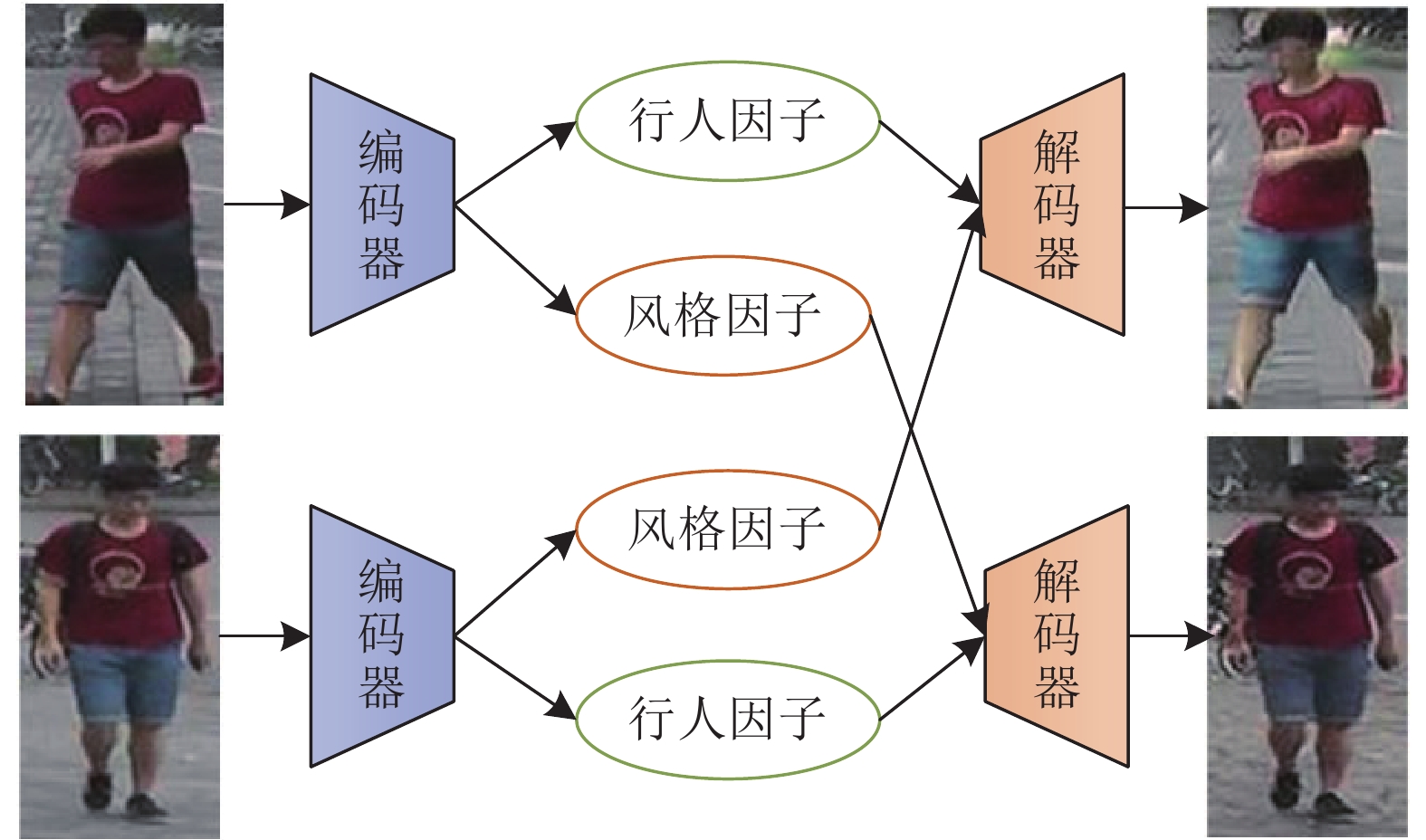
-
摘要: 无监督跨域的行人重识别旨在将从有标签的源域中学习到的知识迁移到无标签的目标域, 具有实用性和有效性而得到广泛关注. 基于聚类的跨域行人重识别可以生成伪标签并对模型进行优化使得其表现较其他方法更优, 然而这类方法由于过于依赖聚类伪标签的准确性, 忽略了对伪标签噪声的处理, 导致噪声随着网络迭代而不断扩大, 影响模型的鲁棒性. 针对这个问题, 提出了基于自适应融合网络的方法, 利用双网络结构共同学习, 并将学习到的知识进行融合得到融合网络; 为了区分两个网络的学习能力, 设计了自适应融合策略; 同时, 利用细粒度风格转换模块对目标域数据集进行处理, 降低行人图像对相机变换的敏感度. 在行人重识别基准数据集Market1501、DukeMTMC-ReID和MSMT17上, 通过评估指标平均精度均值和Rank-n与主流的方法进行了对比实验, 验证了该方法的有效性.Abstract: Unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification aims to transfer the knowledge learned from labeled source domain to unlabeled target domain, which has attracted wide attention due to its practicability and effectiveness. Cross-domain person re-identification based on clustering can generate pseudo-labels and optimize the model to make its performance better than other methods. However, these methods rely too much on the accuracy of clustering pseudo labels and ignore to deal with pseudo-label noise, which leads to the continuous expansion of noise with network iteration and affects the robustness of the models. To address this problem, this paper proposes a method based on fine-grained style transfer and adaptive fusion network, which uses dual network structure to learn together and fuse the learned knowledge to obtain a fusion network. To treat the learning ability of the two networks differently, an adaptive fusion strategy is designed based on the different weights of the two networks in each fusion process. At the same time, a fine-grained style transfer module is used to process the target domain dataset, thereby reducing the sensitivity of person images to camera transformation. On the person re-identification benchmark datasets Market1501, DukeMTMC-ReID and MSMT17, the effectiveness of the proposed method was verified by comparing mean average precision and Rank-n with the state-of-the-art methods.
-
表 1 本文的自适应融合网络模型参数量表
Table 1 The model parameter number of the proposed adaptive fusion network
参数 取值 总参数 23512128 × 2 可训练参数 23512128 × 2 参数大小 (MB) 89.69 × 2 估计总大小 (MB) 1199.45 × 2 表 2 在Market1501和DukeMTMC-ReID上与主流方法比较 (%)
Table 2 Comparison with the state-of-the-art methods on Market1501 and DukeMTMC-ReID (%)
方法 Duke-to-Market Market-to-Duke mAP Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 mAP Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 BUC[34] 38.3 66.2 79.6 84.5 27.5 47.4 62.6 68.4 SSL[35] 37.8 71.7 87.4 37.8 28.6 52.5 63.5 68.9 MMFA[36] 27.4 56.7 75.0 81.8 24.7 45.3 59.8 66.3 TJ-AIDL[11] 26.5 58.2 74.8 81.1 23.0 44.3 59.6 65.0 D-MMD[12] 75.1 89.5 95.6 97.1 62.7 79.3 89.3 92.0 TAL-MIRN[37] 40.0 73.1 86.3 — 41.3 63.5 76.7 — ATNet[13] 25.6 55.7 73.2 79.4 24.9 45.1 59.5 64.2 SPGAN + LMP[14] 26.7 57.7 75.8 82.4 26.2 46.4 62.3 68.0 HHL[16] 31.4 62.2 78.8 84.0 27.2 46.9 61.0 66.7 ECN[17] 43.0 75.1 87.6 91.6 40.4 63.3 75.8 80.4 MAR[18] 67.7 81.9 87.3 40.0 67.1 79.8 84.2 48.0 UDAP[38] 53.7 75.8 89.5 93.2 49.0 68.4 80.1 83.5 PCB-PAST[39] 54.6 78.4 — — 54.3 72.4 — — SSG[20] 58.3 80.0 90.0 92.4 53.4 73.0 80.6 83.2 AD-Cluster[21] 68.3 86.7 94.4 96.5 54.1 72.6 82.5 85.5 MMT-500[23] 71.2 87.7 94.9 96.9 63.1 76.8 88.0 92.2 MEB-Net[40] 76.0 89.9 96.0 97.5 66.1 79.6 88.3 92.2 SILC[41] 61.8 80.7 90.1 93.0 50.3 68.5 80.2 85.4 DRDL[42] 42.7 76.8 88.5 91.6 43.2 65.3 76.9 82.2 PREST[43] 62.4 82.5 92.1 94.9 56.1 74.4 83.7 85.9 SpCL[44] 76.7 90.3 96.2 97.7 68.8 82.9 90.1 92.5 MLOL[45] 70.9 86.6 93.1 95.1 69.8 83.1 90.8 93.0 UNRN[46] 78.1 91.9 96.1 97.8 69.1 82.0 90.7 93.5 本文方法 79.1 91.8 97.1 98.2 68.5 80.7 90.1 92.6 本文方法 + 不确定性 79.9 92.3 97.4 98.3 69.8 82.1 90.5 93.1 表 3 在MSMT17上与主流方法比较 (%)
Table 3 Comparison with the state-of-the-art methods on MSMT17 (%)
方法 Duke-to-MSMT17 Market-to-MSMT17 mAP Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 mAP Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 ECN[17] 10.2 30.2 41.5 46.8 8.5 25.3 36.3 42.1 SSG[20] 13.3 32.2 — 51.2 13.2 31.6 — 49.6 MMT-1500[23] 23.3 50.1 63.9 69.8 22.9 49.2 63.1 68.8 SILC[41] 12.6 33.1 45.2 48.0 10.9 27.8 38.1 45.8 TAL-MIRN[37] 14.2 39.0 51.5 — 11.2 30.9 43.5 — DRDL[42] 14.9 42.0 53.7 59.1 14.7 38.6 51.4 57.1 PREST[43] 18.5 43.8 57.5 63.6 15.9 37.8 51.8 57.8 SpCL[44] 26.5 53.1 65.8 70.5 25.4 51.6 64.3 69.7 MLOL[45] 22.4 48.3 60.7 66.1 21.7 46.9 59.4 64.7 UNRN[46] 26.2 54.9 67.3 70.6 25.3 52.4 64.7 69.7 本文方法 30.2 60.4 73.3 77.9 29.4 59.6 72.8 77.5 本文方法 + 不确定 30.8 61.0 73.9 78.3 30.6 61.0 73.7 78.0 表 4 在Market1501和DukeMTMC-ReID上的消融实验 (%)
Table 4 Ablation experiments on Market1501 and DukeMTMC-ReID (%)
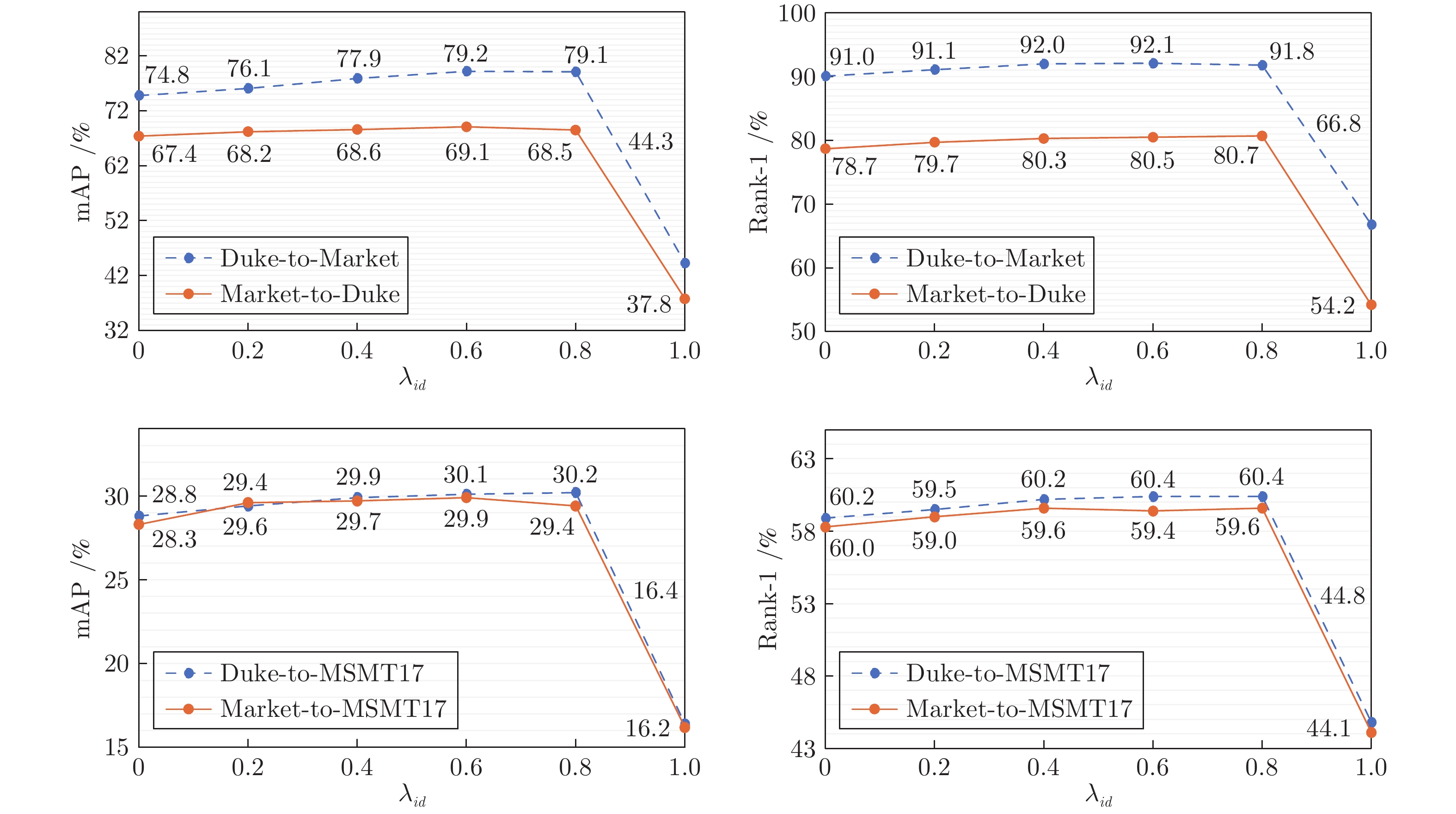
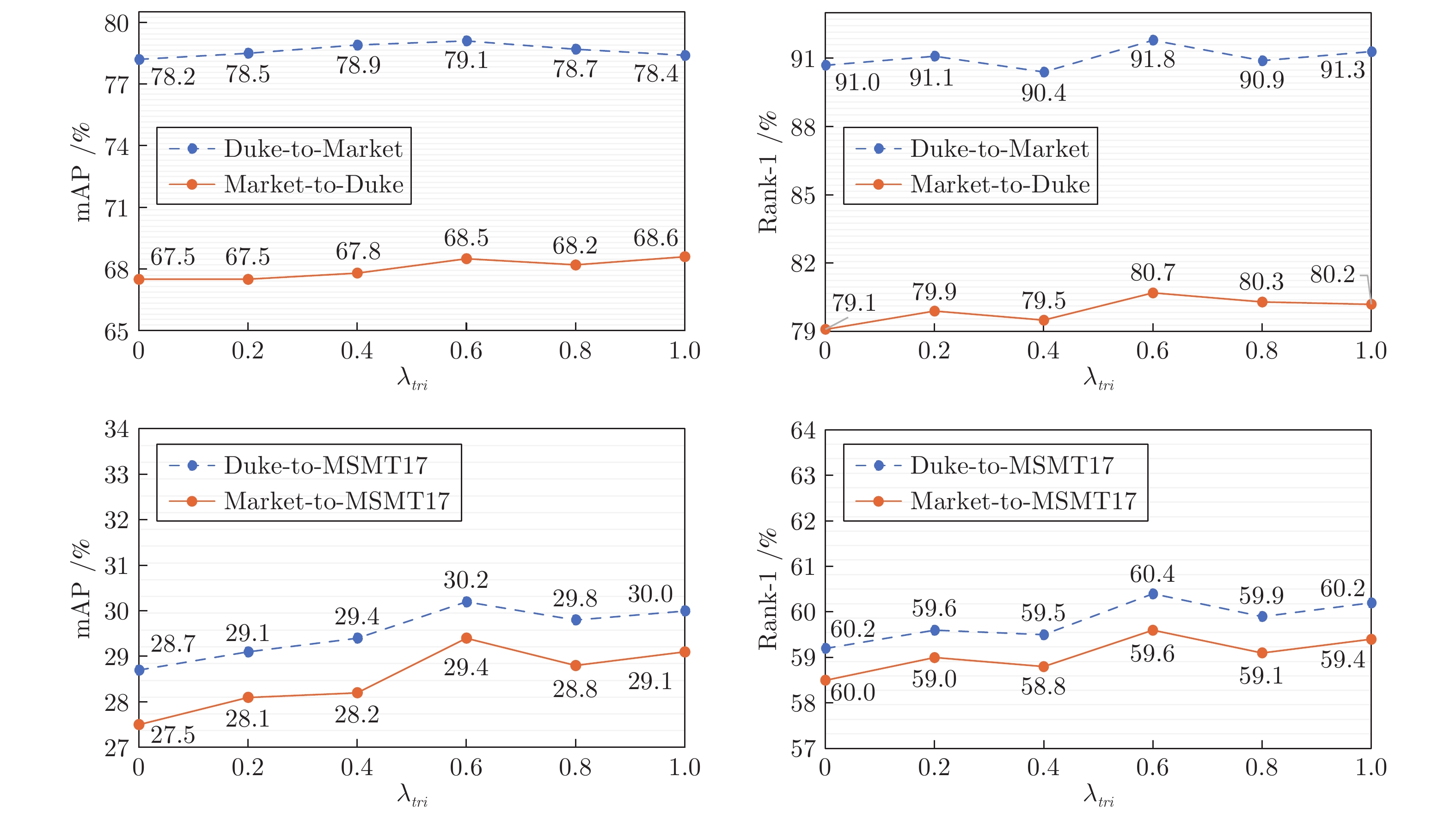
方法 Duke-to-Market Market-to-Duke mAP Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 mAP Rank-1 Rank-5 Rank-10 直接转换 31.8 61.9 76.4 82.2 29.9 46.2 61.9 68.0 基线 53.5 76.0 88.1 91.9 48.2 66.4 79.8 84.0 本文方法 w/F 74.3 90.2 95.8 97.6 62.9 77.1 87.9 91.5 本文方法 w/(F + T) 77.6 91.5 96.8 98.1 66.3 79.0 89.6 92.3 本文方法 w/(F + T + A) 78.2 91.7 96.9 98.1 66.9 79.9 89.7 92.2 本文方法 w/(F + T + S) 78.9 91.2 96.8 98.0 67.5 80.3 89.9 92.4 本文方法 w/(F + T + A + S) 79.1 91.8 97.1 98.2 68.5 80.7 90.1 92.6 表 5 聚类算法对比
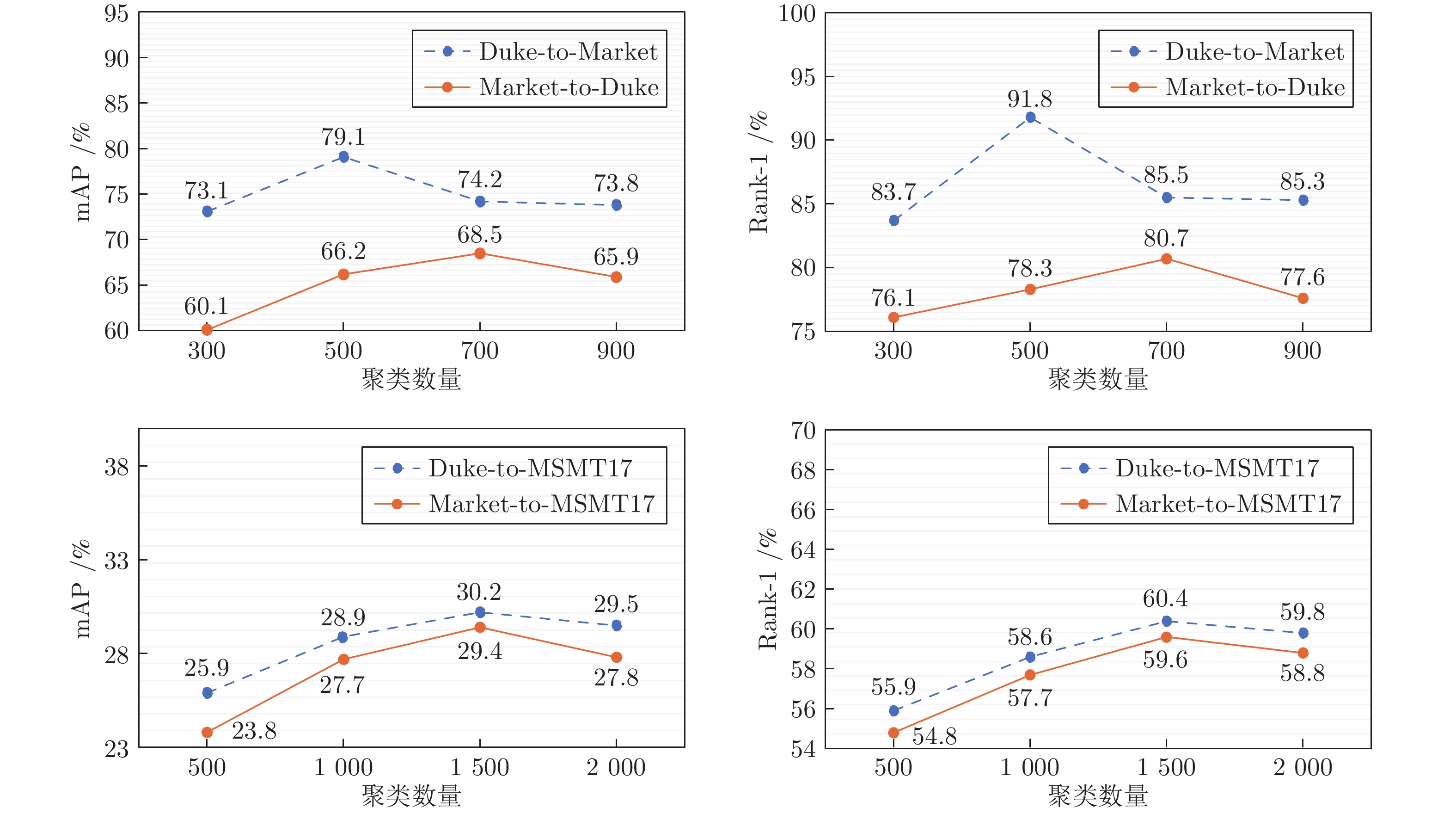
Table 5 Comparison of clustering algorithms
方法 Duke-to-Market Market-to-Duke mAP (%) R-1 (%) R-5 (%) R-10 (%) 运行时间 (s) mAP (%) R-1 (%) R-5 (%) R-10 (%) 运行时间 (s) Mini-Batch k-means 79.1 91.8 97.1 98.2 811 68.5 80.7 90.1 92.6 908 k-means 79.3 91.8 97.2 98.1 1472 68.8 80.9 90.1 92.6 1669 DBSCAN 80.1 92.3 97.4 98.4 3224 69.9 82.1 90.7 92.9 3643 -
[1] 叶钰, 王正, 梁超, 韩镇, 陈军, 胡瑞敏. 多源数据行人重识别研究综述. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(9): 1869-1884Ye Yu, Wang Zheng, Liang Chao, Han Zhen, Chen Jun, Hu Rui-Min. A survey on multi-source person re-identification. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(9): 1869-1884 [2] Ye M, Shen J B, Lin G J, Xiang T, Shao L, Hoi S C H. Deep learning for person re-identification: A survey and outlook. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(6): 2872-2893 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3054775 [3] 李幼蛟, 卓力, 张菁, 李嘉锋, 张辉. 行人再识别技术综述. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(9): 1554-1568Li You-Jiao, Zhuo Li, Zhang Jing, Li Jia-Feng, Zhang Hui. A survey of person re-identification. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(9): 1554-1568 [4] Bai S, Bai X, Tian Q. Scalable person re-identification on supervised smoothed manifold. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (ICCV). Honolulu, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3356−3365 [5] 罗浩, 姜伟, 范星, 张思朋. 基于深度学习的行人重识别研究进展. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(11): 2032-2049Luo Hao, Jiang Wei, Fan Xing, Zhang Si-Peng. A survey on deep learning based person re-identification. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(11): 2032-2049 [6] 张云鹏, 王洪元, 张继, 陈莉, 吴琳钰, 顾嘉晖, 等. 近邻中心迭代策略的单标注视频行人重识别. 软件学报, 2021, 32(12): 4025-4035Zhang Yun-Peng, Wang Hong-Yuan, Zhang Ji, Chen Li, Wu Lin-Yu, Gu Jia-Hui, et al. One-shot video-based person re-identification based on neighborhood center iteration strategy. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(12): 4025-4035 [7] 刘一敏, 蒋建国, 齐美彬, 刘皓, 周华捷. 融合生成对抗网络和姿态估计的视频行人再识别方法. 自动化学报, 2020, 46(3): 576-584Liu Yi-Min, Jiang Jian-Guo, Qi Mei-Bin, Liu Hao, Zhou Hua-Jie. Video-based person re-identification method based on GAN and pose estimation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46(3): 576-584 [8] Wang M L, Lai B S, Huang J Q, Gong X J, Hua X S. Camera-aware proxies for unsupervised person re-identification. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35(4): 2764-2772 doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i4.16381 [9] Wu Y M, Wu X T, Li X, Tian J. MGH: Metadata guided hypergraph modeling for unsupervised person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 29th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Virtual Event China: 2021. 1571−1580 [10] Chen H, Lagadec B, Bremond F. ICE: Inter-instance contrastive encoding for unsupervised person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal, Canada: IEEE, 2021. 14940−14949 [11] Wang J Y, Zhu X T, Gong S G, Li W. Transferable joint attribute-identity deep learning for unsupervised person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 2275−2284 [12] Mekhazni D, Bhuiyan A, Ekladious G, Granger E. Unsupervised domain adaptation in the dissimilarity space for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: 2020. 159−174 [13] Liu J W, Zha Z J, Chen D, Hong R C, Wang M. Adaptive transfer network for cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 7195−7204 [14] Deng W J, Zheng L, Ye Q X, Kang Q L, Yi Y, Jiao J B. Image-image domain adaptation with preserved self-similarity and domain-dissimilarity for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 994−1003 [15] Wei L H, Zhang S L, Wen G, Tian Q. Person transfer GAN to bridge domain gap for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 79−88 [16] Zhong Z, Zheng L, Li S Z, Yang Y. Generalizing a person retrieval model hetero- and homogeneously. In: Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: Springer, 2018. 172−188 [17] Zhong Z, Zheng L, Luo Z M, Li S Z, Yang Y. Invariance matters: Exemplar memory for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 598−607 [18] Yu H X, Zheng W S, Wu A C, Guo X W, Gong S G, Lai J H. Unsupervised person re-identification by soft multilabel learning. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 2143−2152 [19] Saito K, Watanabe K, Ushiku Y, Harada T. Maximum classifier discrepancy for unsupervised domain adaptation. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3723−3732 [20] Fu Y, Wei Y C, Wang G S, Zhou Y Q, Shi H H, Uiuc U, et al. Self-similarity grouping: A simple unsupervised cross domain adaptation approach for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 6111−6120 [21] Zhai Y P, Lu S J, Ye Q X, Shan X B, Chen J, Ji R R, et al. AD-Cluster: Augmented discriminative clustering for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 9018−9027 [22] Yang F X, Li K, Zhong Z, Luo Z M, Sun X, Cheng H, et al. Asymmetric co-teaching for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(7): 12597-12604 doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i07.6950 [23] Ge Y X, Chen D P, Li H S. Mutual mean-teaching: Pseudo label refinery for unsupervised domain adaptation on person re-identification. arXiv: 2001.01526, 2020 [24] Wang W H, Zhao F, Liao S C, Shao L. Attentive WaveBlock: Complementarity-enhanced mutual networks for unsupervised domain adaptation in person re-identification and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 1532-1544 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3140614 [25] Bertocco G C, Andaló F, Rocha A. Unsupervised and self-adaptative techniques for cross-domain person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2021, 16: 4419-4434 doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2021.3107157 [26] Sheng K K, Li K, Zheng X W, Liang J, Dong W M, Huang F Y, et al. On evolving attention towards domain adaptation. arXiv: 2103.13561, 2021 [27] Zheng Z D, Yang X D, Yu Z D, Zheng L, Yang Y, Kautz J. Joint discriminative and generative learning for person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 2133−2142 [28] Hermans A, Beyer L, Leibe B. In defense of the triplet loss for person re-identification. arXiv: 1703.07737, 2017 [29] Zheng L, Shen L Y, Tian L, Wang S J, Wang J D, Tian Q. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark. In: Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Santiago, Chile: IEEE, 2015. 1116−1124 [30] Zheng Z D, Zheng L, Yang Y. Unlabeled samples generated by GAN improve the person re-identification baseline in vitro. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 3774−3782 [31] Felzenszwalb P F, Girshick R B, McAllester D, Ramanan D. Object detection with discriminatively trained part-based models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2010, 32(9): 1627-1645 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2009.167 [32] Ristani E, Solera F, Zou R, Cucchiara R, Tomasi C. Performance measures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 17−35 [33] Russakovsky O, Deng J, Su H, Krause J, Satheesh S, Ma S A, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252 doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [34] Lin Y T, Dong X Y, Zheng L, Yan Y, Yang Y. A bottom-up clustering approach to unsupervised person re-identification. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 8738-8745 doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018738 [35] Lin Y T, Xie L X, Wu Y, Yan C G, Tian Q. Unsupervised person re-identification via softened similarity learning. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Seattle, USA: IEEE, 2020. 3387−3396 [36] Lin S, Li H L, Li C T, Kot A C. Multi-task mid-level feature alignment network for unsupervised cross-dataset person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 29th British Machine Vision Conference. Newcastle, UK: 2018. [37] Li H F, Dong N, Yu Z T, Tao D P, Qi G Q. Triple adversarial learning and multi-view imaginative reasoning for unsupervised domain adaptation person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2022, 32(5): 2814-2830 doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3099943 [38] Song L C, Wang C, Zhang L F, Du B, Zhang Q, Huang C, et al. Unsupervised domain adaptive re-identification: Theory and practice. Pattern Recognition, 2020, 102: Article No. 107173 doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.107173 [39] Zhang X Y, Cao J W, Shen C H, You M Y. Self-training with progressive augmentation for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, Korea (South): IEEE, 2019. 8221−8230 [40] Zhai Y P, Ye Q X, Lu S J, Jia M X, Ji R R, Tian Y H. Multiple expert brainstorming for domain adaptive person re-identification. In: Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision. Glasgow, UK: 2020. 594−611 [41] Ainam J P, Qin K, Owusu J W, Lu G M. Unsupervised domain adaptation for person re-identification with iterative soft clustering. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 212: Article No. 106644 doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106644 [42] Li H F, Xu K X, Li J X, Lu G M, Xu Y, Yu Z T, et al. Dual-stream reciprocal disentanglement learning for domain adaptation person re-identification. arXiv: 2106.13929, 2021 [43] Zhang H, Cao H H, Yang X, Deng C, Tao D C. Self-training with progressive representation enhancement for unsupervised cross-domain person re-identification. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 5287-5298 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3082298 [44] Ge Y X, Zhu F, Chen D P, Zhao R, Li H S. Self-paced contrastive learning with hybrid memory for domain adaptive object re-ID. In: Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Vancouver, Canada: Curran Associates Inc., 2020. 11309−11321 [45] Sun J, Li Y F, Chen H J, Peng Y H, Zhu J L. Unsupervised cross domain person re-identification by multi-loss optimization learning. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2021, 30: 2935-2946 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2021.3056889 [46] Zheng K C, Lan C L, Zeng W J, Zhan Z Z, Zha Z J. Exploiting sample uncertainty for domain adaptive person re-identification. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 35(4): 3538-3546 doi: 10.1609/aaai.v35i4.16468 [47] Zheng Z D, Yang Y. Rectifying pseudo label learning via uncertainty estimation for domain adaptive semantic segmentation. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2021, 129(4): 1106-1120 doi: 10.1007/s11263-020-01395-y -





 下载:
下载: