-
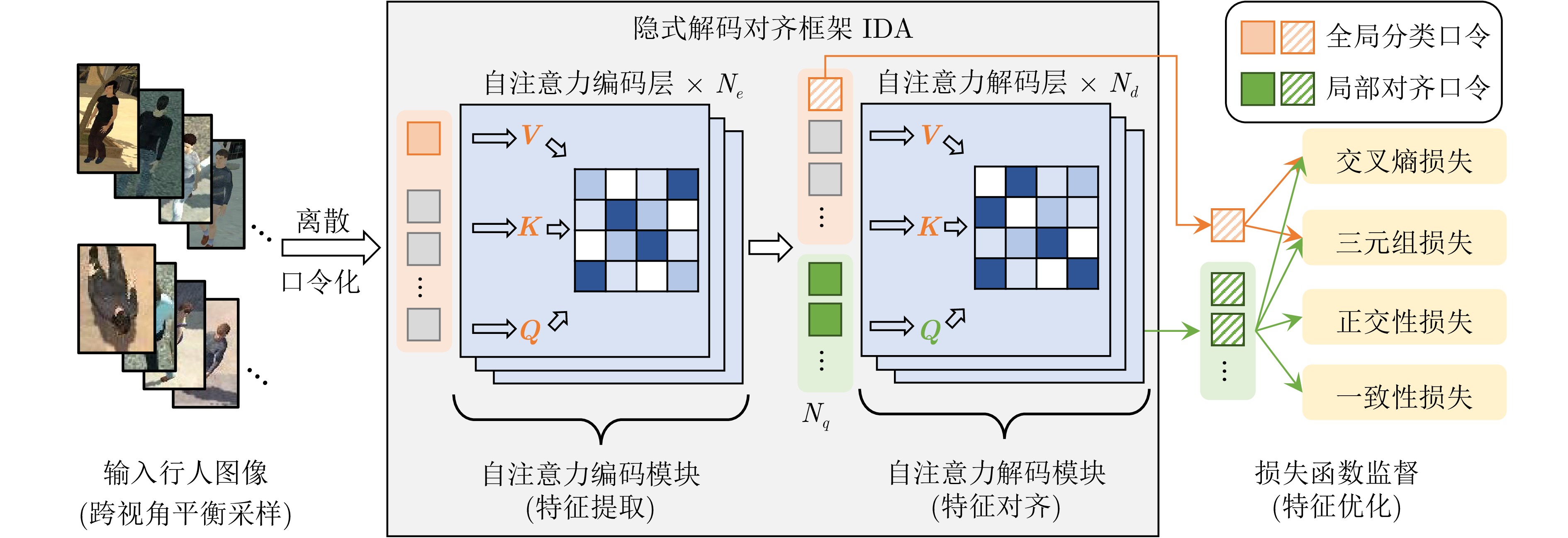
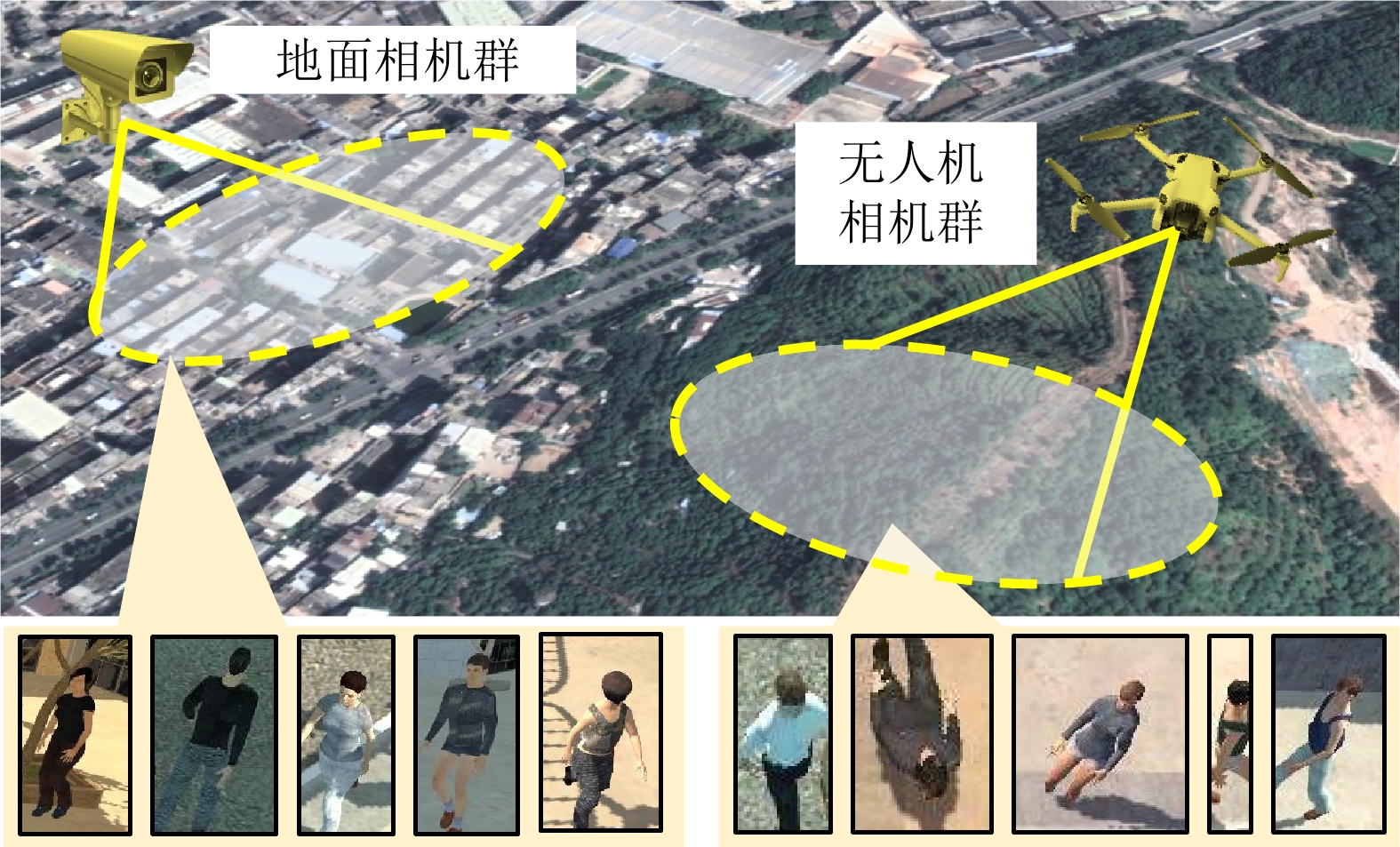
摘要: 空地行人重识别任务旨在包含地面与空中视角的监控相机网络中, 实现对特定行人的精确识别与跨镜关联. 该任务的特有挑战在于克服空地成像设备之间巨大的视角差异对于学习判别性行人身份特征的干扰. 现有工作在行人特征建模方面存在不足, 未充分考虑跨视角特征对齐对识别与检索性能的提升作用. 基于此, 提出一种基于隐式解码对齐的空地行人重识别方法, 主要包含两方面的创新: 在模型设计方面, 提出基于自注意力解码器的隐式对齐框架, 通过在解码阶段利用一组可学习的口令特征挖掘行人判别部件区域, 并提取和对齐行人局部特征, 从而实现判别性行人表征的学习; 在优化目标方面, 提出正交性和一致性损失函数, 前者约束口令特征以多样化判别性行人部件为关注点, 后者缓解了跨视角特征表达的偏置分布. 在当前可用的最大空地重识别数据集CARGO上进行实验, 结果表明所提方法在检索性能上优于现有重识别方法, 实现显著的性能提升.Abstract: Aerial-ground person re-identification (AGPReID) refers to the accurate recognition and cross-camera association of the interest person within a surveillance camera network deployed across aerial and ground views. One of the unique challenges is overcoming the significant view differences between aerial and ground cameras, which interfere with discriminate feature learning of person identity. Existing methods are insufficient in modeling person features, as they fail to fully leverage cross-view feature alignment to enhance recognition and retrieval performance. To this end, the implicit decoder alignment is proposed for AGPReID with two main contributions: In terms of model design, we propose an implicit alignment framework based on a self-attention decoder. This framework leverages a set of learnable token features during the decoding stage to identify discriminative person parts and to extract and align local pedestrian features, enabling discriminative person representation learning. In terms of optimization objectives, we propose orthogonality and consistency loss functions. The former constrains token features to focus on diverse discriminative pedestrian parts, while the latter mitigates biased distributions in cross-view feature representations. Experiments were conducted on the largest publicly available cross-view re-identification dataset, CARGO, where the proposed method outperformed existing re-identification methods, achieving superior retrieval performance.
-
Key words:
- Person re-identification /
- image retrieval /
- image recognition /
- transformer
-
表 1 常用符号及其含义
Table 1 Commonly used symbols and their meanings in our work
符号 含义 $ {\cal{D}},\;{\cal{D}}^{tr},\; {\cal{D}}^{te} $ 空地重识别数据集, 训练集, 测试集 $ B $ 批数据 $ x_i,\; y_i,\; v_i $ 行人图像, 身份标签, 视角标签 $ {\cal{F}},\;{\cal{F}}_e,\; {\cal{F}}_d $ 网络模型, 自注意力编码器和解码器 $ {\boldsymbol{Q}},\;{\boldsymbol{K}},\;{\boldsymbol{V}} $ 注意力操作的查询、键值和内容 $ \theta,\;\theta_e,\; \theta_d $ $ {\cal{F}},\;{\cal{F}}_e,\; {\cal{F}}_d $中的可学习参数 $ {\cal{T}}(\cdot) $ 输入离散口令化 $ t_g,\; t_a $ 可学习口令特征 $ {\boldsymbol{L}} $ 局部口令特征矩阵 $ {\boldsymbol{S}}_{g\leftrightarrow g},\; {\boldsymbol{S}}_{a\leftrightarrow a},\;{\boldsymbol{S}}_{a\leftrightarrow g} $ 相似度矩阵 $ {\cal{L}}_g^c,\; {\cal{L}}_g^t $ 全局特征损失函数 $ {\cal{L}}_a^c,\; {\cal{L}}_a^t,\; {\cal{L}}_a^o,\; {\cal{L}}_a^s $ 局部特征损失函数 $ \left|\cdot\right| $ 集合的阶 表 2 CARGO数据集四种协议的主流方法性能评测(%)
Table 2 The performance evaluation of the mainstream methods for the four protocols of the CARGO dataset (%)
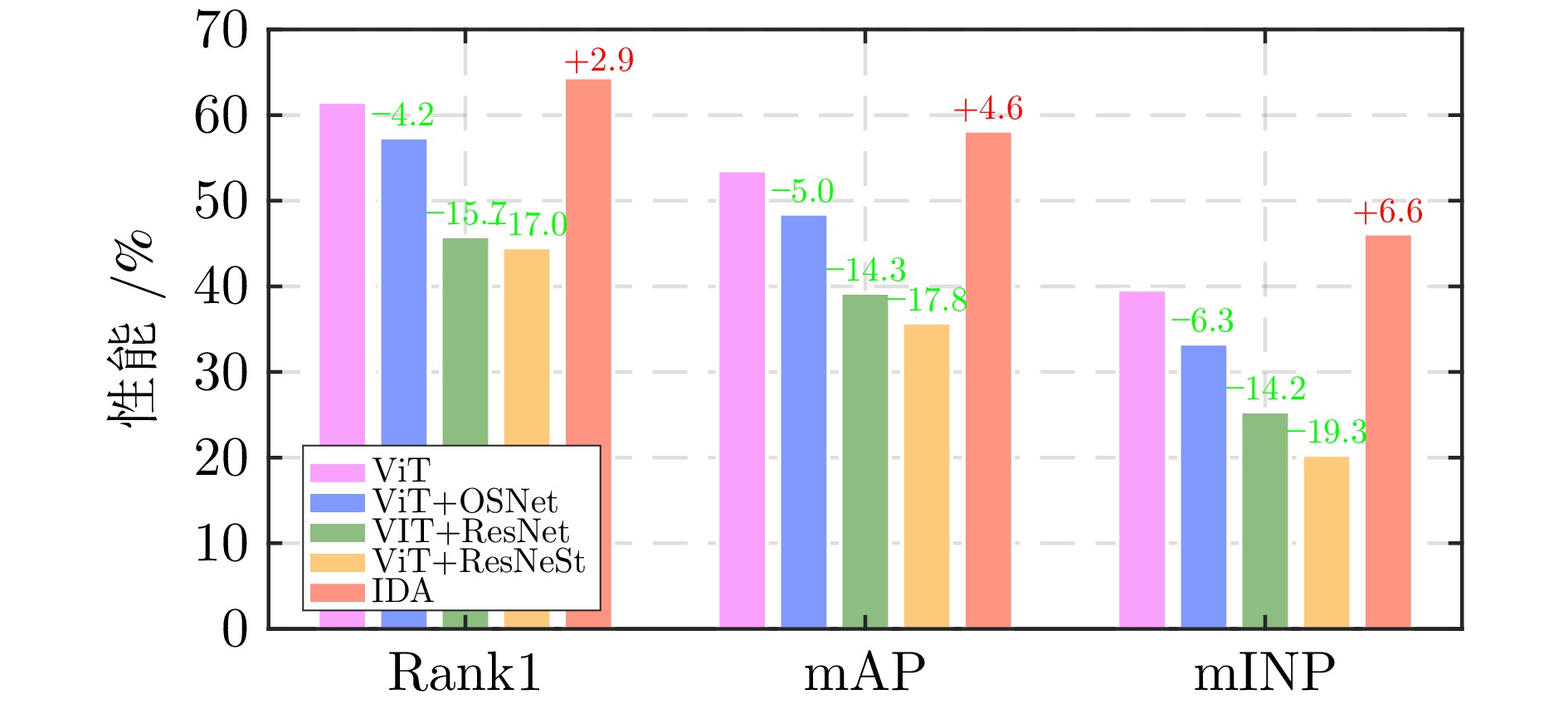
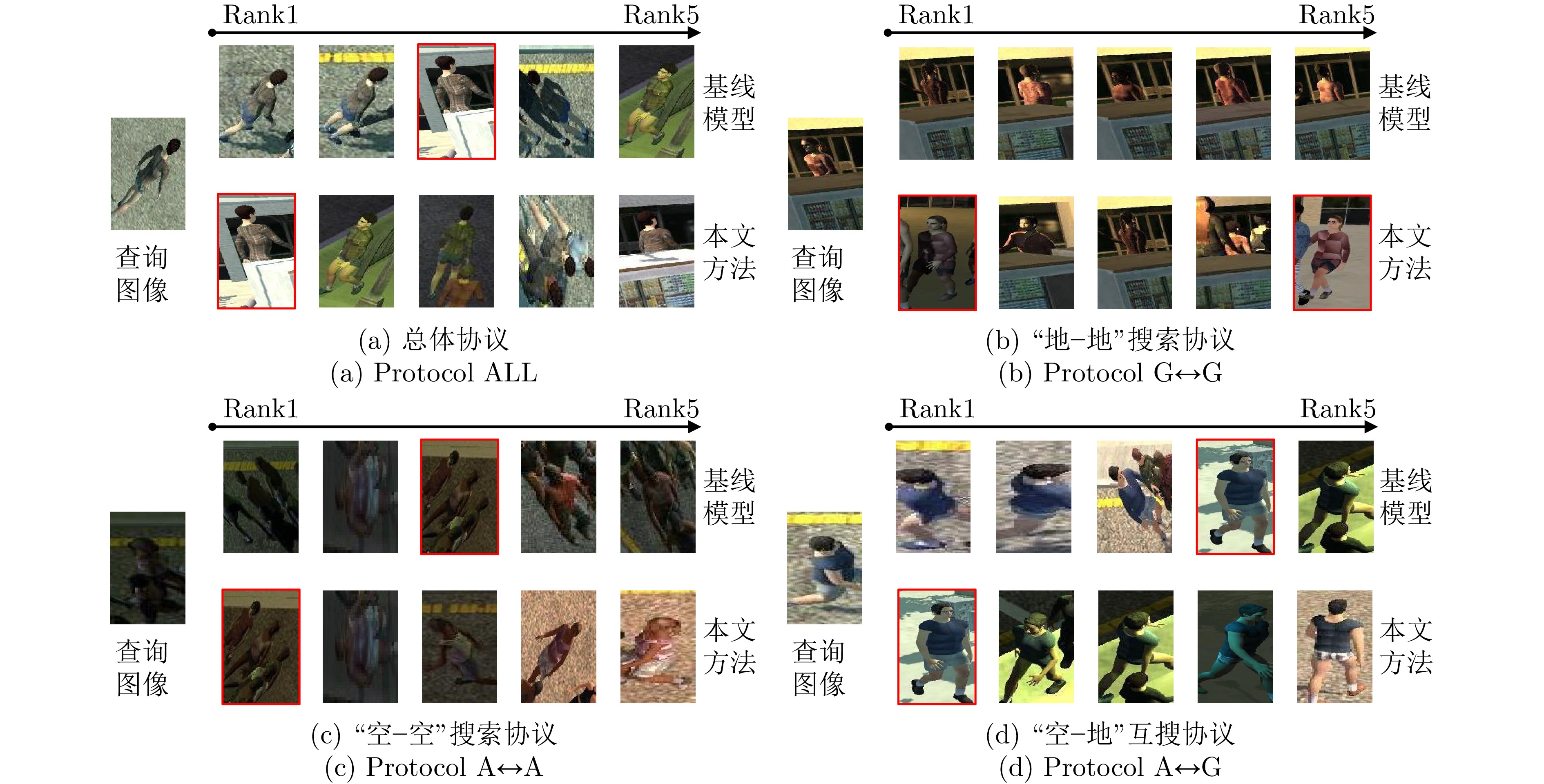
方法 协议1: ALL 协议2: G$ \leftrightarrow $G 协议3: A$ \leftrightarrow $A 协议4: A$ \leftrightarrow $G Rank1 mAP mINP Rank1 mAP mINP Rank1 mAP mINP Rank1 mAP mINP PCB[25−26] 44.23 38.15 26.14 72.32 61.92 45.72 57.50 42.34 22.50 21.25 21.02 14.22 SBS[20] 50.32 43.09 29.76 73.21 62.99 48.24 67.50 49.73 29.32 31.25 29.00 18.71 BoT[33] 54.81 46.49 32.40 77.68 66.47 51.34 65.00 49.79 29.82 36.25 32.56 21.46 MGN[31] 54.49 46.58 33.55 82.14 69.31 53.60 65.00 48.86 27.42 32.50 30.44 21.53 APNet[32] 58.97 50.24 35.76 77.68 66.83 51.85 67.50 54.57 37.35 44.37 39.35 26.76 VV[56] 45.83 38.84 39.57 72.31 62.99 48.24 67.50 49.73 29.32 31.25 29.00 18.71 AGW[2] 60.26 53.44 40.22 81.25 71.66 58.09 67.50 56.48 40.40 43.57 40.90 29.39 TransReID[35] 60.90 53.17 39.57 — — — — — — — — — VDT[51] 64.10 55.20 41.13 82.14 71.59 58.39 82.50 66.83 50.22 48.12 42.76 29.95 基线模型 61.54 53.54 39.62 82.14 71.34 57.55 80.00 64.47 47.07 43.13 40.11 28.20 IDA 64.42 58.17 46.17 83.04 77.04 67.50 82.50 69.65 54.58 48.75 45.13 33.92 表 3 IDA框架消融实验(%)
Table 3 Ablation study of IDA framework (%)
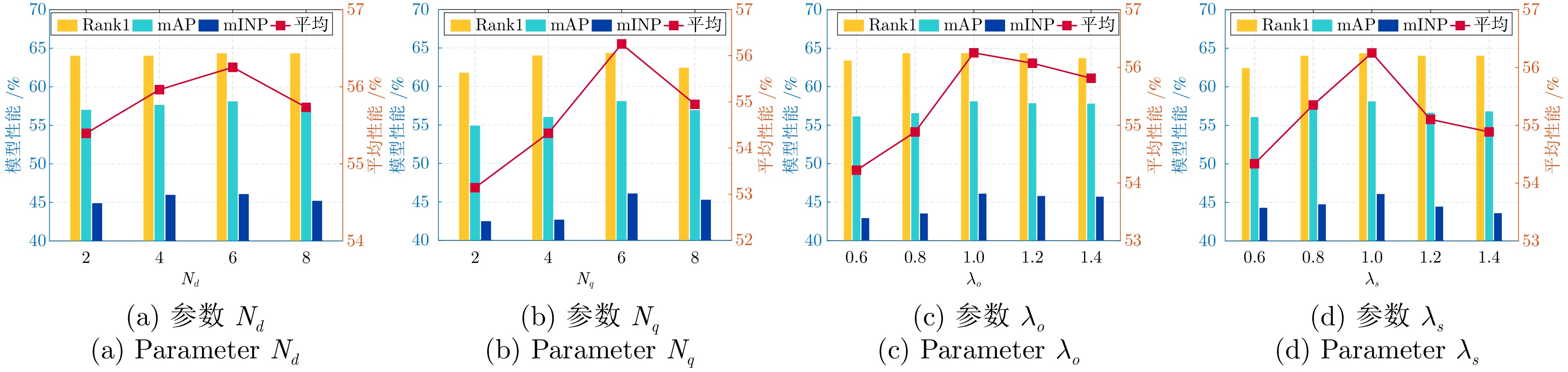
协议1: ALL 协议2: G$ \leftrightarrow $G 协议3: A$ \leftrightarrow $A 协议4: A$ \leftrightarrow $G $ {\cal{F}}(\cdot) $ $ {\cal{L}}_a^o $ $ {\cal{L}}_a^s $ Rank1 mAP mINP Rank1 mAP mINP Rank1 mAP mINP Rank1 mAP mINP $\checkmark$ 60.26 53.89 41.36 81.25 73.66 62.70 75.00 63.94 47.10 43.75 40.33 28.71 $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ 63.78 57.55 45.69 83.93 77.33 68.21 77.50 64.55 47.52 46.25 43.97 32.88 $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ 61.22 55.76 44.22 82.14 75.53 66.28 80.00 69.36 55.21 44.37 41.82 30.88 $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ $\checkmark$ 64.42 58.17 46.17 83.04 77.04 67.50 82.50 69.65 54.58 48.75 45.13 33.92 -
[1] 叶钰, 王正, 梁超, 韩镇, 陈军, 胡瑞敏. 多源数据行人重识别研究综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(9): 1869−1884Ye Yu, Wang Zheng, Liang Chao, Han Zhen, Chen Jun, Hu Rui-Min. A survey on multi-source person re-identification. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(9): 1869−1884 [2] Ye M, Chen S Y, Li C Y, Zheng W S, Crandall D, Du B. Transformer for object re-identification: A survey. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2025, 133(5): 2410−2440 doi: 10.1007/s11263-024-02284-4 [3] Zhang Q, Lai J H, Xie X H, Jin X F, Huang S E. Separable spatial-temporal residual graph for cloth-changing group re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(8): 5791−5805 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3369483 [4] Zhang Q, Lai J H, Feng Z X, Xie X H. Uncertainty modeling for group re-identification. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2024, 132(8): 3046−3066 doi: 10.1007/s11263-024-02013-x [5] 罗浩, 姜伟, 范星, 张思朋. 基于深度学习的行人重识别研究进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2032−2049Luo Hao, Jiang Wei, Fan Xing, Zhang Si-Peng. A survey on deep learning based person re-identification. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2032−2049 [6] 张永飞, 杨航远, 张雨佳, 豆朝鹏, 廖胜才, 郑伟诗, 等. 行人再识别技术研究进展. 中国图象图形学报, 2023, 28(6): 1829−1862 doi: 10.11834/jig.230022Zhang Yong-Fei, Yang Hang-Yuan, Zhang Yu-Jia, Dou Zhao-Peng, Liao Sheng-Cai, Zheng Wei-Shi, et al. Recent progress in person re-ID. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2023, 28(6): 1829−1862 doi: 10.11834/jig.230022 [7] Sarker P K, Zhao Q J, Uddin M K. Transformer-based person re-identification: A comprehensive review. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Vehicles, 2024, 9(7): 5222−5239 doi: 10.1109/TIV.2024.3350669 [8] Yang X, Liu H L, Wang N N, Gao X B. Image-level adaptive adversarial ranking for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2024, 33: 5172−5182 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2024.3456000 [9] Cui Z Y, Zhou J H, Peng Y X. DMA: Dual modality-aware alignment for visible-infrared person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 2696−2708 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2024.3352408 [10] He W Z, Deng Y H, Tang S X, Chen Q H, Xie Q S, Wang Y Z, et al. Instruct-ReID: A multi-purpose person re-identification task with instructions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 17521−17531 [11] Ye M, Shen W, Zhang J W, Yang Y, Du B. SecureReID: Privacy-preserving anonymization for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 2840−2853 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2024.3356233 [12] Zhang Q, Lai J H, Feng Z X, Xie X H. Seeing like a human: Asynchronous learning with dynamic progressive refinement for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 352−365 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3128330 [13] Nguyen H, Nguyen K, Sridharan S, Fookes C. AG-ReID.v2: Bridging aerial and ground views for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2024, 19: 2896−2908 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2024.3353078 [14] Wang L, Zhang Q, Qiu J Y, Lai J H. Rotation exploration transformer for aerial person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Niagara Falls, Canada: IEEE, 2024. 1−6 [15] Qiu J Y, Feng Z X, Wang L, Lai J H. Salient part-aligned and keypoint disentangling transformer for person re-identification in aerial imagery. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Niagara Falls, Canada: IEEE, 2024. 1−6 [16] Khaldi K, Nguyen V D, Mantini P, Shah S. Unsupervised person re-identification in aerial imagery. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2024. 260−269 [17] Ding J, Xue N, Xia G S, Bai X, Yang W, Yang M Y, et al. Object detection in aerial images: A large-scale benchmark and challenges. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(11): 7778−7796 [18] Ye M, Shen J B, Lin G J, Xiang T, Shao L, Hoi S C H. Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(6): 2872−2893 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3054775 [19] Zhu K, Guo H, Zhang S, Wang Y, Liu J, Wang J, et al. AAformer: Auto-aligned transformer for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2024, 35(12): 17307−17317 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2023.3301856 [20] He L X, Liao X Y, Liu W, Liu X C, Cheng P, Mei T. FastReID: A PyTorch toolbox for general instance re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 31st ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Ottawa, Canada: Association for Computing Machinery, 2023. 9664−9667 [21] Farenzena M, Bazzani L, Perina A, Murino V, Cristani M. Person re-identification by symmetry-driven accumulation of local features. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. San Francisco, USA: IEEE, 2010. 2360−2367 [22] Gheissari N, Sebastian T B, Hartley R. Person reidentification using spatiotemporal appearance. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). New York, USA: IEEE, 2006. 1528−1535 [23] Layne R, Hospedales T M, Gong S G. Person re-identification by attributes. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. Surrey, UK: BMVC, 2012. Article No. 24 [24] Liu C X, Gong S G, Loy C C, Lin X G. Person re-identification: What features are important? Computer Vision Workshops-ECCV 2012. Workshops and Demonstrations. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012. 391−401 [25] Sun Y F, Zheng L, Yang Y, Tian Q, Wang S J. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling (and a strong convolutional baseline). In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 501−518 [26] Sun Y F, Zheng L, Li Y L, Yang Y, Tian Q, Wang S J. Learning part-based convolutional features for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(3): 902−917 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2938523 [27] Zhou K Y, Yang Y X, Cavallaro A, Xiang T. Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, Korea: IEEE, 2019. 3701−3711 [28] Zhou K Y, Yang Y X, Cavallaro A, Xiang T. Learning generalisable omni-scale representations for person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(9): 5056−5069 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3069237 [29] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [30] Zhang H, Wu C R, Zhang Z Y, Zhu Y, Lin H B, Zhang Z, et al. ResNeSt: Split-attention networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). New Orleans, USA: IEEE, 2022. 2735−2745 [31] Wang G S, Yuan Y F, Chen X, Li J W, Zhou X. Learning discriminative features with multiple granularities for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Seoul, The Republic of Korea: Association for Computing Machinery, 2018. 274−282 [32] Chen G Y, Gu T P, Lu J W, Bao J A, Zhou J. Person re-identification via attention pyramid. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 7663−7676 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3107211 [33] Luo H, Gu Y Z, Liao X Y, Lai S Q, Jiang W. Bag of tricks and a strong baseline for deep person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1487−1495 [34] Luo H, Jiang W, Zhang X, Fan X, Qian J J, Zhang C. AlignedReID++: Dynamically matching local information for person re-identification. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 94: 53−61 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.05.028 [35] He S T, Luo H, Wang P C, Wang F, Li H, Jiang W. TransReID: Transformer-based object re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 14993−15002 [36] Yang Q, Chen Y K, Peng D Z, Peng X, Zhou J T, Hu P. Noisy-correspondence learning for text-to-image person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 27187−27196 [37] Zhu J Q, Wu H X, Chen Y T, Xu H, Fu Y Q, Zeng H Q, et al. Cross-modal group-relation optimization for visible-infrared person re-identification. Neural Networks, 2024, 179: Article No. 106576 doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2024.106576 [38] Zhu H D, Budhwant P, Zheng Z H, Nevatia R. SEAS: ShapEAligned supervision for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 164−174 [39] Bai S T, Chang H, Ma B P. Incorporating texture and silhouette for video-based person re-identification. Pattern Recognition, 2024, 156: Article No. 110759 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2024.110759 [40] Yu Z Y, Li L S, Xie J L, Wang C S, Li W J, Ning X. Pedestrian 3D shape understanding for person re-identification via multi-view learning. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2024, 34(7): 5589−5602 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2024.3358850 [41] Yang B, Chen J, Ye M. Shallow-deep collaborative learning for unsupervised visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 16870−16879 [42] Nguyen K, Fookes C, Sridharan S, Liu F, Liu X M, Ross A, et al. AG-ReID 2023: Aerial-ground person re-identification challenge results. In: Proceedings of 2023 IEEE International Joint Conference on Biometrics (IJCB). Ljubljana, Slovenia: IEEE, 2023. 1−10 [43] Liu M, Wang F, Wang X P, Wang Y N, Roy-Chowdhury A K. A two-stage noise-tolerant paradigm for label corrupted person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46(7): 4944−4956 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3361491 [44] Huang Y, Wu Q, Zhang Z, Shan C F, Huang Y, Zhong Y, et al. Meta clothing status calibration for long-term person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2024, 33: 2334−2346 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2024.3374634 [45] Rami H, Giraldo J H, Winckler N, Lathuilière S. Source-guided similarity preservation for online person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2024. 1700−1709 [46] Nguyen V D, Mantini P, Shah S K. Temporal 3D shape modeling for video-based cloth-changing person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision Workshops (WACVW). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2024. 173−182 [47] Liu X H, Zhang P P, Yu C Y, Qian X S, Yang X Y, Lu H C. A video is worth three views: Trigeminal transformers for video-based person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25(9): 12818−12828 doi: 10.1109/TITS.2024.3386914 [48] Zhang S Z, Zhang Q, Yang Y F, Wei X, Wang P, Jiao B L, et al. Person re-identification in aerial imagery. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 23: 281−291 doi: 10.1109/TMM.2020.2977528 [49] Li T J, Liu J, Zhang W, Ni Y, Wang W Q, Li Z H. UAV-human: A large benchmark for human behavior understanding with unmanned aerial vehicles. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 16261−16270 [50] Nguyen H, Nguyen K, Sridharan S, Fookes C. Aerial-ground person re-ID. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME). Brisbane, Australia: IEEE, 2023. 2585−2590 [51] Zhang Q, Wang L, Patel V M, Xie X H, Lai J H. View-decoupled transformer for person re-identification under aerial-ground camera network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2024. 22000−22009 [52] He K, Zhang X, Ren S, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. 2016. 770−778 [53] Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez A N, et al. Attention is all you need. In: Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA: Curran Associates Inc., 2017. 6000−6010 [54] Dosovitskiy A, Beyer L, Kolesnikov A, Weissenborn D, Zhai X H, Unterthiner T, et al. An image is worth 16 × 16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. In: Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Learning Representations. ICLR, 2021. 1−21 [55] Wu J B, Liu H, Su Y X, Shi W, Tang H. Learning concordant attention via target-aware alignment for visible-infrared person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Paris, France: IEEE, 2023. 11088−11097 [56] Chen S Y, Ye M, Du B. Rotation invariant transformer for recognizing object in UAVs. In: Proceedings of the 30th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. New York, USA: Association for Computing Machinery, 2022. 2565−2574 [57] Kuma R, Weill E, Aghdasi F, Sriram P. Vehicle re-identification: An efficient baseline using triplet embedding. In: Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN). Budapest, Hungary: IEEE, 2019. 1−9 [58] Deng J, Dong W, Socher R, Li L J, Li K, Li F F. ImageNet: A large-scale hierarchical image database. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Miami, USA: IEEE, 2009. 248−255 [59] Robbins H, Monro S. A stochastic approximation method. The Annals of Mathematical Statistics, 1951, 22(3): 400−407 doi: 10.1214/aoms/1177729586 [60] Paszke A, Gross S, Massa F, Lerer A, Bradbury J, Chanan G, et al. PyTorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library. In: Proceedings of the 33rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2019. Article No. 721 -




 下载:
下载: