Centralized Cooperative Control of Mixed Vehicle Groups Considering Multi-vehicle Influence Under Cloud-Edge-End Collaboration
-
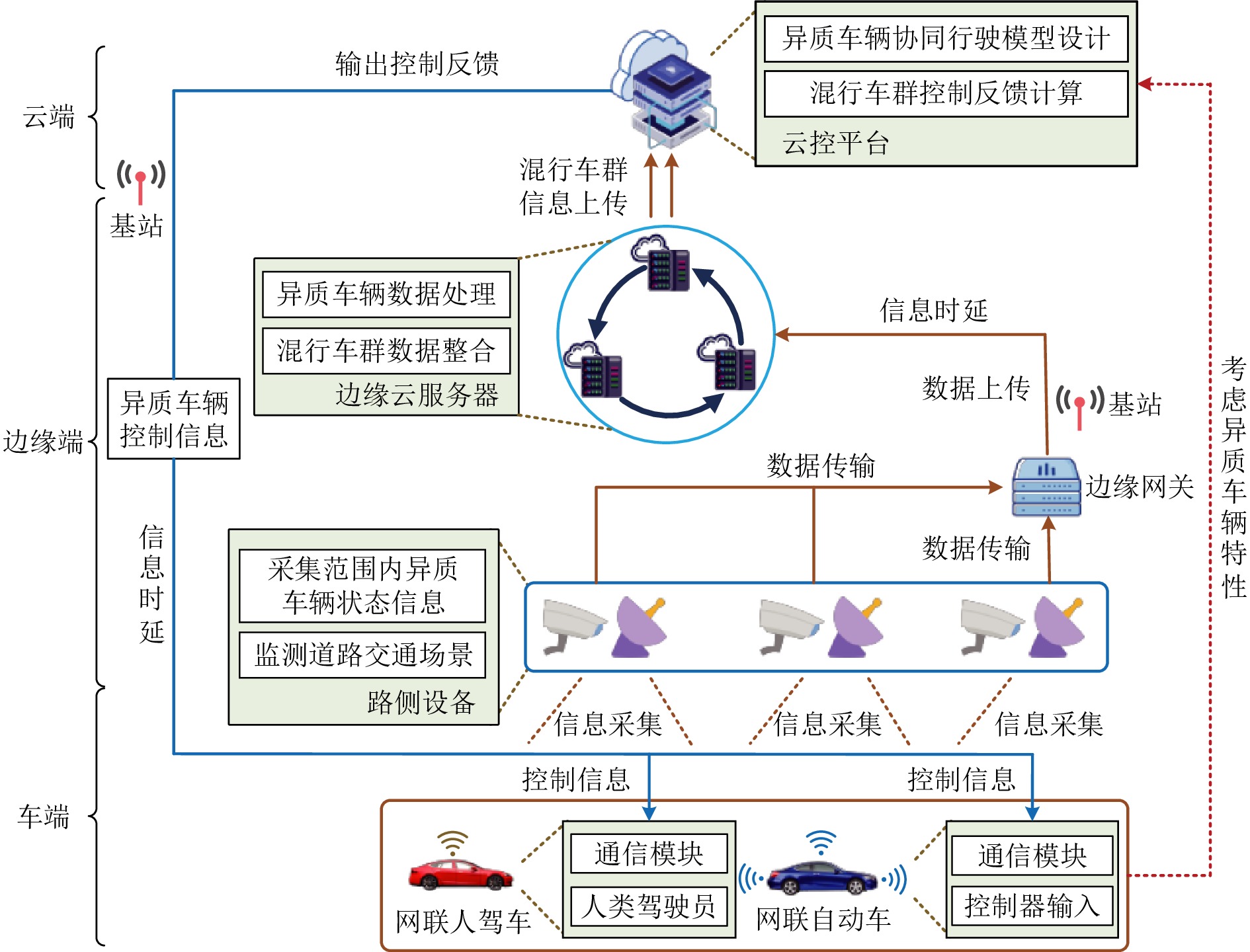
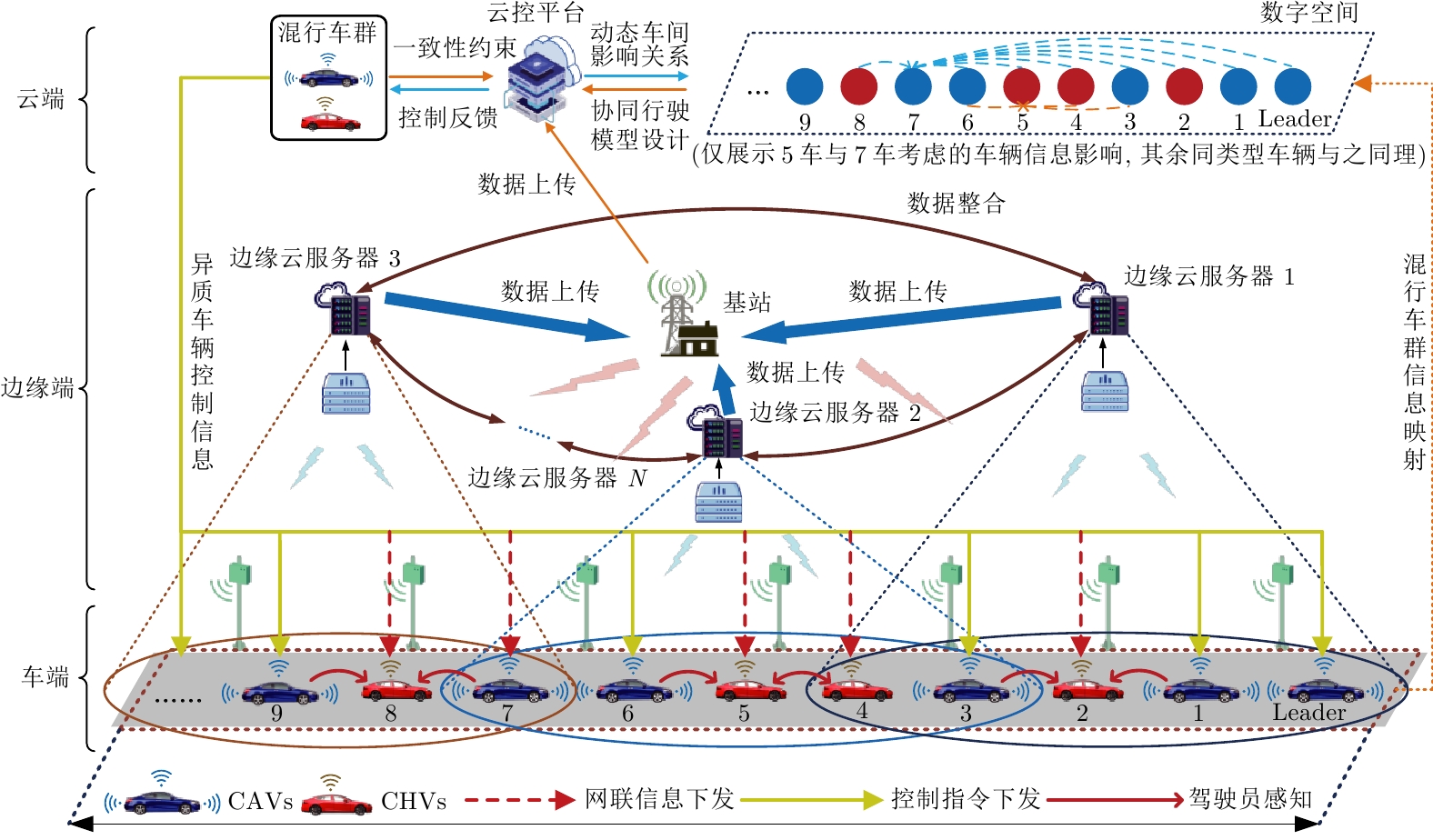
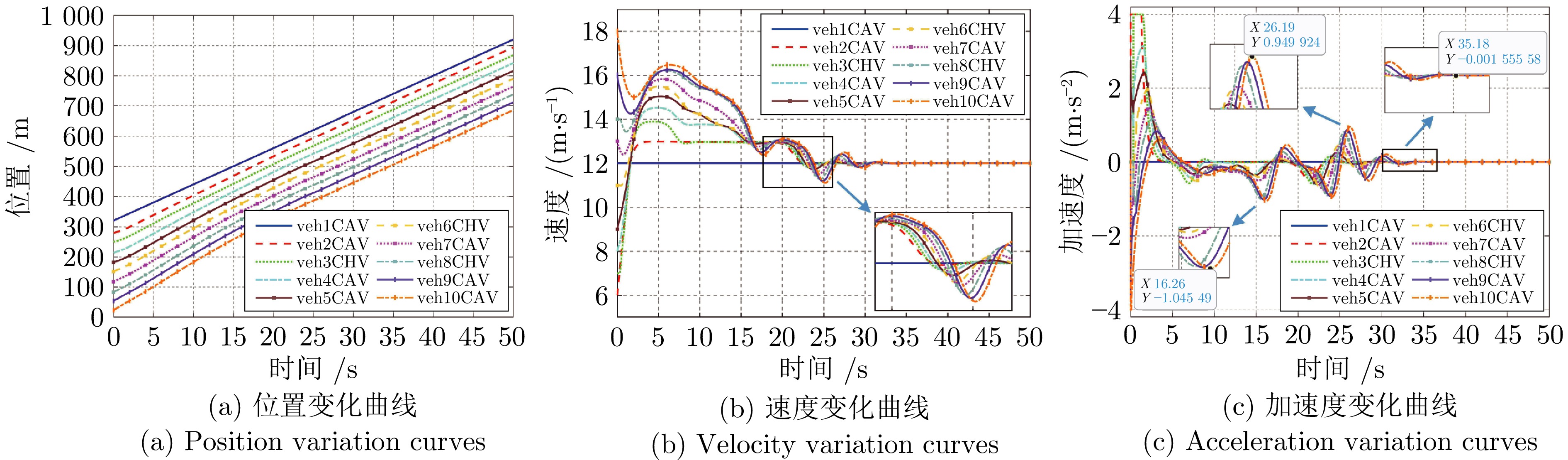
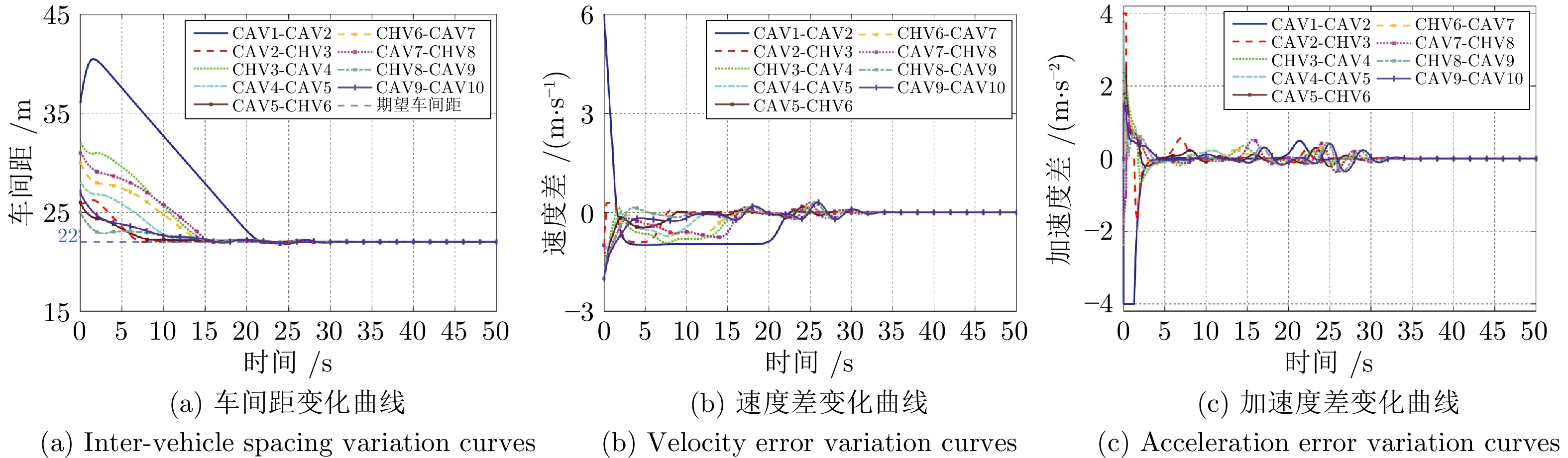
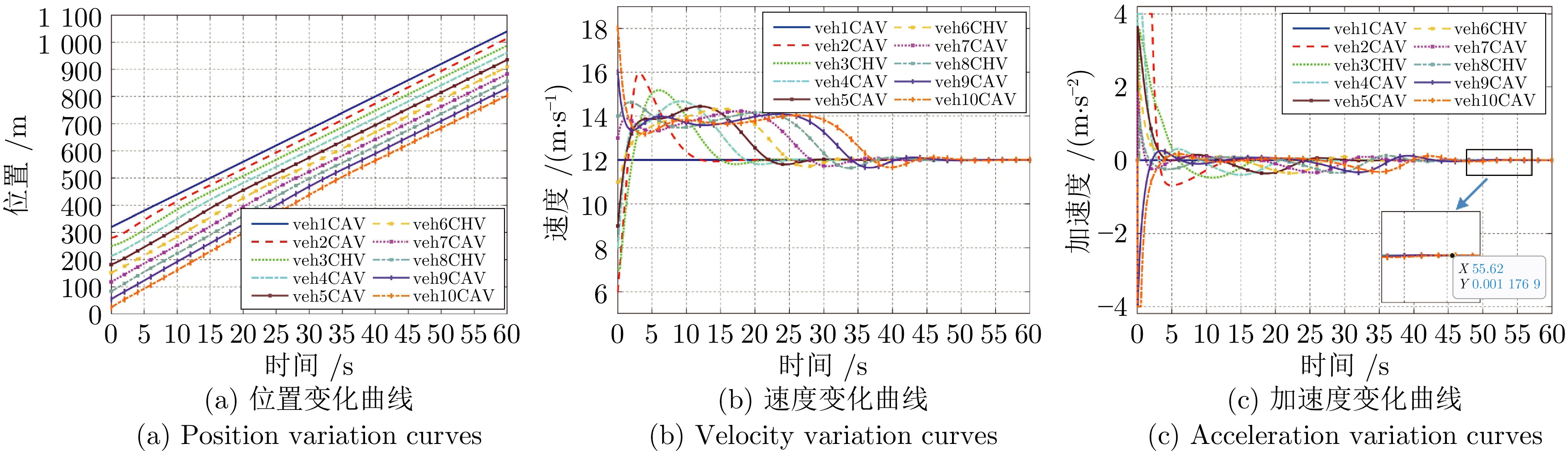
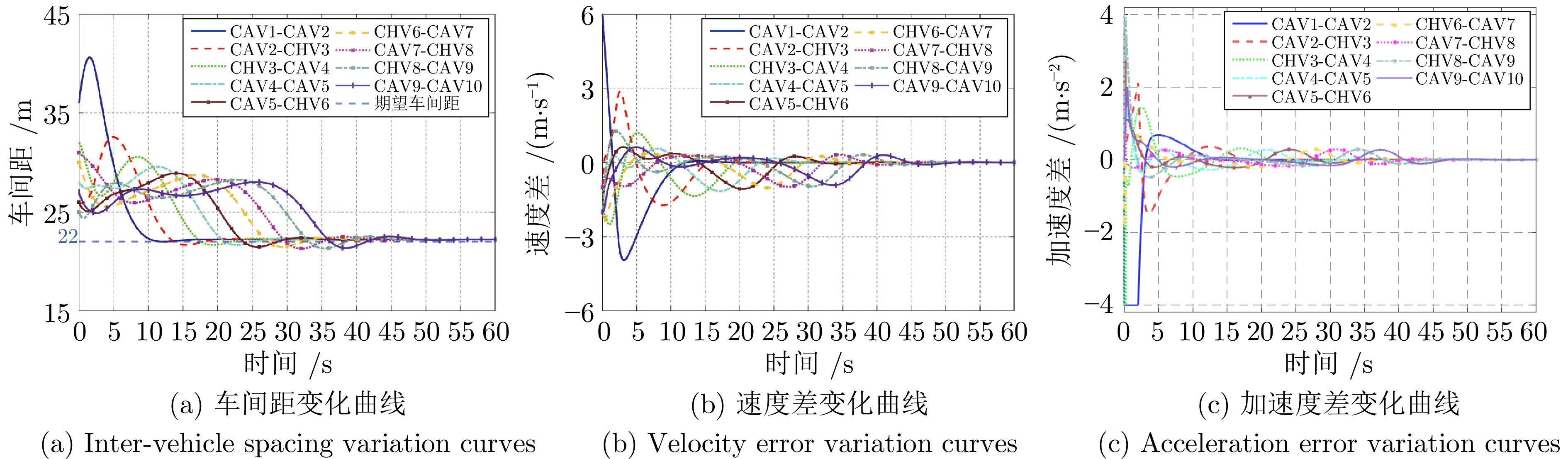
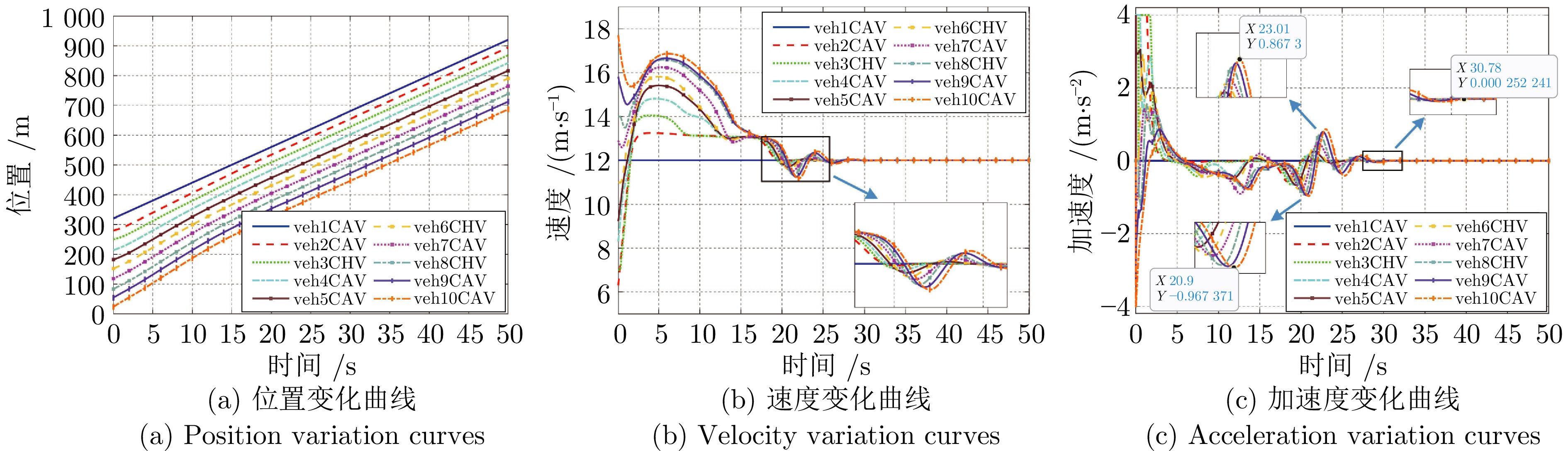
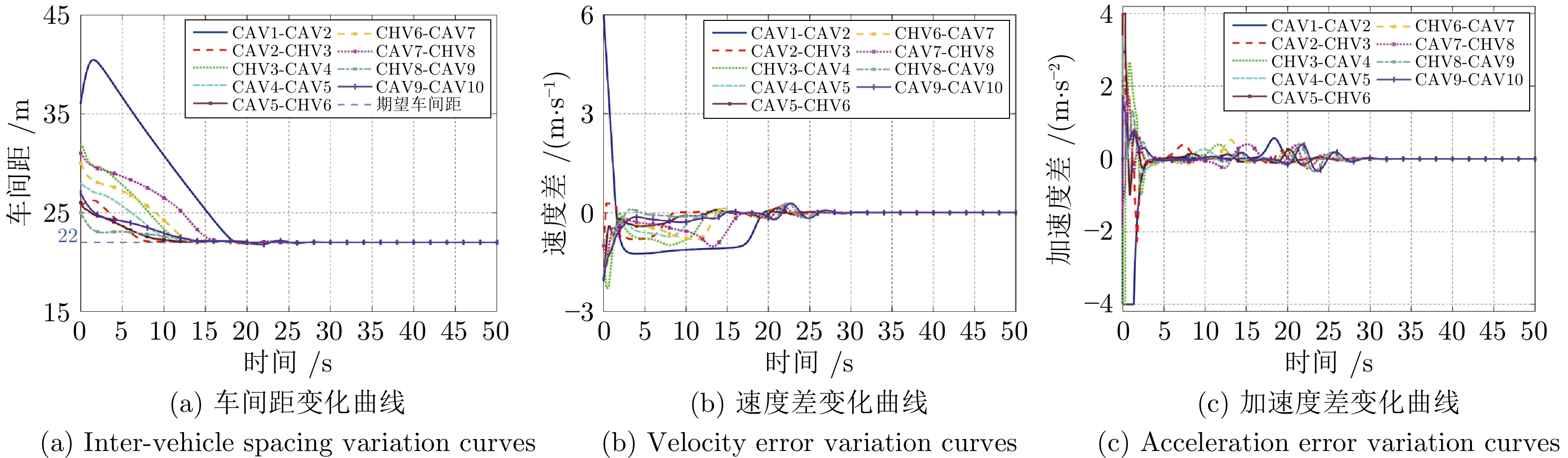
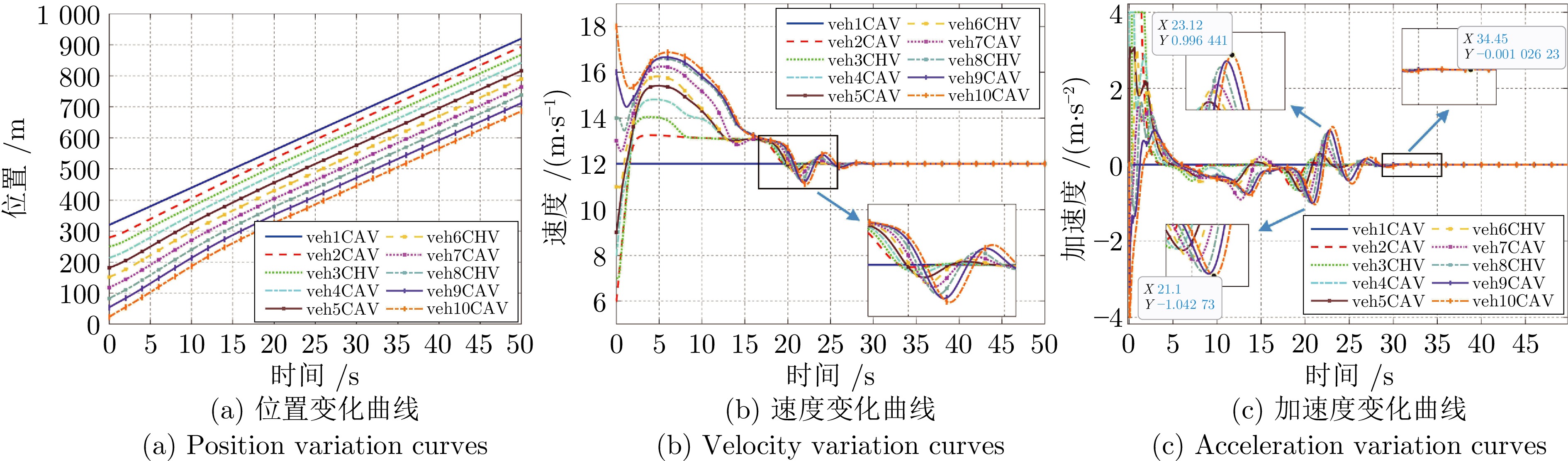
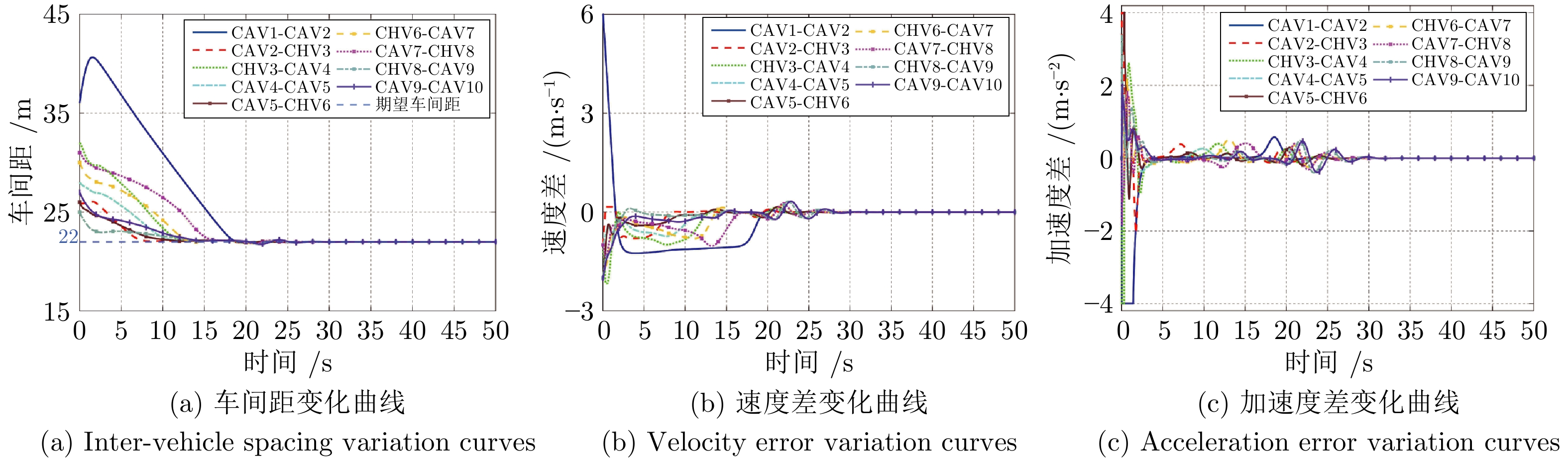
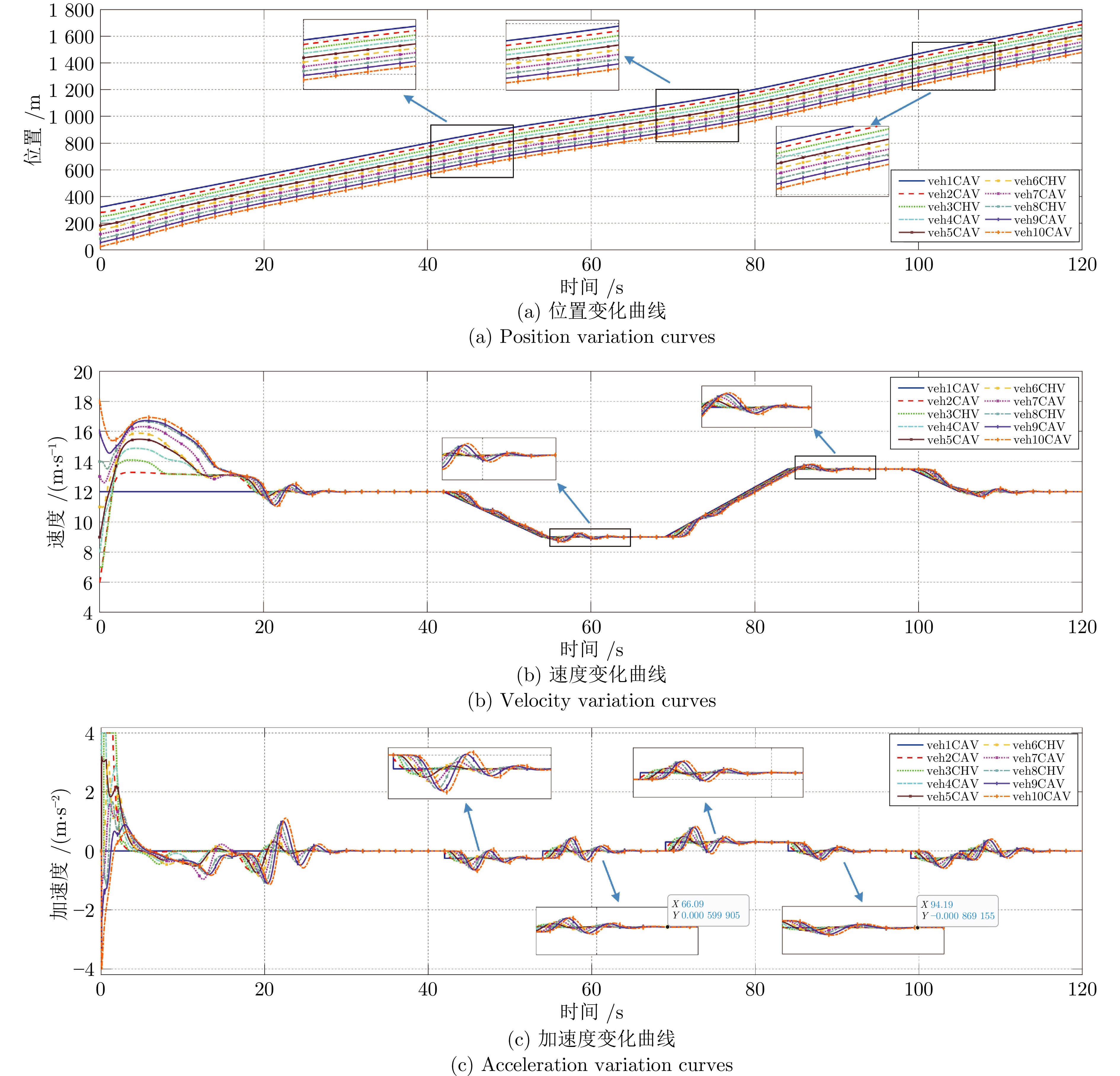
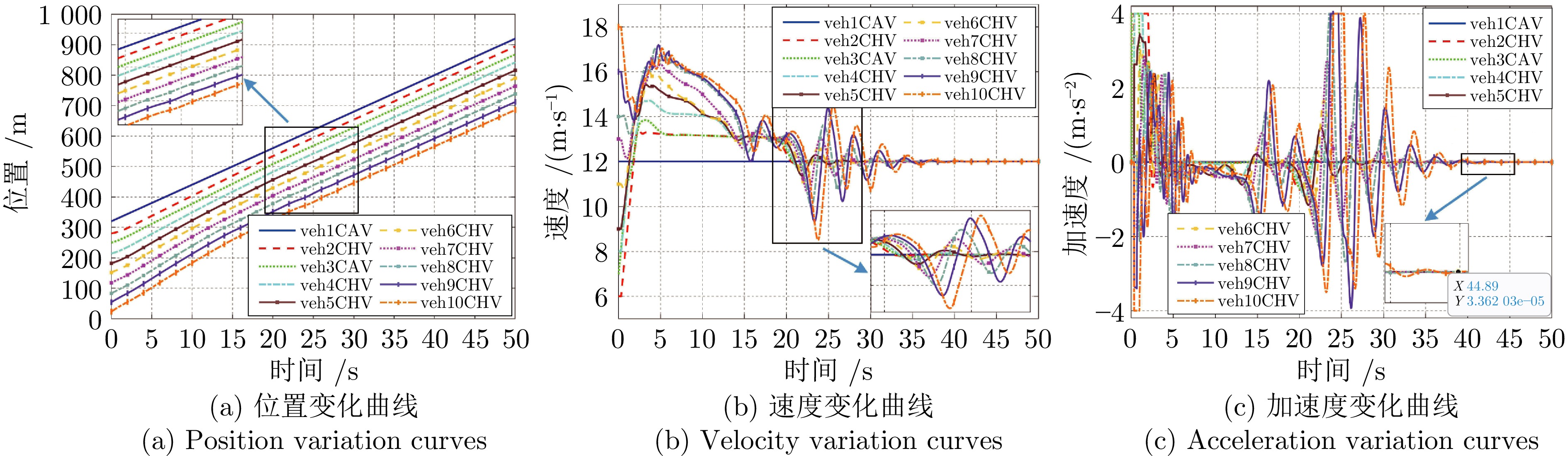
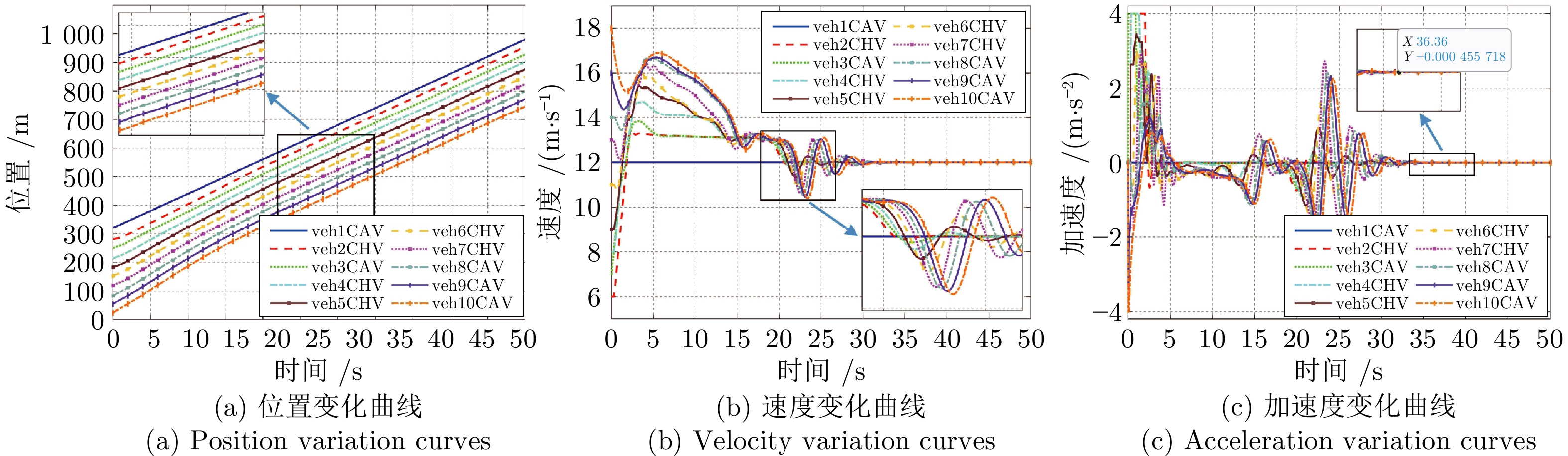
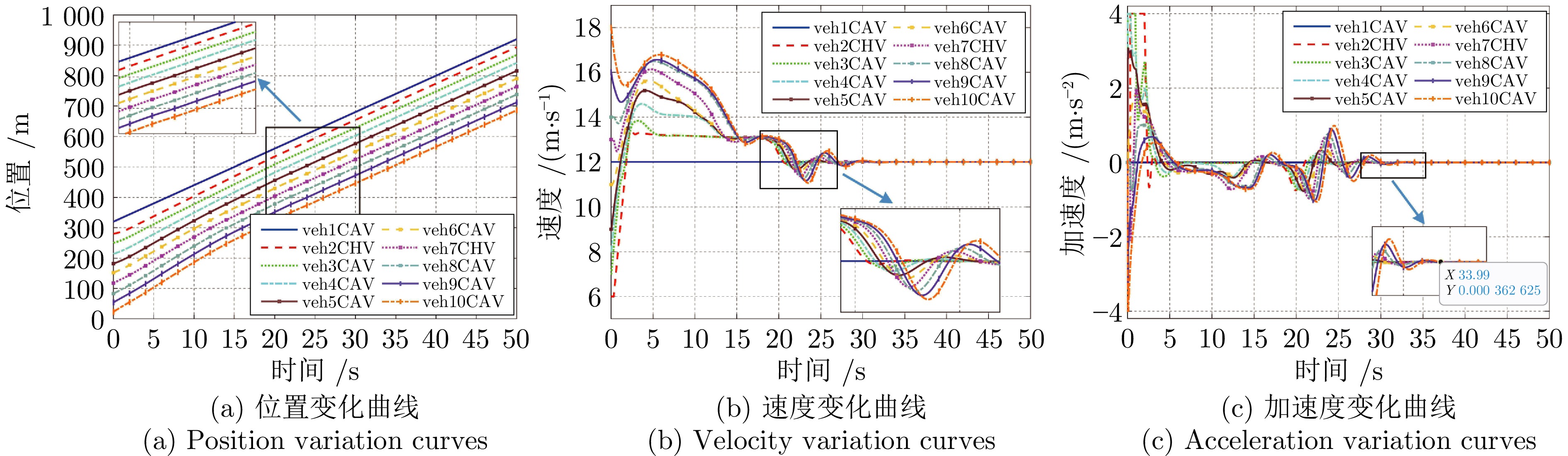
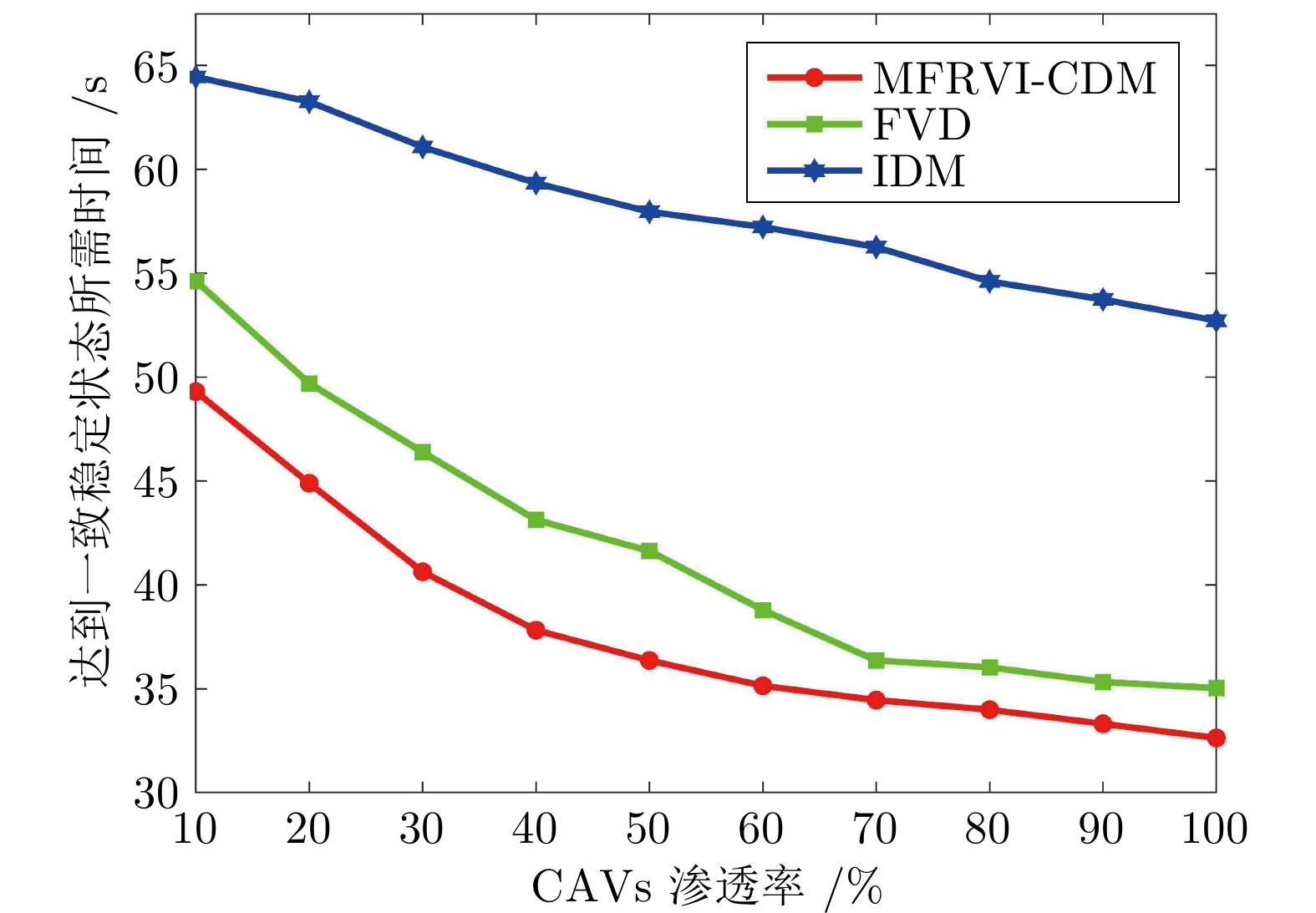
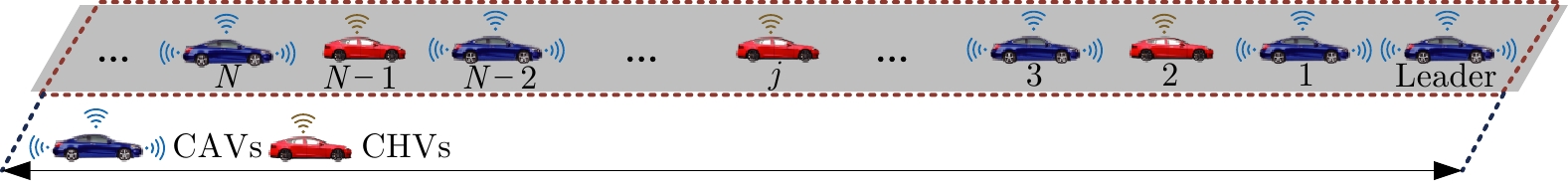
摘要: 随着车联网技术的进步, 由网联人驾车与网联自动车组成的混行车群规模正逐渐增大, 导致混行车群间的协同与交互难度增加, 进而影响混行车群行驶状态的一致性. 为解决此问题, 提出一种云−边−端协同下考虑多车影响的混行车群集中式协同控制方法. 首先, 为有效处理和分析较大规模混行车群产生的海量异构数据, 设计混合交通场景下云−边−端协同架构. 然后, 考虑网联人驾车前方两辆车及紧邻后车状态的影响, 以及网联自动车前方所有车辆及紧邻后车状态的影响, 分别在云控平台建立基于分子动力学的网联自动车和固定权重的网联人驾车协同行驶模型. 再者, 根据混行车群间动态影响关系, 设计基于云−边−端协同架构的混行车群集中式协同控制方法, 并利用稳定性和串稳定性理论获得混行车群协同行驶一致性条件. 最后, 通过对比仿真实验验证了所提方法的有效性.Abstract: With the advancement of vehicle-to-everything technology, the scale of mixed vehicle groups composed of connected human-driving vehicles (CHVs) and connected automated vehicles (CAVs) is gradually increasing, which leads to greater difficulty in cooperation and interaction among mixed vehicle groups, thereby affecting the consistency of their driving states. To address this issue, a centralized cooperative control method of mixed vehicle groups considering multi-vehicle influence under cloud-edge-end collaboration is proposed. First, to effectively process and analyze the massive heterogeneous data generated by large-scale mixed vehicle groups, a cloud-edge-end collaborative architecture is designed for mixed traffic scenarios. Then, considering the influence of the states of the two preceding vehicles and the immediate following vehicle on CHVs, as well as the states of all preceding vehicles and the immediate following vehicle on CAVs, the cooperative driving models for CAVs based on molecular dynamics and for CHVs based on fixed weights are established on the cloud control platform, respectively. Furthermore, based on the dynamic influence relationships among mixed vehicle groups, a centralized cooperative control method for mixed vehicle groups is designed based on the cloud-edge-end collaborative architecture, and the consistency conditions for cooperative driving of mixed vehicle groups are obtained using stability and string stability theory. Finally, the comparative simulation experiments are conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 初始参数设置
Table 1 Initial parameter settings
参数 值 参数 值 $v_{\text{max}}$ $18\ \text{m/s}$ $v_{\text{des}}$ $12\ \text{m/s}$ $a_{\text{max}}$ $4\ \text{m/s}^2$ $d_{\text{des}}$ $26\ \text{m}$ $s_0$ $2\ \text{m}$ $\Delta t$ $0.01\ \text{s}$ $len$ $4\ \text{m}$ $TH$ $50\ \text{s}$ 表 2 异质车辆控制输入参数设置
Table 2 Control input parameter settings for heterogeneous vehicles
CAVs参数 值 CHVs参数 值 $\alpha_c$ $0.49$ $\alpha_h$ $0.51$ $\beta_c$ $0.03$ $\beta_h$ $0.03$ $\gamma_c$ $2.36$ $\gamma_h$ $2.42$ $\mu_c$ $0.32$ $\mu_h$ $0.32$ $\rho_{i,\;j}\; (i>j)$ $0.97$ $\rho_{h1}$ $0.12$ $\rho_{i,\;j}\; (i<j)$ $0.03$ $\rho_{h2}$ $0.84$ $\zeta$ $0.03$ $\rho_{h3}$ $0.04$ $\xi$ $0.32$ -
[1] Feng W H, Wang B H. Stability analysis and delayed feedback control for platoon of connected automated vehicles with V2X and V2V infrastructure. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2025, 658: Article No. 130258 doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2024.130258 [2] Pala S, Katwe M, Singh K, Tsiftsis T A, Li C P. Robust transmission design for RIS-aided full-duplex-RSMA V2X communications via multi-agent DRL. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(1): 761−775 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3453253 [3] Xu Z H, Xu S Y, Ding H X, Xu R T. An ISAC-based beam tracking scheme against inter-region interference for the multi-RSU V2I scenario. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2025, 74(3): 4257−4272 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3488089 [4] Kong W W, Zhu W Z, Li K Q, Zhang Y H, Luo Y G, Xu M C. Robust distributed model predictive control of multi-platoon leader in mixed traffic. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2025, 26(1): 169−181 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3482725 [5] Li C L, Chai L, Jiang K, Zhang Y, Liu J, Wan S H. DNN partition and offloading strategy with improved particle swarm genetic algorithm in VEC. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehi-cles, 2024, 9(9): 5532−5542 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2023.3346506 [6] Ruan T C, Chen Y J, Han G Y, Wang J, Li X P, Jiang R, et al. Cooperative adaptive cruise platoon controller design considering switching control and stability. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2025, 172: Article No. 105024 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2025.105024 [7] Zheng Y, Zhang Y, Qu X, Li S, Ran B. Developing platooning systems of connected and automated vehicles with guaranteed stability and robustness against degradation due to communication disruption. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Tech-nologies, 2024, 168: Article No. 104768 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2024.104768 [8] 李永福, 何昌鹏, 朱浩, 郑太雄. 通信延时环境下异质网联车辆队列非线性纵向控制. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(12): 2841−2856Li Yong-Fu, He Chang-Peng, Zhu Hao, Zheng Tai-Xiong. Nonlinear longitudinal control for heterogeneous connected vehicle platoon in the presence of communication delay. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(12): 2841−2856 [9] Wang B, Luo Y G, Zhong Z H, Li K Q. Risk reduction for safety of the intended functionality of CACC with complex uncertainties: A cooperative robust non-fragile fault tolerant strat-egy. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2022, 144: Article No. 103885 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2022.103885 [10] Cong X Y, Yang B, Gao F K, Chen C L, Guan X P, Tang Y L. A bilevel virtual platoon based coordination framework for CAVs at unsignalized intersection. IEEE Transactions on Veh-icular Technology, 2025, 74(3): 4019−4032 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3503357 [11] 朱永薪, 李永福, 朱浩, 于树友. 通信延时环境下基于观测器的智能网联车辆队列分层协同纵向控制. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(8): 1785−1798 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210311Zhu Yong-Xin, Li Yong-Fu, Zhu Hao, Yu Shu-You. Observer-based longitudinal control for connected and automated vehicles platoon subject to communication delay. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(8): 1785−1798 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c210311 [12] Huang S, Sun D H, Zhao M, Zhang Y C, Liu W N, Liao X Y. SFM-based modeling and string stability analysis of mixed vehicle groups with distributed cooperative method from cyber-physical perspective. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2023, 111(5): 4395−4423 doi: 10.1007/s11071-022-08057-3 [13] Huang S, Sun D H, Zhao M. Distributed MPC-based hierarchical cooperative control for mixed vehicle groups with T-CPS in the vicinity of traffic signal light. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(7): 8003−8016 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3390763 [14] Khan A, Javeed M A, Hassan W U, Niazi A U K, Ahmed S, Zhong Y B, et al. Stability analysis and resilient communication in connected vehicle platooning: Addressing input communication delays and disruptions through Lyapunov analysis and event-triggered control. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2025, 116: 342−350 doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2024.12.063 [15] Pachat J, Karat N S, Mahesh A A, Deepthi P P, Rajan B S. Index coded PSK modulation in vehicle to vehicle communication. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(5): 4753−4766 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3073788 [16] Li Y F, Chen B J, Zhao H, Peeta S, Hu S M, Wang Y B, et al. A car-following model for connected and automated vehicles with heterogeneous time delays under fixed and switching communication topologies. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(9): 14846−14858 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3134419 [17] Lee S H. A spatiotemporal spacing policy and string stability for heterogeneous vehicle platooning. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(11): 16328−16340 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3423474 [18] Li Y, Pan B, Chen Z B, Xing L. Developing a dynamic speed control system for mixed traffic flow to reduce collision risks near freeway bottlenecks. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(11): 12560−12581 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3287269 [19] Mousavi S S, Bahrami S, Kouvelas A. Synthesis of output-feedback controllers for mixed traffic systems in presence of disturbances and uncertainties. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Trans-portation Systems, 2023, 24(6): 6450−6462 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3185155 [20] Yang J S, Zhao D Z, Lan J L, Xue S B, Zhao W J, Tian D X. Eco-driving of general mixed platoons with CAVs and HDVs. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2023, 8(2): 1190−1203 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2022.3224679 [21] Wang Z W, Xue Y, Liu L H, Zhang H J, Qu C H, Fang C. Multi-agent DRL-controlled connected and automated vehicles in mixed traffic with time delays. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(11): 17676−17688 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3435036 [22] Nie Z F, Farzaneh H. Human-inspired anticipative cruise control for enhancing mixed traffic flow. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(11): 17335−17351 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3438211 [23] 黄帅, 孙棣华, 赵敏. 多切入机制下基于信息物理系统的混合车群协同控制. 控制与决策, 2024, 39(1): 17−25 doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.2023Huang Shuai, Sun Di-Hua, Zhao Min. CPS-based mixed vehicle group cooperative control with multiple cut-in maneuvers. Control and Decision, 2024, 39(1): 17−25 doi: 10.13195/j.kzyjc.2022.2023 [24] Guo S C, Orosz G, Molnar T G. Connected cruise and traffic control for pairs of connected automated vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2023, 24(11): 12648−12658 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3285852 [25] Gong Y, Zhu W X. Robust control scheme for the mixed platoon system with time-varying information topologies and inaccurate state information. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2024, 112(24): 22057−22085 doi: 10.1007/s11071-024-10190-0 [26] Wang S Y, Yu B, Wu M Y. MVCM car-following model for connected vehicles and simulation-based traffic analysis in mixed traffic flow. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(6): 5267−5274 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3052818 [27] Qiu T, Chi J C, Zhou X B, Ning Z L, Atiquzzaman M, Wu D O. Edge computing in industrial internet of things: Architecture, advances and challenges. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2020, 22(4): 2462−2488 [28] Xun Y J, Qin J M, Liu J J. Deep learning enhanced driving behavior evaluation based on vehicle-edge-cloud architecture. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2021, 70(6): 6172−6177 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3078482 [29] Arthurs P, Gillam L, Krause P, Wang N, Halder K, Mouzakitis A. A taxonomy and survey of edge cloud computing for intelligent transportation systems and connected vehicles. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(7): 6206−6221 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2021.3084396 [30] Song T, Zhu W X, Su S B, Wang W W. Distributed “End-Edge-Cloud” structural car-following control system for intelligent connected vehicle using sliding mode strategy. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2023, 126: Article No. 107468 doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2023.107468 [31] An J X, Cao L, Wang Y X, Jadoon A K, Wang S H. Adaptive fault-tolerant optimized platoon cloud tracking control for heterogeneous vehicles via dual learning mechanism. IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2025, 22: 4382−4393 doi: 10.1109/TASE.2024.3410642 [32] Zhao J X, Ma Y L, Dai L, Sun Z Q, Xia Y Q. Cloud-edge cooperative distributed MPC with event-triggered switching strategy for heterogeneous vehicle platoon. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2024, 73(10): 14425−14437 doi: 10.1109/TVT.2024.3405625 [33] Wang Z H, Ge H X, Dai P P, Liu H Q. Modeling non-equilibrium mixed traffic flow in composite road environments with “End-Edge-Cloud” structure. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications, 2024, 658: Article No. 130263 [34] Jiang R, Wu Q S, Zhu Z J. Full velocity difference model for a car-following theory. Physical Review E, 2001, 64(1): Article No. 017101 [35] 王建强, 吴剑, 李洋. 基于人−车−路协同的行车风险场概念、原理及建模. 中国公路学报, 2016, 29(1): 105−114Wang Jian-Qiang, Wu Jian, Li Yang. Concept, principle and modeling of driving risk field based on driver-vehicle-road interaction. China Journal of Highway and Transport, 2016, 29(1): 105−114 [36] Wang M. Infrastructure assisted adaptive driving to stabilise heterogeneous vehicle strings. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2018, 91: 276−295 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2018.04.010 [37] Punzo V, Zheng Z D, Montanino M. About calibration of car-following dynamics of automated and human-driven vehicles: Methodology, guidelines and codes. Transportation Research Part C: Emerging Technologies, 2021, 128: Article No. 103165 doi: 10.1016/j.trc.2021.103165 [38] 宗芳, 王猛, 贺正冰. 考虑多车影响的分子动力学智能网联跟驰模型. 交通运输系统工程与信息, 2022, 22(1): 37−48 doi: 10.16097/j.cnki.1009-6744.2022.01.005Zong Fang, Wang Meng, He Zheng-Bing. A molecular dynamics-based car-following model for connected and automated vehicles considering impact of multiple vehicles. Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology, 2022, 22(1): 37−48 doi: 10.16097/j.cnki.1009-6744.2022.01.005 [39] Noor M A, Noor K I, Awan M U. Some quantum estimates for Hermite-Hadamard inequalities. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2015, 251: 675−679 [40] Rajamani R. Vehicle Dynamics and Control (Second Edition). New York: Springer, 2011. [41] Xing H T, Ploeg J, Nijmeijer H. Padé approximation of delays in cooperative ACC based on string stability requirements. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2016, 1(3): 277−286 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2017.2662482 [42] Treiber M, Hennecke A, Helbing D. Congested traffic states in empirical observations and microscopic simulations. Physical Review E, 2000, 62(2): 1805−1824 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.62.1805 -




 下载:
下载: