-
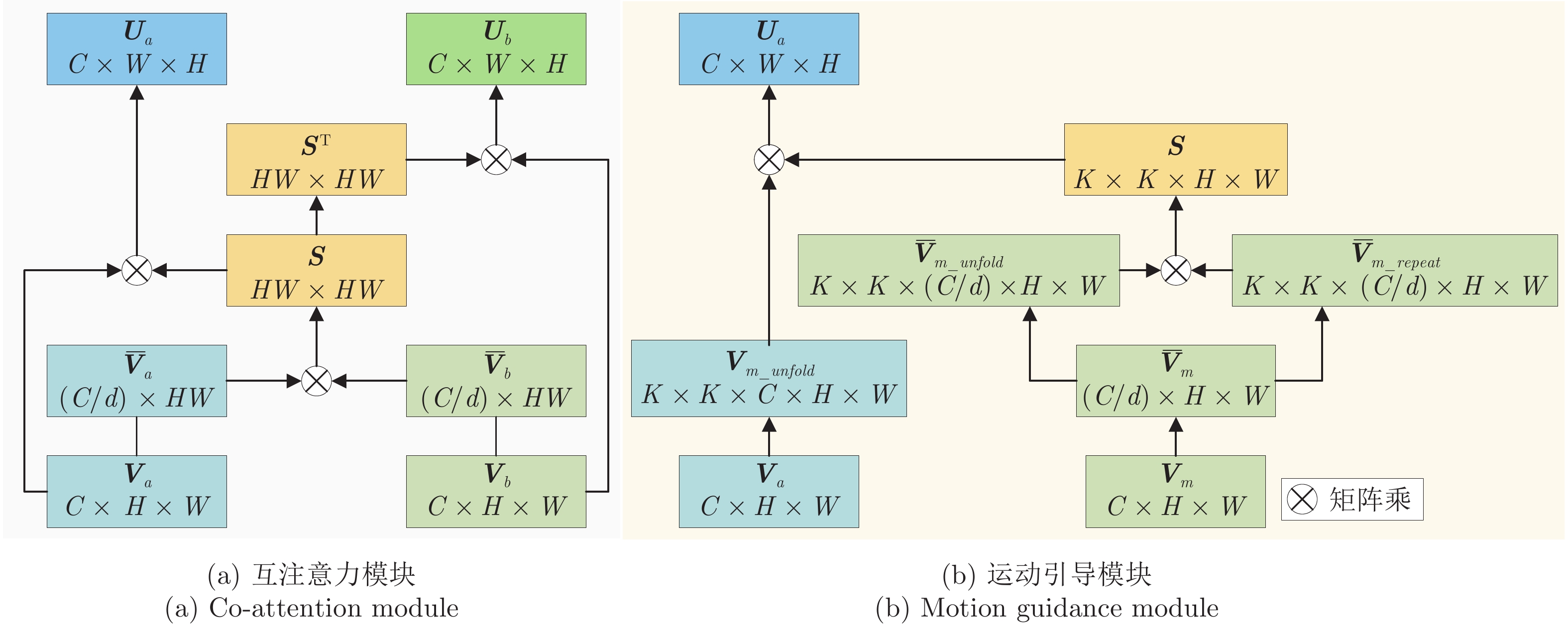
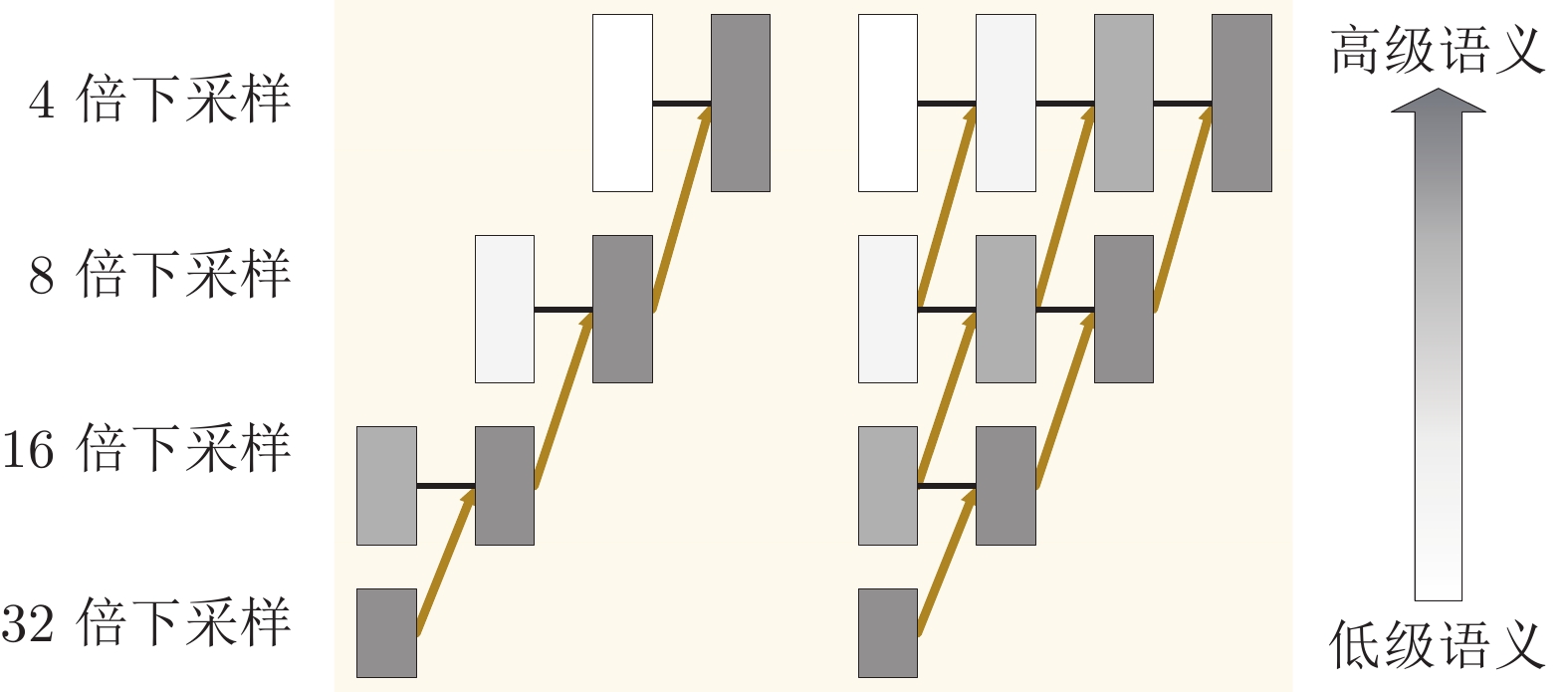
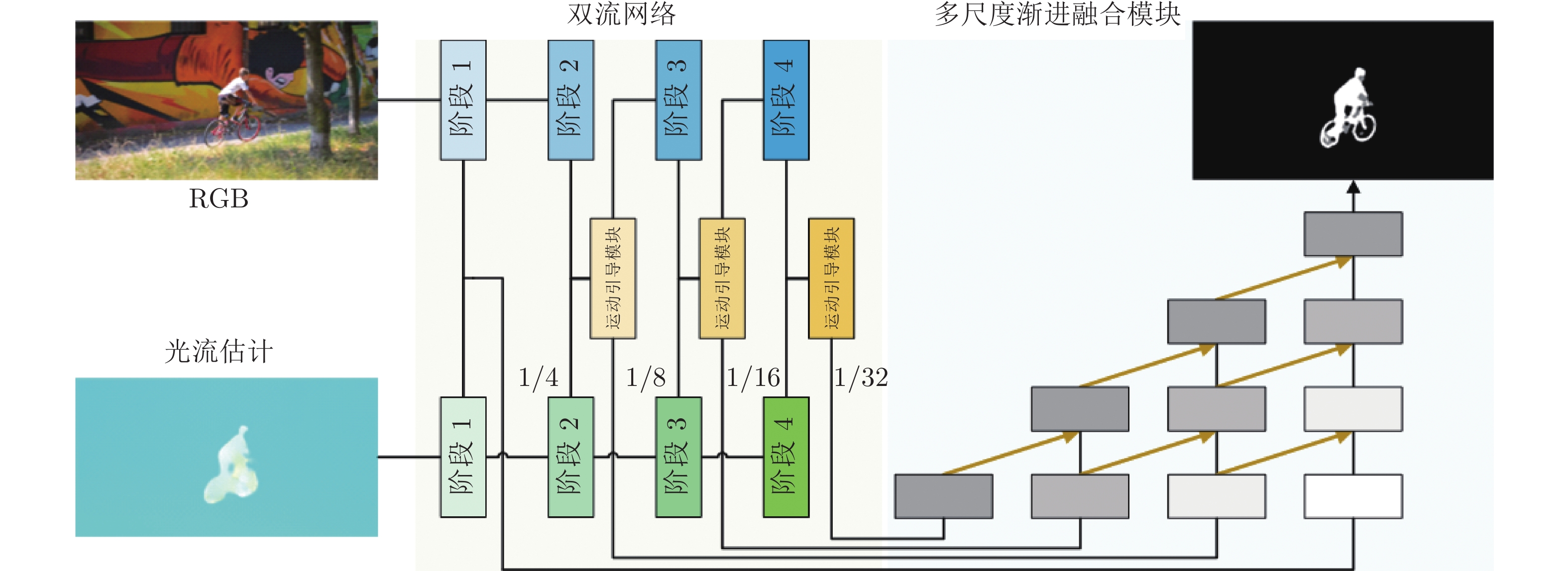
摘要: 大量基于深度学习的无监督视频目标分割(Unsupervised video object segmentation, UVOS)算法存在模型参数量与计算量较大的问题, 这显著限制了算法在实际中的应用. 提出了基于运动引导的视频目标分割网络, 在大幅降低模型参数量与计算量的同时, 提升视频目标分割性能. 整个模型由双流网络、运动引导模块、多尺度渐进融合模块三部分组成. 具体地, 首先, RGB图像与光流估计输入双流网络提取物体外观特征与运动特征; 然后, 运动引导模块通过局部注意力提取运动特征中的语义信息, 用于引导外观特征学习丰富的语义信息; 最后, 多尺度渐进融合模块获取双流网络的各个阶段输出的特征, 将深层特征渐进地融入浅层特征, 最终提升边缘分割效果. 在3个标准数据集上进行了大量评测, 实验结果表明了该方法的优越性能.Abstract: Numerous unsupervised video object segmentation (UVOS) algorithms based on deep learning have super-fluous model parameters and expensive computational overhead, which limits the applications of the algorithms in practice. To relieve the issues, this paper proposes an unsupervised video object segmentation network based on motion guidance, which can significantly reduce the number of model parameters and calculations, and improve the performance of segmentation. The multi-scale progressive fusion module consists of three parts. Specifically, RGB image and optical flow estimation are fed into the dual flow network to extract object appearance features and motion features. Then, the motion guidance module extracts semantic information from motion features through local attention to guide semantical appearance features learning. Finally, the multi-scale progressive fusion module obtains output features of each stage of dual flow network, and gradually integrates deep features with shallow features. Extensive evaluations are conducted on three mainstream datasets, and the results show the superior performance of the proposed method.
-
表 1 不同模块每秒浮点运算数对比
Table 1 Comparison of floating-point operations per second of different modules
输入尺寸 (像素) 互注意模块 (MB) 运动引导模块 (MB) $64 \times 64 \times 16$ 10.0 2.3 $64 \times 32 \times 32$ 153.1 9.0 表 2 不同方法在DAVIS-16 和FBMS数据集的评估结果 (%)
Table 2 Evaluation results of different methods on DAVIS-16 and FBMS datasets (%)
表 3 不同方法在DAVIS-16、FBMS和ViSal数据集的评估结果 (%)
Table 3 Evaluation results of different methods on DAVIS-16、FBMS and ViSal datasets (%)
表 4 不同方法的模型参数量、计算量与推理时延
Table 4 Model parameters, computation and infer latency of different methods
表 5 不同方法在GTX2080 Ti上的性能表现
Table 5 Performance of different methods on GTX2080 Ti
方法 并发量 每秒帧数 时延 (ms) MATNet[17] 18 16 62.40 本文算法 130 161 6.21 表 6 运动引导模块与多尺度渐进融合模块的消融实验(%)
Table 6 Ablation experiment on motion guidance module and multi-scale progressivefusion module (%)
指标 本文算法 $无\; {\rm{FG} }$ ${\rm{FG}}$ $J$ 83.7 75.8 76.1 $F$ 83.4 73.5 75.6 表 7 不同核K大小与堆叠次数对比
Table 7 Comparison of different Kernel sizes and cascading times
K 堆叠层数 $J$ (%) $F$ (%) 3 1 82.8 82.4 3 2 83.4 82.7 3 3 83.7 83.4 3 4 83.5 83.2 5 1 83.2 82.6 7 1 83.4 82.7 9 1 83.1 82.4 -
[1] Papazoglou A, Ferrari V. Fast object segmentation in unconstrained video. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 1777−1784 [2] 黄宏图, 毕笃彦, 侯志强, 胡长城, 高山, 查宇飞, 库涛. 基于稀疏表示的视频目标跟踪研究综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2018, 44(10): 1747-1763HUANG Hong-Tu, BI Du-Yan, HOU Zhi-Qiang, HU Chang-Cheng, GAO Shan, ZHA Yu-Fei, KU Tao. Research of Sparse Representation-based Visual Object Tracking: A Survey. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2018, 44(10): 1747-1763 [3] Wang W, Shen J, Porikli F. Saliency-aware geodesic video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Boston, USA: IEEE, 2015. 3395−3402 [4] 钱生, 陈宗海, 林名强, 张陈斌. 基于条件随机场和图像分割的显著性检测[J]. 自动化学报, 2015, 41(4): 711-724QIAN Sheng, CHEN Zong-Hai, LIN Ming-Qiang, ZHANG Chen-Bin. Saliency Detection Based on Conditional Random Field and Image Segmentation. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2015, 41(4): 711-724. [5] Ochs P, Brox T. Object segmentation in video: A hierarchical variational approach for turning point trajectories into dense regions. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Barcelona, Spain: IEEE, 2011. 1583−1590 [6] 苏亮亮, 唐俊, 梁栋, 王年. 基于最大化子模和RRWM的视频协同分割[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(10): 1532-1541SU Liang-Liang, TANG Jun, LIANG Dong, WANG Nian. A Video Co-segmentation Algorithm by Means of Maximizing Submodular Function and RRWM. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(10): 1532-1541 [7] Ventura C, Bellver M, Girbau A, Salvador A, Marques F, Giroinieto X. RVOS: End-to-end recurrent network for video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 5277−5286 [8] Wang W, Lu X, Shen J, Crandall D J, Shao L. Zero-shot video object segmentation via attentive graph neural networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 9236−9245 [9] Chen L C, Papandreou G, Schroff F, Adam H. Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1706.05587, 2017. [10] Lu X, Wang W, Ma C, Shen J, Shao L, Porikli F. See more, know more: Unsupervised video object segmentation with co-attention siamese networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3623−3632 [11] Faktor A, Irani M. Video segmentation by non-local consensus voting. In: Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. Nottingham, UK: 2014. [12] Perazzi F, Pont-Tuset J, McWilliams B, Van-Gool L, Gross M, Sorkine-Hornung A. A benchmark dataset and evaluation methodology for video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Las Vegas, USA: IEEE, 2016. 724−732 [13] Xu N, Yang L J, Fan Y C, Yang J C, Yue D C, Liang Y C, et al. Youtube-VOS: Sequence-to-sequence video object segmentation. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision.Munich, Germany: 2018. 585−601 [14] Song H, Wang W, Zhao S, Shen J, Lam K M. Pyramid dilated deeper ConvLSTM for video salient object detection. In: Proceed-ings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: 2018. 715−731 [15] Jampani V, Gadde R, Gehler P V. Video propagation networks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 451−461 [16] Tokmakov P, Alahari K, Schmid C. Learning video object segmentation with visual memory. In: Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4481−4490 [17] Zhou T, Li J, Wang S, Tao R, Shen J. Matnet: Motion-attentive transition network for zero-shot video object segmentation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 8326−8338 [18] Chu X, Yang W, Ouyang W, Ma C, Yuille A L, Wang X. Multi-context attention for human pose estimation. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 1831−1840 [19] Chen L, Zhang H, Xiao J, Nie L, Shao J, Liu W, et al. SCA-CNN: Spatial and channel-wise attention in convolutional networks for image captioning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 5659−5667 [20] Lu J, Yang J, Batra D, Parikh D. Hierarchical question-image co-attention for visual question answering. arXiv preprint arXiv: 1606.00061, 2016. [21] Wu Q, Wang P, Shen C, Reid I, Van-Den-Hengel A. Are you talking to me? Reasoned visual dialog generation through adversarial learning. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 6106−6115 [22] Sandler M, Howard A, Zhu M, Zhmoginov A, Chen L C. Mobile-Net v2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 4510−4520 [23] Ronneberger O, Fischer P, Brox T. UNet: Convolutional networksfor biomedical image segmentation. In: Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-assisted Intervention. Munich, Germany: 2015. 234−241 [24] Wang W, Shen J, Shao L. Consistent video saliency using local gradient flow optimization and global refinement. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 4185−4196 [25] Tokmakov P, Alahari K, Schmid C. Learning motion patterns in videos. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Hawaii, USA: IEEE, 2017. 3386−3394 [26] Li S, Seybold B, Vorobyov A, Lei X, Kuo C C J. Unsupervised video object segmentation with motion-based bilateral networks. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Munich, Germany: 2018. 207−223 [27] Wang W, Song H, Zhao S, Shen J, Zhao S, Hoi S C, et al. Learning unsupervised video object segmentation through visual attention. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Long Beach, USA: IEEE, 2019. 3064−3074 [28] Yang Z, Wang Q, Bertinetto L, Hu W, Bai S, Torr P H. Anchor diffusion for unsupervised video object segmentation. In: Procee-dings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Seoul, South Korea: IEEE, 2019. 931−940 [29] Wang W, Shen J, Shao L. Video salient object detection via fully convolutional networks. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 27(1): 38−49 [30] Li G, Xie Y, Wei T, Wang K, Lin L. Flow guided recurrent neural encoder for video salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Salt Lake City, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3243−3252 [31] Ren S, Han C, Yang X, Han G, He S. TENet: Triple excitation network for video salient object detection. In: Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Edinburgh, Scotland: 2020. 212−228 -




 下载:
下载: