3D Spatial Prior-Guided Video Diffusion Models with Controllable Camera Trajectories
-
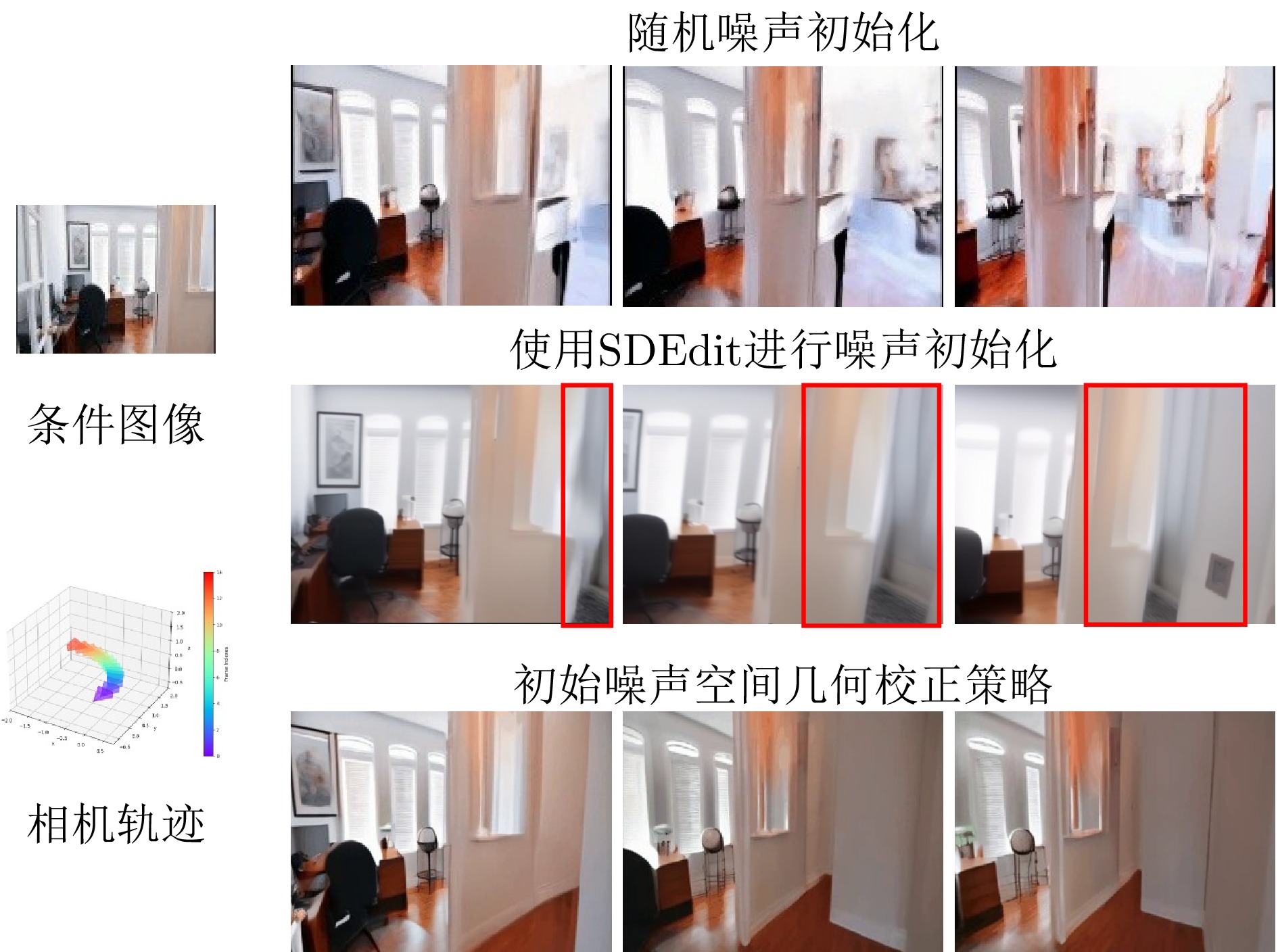
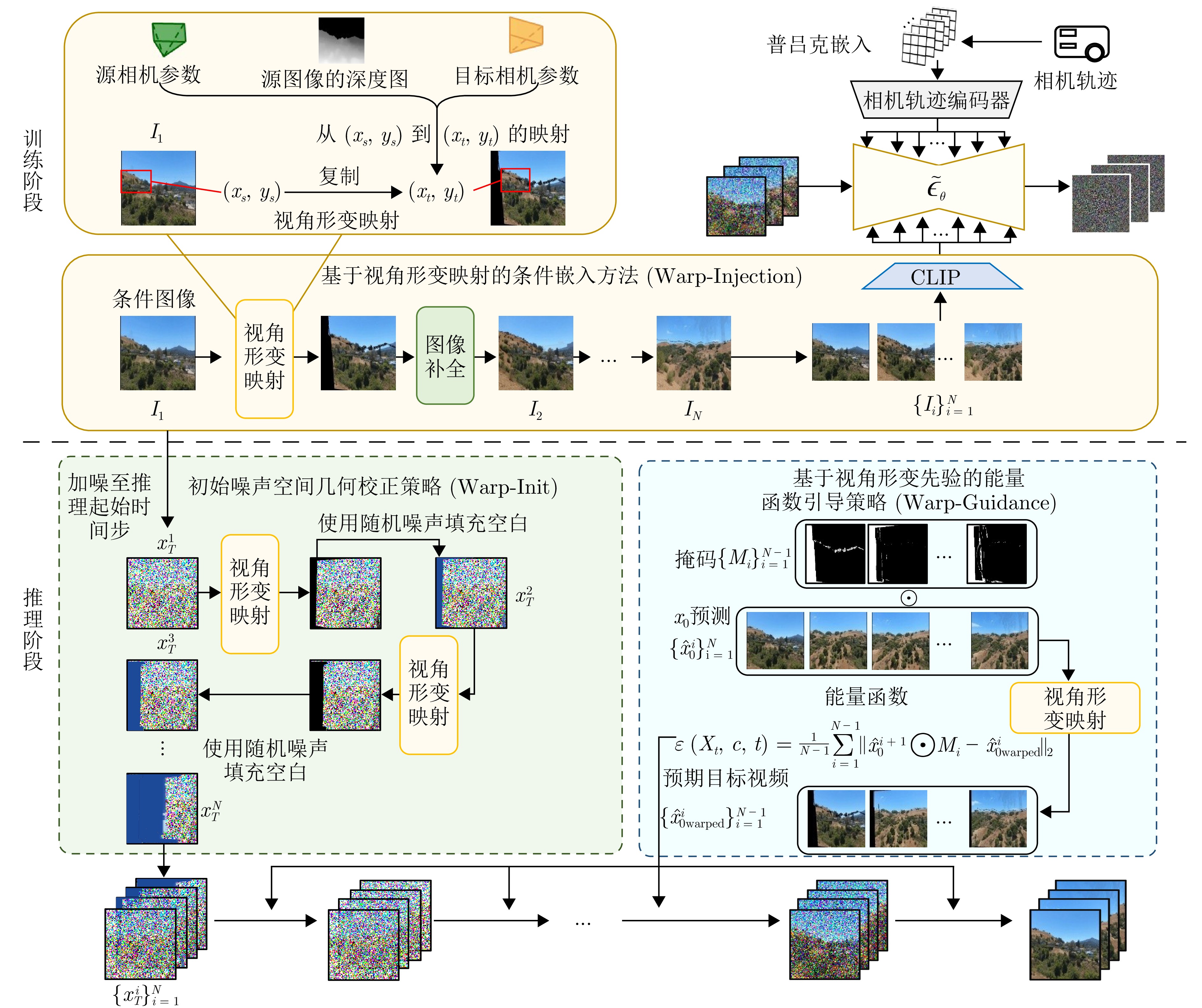
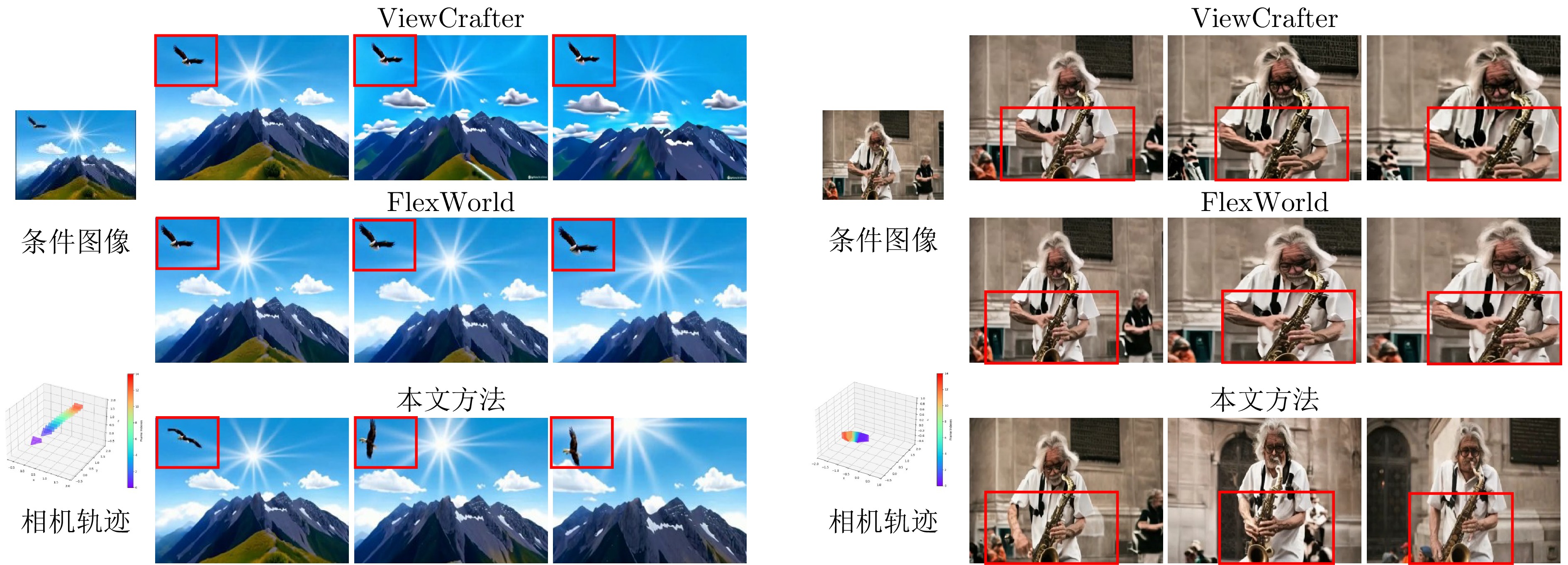
摘要: 近年来, 视频扩散模型在相机可控的图像到视频生成任务中取得了突破性进展. 然而, 现有方法在维持3D空间结构一致性方面仍面临显著挑战, 其生成视频普遍存在空间结构模糊化、多视角下物体形态畸变等缺陷, 这些问题严重制约了生成视频的视觉可信度. 为解决这一问题, 提出在视频扩散模型的训练和推理阶段均引入额外的3D空间先验信息, 以增强生成视频的空间结构一致性. 具体而言, 在模型训练阶段, 设计基于视角形变映射的条件嵌入方法(Warp-Injection), 通过进行逐帧视角形变映射与图像补全构建具备高度空间一致性的参考帧序列, 并将其作为结构先验条件嵌入扩散模型的训练过程. 在推理阶段, 首先提出初始噪声空间几何校正策略(Warp-Init): 对条件图像加噪进行首帧初始化, 此后通过迭代式视角形变映射构建符合3D一致性约束的初始噪声序列. 在此基础上, 进一步在去噪过程中引入基于视角形变先验的能量函数引导策略(Warp-Guidance), 通过减小生成帧与视角形变映射后的预期目标视频之间的距离来实现对视频3D空间一致性的校正. 在标准RealEstate10K数据集上的实验结果表明, 相较于当前最优模型, 本文方法在FVD指标上取得18.03的显著优化, 同时将3D结构估计的失败率(COLMAP error rate) 降低至5.20%. 可视化分析进一步证明, 本文方法能有效维持生成视频的3D空间结构一致性.Abstract: In recent years, video diffusion models have achieved breakthrough progress on camera-controllable image-to-video generation. However, existing methods still face significant challenges in maintaining 3D spatial structural consistency: the generated videos commonly exhibit spatial-structure blurring and cross-view shape distortions of objects, which severely constrain their visual credibility. To address this issue, we introduce additional 3D spatial prior information into both the training and inference stages of video diffusion models to enhance the spatial structural consistency of generated videos. Specifically, during training, we design a conditional embedding method based on warping (Warp-Injection): we perform sequential warping-and-inpainting to construct a reference-frame sequence with high spatial consistency, and embed it as a structural-prior condition into the diffusion model’s training process. At the inference stage, we first propose an initial-noise spatial-geometry correction strategy (Warp-Init): the first frame is initialized by adding noise to the conditioning image, after which an initial noise sequence that satisfies 3D-consistency constraints is constructed via iterative warping. On this basis, we further introduce an energy-function guidance strategy (Warp-Guidance) driven by warping priors during denoising, which corrects the video’s 3D spatial consistency by reducing the distance between the generated frames and the expected target video obtained after warping. Experiments on the standard RealEstate10K dataset show that, compared with the current state-of-the-art model, our method achieves a significant improvement of 18.03 in FVD and reduces the failure rate of 3D structure estimation (COLMAP error rate) to 5.20%. Visualization analyses further demonstrate that our method effectively maintains 3D spatial structural consistency in generated videos.
-
表 1 在RealEstate10K上的定量比较(最佳结果以粗体显示)
Table 1 Quantitative comparison on RealEstate10K (The best results are shown in bold)
表 2 消融实验
Table 2 Ablation experiment
方法 FID$\downarrow$ FVD$\downarrow$ COLMAP error rate $\downarrow$ Transition error $\downarrow$ Rotation error $\downarrow$ 基线方法 11.12 72.31 18.9% 5.4319 2.1482 + Inj. 9.97 61.13 7.60% 3.8512 1.9942 + Inj. + Init. 9.85 58.39 7.10% 3.7125 1.9854 + Inj. + Guid. 9.87 57.83 6.70% 3.7324 1.9691 本文方法 9.61 52.63 5.20% 3.6372 1.9633 -
[1] Zhang L, Rao A, Agrawala M. Adding conditional control to text-to-image diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 3836−3847 [2] Mou C, Wang X, Xie L, Wu Y, Zhang J, Qi Z, et al. T2i-adapter: Learning adapters to dig out more controllable ability for text-to-image diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI). Vancouver, Canada: AAAI, 2024. 4296−4304 [3] Wang C, Gu J, Hu P, Zhao H, Guo Y, Han J, et al. Easycontrol: Transfer controlnet to video diffusion for controllable generation and interpolation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2408.13005, 2024. [4] Zhang Y, Wei Y, Jiang D, Zhang X, Zuo W, Tian Q. Controlvideo: Training-free controllable text-to-video generation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2305.13077, 2023. [5] Zhao M, Wang R, Bao F, Li C, Zhu J. Controlvideo: Adding conditional control for one shot text-to-video editing. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2305.17098, 2023. [6] Zhong Y, Zhao M, You Z, Yu X, Zhang C, Li C. Posecrafter: One-shot personalized video synthesis following flexible pose control. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Milan, Italy: Springer, 2024. 243−260 [7] Zhu S, Chen J L, Dai Z, Dong Z, Xu Y, Cao X, et al. Champ: Controllable and consistent human image animation with 3d parametric guidance. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Milan, Italy: Springer, 2024. 145−162 [8] Wang Z, Yuan Z, Wang X, Li Y, Chen T, Xia M, et al. Motionctrl: A unified and flexible motion controller for video generation. In: Proceedings of the ACM Special Interest Group on ComputerGraphics (SIGGRAPH). Denver, USA: ACM, 2024. 1−11 [9] He H, Xu Y, Guo Y, Wetzstein G, Dai B, Li H, et al. Cameractrl: Enabling camera control for text-to-video generation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2404.02101, 2024. [10] Xu D, Nie W, Liu C, Liu S, Kautz J, Wang Z, et al. Camco: Camera-controllable 3d-consistent image-to-video generation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2406.02509, 2024. [11] Zheng G, Li T, Jiang R, Lu Y, Wu T, Li X. Cami2v: Camera-controlled image-to-video diffusion model. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2410.15957, 2024. [12] Hou C, Wei G, Zeng Y, Chen Z. Training-free camera control for video generation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2406.10126, 2024. [13] You M, Zhu Z, Liu H, Hou J. Nvs-solver: Video diffusion model as zero-shot novel view synthesizer. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2405.15364, 2024. [14] Zhou T, Tucker R, Flynn J, Fyffe G, Snavely N. Stereo magnification: Learning view synthesis using multiplane images. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1805.09817, 2018. [15] Heusel M, Ramsauer H, Unterthiner T, Nessler B, Hochreiter S. Gans trained by a two time-scale update rule converge to a local nash equilibrium. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 30 [16] Unterthiner T, Van Steenkiste S, Kurach K, Marinier R, Michalski M, Gelly S. Towards accurate generative models of video: A new metric and challenges. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1812.01717, 2018. [17] Schonberger J L, Frahm J-M. Structure-from-motion revisited. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 4104−4113 [18] Blattmann A, Rombach R, Ling H, Dockhorn T, Kim S W, Fidler S, et al. Align your latents: High-resolution video synthesis with latent diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR). Vancouver, Canada: IEEE, 2023. 22563−22575 [19] Singer U, Polyak A, Hayes T, Yin X, An J, Zhang S, et al. Make-a-video: Text-to-video generation without text-video data. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2209.14792, 2022. [20] Ho J, Chan W, Saharia C, Whang J, Gao R, Gritsenko A, et al. Imagen video: High definition video generation with diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2210.02303, 2022. [21] Guo Y, Yang C, Rao A, Liang Z, Wang Y, Qiao Y, et al. Animatediff: Animate your personalized text-to-image diffusion models without specific tuning. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2307.04725, 2023. [22] Chen H, Zhang Y, Cun X, Xia M, Wang X, Weng C, et al. Videocrafter2: Overcoming data limitations for high-quality video diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 7310−7320 [23] Hong W, Ding M, Zheng W, Liu X, Tang J. Cogvideo: Large-scale pretraining for text-to-video generation via transformers. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2205.15868, 2022. [24] HaCohen Y, Chiprut N, Brazowski B, Shalem D, Moshe D, Richardson E, et al. Ltx-video: Realtime video latent diffusion. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2501.00103, 2024. [25] Yang Z, Teng J, Zheng W, Ding M, Huang S, Xu J, et al. Cogvideox: Text-to-video diffusion models with an expert transformer. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2408.06072, 2024. [26] Blattmann A, Dockhorn T, Kulal S, Mendelevitch D, Kilian M, Lorenz D, et al. Stable video diffusion: Scaling latent video diffusion models to large datasets. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2311.15127, 2023. [27] Brooks T, Peebles B, Holmes C, DePue W, Guo Y, Jing L, et al. Video generation models as world simulators. [Online], available: https://openai.com/index/video-generation-models-as-world-simulators, August 8, 2025. [28] Bao F, Xiang C, Yue G, He G, Zhu H, Zheng K, et al. Vidu: a highly consistent, dynamic and skilled text-to-video generator with diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2405.04233, 2024. [29] Xing J, Xia M, Zhang Y, Chen H, Yu W, Liu H, et al. Dynamicrafter: Animating open-domain images with video diffusion priors. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Milan, Italy: Springer, 2024. 399−417 [30] Zhang S, Wang J, Zhang Y, Zhao K, Yuan H, Qin Z, et al. I2vgen-xl: High-quality image-to-video synthesis via cascaded diffusion models. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2311.04145, 2023. [31] Chen X, Wang Y, Zhang L, Zhuang S, Ma X, Yu J, et al. Seine: Short-to-long video diffusion model for generative transition and prediction. In: Proceedings of the Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Vienna, Austria: 2024 [32] Zhao M, Zhu H, Xiang C, Zheng K, Li C, Zhu J. Identifying and solving conditional image leakage in image-to-video diffusion model. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2024. 30300−30326 [33] Ho J, Jain A, Abbeel P. Denoising diffusion probabilistic models. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). Virtual Event: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. 6840−6851 [34] Ho J, Salimans T. Classifier-free diffusion guidance. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2207.12598, 2022. [35] Zhao M, Bao F, Li C, Zhu J. Egsde: Unpaired image-to-image translation via energy-guided stochastic differential equations. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2022. 3609−3623 [36] Bao F, Zhao M, Hao Z, Li P, Li C, Zhu J. Equivariant energy-guided sde for inverse molecular design. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Kigali, Rwanda: 2023 [37] Wang X, Yuan H, Zhang S, Chen D, Wang J, Zhang Y, et al. Videocomposer: Compositional video synthesis with motion controllability. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). New Orleans, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2023. 7594−7611 [38] Hu E J, Shen Y, Wallis P, Allen-Zhu Z, Li Y, Wang S, et al. Lora: Low-rank adaptation of large language models. In: Proceedings of the Tenth International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR). Virtual Event: 2022 [39] Fehn C. Depth-image-based rendering (dibr), compression, and transmission for a new approach on 3d-tv. In Proceedings of the Stereoscopic Displays and Virtual Reality Systems XI. San Jose, USA: SPIE, 2004. 93−104 [40] Rombach R, Blattmann A, Lorenz D, Esser P, Ommer B. High-resolution image synthesis with latent diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 10684−10695 [41] Radford A, Kim J W, Hallacy C, Ramesh A, Goh G, Agarwal S, et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML). Virtual Event: PMLR, 2021. 8748−8763 [42] Khachatryan L, Movsisyan A, Tadevosyan V, Henschel R, Wang Z, Navasardyan S, et al. Text2video-zero: Text-to-image diffusion models are zero-shot video generators. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Paris, France: IEEE, 2023. 15954−15964 [43] Ren W, Yang H, Zhang G, Wei C, Du X, Huang W, et al. Consisti2v: Enhancing visual consistency for image-to-video generation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2402.04324, 2024. [44] Ge S, Nah S, Liu G, Poon T, Tao A, Catanzaro B, et al. Preserve your own correlation: A noise prior for video diffusion models. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Paris, France: IEEE, 2023. 22930−22941 [45] Burgert R, Xu Y, Xian W, Pilarski O, Clausen P, He M, et al. Go-with-the-flow: Motion-controllable video diffusion models using real-time warped noise. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2501.08331, 2025. [46] Meng C, He Y, Song Y, Song J, Wu J, Zhu J-Y, et al. Sdedit: Guided image synthesis and editing with stochastic differential equations. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2108.01073, 2021. [47] Dhariwal P, Nichol A. Diffusion models beat gans on image synthesis. In: Proceedings of the Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS). Virtual Event: Curran Associates Inc., 2021. 8780−8794 [48] Yang L, Kang B, Huang Z, Zhao Z, Xu X, Feng J, et al. Depth anything v2. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2406.09414, 2024. [49] Flux. [Online], available: https://github.com/black-forest-labs/flux, August 8, 2025. [50] Chen L, Zhou Z, Zhao M, Wang Y, Zhang G, Huang W, et al. Flexworld: Progressively expanding 3d scenes for flexiable-view synthesis, arXiv preprint arXiv: 2503.13265 [51] Yu W, Xing J, Yuan L, Hu W, Li X, Huang Z, et al. Viewcrafter: Taming video diffusion models for high-fidelity novel view synthesis. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2409.02048, 2024. [52] Ren X, Shen T, Huang J, Ling H, Lu Y, Nimier-David M, et al. Gen3c: 3d-informed world-consistent video gen-eration with precise camera control. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Conference (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2025. 6121−6132 -

计量
- 文章访问数: 359
- HTML全文浏览量: 385
- 被引次数: 0




 下载:
下载: