-
摘要: 孪生网络跟踪算法在训练阶段多数采用
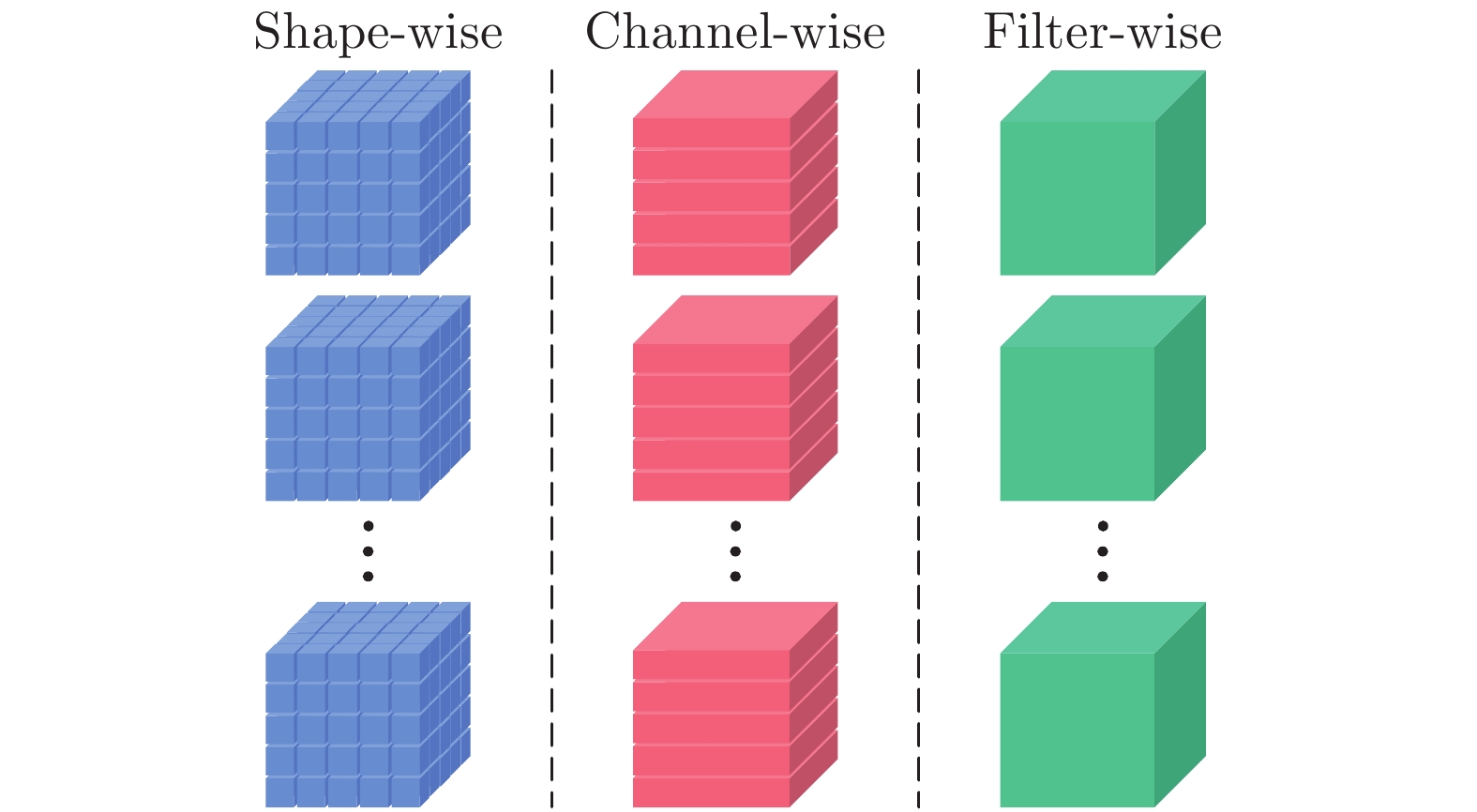
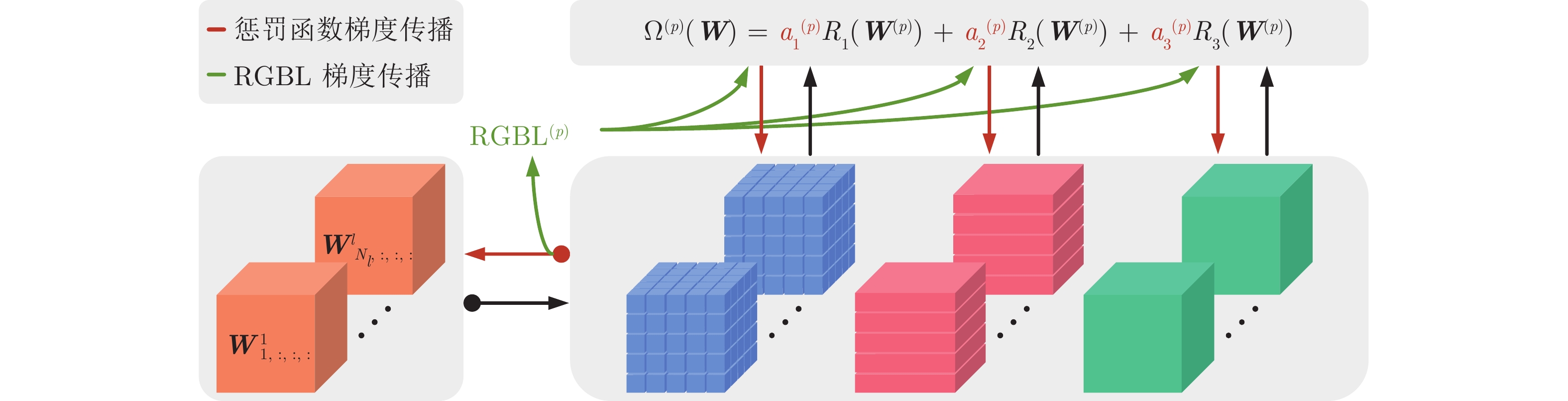
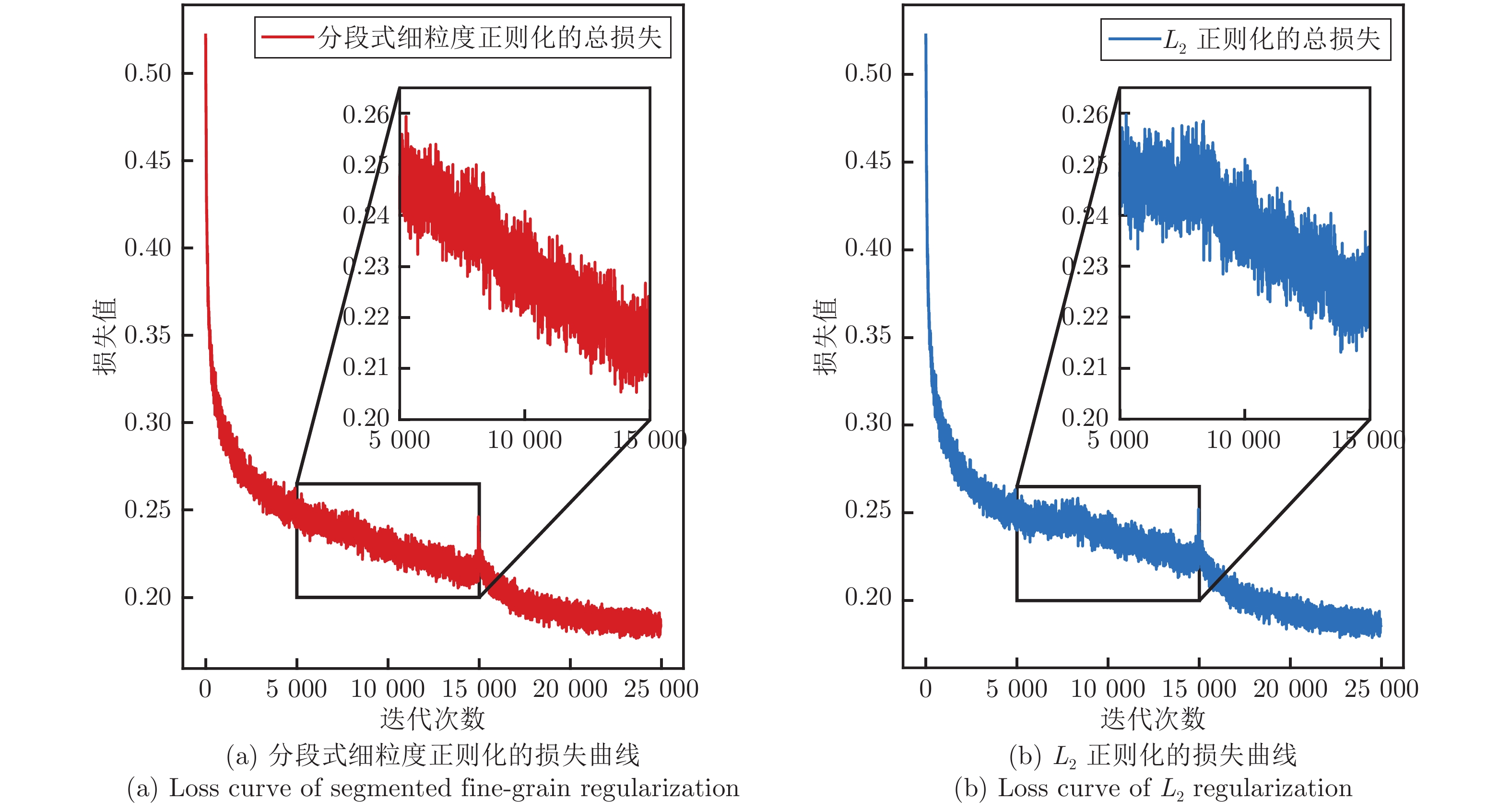
$ {L_2}$ 正则化, 而忽略了网络架构的层次和特点, 因此跟踪的鲁棒性较差. 针对该问题, 提出一种分段式细粒度正则化跟踪(Segmented fine-grained regularization tracking, SFGRT)算法, 将孪生网络的正则化划分为滤波器、通道和神经元三个粒度层次. 创新性地建立了分段式细粒度正则化模型, 分段式可针对不同层次粒度组合, 利用组套索构造惩罚函数, 并通过梯度自平衡优化函数自适应地优化各惩罚函数系数, 该模型可提升网络架构的泛化能力并增强鲁棒性. 最后, 基于VOT2019跟踪数据库的消融实验表明, 与基线算法SiamRPN++比较, 在鲁棒性指标上降低了7.1%及在平均重叠期望(Expected average overlap, EAO)指标上提升了1.7%, 由于鲁棒性指标越小越好, 因此鲁棒性得到显著增强. 基于VOT2018、VOT2019、UAV123和LaSOT等主流数据库的实验也表明, 与国际前沿跟踪算法相比, 所提算法具有较好的鲁棒性和跟踪性能.Abstract: Most of the Siamese network tracking algorithms use$ {L_2}$ regularization in the training stage, while ignoring the hierarchy and characteristic of the network architecture. As a result, such trackers have poor robustness. With this insight, we propose a segmented fine-grained regularization tracking (SFGRT) algorithm, which divides the regularization of Siamese network into three fine-grained levels, namely filter level, channel level and shape level. Then we creatively build a segmented fine-grained regularization model that constructs penalty functions based on group lasso, which combines with different levels of granularity to improve generalization ability and robustness. In addition, aiming at the imbalance of gradient magnitude of each penalty function, our approach constructs a gradient self-balancing optimization function to adaptively optimize the coefficients of each penalty function. Finally, ablation study on VOT2019 show that compared with the baseline algorithm SiamRPN++, our approach achieves relative gains of 7.1% and 1.7% in terms of robustness and expected average overlap (EAO) metrics, respectively. It means that the robustness of our tracker is significantly enhanced over baseline tracker since the smaller the robustness metrics, the better. Extensive experiments based on VOT2018, VOT2019, UAV123 and LaSOT show that the proposed algorithm has better robustness and tracking performance than related state-of-the-art methods.-
Key words:
- Visual tracking /
- Siamese network /
- fine-grained regularization /
- group lasso
-
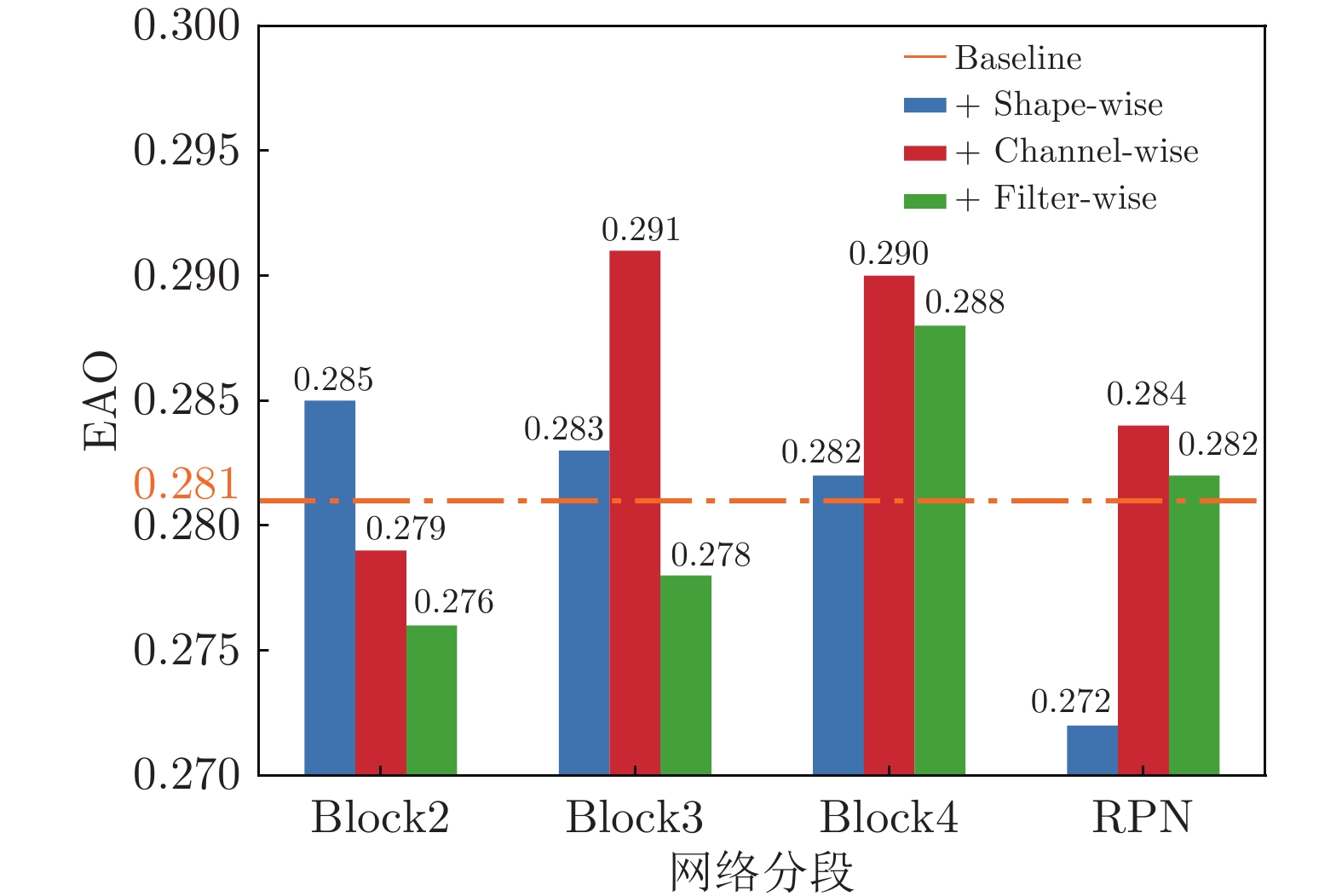
表 1 VOT2019上的消融实验
Table 1 Ablation study on VOT2019
基线算法 +细粒度组套索 +分段式细粒度正则化 EAO↑ 0.287 0.293 0.304 Accuracy↑ 0.595 0.600 0.586 Robustness↓ 0.467 0.456 0.396 表 2 在VOT2018上与SOTA算法的比较
Table 2 Comparison with SOTA trackers on VOT2018
算法 出版 EAO↑ Accuracy↑ Robustness↓ SiamRPN CVPR2018 0.383 0.586 0.276 SiamRPN++ CVPR2019 0.414 0.600 0.234 SiamMask CVPR2019 0.380 0.609 0.276 LADCF ITIP2019 0.389 0.503 0.159 ATOM CVPR2019 0.401 0.590 0.204 GFS-DCF ICCV2019 0.397 0.511 0.143 SiamBAN CVPR2020 0.452 0.597 0.178 SFGRT (Ours) — 0.422 0.589 0.197 表 3 在VOT2019上与SOTA算法的比较
Table 3 Comparison with SOTA trackers on VOT2019
算法 出版 EAO↑ Accuracy↑ Robustness↓ SPM CVPR2019 0.275 0.577 0.507 SiamRPN++ CVPR2019 0.287 0.595 0.467 SiamMask CVPR2019 0.287 0.594 0.461 SiamDW CVPR2019 0.299 0.600 0.467 MemDTC PAMI2019 0.228 0.485 0.587 ATOM CVPR2019 0.292 0.603 0.411 Roam++ CVPR2020 0.281 0.561 0.438 SiamBAN CVPR2020 0.327 0.602 0.396 SFGRT (Ours) — 0.304 0.586 0.396 表 4 在UAV123基准上与SOTA算法在8个挑战性属性下的精度对比
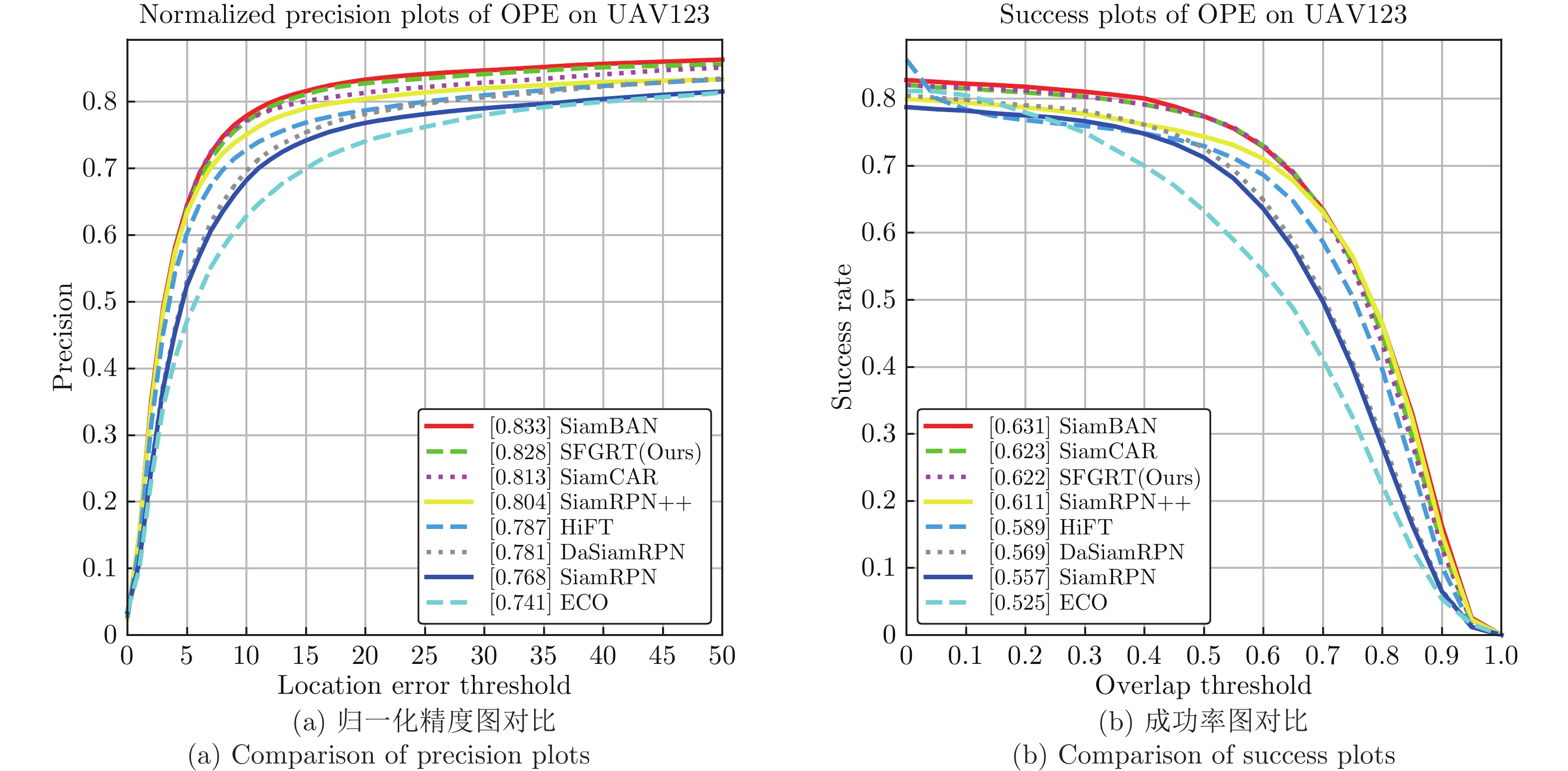
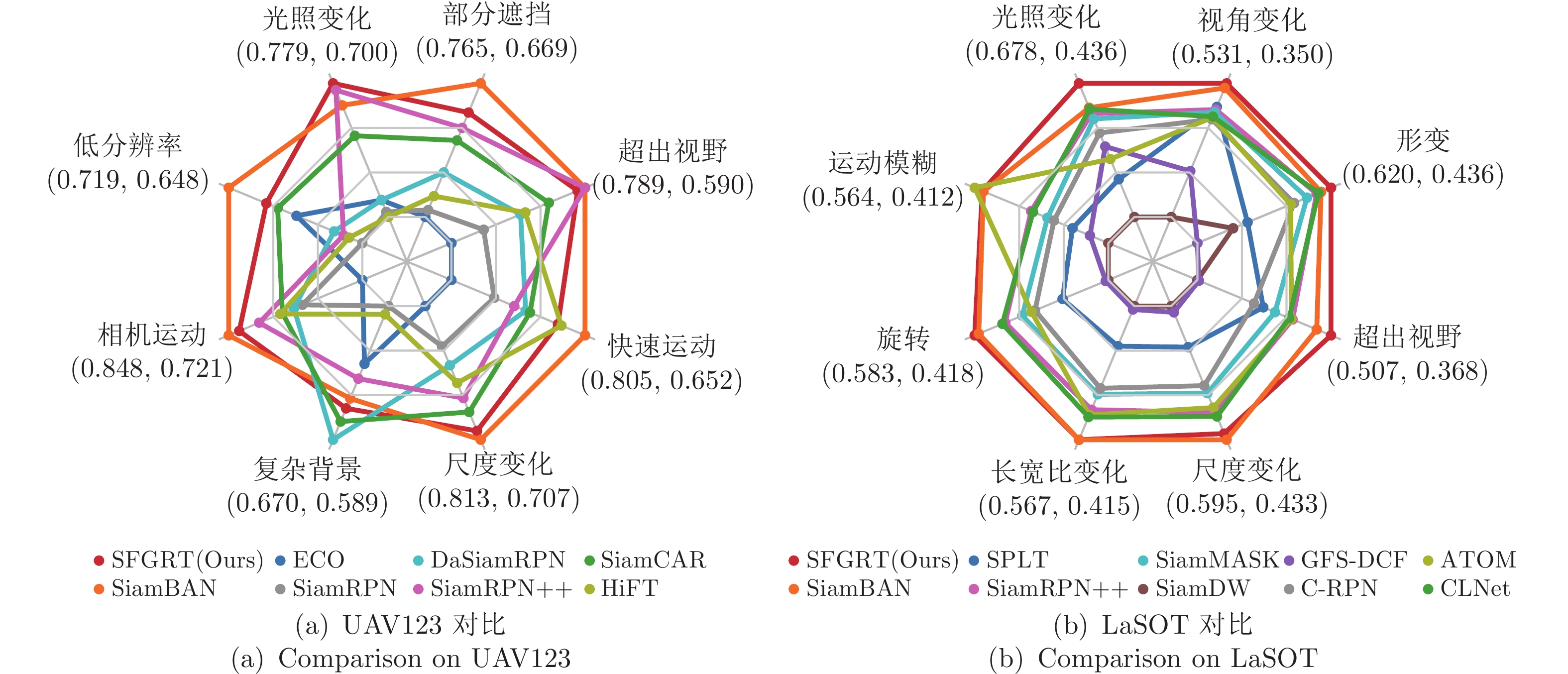
Table 4 Comparison of precision with SOTA trackers on 8 challenging attributes on UAV123
Attribute ECO SiamRPN DaSiamRPN SiamRPN++ SiamCAR SiamBAN HiFT SFGRT CVPR2017 CVPR2018 ECCV2018 CVPR2019 CVPR2020 CVPR2020 ICCV2021 — POC 0.669 0.674 0.701 0.733 0.724 0.765 0.684 0.744 IV 0.710 0.703 0.710 0.775 0.748 0.766 0.700 0.779 CM 0.721 0.778 0.786 0.819 0.797 0.848 0.799 0.838 FM 0.652 0.701 0.737 0.724 0.742 0.805 0.778 0.774 SV 0.707 0.739 0.754 0.780 0.791 0.813 0.768 0.806 BC 0.624 0.589 0.670 0.633 0.659 0.645 0.594 0.651 OV 0.590 0.638 0.693 0.789 0.735 0.789 0.700 0.778 LR 0.683 0.648 0.663 0.658 0.693 0.719 0.655 0.699 Overall 0.741 0.768 0.781 0.804 0.813 0.833 0.787 0.828 表 5 在LaSOT基准上与SOTA算法在8个挑战性属性下的归一化精度对比
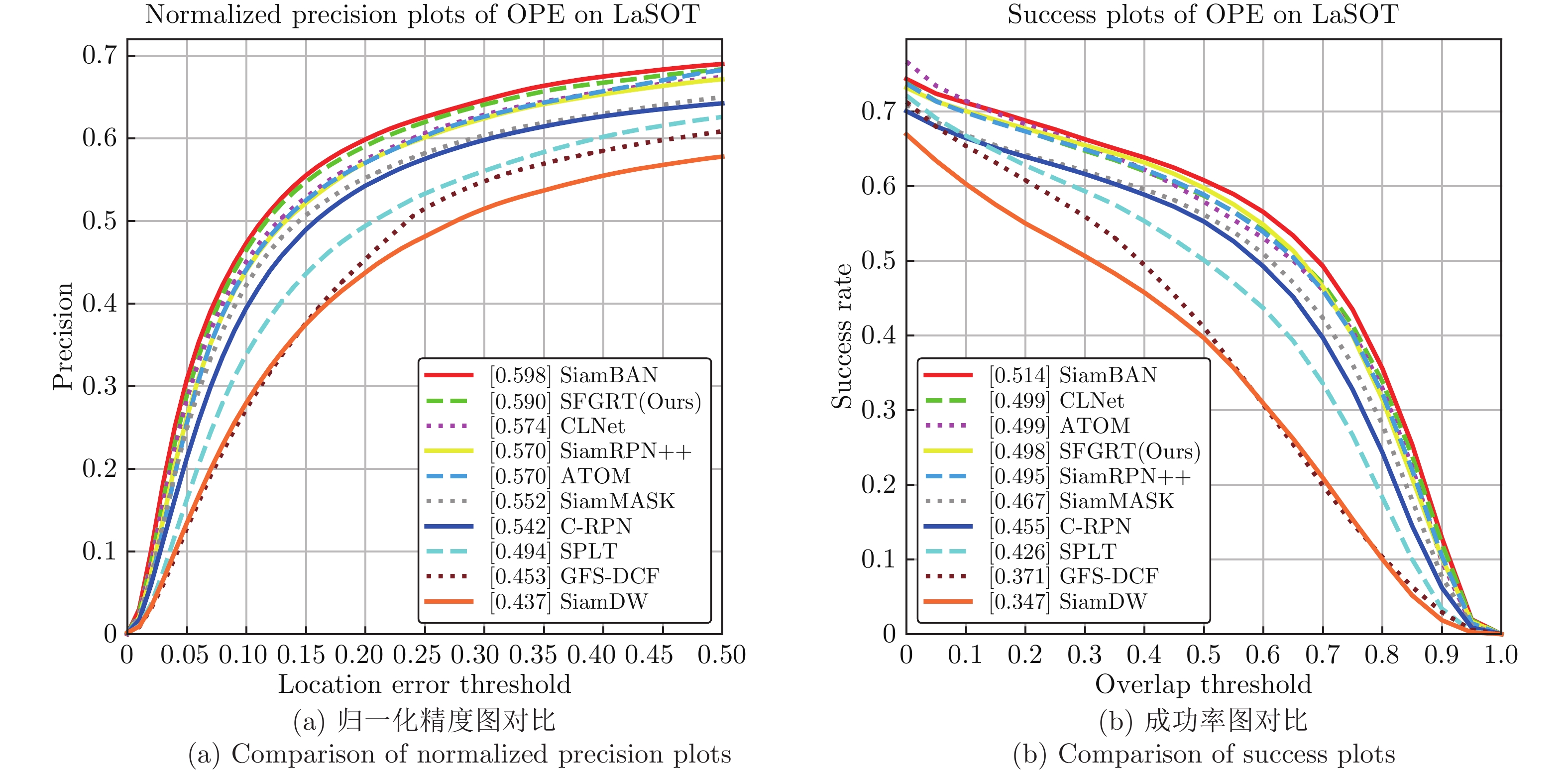
Table 5 Comparison of norm precision with SOTA trackers on 8 challenging attributes on LaSOT
Attribute SPLT C-RPN SiamDW SiamMask SiamRPN++ GFS-DCF ATOM SiamBAN CLNet SFGRT ICCV2019 CVPR2019 CVPR2019 CVPR2019 CVPR2019 ICCV2019 CVPR2019 CVPR2020 ICCV2021 — DEF 0.520 0.578 0.500 0.593 0.604 0.436 0.574 0.609 0.606 0.620 VC 0.505 0.491 0.350 0.499 0.502 0.427 0.493 0.526 0.494 0.531 IV 0.524 0.603 0.436 0.625 0.633 0.581 0.560 0.642 0.640 0.678 MB 0.465 0.486 0.412 0.493 0.510 0.443 0.564 0.556 0.508 0.557 ROT 0.488 0.520 0.418 0.534 0.552 0.425 0.524 0.579 0.555 0.583 ARC 0.473 0.518 0.415 0.524 0.539 0.423 0.544 0.567 0.546 0.567 SV 0.496 0.540 0.433 0.548 0.568 0.447 0.563 0.595 0.572 0.589 OV 0.447 0.438 0.368 0.458 0.474 0.372 0.473 0.495 0.471 0.507 Overall 0.494 0.542 0.437 0.552 0.570 0.453 0.570 0.598 0.574 0.590 表 6 不同跟踪算法的模型大小和平均帧速率对比
Table 6 Comparison of model size and average framerate for different trackers
算法 出版 模型大小(MB) 帧速率(FPS) SiamRPN++ CVPR2019 431.2 80.20 SiamMask CVPR2019 86.1 106.43 SiamBAN CVPR2020 430.9 81.76 SFGRT (Ours) — 431.2 79.99 -
[1] Xing D T, Evangeliou N, Tsoukalas A, Tzes A. Siamese transformer pyramid networks for real-time UAV tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, USA: IEEE, 2022. 1898−1907 [2] Fang L P, Liang N X, Kang W X, Wang Z Y, Feng D D. Real-time hand posture recognition using hand geometric features and fisher vector. Signal Processing: Image Communication, 2020, 82: Article No. 115729 doi: 10.1016/j.image.2019.115729 [3] Ballester I, Fontán A, Civera J, Strobl K H, Triebel R. DOT: Dynamic object tracking for visual SLAM. In: Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA). Xi'an, China: IEEE, 2021. 11705−11711 [4] Wu Y, Lim J, Yang M H. Object tracking benchmark. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9): 1834-1848 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2388226 [5] Tang M, Yu B, Zhang F, Wang J Q. High-speed tracking with multi-kernel correlation filters. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4874−4883 [6] Sun Y X, Sun C, Wang D, He Y, Lu H C. ROI pooled correlation filters for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5783−5791 [7] 仇祝令, 查宇飞, 吴敏, 王青. 基于注意力学习的正则化相关滤波跟踪算法. 电子学报, 2020, 48(9): 1762-1768 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.09.014Qiu Zhu-Ling, Zha Yu-Fei, Wu Min, Wang Qing. Learning attentional regularized correlation filter for visual tracking. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2020, 48(9): 1762-1768 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2020.09.014 [8] 朱建章, 王栋, 卢湖川. 学习时空一致性相关滤波的视觉跟踪. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2020, 50(1): 128-150 doi: 10.1360/N112018-00232Zhu Jian-Zhang, Wang Dong, Lu Hu-Chuan. Learning temporal-spatial consistency correlation filter for visual tracking. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2020, 50(1): 128-150 doi: 10.1360/N112018-00232 [9] Hu H W, Ma B, Shen J B, Shao L. Manifold regularized correlation object tracking. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(5): 1786-1795 doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2688448 [10] Xu T Y, Feng Z H, Wu X J, Kittler J. Joint group feature selection and discriminative filter learning for robust visual object tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 7949−7959 [11] Zhang T Z, Xu C S, Yang M H. Multi-task correlation particle filter for robust object tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 4819−4827 [12] 黄树成, 张瑜, 张天柱, 徐常胜, 王直. 基于条件随机场的深度相关滤波目标跟踪算法. 软件学报, 2019, 30(4): 927-940 doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005662Huang Shu-Cheng, Zhang Yu, Zhang Tian-Zhu, Xu Chang-Sheng, Wang Zhi. Improved deep correlation filters via conditional random field. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(4): 927-940 doi: 10.13328/j.cnki.jos.005662 [13] 张伟俊, 钟胜, 徐文辉, Wu Ying. 融合显著性与运动信息的相关滤波跟踪算法. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(7): 1572-1588 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190122Zhang Wei-Jun, Zhong Sheng, Xu Wen-Hui, Wu Ying. Correlation filter based visual tracking integrating saliency and motion cues. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(7): 1572-1588 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c190122 [14] 郭文, 游思思, 高君宇, 杨小汕, 张天柱, 徐常胜. 深度相对度量学习的视觉跟踪. 中国科学: 信息科学, 2018, 48(1): 60-78 doi: 10.1360/N112017-00124Guo Wen, You Si-Si, Gao Jun-Yu, Yang Xiao-Shan, Zhang Tian-Zhu, Xu Chang-Sheng. Deep relative metric learning for visual tracking. Scientia Sinica Informationis, 2018, 48(1): 60-78 doi: 10.1360/N112017-00124 [15] Bertinetto L, Valmadre J, Henriques J F, Vedaldi A, Torr P H S. Fully-convolutional Siamese networks for object tracking. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 850−865 [16] Krizhevsky A, Sutskever I, Hinton G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, USA: ACM, 2012. 1097−1105 [17] Li B, Yan J J, Wu W, Zhu Z, Hu X L. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 8971−8980 [18] Li B, Wu W, Wang Q, Zhang F Y, Xing J L, Yan J J. SiamRPN++: Evolution of Siamese visual tracking with very deep networks. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 4282−4291 [19] Wang Q, Zhang L, Bertinetto L, Hu W M, Torr P H S. Fast online object tracking and segmentation: A unifying approach. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1328−1338 [20] Zhang Z P, Peng H W. Deeper and wider Siamese networks for real-time visual tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 4591−4600 [21] Chen Z D, Zhong B N, Li G R, Zhang S P, Ji R R. Siamese box adaptive network for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6667−6676 [22] Chen Z D, Zhong B N, Li G R, Zhang S P, Ji R R, Tang Z J, et al. SiamBAN: Target-aware tracking with Siamese box adaptive network. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, DOI: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3195759 [23] 谭建豪, 郑英帅, 王耀南, 马小萍. 基于中心点搜索的无锚框全卷积孪生跟踪器. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(4): 801-812 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200469Tan Jian-Hao, Zheng Ying-Shuai, Wang Yao-Nan, Ma Xiao-Ping. AFST: Anchor-free fully convolutional Siamese tracker with searching center point. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(4): 801-812 doi: 10.16383/j.aas.c200469 [24] Chen X, Yan B, Zhu J W, Wang D, Yang X Y, Lu H C. Transformer tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Nashville, USA: IEEE, 2021. 8122−8131 [25] Cao Z, Fu C H, Ye J J, Li B W, Li Y M. HiFT: Hierarchical feature transformer for aerial tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 15437−15446 [26] Xu T Y, Feng Z H, Wu X J, Kittler J. AFAT: Adaptive failure-aware tracker for robust visual object tracking. arXiv preprint arXiv: 2005.13708, 2020. [27] Kristan M, Matas J, Leonardis A, Felsberg M, Pflugfelder R, Kämäräinen J K, et al. The seventh visual object tracking VOT2019 challenge results. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision Workshop (ICCVW). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 2206−2241 [28] Kristan M, Leonardis A, Matas J, Felsberg M, Pflugfelder R, Zajc L Č, et al. The sixth visual object tracking VOT2018 challenge results. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 3−53 [29] Mueller M, Smith N, Ghanem B. A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking. In: Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 445−461 [30] Fan H, Lin L T, Yang F, Chu P, Deng G, Yu S J, et al. LaSOT: A high-quality benchmark for large-scale single object tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5369−5378 [31] Zhu Z, Wang Q, Li B, Wu W, Yan J J, Hu W M. Distractor-aware Siamese networks for visual object tracking. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 103−119 [32] He K M, Zhang X Y, Ren S Q, Sun J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 770−778 [33] He A F, Luo C, Tian X M, Zeng W J. A twofold Siamese network for real-time object tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4834−4843 [34] Wang Q, Teng Z, Xing J L, Gao J, Hu W M, Maybank S. Learning attentions: Residual attentional Siamese network for high performance online visual tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4854−4863 [35] Du F, Liu P, Zhao W, Tang X L. Correlation-guided attention for corner detection based visual tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6835−6844 [36] Li F, Tian C, Zuo W M, Zhang L, Yang M H. Learning spatial-temporal regularized correlation filters for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4904−4913 [37] Huang Z Y, Fu C H, Li Y M, Lin F L, Lu P. Learning aberrance repressed correlation filters for real-time UAV tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 2891−2900 [38] Li Y M, Fu C H, Ding F Q, Huang Z Y, Lu G. AutoTrack: Towards high-performance visual tracking for UAV with automatic spatio-temporal regularization. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 11920−11929 [39] Liu X N, Zhou Y, Zhao J Q, Yao R, Liu B, Zheng Y. Siamese convolutional neural networks for remote sensing scene classification. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2019, 16(8): 1200-1204 doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2019.2894399 [40] Fiaz M, Mahmood A, Baek K Y, Farooq S S, Jung S K. Improving object tracking by added noise and channel attention. Sensors, 2020, 20(13): Article No. 3780 doi: 10.3390/s20133780 [41] Jia S, Ma C, Song Y B, Yang X K. Robust tracking against adversarial attacks. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 69−84 [42] Yuan M, Lin Y. Model selection and estimation in regression with grouped variables. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology), 2006, 68(1): 49-67 doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2005.00532.x [43] Nie F P, Huang H, Cai X, Ding C. Efficient and robust feature selection via joint $ \ell_2, 1$-norms minimization. In: Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: ACM, 2010. 1813−1821 [44] Bach F, Jenatton R, Mairal J, Obozinski G. Structured sparsity through convex optimization. Statistical Science, 2012, 27(4): 450-468 [45] Yoon J, Hwang S J. Combined group and exclusive sparsity for deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. Sydney, Australia: JMLR.org, 2017. 3958−3966 [46] Hu Y H, Li C, Meng K W, Qin J, Yang X Q. Group sparse optimization via $ L_p, q$ regularization. The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2017, 18(1): 960-1011[47] Wen W, Wu C P, Wang Y D, Chen Y R, Li H. Learning structured sparsity in deep neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Barcelona, Spain: ACM, 2016. 2082−2090 [48] Szegedy C, Zaremba W, Sutskever I, Bruna J, Erhan D, Goodfellow I, et al. Intriguing properties of neural networks. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1312.6199, 2013. [49] Chen Z, Badrinarayanan V, Lee C Y, Rabinovich A. GradNorm: Gradient normalization for adaptive loss balancing in deep multitask networks. In: Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm, Sweden: PMLR, 2018. 793−802 [50] Lin T Y, Maire M, Belongie S, Hays J, Perona P, Ramanan D, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context. In: Proceedings of the 13th European Conference on Computer Vision. Zurich, Switzerland: Springer, 2014. 740−755 [51] Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S A, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [52] Real E, Shlens J, Mazzocchi S, Pan X, Vanhoucke V. YouTube-BoundingBoxes: A large high-precision human-annotated data set for object detection in video. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 7464−7473 [53] Huang L H, Zhao X, Huang K Q. GOT-10k: A large high-diversity benchmark for generic object tracking in the wild. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(5): 1562-1577 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2957464 [54] Guo D Y, Wang J, Cui Y, Wang Z H, Chen S Y. SiamCAR: Siamese fully convolutional classification and regression for visual tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6268−6276 [55] Dong X P, Shen J B, Shao L, Porikli F. CLNet: A compact latent network for fast adjusting Siamese trackers. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: Springer, 2020. 378−395 [56] Yang T Y, Xu P F, Hu R B, Chai H, Chan A B. ROAM: Recurrently optimizing tracking model. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 6717−6726 [57] Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. ATOM: Accurate tracking by overlap maximization. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 4660−4669 [58] Yan B, Zhao H J, Wang D, Lu H C, Yang X Y. ‘Skimming-perusal’ tracking: A framework for real-time and robust long-term tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 2385−2393 [59] Fan H, Ling H B. Siamese cascaded region proposal networks for real-time visual tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7952−7961 [60] Yang T Y, Chan A B. Visual tracking via dynamic memory networks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(1): 360-374 [61] Xu T Y, Feng Z H, Wu X J, Kittler J. Learning adaptive discriminative correlation filters via temporal consistency preserving spatial feature selection for robust visual object tracking. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(11): 5596-5609 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2919201 [62] Danelljan M, Bhat G, Khan F S, Felsberg M. ECO: Efficient convolution operators for tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 6931−6939 [63] Wang G T, Luo C, Xiong Z W, Zeng W J. SPM-Tracker: Series-parallel matching for real-time visual object tracking. In: Proceedings of IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3643−3652 -






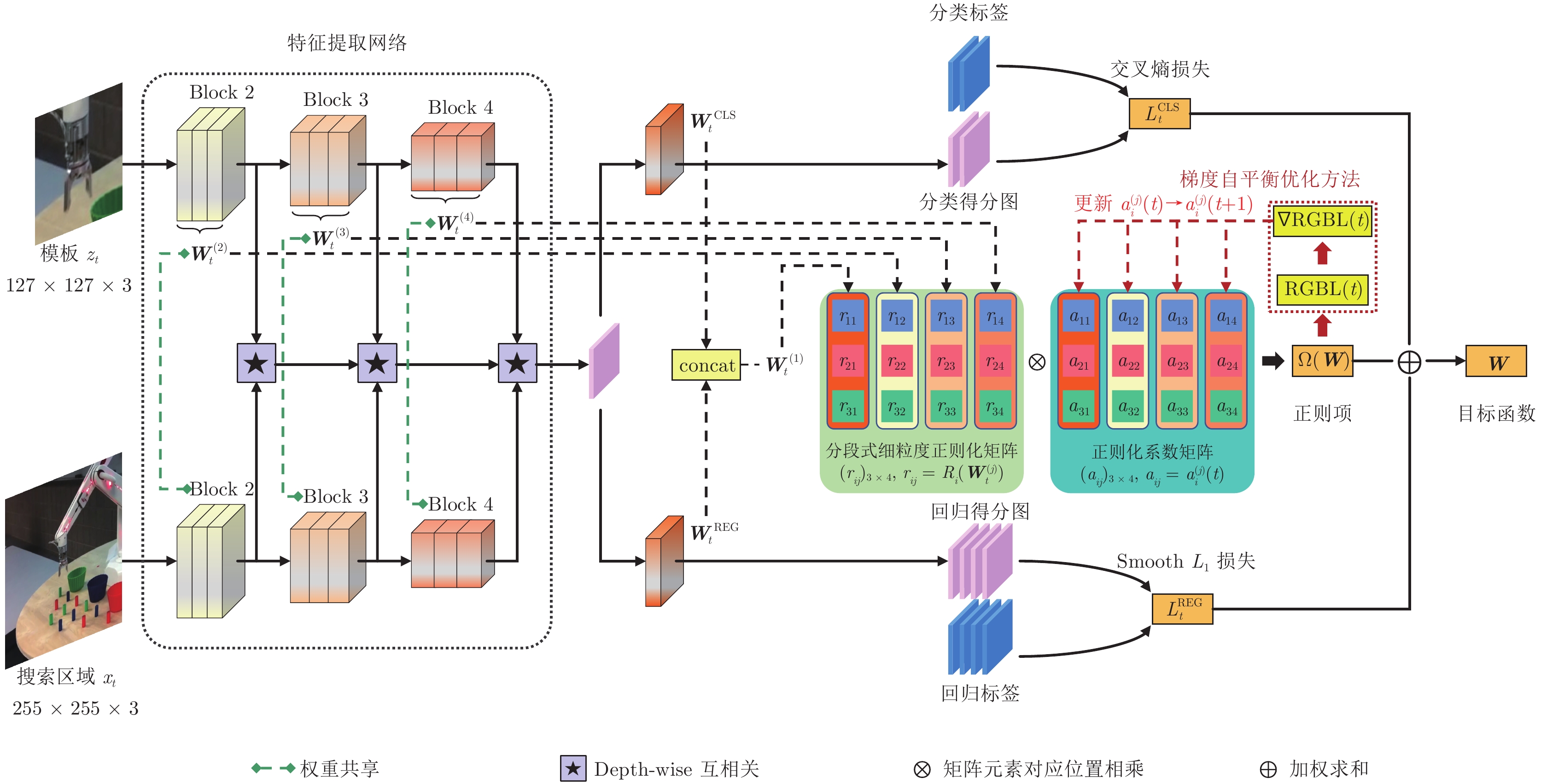
 下载:
下载: