A Technology Forecasting Model Integrating Spatiotemporal Features Under the “Structure-Content” Framework
-
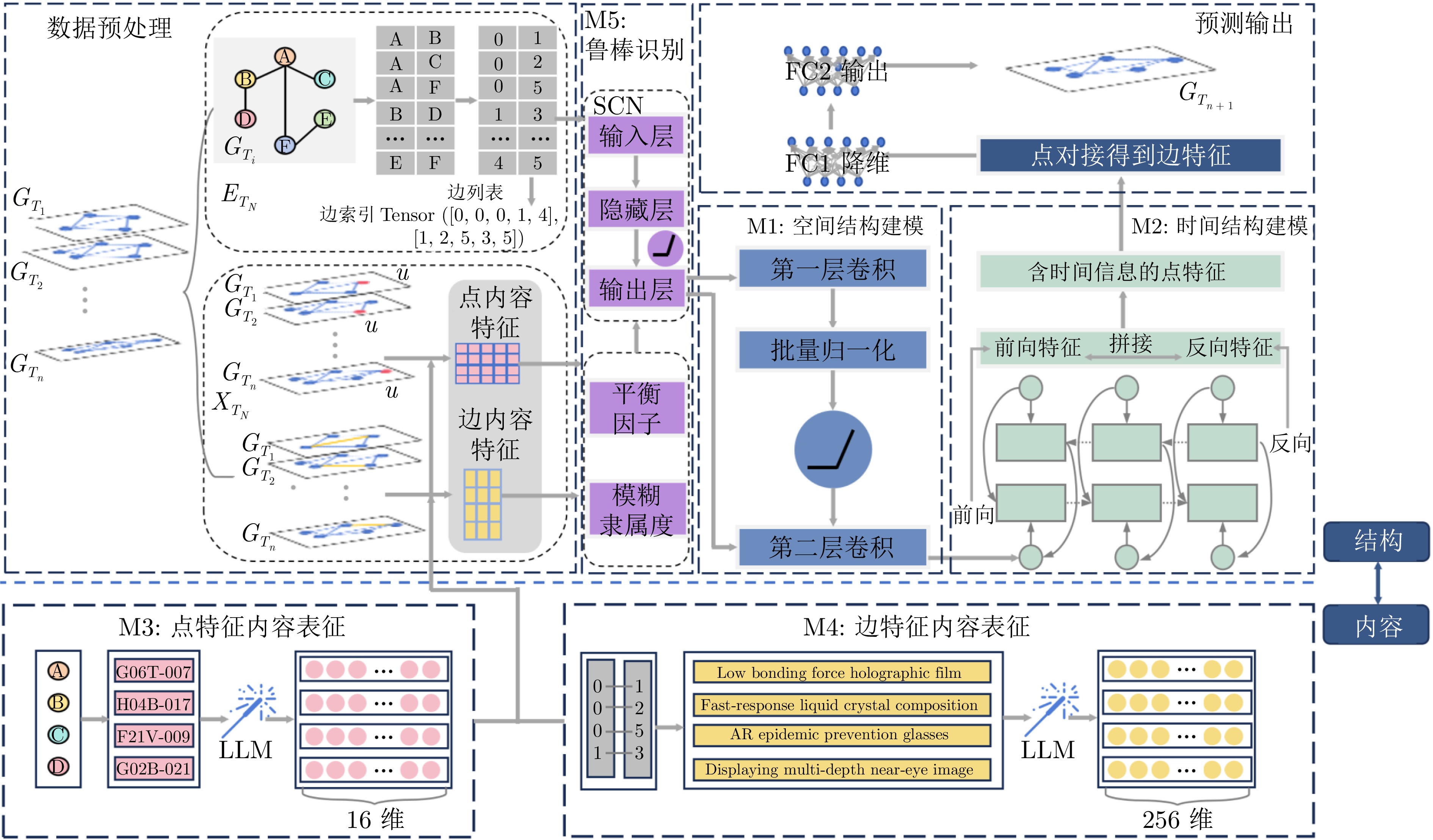
摘要: 科学技术发展是一种动态非线性的复杂演进过程. 为提升技术预测的精确度, 基于大语言模型、图卷积神经网络、双向长短期记忆神经网络以及鲁棒随机配置网络(RSCN), 提出一种全新的“结构−内容”时空技术预测模型. 首先, 通过结合图卷积神经网络和双向长短期记忆神经网络, 分别捕捉技术网络中的空间依赖关系和时间演化规律, 从而突破传统预测模型在动态性和结构表征上的局限性, 克服传统技术预测模型的“伪动态”和“静态”限制. 其次, 引入大语言模型对技术网络中的节点特征和边特征进行双重语义表征, 将预测框架从单一的结构维度扩展至“结构−内容”双维度分析, 显著增强了模型对技术发展信息的理解能力和表征深度. 最后, 通过集成RSCN, 模型能够有效应对极端不均衡数据分布的挑战, 进一步提升了预测的鲁棒性和准确性. 提出的预测框架在多个指标上均优于当前多种技术预测方法, 为推动技术预测建模和评估未来技术发展轨迹提供了有力的支持.
-
关键词:
- 科学技术发展 /
- 图卷积神经网络 /
- 大语言模型 /
- 双向长短期记忆神经网络 /
- 鲁棒随机配置网络
Abstract: The development of science and technology is a dynamic, nonlinear, and complex evolutionary process. To enhance the precision of technological development predictions, this paper proposes a novel “structure-content” spatiotemporal technological forecasting model based on large language models, graph convolutional neural networks, bidirectional long short-term memory neural networks, and robust stochastic configuration networks (RSCN). Firstly, by integrating graph convolutional neural networks and bidirectional long short-term memory neural networks, the model captures the spatial dependencies and temporal evolution patterns within technological networks, thereby overcoming the limitations of traditional forecasting models in terms of dynamic behavior and structural representation, and addressing the “pseudo-dynamic” and “static” constraints of conventional technological forecasting models. Secondly, the introduction of large language models enables dual semantic representation of node and edge features within the technological network, expanding the predictive framework from a single structural dimension to a dual-dimensional “structure-content” analysis. This significantly enhances the model's ability to understand and represent information related to technological development. Finally, by incorporating RSCN, the model effectively addresses the challenges posed by extremely imbalanced data distributions, further improving the robustness and accuracy of predictions. The proposed forecasting framework outperforms various current technological forecasting methods across multiple metrics, providing strong support for advancing technological forecasting modeling and evaluating future technological development trajectories. -
表 1 模型性能指标的计算方法
Table 1 Calculation method of model performance measure index
测度指标 计算公式 Recall $\dfrac{\mathrm{ TP}}{\mathrm{TP} + \mathrm{FN}}$ Precision $\dfrac{\mathrm{TP}}{\mathrm{TP} + \mathrm{FP}}$ AUC $ \sum\limits_{k=1}^{m-1}\dfrac{(\mathrm{FPR}_{k+1}-\mathrm{FPR}_k)\times(\mathrm{TPR}_{k+1}+\mathrm{TPR}_k)}{2} $ AUPR $ \sum\limits_{k=1}^{m-1}\dfrac{(R_{k+1}-R_k)\times(P_{k+1}+P_k)}{2} $ F1 $2 \times \dfrac{\text{Precision} \times \text{Recall}}{\text{Precision} + \text{Recall}}$ 表 2 所提模型与基线模型性能比较
Table 2 Performance comparison between the proposed model and the baseline models
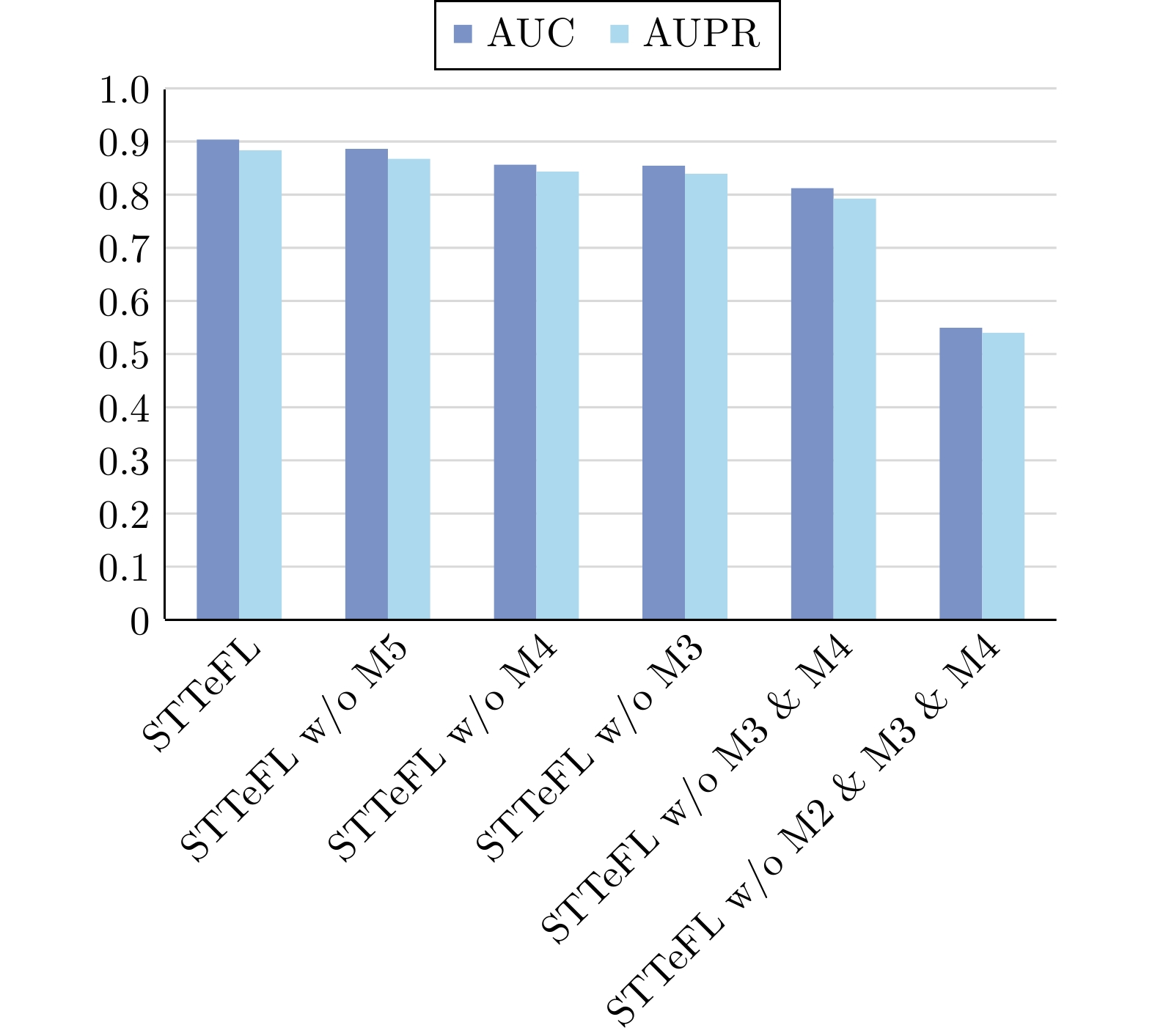
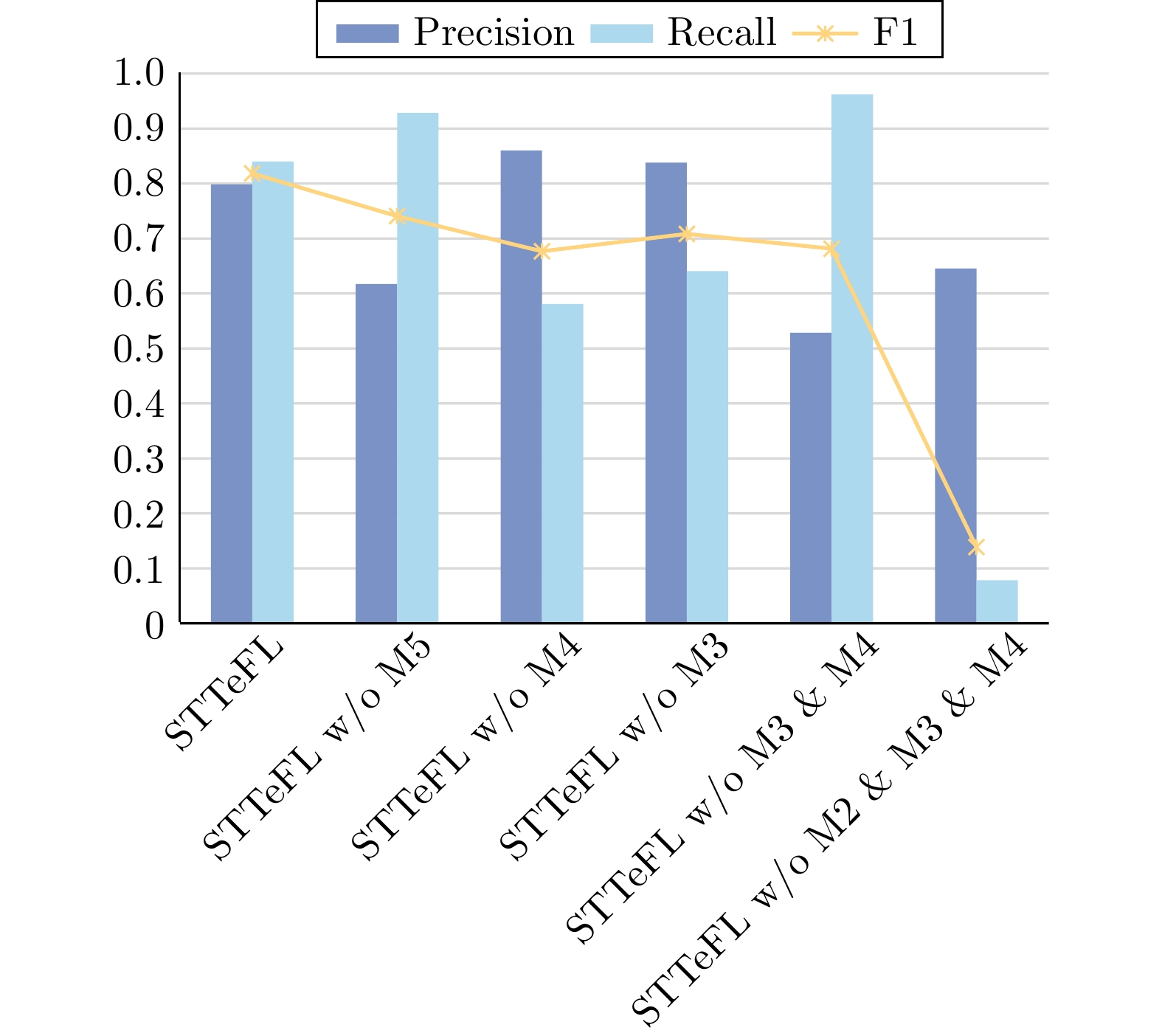
模型 特征 AUC Precision Recall F1 AUPR STTeFL 内容LLM表征 0.8837 ±0.0024 0.8361 ±0.0166 0.8066 ±0.0134 0.8206 ±0.0084 0.9054 ±0.0026 LogR 链路相似性 0.6279 ±0.0141 0.7383 ±0.0370 0.2565 ±0.0282 0.3807 ±0.0313 0.5002 ±0.0265 SVM 链路相似性 0.5113 ±0.0137 0.7778 ±0.1070 0.0227 ±0.0321 0.0442 ±0.0371 0.4039 ±0.0332 RF 链路相似性 0.6915 ±0.0115 0.6650 ±0.0236 0.3844 ±0.0231 0.4867 ±0.0649 0.5270 ±0.0368 XGBoost 链路相似性 0.8004 ±0.0149 0.4773 ±0.0170 0.6058 ±0.0301 0.5335 ±0.0301 0.5431 ±0.0135 AdaBoost 链路相似性 0.7085 ±0.0267 0.6324 ±0.1254 0.4188 ±0.0406 0.5039 ±0.0351 0.5278 ±0.0483 表 3 对比模型的实验结果
Table 3 Experimental results under different comparative models
对比方式 模型 AUC Precision Recall F1 AUPR 大模型 STTeFL_gpt 0.8781 ±0.0042 0.7031 ±0.0199 0.8855 ±0.0098 0.7835 ±0.0089 0.9000 ±0.0062 STTeFL_bert 0.8803 ±0.0052 0.8163 ±0.0126 0.8061 ±0.0242 0.8135 ±0.0085 0.8959 ±0.0083 特征表达 STTeFL_doc 0.7872 ±0.0606 0.6306 ±0.1107 0.8477 ±0.1253 0.7052 ±0.0400 0.8026 ±0.0630 STTeFL_sim 0.8677 ±0.0076 0.6037 ±0.0221 0.9333 ±0.0093 0.7328 ±0.0135 0.8842 ±0.0105 维数选择 STTeFL_32N 0.8700 ±0.0001 0.5553 ±0.0201 0.9595 ±0.0006 0.7017 ±0.0088 0.8870 ±0.0024 STTeFL_128L 0.8708 ±0.0000 0.6289 ±0.0014 0.9255 ±0.0002 0.7480 ±0.0005 0.8882 ±0.0000 表 4 深度学习领域未来潜在技术举例
Table 4 Examples of potential future technologies in the deep learning area
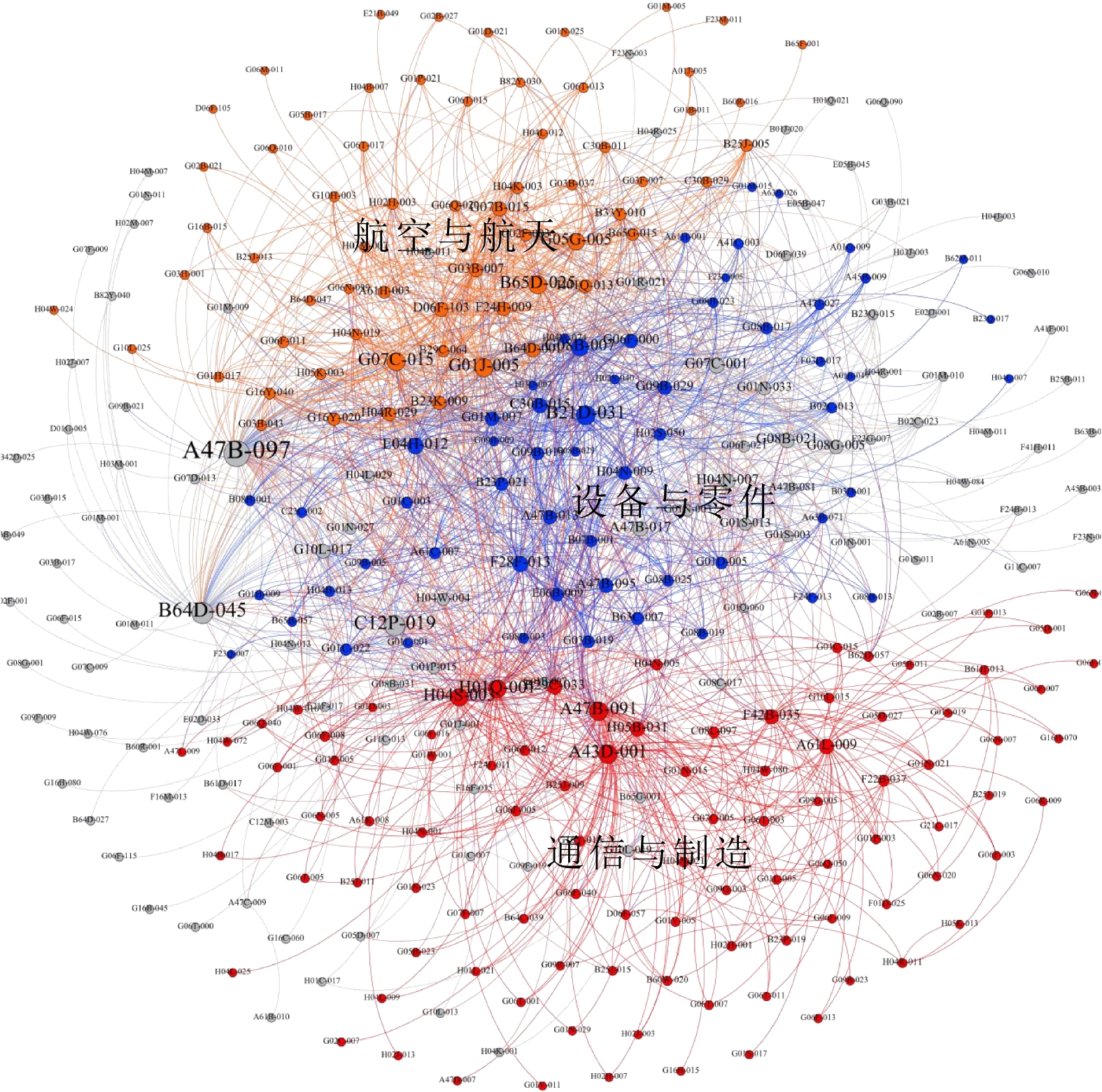
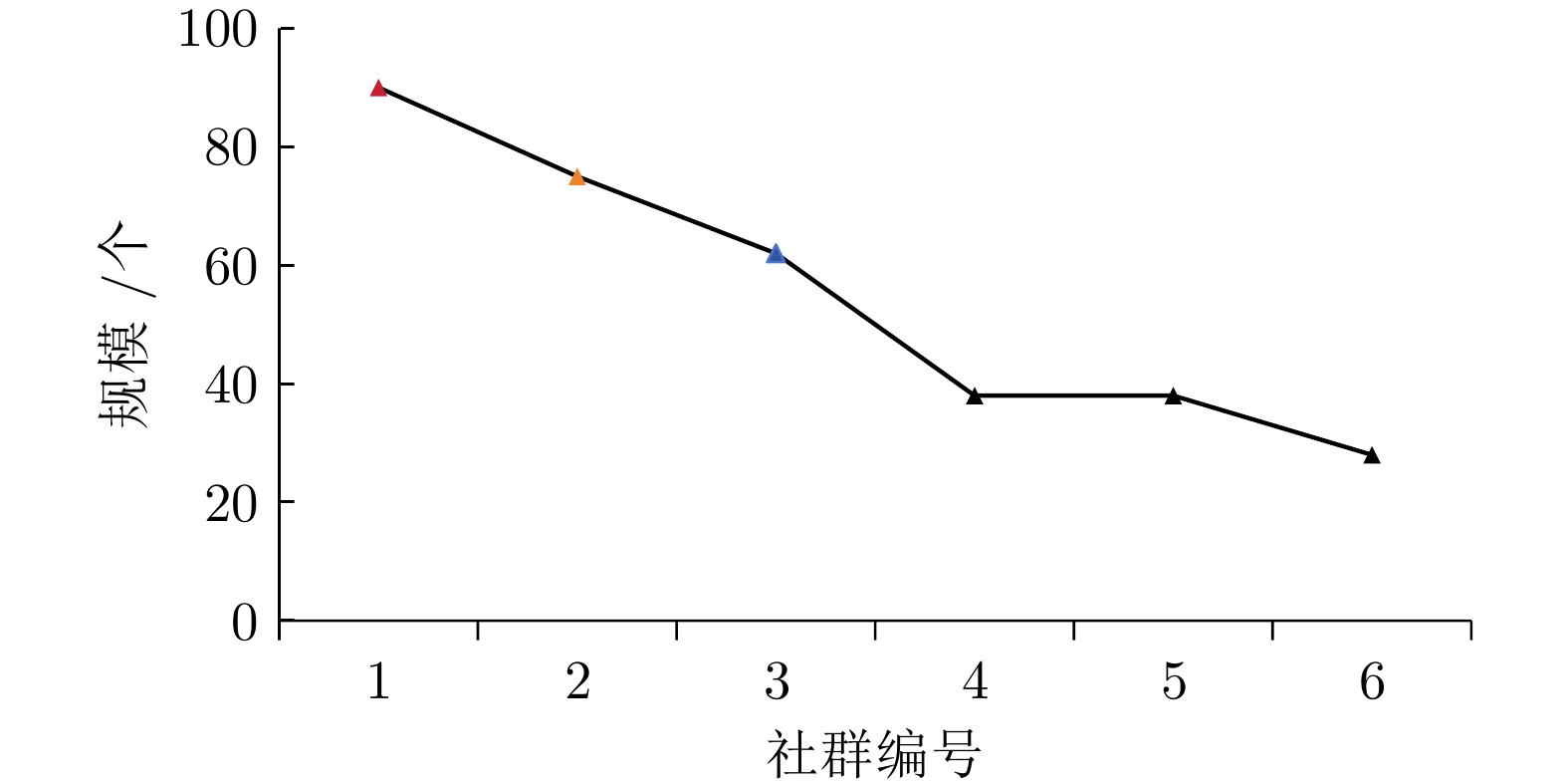
序号 核心节点 潜在可能技术 涉及领域 1 A43D-001; A47B-091; H01Q-001; H04S-003 天线设计与优化、立体声与多声道音频处理、塑料成型与模具 5G通信、虚拟现实、汽车制造 2 G01J-005; B65D-025; G07C-015; G05G-005 光学测量与传感器、航空设备与飞行控制、时间记录与考勤系统 环境监测、航空航天、企业管理 3 B21D-037; G08B-007; E04H-012; F28F-013 计算机硬件与软件、机械测试与测量、金属成型与加工 设备监测、零部件制造、金融科技 A1 LLM 模型的参数设置
A1 LLM model parameter settings
模型 参数设置 activation_function (激活函数): gelu_new n_embd (嵌入维度): 1600 n_layer (Transformer 层的数量): 48 n_head (每个 Transformer 层中的自注意力
头数): 25vocab_size (词汇表大小): 50257 n_ctx (上下文窗口大小): 1024 n_positions (最大位置编码数): 1024 gpt2-xl initializer_range (初始化范围): 0.02 layer_norm_epsilon (层归一化的 epsilon 值): 1e−5 attn_pdrop (注意力层的丢弃率): 0.1 embd_pdrop (嵌入层的丢弃率): 0.1 resid_pdrop (残差连接的丢弃率): 0.1 bos_token_id (开始标记 ID): 50256 eos_token_id (结束标记 ID): 50256 max_length (生成文本的最大长度): 16 hidden_size (隐藏层大小): 2 048 Sheared-LLaMA-1.3B num_attention_heads (每个 Transformer 层中的
自注意力头数): 16num_hidden_layers (Transformer 层的数量): 24 Sheared-LLaMA-1.3B vocab_size (词汇表大小): 32000 max_position_embeddings (最大位置编码数): 4096 intermediate_size (前馈神经网络的隐藏层大小): 5504 hidden_act (隐藏层激活函数): silu bos_token_id (开始标记 ID): 1 eos_token_id (结束标记 ID): 2 pad_token_id (填充标记 ID): 0 pretraining_tp (预训练 TP): 1 rms_norm_eps (RMS 层归一化的 epsilon 值): 1e−5 rope_theta (位置编码的 theta 值): 10000.0 max_length (生成文本的最大长度): 16 activation_function (激活函数): gelu n_embd (嵌入维度): 768 n_layer (Transformer 层的数量): 12 n_head (每个 Transformer 层中的自注意力头数): 12 vocab_size (词汇表大小): 30522 n_ctx (上下文窗口大小): 512 n_positions (最大位置编码数): 512 bert-base-
uncasedlayer_norm_epsilon (层归一化的 epsilon 值): 1e−12 attn_pdrop (注意力层的丢弃率): 0.1 hidden_dropout_prob (隐藏层丢弃率): 0.1 bos_token_id (开始标记 ID): 101 eos_token_id (结束标记 ID): 102 pad_token_id (填充标记 ID): 0 position_embedding_type (位置编码类型): absolute Linear Layer: 输入维度: 768 输出维度: 16 -
[1] Zhao J Y, Dong Z J, Yao X L, Xi X. Optimizing collaboration decisions in technological innovation through machine learning: Identify trend and partners in collaboration-knowledge interdependent networks. Annals of Operations Research, DOI: 10.1007/s10479-024-05867-z [2] 连芷萱, 王芳, 康佳, 袁畅. 基于图神经网络和粒子群算法的技术预测模型. 情报学报, 2023, 42(4): 420−435Lian Zhi-Xuan, Wang Fang, Kang Jia, Yuan Chang. Graph neural network-based and particle swarm optimization technological prediction model. Journal of the China Society for Scientific and Technical Information, 2023, 42(4): 420−435 [3] Xi X, Ren F F, Yu L A, Yang J. Detecting the technology' s evolutionary pathway using HiDS-trait-driven tech mining strategy. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2023, 195: Article No. 122777 doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2023.122777 [4] 潘文雯, 赵洲, 俞俊, 吴飞. 基于文本引导的注意力图像转发预测排序网络. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(11): 2547−2556Pan Wen-Wen, Zhao Zhou, Yu Jun, Wu Fei. Textually guided ranking network for attentional image retweet modeling. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(11): 2547−2556 [5] Daud N N, ab Hamid S H, Saadoon M, Sahran F, Anuar N B. Applications of link prediction in social networks: A review. Journal of Network and Computer Applications, 2020, 166: Article No. 102716 doi: 10.1016/j.jnca.2020.102716 [6] Lee W S, Han E J, Sohn S Y. Predicting the pattern of technology convergence using big-data technology on large-scale triadic patents. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2015, 100: 317−329 doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2015.07.022 [7] 张斌, 李亚婷. 学科合作网络链路预测结果的排序鲁棒性. 信息资源管理学报, 2018, 8(4): 89−97Zhang Bin, Li Ya-Ting. Ranking robustness of link prediction results in disciplinary collaboration network. Journal of Information Resources Management, 2018, 8(4): 89−97 [8] Xi X, Zhao J Y, Yu L A, Wang C. Exploring the potentials of artificial intelligence towards carbon neutrality: Technological convergence forecasting through link prediction and community detection. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2024, 190: Article No. 110015 [9] Sasaki H, Sakata I. Identifying potential technological spin-offs using hierarchical information in international patent classification. Technovation, 2021, 100: Article No. 102192 doi: 10.1016/j.technovation.2020.102192 [10] 贾承丰, 韩华, 吕亚楠, 张路. 基于Word2vec和粒子群的链路预测算法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(8): 1703−1713Jia Cheng-Feng, Han Hua, Lv Ya-Nan, Zhang Lu. Link prediction algorithm based on Word2vec and particle swarm. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(8): 1703−1713 [11] 王守辉, 于洪涛, 黄瑞阳, 马青青. 基于模体演化的时序链路预测方法. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(5): 735−745Wang Shou-Hui, Yu Hong-Tao, Huang Rui-Yang, Ma Qing-Qing. A temporal link prediction method based on motif evolution. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(5): 735−745 [12] Kwon O, An Y, Kim M, Lee C. Anticipating technology-driven industry convergence: Evidence from large-scale patent analysis. Technology Analysis & Strategic Management, 2020, 32(4): 363−378 [13] Kipf T N, Welling M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks. In: Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations. Toulon, France: OpenReview.net, 2017. [14] Zhou L X, Schellaert W, Martínez-Plumed F, Moros-Daval F, Ferri C, Hernández-Orallo J. Larger and more instructable language models become less reliable. Nature, 2024, 634(8032): 61−68 doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07930-y [15] 代伟, 李德鹏, 杨春雨, 马小平. 一种随机配置网络的模型与数据混合并行学习方法. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(10): 2427−2437Dai Wei, Li De-Peng, Yang Chun-Yu, Ma Xiao-Ping. A model and data hybrid parallel learning method for stochastic configuration networks. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(10): 2427−2437 [16] Lee C, Hong S, Kim J. Anticipating multi-technology convergence: A machine learning approach using patent information. Scientometrics, 2021, 126(3): 1867−1896 doi: 10.1007/s11192-020-03842-6 [17] Wang J T, Lee J J. Predicting and analyzing technology convergence for exploring technological opportunities in the smart health industry. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2023, 182: Article No. 109352 [18] Hong S, Lee C. Effective indexes and classification algorithms for supervised link prediction approach to anticipating technology convergence: A comparative study. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management, 2023, 70(4): 1430−1441 doi: 10.1109/TEM.2021.3098602 [19] Grover A, Leskovec J. Node2vec: Scalable feature learning for networks. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining. San Francisco, USA: ACM, 2016. 855−864 [20] Dastile X, Celik T, Potsane M. Statistical and machine learning models in credit scoring: A systematic literature survey. Applied Soft Computing, 2020, 91: Article No. 106263 doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2020.106263 [21] Kim T S, Sohn S Y. Machine-learning-based deep semantic analysis approach for forecasting new technology convergence. Technological Forecasting and Social Change, 2020, 157: Article No. 120095 doi: 10.1016/j.techfore.2020.120095 [22] Zhao H K, Zhao C, Zhang X, Liu N L, Zhu H S, Liu Q, et al. An ensemble learning approach with gradient resampling for class-imbalance problems. INFORMS Journal on Computing, 2023, 35(4): 747−763 doi: 10.1287/ijoc.2023.1274 [23] Kumar A, Singh S S, Singh K, Biswas B. Link prediction techniques, applications, and performance: A survey. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2020, 553: Article No. 124289 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2020.124289 [24] Kim K S, Cho N W. Predicting the patterns of technology convergence in defense technologies. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Big Data and Smart Computing (BigComp). Daegu, Korea: IEEE, 2022. 72−75 -




 下载:
下载: