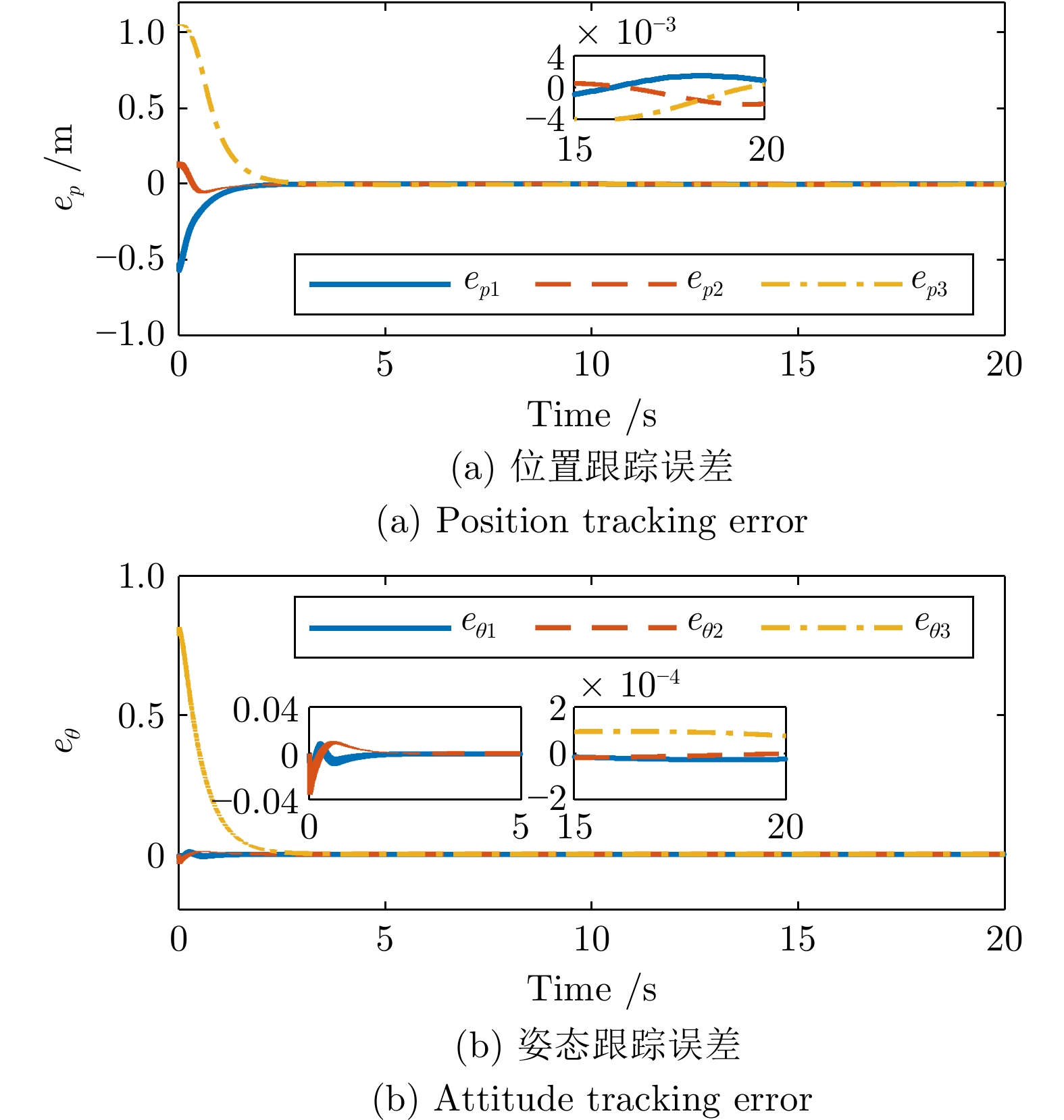
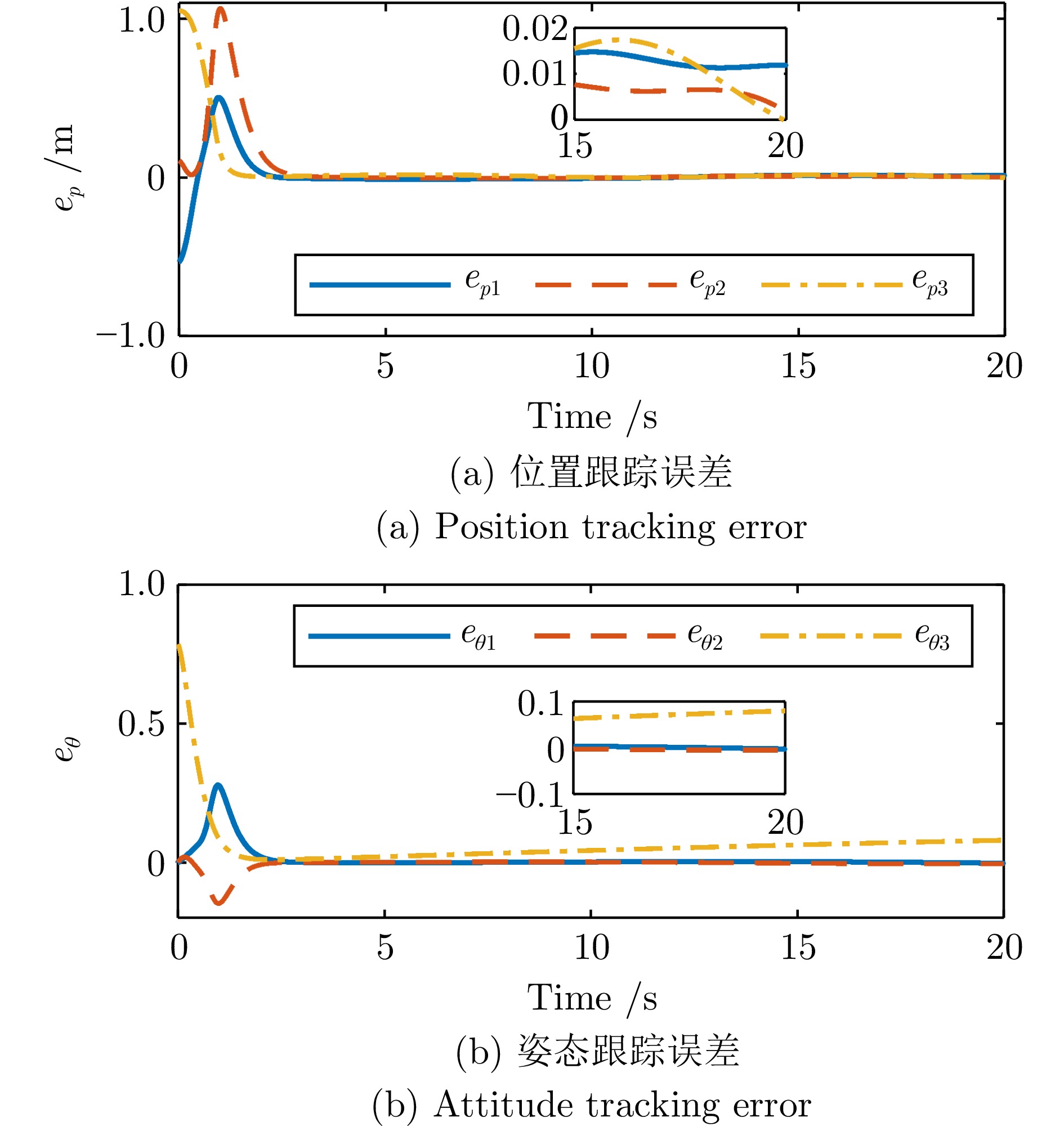
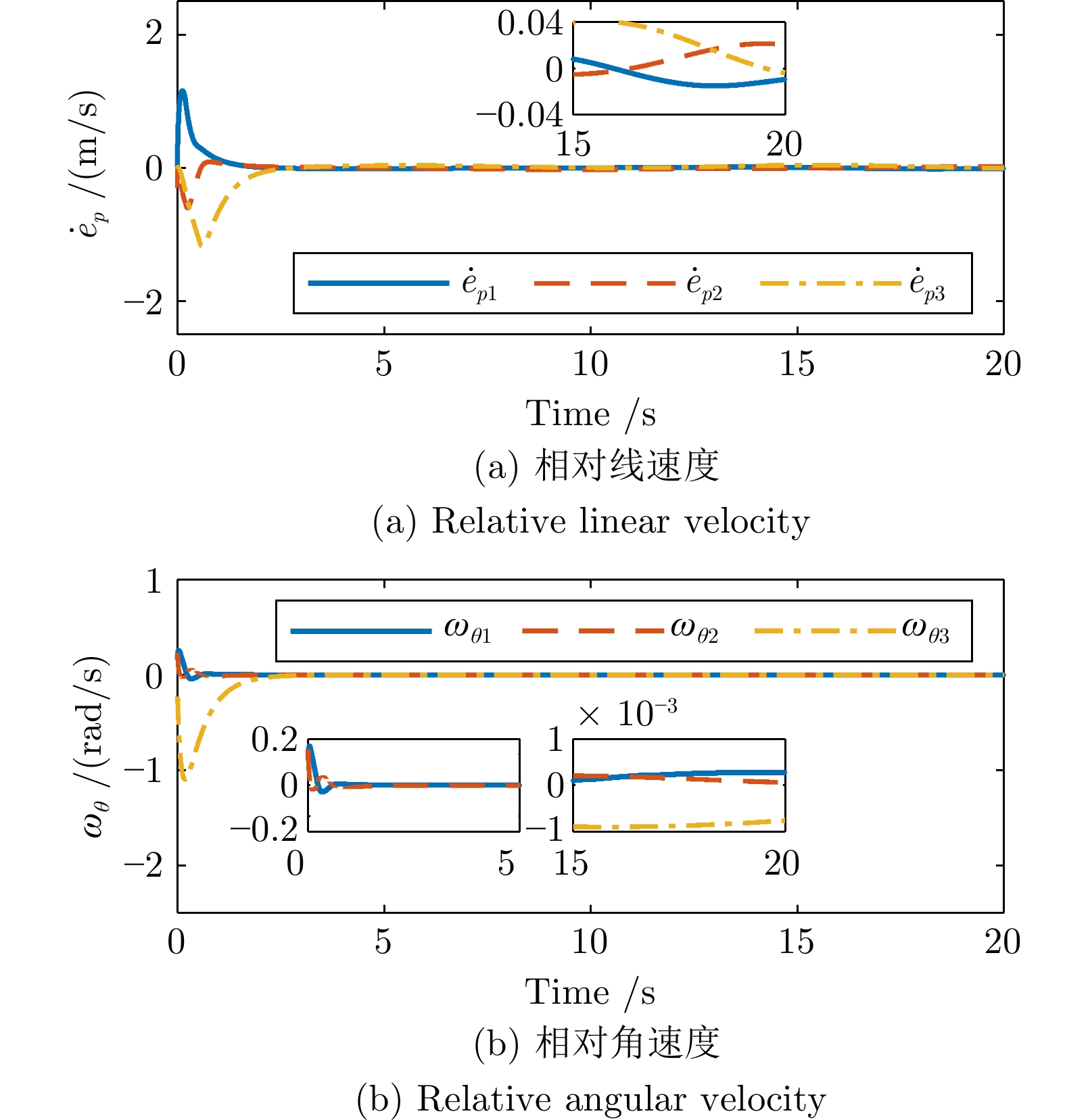
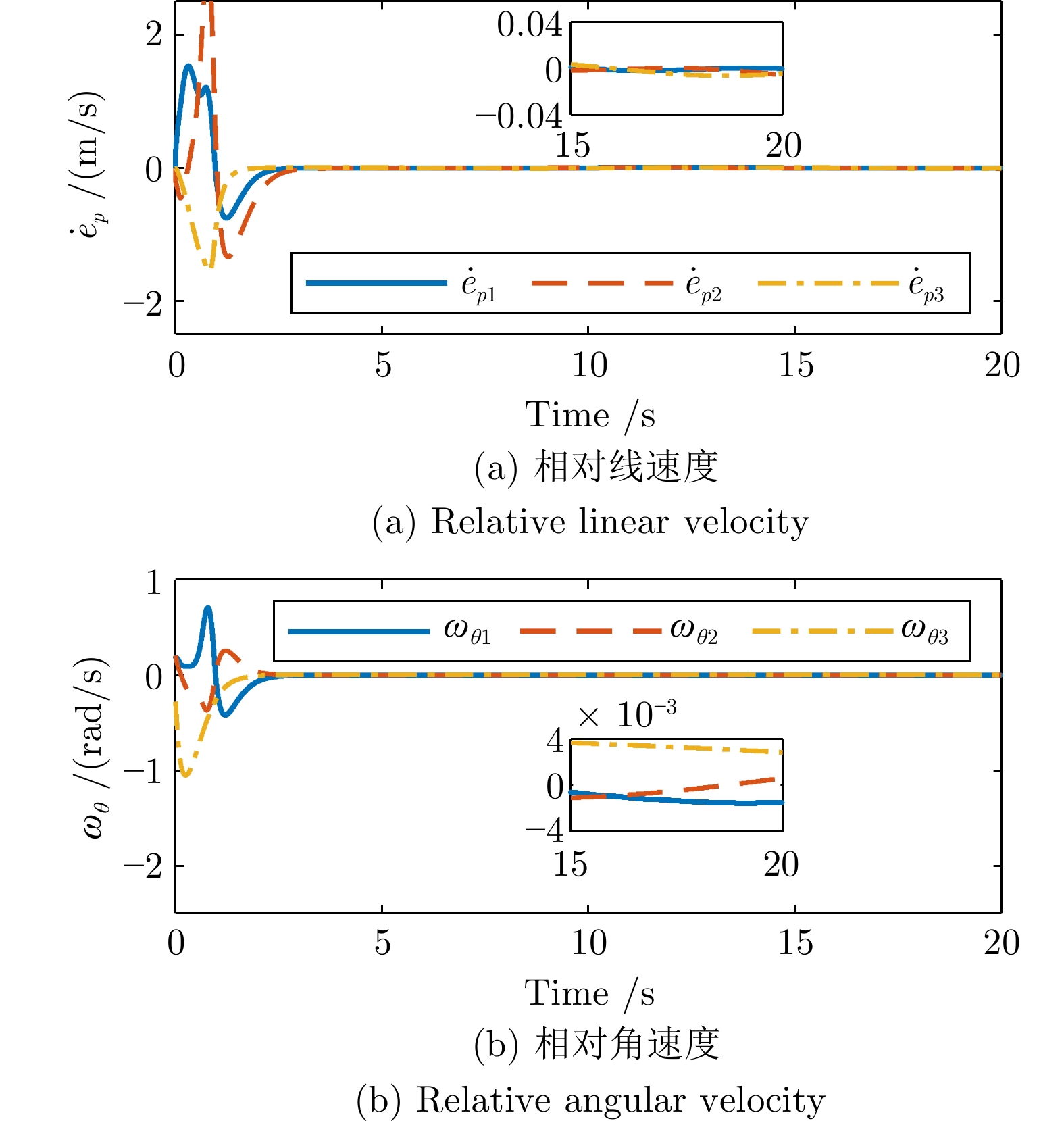
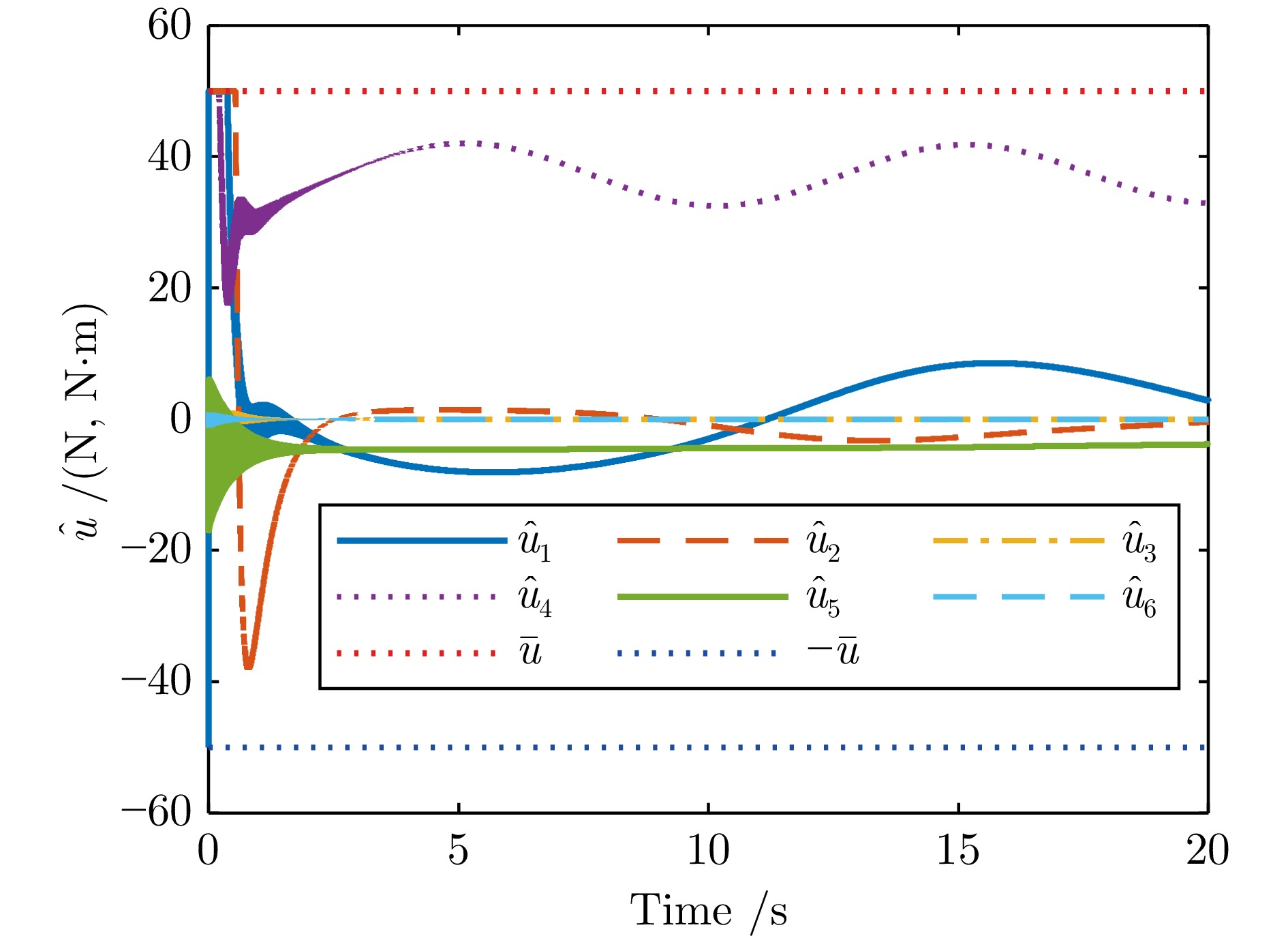
-
摘要: 针对存在参数不确定性、外部扰动和输入饱和约束的移动机械臂跟踪控制问题, 提出一种基于自适应动态规划的鲁棒$H_{\infty} $控制方案. 首先, 通过设计神经网络辨识器, 对跟踪误差动力学中的不确定性进行在线估计. 然后, 考虑外部扰动、目标运动扰动和辨识误差, 将鲁棒$H_{\infty} $控制转化为零和博弈问题进行求解, 并在值函数中引入广义非二次泛函来处理输入饱和约束. 进一步, 构建评价网络逼近最优值函数, 获得近似最优控制律及最坏情况下的总扰动估计, 实现闭环系统跟踪误差和评价网络权值估计误差的一致最终有界. 仿真结果验证了所提方案的有效性.Abstract: A robust $H_{\infty} $ control scheme is proposed for the tracking control problem of mobile manipulators based on adaptive dynamic programming under parametric uncertainties, external disturbances and input saturation constraints. First, a neural network identifier is designed to estimate the uncertain dynamics of the tracking error online. Then, considering external disturbances, target motion perturbations and identification error, the robust $H_{\infty} $ control is formulated as a zero-sum game problem for solution, in which a generalized non-quadratic functional is introduced into the value function to address the input saturation constraints. A critic network is further constructed to approximate the optimal value function, and the approximate optimal control law and the estimated worst-case lumped disturbances are obtained. The proposed scheme can achieve the uniform ultimate boundedness of the closed-loop system tracking error and the weight estimation error of the critic network. Simulation results validate the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
-
Key words:
- Mobile manipulator /
- robust H∞ control /
- adaptive dynamic programming /
- visual servoing
-
表 1 两种方法的控制成本对比
Table 1 Comparison of control costs between two methods
控制方案 0 ~ 5 s 0 ~ 20 s $ H_\infty $ 控制方案 5.1867 × 1031.6188 × 104LSMC方法 6.3742 × 1031.7338 × 104 -
[1] Zeng Y D, Zhang D Y, Chien S Y, Tju H S, Wiesse C, Cao F. Task sensing and adaptive control for mobile manipulator in indoor painting application. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2024, 29(4): 2956−2963 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2024.3399787 [2] Zhang S J, Cheng S H, Jin Z L. Variable trajectory impedance: A super-twisting sliding mode control method for mobile manipulator based on identification model. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2025, 72(1): 610−619 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2024.3383042 [3] Xian C X, Zhao Y, Wen G H, Chen G R. Robust event-triggered distributed optimal coordination of heterogeneous systems over directed networks. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2024, 69(7): 4522−4537 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2023.3335797 [4] Wen G H, Zhao Y, Duan Z S, Yu W W, Chen G R. Containment of higher-order multi-leader multi-agent systems: A dynamic output approach. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2016, 61(4): 1135−1140 doi: 10.1109/TAC.2015.2465071 [5] Huang Y, Jia Y M. Nonlinear robust H∞ control for spacecraft body-fixed hovering around noncooperative target via modified θ-D method. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(5): 2451−2463 doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2890351 [6] Wu S N, Chu W M, Ma X, Radice G, Wu Z G. Multi-objective integrated robust H∞ control for attitude tracking of a flexible spacecraft. Acta Astronautica, 2018, 151: 80−87 doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2018.05.062 [7] Wang Z, Li Y. Rigid spacecraft nonlinear robust H∞ attitude controller design under actuator misalignments. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2023, 111: 15037−15054 doi: 10.1007/s11071-023-08620-6 [8] Zuo Y, Wang Y N, Liu X Z, Yang S X, Huang L H, Wu X R, et al. Neural network robust H∞ tracking control strategy for robot manipulators. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2010, 34(7): 1823−1838 doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2009.09.026 [9] da Cruz Figueredo L F, Adorno B V, Ishihara J Y. Robust H∞ kinematic control of manipulator robots using dual quaternion algebra. Automatica, 2021, 132: Article No. 109817 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2021.109817 [10] Song G I, Park H Y, Kim J H. The H∞ robust stability and performance conditions for uncertain robot manipulators. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2025, 12(1): 270−272 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2024.124701 [11] Alinezhad H S, Esfanjani R M. Nonlinear H∞ control for synchronization of networked manipulators subject to delayed communication. Journal of the Franklin Institute, 2022, 359(2): 999−1017 doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2021.11.025 [12] Liu H T, Tian X H, Wang G, Zhang T. Finite-time H∞ control for high-precision tracking in robotic manipulators using backstepping control. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2016, 63(9): 5501−5513 doi: 10.1109/TIE.2016.2583998 [13] 黄琳. 稳定性与鲁棒性的理论基础. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003. 502−511Huang Lin. Theoretical Foundation of Stability and Robustness. Beijing: Science Press, 2003. 502−511 [14] Wang D, Gao N, Liu D R, Li J N, Lewis F L. Recent progress in reinforcement learning and adaptive dynamic programming for advanced control applications. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2024, 11(1): 18−36 doi: 10.1109/JAS.2023.123843 [15] Lewis F L, Vrabie D, Vamvoudakis K G. Reinforcement learning and feedback control: Using natural decision methods to design optimal adaptive controllers. IEEE Control Systems Magazine, 2012, 32(6): 76−105 doi: 10.1109/MCS.2012.2214134 [16] 王鼎. 基于学习的鲁棒自适应评判控制研究进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(6): 1031−1043Wang Ding. Research progress on learning-based robust adaptive critic control. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(6): 1031−1043 [17] Wei Q L, Song R Z, Yan P F. Data-driven zero-sum neuro-optimal control for a class of continuous-time unknown nonlinear systems with disturbance using ADP. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2016, 27(2): 444−458 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2464080 [18] Xue S, Luo B, Liu D R. Event-triggered adaptive dynamic programming for zero-sum game of partially unknown continuous-time nonlinear systems. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2020, 50(9): 3189−3199 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2018.2852810 [19] Xue S, Luo B, Liu D R, Yang Y. Constrained event-triggered H∞ control based on adaptive dynamic programming with concurrent learning. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(1): 357−369 doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.2997559 [20] Rizvi S A A, Lin Z L. Output feedback Q-learning for discrete-time linear zero-sum games with application to the H-infinity control. Automatica, 2018, 95: 213−221 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.05.027 [21] Hu G J, Guo J G, Guo Z Y, Cieslak J, Henry D. ADP-based intelligent tracking algorithm for reentry vehicles subjected to model and state uncertainties. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19(4): 6047−6055 doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3171327 [22] Dong B, An T J, Zhu X Y, Li Y C, Liu K P. Zero-sum game-based neuro-optimal control of modular robot manipulators with uncertain disturbance using critic only policy iteration. Neurocomputing, 2021, 450: 183−196 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.04.032 [23] 高为炳. 非线性控制系统导论. 北京: 科学出版社, 1988. 500−501Gao Wei-Bing. Introduction to Nonlinear Control Systems. Beijing: Science Press, 1988. 500−501 [24] Wang D, Mu C X, Liu D R, Ma H W. On mixed data and event driven design for adaptive-critic-based nonlinear H∞ control. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(4): 993−1005 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2016.2642128 [25] Hu C, Wang Z, Bu X W, Zhao J, Na J, Gao H B. Optimal tracking control for autonomous vehicle with prescribed performance via adaptive dynamic programming. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(9): 12437−12449 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3384113 [26] Yang T, Sun N, Chen H, Fang Y C. Adaptive optimal motion control of uncertain underactuated mechatronic systems with actuator constraints. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2023, 28(1): 210−222 doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2022.3192002 [27] Wang Y X, An T J, Dong B, Zhu M C, Li Y C. Adaptive dynamic programming-based finite-time optimal backstepping force/position control of reconfigurable robot manipulators via pareto optimal. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 10660−10671 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2025.3527569 [28] Spong M W, Hutchinson S, Vidyasagar M. Robot Modeling and Control. Hoboken: John Wiley & Sons, 2006. 50−53 [29] Siciliano B, Khatib O. Springer Handbook of Robotics (Second Edition). Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2016. 851−853 [30] Li Z J, Ge S S. Fundamentals in Modeling and Control of Mobile Manipulators. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2013. 17−40 [31] 霍伟. 机器人动力学与控制. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2005. 55−63Huo Wei. Robot Dynamics and Control. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2005. 55−63 [32] 高为炳. 变结构控制理论基础. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 1990. 265−267Gao Wei-Bing. Fundamentals of Variable Structure Control Theory. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 1990. 265−267 [33] 黄琳. 系统与控制理论中的线性代数(上册) (第二版). 北京: 科学出版社, 2018. 225−228Huang Lin. Linear Algebra in System and Control Theory: Volume I (Second Edition). Beijing: Science Press, 2018. 225−228 [34] Abu-Khalaf M, Lewis F L. Nearly optimal control laws for nonlinear systems with saturating actuators using a neural network HJB approach. Automatica, 2005, 41(5): 779−791 doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2004.11.034 [35] 黄琳. 最优控制理论讲义. 北京: 科学出版社, 2021. 52−59Huang Lin. Lectures on Optimal Control Theory. Beijing: Science Press, 2021. 52−59 [36] 贾英民. 鲁棒H∞ 控制. 北京: 科学出版社, 2007. 57−67Jia Ying-Min. Robust H∞ Control. Beijing: Science Press, 2007. 57−67 [37] Kong L H, Zhang S, Yu X B. Approximate optimal control for an uncertain robot based on adaptive dynamic programming. Neurocomputing, 2021, 423: 308−317 doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.10.012 -





 下载:
下载: