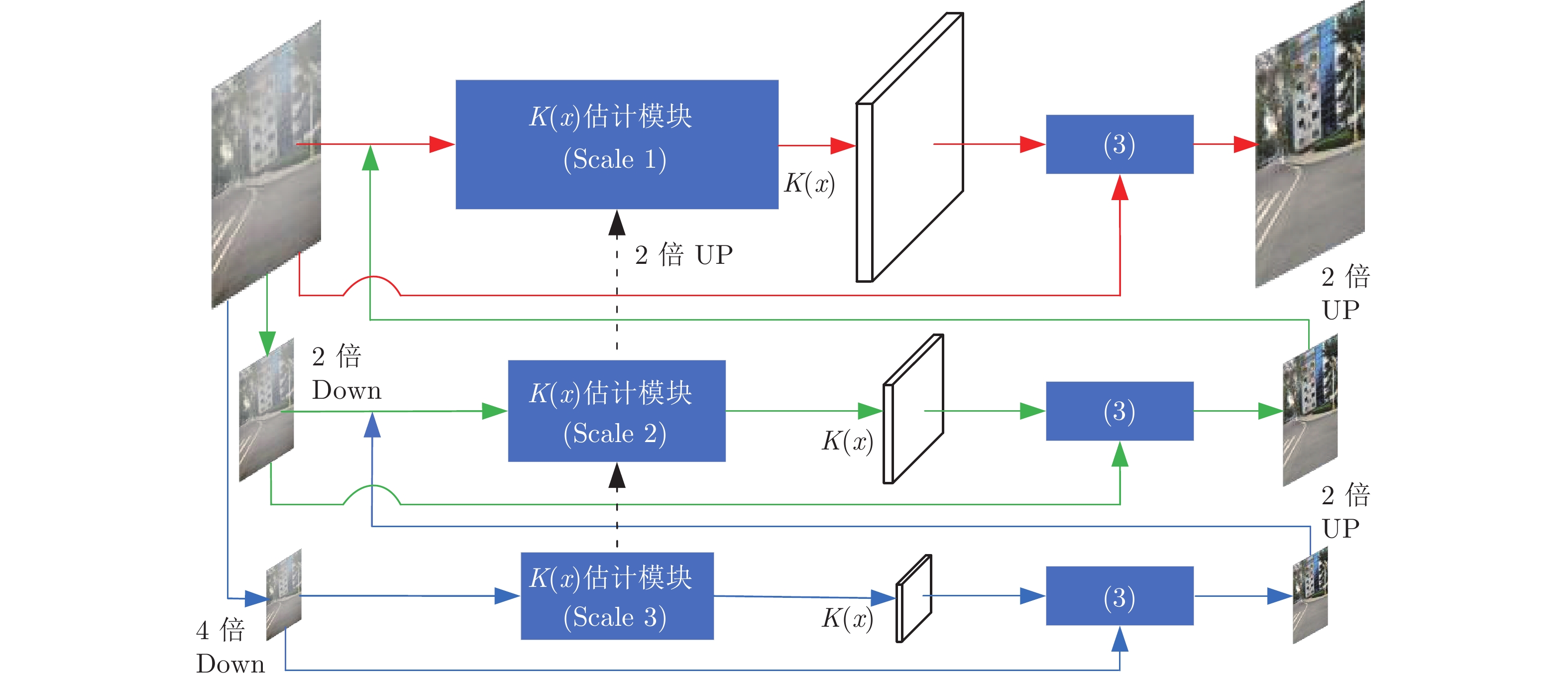
-
摘要: 针对航拍图像易受雾气影响, AOD-Net (All in one dehazing network)算法对图像去雾后容易出现细节模糊、对比度过高和图像偏暗等问题, 本文提出了一种基于改进AOD-Net的航拍图像去雾算法. 本文主要从网络结构、损失函数、训练方式三个方面对AOD-Net进行改良. 首先在AOD-Net的第二个特征融合层上添加了第一层的特征图, 用全逐点卷积替换了传统卷积方式, 并用多尺度结构提升了网络对细节的处理能力. 然后用包含有图像重构损失函数、SSIM (Structural similarity)损失函数以及TV (Total variation)损失函数的复合损失函数优化去雾图的对比度、亮度以及色彩饱和度. 最后采用分段式的训练方式进一步提升了去雾图的质量. 实验结果表明, 经该算法去雾后的图像拥有令人满意的去雾结果, 图像的饱和度和对比度相较于AOD-Net更自然. 与其他对比算法相比, 该算法在合成图像实验、真实航拍图像实验以及算法耗时测试的综合表现上更好, 更适用于航拍图像实时去雾.Abstract: As the aerial images are easily affected by fog, the defogging image processed by AOD-Net is prone to problems such as blurring of image details, excessive contrast and low brightness. A defogging algorithm for aerial image with improved AOD-Net was proposed. We mainly improve AOD-Net from three aspects: network structure, loss function and training method. Firstly, we add the feature image of the first layer to the second feature fusion layer of AOD-Net, the traditional convolution method is replaced by the fully point-wise convolution, and the multi-scale structure is used to enhance the ability of the network to deal with details. Then, in this paper, a composite loss function including image reconstruction loss function, SSIM loss function and TV loss function is used to optimize the contrast, brightness and color saturation of the defogging image. Finally, we use a segmented training method to further improve the quality of the defogging image. The experimental results show that the image defogged by the proposed algorithm has satisfactory defogging results, the saturation and contrast are more natural than AOD-Net. Compared with other comparison algorithms, the proposed algorithm has better comprehensive performance in synthetic image experiments, real aerial image experiments and time-consuming tests, and is more suitable for real-time defogging of aerial images.
-
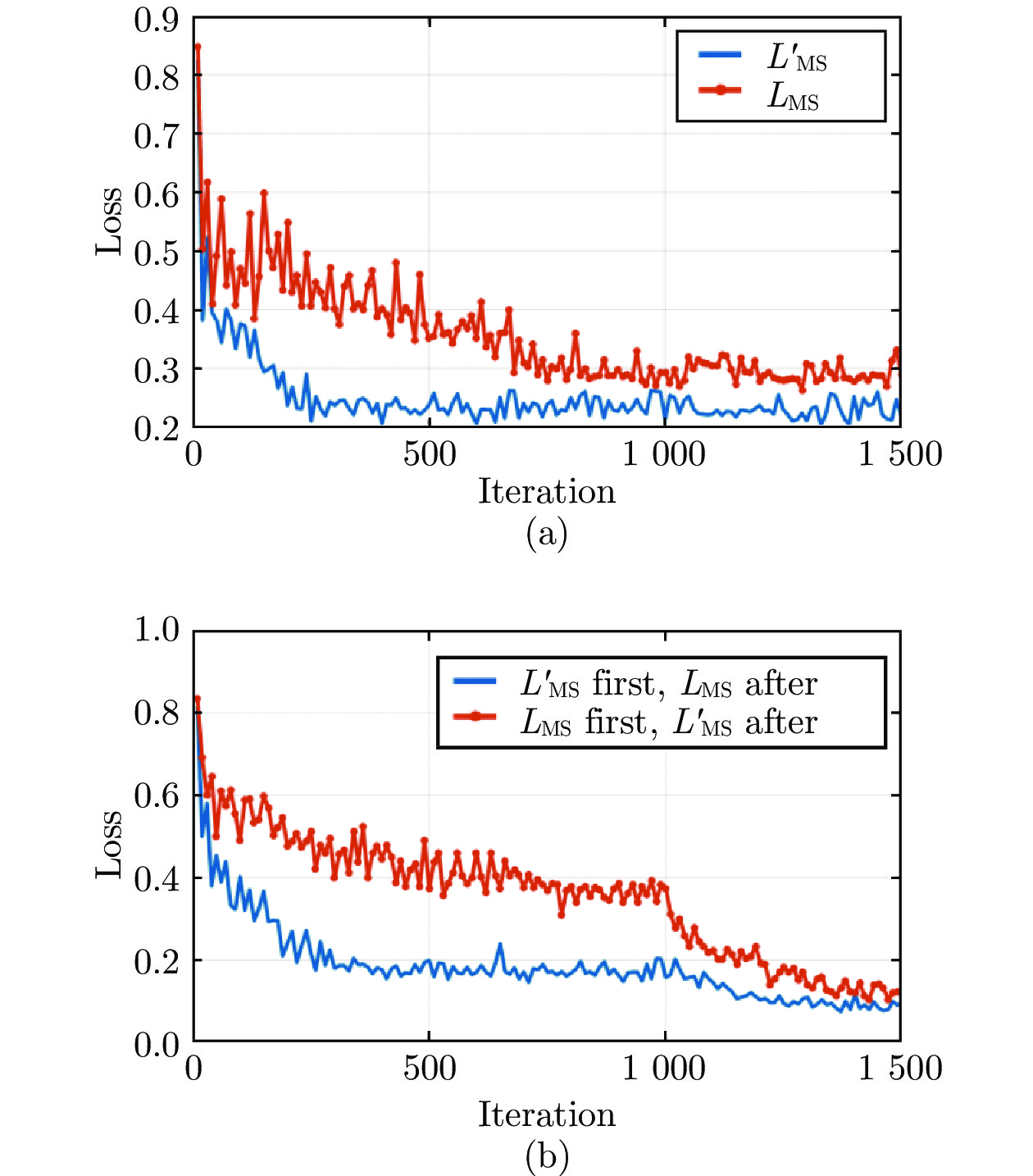
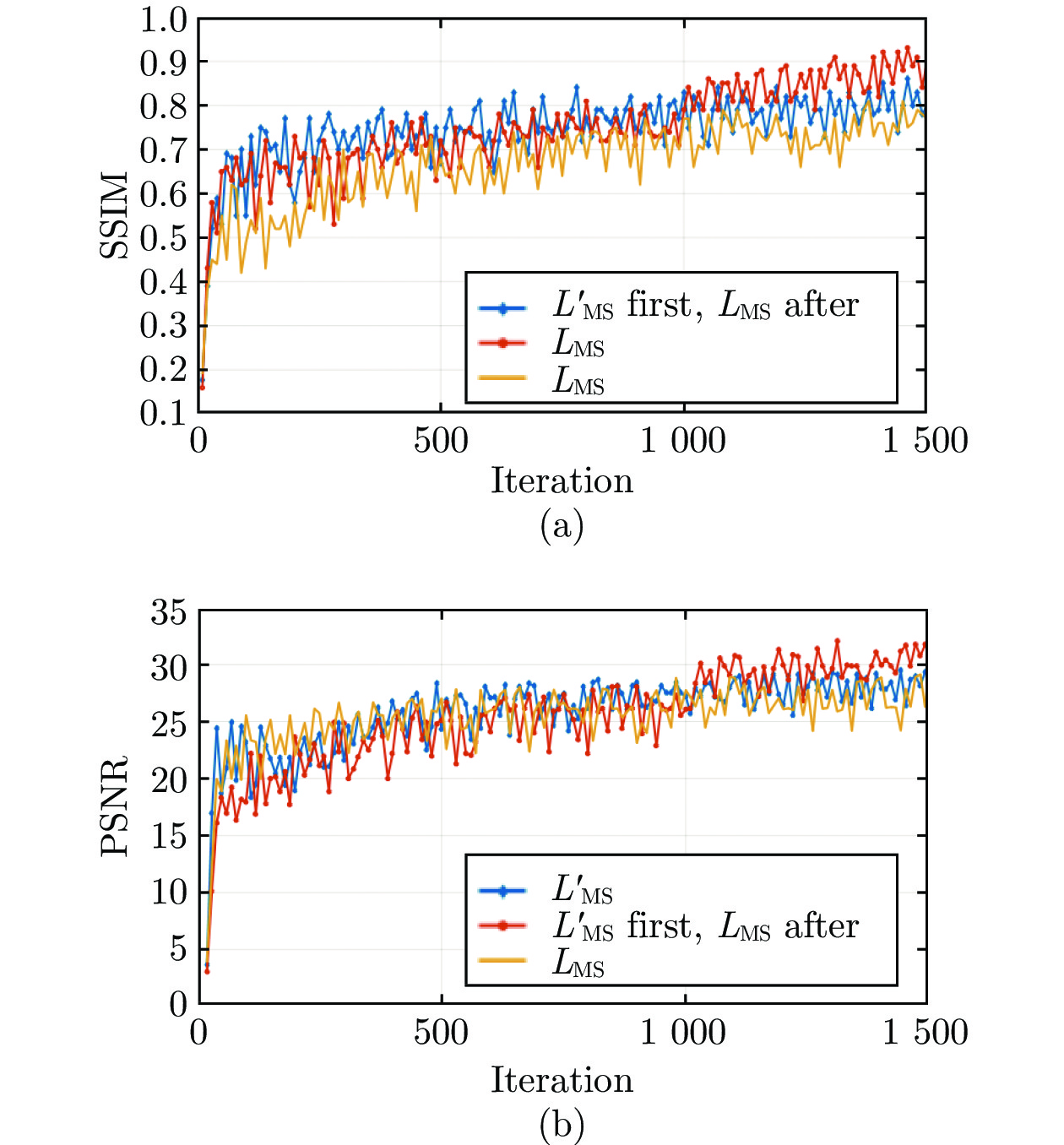
图 7 两种不同训练方法下的去雾效果 ((a) 合成雾图; (b) ground truth; (c) 所提模型用LMS训练1000次的效果; (d) 所提模型用LMS训练1500次的效果; (e) 所提模型用式L训练1000次的效果; (f) 所提模型用式L训练1500次的效果)
Fig. 7 Defogging effect of two different training method ((a) Synthetic fog image; (b) Ground truth; (c) The proposed model was trained after 1000 times by LMS; (d) The proposed model was trained after 1500 times by LMS; (e) The proposed model was trained after 1000 times by L; (f) The proposed model was trained after 1500 times by L)
图 8 合成有雾图像的实验结果展示 ((a) 有雾图像; (b) Ground truth; (c) DCP; (d) BCCR; (e) CAP; (f) DehazeNet;(g) MSCNN; (h) AOD-Net; (i) GFN; (j) GCANet; (k) FFANet; (l) 本文算法)
Fig. 8 Experimental results of the synthetic fog images ((a) Fog image; (b) Ground truth; (c) DCP; (d) BCCR; (e) CAP; (f) DehazeNet; (g) MSCNN; (h) AOD-Net; (i) GFN; (j) GCANet; (k) FFANet; (l) Proposed algorithm)
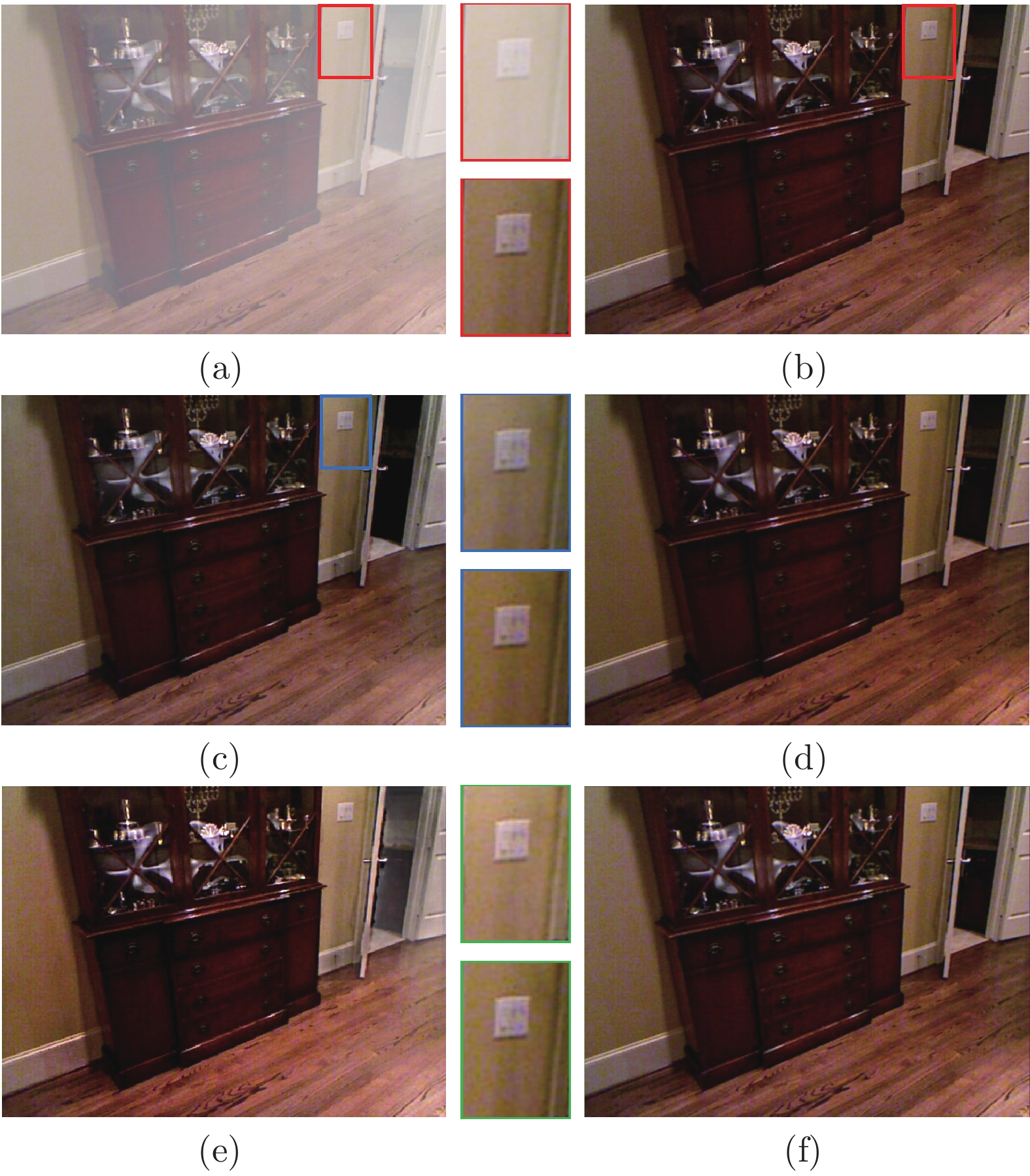
图 9 真实有雾航拍图像的实验结果展示 ((a) 有雾图像; (b) DCP; (c) BCCR; (d) CAP; (e) DehazeNet; (f) MSCNN;(g) AOD-Net; (h) GFN; (i) GCANet; (j) FFANet; (k) 本文算法)
Fig. 9 Experimental results of the real aerial fog images ((a) Aerial fog image; (b) DCP; (c) BCCR; (d) CAP; (e) DehazeNet; (f) MSCNN; (g) AOD-Net; (h) GFN; (i) GCANet; (j) FFANet; (k) Proposed algorithm)
图 11 消融实验结果 ((a) 航拍雾图像; (b) 本文方法; (c) 缺少L1与L2; (d) 缺少LS; (e) 缺少LTV; (f) 无多尺度(Mutil-Scale, MS)结构; (g) 无MS结构和L (损失函数为均方误差); (h) AOD-Net)
Fig. 11 Experimental results of ablation study ((a) Aerial fog image; (b) Proposed algorithm; (c) w/o L1 and L2 loss function; (d) w/o LS loss function; (e) w/o LTV loss function; (f) w/o MS structure; (g) w/o MS structure and L (The loss function is the mean square error); (h) AOD-Net)
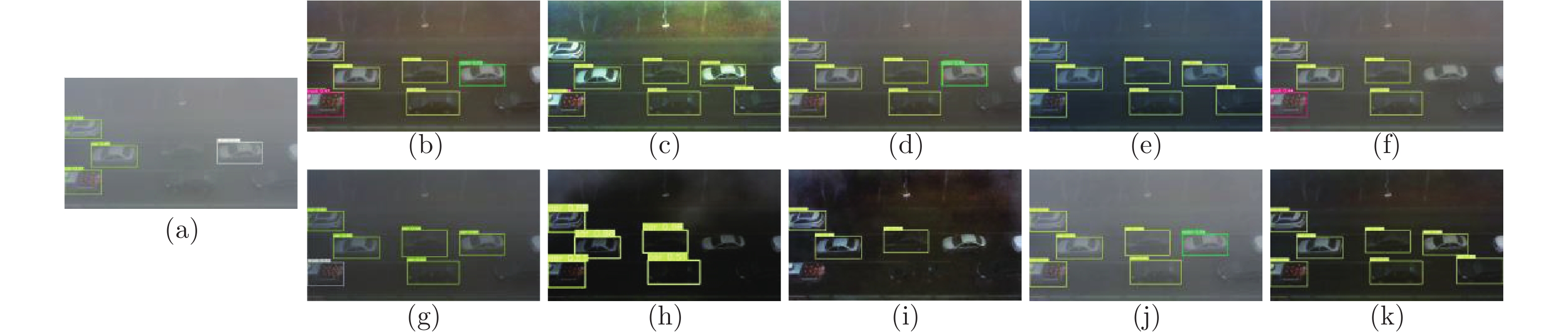
图 15 航拍去雾图像中车辆检测结果示例 ((a) 原图; (b) DCP; (c) BCCR; (d) CAP; (e) DehazeNet; (f) MSCNN;(g) AOD-Net; (h) GFN; (i) GCANet; (j) FFANet; (k) 本文算法)
Fig. 15 Example of aerial image dehazing in vehicle detection ((a) Original; (b) DCP; (c) BCCR; (d) CAP; (e) DehazeNet; (f) MSCNN; (g) AOD-Net; (h) GFN; (i) GCANet; (j) FFANet; (k) Proposed algorithm)
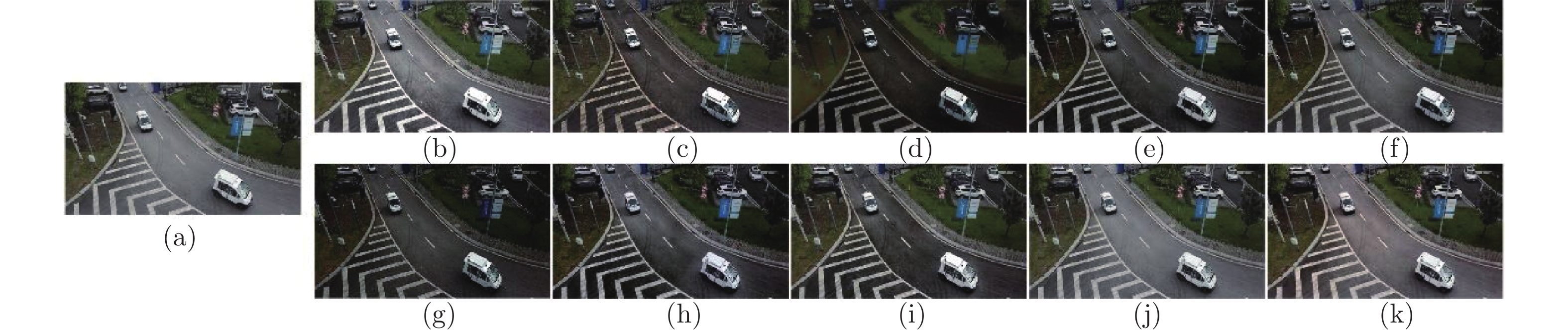
图 16 清晰图像上的去雾效果对比( (a) 原图; (b) DCP; (c) BCCR; (d) CAP; (e) DehazeNet; (f) MSCNN; (g) AOD-Net; (h) GFN; (i) GCANet; (j) FFANet; (k) 本文算法)
Fig. 16 Comparison of dehazing effects on clear images ((a) Original; (b) DCP; (c) BCCR; (d) CAP; (e) DehazeNet; (f) MSCNN; (g) AOD-Net; (h) GFN; (i) GCANet; (j) FFANet; (k) Proposed algorithm)
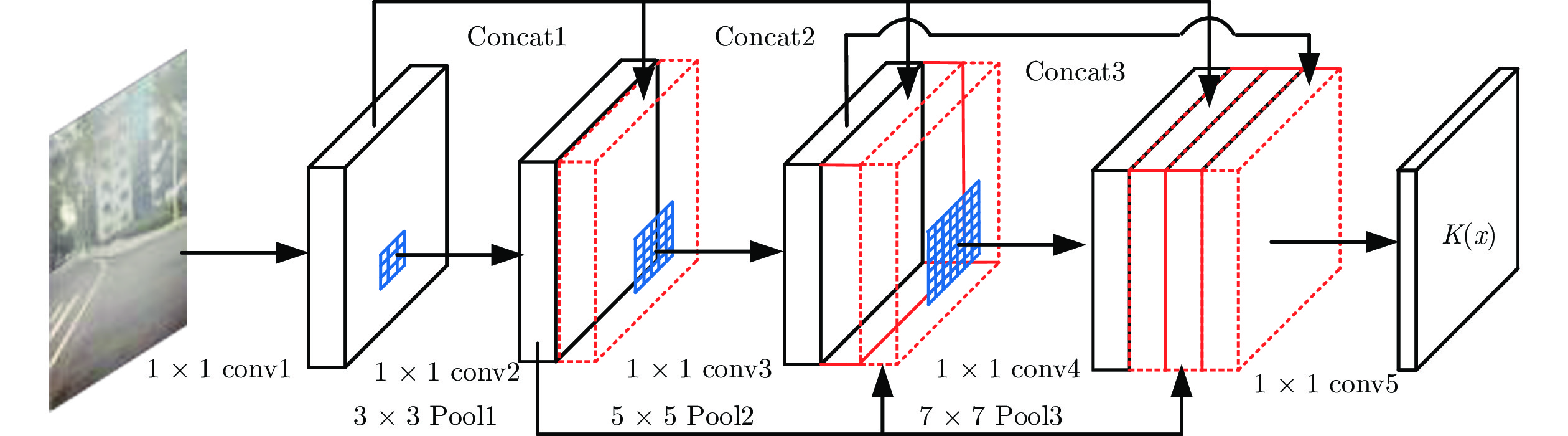
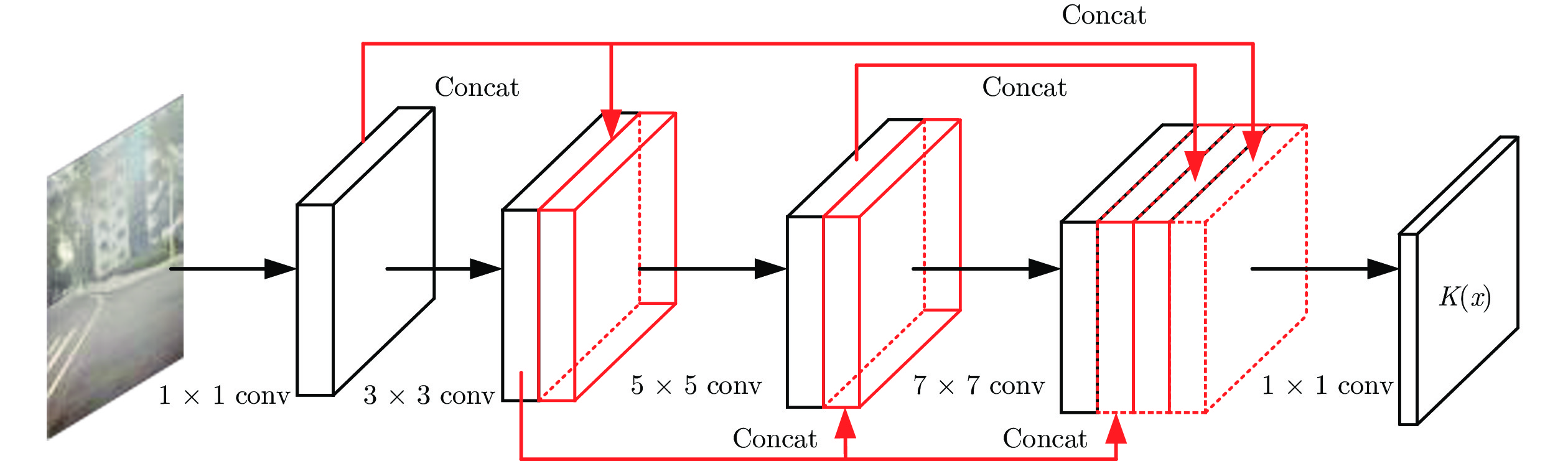
表 1 本文所提网络的参数
Table 1 The architectures of proposed network
Layer Input Size Num Filter Pad Conv1 128×128×3 32 1×1 0 Conv2 128×128×32 32 1×1 0 Pool1 128×128×32 — 3×3 1 Concat1 128×128×64 — — — Conv3 128×128×64 32 1×1 0 Pool2 128×128×32 — 5×5 2 Concat2 128×128×96 — — — Conv4 128×128×96 32 1×1 0 Pool3 128×128×32 — 7×7 3 Concat3 128×128×128 — — — Conv5 128×128×128 3 1×1 0 表 2 在合成有雾图像上的SSIM与PSNR结果
Table 2 Comparison of SSIM and PSNR tested on synthetic fog images
Model SSIM PSNR (dB) Indoor Outdoor Average Indoor Outdoor Average DCP[6] 0.7418 0.7901 0.7659 17.3148 15.5323 16.4236 BCCR[7] 0.8088 0.7719 0.7904 17.2119 16.3041 16.7580 CAP[8] 0.7942 0.8255 0.8099 16.9496 19.0829 18.0163 DehazeNet[11] 0.8653 0.8317 0.8485 20.0545 21.9992 21.0269 MSCNN[12] 0.7796 0.7931 0.7864 16.8927 19.0019 17.9473 AOD-Net[13] 0.8334 0.8848 0.8591 20.0267 18.4105 19.2186 GFN[14] 0.9039 0.8814 0.8927 21.1079 25.5399 23.3239 GCANet[15] 0.9025 0.8582 0.8804 22.3363 26.1431 24.2397 FFANet[16] 0.9313 0.9082 0.9198 28.4057 27.9932 28.1995 Proposed 0.8794 0.9011 0.8903 21.1924 23.4073 22.8994 表 3 在真实航拍雾图上的客观数值评价: (1) 最好的结果; (2) 次好的结果; (3) 第三好的结果
Table 3 Objective numerical evaluation on the fog map of real aerial photography: (1) The best result; (2) The second-best result; (3) The third-best result
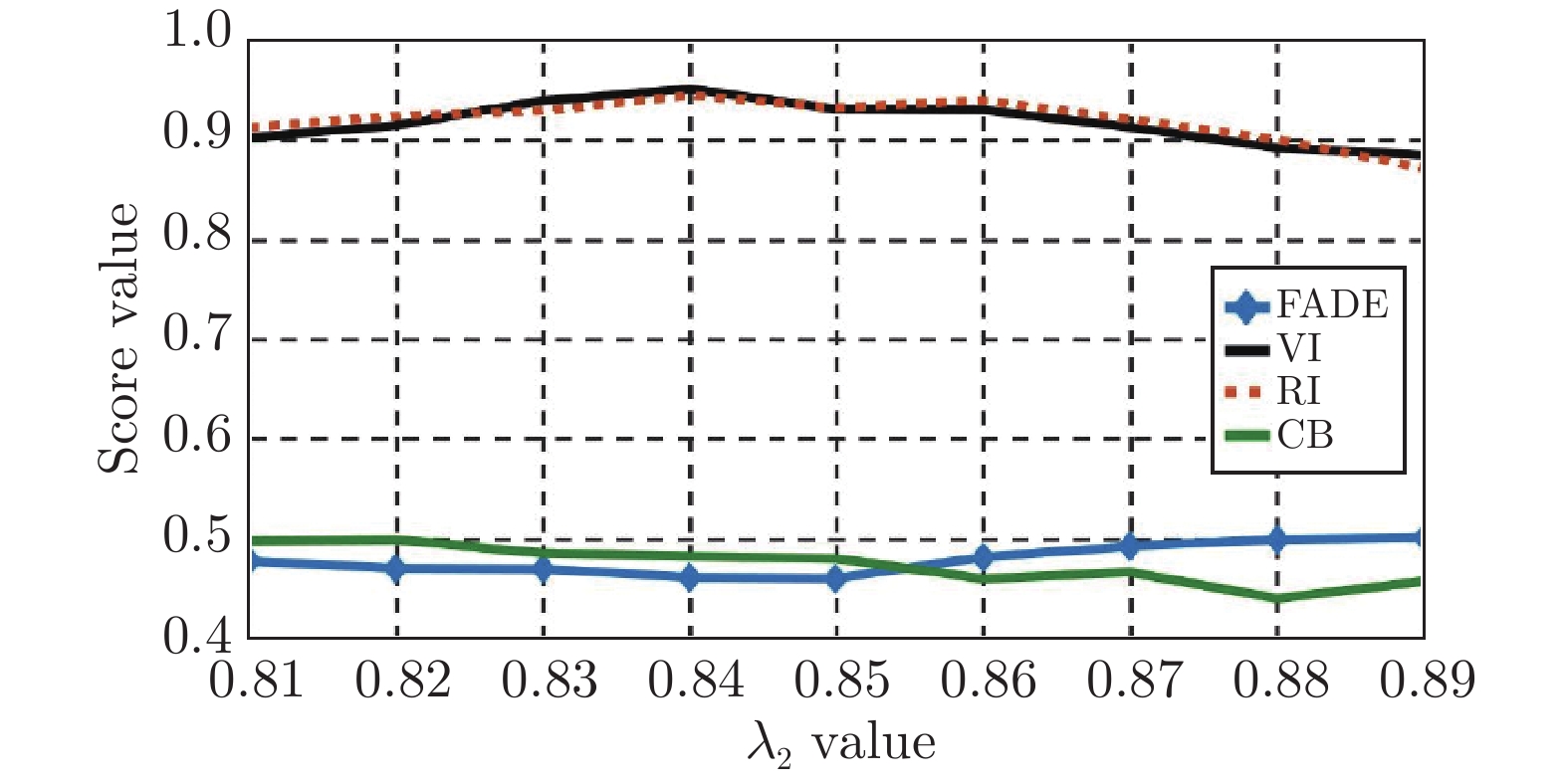
Model BIQME FADE VI RI CB VIF GB Entropy DCP[6] 0.6235 0.6902 0.8992 (1) 0.9407 0.3884 0.9957 0.5814 7.4427 BCCR[7] 0.5751 0.7091 0.8639 0.9263 0.4239 0.9211 0.5112 7.3983 CAP[8] 0.6380 0.8206 0.8026 0.9201 0.3398 0.8892 0.6413 7.4115 DehazeNet[11] 0.6917 (3) 0.5984 0.8845 (2) 0.9496 (2) 0.4203 1.0396 0.6448 7.7265 MSCNN[12] 0.7131 (2) 0.6261 0.8721 (3) 0.9425 (3) 0.4439 1.1513 (1) 0.7352 7.3524 AOD-Net[13] 0.6013 0.8459 0.8365 0.9208 0.3995 0.9532 0.6968 7.4785 GFN[14] 0.7795 (1) 0.4119 (1) 0.8573 0.9498 (1) 0.4880 (1) 1.0872 0.8065 (2) 7.8334 (3) GCANet[15] 0.6244 0.4743 (2) 0.8512 0.9328 0.4566 (3) 1.1473 (2) 0.7518 7.8891 (1) FFANet[16] 0.6397 0.9752 0.8115 0.9074 0.4429 1.0724 0.9127 (1) 7.3193 Proposed 0.6694 0.5625 (3) 0.8649 0.9411 0.4753 (2) 1.1109 (3) 0.7749 (3) 7.8799 (2) 表 4 消融实验中的数值指标
Table 4 The numerical index in ablation experiment
Model w/o part SSIM PSNR VI RI FADE GB Proposed MS 0.7344 26.6419 0.8195 0.9004 0.6971 0.6806 L1 and L2 0.7659 28.0417 0.8547 0.9198 0.5832 0.7612 LS 0.7177 27.1259 0.8026 0.9035 0.7043 0.6327 LTV 0.7392 21.7884 0.6952 0.7259 0.8826 0.6122 MS and L 0.7293 25.5332 0.7919 0.8827 0.7033 0.6303 — 0.8903 28.8994 0.8996 0.9328 0.5108 0.7749 AOD-Net — 0.7031 23.3903 0.7523 0.9002 0.7439 0.7114 表 5 去雾耗时对比(s)
Table 5 Comparison of the defogging time-cost (s)
表 6 参数量与模型大小比较
Table 6 Comparison of the parameters and model size
表 7 车辆检测的置信度数值, 标出三个最优的结果: (1) 最好的结果; (2) 次好的结果; (3) 第三好的结果
Table 7 Confidence value of vehicle detection, marking the three best results: (1) The best result; (2) The second-best result; (3) The third-best result
Dehazing model Detection confidence before dehazing Detection confidence after dehazing The number of identified car Detection confidence improvement Original 0.6837 — 3.74 — DCP[6] — 0.7917 5.42 15.80% BCCR[7] — 0.8233 (2) 7.84 (1) 20.42% (2) CAP[8] — 0.6467 6.26 −5.41% DehazeNet[11] — 0.8033 (3) 7.32 (3) 17.49% (3) MSCNN[12] — 0.7835 4.39 14.60% AOD-Net[13] — 0.6471 5.53 −5.35% GFN[14] — 0.7227 5.95 5.70% GCANet[15] — 0.7980 4.25 16.72% FFANet[16] — 0.7539 5.50 10.27% Proposed — 0.8362 (1) 7.48 (2) 22.31% (1) 表 8 清晰航拍图像上的客观数值评价
Table 8 Objective numerical evaluation on the clear images of aerial photography
-
[1] 韩敏, 闫阔, 秦国帅. 基于改进KAZE的无人机航拍图像拼接算法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(2): 305-314. Han Ming, Yan Kuo, Qin Guo-Shuai. A mosaic algorithm for UAV aerial image with improved KAZE. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(2): 305-314 [2] Patsiouras E, Tefas A, Pitas I. Few-shot image recognition for UAV sports cinematography. In: Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020. 965−969 [3] 周剑, 贾金岩, 张震, 陈盛伟. 面向应急保障的 5G 网联无人机关键技术. 重庆邮电大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 32(4): 511-518. Zhou Jian, Jia Jin-Yan, Zhang Zhen, Chen Sheng-Wei. Key technologies for emergency communication based on 5G networked UAVs. Journal of Chongqing University of Posts and Telecommunications (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 32(4): 511-518 [4] Liu P J, Horng S J, Lin J S, Li T R. Contrast in haze removal: configurable contrast enhancement model based on dark channel prior. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2212−2227 [5] . Bui M T, Kim W. Single image dehazing using color ellipsoid prior. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(2): 999-1009 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2771158 [6] . He K M, Sun J, Tang X O. Single image haze removal using dark channel prior. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence (TPAMI), 2011, 33(12): 2341-2353 doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2010.168 [7] Meng G F, Wang Y, Duan J Y, Xiang S M, Pan C H. Efficient image dehazing with boundary constraint and contextual regularization. In: Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Sydney, Australia: IEEE, 2013. 617−624 [8] . Zhu Q S, Mai J M, Shao L. A fast single image haze removal algorithm using color attenuation prior. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3522-3533 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2015.2446191 [9] Chen W, Chen R Q, Lu Y, Yan Y, Wang H Z. Recurrent context aggregation network for single image dehazing. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 419−423 [10] . Chen W T, Fang H Y, Ding J J, Kuo S Y. PMHLD: Patch map-based hybrid learning DehazeNet for single image haze removal. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 6773-6788 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2020.2993407 [11] . Cai B L, Xu X M, Jia K, Qing C M, Tao D C. DehazeNet: an end-to-end system for single image haze removal. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(11): 5187-5198 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2598681 [12] Ren W Q, Liu S, Zhang H, Pan J S. Single image dehazing via multi-scale convolutional neural networks. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV). Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 154−169 [13] Li B Y, Peng X L, Wang Z Y, Xu J Z, Feng D. AOD-Net: all-in-one dehazing network. In: Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). Venice, Italy: IEEE, 2017. 4780−4788 [14] Ren W Q, Ma L, Zhang J W, Pan J S, Cao X C, Liu W, et al. Gated fusion network for single image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3253−3261 [15] Chen D D, He M M, Fan Q N, Liao J, Zhang L H, Hou D D, et al. Gated context aggregation network for image dehazing and deraining. In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). Waikoloa, HI, USA: IEEE, 2019. 1375−1383 [16] Qin X, Wang Z L, Bai Y C, Xie X D, Jia H Z. FFA-Net: Feature fusion attention network for single image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the Association for the Advance of Artificial Intelligence. Hilton Midtown, New York: AAAI, 2020. 11908−11915 [17] 杨燕, 陈高科, 周杰. 基于高斯权重衰减的迭代优化去雾算法. 自动化学报, 2019, 45(4): 819-828. Yang Yan, Chen Gao-Ke, Zhou Jie. Iterative optimization defogging algorithm using gaussian weight decay. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2019, 45(4): 819-828 [18] Zhang J, Cao Y, Wang Y, Wen C L, Chen W C. Fully point-wise convolutional neural network for modeling statistical regularities in natural images. In: Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia. Seoul, Korea: ACM, 2018. 984−992 [19] Silberman N, Hoiem D, Kohli P, Fergus R. Indoor segmentation and support inference from RGBD images. In: Proceedings of the 12th European conference on Computer Vision-Volume Part V. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer, 2012. 746−760 [20] . Ephraim Y, Malah D. Speech enhancement using a minimum mean-square error log-spectral amplitude estimator. IEEE Transactions on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, 1985, 33(2): 443-445 doi: 10.1109/TASSP.1985.1164550 [21] . Zhang J, Tao D C. FAMED-Net: A fast and accurate multi-scale end-to-end dehazing network. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29: 72-84 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2019.2922837 [22] Guo C L, Li C Y, Guo J C, Loy C, Hou J H, Kwong S, et al. Zero-reference deep curve estimation for low-light image enhancement. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020. 1777−1786 [23] Zhang H, Patel V M. Densely connected pyramid dehazing network. In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Salt Lake City, UT, USA: IEEE, 2018. 3194−3203 [24] Das S, Dutta S. Fast deep multi-patch hierarchical network for nonhomogeneous image dehazing. In: Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Seattle, WA, USA: IEEE, 2020. 1994−2001 [25] Chen S X, Chen Y Z, Qu Y Y, Huang J Y, Hong M. Multi-scale adaptive dehazing network, In: Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (CVPRW). Long Beach, CA, USA: IEEE, 2019. 2051−2059 [26] . Zhou W, Bovik A, Sheikh H, Simoncelli E. Image quality assessment: from error visibility to structural similarity. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2004, 13(4): 600-612 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2003.819861 [27] Justin J, Alexandre A, Li F F. Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution. In: Proceedings of the 2016 European conference on computer vision (ECCV). Amsterdam, Netherlands: Springer, 2016. 694−711 [28] . Zhao H, Gallo O, Frosio I, Kautz J. Loss functions for image restoration with neural networks. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 3(1): 47-57 doi: 10.1109/TCI.2016.2644865 [29] . Li B Y, Ren W Q, Fu D P, Tao D C, Feng D, Zeng W J, et al. Benchmarking single-image dehazing and beyond. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(1): 492-505 doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2867951 [30] Gu K, Tao D C, Qiao J F, Lin W S. Learning a no-reference quality assessment model of enhanced images with big data. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(4): 1301−1313 [31] Choi L K, You J, Bovik A. Referenceless prediction of perceptual fog density and perceptual image defogging. IEEE Transations on Image Processing, 2015, 24(11): 3888−3901 [32] Zhao S Y, Zhang L, Huang S Y, Shen Y, Zhao S J. Dehazing evaluation: Real-world benchmark datasets, criteria, and baselines. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2020, 29, 6947−6962 [33] . Zhu Z Q, Wei H Y, Hu Gang, Li Y Y, Qi G Q, et al. A novel fast single image dehazing algorithm based on artificial multiexposure image fusion. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement. 2021, 70, 5001523 [34] Liu Z, Blasch E, Xue Z Y, Zhao J Y, Laganiere R, et al. Objective assessment of multiresolution image fusion algorithms for context enhancement in night vision: A comparative study. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(1): 94−109 [35] Sheikh H, Bovik A. Image information and visual quality. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(2): 430−444 [36] Xydeas C, Petrovic V. Objective image fusion performance measure. Electronics Letters, 2000, 36(4): 308−309 [37] 程宇, 邓德祥, 颜佳, 范赐恩. 基于卷积神经网络的弱光照图像增强算法. 计算机应用, 2019, 39(4): 1162-1169 doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018091979. Chen Yu, Deng De-Xiang, Yan Jia, Fan Ci-En. Weakly illuminated image enhancement algorithm based on convolutional neural network. Journal of Computer Applications, 2019, 39(4): 1162-1169 doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2018091979 [38] Redmon J, Divvala S, Girshick R, Farhadi A. You only look once: unified, real-time object detection. In: Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR). Las Vegas, NV, USA: IEEE, 2016. 779−788 -




 下载:
下载: